Antibiotic-Resistant and Non-Resistant Bacteria Display Similar Susceptibility to Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma
Abstract
1. Introduction
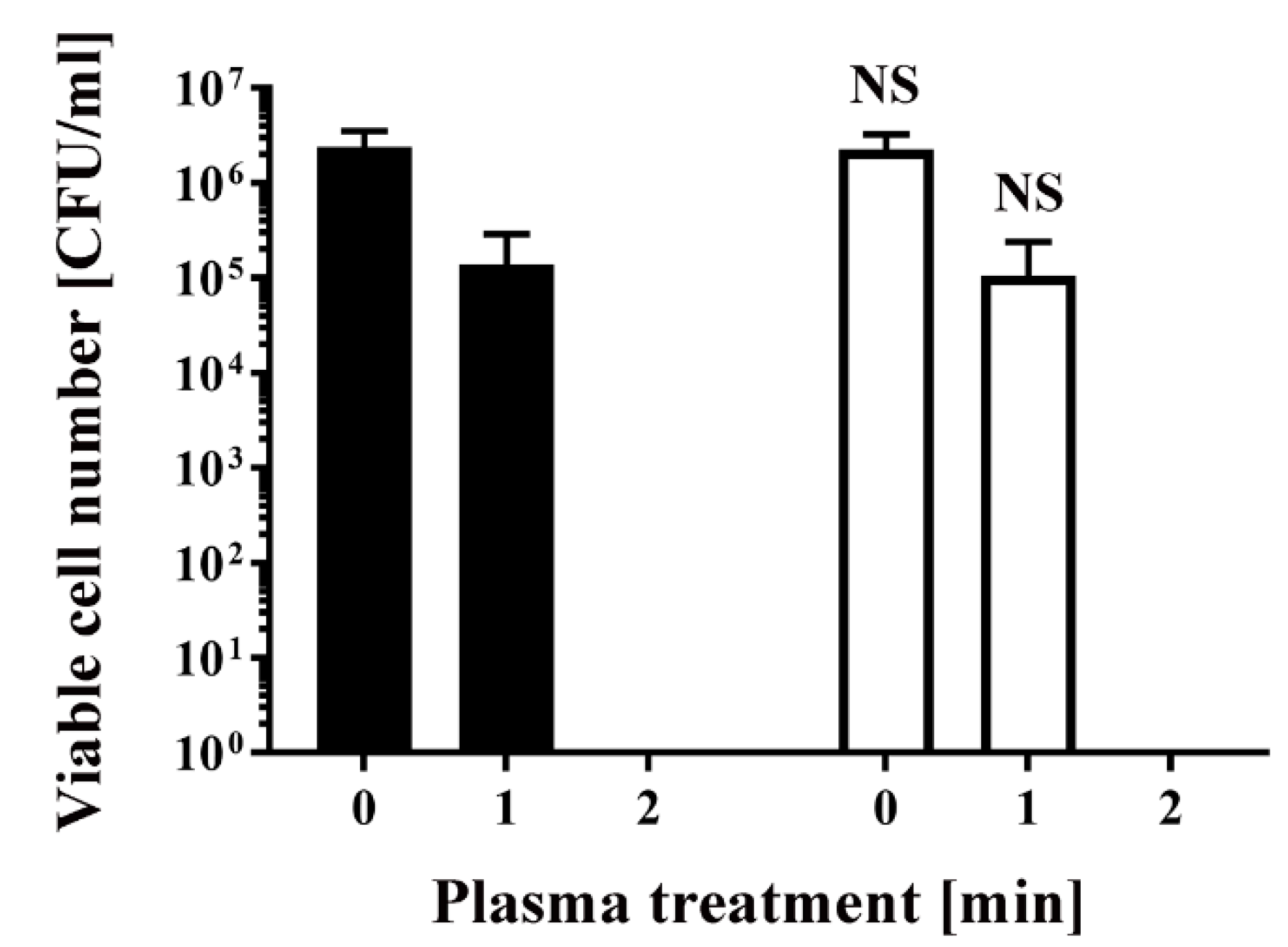
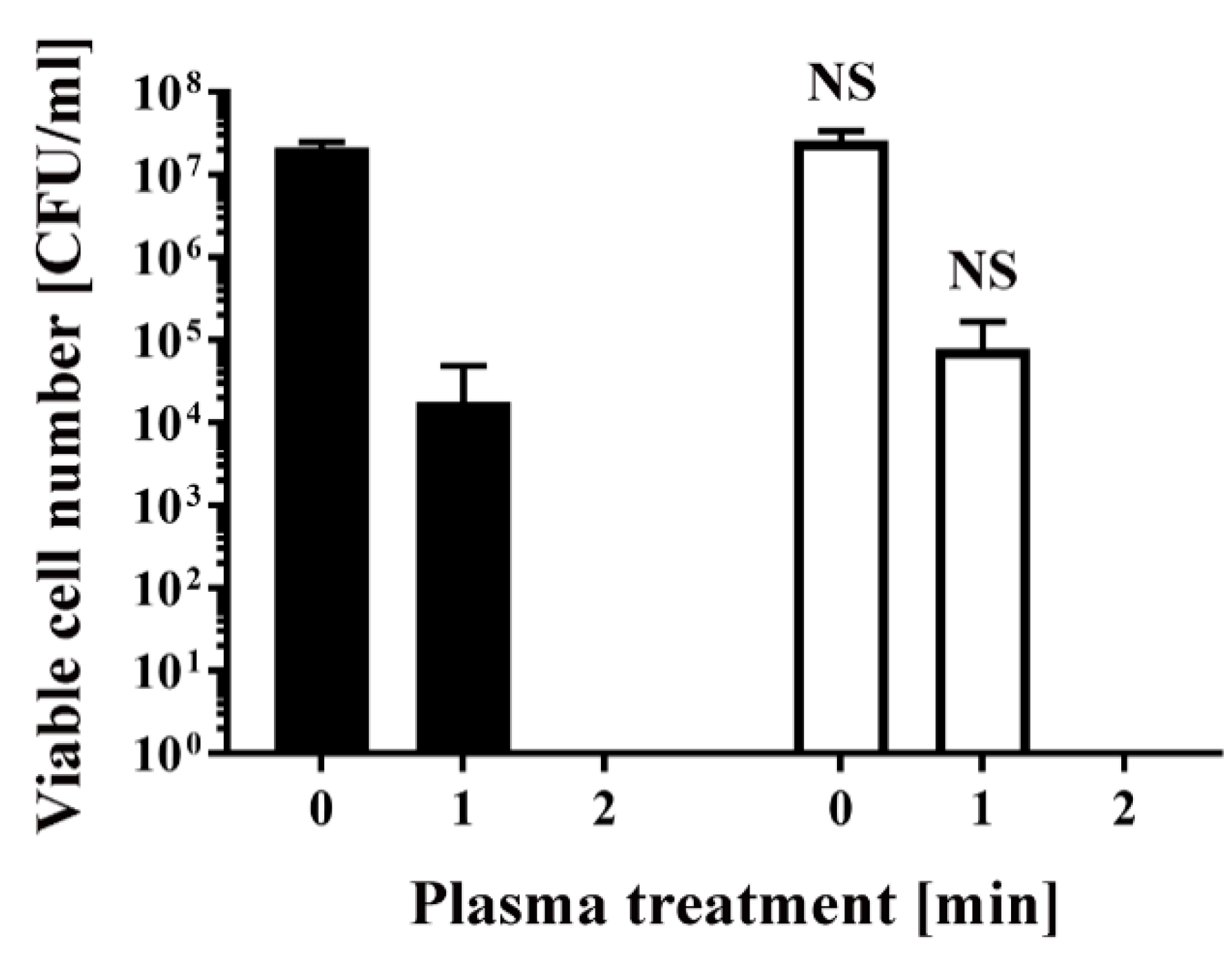
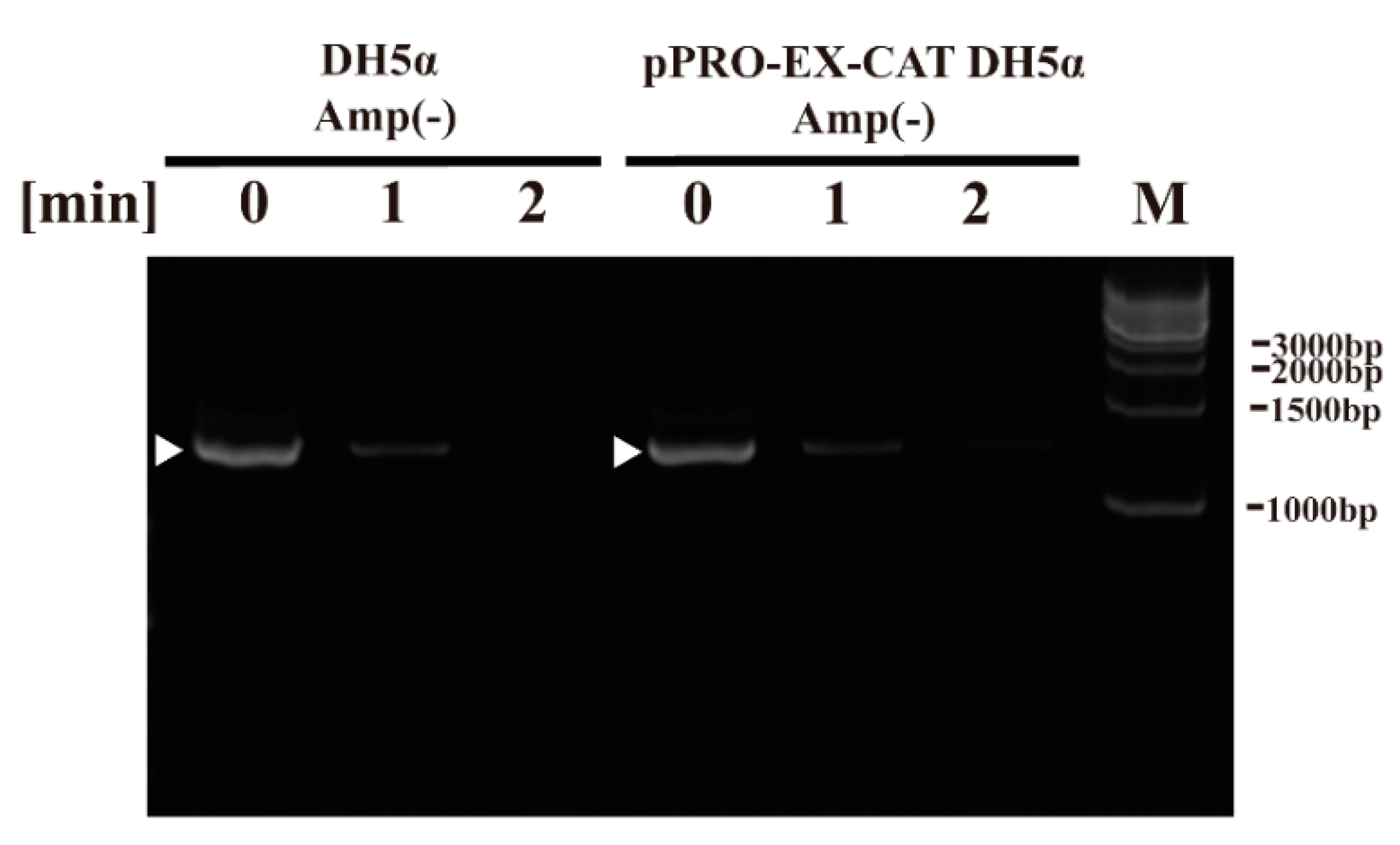
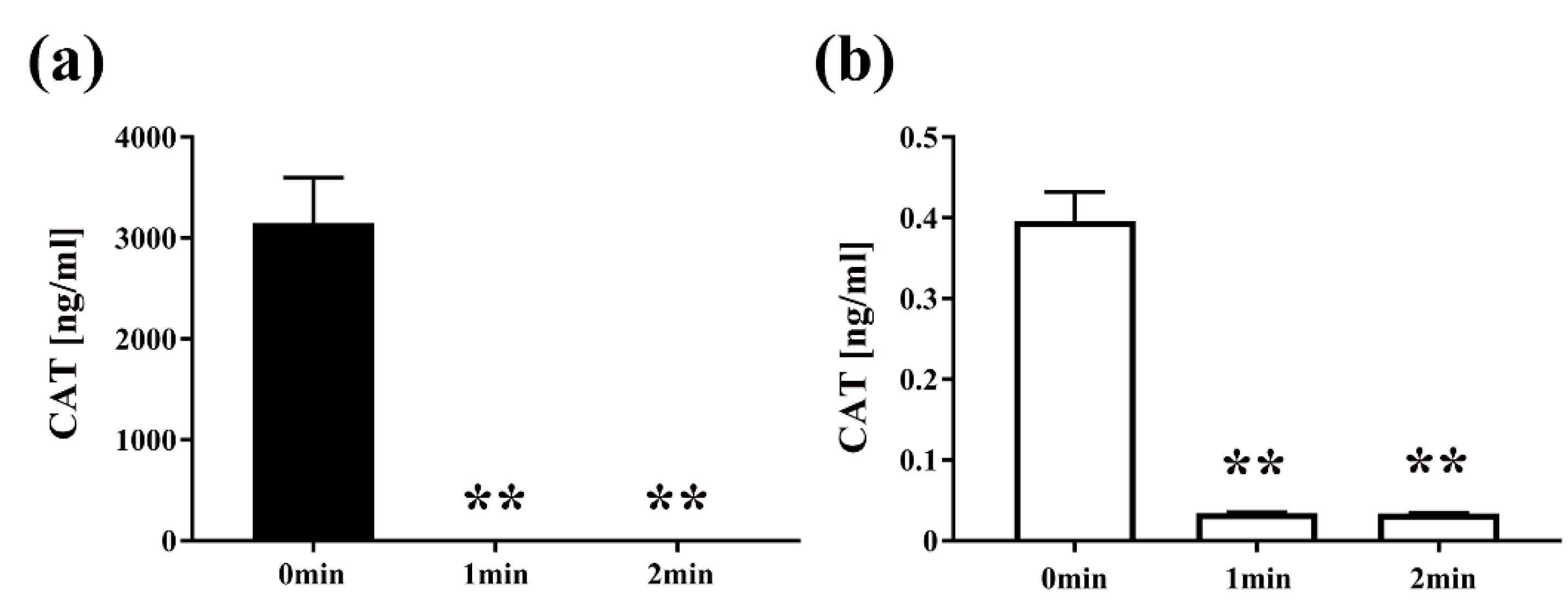
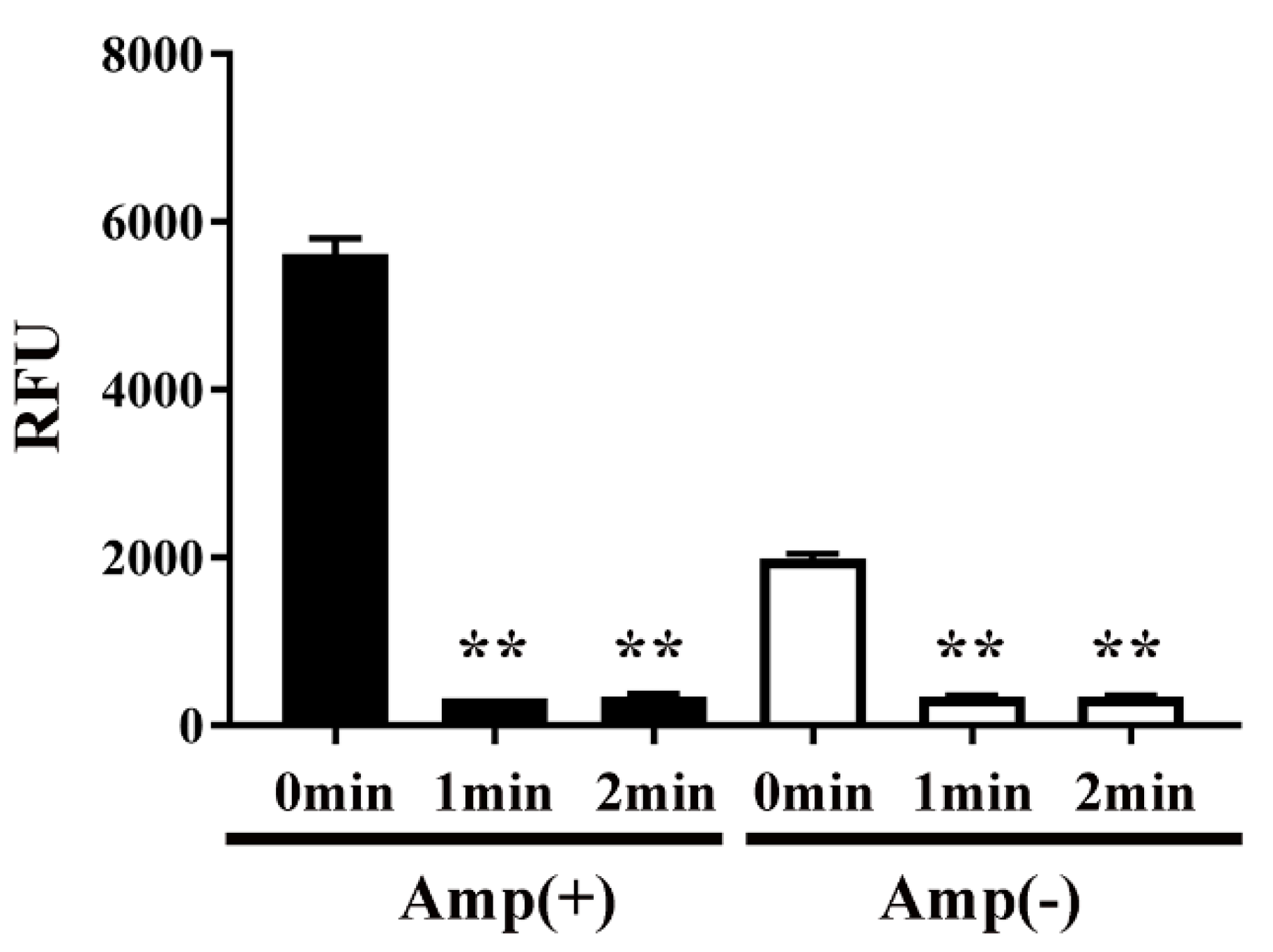
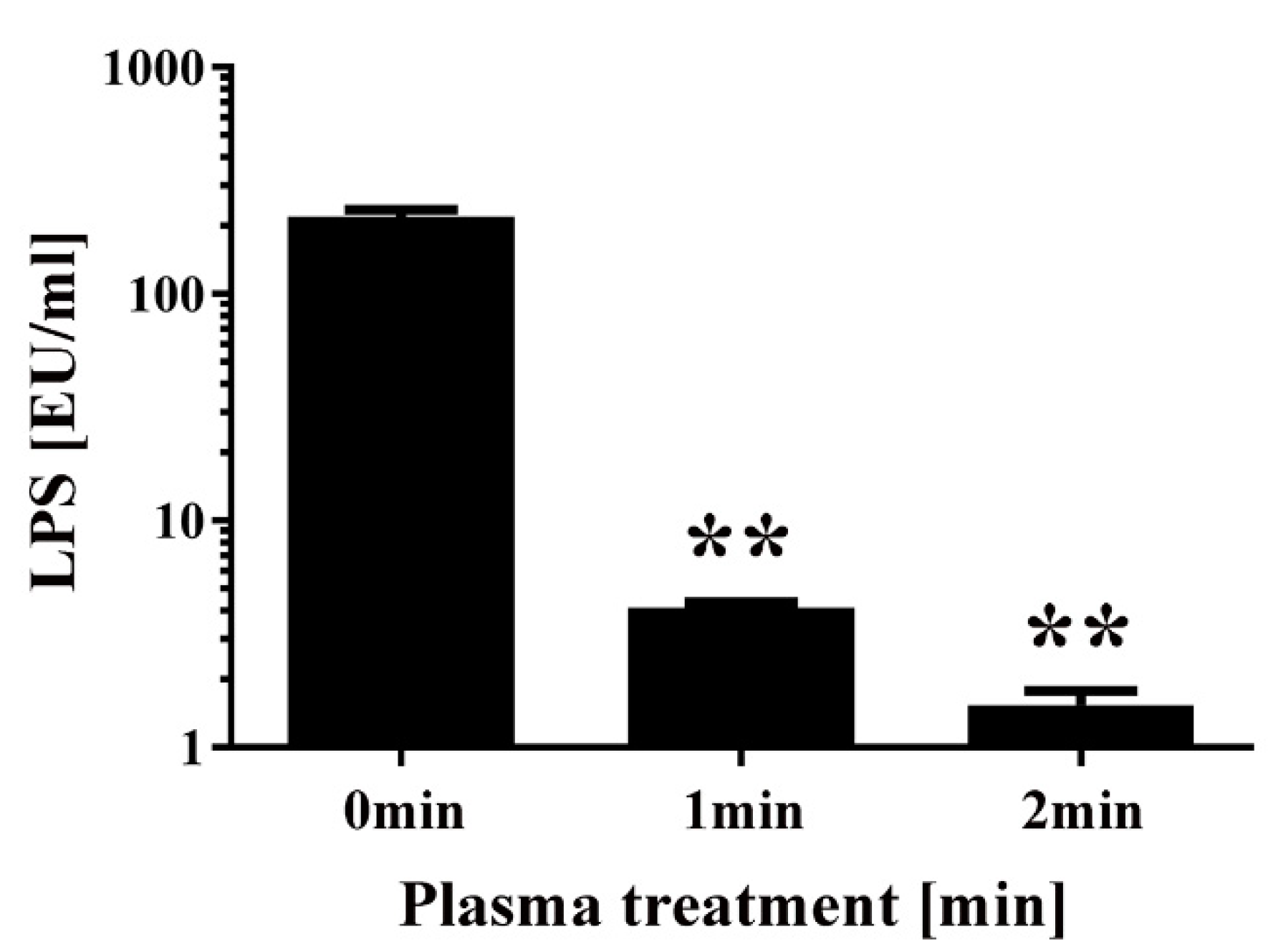
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
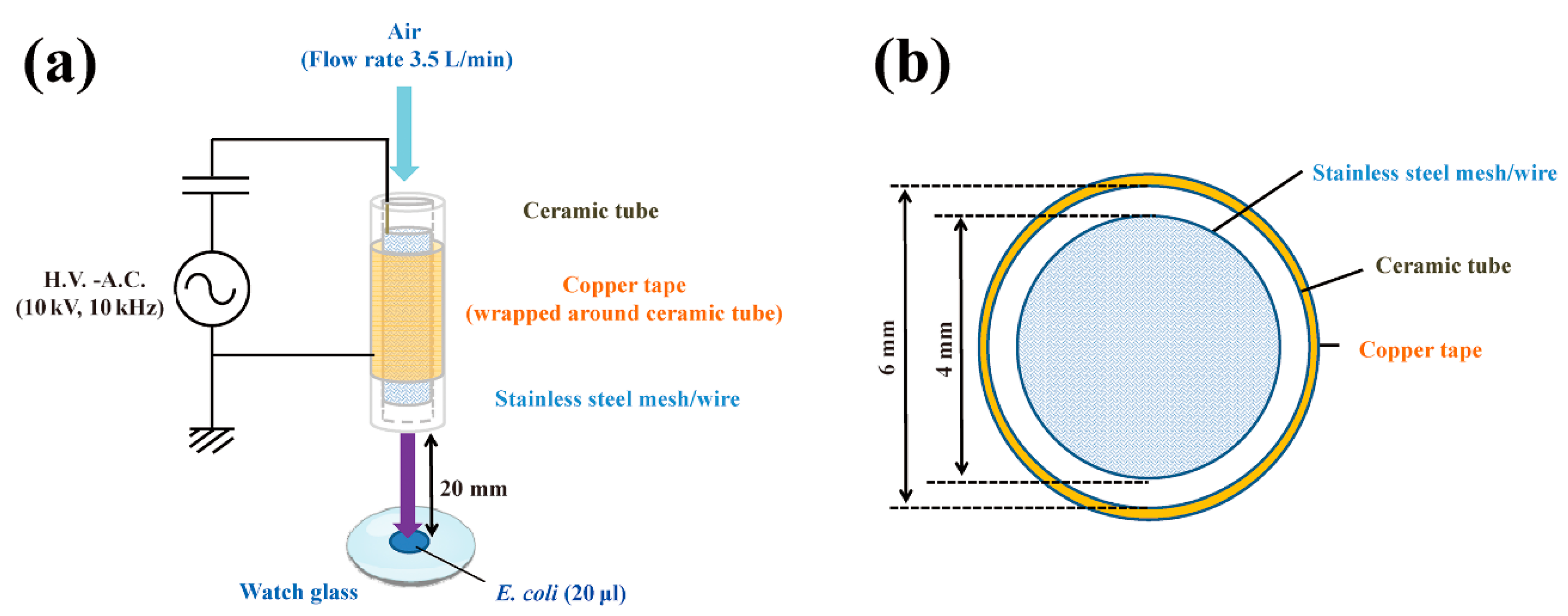
4.1. DBD Plasma Torch
4.2. Plasma Treatment of Transformed Bacteria and Colony Counting
4.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.4. Acetyltransferase Activity Assay
4.5. PCR
4.6. Measurement of LPS
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| CAT | Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase |
| CFU | Colony forming units |
| DBD | Dielectric barrier discharge |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ESBL | Extended-Spectrum β-lactamase |
| ESR | Electron spin resonance |
| EU | Endotoxin Units |
| H· | H radical |
| LB | Luria-Bertani |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharides |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant S. aureus |
| OH· | OH radical |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| RFU | Relative fluorescence units |
