Myostatin Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Local 14q32 microRNA Expression, But Not Systemic Inflammation or Restenosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
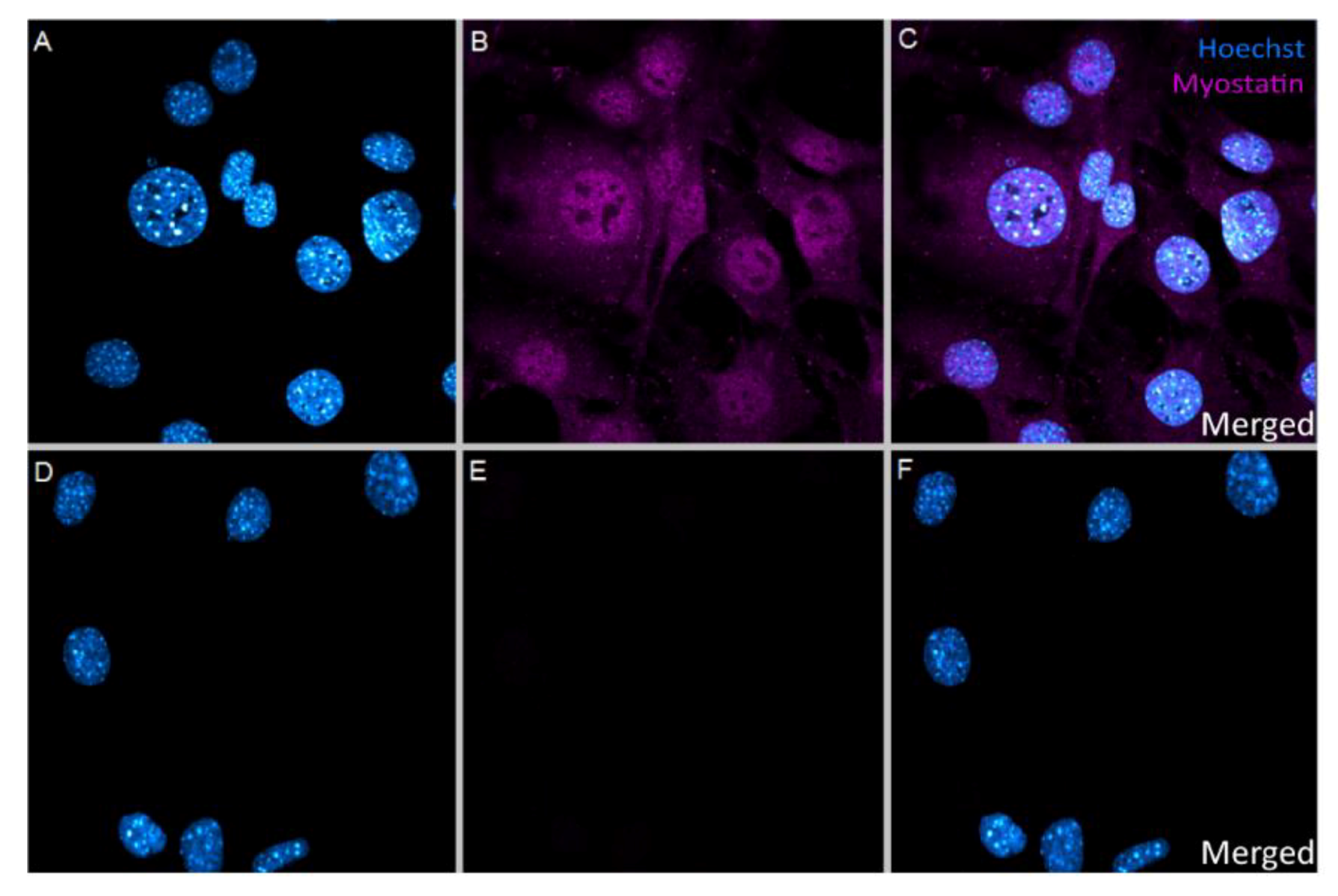
