YB-1 Interferes with TNFα–TNFR Binding and Modulates Progranulin-Mediated Inhibition of TNFα Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
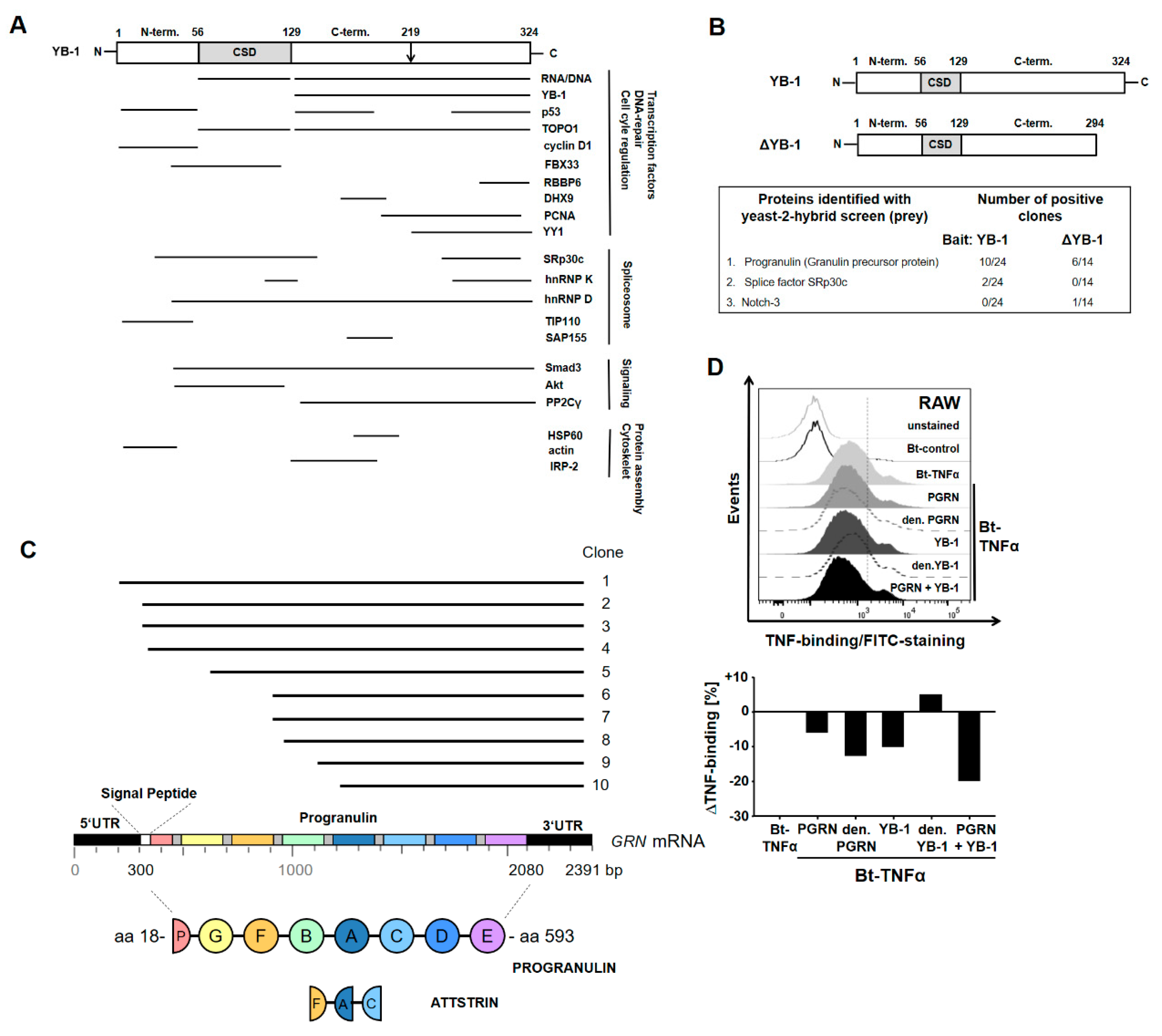
2.1. YB-1/PGRN Interaction
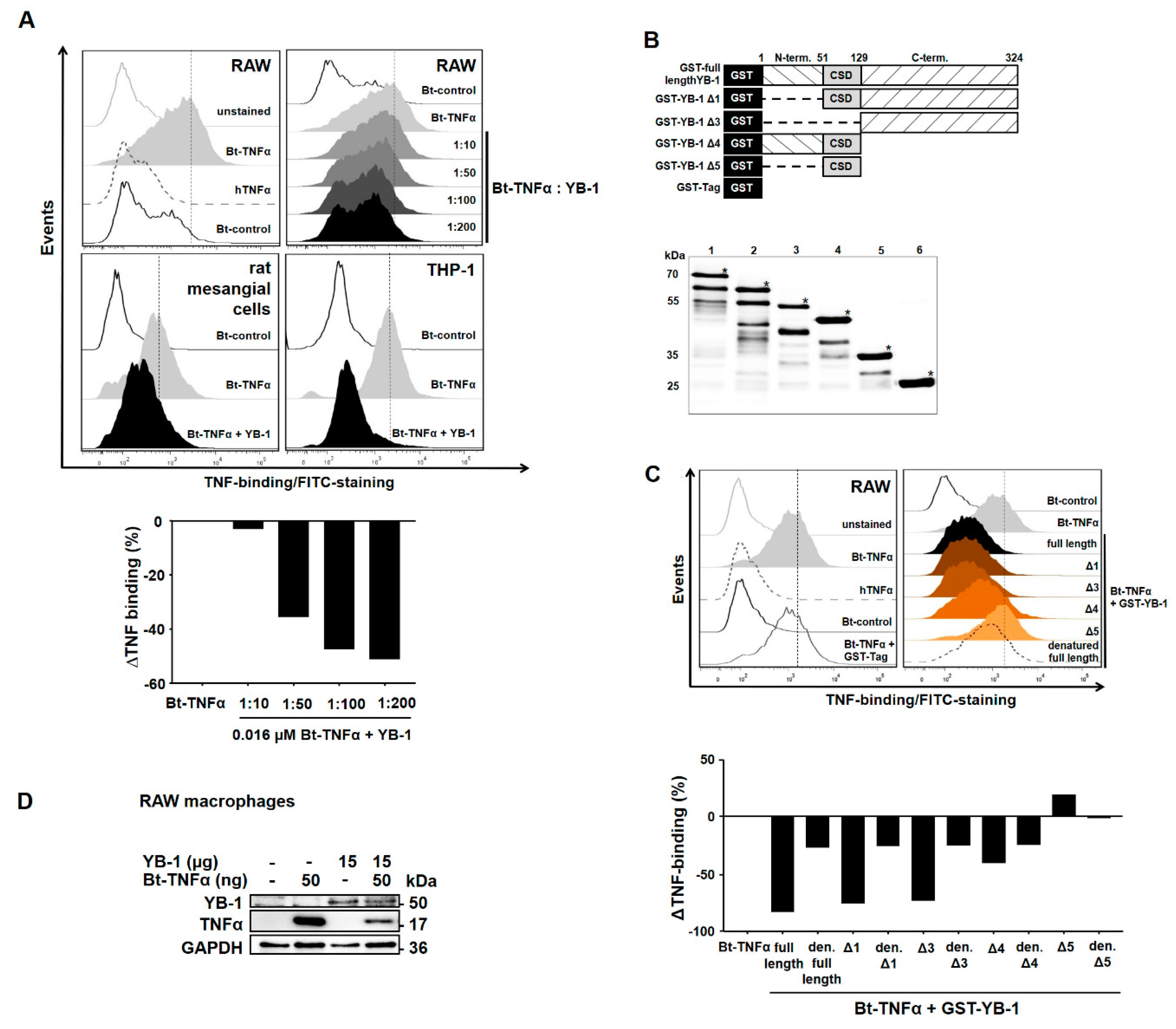
2.2. YB-1 Inhibits TNFα-Binding to Its Receptors
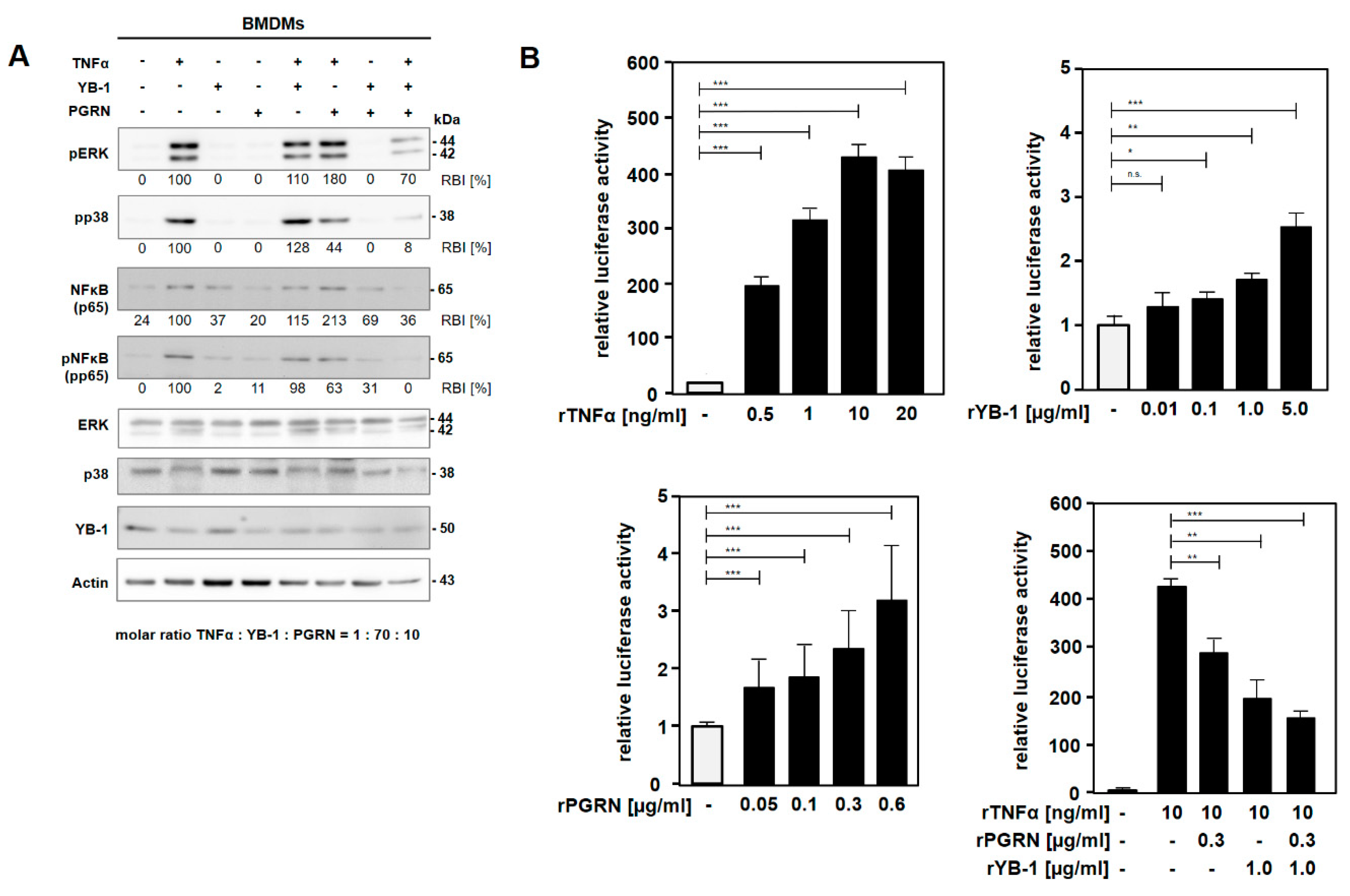
2.3. YB-1/PGRN Inhibits TNFα-Mediated Signaling
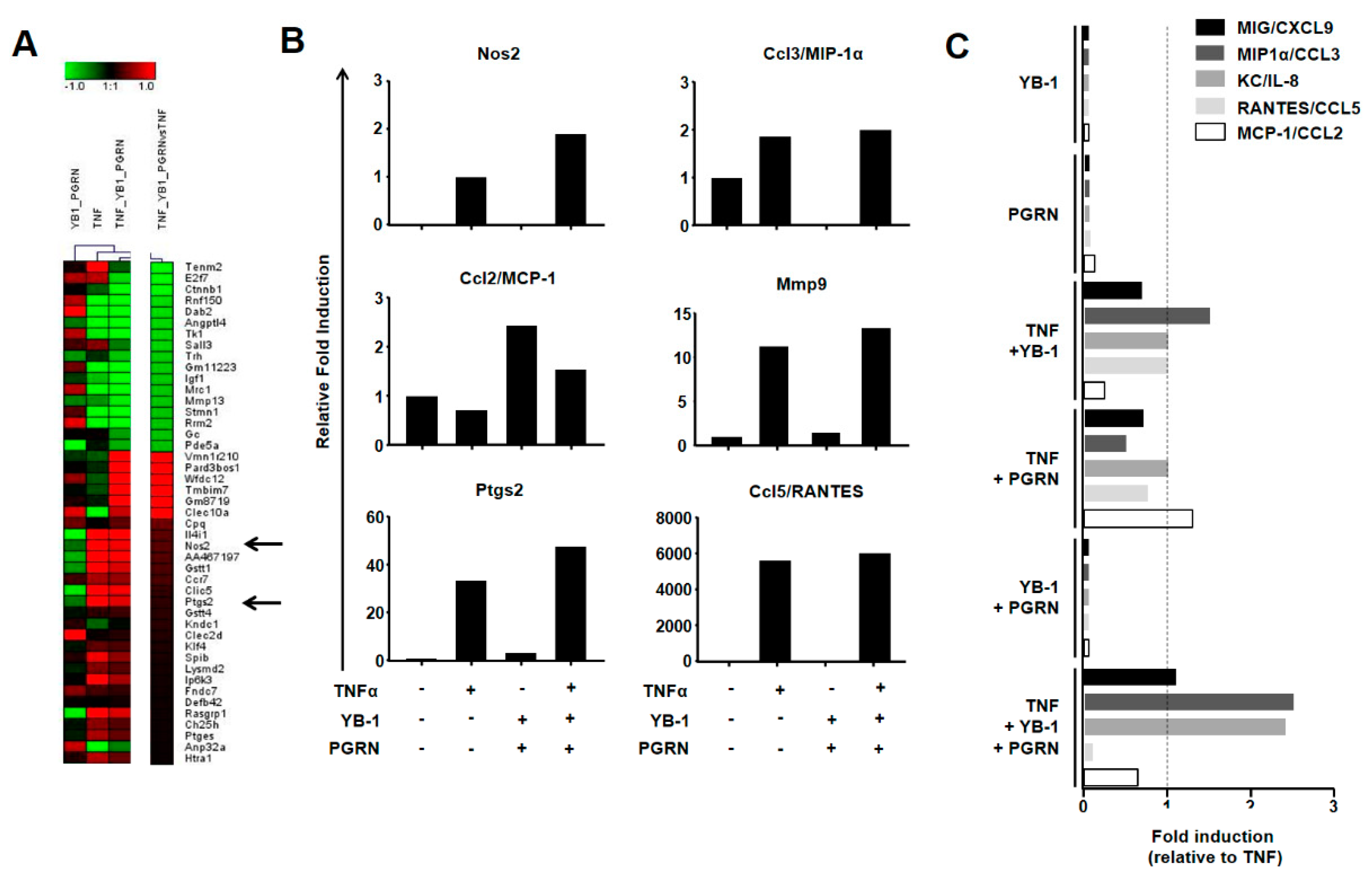
2.4. YB-1/PGRN Alters the TNFα-Induced Gene Expression Profile
2.5. YB-1/PGRN-Mediated Inhibition Modulates TNF-Induced Cytokine/Chemokine Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Recombinant Proteins
4.2. Cell Culture
4.2.1. Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages (BMDMs)
4.2.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Competitive TNFα-Binding Assay
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Quantification of Serum YB-1 Levels
4.6. NF-κB Luciferase Activity
4.7. Yeast Two-Hybrid Screen
4.8. RNA Analysis
4.9. Cytokine Measurement
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMDMs | bone marrow-derived macrophages |
| CCL2/MCP-1 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2/monocyte chemotactic protein 1 |
| CCL3/MIP1α | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3/macrophage inflammatory protein 1-alpha |
| CCL5/RANTES | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 |
| CSD | cold shock domain |
| CXCL1/KC | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 |
| CXCL9/MIG | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9/monokine induced by gamma interferon |
| ERK | extracellular-signal regulated kinase |
| FCS | fetal calf serum |
| GST | glutathione S-transferase |
| MMP-9 | matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-B |
| NOS2 | nitric oxide synthase 2 |
| PGRN | progranulin |
| PTGS2/COX2 | prostaglandin-endoperoxidase synthase 2/cyclooxygenase 2 |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TNFR1/2 | tumor necrosis factor receptor 1/2 |
| YB-1 | Y-box binding protein-1 |
References
- Didier, D.K.; Schiffenbauer, J.; Woulfe, S.L.; Zacheis, M.; Schwartz, B.D. Characterization of the cDNA encoding a protein binding to the major histocompatibility complex class II Y box. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7322–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliseeva, I.A.; Kim, E.R.; Guryanov, S.G.; Ovchinnikov, L.P.; Lyabin, D.N. Y-box-binding protein 1 (YB-1) and its functions. Biochemistry 2011, 76, 1402–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, K.; Izumi, H.; Uchiumi, T.; Ashizuka, M.; Kuwano, M. The pleiotropic functions of the Y-box-binding protein, YB-1. Bioessays 2003, 25, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosnopfel, C.; Sinnberg, T.; Sauer, B.; Busch, C.; Niessner, H.; Schmitt, A.; Forchhammer, S.; Grimmel, C.; Mertens, P.R.; Hailfinger, S.; et al. YB-1 Expression and Phosphorylation Regulate Tumorigenicity and Invasiveness in Melanoma by Influencing EMT. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2018, 16, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosnopfel, C.; Sinnberg, T.; Schittek, B. Y-box binding protein 1--a prognostic marker and target in tumour therapy. