Abstract
Acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI/ARDS) are characterized by an inflammatory response, alveolar edema, and hypoxemia. ARDS occurs most often in the settings of pneumonia, sepsis, aspiration of gastric contents, or severe trauma. The prevalence of ARDS is approximately 10% in patients of intensive care. There is no effective remedy with mortality high at 30–40%. Most functional proteins are dynamic and stringently governed by ubiquitin proteasomal degradation. Protein ubiquitination is reversible, the covalently attached monoubiquitin or polyubiquitin moieties within the targeted protein can be removed by a group of enzymes called deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs). Deubiquitination plays an important role in the pathobiology of ALI/ARDS as it regulates proteins critical in engagement of the alveolo-capillary barrier and in the inflammatory response. In this review, we provide an overview of how DUBs emerge in pathogen-induced pulmonary inflammation and related aspects in ALI/ARDS. Better understanding of deubiquitination-relatedsignaling may lead to novel therapeutic approaches by targeting specific elements of the deubiquitination pathways.
1. Introduction
Acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI/ARDS) are a group of illnesses with features of lung inflammation, air–blood barrier disfunction, and hypoxemia. ALI/ARDS are life-threatening with a severe public health concern, approximately 200,000 people per year develop into ALI/ARDS in the United States, and the mortality rates are high at 30–40% [1,2,3,4,5]. It is believed that about ~10% of patients in intensive care units eventually develop into ALI/ARDS worldwide. Etiologically, microbial pneumonia, sepsis, aspiration of gastric contents, or severe trauma are the major causes of ALI/ARDS. Approximately 40% of the ALI/ARDS patients are linked with viral and bacterial pneumonia. The outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has become a pandemic disease. By now, millions of people have suffered from this disease with hundreds of thousands of deaths in almost all countries all over the world because of the pandemic, and the numbers of the diagnosed patients and the deaths due to this disease are climbing each day (https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map). For severe COVID-19 patients, ALI/ARDS represent one of the major pathological changes; phenotypes include inflammatory infiltration and inflammatory storm, alveolar epithelial–capillary damage, lung embolism and hemorrhage, hypoxia, and poor prognosis with high mortality. The pathobiology of the disease is incompletely understood [1,6,7,8]. Furthermore, no specific effective therapeutic method has been developed to treat the illness. Thus, understanding the molecular mechanisms of ALI/ARDS is of particular important in developing effective remedies against the illness.
Overwhelmed immune responses are believed to be a major contributing factor in the pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. In the initial pulmonary infection, invaded microbial pathogens including viruses and bacteria attract and activate residential microphages to release chemokines and cytokines, along with infiltration of leukocytes, particularly neutrophils and lymphocytes, into the alveolar sacs [5,9]. In ideal scenarios, host immune responses clear and exclude the invaded pathogens and repair the diseased tissues. However, host immune responses may be unable to achieve this goal due to the pathogenicity of the microbe or the compromised capacity of the host defense, such as in patients with cancer, organ transplantation, diabetes, or HIV infection. Higher inflammatory responses may occur in these cases and an over-reacted inflammatory response eventually leads to an overwhelmed inflammatory response. An overwhelmed inflammatory response is increasingly noticed as one of the key contributors to the poor prognosis of ALI/ARDS. A dysregulated high inflammatory response, also referred to as a “cytokine storm”, increases mortality in ALI/ARDS patients [10,11]. Along with the process of cytokine storm, dysregulated molecular signaling may cause deleterious damage independent of microbial pathogens that increase mortality. However, a high inflammatory storm turns into low inflammation in the later stage due to immune paralysis that may lead to immunosuppression, which contributes to secondary infection and worsens the prognosis of the patients as well [1].
In the meantime, the invasion of microbial pathogens causes airway epithelial and pulmonary endothelial cell death, destroys alveolar architecture, and damages the air–blood barrier [5,12]. These pathological changes impair effective air–blood exchange, which results in edema and hypoxemia. Clinically, hypoxemia in patients with ARDS is caused by ventilation-to-perfusion mismatch, as well as right-to-left intrapulmonary shunting [4]. In addition, impaired excretion of carbon dioxide is a major component of respiratory failure, resulting in elevated minute ventilation that is associated with an increase in pulmonary dead space (that is, the volume of a breath that does not participate in carbon dioxide excretion). Elevation of pulmonary dead space and a decrease in respiratory compliance are independent predictors of mortality in ARDS [13]. The pathophysiological mechanisms of ALI/ARDS are yet to be fully understood. A large number of signal transduction pathways have been revealed to be involved in this process. Signal transductions in control of protein stability and availability, including protein ubiquitination and degradation, are typical among the pathways. Several review articles have introduced the role of ubiquitination and proteolysis in lung diseases [14,15,16]. In this review, we summarize recent findings regarding the importance of deubiquitination and DUBs in regulation of inflammation and related pathologies and highlight the role of DUBs in ALI/ARDS.
2. Protein Ubiquitin Proteasomal Degradation and Deubiquitination
Proteins dynamically exert their diversified functions in life processes in response to different pathophysiological settings. In concert with gene transcription, ubiquitin proteasome degradation governs the abundance and availability of the protein in the cell. Most of the proteins modified by a post translational modification called ubiquitination are deemed to be degraded [17,18]. Ubiquitination involves the covalent attachment of the small conserved protein called ubiquitin (Ub, 87 amino acids in length) to a target protein, almost exclusively at a lysine residue. Ubiquitination is an enzymatic cascade that requires the orchestrated interplay of three different enzymes (Figure 1). E1 Ub-activating enzymes bind to both ATP and ubiquitin and expose a cysteine residue, the active site of ubiquitin, with the release of an AMP. E2 Ub-conjugating enzymes take over activated ubiquitin from E1 enzymes and cooperate with E3 Ub-ligases. The E3 Ub-ligases interact with E2 enzymes and recruit protein substrates to initiate conjugation of single ubiquitin or polymeric ubiquitin chains to the protein substrates. E3 Ub-ligases recognize the protein substrates and determine the specificity of protein substrates [19,20]. In humans, there are two E1 Ub-activating enzymes, 14 E2 Ub-conjugating enzymes, and approximately 1000 E3 Ub-ligases [21].
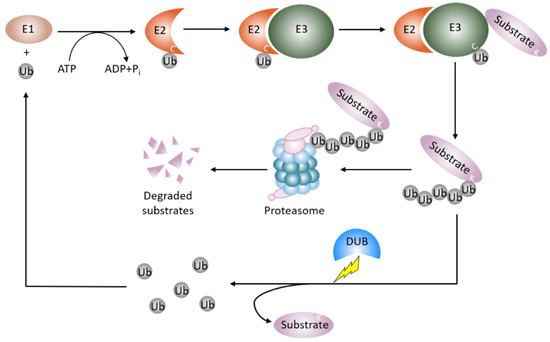
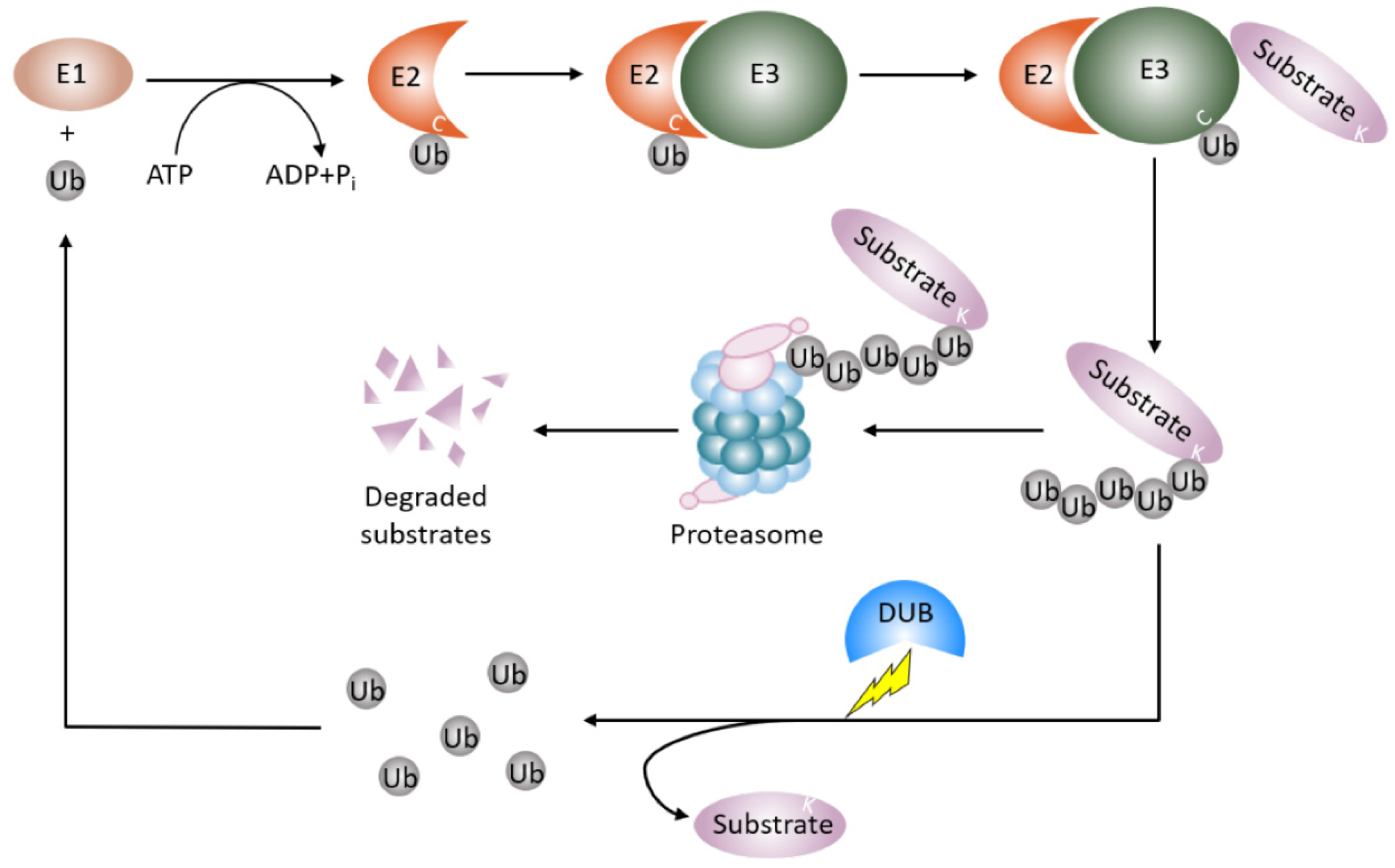
Figure 1.