2.1. In Vitro Uptake of Myostatin in VSMC
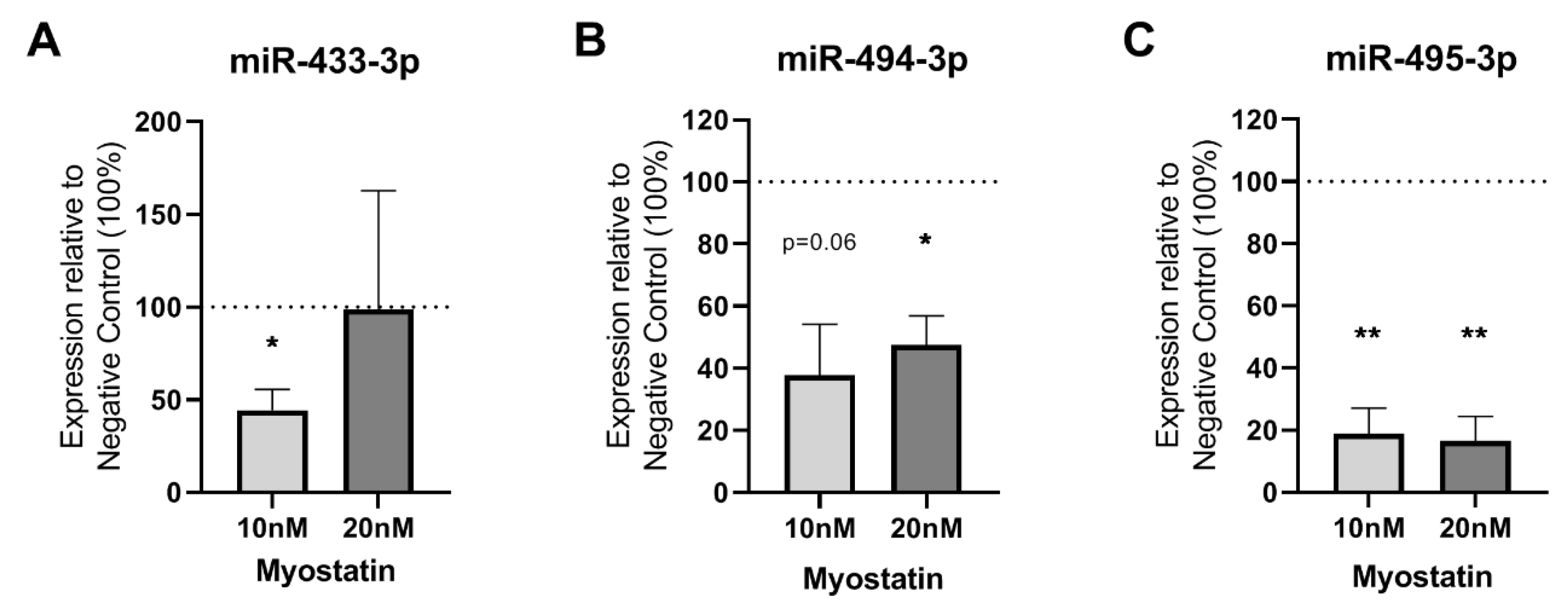
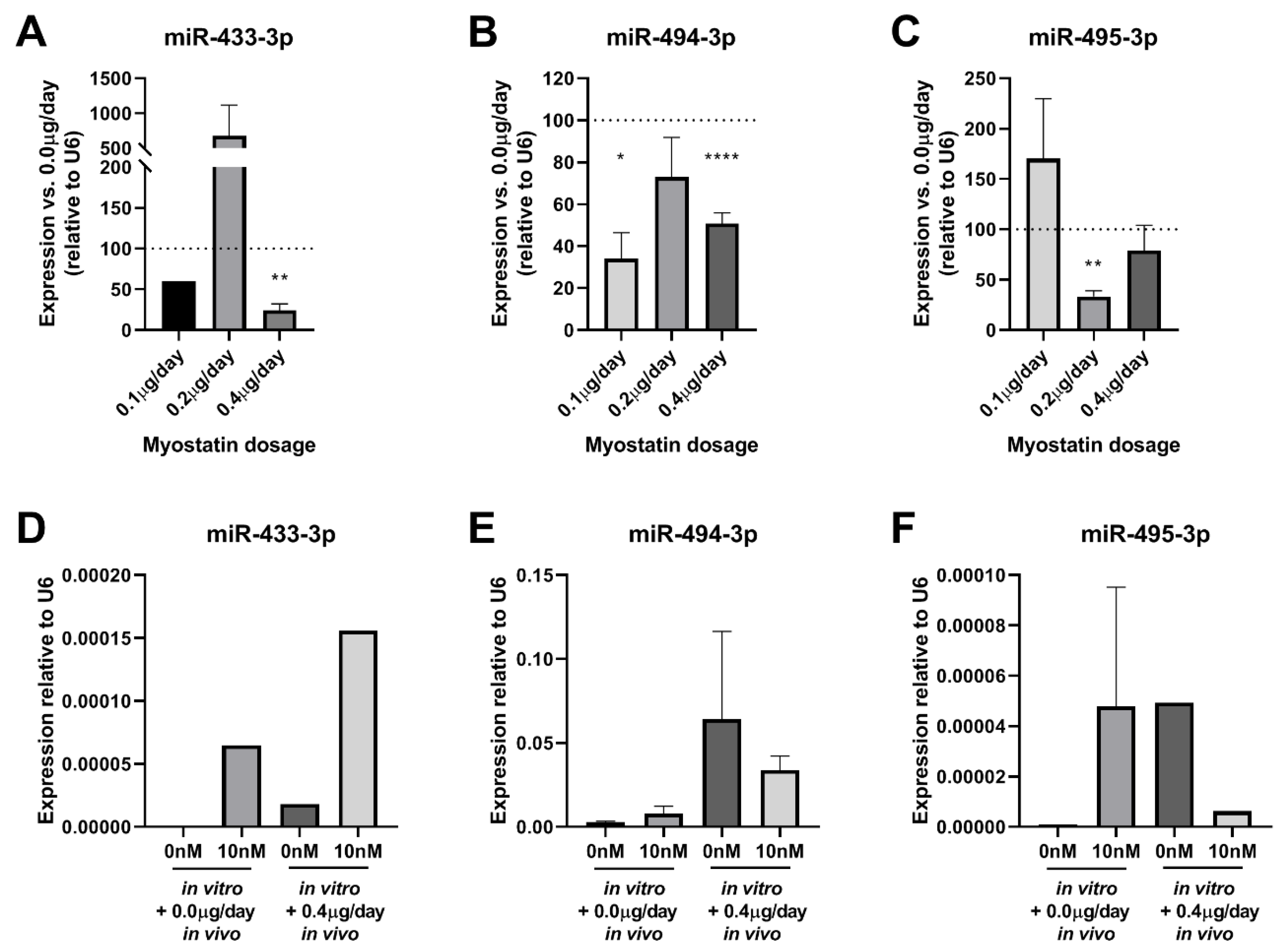
2.2. Effect of Myostatin on 14q32 microRNAs in VSMCs
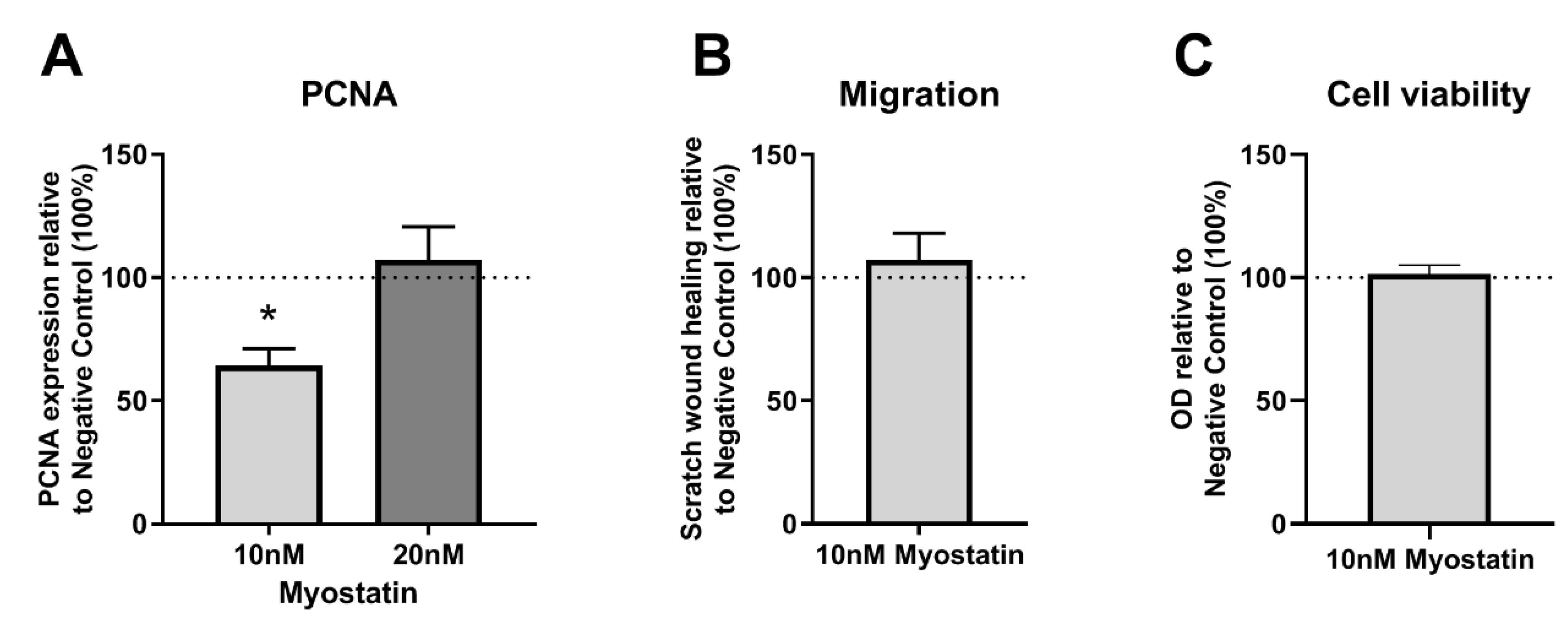
2.3. Functional Effects of MSTN on VSMCs