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 93, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, B.C.; Halfter, S.; Djudjaj, S.; Muehlenberg, P.; Weber, S.; Raffetseder, U.; En-Nia, A.; Knott, H.; Baron, J.M.; Dooley, S.; et al. Y-box protein-1 is actively secreted through a non-classical pathway and acts as an extracellular mitogen. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauen, T.; Raffetseder, U.; Frye, B.C.; Djudjaj, S.; Muhlenberg, P.J.; Eitner, F.; Lendahl, U.; Bernhagen, J.; Dooley, S.; Mertens, P.R. YB-1 acts as a ligand for Notch-3 receptors and modulates receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26928–26940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, L.; Alidousty, C.; Djudjaj, S.; Frye, B.C.; Rauen, T.; Boor, P.; Mertens, P.R.; van Roeyen, C.R.; Tacke, F.; Heymann, F.; et al. YB-1 is an early and central mediator of bacterial and sterile inflammation in vivo. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 2604–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, X.; Fu, M.; Ji, N.; Wang, D.; Qiu, J.; et al. Kindlin-2 interacts with beta-catenin and YB-1 to enhance EGFR transcription during glioma progression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 74872–74885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosnopfel, C.; Sinnberg, T.; Sauer, B.; Niessner, H.; Muenchow, A.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; Mertens, P.R.; Garbe, C.; Thakur, B.K.; et al. Tumour Progression Stage-Dependent Secretion of YB-1 Stimulates Melanoma Cell Migration and Invasion. Cancers 2020, 12, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djudjaj, S.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Raffetseder, U.; Guerrot, D.; Dussaule, J.C.; Boor, P.; Kerroch, M.; Hanssen, L.; Brandt, S.; Dittrich, A.; et al. Notch-3 receptor activation drives inflammation and fibrosis following tubulointerstitial kidney injury. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffetseder, U.; Rauen, T.; Boor, P.; Ostendorf, T.; Hanssen, L.; Floege, J.; En-Nia, A.; Djudjaj, S.; Frye, B.C.; Mertens, P.R. Extracellular YB-1 blockade in experimental nephritis upregulates Notch-3 receptor expression and signaling. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2011, 118, e100–e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordovkina, D.A.; Kim, E.R.; Buldakov, I.A.; Sorokin, A.V.; Eliseeva, I.A.; Lyabin, D.N.; Ovchinnikov, L.P. Transportin-1-dependent YB-1 nuclear import. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 480, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Ohashi, S.; Kobayashi, S. Four nucleocytoplasmic-shuttling proteins and p53 interact specifically with the YB-NLS and are involved in anticancer reagent-induced nuclear localization of YB-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Roeyen, C.R.; Scurt, F.G.; Brandt, S.; Kuhl, V.A.; Martinkus, S.; Djudjaj, S.; Raffetseder, U.; Royer, H.D.; Stefanidis, I.; Dunn, S.E.; et al. Cold shock Y-box protein-1 proteolysis autoregulates its transcriptional activities. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, S.; Atsumi, M.; Kobayashi, S. HSP60 interacts with YB-1 and affects its polysome association and subcellular localization. Biochem Biophys Res. Commun. 2009, 385, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, S.; Saatci, U.; Tinaztepe, K.; Bakkaloglu, A.; Barut, A. Urinary tumor necrosis factor levels in primary glomerulopathies. Nephron 1994, 66, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.H.; Wu, S.C.; Huang, T.P.; Yu, C.L.; Tsai, C.Y. Increased excretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 beta in urine from patients with IgA nephropathy and Schonlein-Henoch purpura. Nephron 1996, 74, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futrakul, N.; Butthep, P.; Patumraj, S.; Tipprukmas, N.; Futrakul, P. Enhanced tumor necrosis factor in the serum and renal hypoperfusion in nephrosis associated with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Ren. Fail. 2000, 22, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkar, A.M.; Smith, J.; Pusey, C.D. Prevention and treatment of experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis by blocking tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.N.; Masuzaki, H.; Fujishita, A.; Kitajima, M.; Hiraki, K.; Sekine, I.; Matsuyama, T.; Ishimaru, T. Interleukin-6- and tumour necrosis factor alpha-mediated expression of hepatocyte growth factor by stromal cells and its involvement in the growth of endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2005, 20, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tak, P.P.; Kalden, J.R. Advances in rheumatology: New targeted therapeutics. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13 (Suppl. 1), S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Huerta, D.I.; Alvarez-Rodriguez, B.A.; Topete-Reyes, J.F.; Munoz-Valle, J.F.; Parra-Michel, R.; Fuentes-Ramirez, F.; Salazar-Lopez, M.A.; Valle, Y.; Reyes-Castillo, Z.; Cruz-Gonzalez, A.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha -238 G/A and -308 G/A polymorphisms and soluble TNF-alpha levels in chronic kidney disease: Correlation with clinical variables. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Lee, C.K.; Cha, H.S.; Choe, J.Y.; Park, E.J.; Kim, J. Effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and chronic kidney disease. Rheumatol Int. 2015, 35, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, A.T.; Bertrand, M.J. More to Life than NF-kappaB in TNFR1 Signaling. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lamki, R.S.; Sadler, T.J.; Wang, J.; Reid, M.J.; Warren, A.Y.; Movassagh, M.; Lu, W.; Mills, I.G.; Neal, D.E.; Burge, J.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor expression and signaling in renal cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubitz, A.; Schwarz, M.; Eltrich, N.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Vielhauer, V. Distinct contributions of TNF receptor 1 and 2 to TNF-induced glomerular inflammation in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielhauer, V.; Mayadas, T.N. Functions of TNF and its receptors in renal disease: Distinct roles in inflammatory tissue injury and immune regulation. Semin. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 286–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speeckaert, M.M.; Speeckaert, R.; Laute, M.; Vanholder, R.; Delanghe, J.R. Tumor necrosis factor receptors: Biology and therapeutic potential in kidney diseases. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 36, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lamki, R.S.; Mayadas, T.N. TNF receptors: Signaling pathways and contribution to renal dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraishi, M. Comparative overview of safety of the biologics in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2009, 82, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedger, L.M.; McDermott, M.F. TNF and TNF-receptors: From mediators of cell death and inflammation to therapeutic giants - past, present and future. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteson, E.L.; Bongartz, T. Tumor necrosis factor antagonists and cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2007, 3, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askling, J.; Baecklund, E.; Granath, F.; Geborek, P.; Fored, M.; Backlin, C.; Bertilsson, L.; Coster, L.; Jacobsson, L.T.; Lindblad, S.; et al. Anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and risk of malignant lymphomas: Relative risks and time trends in the Swedish Biologics Register. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askling, J.; Bongartz, T. Malignancy and biologic therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2008, 20, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askling, J.; Dixon, W. The safety of anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2008, 20, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffetseder, U.; Frye, B.; Rauen, T.; Jurchott, K.; Royer, H.D.; Jansen, P.L.; Mertens, P.R. Splicing factor SRp30c interaction with Y-box protein-1 confers nuclear YB-1 shuttling and alternative splice site selection. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 18241–18248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Lu, Y.; Tian, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, F.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Syed, N.M.; Lai, Y.; Lin, E.A.; Kong, L.; et al. The growth factor progranulin binds to TNF receptors and is therapeutic against inflammatory arthritis in mice. Science 2011, 332, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J. Progranulin: A promising therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3675–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Izumi, H.; Imamura, T.; Takano, H.; Ise, T.; Uchiumi, T.; Kuwano, M.; Kohno, K. Direct interaction of p53 with the Y-box binding protein, YB-1: A mechanism for regulation of human gene expression. Oncogene 2000, 19, 6194–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, P.R.; Alfonso-Jaume, M.A.; Steinmann, K.; Lovett, D.H. A synergistic interaction of transcription factors AP2 and YB-1 regulates gelatinase A enhancer-dependent transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32957–32965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindquist, J.A.; Brandt, S.; Bernhardt, A.; Zhu, C.; Mertens, P.R. The role of cold shock domain proteins in inflammatory diseases. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2014, 92, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohn, R.; Raffetseder, U.; Bot, I.; Zernecke, A.; Shagdarsuren, E.; Liehn, E.A.; van Santbrink, P.J.; Nelson, P.J.; Biessen, E.A.; Mertens, P.R.; et al. Y-box binding protein-1 controls CC chemokine ligand-5 (CCL5) expression in smooth muscle cells and contributes to neointima formation in atherosclerosis-prone mice. Circulation 2007, 116, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffetseder, U.; Rauen, T.; Djudjaj, S.; Kretzler, M.; En-Nia, A.; Tacke, F.; Zimmermann, H.W.; Nelson, P.J.; Frye, B.C.; Floege, J.; et al. Differential regulation of chemokine CCL5 expression in monocytes/macrophages and renal cells by Y-box protein-1. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, A.; Fehr, A.; Brandt, S.; Jerchel, S.; Ballhause, T.M.; Philipsen, L.; Stolze, S.; Geffers, R.; Weng, H.; Fischer, K.D.; et al. Inflammatory cell infiltration and resolution of kidney inflammation is orchestrated by the cold-shock protein Y-box binding protein-1. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1157–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, D.J.; Phillips, A.O.; Zhang, X.; van Roeyen, C.R.; Muehlenberg, P.; En-Nia, A.; Mertens, P.R. Y-box protein-1 controls transforming growth factor-beta1 translation in proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Lee, T.A.; Ra, E.A.; Lee, E.; Choi, H.; Lee, S.; Park, B. Differential control of interleukin-6 mRNA levels by cellular distribution of YB-1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Djudjaj, S.; Gibbert, L.; Lennartz, V.; Breitkopf, D.M.; Rauen, T.; Hermert, D.; Martin, I.V.; Boor, P.; Braun, G.S.; et al. YB-1 orchestrates onset and resolution of renal inflammation via IL10 gene regulation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3494–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, S.; Mertens, P.R. A remedy for kidney disease successfully alters the cold shock protein response during inflammation. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermert, D.; Martin, I.V.; Reiss, L.K.; Liu, X.; Breitkopf, D.M.; Reimer, K.C.; Alidousty, C.; Rauen, T.; Floege, J.; Ostendorf, T.; et al. The nucleic acid binding protein YB-1-controlled expression of CXCL-1 modulates kidney damage in liver fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewert, L.; Fischer, A.; Brandt, S.; Scurt, F.G.; Philipsen, L.; Muller, A.J.; Girndt, M.; Zenclussen, A.C.; Lindquist, J.A.; Gorny, X.; et al. Cold shock Y-box binding protein-1 acetylation status in monocytes is associated with systemic inflammation and vascular damage. Atherosclerosis 2018, 278, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, S.; Ewert, L.; Scurt, F.G.; Reichardt, C.; Lindquist, J.A.; Gorny, X.; Isermann, B.; Mertens, P.R. Altered monocytic phenotypes are linked with systemic inflammation and may be linked to