Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarisation and Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction: Physiology and Pathology of Adipose Tissue
2. Pathways Involved in Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance
3. Overview of Insulin Signalling, Resistance and the Onset of Type-2 Diabetes
4. Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation and Adipose Insulin Resistance
4.1. JNK Signalling in Adipocyte Insulin Resistance
4.2. NFκB Signalling in Adipocyte Insulin Resistance
4.3. Macrophage-Derived Cytokine Signalling and Adipose Tissue Inflammation
4.4. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: IL1B and IL18 Signalling
4.5. Macrophage-Derived IL6 and TNF Signalling
5. Transcriptional Control of ATM Polarisation
5.1. Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription: JAK-STAT Signalling
5.2. Type-1 Interferon Signalling and Transcription Control
6. Metabolic Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarisation
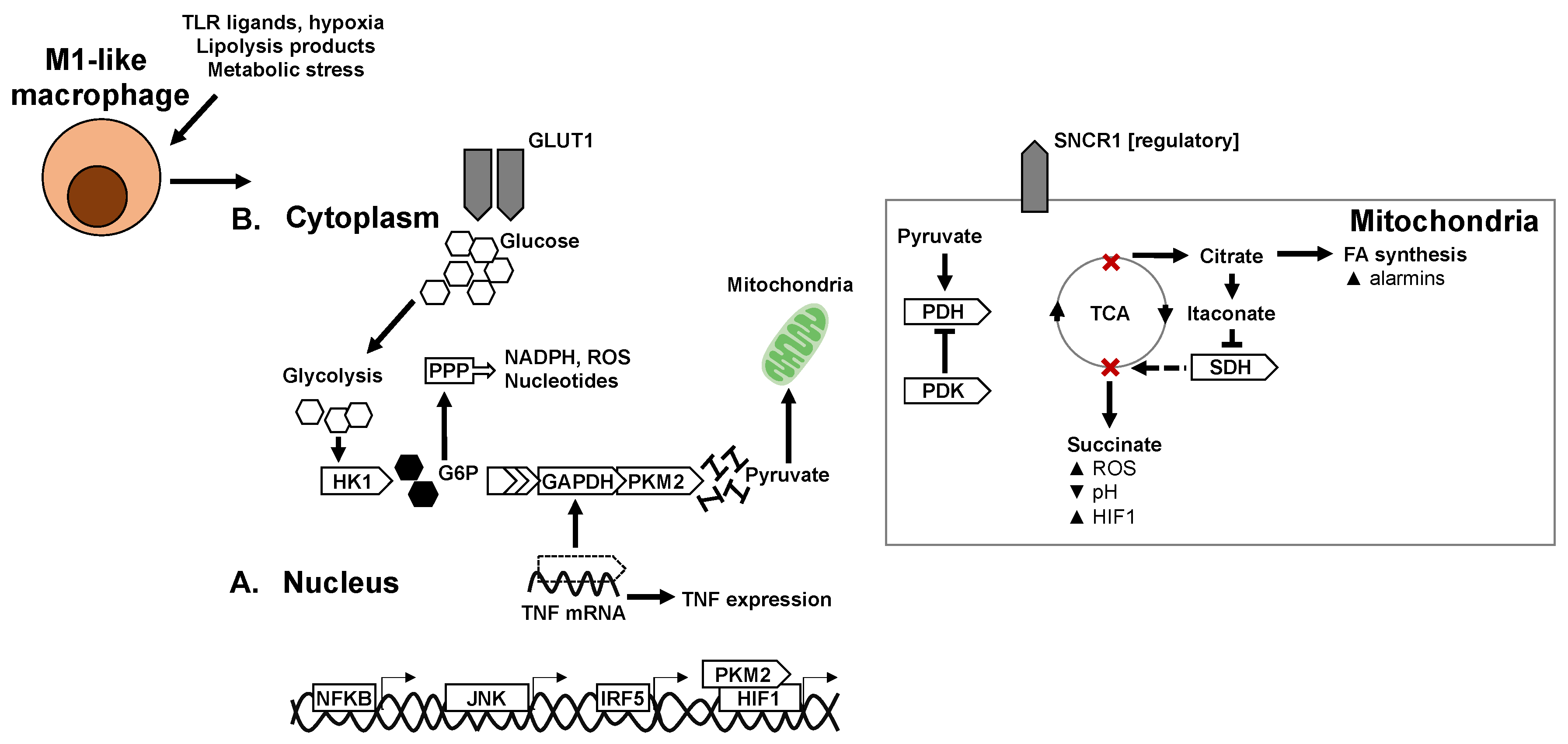
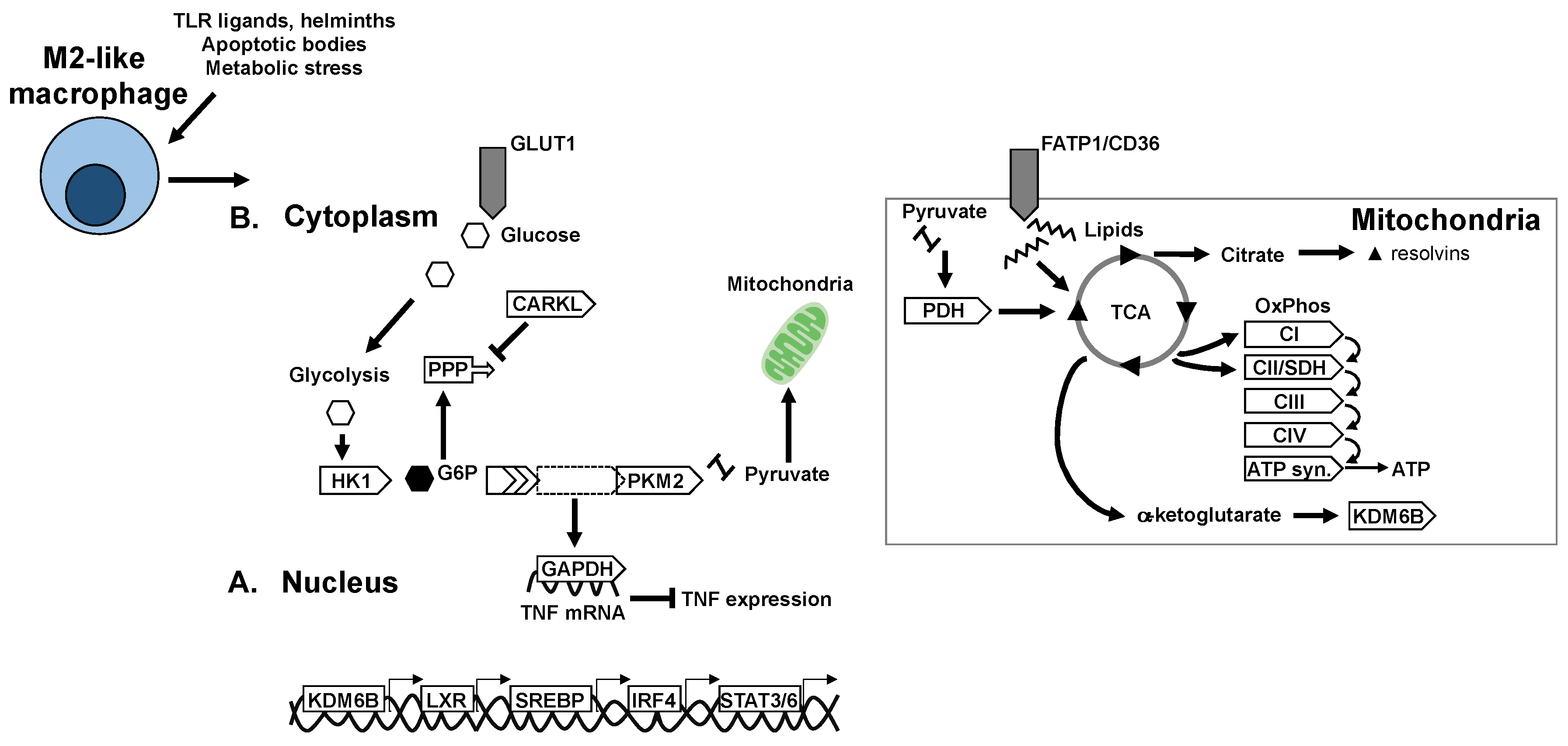
6.1. Glycolysis in Macrophage Polarisation
6.2. Mitochondria and Mitochondrial Respiration in Macrophage Polarisation
6.3. TCA Cycle and Intermediates in Macrophage Polarisation
7. Nuclear Receptors and Transcriptional Control of Macrophage Metabolism
8. Perspectives and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T2D | Type-2 diabetes |
| AT | Adipose tissue |
| ATM | Adipose tissue macrophages |
| SVF | Stromal vascular fraction |
| TNF | Tumour necrosis factor |
| IRS | Insulin receptor substrate |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| NFκB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| PKB | Protein kinase B |
| IκB | Inhibitors of κB |
| IL6 | Interleukin 6 |
| CCL2/MCP1 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligang 2/Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| IKKβ | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta |
| PPR | Pattern recognition receptors |
| TLR | Toll-like receptors |
| NLR | NOD-like receptors |
| DAMP | Damage-associated molecular pattern |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular pattern |
| NLRP3 | Gene encoding NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 |
| ASC | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD |
| IL1B | Interleukin 1 beta |
| IL18 | Interleukin 18 |
| IL1R | Interleukin 1 receptor |
| MyD88 | Myeloid primary response differentiation-88 protein |
| IRAK | Interleukin 1 associated kinase |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| IL4R | Interleukin 4 receptor |
| TNFR | TNF receptor |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IRF | Interferon regulatory factor |
| GLUT | Glucose transporter |
| HK | Hexokinase |
| mTORC1 | Mammalian target of rapamycin complex |
| HIF1 | Hypoxia inducible factor-1 |
| TCA | tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| CARKL | Carbohydrate kinase-like |
| PPP | Pentose phosphate pathway |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| MCSF | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| OXPHOS | oxidative phosphorylation |
| FAO | Fatty acid oxidation |
| IL4 | Interleukin 4 |
| LAL | Lysosomal acid lipase |
| FATP1 | Fatty acid transporter 1 |
| FABP | Fatty acid binding protein |
| CPT | Carnitine palmitoyl transferase |
| αKG | Alpha-ketoglutarate |
| SUCNR1 | Succinate receptor |
| PDH | Pyruvate dehydrogenase |
| PDK | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family A member 1 |
| ABCG1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family G member 1 |
| APOE | Apolipoprotein E |
| APOC | Apolipoprotein C |
| ARG2 | Arginase-2 |
| SREBP | Sterol regulatory element binding protein |
| NLRP1A | Gene encoding NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 1A |
| FASN | Fatty acid synthase |
References