Protein ubiquitin proteasomal degradation and deubiquitination. A protein destined for degradation unleashes a cascade of enzymatic activity involving ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. E1 Ub-activating enzymes activate ubiquitin and pass the ubiquitin to E2-Ub-conjugating enzymes. E3 Ub-ligases recognize the protein substrates and couple E2-Ub-conjugating enzymes to covalently add the ubiquitin or ubiquitin moieties to the protein substrates. The ubiquitinated proteins are then degraded by the proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes remove the mono-ubiquitin or polyubiquitin chains from the ubiquitinated protein to stabilize the protein from proteasomal degradation and recycle ubiquitin units. Ub: ubiquitin; E1: E1 Ub-activating enzyme; E2: E2-Ub-conjugating enzyme, E3: E3 Ub-ligases; DUB: deubiquitinating enzyme.
The process of ubiquitination is reversible, a group of enzymes called deubiquitination enzymes conduct the enzymatic process [22] (Figure 1). Deubiquitination is the reverse process of ubiquitination, that removes the mono-ubiquitin and poly-ubiquitin chains from the modified proteins to generate free ubiquitin, which terminates the function of ubiquitinated protein, and specifically, stabilizes the ubiquitinated protein from degradation. Deubiquitination also replenishes the ubiquitin pool, and maintains homeostasis of the cellular ubiquitin [23]. This process is performed by deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), which are a large set of proteases. The number of DUBs in humans is about 100, while ~20 DUBs exist in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae [24,25,26]. A number of approaches are utilized in studying DUBs and the related diseases. These approaches include conventional protein–protein interaction techniques such as immunoprecipitation, enzymatic assays, bioinformatics, proteomic, transcriptomic, and structure analysis techniques. Based on the architecture of their catalytic domains, to date, six structurally distinct DUB families have been described [27]. Five families of DUBs are cysteine proteases, including54 members of USPs(ubiquitin-specific proteases)in humans, four members of UCHs(ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolases), 16 members of OTUs(ovarian tumor proteases), four members of MJDs (Machado–Josephin disease protein domain protease) [25,26], and four members of MINDYs (motif interacting with ubiquitin (MIU)-containing novel DUB family) [28]. The sixth subfamily is JAMMs (Zn-JAB1/MPN/MOV34 domain protease), which includes a conserved zinc metallopeptidase [25,26]. All DUB family members bear a catalytic domain that removes ubiquitin from the protein substrates [27]. The catalytic domain of MIU family sub-members is a new folding variant within the superfamily of cysteine protease and shows a remarkable selectivity for cleaving long lysine 48 (K48)-linked ubiquitin chains. In particular, cleavage selectivity of DUBs is determined by catalytic domain alone, whereas a DUB called MINDY requires a motif interacting with ubiquitin (MIU) as well as a catalytic domain for maximal DUB activity [28]. The physiological roles of DUBs include controlling protein stability and quality, maintaining ubiquitin homeostasis, and regulating ubiquitin signals against the functions of E3 Ub ligase [23]. Therefore, DUBs regulate numerous cellular events such as the cell cycle, DNA damage response, inflammatory signaling, and proliferation and cell death.
3. Molecular Mechanisms of DUBs in the Pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS
Mounting studies have focused on inflammation to dissect its underlying molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. Deubiquitinating enzymes play crucial roles in modulation of inflammation by changing the protein stability of the critical molecules (Table 1). Several USPs have proved to play emerging roles in the regulation of lung inflammation [29,30]. Innate immunity provides the first line of host defense against pathogens. In lung inflammation, USP14 protein is over-expressed, reducing I-κB protein levels and thus increasing cytokine release in lung epithelial cells [31,32]. USP7 acts as a negative regulator of the NF-κB pathway by mediating the deubiquitination of NEMO, TRAF6 and IKKγ, which leads to the retention of NF-κB in the cytosol, thus suppressing its activity [33,34]. Pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines increase in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and circulating plasma of patients at different stages of ARDS. TNF-α and IL-1β are important proinflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of ARDS [35]. After their receptor activation, cIAP-mediated K63-ubiquitination of RIPK1 and the TRAF proteins leads to the recruitment of linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC). The stability of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA1) is up-regulated by ubiquitin-specific protease 11 (USP11), which deubiquitinates LPA1 and enhances LPA1-mediated proinflammatory effects [33,36,37,38,39]. Furthermore, the deubiquitinating enzyme USP13 stabilizes the anti-inflammatory receptor IL-1R8/Sigirr to suppress lung inflammation [40,41,42].

Table 1.
The roles of DUBs in ALI/ARDS.
Alveolar residential macrophages are central to the development of the inflammatory response by recruiting neutrophils and circulating macrophages to the site of injury, their functions are modulated by deubiquitinating enzymes [96,97]. These cells secrete cytokines, chemokines, reactive oxygen species, proteases, and other mediators that modulate the inflammatory responses and injure the alveolocapillary barrier. Gram-negative bacteria-derived endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS) promotes stability of a histone acetyltransferase HBO1 via the function of USP25. HBO1 is believed to fire DNA replication licensing at the S-phase of the cell cycle, however, it also regulates inflammatory gene transcription in settings of pulmonary infection. USP25-stabilized HBO1 promotes inflammatory gene transcription in monocyte THP-1 cells [67]. In addition, inhibition of USP7 and USP47 blocks the NLRP3 inflammasome by preventing apeck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC) oligomerization and speck formation in macrophages [38]. USP17 mediates macrophage-promoted inflammation and stemness in lung cancer cells by regulating TRAF2/TRAF3 complex formation [59]. The activity of deubiquitination regulates inflammasome assembly and function. Deubiquitination of NLRP3 has been suggested to contribute to inflammasome activation. Upon treatment with NLRP3 ligands after the priming step, ABRO1, a subunit of the BRISC deubiquitinating complex, is required for optimal NLRP3-ASC complex formation, ASC oligomerization, caspase-1 activation, and IL-1β and IL-18 production. This evidence indicates that efficient NLRP3 activation requires ABRO1 [98]. Protein kinase JNK1 catalyzes NLRP3 phosphorylation at S194 within NLRP3, which is critical for NLRP3 deubiquitination and facilitates its self-association and the subsequent inflammasome assembly [99]. Another inflammasome component NALP7 is regulated by the deubiquitinating enzyme STAM-binding protein (STAMBP), targeting the STAMBP with a small molecule that inhibits NALP7 inflammasome activity [95].
The activities of deubiquitinating enzymes are involved in many aspects of the pathogenesis in ALI/ARD. Lung epithelial cell death is a hallmark in ALI/ARDS. Massive lung epithelial cell death has been reported in ARDS patients. Lung epithelial cell death is regulated by deubiquitinating enzymes. Loss of DUB CYLD can activate NF-κB to inhibit apoptosis in lung epithelial cells [100]. In lung infection, USP13 are aberrantly expressed, inhibition of USP13 reduces the abundance of anti-apoptotic protein MCL1 in the lung [42]. On the other hand, recent mechanistic studies have reported that lung epithelial cells may defend from bacterial invasion through several mechanisms. USP25 may regulate the degradation of a deacetylation enzyme HDAC11 to modulate cellular Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterial load, probably via interferon signaling in bronchial lung epithelial cells [68]. OTUB1 interferes with bacterial uptake by modulating the RhoA level [78]. Furthermore, deubiquitination has been proposed to play an important role in alveolar epithelial dysfunction during ALI. USP10 exerts an effect on mucociliary clearance by regulating the endocytic recycling of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) in airway epithelial cells [37,52]. In addition, accumulating data suggest that deubiquitination may regulate structural components of the alveolar epithelial monolayer. Structural integrity of epithelial cells and intercellular junctions plays an important role in the maintenance of alveolar epithelial barrier integrity. A study suggests that phosphorylated E2F1 is stabilized by nuclear USP11 to drive Peg10 gene expression and activate proliferation of lung epithelial cells [54]. Finally, airway barrier integrity is primarily maintained by intercellular junctions, which in turn control the paracellular transport of proteins, fluids, and small molecules. Cell junction and junctional protein recycling and remodeling is pivotal in barrier integrity. Deubiquitination and DUBs have been shown to regulate adherence of junctional proteins [101]. For example, USP48 regulates E-cadherin mRNA levels through stabilizing the TRAF2-JNK pathway in lung epithelial cells [69]. This study exhibits an indirect effect of DUBs on regulation of E-cadherin levels and lung epithelial barrier integrity.