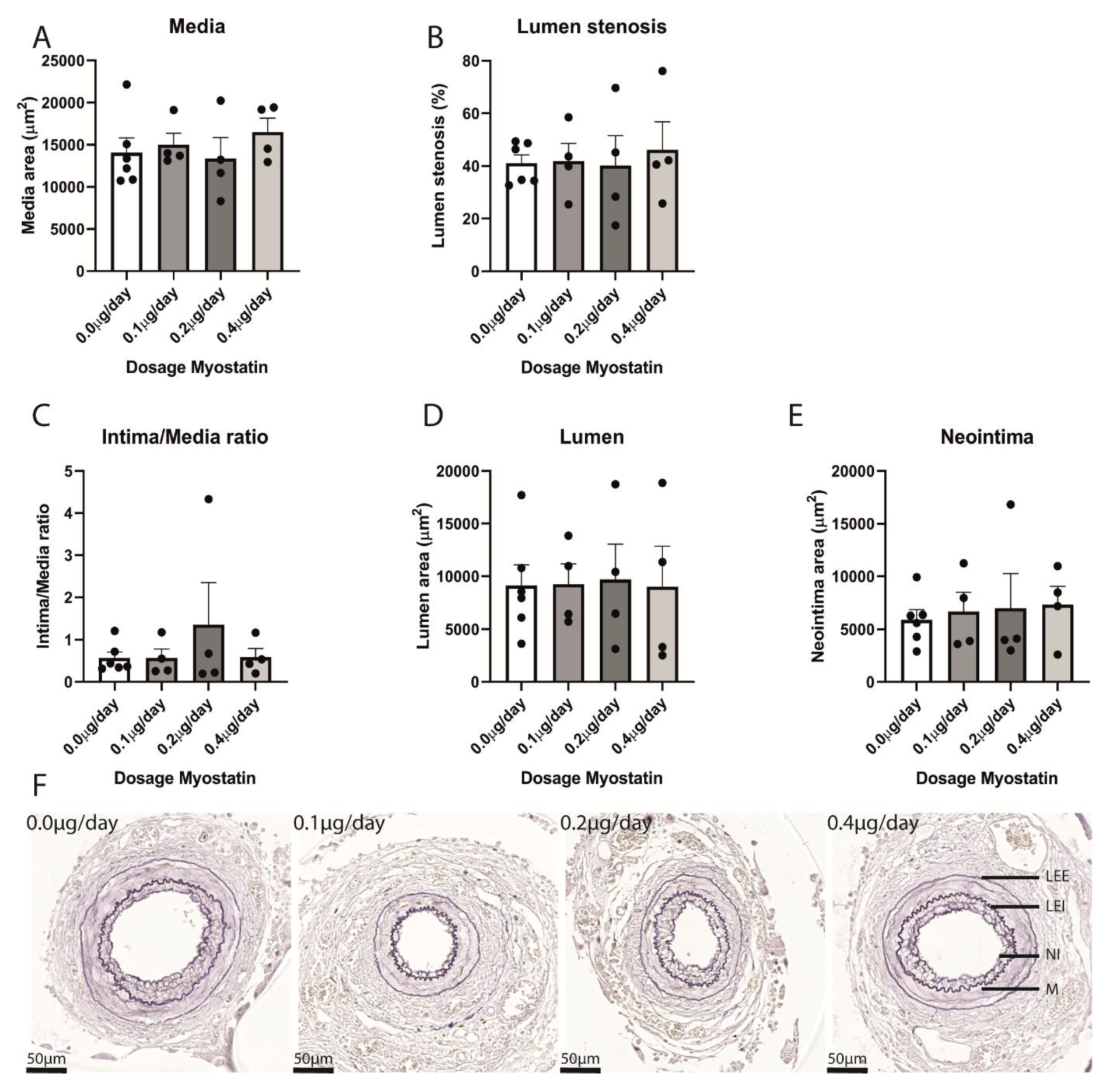
2.4. Restenosis in Myostatin-Treated Mice
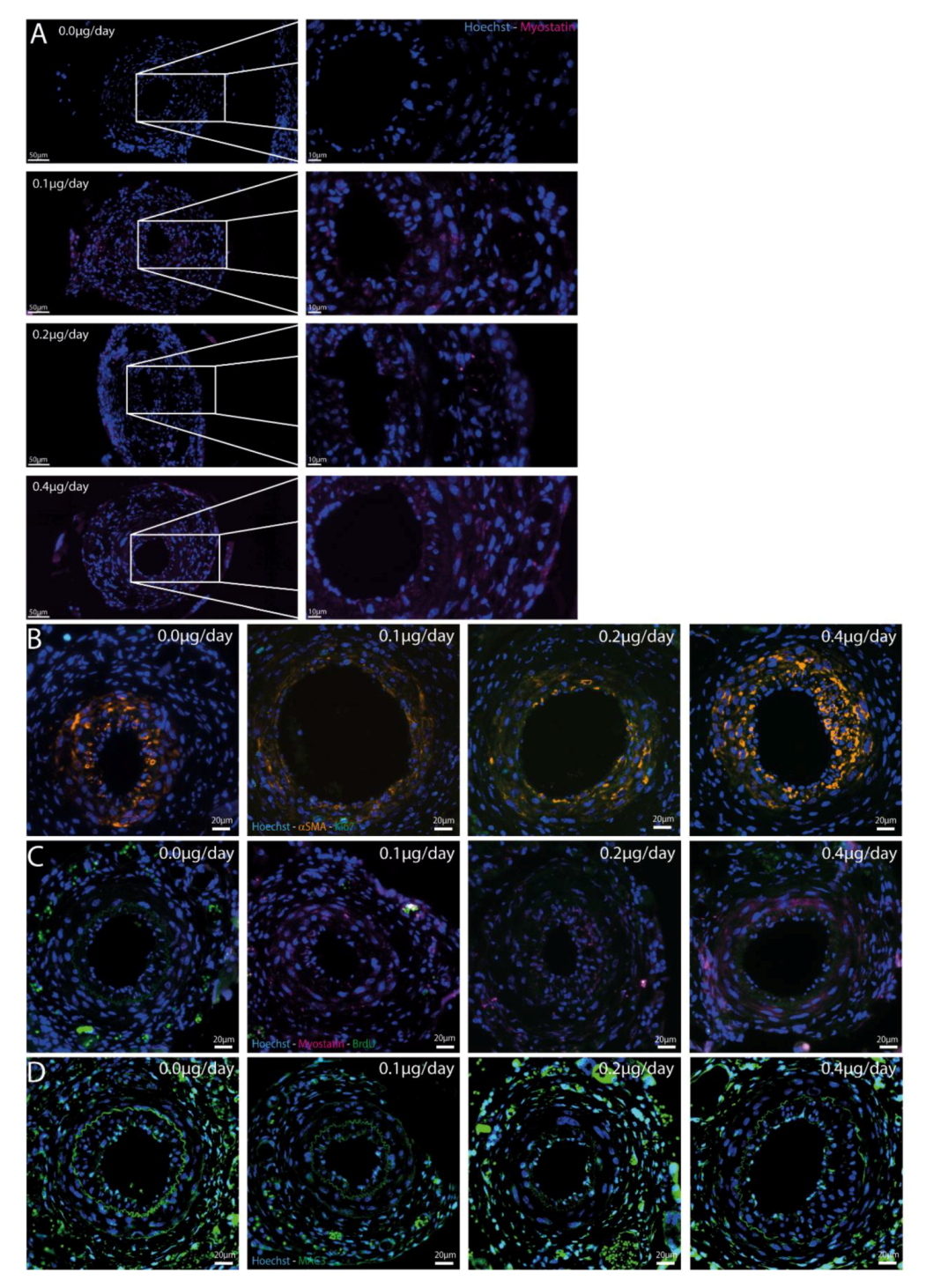
2.5. Myostatin in Cuffed Femoral Arteries
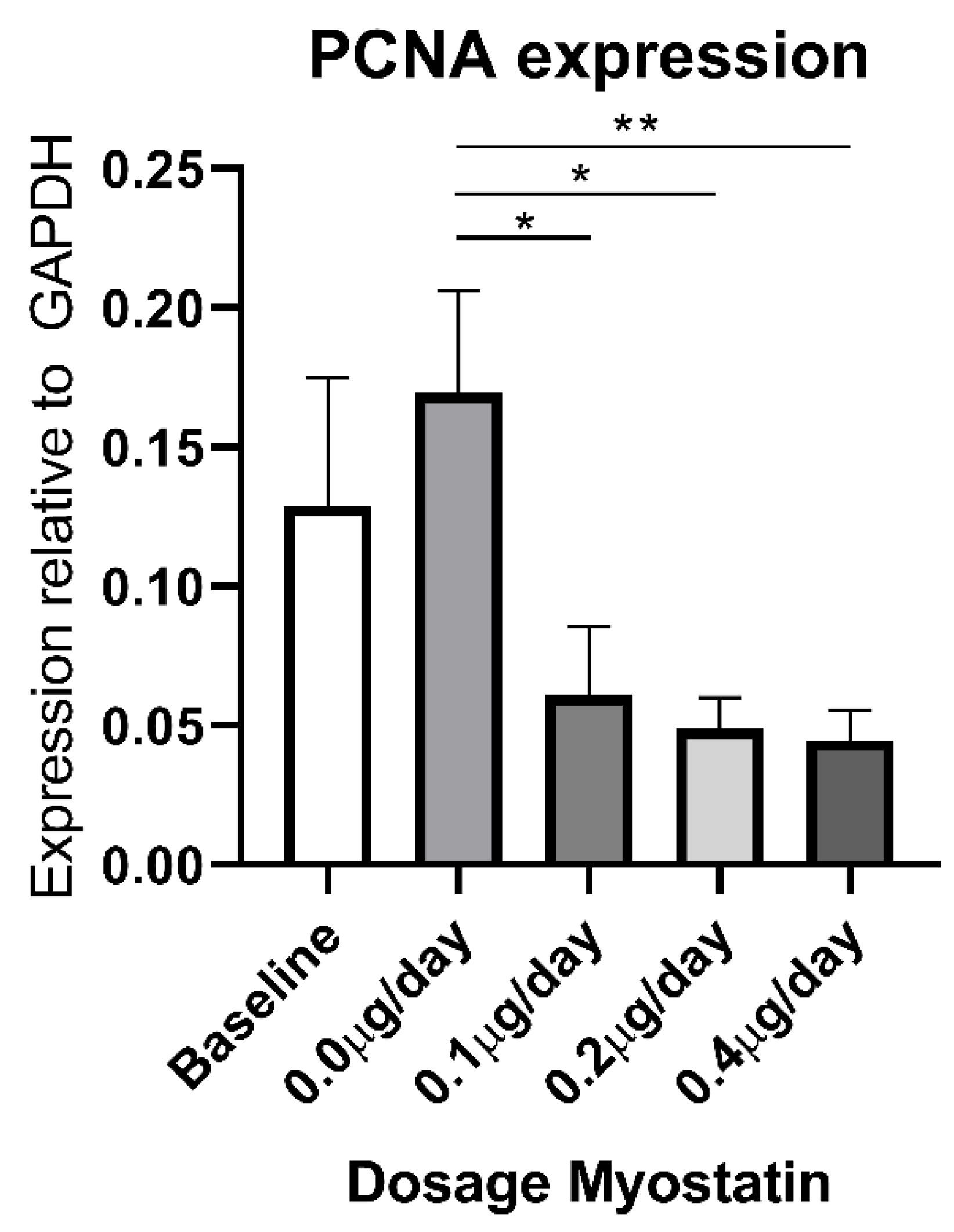
2.6. Effect of Myostatin Treatment on Proliferation