| SMD | Surface micro-discharge |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Wen, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, Z. Insight into effects of antibiotics on reactor performance and evolutions of antibiotic resistance genes and microbial community in a membrane reactor. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskiniemi, S.; Virtanen, P. Selective killing of antibiotic-resistant bacteria from within. Nature 2019, 570, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, S.J.; Connor, C.; McNally, A. The evolution and transmission of multi-drug resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae: The complexity of clones and plasmids. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathers, A.J.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D. The role of epidemic resistance plasmids and international high-risk clones in the spread of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 565–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, S.B.; Veve, M.P.; Wagner, J.L. Cephalosporins: A focus on side chains and beta-lactam cross-reactivity. Pharmacy 2019, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, S.; Ewers, C.; Wieler, L.H. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases producing E. coli in wildlife, yet another form of environmental pollution? Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A review of antibiotic use in food animals: Perspective, policy, and potential. Public Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Breda, L.K.; Ward, M.P. Evidence of antimicrobial and disinfectant resistance in a remote, isolated wild pig population. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 147, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.H.; Juhrend, B.; Olson, T.M.; Marrs, C.F.; Wigginton, K.R. Degradation of extracellular antibiotic resistance genes with UV254 treatment. Environ. Sci Technol. 2017, 51, 6185–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Obra Jimenez, I.; Lopez, J.L.C.; Ibanez, G.R.; Garcia, B.E.; Perez, J.A.S. Kinetic assessment of antibiotic resistant bacteria inactivation by solar photo-Fenton in batch and continuous flow mode for wastewater reuse. Water Res. 2019, 159, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wang, K.; Hou, S.; Wan, L.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, J. H2O2 and/or TiO2 photocatalysis under UV irradiation for the removal of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their antibiotic resistance genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323(Pt. B), 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Yin, H.