Until now, the mechanism of COVID-19 infection has not been well illustrated yet. From the biopsy or autopsy of COVID-19 patients, diffuse damage of lung parenchyma has been shown [102,103]. Experts hypothesized that SARS-COV-2 invasion severely interrupts the integrity of the airway barrier, thus inducing aberrant inflammatory release (“cytokine storm”) and further worsening the lung injury and microcirculation dysfunction, resulting in uncontrolled sepsis in severe cases [104]. Whether DUBs participate in the mechanism of SARS-COV-2 infection has not been reported. The coronavirus family contains six members. SARS-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) are the two members that have brought an epidemic in recent years. SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, containing the papain-like cysteine proteases (PLpro), termed SARS-CoVPLpro and MERS-CoVPLpro respectively, are antagonists of the host antiviral immune response as they remove ubiquitin and its modifier interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) signals from host cell factors [105,106]. Whether such a protease encoded by the SARS-CoV-2 genome exists has not been reported, which might expand the field of SARS-CoV-2 study. Furthermore, human DUBs might be potential targets for SARS-CoV-2 invasion. We scanned the related dataset of genes and proteins in COVID-19 and the SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Data showed that a majority of DUBs are decreased in human iPSC-cardiomyocytes infected with SARS-COV-2 via RNA-sequencing [107]. In ACE2 positive type II pneumocytes, a number of USPs including USP11 and USP38 are elevated compared to ACE2 negative cells using next generation sequencing [108]. SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein invades human tissue through binding angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which reminds us that USPs might play an important role in COVID-19 development. However, in the sera of COVID-19 patients, no DUBs have been found through proteomics [109]. In all, the above data revealed that DUBs might be involved in the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 infections, but further studies are still urged to explore the function of DUBs in COVID-19.
4. Deubiquitinating Enzymes Involved in ALI/ARDS
4.1. USPs
The USP subfamily contains the majority of DUBs encoded by the human genome, which are the most diversified members within the DUB family [110,111,112]. The most studied DUB family member in USPs is cylindromatosis (CYLD). CYLD was originally identified as a tumor suppressor, where loss of which causes a benign human syndrome CYLD [113]. With sequence homology to the catalytic domain of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolases (UCH), CYLD cleaves K63-linked polyubiquitin chains off its target proteins [114,115,116]. CYLD is proven to be induced by Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial pathogens or their products [45,46,48,117]. The transcription factor NF-κB activated by bacteria is essential for induction of CYLD, in turn, induced CYLD negatively regulates the bacteria induced NF-κB signaling [46,117]. CYLD deubiquitinates TRAF6 and TRAF7 to negatively regulate peptidoglycan-induced Toll-Like receptor 2 (TLR2) signaling and inflammation [45]. CYLD is also highly induced by pneumolysin (PLY). CYLD deficiency protects mice from acute lung injury in lethal Streptococcus pneumoniae infections by inhibiting plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) expression [44,48]. Furthermore, evidence shows that CYLD negatively regulates the S. pneumoniae-induced nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT)signaling pathway by deubiquitinating TGF-β-activated kinase 1(TAK1) [43]. In contrast, CYLD(-/-) mice are hypersusceptible to Escherichia coli pneumonia with enhanced NF-κB activation [118]. Perhaps different pathogens may use distinct mechanisms to promote lung inflammation. In the late stage of bacterial infection, CYLD exhibits negative effects on injury-induced lung fibrotic response by inhibiting TGF-β-signaling [47]. These discoveries indicated that CYLD might possess a potential drug target for the treatment of bacterial infection pneumonia.
USP7 (HAUSP)is originally identified as a viral binding protein that preferentially cleaves K11-, K63- and K48-linked ubiquitin chains [119,120]. USP7 is involved in viral infection by targeting virus related protein to modulate virus replication and production [49,50,51]. USP7 is reported to deubiquitinate and stabilize NF-κB to increase its transcriptional activity in TLR-induced inflammatory gene expression [39]. Furthermore, USP10 fine-tunes NOTCH signaling in angiogenic sprouting by deubiquitinatingNOTCH1 intracellular domain (NICD1) to slow down its turnover of the short-lived form of the activated NOTCH1 receptor [53].
UPS13 is also reported to regulate antiviral responses, however, its function is controversial. USP13 is considered to promote IFN signaling and play an antiviral role by stabilizing STAT1 [55]. Nevertheless, USP13 deficiency enhances antiviral responses through deubiquitinating stimulator of interferon (STING) [56]. During bacterial infection, USP15 loses its activity for IκBα deubiquitination by interacting with E3 Ub-ligase Hrd1 to promote TLR4-induced inflammation [57]. USP17 mediates deubiquitination and stabilization of HDAC2 in cigarette smoke extract-induced inflammation [58]. USP19 also preserves a negative effect on TNF-α- and IL-1β-triggered NF-κB activation by deubiquitinating TAK1 [60]. USP19 interacts with TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β (TRIF), and thus impairs its recruitment to TLR3/4 [61]. USP19 deficient mice produce exacerbated inflammatory cytokines and are more susceptible to septicemia death [60,61]. USP19 affects DDX58/RIG-I-mediated type I interferon signaling through ubiquitinating BECN1 and promoting the formation of autophagosomes [62]. USP25 plays a protective role in virus or bacterial infection. Several studies showed that USP25 negatively regulates virus-induced type I IFN signaling by stabilizing TRAF2, TRAF3 and TRAF6 [64,65,75,87,121,122,123,124]. Furthermore, USP25 inhibits TLR4-activated innate immunity via removing K48 ubiquitination of TRAF3 [63]. USP25 deficient mice have been shown to be more susceptible to virus infection and LPS-induced septic shock [63,65].IL-17-mediated inflammation is also attenuated by USP25 through TRAF5 and TRAF6 deubiquitination [66]. The anti-malarial drug chloroquine is suggested to alleviate LPS-induced inflammation by up regulatingUSP25 in macrophages [125].
4.2. OTUs
The OTU family DUBs can be divided into four subfamilies, including OTULINs (OTULIN and FAM105A), OTUBs/Otubains (OTUB1 and OTUB2), OTUDs (OTUD1, OTUD2/YOD1, OTUD3, OTUD4, OTUD5/DUBA, OTUD6A, OTUD6B, ALG13, and HIN1L), and A20s (A20, Cezanne, Cezanne2, TRABID, and VCPIP) [126]. The majority of OTU members are reported to regulate pathogen-induced cell signaling cascades. In innate and adaptive immunity, OTULIN is an essential negative regulator of LUBAC, which hydrolyzes LUBAC induced Met-1 lineal ubiquitination to prevent NF-κB- or TNF-induced inflammation augmentation [71,72,73,127]. OTULIN can also control antiviral signaling by regulating the lineal ubiquitination chain of STAT1 [74]. For the negative role of OTULIN in immune responses, OTULIN deficiency might cause auto-inflammatory syndrome [128].
OTUB1 and OTUB2 regulate virus-triggered IFN inflammation by deubiquitinating TRAF3 and TRAF6 [75]. OTUB1 suppresses the E3 ubiquitin-ligase by co-opting K48 ubiquitin recognition to regulate DNA damage [76,129,130,131,132]. Recent studies also show that OTUB1 augments NF-κB-dependent immune responses in dendritic cells in infection and inflammation by stabilizing UBC13 [76]. OTUB1 recruits phosphorylated SMAD2/3 and inhibits its ubiquitination by binding with E2 Ub-conjugating enzyme to enhance TGF-β signaling [80]. OTUB1 regulates the maturation and activation of NK and CD8+T cells via inhibiting AKT ubiquitination [77]. Furthermore, virus-induced OTUB1 degradation blocks the RIG-I-dependent immune signaling cascade and antiviral response [79]. Several studies showed that OTUD1 plays an important role in inflammation regulation [81,82]. RNA viruses induceOTUD1 to promote the degradation of the MAVS/TRAF3/TRAF6 signalosome to inhibit innate immunity [81]. Furthermore, OTUD1 inhibits type 1 IFN induction after virus infection through cleaving noncanonical K6-linked ubiquitination of IRF3 [83].
OTUD1 knockout mice show more resistance to virus infection and LPS stimulation [81,83]. OTUD4 is a K48-specific deubiquitinating enzyme that is previously been reported to maintain the stability of the alkylation repair enzyme ALKBH3 for promoting DNA damage repair [86]. However, OTUD4 also preserves K63-linked deubiquitinating activity, specifically targetingMyD88 to inhibit NF-κB signaling [84]. A recent study shows the role of OTUD4 in innate antiviral immunity. OTUD4 is induced by virus infection and targets MAVS ubiquitination, triggeringIRF3 and NF-κB signaling to sustain antiviral responses [85].Like most of the DUBs, the family member A20 shows the negative effect on the activation of NF-κB signaling [87,88,133].Myeloid-A20-deficiency shows a higher inflammatory reaction and sustained NF-κB activation [133]. A20 terminates TLR signals by targeting TRAF6 deubiquitination [87]. Similar to OTUB1, A20 suppresses NF-κB signaling by conjugating to E3 Ub-ligase [88]. Histone methyltransferase-enhanced A20 can also suppress the inflammatory response by modulation of NEMO and deubiquitination of TRAF6 [134]. Due to its role in inflammation inhibition, A20 induced by TNFα participates in age-related macrophage dysfunction in the lung [135]. OTUDs are newly discovered in antiviral immune responses, which reminds us of the potential drug target for the treatment of virus-induced lung injury.
