Structural Characteristics in the γ Chain Variants Associated with Fibrinogen Storage Disease Suggest the Underlying Pathogenic Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
2.1. Clinical Data
2.2. Morphological Studies
2.3. Molecular Analysis
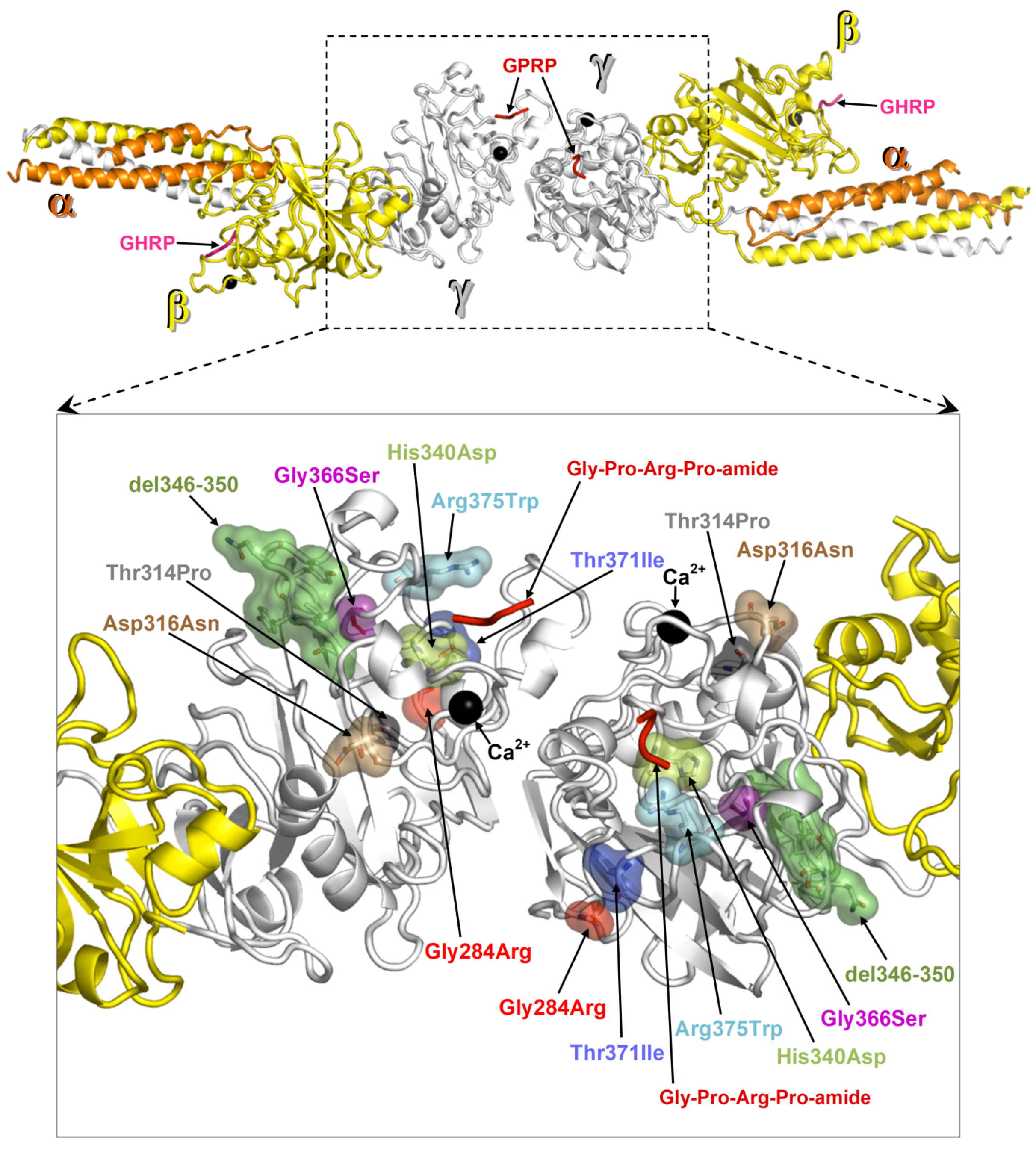
2.4. Protein Structural Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosesson, M.W.; Siebenlist, K.B.; Meh, D.A. The structure and biological features of fibrinogen and fibrin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 936, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosesson, M.W. Hereditary fibrinogen abnormalities. In Williams Hematology, 7th ed.; Mac Grow-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1909–1927. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, S.O.; Wyatt, J.; Medicina, D.; Callea, F.; George, P.M. Fibrinogen Brescia. Fibrinogen brescia: Hepatic endoplasmic reticulum storage and hypofibrinogenemia because of a gamma284 Gly-->Arg mutation. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callea, F.; De Vos, R.; Pinackat, J.; Favret, M.; Fiaccavento, S.; Ascari, E.; Tortora, O.; Albertini, A.; Henschen, A.; Desmet, V.J. Herediray hypofibrinogenemia with hepatic storage of fibrinogen. A new endoplasmic reticulum storage disease. In Fibrinogen 2. Biochemistry, Physiology and Clinical Relevance; Lowe, G.D.O., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Callea, F.; Brisigotti, M.; Fabbretti, G.; Bonino, F.; Desmet, V.J. Hepatic Endoplasmic Storage Diseases. Liver 1992, 12, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francalanci, P.; Santorelli, F.; Talini, I.; Boldrini, R.; Devito, R.; Diomedi-Camassei, F.; Maggiore, G.; Callea, F. Severe liver disease in early childhood due to fibrinogen storage and de novo gamma375Arg-Try gene mutation. J. Pediatr. 2006, 148, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skymkowitz, J.; Borg, J.; Stricher, F.; Nys, R.; Rousseau, F.; Serrano, L. The FoldX web server: An online force field. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 3, W382–W388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, S.O.; Wyatt, J.M.; Fellowes, A.P.; Dlott, I.S.; Triplet Da George, P.M. Gamma 371Thr-Ile substitution in the fibrinogen gammaD domain causes hypofibrinogenemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1550, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, S.O.; Maghzal, G.; Schneider, B.L.; Gordon, R.; Magid, M.S.; George, P.M. Novel fibrinogen gamma375 Arg-->Trp mutation (fibrinogen Aguadilla) causes hepatic endoplasmic reticulum storage and hypofibrinogenemia. Hepatology 2002, 36, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, N.; Queloin, F.; Ternisien, C.; Hanss, M.; Michalak, S.; De Mazancourt, P.; Rousselet, M.C.; Cales, P. Fibrinogen angers with a new deletion (gamma GVYY 346–350 causes hypofibrinogenemia with hepatic storage. J. Thromb. Hemost. 2007, 5, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, S.O.; Davis, R.L.; Conard, K.; Savo, A.; Furuya, K.N. Novel fibrinogen mutation gammaThr-Pro (fibrinogen Al du Pont) associated with hepatic fibrinogen storage disease and hypofibrinogenemia. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselta, R.; Robusto, M.; Braidorri, P.; Pevvandi, E.; Nastasio, S.; D’Antiga, O.; Perisic, V.N.; Maggiore, G.; Caccia, S.; Duga, S. Hepatic fibrinogen storage disease: Identification of two novel mutations (p.Asp316Asn, fibrinogen Pisa and p.Gly366Ser, fibrinogen Beograd) impacting on the fibrinogen γ-module. J. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 13, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callea, F.; Giovannoni, I.; Sari, S.; Aksu, A.U.; Esendaghy, G.; Dalgic, B.; Boldrini, R.; Akyol, G.; Francalanci, P.; Bellacchio, E. Fibrinogen gamma chain mutation (c.1096C>G p.His340Asp) fibrinogen Ankara, causing hypofibrinogenemia and hepatic storage. Pathology 2017, 49, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudano, A.P.; Doolittle, R.F. Studies on synthetic peptides that bind to fibrinogen and prevent fibrin polymerization. Structural requirements, number of binding sites, and species differences. Biochemistry 1980, 19, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheen, C.R.; Dear, A.; Brennan, S.O. Expression of four mutant fibrinogen gammaC domains in Pichia pastoris confirms them as causes of hypofibrinogenemia. Protein Expr. Purif. 2010, 73, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callea, F.; Giovannoni, I.; Sari, S.; Guldal, E.; Dalgic, B.; Akyol, G.; Sogo, T.; Al-Hussaini, A.; Maggiore, G.; Bartuli, A.; et al. Fibrinogen gamma chain mutations provoke fibrinogen and apolipoptotein B plasma deficiency and liver storage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medicina, D.; Fabbretti, G.; Brennan, S.O.; George, P.M.; Kudryk, B.; Callea, F. Genetical and immunological characterization of fibrinogen inclusion bodies in patients with hepatic fibrinogen storage and liver disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 936, 522–525. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Pham, K.; Li, D.; Shutte, R.J.; Gonzalo, D.H.; Zhang, P.; Oshins, R.; Tan, W.; Brantly, M.; Liu, C.; et al. A novel small molecule inhibits intrahepatocellular accumulation of Z-variant alpha-1-antitrypsin in vitro and in vivo. Cells 2019, 12, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, K.; Dear, A.; Kartenbrund, E.R.; Crum, B.E.; George, P.M.; Brennan, O.S. Mutant fibrinogen clearance fo Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated Protein Degradation and autophagy: An explanation for liver disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puls, F.; Goldschmidt, I.; Bartel, H.; Agne, C.; Broker, V.; Damrich, M.; Lhemann, U.; Berrang, J.; Pfister, E.D.; Kreipe, H.H.; et al. Autophagy-enhancing drug carbamazepine diminishes hepatocellular death in fibrinogen storage disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.H.; Knisely, A.S.; Wang, N.L.; Gong, J.Y.; Wang, S. Fibrinogen storage disease in a chines boy with de novo fibriniogen Aguadilla mutation. Incomplete response to caqrbamazepine and ursodeoxycholic acid. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, S.; Yilmaz, G.; Gonul, I.; Dalgic, B.; Alkyol, G.; Giovannoni, I.; Francalanci, P.; Callea, F. Fibrinogen storage disease and cirrhosis associated with hypobetaliproteinemia owing to fibrinogen Aguadilla in a Turkish child. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2501–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogo, T.; Nagasaka, H.; Komatsu, H.; Inui, A.; Miida, T.; Callea, F.; Francalanci, P.; Hirano, K.; Kitamura, H.; Yorifuji, T. Fibrinogen storage disease caused by Aguadilla mutation presenting with hypo-betalipoproteinemia and considerable liver disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubbia-Brant, L.; Neerman Arbez, M.; Rongemont, A.L.; Male, P.J.; Spahr, I. Fibrinogen gamma 375Arg-Trp mutation (fibrinogen Aguadilla) causes hereditary hypofibrinogenemia, hepatic endoplasmic reticulum storage disease and cirrhosis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hussaini, A.; Altahyli, A.; El Hag, I.; Al Hussaini, H.; Francalanci, P.; Giovannoni, I.; Callea, F. Hepatic fibrinogen storage disease due to fibrinogen gamma375Arg-Trp mutation “fibrinogen Aguadilla” is present in Arabs. Saudi. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callea, F.; Fevery, J.; NMassi, G.; Lievens, C.; De Groote, J.; Desmet, V.J. Detection of Pi Z phenotype individuals by alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT) immunohistochemistry in paraffin embedded liver tissue specimens. J. Hepatol. 1986, 3, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, A.D. The selective advantage of alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. The selective advantage of alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variant | ΔΔG (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|
| γ Chain C* | γ Chain F* | |
| Thr371Ile | 0.7 (0.1) | 0.8 (0.3) |
| Gly284Arg | 10.5 (0.4) | 14.4 (0.9) |
| Arg375Trp | 1.9 (1.2) | 2.1 (1.0) |
| Thr314Pro | 1.0 (0.3) | 2.5 (0.0) |
| Asp316Asn | −0.3 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Gly366Ser | 6.3 (0.8) | 4.4 (0.2) |
| His340Asp | 2.8 (0.3) | 2.2 (0.0) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burcu, G.; Bellacchio, E.; Sag, E.; Cebi, A.H.; Saygin, I.; Bahadir, A.; Yilmaz, G.; Corbeddu, M.; Cakir, M.; Callea, F. Structural Characteristics in the γ Chain Variants Associated with Fibrinogen Storage Disease Suggest the Underlying Pathogenic Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145139
Burcu G, Bellacchio E, Sag E, Cebi AH, Saygin I, Bahadir A, Yilmaz G, Corbeddu M, Cakir M, Callea F. Structural Characteristics in the γ Chain Variants Associated with Fibrinogen Storage Disease Suggest the Underlying Pathogenic Mechanism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145139
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurcu, Guven, Emanuele Bellacchio, Elif Sag, Alper Han Cebi, Ismail Saygin, Aysenur Bahadir, Guldal Yilmaz, Marialuisa Corbeddu, Murat Cakir, and Francesco Callea. 2020. "Structural Characteristics in the γ Chain Variants Associated with Fibrinogen Storage Disease Suggest the Underlying Pathogenic Mechanism" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145139
APA StyleBurcu, G., Bellacchio, E., Sag, E., Cebi, A. H., Saygin, I., Bahadir, A., Yilmaz, G., Corbeddu, M., Cakir, M., & Callea, F. (2020). Structural Characteristics in the γ Chain Variants Associated with Fibrinogen Storage Disease Suggest the Underlying Pathogenic Mechanism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145139