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; An, T.; Wong, P.K.; Zhao, H. Elimination of antibiotic-resistance bacterium and its associated/dissociative blaTEM-1 and aac(3)-II antibiotic-resistance genes in aqueous system via photoelectrocatalytic process. Water Res. 2017, 125, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung le, M.; Cong, N.X.; Huy le, T.; Lan, N.T.; Phan, V.N.; Hoa, N.Q.; Vinh le, K.; Thinh, N.V.; Tai le, T.; Ngo, D.T.; et al. Synthesis, Characterizations of superparamagnetic Fe3O4-Ag hybrid nanoparticles and their application for highly effective bacteria inactivation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 5902–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, M. Effects of advanced treatment systems on the removal of antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment plants from Hangzhou, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8157–8163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.M.; Macedo, G.; Pedrosa, M.; Becerra-Castro, C.; Castro-Silva, S.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Ozonation and UV254nm radiation for the removal of microorganisms and antibiotic resistance genes from urban wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wan, K.; Yang, Z.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Yu, X. Inactivation of antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli and degradation of its resistance genes by glow discharge plasma in an aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, K.A.; Kehrenberg, C.; Boulaaba, A.; von Kockritz-Blickwede, M.; Binder, S.; Li, Y.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Pfeifer, Y.; Ahlfeld, B. Inactivation of multidrug-resistant pathogens and Yersinia enterocolitica with cold atmospheric-pressure plasma on stainless-steel surfaces. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Burriel, M.; Keys, M.; Campillo-Artero, C.; Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M.; Gikas, A.; Palos, C.; Lopez-Casasnovas, G. Impact of multi-drug resistant bacteria on economic and clinical outcomes of healthcare-associated infections in adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvam, E.; Davis, B.; Mondello, F.; Garner, A.L. Nonthermal atmospheric plasma rapidly disinfects multidrug-resistant microbes by inducing cell surface damage. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Bernabe, G.; Marchiori, C.; Scarpa, M.; Zuin, M.; Cavazzana, R.; Zaniol, B.; Martines, E. Antibacterial efficacy and mechanisms of action of low power atmospheric pressure cold plasma: Membrane permeability, biofilm penetration and antimicrobial sensitization. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.G.; Paff, M.