- Bora, P.; Majumdar, A.S. Adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction in regenerative medicine: A brief review on biology and translation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Deyoung, S.M.; Saltiel, A.R. Macrophages block insulin action in adipocytes by altering expression of signaling and glucose transport proteins. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E166–E174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoldi, A.; Naffah de Souza, C.; Camara, N.O.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M. The Macrophage Switch in Obesity Development. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coats, B.R.; Schoenfelt, K.Q.; Barbosa-Lorenzi, V.C.; Peris, E.; Cui, C.; Hoffman, A.; Zhou, G.; Fernandez, S.; Zhai, L.; Hall, B.A.; et al. Metabolically Activated Adipose Tissue Macrophages Perform Detrimental and Beneficial Functions during Diet-Induced Obesity. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 3149–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Arner, P.; Caro, J.F.; Atkinson, R.L.; Spiegelman, B.M. Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, K.T.; Wiesbrock, S.M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Functional analysis of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors in TNF-alpha-mediated insulin resistance in genetic obesity. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4832–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimobayashi, M.; Albert, V.; Woelnerhanssen, B.; Frei, I.C.; Weissenberger, D.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Clement, N.; Moes, S.; Colombi, M.; Meier, J.A.; et al. Insulin resistance causes inflammation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Li, P.; Huh, J.Y.; Hwang, I.J.; Lu, M.; Kim, J.I.; Ham, M.; Talukdar, S.; Chen, A.; Lu, W.J.; et al. Inflammation is necessary for long-term but not short-term high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Salomon, C.; Freeman, D.J. Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose Tissue-A Potential Role in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes? Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamzina, L.; Gruppuso, P.A.; Wands, J.R. Insulin signaling through insulin receptor substrate 1 and 2 in normal liver development. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandona, P.; Weinstock, R.; Thusu, K.; Abdel-Rahman, E.; Aljada, A.; Wadden, T. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in sera of obese patients: Fall with weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 2907–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, P.A.; Ranganathan, S.; Li, C.; Wood, L.; Ranganathan, G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E745–E751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmas, E.; Toubal, A.; Alzaid, F.; Blazek, K.; Eames, H.L.; Lebozec, K.; Pini, M.; Hainault, I.; Montastier, E.; Denis, R.G.; et al. Irf5 deficiency in macrophages promotes beneficial adipose tissue expansion and insulin sensitivity during obesity. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Konstantopoulos, N.; Lee, J.; Hansen, L.; Li, Z.W.; Karin, M.; Shoelson, S.E. Reversal of obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance with salicylates or targeted disruption of Ikkbeta. Science 2001, 293, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerson, A.B.; Hundal, R.S.; Dufour, S.; Lebon, V.; Befroy, D.; Cline, G.W.; Enocksson, S.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Shulman, G.I.; Petersen, K.F. The effects of rosiglitazone on insulin sensitivity, lipolysis, and hepatic and skeletal muscle triglyceride content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drareni, K.; Gautier, J.F.; Venteclef, N.; Alzaid, F. Transcriptional control of macrophage polarisation in type 2 diabetes. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, Y.; Kaneto, H.; Kawamori, D.; Hatazaki, M.; Miyatsuka, T.; Matsuoka, T.A.; Kajimoto, Y.; Matsuhisa, M.; Yamasaki, Y.; Hori, M. Modulation of the JNK pathway in liver affects insulin resistance status. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45803–45809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluher, M.; Bashan, N.; Shai, I.; Harman-Boehm, I.; Tarnovscki, T.; Avinaoch, E.; Stumvoll, M.; Dietrich, A.; Kloting, N.; Rudich, A. Activated Ask1-MKK4-p38MAPK/JNK stress signaling pathway in human omental fat tissue may link macrophage infiltration to whole-body Insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.G.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-kappaB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmi, B.K.; Hasty, A.H. Macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue: Initiation, propagation and remodeling. Future Lipidol. 2008, 3, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, J.; Weyer, U.; Immig, K.; Kloting, N.; Bluher, M.; Eilers, J.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. Local proliferation of macrophages in adipose tissue during obesity-induced inflammation. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solinas, G.; Naugler, W.; Galimi, F.; Lee, M.S.; Karin, M. Saturated fatty acids inhibit induction of insulin gene transcription by JNK-mediated phosphorylation of insulin-receptor substrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16454–16459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, U.; Cao, Q.; Yilmaz, E.; Lee, A.H.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Ozdelen, E.; Tuncman, G.; Gorgun, C.; Glimcher, L.H.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 2004, 306, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, V.; Uchida, T.; Yenush, L.; Davis, R.; White, M.F. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9047–9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanti, J.F.; Gremeaux, T.; Van Obberghen, E.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y. Insulin receptor substrate 1 is phosphorylated by the serine kinase activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Biochem. J. 1994, 304, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gual, P.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Tanti, J.F. Positive and negative regulation of insulin signaling through IRS-1 phosphorylation. Biochimie 2005, 87, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnier, C.H.; Song, H.Y.; Gao, X.; Goeddel, D.V.; Cao, Z.; Rothe, M. Identification and characterization of an IkappaB kinase. Cell 1997, 90, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covert, M.W.; Leung, T.H.; Gaston, J.E.; Baltimore, D. Achieving stability of lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB activation. Science 2005, 309, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Ma, J.; Feng, B.; Zhang, H.; Diehl, J.A.; Chin, Y.E.; Yan, W.; Xu, H. FFA-induced adipocyte inflammation and insulin resistance: Involvement of ER stress and IKKbeta pathways. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2011, 19, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orliaguet, L.; Dalmas, E.; Drareni, K.; Venteclef, N.; Alzaid, F. Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarization in Insulin Signaling and Sensitivity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandanmagsar, B.; Youm, Y.H.; Ravussin, A.; Galgani, J.E.; Stadler, K.; Mynatt, R.L.; Ravussin, E.; Stephens, J.M.; Dixit, V.D. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Zhou, R.; Tschopp, J. The NLRP3 inflammasome: A sensor for metabolic danger? Science 2010, 327, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Schumann, D.M.; Faulenbach, M.; Ellingsgaard, H.; Perren, A.; Ehses, J.A. Islet inflammation in type 2 diabetes: From metabolic stress to therapy. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, S161–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagathu, C.; Yvan-Charvet, L.; Bastard, J.P.; Maachi, M.; Quignard-Boulange, A.; Capeau, J.; Caron, M. Long-term treatment with interleukin-1beta induces insulin resistance in murine and human adipocytes. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Madi, M.; Ding, C.; Fok, M.; Steele, T.; Ford, C.; Hunter, L.; Bing, C. Interleukin-1beta mediates macrophage-induced impairment of insulin signaling in human primary adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 307, E289–E304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballak, D.B.; Stienstra, R.; Tack, C.J.; Dinarello, C.A.; van Diepen, J.A. IL-1 family members in the pathogenesis and treatment of metabolic disease: Focus on adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. Cytokine 2015, 75, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, I.S.; Wang, B.; Jenkins, J.R.; Trayhurn, P. The pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-18 is expressed in human adipose tissue and strongly upregulated by TNFalpha in human adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 337, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilverschoon, G.R.; Tack, C.J.; Joosten, L.A.; Kullberg, B.J.; van der Meer, J.W.; Netea, M.G. Interleukin-18 resistance in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, R.Z.; Creer, A.J.; Lorenzo-Arteaga, K.M.; Ostlund, K.R.; Sarvetnick, N.E. Interleukin (IL)-18 Binding Protein Deficiency Disrupts Natural Killer Cell Maturation and Diminishes Circulating IL-18. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feve, B.; Bastard, J.P. The role of interleukins in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodington, D.W.; Desai, H.R.; Woo, M. JAK/STAT—Emerging Players in Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagathu, C.; Bastard, J.P.; Auclair, M.; Maachi, M.; Capeau, J.; Caron, M. Chronic interleukin-6 (IL-6) treatment increased IL-6 secretion and induced insulin resistance in adipocyte: Prevention by rosiglitazone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 311, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Cardone, R.L.; Petersen, M.C.; Zhang, D.; Fouqueray, P.; Hallakou-Bozec, S.; Bolze, S.; Shulman, G.I.; Petersen, K.F.; Kibbey, R.G. Imeglimin lowers glucose primarily by amplifying glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in high-fat-fed rodents. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E461–E470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Camporez, J.G.; Kursawe, R.; Titchenell, P.M.; Zhang, D.; Perry, C.J.; Jurczak, M.J.; Abudukadier, A.; Han, M.S.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. Hepatic acetyl CoA links adipose tissue inflammation to hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Cell 2015, 160, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, G.; Das, M.; Mora, A.; Zhang, Z.; Jun, J.Y.; Ko, H.J.; Barrett, T.; Kim, J.K.; Davis, R.J. A stress signaling pathway in adipose tissue regulates hepatic insulin resistance. Science 2008, 322, 1539–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, B.; Greenwald, D.; Hulmes, J.D.; Chang, M.; Pan, Y.C.; Mathison, J.; Ulevitch, R.; Cerami, A. Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature 1985, 316, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torti, F.M.; Dieckmann, B.; Beutler, B.; Cerami, A.; Ringold, G.M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: An in vitro model of cachexia. Science 1985, 229, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatanaga, T.; Hwang, C.D.; Kohr, W.; Cappuccini, F.; Lucci, J.A., 3rd; Jeffes, E.W.; Lentz, R.; Tomich, J.; Yamamoto, R.S.; Granger, G.A. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor (soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor) for tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin obtained from the serum ultrafiltrates of human cancer patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8781–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraldi, P.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Buurman, W.A.; White, M.F.; Spiegelman, B.M. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibits insulin signaling through stimulation of the p55 TNF receptor and activation of sphingomyelinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13018–13022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Arner, P.; Atkinson, R.L.; Spiegelman, B.M. Differential regulation of the p80 tumor necrosis factor receptor in human obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 1997, 46, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.; Tuncman, G.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Samad, F. Divergent roles for p55 and p75 TNF-alpha receptors in the induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthorn, W.P.; Sethi, J.K. TNF-alpha and adipocyte biology. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisoli, E.; Briscini, L.; Giordano, A.; Tonello, C.; Wiesbrock, S.M.; Uysal, K.T.; Cinti, S.; Carruba, M.O.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha mediates apoptosis of brown adipocytes and defective brown adipocyte function in obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8033–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Jeon, J.H.; Yoon, S.R.; Choi, I.; Yang, Y. c-Jun N-terminal kinase is involved in the suppression of adiponectin expression by TNF-alpha in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, G.N.; Kwak, S.J. NF-kappaB is involved in the TNF-alpha induced inhibition of the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells by reducing PPARgamma expression. Exp. Mol. Med. 2003, 35, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J.M.; Lee, J.; Pilch, P.F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is accompanied by a loss of insulin receptor substrate-1 and GLUT4 expression without a loss of insulin receptor-mediated signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Miles, P.D.; Ladd, C.M.; Ross, K.; Golub, T.R.; Olefsky, J.M.; Lodish, H.F. Profiling gene transcription in vivo reveals adipose tissue as an immediate target of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Implications for insulin resistance. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3176–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Hacohen, N.; Golub, T.R.; Van Parijs, L.; Lodish, H.F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppresses adipocyte-specific genes and activates expression of preadipocyte genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: Nuclear factor-kappaB activation by TNF-alpha is obligatory. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1319–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, C.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: The JAK-STAT pathway. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 621–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, A.J.; Stephens, J.M. Emerging roles of JAK-STAT signaling pathways in adipocytes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, A.J.; Stephens, J.M. The role of JAK-STAT signaling in adipose tissue function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurzov, E.N.; Stanley, W.J.; Pappas, E.G.; Thomas, H.E.; Gough, D.J. The JAK/STAT pathway in obesity and diabetes. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 3002–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filgueiras, L.R.; Brandt, S.L.; Ramalho, T.R.; Jancar, S.; Serezani, C.H. Imbalance between HDAC and HAT activities drives aberrant STAT1/MyD88 expression in macrophages from type 1 diabetic mice. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasamsetti, S.B.; Karnewar, S.; Kanugula, A.K.; Thatipalli, A.R.; Kumar, J.M.; Kotamraju, S. Metformin inhibits monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation via AMPK-mediated inhibition of STAT3 activation: Potential role in atherosclerosis. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2028–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, H.R.; Sivasubramaniyam, T.; Revelo, X.S.; Schroer, S.A.; Luk, C.T.; Rikkala, P.R.; Metherel, A.H.; Dodington, D.W.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, M.J.; et al. Macrophage JAK2 deficiency protects against high-fat diet-induced inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajic, T.; Hainard, A.; Scherl, A.; Wohlwend, A.; Negro, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Szanto, I. STAT6 promotes bi-directional modulation of PKM2 in liver and adipose inflammatory cells in rosiglitazone-treated mice. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.R. Interferons: From molecular biology to man. Part 1. Genetics and molecular biology of the interferon system. Microbiol. Sci. 1986, 3, 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- Kumaran Satyanarayanan, S.; El Kebir, D.; Soboh, S.; Butenko, S.; Sekheri, M.; Saadi, J.; Peled, N.; Assi, S.; Othman, A.; Schif-Zuck, S.; et al. IFN-beta is a macrophage-derived effector cytokine facilitating the resolution of bacterial inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.N.; Jiang, D.S.; Li, H. Interferon regulatory factors: At the crossroads of immunity, metabolism, and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Royer, W.E., Jr. Structural insights into interferon regulatory factor activation. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, J.S.; Puglisi, M.J.; Ellacott, K.L.; Lumeng, C.N.; Wasserman, D.H.; Hasty, A.H. Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency promotes the alternative activation of adipose tissue macrophages. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, J.; Kong, X.; Tenta, M.; Wang, X.; Kang, S.; Rosen, E.D. Interferon regulatory factor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation through regulation of adipose tissue macrophage polarization. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3394–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Kershaw, E.E.; Chiu, P.C.; Dushay, J.; Estall, J.L.; Klein, U.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Rosen, E.D. Transcriptional control of adipose lipid handling by IRF4. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemerman, A.J.; Johnson, A.R.; Sacks, G.N.; Milner, J.J.; Kirk, E.L.; Troester, M.A.; Macintyre, A.N.; Goraksha-Hicks, P.; Rathmell, J.C.; Makowski, L. Metabolic reprogramming of macrophages: Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1)-mediated glucose metabolism drives a proinflammatory phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7884–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Kanter, J.E.; Kramer, F.; Barnhart, S.; Shen, X.; Vivekanandan-Giri, A.; Wall, V.Z.; Kowitz, J.; Devaraj, S.; O’Brien, K.D.; et al. Testing the role of myeloid cell glucose flux in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.S.; Hisata, S.; Park, M.A.; DeNicola, G.M.; Ryter, S.W.; Nakahira, K.; Choi, A.M.K. mTORC1-Induced HK1-Dependent Glycolysis Regulates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannahill, G.M.; Curtis, A.M.; Adamik, J.