mortality in dialysis patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Roeyen, C.R.; Eitner, F.; Martinkus, S.; Thieltges, S.R.; Ostendorf, T.; Bokemeyer, D.; Luscher, B.; Luscher-Firzlaff, J.M.; Floege, J.; Mertens, P.R. Y-box protein 1 mediates PDGF-B effects in mesangioproliferative glomerular disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2985–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, S.; Raffetseder, U.; Djudjaj, S.; Schreiter, A.; Kadereit, B.; Michele, M.; Pabst, M.; Zhu, C.; Mertens, P.R. Cold shock Y-box protein-1 participates in signaling circuits with auto-regulatory activities. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 91, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. TNF: A master switch for inflammation to cancer. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5094–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Hua, L.; Wang, B.; Wei, H.; Prabhu, L.; Hartley, A.V.; Jiang, G.; Liu, Y.; Lu, T. Novel Serine 176 Phosphorylation of YBX1 Activates NF-kappaB in Colon Cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 3433–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, L.; Mundade, R.; Wang, B.; Wei, H.; Hartley, A.V.; Martin, M.; McElyea, K.; Temm, C.J.; Sandusky, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Critical role of phosphorylation of serine 165 of YBX1 on the activation of NF-kappaB in colon cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29396–29412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Plaza-Sirvent, C.; Weinert, S.; Buchbinder, J.H.; Lavrik, I.N.; Mertens, P.R.; Schmitz, I.; Lindquist, J.A. YB-1 Mediates TNF-Induced Pro-Survival Signaling by Regulating NF-kappaB Activation. Cancers 2020, 12, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltendorf, S.; Fu, H.; Pierau, M.; Lindquist, J.A.; Finzel, S.; Mertens, P.R.; Gieseler-Halbach, S.; Ambach, A.; Thomas, U.; Lingel, H.; et al. Cell Survival Failure in Effector T Cells from Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Following Insufficient Up-Regulation of Cold-Shock Y-Box Binding Protein 1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieseler-Halbach, S.; Meltendorf, S.; Pierau, M.; Weinert, S.; Heidel, F.H.; Fischer, T.; Handschuh, J.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Schrappe, M.; Lindquist, J.A.; et al. RSK-mediated nuclear accumulation of the cold-shock Y-box protein-1 controls proliferation of T cells T-ALL blasts. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capowski, E.E.; Esnault, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Malter, J.S. Y box-binding factor promotes eosinophil survival by stabilizing granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNA. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5970–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coles, L.S.; Diamond, P.; Occhiodoro, F.; Vadas, M.A.; Shannon, M.F. Cold shock domain proteins repress transcription from the GM-CSF promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, P.; Shannon, M.F.; Vadas, M.A.; Coles, L.S. Cold shock domain factors activate the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promoter in stimulated Jurkat T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7943–7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Kruys, V.; Huez, G.; Gueydan, C. AU-rich element-mediated translational control: Complexity and multiple activities of trans-activating factors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002, 30, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, S.M.; Achorn, C.; Kedersha, N.L.; Anderson, P.J.; Ivanov, P. YB-1 regulates tiRNA-induced Stress Granule formation but not translational repression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6949–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somasekharan, S.P.; El-Naggar, A.; Leprivier, G.; Cheng, H.; Hajee, S.; Grunewald, T.G.; Zhang, F.; Ng, T.; Delattre, O.; Evdokimova, V.; et al. YB-1 regulates stress granule formation and tumor progression by translationally activating G3BP1. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 913–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamou, P.; Kontoyiannis, D.L. Posttranscriptional regulation of TNF mRNA: A paradigm of signal-dependent mRNA utilization and its relevance to pathology. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2010, 11, 61–79. [Google Scholar]
- Borghi, A.; Verstrepen, L.; Beyaert, R. TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-kappaB, MAP kinases and cell death. Biochem. Pharmacol 2016, 116, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Regulation of NF-kappaB by TNF family cytokines. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltzer, N.; Darding, M.; Walczak, H. Holding RIPK1 on the Ubiquitin Leash in TNFR1 Signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, G.V.; Safak, M.; MacDonald, G.H.; Khalili, K. Transcriptional regulation of human polyomavirus JC: Evidence for a functional interaction between RelA (p65) and the Y-box-binding protein, YB-1. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5944–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratford, A.L.; Fry, C.J.; Desilets, C.; Davies, A.H.; Cho, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Berquin, I.M.; Roux, P.P.; Dunn, S.E. Y-box binding protein-1 serine 102 is a downstream target of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase in basal-like breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, B.W.; Kucab, J.; Wu, J.; Lee, C.; Cheang, M.C.; Yorida, E.; Turbin, D.; Dedhar, S.; Nelson, C.; Pollak, M.; et al. Akt phosphorylates the Y-box binding protein 1 at Ser102 located in the cold shock domain and affects the anchorage-independent growth of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4281–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Scheurich, P. Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karathanasis, C.; Medler, J.; Fricke, F.; Smith, S.; Malkusch, S.; Widera, D.; Fulda, S.; Wajant, H.; van Wijk, S.J.L.; Dikic, I.; et al. Single-molecule imaging reveals the oligomeric state of functional TNFalpha-induced plasma membrane TNFR1 clusters in cells. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, R.; Kontermann, R.E.; Pfizenmaier, K. Selective Targeting of TNF Receptors as a Novel Therapeutic Approach. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, C.; Vasic, V.; Hardt, S.; Heidler, J.; Haussler, A.; Wittig, I.; Schmidt, M.H.; Tegeder, I. Progranulin promotes peripheral nerve regeneration and reinnervation: Role of notch signaling. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, H.G.; Lindquist, J.A.; Keilhoff, G.; Dobrowolny, H.; Brandt, S.; Steiner, J.; Bogerts, B.; Mertens, P.R. Differential distribution of Y-box-binding protein 1 and cold shock domain protein A in developing and adult human brain. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Pickering-Brown, S.M.; Gass, J.; Rademakers, R.; Lindholm, C.; Snowden, J.; Adamson, J.; Sadovnick, A.D.; Rollinson, S.; et al. Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature 2006, 442, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, I.R.; Baker, M.; Pickering-Brown, S.; Hsiung, G.Y.; Lindholm, C.; Dwosh, E.; Gass, J.; Cannon, A.; Rademakers, R.; Hutton, M.; et al. The neuropathology of frontotemporal lobar degeneration caused by mutations in the progranulin gene. Brain 2006, 129, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, T.; Buraschi, S.; Goyal, A.; Sharpe, C.; Natkanski, E.; Schaefer, L.; Morrione, A.; Iozzo, R.V. EphA2 is a functional receptor for the growth factor progranulin. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 215, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, H.; Imamura, T.; Nagatani, G.; Ise, T.; Murakami, T.; Uramoto, H.; Torigoe, T.; Ishiguchi, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Nomoto, M.; et al. Y box-binding protein-1 binds preferentially to single-stranded nucleic acids and exhibits 3’-->5’ exonuclease activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hessman, C.L.; Hildebrandt, J.; Shah, A.; Brandt, S.; Bock, A.; Frye, B.C.; Raffetseder, U.; Geffers, R.; Brunner-Weinzierl, M.C.; Isermann, B.; et al. YB-1 Interferes with TNFα–TNFR Binding and Modulates Progranulin-Mediated Inhibition of TNFα Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197076
Hessman CL, Hildebrandt J, Shah A, Brandt S, Bock A, Frye BC, Raffetseder U, Geffers R, Brunner-Weinzierl MC, Isermann B, et al. YB-1 Interferes with TNFα–TNFR Binding and Modulates Progranulin-Mediated Inhibition of TNFα Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197076
Chicago/Turabian StyleHessman, Christopher L., Josephine Hildebrandt, Aneri Shah, Sabine Brandt, Antonia Bock, Björn C. Frye, Ute Raffetseder, Robert Geffers, Monika C. Brunner-Weinzierl, Berend Isermann, and et al. 2020. "YB-1 Interferes with TNFα–TNFR Binding and Modulates Progranulin-Mediated Inhibition of TNFα Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197076
APA StyleHessman, C. L., Hildebrandt, J., Shah, A., Brandt, S., Bock, A., Frye, B. C., Raffetseder, U., Geffers, R., Brunner-Weinzierl, M. C., Isermann, B., Mertens, P. R., & Lindquist, J. A. (2020). YB-1 Interferes with TNFα–TNFR Binding and Modulates Progranulin-Mediated Inhibition of TNFα Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197076