4.3. JAMMs
The JAMMs are the third largest subfamily in DUBs, and it comprises 12 members: COP9 signalosome subunit (CSN)5, 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 14 (POH1), BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex subunit 3 (BRCC3, also known as BRCC36 in humans), MPN domain containing (MPND, myb-like SWIRM and MPN domains 1 (MYSM1), eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit (EIF3)H, CSN6,26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 7 (PSMD7), EIF3F, anti-Müllerian hormone (AMSH), AMSH-LP, and pre-mRNA-processing-splicing factor 8 (PRPF8) [93,136,137,138,139].STAMBP (also known as the associated molecule with the SH3 domain of STAM or AMSH), a metalloprotease and a member of the Jab1/MPN metalloenzyme (JAMM) family of DUBs, impedes the lysosomal degradation of NACHT, LRR and PYD domain-containing protein 7 (NALP7)to inhibit inflammasome activity [95,140]. POH1 deubiquitinates pro-IL-1β and inhibits mature IL-1β production, thus restricting inflammasome activity and LPS-induced inflammation [93]. DUBBRCC3 forms a multi-protein complex (BRISC) with ABRO1, NBA1, and BRE that specifically cleaves K63-linked ubiquitin in the cytoplasm [141]. ABRO1 is important in efficient NLRP3 activation. ABRO1 deubiquitinates NLRP3 to promote NLRP3 inflammasome activation [98]. BRCC3 also targets NLRP2 to regulate inflammasome formation [94].
4.4. OTHER DUBs
The enzymes of the UCH protein family includes four members, UCHL1/PGP9.5 (protein gene product 9.5), UCHL3, UCHL5/UCH37, and BRCA1 associated protein-1(BAP1), which contain a conserved catalytic UCH domain of ~230 amino acids [142,143]. The activities of these proteins have been associated with the occurrence and development of cancer [143]. UCHL5/UCH37 is suggested to play an anti-apoptotic role in lung epithelial cells through altering Bax/Bcl-2, caspase 3, and caspase9 signals [144]. UCH5/UCH37 deubiquitinates both smad2 and smad3 to promote TGFβ-1 induced lung fibrosis [70]. Studies of UCHs in lung injury and pathogen invasion are still lacking.
The MJD family onlycontains four members: Ataxin (ATXN)3, ATXN3L, Josephin domain containing (JOSD), and JOSD2 [145]. Studies show that ATXN3 andJOSD1 are involved in antiviral responses. ATXN3 enhances type 1 IFN signaling during viral infection through deubiquitinating and stabilizing HDAC3 [90]. Nevertheless, JOSD1 exhibits a negative role in antiviral activity. JOSD1 inhibits the IFN signal cascade via deubiquitinating and stabilizing SOCS1 [92].
The MCPIP, also known as ZC3H12A (zinc finger CCCH-type containing 12A) family includes MCPIP1-7 members [146,147,148]. MCPIP implicates a negative role in regulation of the cellular inflammatory responses [149]. MCPIP1 is the most studied in the MCPIP family. Acting as a deubiquitinating enzyme, MCPIP1 inhibits NF-κB and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathways by removing the ubiquitin moieties from TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs), including TRAF2, TRAF3 and TRAF6 [150].As an RNase, MCPIP also regulates inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 by regulating RNA decay [151] and innate defense via degrading viral RNA [152]. MCPIP deubiquitinates TRAF6 to impede NF-κB signaling [89].
Like the recently identified DUBs, the MINDY family contains four members: MINDY1–4 [145], which are highly selective at hydrolyzing K48-linked poly-ubiquitin. No data about MINDYs in ALI/ARDS pathogenesis has been reported. The above DUBs play essential roles in the initial development of cancer. However, their functions in lung injury are not fully elucidated.
5. Potential Therapeutic Approaches Targeting DUBS in ALI/ARDS
Pathogen-related DUBs are promising potential targets of drug discovery for human pathogen infection and associated inflammatory disorders. Bacteria-encoded DUBs might promote bacterial pathogenicity through inhibiting the human ubiquitin–proteasome system [153]. Furthermore, viruses with genes for DUBs might inhibit the antiviral pathways using a DUB strategy to modulate protein–protein interactions. The SARS-CoVPLpro and MERS-CoVPLpro papain-like cysteine proteases have been reported, showing a conserved similar structure to the USP family of DUBs by X-ray structure, which shows the potential targets of DUBs for antiviral drug discovery [154,155]. In addition, several RNA virus-related proteases containing the OUT domain can also remove ubiquitin and ISG-15 signals from host cellular proteins, which represents a potential promising domain for antiviral therapy [156]. The above findings present great interest to explore a DUB-associated anti-infective strategy for human pathogen invasions. However, despite the possibility of DUBs as drug targets, the drug discovery for ALI/ARDS is still challenging, with few DUB inhibitors or activators having been explored.
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
During the past decade, studies began to dissect the role of DUBs in ALI/ARDS. Increasing evidence proved that immune responses, inflammation, cell death, air–blood barrier integrity, and invasiveness of the pathogens are fine-tuned by DUBs in ALI/ARDS (Figure 2). Modulation of critical proteins via UPS and DUBs plays a central role in the pathogenesis of diseases such as cancer and autoimmune disease. Furthermore, DUBs are drawing increasing interest as therapeutic targets against these diseases. Our understanding of DUBs in ALI/ARDS is limited, and the specific role of DUBs remains largely unknown. Particularly, the global outbreak of COVID-19 has raised the demand for research on the pathological mechanisms of ALI/ARDS. Discovery of the role of DUBs in ALI/ARDS might bring valuable information on the pathogenesis of the illness and thereafter drug discovery. The diversified microbial pathogens may cause ALI/ARDS via distinct molecular mechanisms, which increase the complexity of the whole picture that we are attempting to figure out. On the other hand, the current studies are mostly focused on the function of DUBs on the regulation of protein degradation and stability. The functions of DUBs other than protein stability are yet to be studied in the setting of ALI/ARDS.As a post-translational modification, ubiquitinated proteins may exert a range of functions in life processes and in the pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS, such as signaling transduced via ubiquitinated protein. It is hoped that more data on DUBs might lead to identification of novel molecular mechanisms in ALI/ARDS, thus allowing the development of specific DUB inhibitors/agonists for the treatment of this acute and severe respiratory illness.
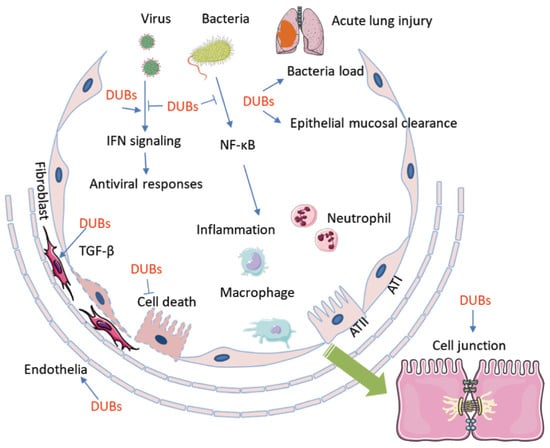
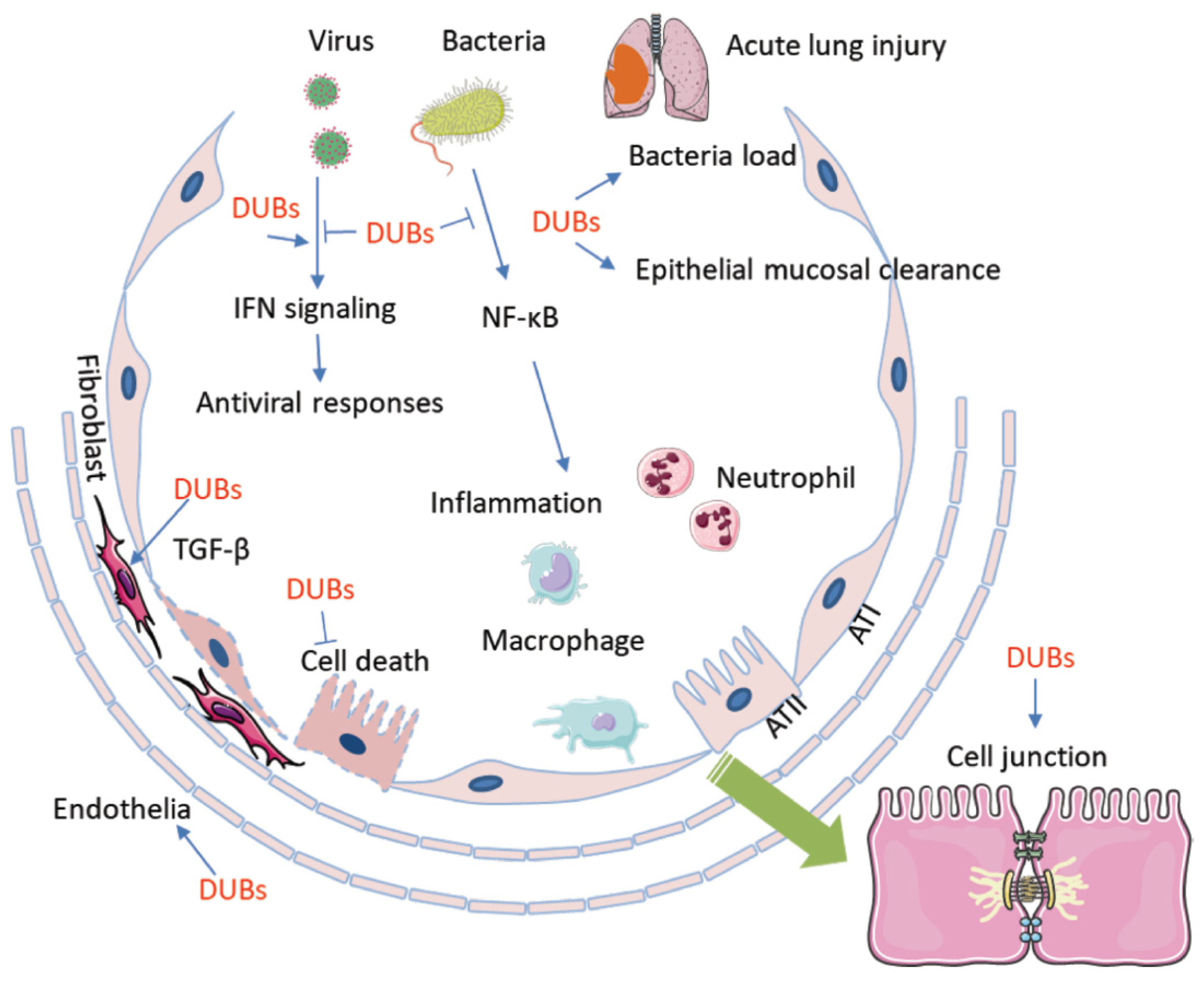
Figure 2.
