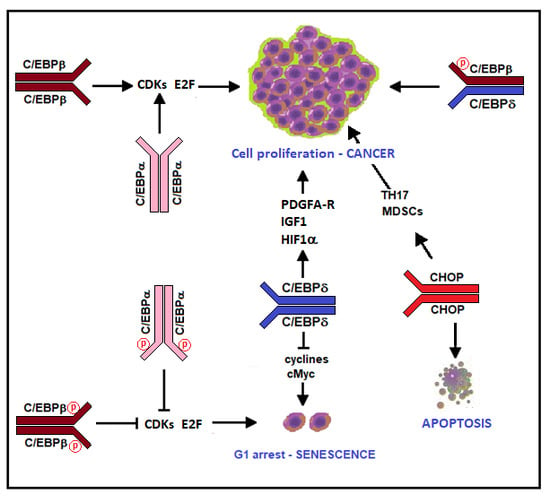
The “Janus” Role of C/EBPs Family Members in Cancer Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. C/EBPs Structure and Isoforms
3. C/EBPs Functions
4. C/EBPs and Cancer
4.1. C/EBPα
4.2. C/EBPβ
4.3. C/EBPδ
4.4. C/EBPγ
4.5. C/EBPε
4.6. CHOP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramji, D.P.; Foka, P. CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: Structure, function and regulation. Biochem. J. 2002, 365, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerlov, C. The C/EBP family of transcription factors: A paradigm for interaction between gene expression and proliferation control. Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinson, C.R.; Sigler, P.B.; McKnight, S.L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science 1989, 246, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Nishihara, T.; Imagawa, M. DNA binding specificity of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein transcription factor family. J. Biologic. Chem. 1996, 271, 3891–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.C.; Baer, M.; Dillner, A.J.; Johnson, P.F. CRP2 (C/EBPβ) contains a bipartite regulatory domain that controls transcriptional activation, DNA binding and cell specificity. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 3170–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descombes, P.; Schibler, U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell 1991, 67, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welm, A.L.; Timochenko, N.A.; Darlington, G.J. C/EBPα regulates generation of C/EBPβ isoforms through activation of specific proteolytic cleavage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, R.; Kim, G.D.; Radomska, H.S.; Lekstrom-Himes, J.; Smith, L.T.; Antonson, P.; Tenen, D.G.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein ε is preferentially up-regulated during granulocyte differentiation and its functional versatility is determined by alternative use of promoters and differential splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6462–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.D.; Finegold, M.J.; Bradley, A.; Ou, C.N.; Abdelsayed, S.V.; Wilde, M.D.; Taylor, L.R.; Wilson, D.R.; Darlington, G.J. Impaired energy homeostasis in C/EBPα knockout mice. Science 1995, 269, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.T.; Lane, M.D. Antisense CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein RNA suppresses coordinate gene expression and triglyceride accumulation during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Genes Dev. 1992, 6, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freytag, S.O.; Paielli, D.L.; Gilbert, J.D. Ectopic expression of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α promotes the adipogenic program in a variety of mouse fibroblastic cells. Genes Dev. 1994, 15, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Yoshida, N.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. Defective adipocyte differentiation in mice lacking the C/EBPβ and/or C/EBPδ gene. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 7432–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.M.; Civin, C.I.; Rorth, P.; Friedman, A.D. A novel temporal expression pattern of three C/EBP family members in differentiating myelomonocytic cells. Blood 1992, 80, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morosetti, R.; Park, D.J.; Chumakov, A.M.; Grillier, I.; Shiohara, M.; Gombart, A.F.; Nakamaki, T.; Weinberg, K.; Koeffler, H.P. A novel, myeloid transcription factor, C/EBPε, is upregulated during granulocytic, but not monocytic, differentiation. Blood 1997, 90, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsuka, S.; Akira, S.; Nishio, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Sugita, T.; Isshiki, H.; Kishimoto, T. Macrophage differentiation-specific expression of NF-IL6, transcription factor for IL-6. Blood 1992, 79, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flodby, P.; Barlow, C.; Kylefjord, H.; Ahrlund-Richter, L.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. Increased hepatic cell proliferation and lung abnormalities in mice deficient in CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 24753–24760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.W.; Johnson, P.F.; Hennighausen, L.; Sterneck, E. The C/EBPβ transcription factor regulates epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation in the mammary gland. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Oh, H.S.; Shim, M.; Sterneck, E.; Johnson, P.F.; Smart, R.C. C/EBPβ modulates the early events of keratinocyte differentiation involving growth arrest and keratin 1 and keratin 10 expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 7181–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Canteli, M.; Pignatelli, M.; Santos, A.; Perez-Castillo, A. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β plays a regulatory role in differentiation and apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5460–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, C.; Gordon, J.I. Cell lineage-specific and differentiation dependent patterns of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α in the gut epithelium of normal and transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8871–8875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlington, G.J.; Ross, S.E.; MacDougald, O.A. The role of C/EBP genes in adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 273, 30057–30060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubenfeld, S.M.; Wiig, K.A.; Monti, B.; Dolan, B.; Pollonini, G.; Alberini, C.M. Fornix-dependent induction of hippocampal CCAAT enhancer-binding protein β and δ co-localizes with phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein and accompanies long-term memory consolidation. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umek, R.M.; Friedman, A.D.; McKnight, S.L. CCAAT-enhancer binding protein: A component of a differentiation switch. Science 1991, 251, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Iakova, P.; Wilde, M.; Welm, A.; Goode, T.; Roesler, W.J.; Timchenko, N.A. C/EBPalpha arrests cell proliferation through direct inhibition of Cdk2 and Cdk4. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.E.; Albrecht, J.H.; Nakanishi, M.; Darlington, G.J. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha cooperates with p21 to inhibit cyclin-dependent kinase-2 activity and induces growth arrest independent of DNA binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 29200–29209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomiany, B.A.; D’Arigo, K.L.; Kelly, M.M.; Kurtz, D.T. C/EBPalpha inhibits cell growth via direct repression of E2F-DP-mediated transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 5986–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.; Smart, R.C. C/EBPalpha is a DNA damage-inducible p53-regulated mediator of the G1 checkpoint in keratinocytes. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 10650–10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkhoven, C.F.; Bouwman, P.R.; Snippe, L.; Ab, G. Translation start site multiplicity of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha mRNA is dictated by a small 5′ open reading frame. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 5540–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.E.; Zhang, P.; Wang, N.D.; Hetherington, C.J.; Darlington, G.J.; Tenen, D.G. Absence of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor signaling and neutrophil development in CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Iwasaki-Arai, J.; Iwasaki, H.; Fenyus, M.L.; Dayaram, T.; Owens, B.M.; Shigematsu, H.; Levantini, E.; Huettner, C.S.; Lekstrom-Himes, J.A.; et al. Enhancement of hematopoietic stem cell repopulating capacity and self-renewal in the absence of the transcription factor C/EBP alpha. Immunity 2004, 21, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Zhang, H.; Amabile, G.; Yang, H.; Staber, P.B.; Zhang, P.; Levantini, E.; Alberich-Jordà, M.; Zhang, J.; Kawasaki, A.; et al. C/EBPa controls acquisition and maintenance of adult haematopoietic stem cell quiescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, T.; Mueller, B.U.; Harakawa, N.; Schoch, C.; Haferlach, T.; Behre, G.; Hiddemann, W.; Zhang, D.E.; Tenen, D.G. AML1-ETO downregulates the granulocytic differentiation factor C/EBPalpha in t(8;21) myeloid leukemia. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotti, D.; Cesi, V.; Trotta, R.; Guerzoni, C.; Santilli, G.; Campbell, K.; Iervolino, A.; Condorelli, F.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Caligiuri, M.A.; et al. BCR-ABL suppresses C/EBPalpha expression through inhibitory action of hnRNP E2. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbauer, F.; Tenen, D.G. Transcription factors in myeloid development: Balancing differentiation with transformation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Friedman, A.D.; Levis, M.; Li, L.; Weir, E.G.; Small, D. Internal tandem duplication mutation of FLT3 blocks myeloid differentiation through suppression of C/EBPalpha expression. Blood 2004, 103, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, A.-R.; Coffer, P.J. A tumor suppressor role for C/EBPα in solid tumors: More than fat and blood. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Watanabe, K.; Saisho, H.; Nakagawara, A.; Tagawa, M. Down-regulated expression of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha and beta genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma: A possible prognostic marker. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 351–354. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, H.H.; Hwang, Y.H.; Yeh, K.T.; Chang, J.G.; Chen, Y.L.; Yu, H.S. Reduced expression of C/EBP alpha protein in HCC is associated with advanced tumor stage and shortened patient survival. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.D.; Ang, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Tamilarasi, J.; Yan, B.; Lim, Y.C.; Srivastava, S.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Hui, K.M.; Shen, H.M. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α predicts poorer prognosis and prevents energy starvation-induced cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 61, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.G.; Kytola, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Larsson, C.; Ekstrom, T.J. Comparative genomic hybridization reveals population-based genetic alterations in hepatoblastomas. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Iakova, P.; Wilde, M.; Awad, S.; Timchenko, N.A. Liver tumors escape negative control of proliferation via PI3K/Akt-mediated block of C/EBP alpha growth inhibitory activity. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cast, A.; Valanejad, L.; Wright, M.; Nguyen, P.; Gupta, A.; Zhu, L.; Shin, S.; Timchenko, N. C/EBPα-dependent preneoplastic tumor foci are the origin of hepatocellular carcinoma and aggressive pediatric liver cancer. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1857–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Shi, X.; Haefliger, S.; Jin, J.; Major, A.; Iakova, P.; Finegold, M.; Timchenko, N.A. Elimination of C/EBPα through the ubiquitin–proteasome system promotes the development of liver cancer in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2549–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Iakova, P.; Jin, J.; Sullivan, S.; Sharin, V.; Hong, I.-H.; Anakk, S.; Mayor, A.; Darlington, G.; Finegold, M.; et al. FXR inhibits gankyrin in mouse livers and prevents development of liver cancer. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valanejad, L.; Lewis, K.; Wright, M.; Jiang, Y.; D’Souza, A.; Karns, R.; Sheridan, R.; Gupta, A.; Bove, K.; Witte, D.; et al. FXR–gankyrin axis is involved in development of pediatric liver cancer. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Isshiki, H.; Sugita, T.; Tanabe, O.; Kinoshita, S.; Nishio, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Hirano, T.; Kishimoto, T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, I.V.; Krammer, P.H.; Li-Weber, M. Nuclear factor-IL6 activates the human IL-4 promoter in T cells. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 5273–5279. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk, T.B.; Baltus, B.; Raaijmakers, J.A.; Lammers, J.W.; Koenderman, L.; de Groot, R.P. A composite C/EBP binding site is essential for the activity of the promoter of the IL-3/IL-5/granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor beta c gene. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 2674–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwel, P.; Tanaka, S.; Penkov, D.; Zhang, W.; Olive, M.; Moll, J.; Vinson, C.; Di Liberto, M.; Ramirez, F. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Inhibits Type I Collagen Synthesis through Repressive CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffell, D.; Mourkioti, F.; Gambardella, A.; Kirstetter, P.; Lopez, R.G.; Rosenthal, N.; Nerlov, C. A CREB-C/EBPbeta cascade induces M2 macrophage-specific gene expression and promotes muscle injury repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17475–17480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Ambrosino, C.; Ruocco, M.R.; Poli, V.; Romani, L.; Quinto, I.; Barbieri, S.; Holmes, K.L.; Venuta, S.; et al. Impaired generation of bone marrow B lymphocytes in mice deficient in C/EBPbeta. Blood 1997, 90, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kovács, K.A.; Steinmann, M.; Magistretti, P.J.; Halfon, O.; Cardinaux, J.R. C/EBPbeta couples dopamine signalling to substance P precursor gene expression in striatal neurones. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Uchiumi, T.; Hinoshita, E.; Inokuchi, A.; Toh, S.; Wada, M.; Takano, H.; Kohno, K.; Kuwano, M. The human multidrug resistance protein 2 gene: Functional characterization of the 5′-flanking region and expression in hepatic cells. Hepatology 1999, 30, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.K.; Sale, S.; Tan, T.; Ermoian, R.P.; Sikic, B.I. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (nuclear factor for interleukin 6) transactivates the human MDR1 gene by interaction with an inverted CCAAT box in human cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, T.; Malik, R.; Thomas, S.; Sage, J.; Johnson, P.F. C/EBPbeta cooperates with RB:E2F to implement Ras(V12)-induced cellular senescence. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3301–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, J. Senescent cells, tumor suppression, and organismal aging: Good citizens, bad neighbors. Cell 2005, 120, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.; Blasco, M.A.; Serrano, M. Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell 2007, 130, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.D. Healing and hurting: Molecular mechanisms, functions, and pathologies of cellular senescence. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterneck, E.; Zhu, S.; Ramirez, A.; Jorcano, J.L.; Smart, R.C. Conditional ablation of C/EBP beta demonstrates its keratinocyte-specific requirement for cell survival and mouse skin tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowenz-Leutz, E.; Twamley, G.; Ansieau, S.; Leutz, A. Novel mechanism of C/EBP β (NF-M) transcriptional control: Activation through derepression. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Kowenz-Leutz, E.; Xu, H.; Leutz, A. Ras induces mediator complex exchange on C/EBP beta. Mol. Cell 2004, 13, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Shuman, J.D.; Guszczynski, T.; Sakchaisri, K.; Sebastian, T.; Copeland, T.D.; Miller, M.; Cohen, M.S.; Taunton, J.; Smart, R.C.; et al. RSK-mediated phosphorylation in the C/EBP β leucine zipper regulates DNA binding, dimerization, and growth arrest activity. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 30, 2621–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.K.; Malik, R.; Huggins, C.J.; Lee, S.; Sebastian, T.; Sakchaisri, K.; Quiñones, O.A.; Alvord, W.G.; Johnson, P.F. 3′UTR elements inhibit Ras-induced C/EBPβ post-translational activation and senescence in tumour cells. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3714–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.K.; Gonit, M.; Salotti, J.; Chen, J.; Bhat, A.; Gorospe, M.; Viollet, B.; Claffey, K.P.; Johnson, P.F. A RAS-CaMKKβ-AMPKα2 pathway promotes senescence by licensing post-translational activation of C/EBPβ through a novel 3′UTR mechanism. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3528–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahnow, C.A. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta: Its role in breast cancer and associations with receptor tyrosine kinases. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis, R.R.; Alarcón, C.; Nadal, C.; Van Poznak, C.; Massagué, J. C/EBPbeta at the core of the TGFbeta cytostatic response and its evasion in metastatic breast cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, S.C.; Huber, R.; Gutsch, R.; Kandemir, J.D.; Cappello, C.; Krauter, J.; Duyster, J.; Ganser, A.; Brand, K. ITD- and FL-induced FLT3 signal transduction leads to increased C/EBPβ-LIP expression and LIP/LAP ratio by different signalling modules. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, J.P.; Newbound, G.C.; Hutt, J.A.; DeWille, J. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta regulates mammary epithelial cell G0 growth arrest and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 16582–16589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearth, L.R.; DeWille, J. Posttranscriptional and posttranslational regulation of C/EBP delta in G0 growth-arrested mammary epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11246–11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.M.; Montagna, C.; Sharan, S.; Ni, Y.; Ried, T.; Sterneck, E. Loss of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta promotes chromosomal instability. Oncogene 2004, 23, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutt, J.A.; DeWille, J.W. Oncostatin M induces growth arrest of mammary epithelium via a CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta-dependent pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balamurugan, K.; Sterneck, E. The many faces of C/EBPdelta and their relevance for inflammation and cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.A.; Sarkar, T.; Balamurugan, K.; Sharan, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dowdy, S.F.; Huang, A.M.; Sterneck, E. C/EBP{delta} targets cyclin D1 for proteasome-mediated degradation via induction of CDC27/APC3 expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9210–9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Hofmann, W.K.; Tidow, N.; Ehrich, M.; van den Boom, D.; Koschmieder, S.; Berdel, W.E.; Serve, H.; Müller-Tidow, C. The C/EBPdelta tumor suppressor is silenced by hypermethylation in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2007, 109, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radich, J.P.; Dai, H.; Mao, M.; Oehler, V.; Schelter, J.; Druker, B.; Sawyers, C.; Shah, N.; Stock, W.; Willman, C.L.; et al. Gene expression changes associated with progression and response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2794–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gery, S.; Tanosaki, S.; Hofmann, W.K.; Koppel, A.; Koeffler, H.P. C/EBPδ expression in a BCR-ABL-positive cell line induces growth arrest and myeloid differentiation. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.F.; Friedman, A.D. CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins are required for granulopoiesis independent of their induction of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor. Blood 2002, 99, 2776–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Xie, N.; Cui, H.; Tan, Z.; Yang, S.; Icyuz, M.; Abraham, E.; Liu, G. MicroRNA let-7c regulates macrophage polarization. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6542–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikezoe, T.; Gery, S.; Yin, D.; O’Kelly, J.; Binderup, L.; Lemp, N.; Taguchi, H.; Koeffler, H.P. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta: A molecular target of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in androgen-responsive prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4762–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umayahara, Y.; Ji, C.; Centrella, M.; Rotwein, P.; McCarthy, T.L. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta activates insulin-like growth factor-I gene transcription in osteoblasts. Identification of a novel cyclic AMP signaling pathway in bone. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, T.; Kitami, Y.; Okura, T.; Hiwada, K. Transcriptional regulation of the platelet-derived growth factor alpha receptor gene via CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-delta in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25576–25582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamurugan, K.; Wang, J.M.; Tsai, H.H.; Sharan, S.; Anver, M.; Leighty, R.; Sterneck, E. The tumour suppressor C/EBPδ inhibits FBXW7 expression and promotes mammary tumour metastasis. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 4106–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.A.; Gutman, D.A.; Chisolm, C.; Appin, C.; Kong, J.; Rong, Y.; Kurc, T.; Van Meir, E.G.; Saltz, J.H.; Moreno, C.S.; et al. The tumor microenvironment strongly impacts master transcriptional regulators and gene expression class of glioblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 2108–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carro, M.S.; Lim, W.K.; Alvarez, M.J.; Bollo, R.J.; Zhao, X.; Snyder, E.Y.; Sulman, E.P.; Anne, S.L.; Doetsch, F.; Colman, H.; et al. The transcriptional network for mesenchymal transformation of brain tumours. Nature 2010, 463, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, G. Role of the ubiquitin ligase Fbw7 in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sif, S.; DeWille, J. The mouse C/EBPdelta gene promoter is regulated by STAT3 and Sp1 transcriptional activators, chromatin remodeling and c-Myc repression. J. Cell Biochem. 2007, 102, 1256–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.M. Role of STATs as downstream signal transducers in Src family kinase-mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8017–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, C.L.; Courtneidge, S.A. Src family tyrosine kinases and growth factor signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 254, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, T.R.; Sharan, S.; Wang, J.; Pawar, S.A.; Cantwell, C.A.; Johnson, P.F.; Morrison, D.K.; Wang, J.M.; Sterneck, E. Identification of a Src tyrosine kinase/SIAH2 E3 ubiquitin ligase pathway that regulates C/EBPdelta expression and contributes to transformation of breast tumor cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.; Henderson, A.; Artandi, S.; Avitahl, N.; Calame, K. Ig/EBP (C/EBPγ) is a transdominant negative inhibitor of C/EBP family transcriptional activators. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 4371–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaisho, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Tanaka, T.; Tsujimura, T.; Takeda, K.; Kawai, T.; Yoshida, N.; Nakanishi, K.; Akira, S. Impairment of natural killer cytotoxic activity and interferon gamma production in CCAAT/enhancer binding protein gamma-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggins, C.J.; Malik, R.; Lee, S.; Salotti, J.; Thomas, S.; Martin, N.; Quinones, O.A.; Alvord, W.G.; Olanich, M.E.; Keller, J.R.; et al. C/EBPγ suppresses senescence and inflammatory gene expression by heterodimerizing with C/EBPβ. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 3242–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, S.E.; Baer, M.; Copeland, T.D.; Schwartz, R.C.; Johnson, P.F. Regulation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) activator proteins by heterodimerization with C/EBPγ (Ig/EBP). J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23563–23572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.A.; Xu, H.N.; Gombart, A.F.; Verbeek, W.; Chumakov, A.M.; Friedman, A.D.; Koeffler, H.P. Identification of transcriptional activation and repression domains in human CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein epsilon. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14796–14804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumakov, A.M.; Grillier, I.; Chumakova, E.; Chih, D.; Slater, J.; Koeffler, H.P. Cloning of the novel human myeloid-cell-specific C/EBP-epsilon transcription factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedi, R.; Du, J.; Sharma, A.K.; Gomes, I.; Ackerman, S.J. Human. C/EBP-epsilon activator and repressor isoforms differentially reprogram myeloid lineage commitment and differentiation. Blood 2009, 113, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, M.; Chumakov, A.M.; Takeuchi, S.; Tasaka, T.; Yang, R.; Nakamaki, T.; Tsuruoka, N.; Koeffler, H.P. C/EBP-epsilon: Chromosomal mapping and mutational analysis of the gene in leukemia and preleukemia. Leuk. Res. 1997, 21, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyadomari, S.; Mori, M. Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.L.; Lebeau, J.; Guillaumot, P.; Petrilli, V.; Malek, M.; Chilloux, J.; Fauvet, F.; Payen, L.; Kfoury, A.; Renno, T.; et al. p58(IPK)-mediated attenuation of the proapoptotic PERK-CHOP pathway allows malignant progression upon low glucose. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Umemura, A.; Taniguchi, K.; Font-Burgada, J.; Dhar, D.; Ogata, H.; Zhong, Z.; Valasek, M.A.; Seki, E.; Hidalgo, J. ER stress cooperates with hypernutrition to trigger TNF-dependent spontaneous HCC development. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.P.; Klocke, B.J.; Ballestas, M.E.; Roth, K.A. CHOP potentially co-operates with FOXO3a in neuronal cells to regulate PUMA and BIM expression in response to ER stress. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galehdar, Z.; Swan, P.; Fuerth, B.; Callaghan, S.M.; Park, D.S.; Cregan, S.P. Neuronal apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress is regulated by ATF4-CHOP-mediated induction of the Bcl-2 homology 3-only member PUMA. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 16938–16948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Lawrence, D.A.; Marsters, S.; Acosta-Alvear, D.; Kimmig, P.; Mendez, A.S.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Walter, P.; Ashkenazi, A. Opposing unfolded-protein-response signals converge on death receptor 5 to control apoptosis. Science 2014, 345, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, S.J.; Yun, C.Y.; Oyadomari, S.; Novoa, I.; Zhang, Y.; Jungreis, R.; Nagata, K.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. CHOP induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the stressed endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 3066–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihailidou, C.; Chatzistamou, I.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Kiaris, H. Regulation of P21 during diabetes-associated stress of the endoplasmic reticulum. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van Galen, P.; Kreso, A.; Mbong, N.; Kent, D.G.; Fitzmaurice, T.; Chambers, J.E.; Xie, S.; Laurenti, E.; Hermans, K.; Eppert, K.; et al. The unfolded protein response governs integrity of the haematopoietic stem-cell pool during stress. Nature 2014, 510, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.; Ahmed Kabeer Rasheed, S.; Abba, M.; Hendrik Leupold, J.; Schwarzbach, M.; Allgayer, H. A mechanistic study on the metastasis inducing function of FUS-CHOP fusion protein in liposarcoma. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 2808–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaiewicz, V.; Nahmias, A.; Chung, R.T.; Mueller, T.; Tirosh, B.; Shibolet, O. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous (CHOP) protein promotes carcinogenesis in the DEN-induced hepatocellular carcinoma model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenot, P.T.; Sierra, R.A.; Raber, P.L.; Al-Khami, A.A.; Trillo-Tinoco, J.; Zarreii, P.; Ochoa, A.C.; Cui, Y.; Del Valle, L.; Rodriguez, P.C. The stress-response sensor chop regulates the function and accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumors. Immunity 2014, 41, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, K.; Tang, Y.; Jin, X.; An, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; et al. Destruction of DDIT3/CHOP protein by wild-type SPOP but not prostate cancer-associated mutants. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, J.C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; McNeill, L.; Ellis, L.; Saudek, V.; Gaston, J.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced transcription factor, CHOP, is crucial for dendritic cell IL-23 expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17698–17703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yi, T.; Kortylewski, M.; Pardoll, D.M.; Zeng, D.; Yu, H. IL-17 can promote tumor growth through an IL-6-Stat3 signaling pathway. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.; Tornin, J.; Suarez, C.; Astudillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Yauk, C.; Williams, A.; Rosu-Myles, M.; Funes, J.M.; Boshoff, C.; et al. Expression of FUS-CHOP fusion protein in immortalized/transformed human mesenchymal stem cells drives mixoid liposarcoma formation. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Cin, P.; Sciot, R.; Panagopoulos, I.; Aman, P.; Samson, I.; Mandahl, N.; Mitelman, F.; Van den Berghe, H.; Fletcher, C.D. Additional evidence of a variant translocation t(12;22) with EWS/CHOP fusion in myxoid liposarcoma: Clinicopathological features. J. Pathol. 1997, 182, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, X.H.; Guo, X.; Yuan, T.; Tang, Z.H.; Jiang, X.M.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; et al. Activation of notch 3/c-MYC/CHOP axis regulates apoptosis and promotes sensitivity of lung cancer cells to mTOR inhibitor everolimus. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 175, 113921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ren, L.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Du, G. Withaferin A triggers G2/M arrest and intrinsic apoptosis in glioblastoma cells via ATF4-ATF3-CHOP axis. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Huang, K.W.; Andrikakou, P.; Vasconcelos, D.; Swiderski, P.; Reebye, V.; Sodergren, M.; Habib, N.; Rossi, J.J. Targeted Delivery of C/EBPα-saRNA by RNA Aptamers Shows Anti-tumor Effects in a Mouse Model of Advanced PDAC. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, R.; Maurya, R.; Mishra, D.P. Medicarpin, a legume phytoalexin sensitizes myeloid leukemia cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the induction of DR5 and activation of the ROS-JNK-CHOP pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.J.; Min, K.J.; Bae, J.H.; Kwon, T.K. Carnosic acid sensitized TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through down-regulation of c-FLIP and Bcl-2 expression at the post translational levels and CHOP-dependent up-regulation of DR5, Bim, and PUMA expression in human carcinoma caki cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| C/EBPα: adipose tissue, blood mononuclear cells, liver, intestine, lung, adrenal gland, blood, nervous system, and placenta. |
| C/EBPβ: liver, adipose tissue, myelomonocytic cells, intestine, lung, spleen, kidney, and nervous system. |
| C/EBPδ: adipose tissue, myeloid cells, lung, intestine, and nervous system. |
| C/EBPε: myeloid and lymphoid cells. |
| C/EBPγ: ubiquitous expression. |
| CHOP: ubiquitous expression. |
| C/EBP Type | Tumor Suppressor Activity | Tumor Promoting Activity | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| C/EBPα | Phosphorylated form at Ser 190 (193). | Dephosphorylated form at Ser 190 (193). Mutation of Ser 193 to Ala. | [39,40] |
| C/EBPβ | Phosphorylated isoform. | Dephosphorylated isoform. | [58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65] |
| β:β homodimers. | β:γ heterodimers. | ||
| Compartmentalization in perinuclear cytoplasm. | Compartmentalization in peripheral cytoplasm. | ||
| Low LIP/LAP ratios. | High LIP/LAP ratios. | ||
| C/EBPδ | Downregulation of cyclin D/E, C-Myc and upregulation of P27CIP2 in the early stages of tumor development. | Increasing translational activity of HIF-1α in breast cancer metastasis. Overexpression of HIF-1 α and downregulation of FBXW7α in glioblastoma. Overexpression of IGF-1 and PDGFA-R in cultured osteoblasts. | [54,66,71,78,79,80,83] |
| C/EBPγ | Inability to suppress C/EBP-mediated growth arrest in hepatoma cells. Inability to suppress C/EBPα growth arrest in different cell lines. | Inhibition of cellular senescence through heterodimerization with C/EBPβ. | [90,91] |
| C/EBPε | C/EBP-ε32 and C/EBP-ε30 isoforms are transcriptional activators that cause exclusively eosinophil differentiation. No specific effects on cancer. | C/EBP-ϵ27 is an inhibitor of GATA-1 inhibits eosinophil differentiation promoting granulocyte-macrophage differentiation. C/EBP-ε acts as a dominant-negative regulator. No specific effects on cancer. | [92,93,94] |
| CHOP | Induction of apoptosis by inhibition of Bcl-2 and upregulation of Bim, PUMA, DR5 and p21. | Activation of MDSCs. TH17 propagation that promotes tumor growth via IL6-STAT3 pathway. Fusion with FUS/TLS or EWS by genomic rearrangement. | [98,99,100,101,102,106,108,109,110,111] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tolomeo, M.; Grimaudo, S. The “Janus” Role of C/EBPs Family Members in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124308
Tolomeo M, Grimaudo S. The “Janus” Role of C/EBPs Family Members in Cancer Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(12):4308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124308
Chicago/Turabian StyleTolomeo, Manlio, and Stefania Grimaudo. 2020. "The “Janus” Role of C/EBPs Family Members in Cancer Progression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 12: 4308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124308
APA StyleTolomeo, M., & Grimaudo, S. (2020). The “Janus” Role of C/EBPs Family Members in Cancer Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 4308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124308