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; McGettrick, A.F.; Goel, G.; Frezza, C.; Bernard, N.J.; Kelly, B.; Foley, N.H.; et al. Succinate is an inflammatory signal that induces IL-1beta through HIF-1alpha. Nature 2013, 496, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.J.; Garg, N.J. Metabolic programming of macrophage functions and pathogens control. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Curtis, A.M.; Goel, G.; Lauterbach, M.A.R.; Sheedy, F.J.; Gleeson, L.E.; van den Bosch, M.W.M.; Quinn, S.R.; Domingo-Fernandez, R.; Johnston, D.G.W.; et al. Pyruvate Kinase M2 Regulates Hif-1alpha Activity and IL-1beta Induction and Is a Critical Determinant of the Warburg Effect in LPS-Activated Macrophages. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, P.; Vachharajani, V.; McPhail, L.; Yoza, B.; McCall, C.E. GAPDH Binding to TNF-alpha mRNA Contributes to Posttranscriptional Repression in Monocytes: A Novel Mechanism of Communication between Inflammation and Metabolism. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Huang, S.C.; Sergushichev, A.; Lampropoulou, V.; Ivanova, Y.; Loginicheva, E.; Chmielewski, K.; Stewart, K.M.; Ashall, J.; Everts, B.; et al. Network integration of parallel metabolic and transcriptional data reveals metabolic modules that regulate macrophage polarization. Immunity 2015, 42, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, A.N.; Edsfeldt, A.; Cole, J.E.; Kassiteridi, C.; Swart, M.; Park, I.; Green, P.; Khoyratty, T.; Saliba, D.; Goddard, M.E.; et al. Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 Controls Necrotic Core Formation in Atherosclerotic Lesions by Impairing Efferocytosis. Circulation 2017, 136, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedl, M.; Yan, J.; Abraham, C. IRF5 and IRF5 Disease-Risk Variants Increase Glycolysis and Human M1 Macrophage Polarization by Regulating Proximal Signaling and Akt2 Activation. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2442–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.C.; Smith, A.M.; Everts, B.; Colonna, M.; Pearce, E.L.; Schilling, J.D.; Pearce, E.J. Metabolic Reprogramming Mediated by the mTORC2-IRF4 Signaling Axis Is Essential for Macrophage Alternative Activation. Immunity 2016, 45, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Xie, N.; Cui, H.C.; Moellering, D.R.; Abraham, E.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, G. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 1 Participates in Macrophage Polarization via Regulating Glucose Metabolism. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 6082–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, A.H.; Costa, A.B.; Engel, J.D.G.; Rezin, G.T. Mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity. Life Sci. 2018, 192, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Lanza, I.R.; Swain, J.M.; Sarr, M.G.; Nair, K.S.; Jensen, M.D. Adipocyte Mitochondrial Function Is Reduced in Human Obesity Independent of Fat Cell Size. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E209–E216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escames, G.; Lopez, L.C.; Garcia, J.A.; Garcia-Corzo, L.; Ortiz, F.; Acuna-Castroviejo, D. Mitochondrial DNA and inflammatory diseases. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Armada, M.J.; Riveiro-Naveira, R.R.; Vaamonde-Garcia, C.; Valcarcel-Ares, M.N. Mitochondrial dysfunction and the inflammatory response. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilbronn, L.; Smith, S.R.; Ravussin, E. Failure of fat cell proliferation, mitochondrial function and fat oxidation results in ectopic fat storage, insulin resistance and type II diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, S12–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.H.; Shiau, M.Y.; Chuang, P.H.; Chang, Y.H.; Hwang, J. Interleukin-4 regulates lipid metabolism by inhibiting adipogenesis and promoting lipolysis. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namgaladze, D.; Brune, B. Macrophage fatty acid oxidation and its roles in macrophage polarization and fatty acid-induced inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Liu, J.; Rovira, I.I.; Gonzalez-Hurtado, E.; Lee, J.; Wolfgang, M.J.; Finkel, T. Fatty acid oxidation in macrophage polarization. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, D.; Mukundan, L.; Odegaard, J.I.; Zhang, L.; Smith, K.L.; Morel, C.R.; Wagner, R.A.; Greaves, D.R.; Murray, P.J.; Chawla, A. Oxidative metabolism and PGC-1beta attenuate macrophage-mediated inflammation. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Everts, B.; Ivanova, Y.; O’Sullivan, D.; Nascimento, M.; Smith, A.M.; Beatty, W.; Love-Gregory, L.; Lam, W.Y.; O’Neill, C.M.; et al. Cell-intrinsic lysosomal lipolysis is essential for alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Fucho, R.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Tuncman, G.; Cao, H.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Adipocyte/macrophage fatty acid-binding proteins contribute to metabolic deterioration through actions in both macrophages and adipocytes in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, P.; Munoz, A.; Sola, A.; Hotter, G. CPT1a gene expression reverses the inflammatory and anti-phagocytic effect of 7-ketocholesterol in RAW264.7 macrophages. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgaladze, D.; Brune, B. Fatty acid oxidation is dispensable for human macrophage IL-4-induced polarization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaslona, Z.; Serezani, C.H.; Okunishi, K.; Aronoff, D.M.; Peters-Golden, M. Prostaglandin E2 restrains macrophage maturation via E prostanoid receptor 2/protein kinase A signaling. Blood 2012, 119, 2358–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulou, V.; Sergushichev, A.; Bambouskova, M.; Nair, S.; Vincent, E.E.; Loginicheva, E.; Cervantes-Barragan, L.; Ma, X.; Huang, S.C.; Griss, T.; et al. Itaconate Links Inhibition of Succinate Dehydrogenase with Macrophage Metabolic Remodeling and Regulation of Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Kelly, B.; Logan, A.; Costa, A.S.H.; Varma, M.; Bryant, C.E.; Tourlomousis, P.; Dabritz, J.H.M.; Gottlieb, E.; Latorre, I.; et al. Succinate Dehydrogenase Supports Metabolic Repurposing of Mitochondria to Drive Inflammatory Macrophages. Cell 2016, 167, 457–470.e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlewood-Evans, A.; Sarret, S.; Apfel, V.; Loesle, P.; Dawson, J.; Zhang, J.; Muller, A.; Tigani, B.; Kneuer, R.; Patel, S.; et al. GPR91 senses extracellular succinate released from inflammatory macrophages and exacerbates rheumatoid arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiran, N.; Ceperuelo-Mallafre, V.; Calvo, E.; Hernandez-Alvarez, M.I.; Ejarque, M.; Nunez-Roa, C.; Horrillo, D.; Maymo-Masip, E.; Rodriguez, M.M.; Fradera, R.; et al. SUCNR1 controls an anti-inflammatory program in macrophages to regulate the metabolic response to obesity. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.S.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Chao, T.; Teav, T.; Christen, S.; Di Conza, G.; Cheng, W.C.; Chou, C.H.; Vavakova, M.; et al. alpha-ketoglutarate orchestrates macrophage activation through metabolic and epigenetic reprogramming. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.K.; Park, S.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, D.W.; Ham, H.J.; Ha, C.M.; Choi, B.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, C.J.; Yoo, E.K.; et al. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase Is a Metabolic Checkpoint for Polarization of Macrophages to the M1 Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiser, J.; Kramer, L.; Sapcariu, S.C.; Battello, N.; Ghelfi, J.; D’Herouel, A.F.; Skupin, A.; Hiller, K. Pro-inflammatory Macrophages Sustain Pyruvate Oxidation through Pyruvate Dehydrogenase for the Synthesis of Itaconate and to Enable Cytokine Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3932–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Reilly, S.M.; Karabacak, V.; Gangl, M.R.; Fitzgerald, K.; Hatano, B.; Lee, C.H. Adipocyte-derived Th2 cytokines and myeloid PPARdelta regulate macrophage polarization and insulin sensitivity. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegaard, J.I.