Deubiquitination and DUBs are involved in the pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. DUBs conduct deubiquitination that is exclusively involved in every aspects of the pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. Microbial pathogens regulate the activity and availability of DUBs to impact host immune defense and the inflammatory response, which includes chemokine and cytokine release, macrophage activation, and neutrophil and lymphocyte infiltration. On the other hand, DUBs participate in pathogen-mediated lung epithelial and endothelial cell proliferation and death. Furthermore, DUBs may affect epithelial mucosal clearance and regulate the bacterial load in small airway alveolar epithelial cells. In addition, DUBs impair cell junctions and the air–blood barrier. AT1: alveolar type 1 epithelial cell; AT2: alvelolar type 2 epithelial cell; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β; DUB: Deubiquinating enzyme.
Funding
This work is supported with R01 grants (HL125435 and HL142997) from National Institute of Health at The United States to C.Z.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| ABRO1 | Abraxas Brother 1 |
| ALI | Acute lung injury |
| ALKBH3 | AlkB homologue 3 |
| AMSH | Anti-Müllerian hormone |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| ASC | Apeck-like protein containing a CARD |
| ATXN3 | Ataxin3 |
| BRISC | BRCC36 isopeptidase complex |
| CBP | CREB-binding protein |
| cIAP-1 | Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein-1 |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
| CSN5 | COP9 signalosome 5 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CYLD | Cylindromatosis |
| DUBs | Deubiquitinating enzymes |
| E2F1 | E2F transcription factor 1 |
| EIF3 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 |
| HBO1 | Histone acetyltransferase binding to origin recognition complex 1 |
| HDAC2 | Histone deacetylase 2 |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IKKγ | IκB kinase γ |
| IL-1β | Interlukin-1β |
| IRF3 | Interferon regulatory factor 3 |
| JAMMs | Zn-JAB1/MPN/MOV34 domain metallopeptidase |
| LPA1 | Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LUBAC | Linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex |
| MAVS | Mitochondria antiviral-signaling protein |
| MCL1 | Myeloid cell leukemia 1 |
| MINDYs | Motif interacting with ubiquitin - containing novel DUB family |
| MJDs | Machado-Josephin disease protein domain protease |
| NEMO | Nuclear factor (NF)-κB essential modulator |
| NALP7 | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 7 |
| NFAT | Nuclear factor of activated T cells |
| NICD1 | NOTCH1 intracellular domain |
| NLRP3 | NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| MYSM1 | MPN domain containing (MPND, myb-like SWIRM and MPN domains 1 |
| OTUs | Ovarian tumor proteases |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| PEG10 | Paternally expressed gene 10 |
| PLY | Pneumolysin |
| POH1 | Proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 14 |
| PRPF8 | Pre-mRNA-processing-splicing factor 8 |
| PSMD7 | Proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 7 |
| RIG-1 | Retinoic acid-inducible gene I |
| RIPK1 | Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| STAMBP | STAM-binding protein |
| STING | Stimulator of interferon |
| TAK1 | TGF-β-activated kinase 1 |
| TGFβ-1 | Transforming growth factor β-1 |
| TRIF | TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| TRAF | Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor |
| UBA | Ub-activating enzymes |
| UBC | Ub-conjugating enzymes |
| UCHs | Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolases |
| USPs | Ubiquitin-specific proteases |
References
- Han, S.; Mallampalli, R.K. The acute respiratory distress syndrome: From mechanism to translation. J. Immunol 2015, 194, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Force, A.D.T.; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Matthay, M.A.; Song, Y.; Bai, C.; Jones, K.D. The acute respiratory distress syndrome in 2013. Transl. Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Confalonieri, M.; Salton, F.; Fabiano, F. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, M.A.; Zemans, R.L.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Arabi, Y.M.; Beitler, J.R.; Mercat, A.; Herridge, M.; Randolph, A.G.; Calfee, C.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, S.; Gabrielli, N.M.; Vadasz, I. Novel concepts of acute lung injury and alveolar-capillary barrier dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 305, L665–L681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, L.A.; Sznajder, J.I. Mechanisms of pulmonary edema clearance during acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: Role of the Na,K-ATPase. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31 (Suppl. 4), S248–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.G.; Sznajder, J.I. Healthcare disparities in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Toward Equity. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 631–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A.; Foxman, E.F.; Molony, R.D. Early local immune defences in the respiratory tract. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, B.; Mao, J. The pathogenesis and treatment of the ‘Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisoncik, J.R.; Korth, M.J.; Simmons, C.P.; Farrar, J.; Martin, T.R.; Katze, M.G. Into the eye of the cytokine storm. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, M.A.; Zemans, R.L. The acute respiratory distress syndrome: Pathogenesis and treatment. Annu. Rev. Pathol 2011, 6, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuckton, T.J.; Alonso, J.A.; Kallet, R.H.; Daniel, B.M.; Pittet, J.F.; Eisner, M.D.; Matthay, M.A. Pulmonary dead-space fraction as a risk factor for death in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, N.D.; Dada, L.A.; Sznajder, J.I. Ubiquitin-proteasome signaling in lung injury. Transl. Res. 2018, 198, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadasz, I.; Weiss, C.H.; Sznajder, J.I. Ubiquitination and proteolysis in acute lung injury. Chest 2012, 141, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Helenius, I.T.; Dada, L.A.; Sznajder, J.I. Role of ubiquitination in Na,K-ATPase regulation during lung injury. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2010, 7, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glickman, M.H.; Ciechanover, A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: Destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 373–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershko, A.; Ciechanover, A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 425–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Kim, N.G.; Gumbiner, B.M. Regulation of protein stability by GSK3 mediated phosphorylation. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 4032–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravid, T.; Hochstrasser, M. Diversity of degradation signals in the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weathington, N.M.; Sznajder, J.I.; Mallampalli, R.K. The emerging role of the ubiquitin proteasome in pulmonary biology and disease. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, K.D. Ubiquitination and deubiquitination: Targeting of proteins for degradation by the proteasome. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 11, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanpude, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Dey, A.K.; Maiti, T.K. Deubiquitinating enzymes in cellular signaling and disease regulation. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Turcu, F.E.; Ventii, K.H.; Wilkinson, K.D. Regulation and cellular roles of ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinating enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 363–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clague, M.J.; Barsukov, I.; Coulson, J.M.; Liu, H.; Rigden, D.J.; Urbe, S. Deubiquitylases from genes to organism. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1289–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komander, D.; Clague, M.J.; Urbe, S. Breaking the chains: Structure and function of the deubiquitinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevissen, T.E.T.; Komander, D. Mechanisms of Deubiquitinase Specificity and Regulation. Annu Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 159–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rehman, S.A.; Kristariyanto, Y.A.; Choi, S.Y.; Nkosi, P.J.; Weidlich, S.; Labib, K.; Hofmann, K.; Kulathu, Y. MINDY-1 Is a Member of an Evolutionarily Conserved and Structurally Distinct New Family of Deubiquitinating Enzymes. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2008, 1143, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Innate immune recognition of viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mialki, R.K.; Zhao, J.; Wei, J.; Mallampalli, D.F.; Zhao, Y. Overexpression of USP14 protease reduces I-kappaB protein levels and increases cytokine release in lung epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 15437–15441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Dong, S.; Bowser, R.K.; Khoo, A.; Zhang, L.; Jacko, A.M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. Regulation of the ubiquitylation and deubiquitylation of CREB-binding protein modulates histone acetylation and lung inflammation. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Guan, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X. HSCARG downregulates NF-kappaB signaling by interacting with USP7 and inhibiting NEMO ubiquitination. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubeuf, S.; Singh, D.; Tan, Y.; Liu, H.; Federoff, H.J.; Bowers, W.J.; Tolba, K. HSV ICP0 recruits USP7 to modulate TLR-mediated innate response. Blood 2009, 113, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldoveanu, B.; Otmishi, P.; Jani, P.; Walker, J.; Sarmiento, X.; Guardiola, J.; Saad, M.; Yu, J. Inflammatory mechanisms in the lung. J. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wei, J.; Dong, S.; Bowser, R.K.; Zhang, L.; Jacko, A.M.; Zhao, Y. Destabilization of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 Reduces Cytokine Release and Protects Against Lung Injury. EBioMedicine 2016, 10, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomberger, J.M.; Barnaby, R.L.; Stanton, B.A. The deubiquitinating enzyme USP10 regulates the endocytic recycling of CFTR in airway epithelial cells. Channels (Austin) 2010, 4, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazon-Riquelme, P.; Worboys, J.D.; Green, J.; Valera, A.; Martin-Sanchez, F.; Pellegrini, C.; Brough, D.; Lopez-Castejon, G. USP7 and USP47 deubiquitinases regulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colleran, A.; Collins, P.E.; O’Carroll, C.; Ahmed, A.; Mao, X.; McManus, B.; Kiely, P.A.; Burstein, E.; Carmody, R.J. Deubiquitination of NF-kappaB by Ubiquitin-Specific Protease-7 promotes transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wei, J.; Li, S.; Jacko, A.M.; Weathington, N.M.; Mallampalli, R.K.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y. The deubiquitinase USP13 stabilizes the anti-inflammatory receptor IL-1R8/Sigirr to suppress lung inflammation. EBioMedicine 2019, 45, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Jiang, D.; Liang, J.; Jiang, D.; Wang, C.; Dai, H. Down-regulation of USP13 mediates phenotype transformation of fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 2015, 16, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Jing, Y.; Yin, X.; Ma, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Di, W.; Zhuang, G. Deubiquitinase USP13 dictates MCL1 stability and sensitivity to BH3 mimetic inhibitors. Nat. Commun 2018, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, T.; Lim, J.H.; Jono, H.; Ha, U.H.; Xu, H.; Ishinaga, H.; Morino, S.; Xu, X.; Yan, C.; Kai, H.; et al. Tumor suppressor cylindromatosis acts as a negative regulator for Streptococcus pneumoniae-induced NFAT signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12546–12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y. Cylindromatosis (CYLD) inhibits Streptococcus pneumonia-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression via interacting with TRAF-6. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Jono, H.; Kai, H.; Li, J.D. The tumor suppressor cylindromatosis (CYLD) acts as a negative regulator for toll-like receptor 2 signaling via negative cross-talk with TRAF6 AND TRAF7. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 41111–41121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.H.; Jono, H.; Koga, T.; Woo, C.H.; Ishinaga, H.; Bourne, P.; Xu, H.; Ha, U.H.; Xu, H.; Li, J.D. Tumor suppressor CYLD acts as a negative regulator for non-typeable Haemophilus influenza-induced inflammation in the middle ear and lung of mice. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.H.; Jono, H.; Komatsu, K.; Woo, C.H.; Lee, J.; Miyata, M.; Matsuno, T.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. CYLD negatively regulates transforming growth factor-beta-signalling via deubiquitinating Akt. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.H.; Stirling, B.; Derry, J.; Koga, T.; Jono, H.; Woo, C.H.; Xu, H.; Bourne, P.; Ha, U.H.; Ishinaga, H.; et al. Tumor suppressor CYLD regulates acute lung injury in lethal Streptococcus pneumoniae infections. Immunity 2007, 27, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, S.; El Motiam, A.; Seoane, R.; Preitakaite, V.; Bouzaher, Y.H.; Gomez-Medina, S.; San Martin, C.; Rodriguez, D.; Rejas, M.T.; Baz-Martinez, M.; et al. Regulation of the Ebola Virus VP24 Protein by SUMO. J. Virol. 2019, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Raja, R.; Farooqui, S.R.; Ahmad, S.; Banerjea, A.C. USP7 deubiquitinase controls HIV-1 production by stabilizing Tat protein. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1653–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Ju, H.; Nicholas, J. USP7-Dependent Regulation of TRAF Activation and Signaling by a Viral Interferon Regulatory Factor Homologue. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomberger, J.M.; Ye, S.; Maceachran, D.P.; Koeppen, K.; Barnaby, R.L.; O’Toole, G.A.; Stanton, B.A. A Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin that hijacks the host ubiquitin proteolytic system. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.; Sugino, T.; Nolte, H.; Andrade, J.; Zimmermann, B.; Shi, C.; Doddaballapur, A.; Ong, Y.T.; Wilhelm, K.; Fasse, J.W.D.; et al. Deubiquitinase USP10 regulates Notch signaling in the endothelium. Science 2019, 364, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Wei, J.; Nan, L.; Mallampalli, R.K.; Weathington, N.M.; Ma, H.; Zhao, Y. Phosphorylated E2F1 is stabilized by nuclear USP11 to drive Peg10 gene expression and activate lung epithelial cells. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 10, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, H.M.; Yu, C.Y.; Yang, H.C.; Ko, S.H.; Liao, C.L.; Lin, Y.L. Ubiquitin-specific protease 13 regulates IFN signaling by stabilizing STAT1. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3328–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jing, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Cai, Z.; Liuyu, T.; Zhang, Z.D.; Xiong, T.C.; Wu, Y.; et al. USP13 negatively regulates antiviral responses by deubiquitinating STING. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, P.; Chang, H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, F.; Ma, L.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, J.; et al. ER-localized Hrd1 ubiquitinates and inactivates Usp15 to promote TLR4-induced inflammation during bacterial infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2331–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Tao, L.; Chen, C.; Pan, L.; Hao, J.; Ni, Y.; Li, D.; Li, B.; Shi, G. USP17-mediated deubiquitination and stabilization of HDAC2 in cigarette smoke extract-induced inflammation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10707–10715. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.H.; Yeh, D.W.; Lai, C.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Huang, L.R.; Lee, A.Y.; Jin, S.C.; Chuang, T.H. USP17 mediates macrophage-promoted inflammation and stemness in lung cancer cells by regulating TRAF2/TRAF3 complex formation. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6327–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.Q.; Wu, X.; Zhong, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, B.; Shu, H.B. USP19 Inhibits TNF-alpha- and IL-1beta-Triggered NF-kappaB Activation by Deubiquitinating TAK1. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lei, C.; Xia, T.; Zhong, X.; Yang, Q.; Shu, H.B. Regulation of TRIF-mediated innate immune response by K27-linked polyubiquitination and deubiquitination. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Jin, S.; Wang, R.F. The BECN1-USP19 axis plays a role in the crosstalk between autophagy and antiviral immune responses. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1210–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Darnay, B.G.; Lin, X.; Sun, S.C.; Dong, C. Ubiquitin-specific protease 25 regulates TLR4-dependent innate immune responses through deubiquitination of the adaptor protein TRAF3. Sci Signal. 2013, 6, ra35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Wang, D.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Luo, R.; Shang, M.; Ouyang, C.; Ouyang, H.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S. Ubiquitin-specific proteases 25 negatively regulates virus-induced type I interferon signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.X.; Ren, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhao, Q.; Pan, Z.; Wu, M.; Shu, H.B.; Dong, C.; et al. Induction of USP25 by viral infection promotes innate antiviral responses by mediating the stabilization of TRAF3 and TRAF6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11324–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Chang, S.H.; Liu, X.; Wang, A.; Reynolds, J.M.; Dong, C. Negative regulation of IL-17-mediated signaling and inflammation by the ubiquitin-specific protease USP25. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Lai, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Zou, C. LPS promotes HBO1 stability via USP25 to modulate inflammatory gene transcription in THP-1 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2018, 1861, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Lai, Y.; Li, T.; Nyunoya, T.; Zou, C. Cigarette smoke extract modulates Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterial load via USP25/HDAC11 axis in lung epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L252–L263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Weathington, N.M.; Shang, D.; Zhao, Y. The deubiquitinating enzyme USP48 stabilizes TRAF2 and reduces E-cadherin-mediated adherens junctions. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Jacko, A.M.; Tan, J.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Kass, D.J.; Ma, H.; Zhao, Y. Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase-L5 promotes TGFbeta-1 signaling by de-ubiquitinating and stabilizing Smad2/Smad3 in pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiil, B.K.; Damgaard, R.B.; Wagner, S.A.; Keusekotten, K.; Fritsch, M.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; Mailand, N.; Choudhary, C.; Komander, D.; Gyrd-Hansen, M. OTULIN restricts Met1-linked ubiquitination to control innate immune signaling. Mol. Cell 2013, 50, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keusekotten, K.; Elliott, P.R.; Glockner, L.; Fiil, B.K.; Damgaard, R.B.; Kulathu, Y.; Wauer, T.; Hospenthal, M.K.; Gyrd-Hansen, M.; Krappmann, D.; et al. OTULIN antagonizes LUBAC signaling by specifically hydrolyzing Met1-linked polyubiquitin. Cell 2013, 153, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgaard, R.B.; Walker, J.A.; Marco-Casanova, P.; Morgan, N.V.; Titheradge, H.L.; Elliott, P.R.; McHale, D.; Maher, E.R.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Komander, D. The Deubiquitinase OTULIN Is an Essential Negative Regulator of Inflammation and Autoimmunity. Cell 2016, 166, 1215.e20–1230.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jin, L.; Huang, F.; Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Guo, T.; et al. Regulation of the linear ubiquitination of STAT1 controls antiviral interferon signaling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zheng, H.; Mao, A.P.; Zhong, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ran, Y.; Tien, P.; Shu, H.B. Regulation of virus-triggered signaling by OTUB1- and OTUB2-mediated deubiquitination of TRAF3 and TRAF6. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4291–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulas, F.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Nishanth, G.; Yi, W.; Brunn, A.; Larsen, P.K.; Isermann, B.; Kalinke, U.; Barragan, A.; et al. The deubiquitinase OTUB1 augments NF-kappaB-dependent immune responses in dendritic cells in infection and inflammation by stabilizing UBC13. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, B.; Manyam, G.C.; Zhang, L.; Schluns, K.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Sun, S.C. The deubiquitinase Otub1 controls the activation of CD8(+) T cells and NK cells by regulating IL-15-mediated priming. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmann, M.J.; Kramer, H.B.; Altun, M.; Kessler, B.M. Post-translational modification of the deubiquitinating enzyme otubain 1 modulates active RhoA levels and susceptibility to Yersinia invasion. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2515–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, A.S.; Biquand, E.; Munoz-Moreno, R.; Le Quang, A.; Mok, C.K.; Wong, H.H.; Teo, Q.W.; Valkenburg, S.A.; Chin, A.W.H.; Man Poon, L.L.; et al. OTUB1 Is a Key Regulator of RIG-I-Dependent Immune Signaling and Is Targeted for Proteasomal Degradation by Influenza A NS1. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1570.e6–1584.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herhaus, L.; Al-Salihi, M.; Macartney, T.; Weidlich, S.; Sapkota, G.P. OTUB1 enhances TGFbeta signalling by inhibiting the ubiquitylation and degradation of active SMAD2/3. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Qian, L.; Feng, Q.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Miao, Y.; Guo, T.; et al. Induction of OTUD1 by RNA viruses potently inhibits innate immune responses by promoting degradation of the MAVS/TRAF3/TRAF6 signalosome. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Song, J.; Sun, Y.; Qi, F.; Liu, L.; Jin, Y.; McNutt, M.A.; Yin, Y. Mutations of deubiquitinase OTUD1 are associated with autoimmune disorders. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 94, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; You, F. OTUD1 Negatively Regulates Type I IFN Induction by Disrupting Noncanonical Ubiquitination of IRF3. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1904–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Mudge, M.C.; Soll, J.M.; Rodrigues, R.B.; Byrum, A.K.; Schwarzkopf, E.A.; Bradstreet, T.R.; Gygi, S.P.; Edelson, B.T.; Mosammaparast, N. OTUD4 Is a Phospho-Activated K63 Deubiquitinase that Regulates MyD88-Dependent Signaling. Mol. Cell. 2018, 69, 505.e5–516.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuyu, T.; Yu, K.; Ye, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Lin, D.; Zhong, B. Induction of OTUD4 by viral infection promotes antiviral responses through deubiquitinating and stabilizing MAVS. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Majid, M.C.; Soll, J.M.; Brickner, J.R.; Dango, S.; Mosammaparast, N. Noncanonical regulation of alkylation damage resistance by the OTUD4 deubiquitinase. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 1687–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, D.L.; Turer, E.E.; Lee, E.G.; Ahmad, R.C.; Wheeler, M.T.; Tsui, C.; Hurley, P.; Chien, M.; Chai, S.; Hitotsumatsu, O.; et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shembade, N.; Ma, A.; Harhaj, E.W. Inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling by A20 through disruption of ubiquitin enzyme complexes. Science 2010, 327, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jia, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, X.; Han, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Guan, H.; Hu, D. Klf4 Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation by Inducing Expression of MCP-1 Induced Protein 1 to Deubiquitinate TRAF6. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2278–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Miao, Y.; Ge, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Qian, L.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Q.; Guo, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. ATXN3 Positively Regulates Type I IFN Antiviral Response by Deubiquitinating and Stabilizing HDAC3. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, P.; Chang, W.; Wang, Y.; Shu, T.; Ding, F.; Li, B.; Liu, Z. JOSD1 inhibits mitochondrial apoptotic signalling to drive acquired chemoresistance in gynaecological cancer by stabilizing MCL1. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Qian, L.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, W.; Zuo, Y.; et al. JOSD1 Negatively Regulates Type-I Interferon Antiviral Activity by Deubiquitinating and Stabilizing SOCS1. Viral Immunol. 2017, 30, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, G.; Yang, Z.; Tang, M.; Ma, A.; Jing, T.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. POH1 deubiquitinates pro-interleukin-1beta and restricts inflammasome activity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Py, B.F.; Kim, M.S.; Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg, H.; Yuan, J. Deubiquitination of NLRP3 by BRCC3 critically regulates inflammasome activity. Mol. Cell. 2013, 49, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednash, J.S.; Weathington, N.; Londino, J.; Rojas, M.; Gulick, D.L.; Fort, R.; Han, S.; McKelvey, A.C.; Chen, B.B.; Mallampalli, R.K. Targeting the deubiquitinase STAMBP inhibits NALP7 inflammasome activity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, N.R.; King, L.S.; D’Alessio, F.R. Diverse macrophage populations mediate acute lung inflammation and resolution. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L709–L725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Hibbs, M.L.; Chen, W. The contributions of lung macrophage and monocyte heterogeneity to influenza pathogenesis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.; Song, P.; Lai, L.; Chen, H.; et al. ABRO1 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation through regulation of NLRP3 deubiquitination. EMBO J. 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Liu, Z.S.; Xue, W.; Bai, Z.F.; Wang, Q.Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.J.; Cai, H.; Zhan, X.Y.; et al. NLRP3 Phosphorylation Is an Essential Priming Event for Inflammasome Activation. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 185.e6–197.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummelkamp, T.R.; Nijman, S.M.; Dirac, A.M.; Bernards, R. Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-kappaB. Nature 2003, 424, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Culley, M.K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. The role of ubiquitination and deubiquitination in the regulation of cell junctions. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Hu, W.; Niu, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Xiao, S.Y. Pulmonary Pathology of Early-Phase 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pneumonia in Two Patients with Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Dai, H.; Tang, N.; Su, X.; Cao, B. SARS-CoV-2 and viral sepsis: Observations and hypotheses. Lancet 2020, 395, P1517–P1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekes, M.; Rut, W.; Kasperkiewicz, P.; Mulder, M.P.; Ovaa, H.; Drag, M.; Lima, C.D.; Huang, T.T. SARS hCoV papain-like protease is a unique Lys48 linkage-specific di-distributive deubiquitinating enzyme. Biochem. J. 2015, 468, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratia, K.; Pegan, S.; Takayama, J.; Sleeman, K.; Coughlin, M.; Baliji, S.; Chaudhuri, R.; Fu, W.; Prabhakar, B.S.; Johnson, M.E.; et al. A noncovalent class of papain-like protease/deubiquitinase inhibitors blocks SARS virus replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16119–16124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Garcia, G.; Arumugaswami, V.; Svendsen, C.N. Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes are Susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, C.G.K.; Allon, S.J.; Nyquist, S.K.; Mbano, I.M.; Miao, V.N.; Tzouanas, C.N.; Cao, Y.; Yousif, A.S.; Bals, J.; Hauser, B.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues. Cell 2020, 181, 1016.e19–1035.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yi, X.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, C.; Quan, S.; Zhang, F.; Sun, R.; Qian, L.; et al. Proteomic and Metabolomic Characterization of COVID-19 Patient Sera. Cell 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Renatus, M.; Parrado, S.G.; D’Arcy, A.; Eidhoff, U.; Gerhartz, B.; Hassiepen, U.; Pierrat, B.; Riedl, R.; Vinzenz, D.; Worpenberg, S.; et al. Structural basis of ubiquitin recognition by the deubiquitinating protease USP2. Structure 2006, 14, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avvakumov, G.V.; Walker, J.R.; Xue, S.; Finerty, P.J., Jr.; Mackenzie, F.; Newman, E.M.; Dhe-Paganon, S. Amino-terminal dimerization, NRDP1-rhodanese interaction, and inhibited catalytic domain conformation of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 (USP8). J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 38061–38070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, P.; Song, L.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Chenova, T.A.; Wilkinson, K.D.; Cohen, R.E.; Shi, Y. Structure and mechanisms of the proteasome-associated deubiquitinating enzyme USP14. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3747–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignell, G.R.; Warren, W.; Seal, S.; Takahashi, M.; Rapley, E.; Barfoot, R.; Green, H.; Brown, C.; Biggs, P.J.; Lakhani, S.R.; et al. Identification of the familial cylindromatosis tumour-suppressor gene. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massoumi, R. CYLD: A deubiquitination enzyme with multiple roles in cancer. Future Oncol. 2011, 7, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalenko, A.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Cantarella, G.; Israel, A.; Wallach, D.; Courtois, G. The tumour suppressor CYLD negatively regulates NF-kappaB signalling by deubiquitination. Nature 2003, 424, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trompouki, E.; Hatzivassiliou, E.; Tsichritzis, T.; Farmer, H.; Ashworth, A.; Mosialos, G. CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-kappaB activation by TNFR family members. Nature 2003, 424, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jono, H.; Lim, J.H.; Chen, L.F.; Xu, H.; Trompouki, E.; Pan, Z.K.; Mosialos, G.; Li, J.D. NF-kappaB is essential for induction of CYLD, the negative regulator of NF-kappaB: Evidence for a novel inducible autoregulatory feedback pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 36171–36174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Ha, U.H.; Woo, C.H.; Xu, H.; Li, J.D. CYLD is a crucial negative regulator of innate immune response in Escherichia coli pneumonia. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daviet, L.; Colland, F. Targeting ubiquitin specific proteases for drug discovery. Biochimie 2008, 90, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritorto, M.S.; Ewan, R.; Perez-Oliva, A.B.; Knebel, A.; Buhrlage, S.J.; Wightman, M.; Kelly, S.M.; Wood, N.T.; Virdee, S.; Gray, N.S.; et al. Screening of DUB activity and specificity by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Nat. Commun 2014, 5, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oganesyan, G.; Saha, S.K.; Guo, B.; He, J.Q.; Shahangian, A.; Zarnegar, B.; Perry, A.; Cheng, G. Critical role of TRAF3 in the Toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent antiviral response. Nature 2006, 439, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, H.; Redecke, V.; Blagoev, B.; Kratchmarova, I.; Hsu, L.C.; Wang, G.G.; Kamps, M.P.; Raz, E.; Wagner, H.; Hacker, G.; et al. Specificity in Toll-like receptor signalling through distinct effector functions of TRAF3 and TRAF6. Nature 2006, 439, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.K.; Pietras, E.M.; He, J.Q.; Kang, J.R.; Liu, S.Y.; Oganesyan, G.; Shahangian, A.; Zarnegar, B.; Shiba, T.L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Regulation of antiviral responses by a direct and specific interaction between TRAF3 and Cardif. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3257–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayagaki, N.; Phung, Q.; Chan, S.; Chaudhari, R.; Quan, C.; O’Rourke, K.M.; Eby, M.; Pietras, E.; Cheng, G.; Bazan, J.F.; et al. DUBA: A deubiquitinase that regulates type I interferon production. Science 2007, 318, 1628–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Li, F.; Long, Y.; Zheng, J. Chloroquine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through upregulation of USP25. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 95, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mevissen, T.E.; Hospenthal, M.K.; Geurink, P.P.; Elliott, P.R.; Akutsu, M.; Arnaudo, N.; Ekkebus, R.; Kulathu, Y.; Wauer, T.; El Oualid, F.; et al. OTU deubiquitinases reveal mechanisms of linkage specificity and enable ubiquitin chain restriction analysis. Cell 2013, 154, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, F. Linear ubiquitination signals in adaptive immune responses. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 266, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiil, B.K.; Gyrd-Hansen, M. OTULIN deficiency causes auto-inflammatory syndrome. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 1176–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Juang, Y.C.; Landry, M.C.; Sanches, M.; Vittal, V.; Leung, C.C.; Ceccarelli, D.F.; Mateo, A.R.; Pruneda, J.N.; Mao, D.Y.; Szilard, R.K.; et al. OTUB1 co-opts Lys48-linked ubiquitin recognition to suppress E2 enzyme function. Mol. Cell 2012, 45, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, S.; Tai, I.; Panier, S.; Al-Hakim, A.; Iemura, S.; Juang, Y.C.; O’Donnell, L.; Kumakubo, A.; Munro, M.; Sicheri, F.; et al. Non-canonical inhibition of DNA damage-dependent ubiquitination by OTUB1. Nature 2010, 466, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yin, L.; Cooper, E.M.; Lai, M.Y.; Dickey, S.; Pickart, C.M.; Fushman, D.; Wilkinson, K.D.; Cohen, R.E.; Wolberger, C. Evidence for bidentate substrate binding as the basis for the K48 linkage specificity of otubain 1. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Wolberger, C. The mechanism of OTUB1-mediated inhibition of ubiquitination. Nature 2012, 483, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matmati, M.; Jacques, P.; Maelfait, J.; Verheugen, E.; Kool, M.; Sze, M.; Geboes, L.; Louagie, E.; Mc Guire, C.; Vereecke, L.; et al. A20 (TNFAIP3) deficiency in myeloid cells triggers erosive polyarthritis resembling rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Han, C.; Song, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Histone methyltransferase Ash1l suppresses interleukin-6 production and inflammatory autoimmune diseases by inducing the ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20. Immunity 2013, 39, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinojosa, C.A.; Akula Suresh Babu, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Fernandes, G.; Boyd, A.R.; Orihuela, C.J. Elevated A20 contributes to age-dependent macrophage dysfunction in the lungs. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 54, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ma, A.; Zhang, L.; Jin, W.L.; Qian, Y.; Xu, G.; Qiu, B.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Q.; et al. POH1 deubiquitylates and stabilizes E2F1 to promote tumour formation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, E.M.; Cutcliffe, C.; Kristiansen, T.Z.; Pandey, A.; Pickart, C.M.; Cohen, R.E. K63-specific deubiquitination by two JAMM/MPN+ complexes: BRISC-associated Brcc36 and proteasomal Poh1. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Yoshikawa, A.; Yamagata, A.; Mimura, H.; Yamashita, M.; Ookata, K.; Nureki, O.; Iwai, K.; Komada, M.; Fukai, S. Structural basis for specific cleavage of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitin chains. Nature 2008, 455, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, A.J.; Mallery, D.L.; Watkinson, R.E.; Dickson, C.F.; James, L.C. Sequential ubiquitination and deubiquitination enzymes synchronize the dual sensor and effector functions of TRIM21. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10014–10019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, J.; Row, P.E.; Lorenzo, O.; Doherty, M.; Beynon, R.; Clague, M.J.; Urbe, S. Activation of the endosome-associated ubiquitin isopeptidase AMSH by STAM, a component of the multivesicular body-sorting machinery. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. The Lys63-specific deubiquitinating enzyme BRCC36 is regulated by two scaffold proteins localizing in different subcellular compartments. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 30982–30988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carolan, B.J.; Heguy, A.; Harvey, B.G.; Leopold, P.L.; Ferris, B.; Crystal, R.G. Up-regulation of expression of the ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 gene in human airway epithelium of cigarette smokers. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10729–10740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Shen, X. Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolases: Involvement in cancer progression and clinical implications. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Niu, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Ye, X.; Lu, S.; Chen, Z. Effect of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase 37 on apoptotic in A549 cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2011, 29, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan, J.A.; Jacq, X.; Martin, N.M.; Jackson, S.P. Deubiquitylating enzymes and drug discovery: Emerging opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Azfer, A.; Zhelyabovska, O.; Fatma, S.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1 promotes angiogenesis via a novel transcription factor, MCP-1-induced protein (MCPIP). J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14542–14551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalniak, L.; Mizgalska, D.; Zarebski, A.; Wyrzykowska, P.; Koj, A.; Jura, J. Regulatory feedback loop between NF-kappaB and MCP-1-induced protein 1 RNase. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5892–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Miao, R.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.E.; Xin, H.B.; Zhang, J.; Fu, M. MCPIP1 negatively regulates toll-like receptor 4 signaling and protects mice from LPS-induced septic shock. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Azfer, A.; Song, W.; Tromp, G.; Kolattukudy, P.E.; Fu, M. A novel CCCH-zinc finger protein family regulates proinflammatory activation of macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 6337–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Saad, Y.; Lei, T.; Wang, J.; Qi, D.; Yang, Q.; Kolattukudy, P.E.; Fu, M. MCP-induced protein 1 deubiquitinates TRAF proteins and negatively regulates JNK and NF-kappaB signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2959–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Standley, D.M.; Kumagai, Y.; Kawagoe, T.; Miyake, T.; Satoh, T.; Kato, H.; Tsujimura, T.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Zc3h12a is an RNase essential for controlling immune responses by regulating mRNA decay. Nature 2009, 458, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.J.; Chien, H.L.; Lin, S.Y.; Chang, B.L.; Yu, H.P.; Tang, W.C.; Lin, Y.L. MCPIP1 ribonuclease exhibits broad-spectrum antiviral effects through viral RNA binding and degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 3314–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruneda, J.N.; Durkin, C.H.; Geurink, P.P.; Ovaa, H.; Santhanam, B.; Holden, D.W.; Komander, D. The Molecular Basis for Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-like Specificities in Bacterial Effector Proteases. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey-Elkin, B.A.; Knaap, R.C.; Johnson, G.G.; Dalebout, T.J.; Ninaber, D.K.; van Kasteren, P.B.; Bredenbeek, P.J.; Snijder, E.J.; Kikkert, M.; Mark, B.L. Crystal structure of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) papain-like protease bound to ubiquitin facilitates targeted disruption of deubiquitinating activity to demonstrate its role in innate immune suppression. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34667–34682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Mesters, J.R.; Drosten, C.; Anemuller, S.; Ma, Q.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal structure of the papain-like protease of MERS coronavirus reveals unusual, potentially druggable active-site features. Antiviral Res. 2014, 109, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias-Staheli, N.; Giannakopoulos, N.V.; Kikkert, M.; Taylor, S.L.; Bridgen, A.; Paragas, J.; Richt, J.A.; Rowland, R.R.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Lenschow, D.J.; et al. Ovarian tumor domain-containing viral proteases evade ubiquitin- and ISG15-dependent innate immune responses. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).