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Brooks, A.D. Control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in planktonic form and biofilms: A biocidal efficacy study of nonthermal dielectric-barrier discharge plasma. Am. J. Infect. Control 2010, 38, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Kim, J.I. Decomposition of biological macromolecules by plasma generated with helium and oxygen. J. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Toyokawa, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Imanishi, Y.; Sakudo, A. Inactivation of Salmonella by nitrogen gas plasma generated by a static induction thyristor as a pulsed power supply. Food Control 2015, 52, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modic, M.; McLeod, N.P.; Sutton, J.M.; Walsh, J.L. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma elimination of clinically important single- and mixed-species biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakudo, A.; Toyokawa, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Yagyu, Y.; Imanishi, Y. Nitrogen gas plasma treatment of bacterial spores induces oxidative stress that damages the genomic DNA. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, H.; Sakudo, A.; Burke, P.; McDonnell, G. Gas plasma sterilization of microorganisms and mechanisms of action. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, H.; Shimizu, N.; Imanishi, Y.; Sekiya, T.; Tamazawa, K.; Taniguchi, A.; Kido, N. Inactivation of microorganisms and endotoxins by low temperature nitrogen gas plasma exposure. Biocontrol Sci. 2007, 12, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamashiro, R.; Misawa, T.; Sakudo, A. Key role of singlet oxygen and peroxynitrite in viral RNA damage during virucidal effect of plasma torch on feline calicivirus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Yamashiro, R.; Haritani, M.; Furusaki, K.; Onishi, R.; Onodera, T. Inactivation of non-enveloped viruses and bacteria by an electrically charged disinfectant containing meso-structure nanoparticles via modification of the genome. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Yagyu, Y.; Onodera, T. Disinfection and sterilization using plasma technology: Fundamentals and future perspectives for biological applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Lopez, C.; Usai, D.; Donadu, M.G.; Serio, A.; Gonzalez-Mina, R.T.; Simeoni, M.C.; Molicotti, P.; Zanetti, S.; Pinna, A.; Paparella, A. potential of Borojoa patinoi Cuatrecasas water extract to inhibit nosocomial antibiotic resistant bacteria and cancer cell proliferation in vitro. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2725–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usai, D.; Donadu, M.; Bua, A.; Molicotti, P.; Zanetti, S.; Piras, S.; Corona, P.; Ibba, R.; Carta, A. Enhancement of antimicrobial activity of pump inhibitors associating drugs. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyokawa, Y.; Yagyu, Y.; Misawa, T.; Sakudo, A. A new roller conveyer system of non-thermal gas plasma as a potential control measure of plant pathogenic bacteria in primary food production. Food Control 2017, 72, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Miyagi, H.; Horikawa, T.; Yamashiro, R.; Misawa, T. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori with dielectric barrier discharge plasma causes UV induced damage to genomic DNA leading to cell death. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 4th ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakudo, A.; Misawa, T. Antibiotic-Resistant and Non-Resistant Bacteria Display Similar Susceptibility to Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176326
Sakudo A, Misawa T. Antibiotic-Resistant and Non-Resistant Bacteria Display Similar Susceptibility to Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176326
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakudo, Akikazu, and Tatsuya Misawa. 2020. "Antibiotic-Resistant and Non-Resistant Bacteria Display Similar Susceptibility to Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176326
APA StyleSakudo, A., & Misawa, T. (2020). Antibiotic-Resistant and Non-Resistant Bacteria Display Similar Susceptibility to Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176326