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Goforth, M.H.; Morel, C.R.; Subramanian, V.; Mukundan, L.; Red Eagle, A.; Vats, D.; Brombacher, F.; Ferrante, A.W.; et al. Macrophage-specific PPARgamma controls alternative activation and improves insulin resistance. Nature 2007, 447, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, A.; Laffitte, B.A.; Joseph, S.B.; Mak, P.A.; Wilpitz, D.C.; Edwards, P.A.; Tontonoz, P. Control of cellular cholesterol efflux by the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXR alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12097–12102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.B.; Bradley, M.N.; Castrillo, A.; Bruhn, K.W.; Mak, P.A.; Pei, L.; Hogenesch, J.; O’Connell, R.M.; Cheng, G.; Saez, E.; et al. LXR-dependent gene expression is important for macrophage survival and the innate immune response. Cell 2004, 119, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, C.; Bradley, M.N.; Hong, C.; Lopez, F.; Ruiz de Galarreta, C.M.; Tontonoz, P.; Castrillo, A. The arginase II gene is an anti-inflammatory target of liver X receptor in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 32197–32206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, S.S.; Yousef, L.; Blaschitz, C.; Liu, J.Z.; Edwards, R.A.; Young, S.G.; Raffatellu, M.; Osborne, T.F. Linking lipid metabolism to the innate immune response in macrophages through sterol regulatory element binding protein-1a. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Phelan, P.; Shin, M.; Oh, B.C.; Han, X.; Im, S.S.; Osborne, T.F. SREBP-1a-stimulated lipid synthesis is required for macrophage phagocytosis downstream of TLR4-directed mTORC1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E12228–E12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, J.F.; Patel, R.; Yadav, U.C.S. Sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP) -1 mediates oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) induced macrophage foam cell formation through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Signal. 2019, 53, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, Y.; Spann, N.J.; Link, V.M.; Muse, E.D.; Strid, T.; Edillor, C.; Kolar, M.J.; Matsuzaka, T.; Hayakawa, S.; Tao, J.; et al. SREBP1 Contributes to Resolution of Pro-inflammatory TLR4 Signaling by Reprogramming Fatty Acid Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Song, H.; Yin, L.; Rizzo, M.G.; Sidhu, R.; Covey, D.F.; Ory, D.S.; Semenkovich, C.F. Fatty acid synthesis configures the plasma membrane for inflammation in diabetes. Nature 2016, 539, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejadmoghaddam, M.R.; Minai-Tehrani, A.; Ghahremanzadeh, R.; Mahmoudi, M.; Dinarvand, R.; Zarnani, A.H. Antibody-Drug Conjugates: Possibilities and Challenges. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2019, 11, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
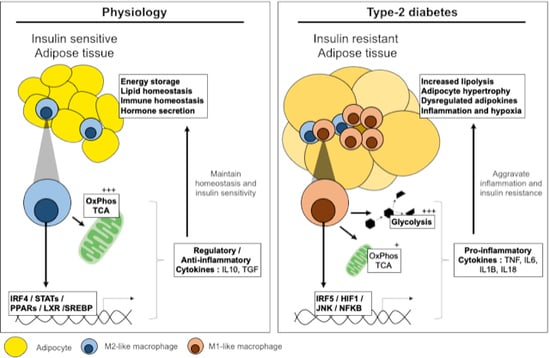
| Insulin Resistant State | Insulin Sensitive State | |
|---|---|---|
| ATM polarisation | M1-like | M2-Like |
| Canonnical stimuli | Bacterial/viral stimuli (TLR/NLR ligands) | Helminths (TLR, lectin receptors) |
| Stimuli in T2D | Inflammatory cytokines/chemokines Free fatty acids, Hypoxia TLR/NLR ligands | Regulatory/Anti-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines Fatty acids, apoptotic bodies, CD36/FATP1 ligation Metformin, hormone signalling (leptin, adiponectin) |
| Pathway/TFs | JNK, NFKB, NLRP3, IRF5, HIF1 | STAT3/6, IRF4, KDM6B, LXR, SREBPs |
| Cytokines/Chemokines | IL1B, IL18, IL6, TNF, IFNα, β, κ and ω | IL10, TGF, CCL1, IL1Ra *succinate |
| Glycolysis and PPP adaptation |
|
|
| Mitochondria and oxidative metabolism |
|
|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orliaguet, L.; Ejlalmanesh, T.; Alzaid, F. Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarisation and Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165731
Orliaguet L, Ejlalmanesh T, Alzaid F. Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarisation and Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(16):5731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165731
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrliaguet, Lucie, Tina Ejlalmanesh, and Fawaz Alzaid. 2020. "Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarisation and Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 16: 5731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165731
APA StyleOrliaguet, L., Ejlalmanesh, T., & Alzaid, F. (2020). Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarisation and Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(16), 5731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165731