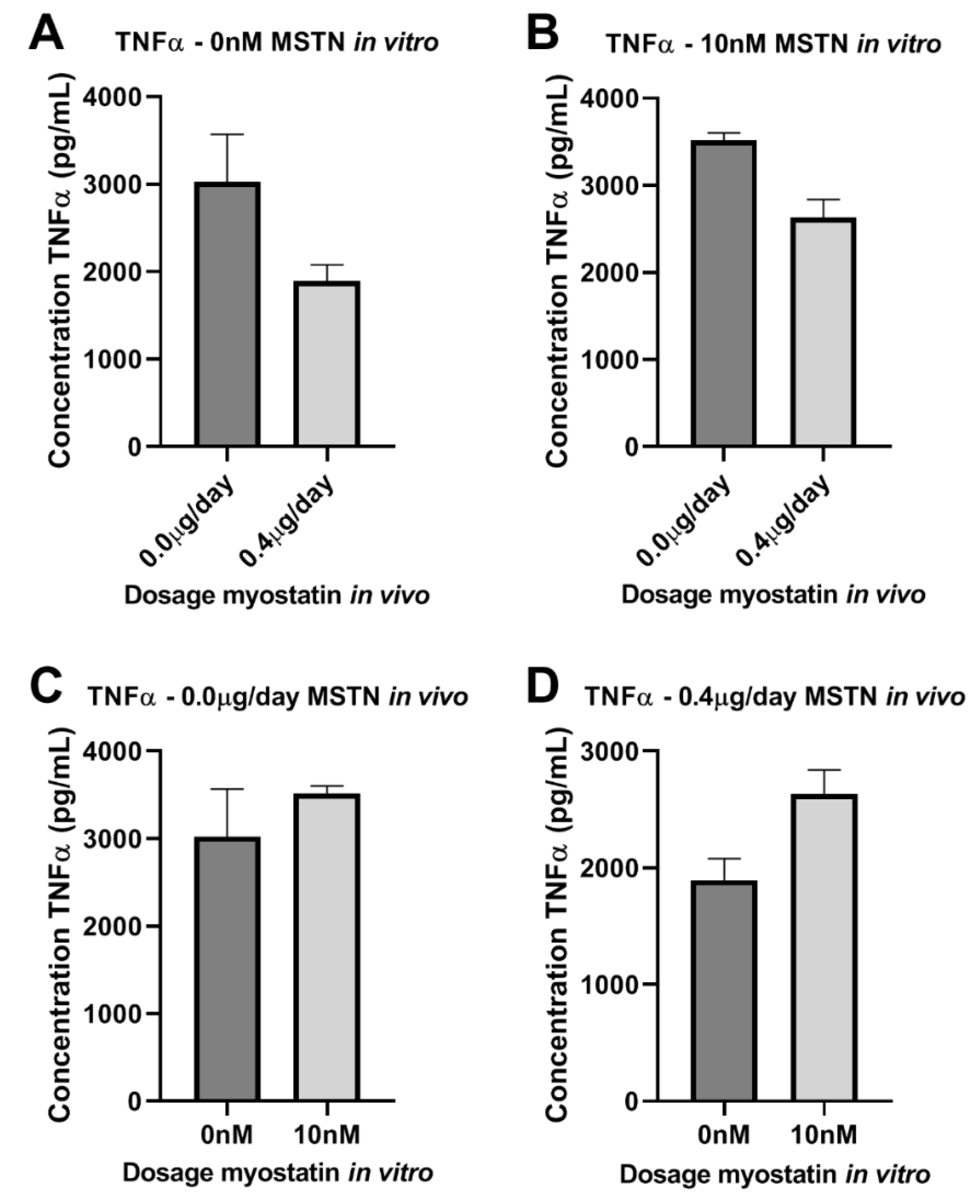
2.7. Effect of Myostatin on Macrophages
2.8. Effect of Myostatin Treatment on 14q32 microRNA Expression In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Femoral ArteRy Cuff Mouse Model
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. In Vitro Addition of Myostatin to VSMCs
4.4. Scratch-Wound Healing Assay
4.5. MTT Viability Assay
4.6. RNA Isolation
4.7. MicroRNA Quantification
4.8. mRNA Quantification
4.9. Immunocytochemistry
4.10. Histological and Immunohistochemical Assessment of Cuffed Femoral Arteries
4.11. Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage Isolation and Stimulation
4.12. Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay (ELISA) of Supernatant Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages
4.13. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibanez, B.; James, S.; Antunes, M.J.; Bucciarelli-Ducci, C.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Crea, F.; Goudevenos, J.A.; Halvorsen, S.; Kastrati, A.; Lenzen, M.J.; et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. Eur. Hear. J. 2017, 39, 119–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffi, M.; Patrono, C.; Collet, J.-P.; Mueller, C.; Valgimigli, M.; Andreotti, F.; Bax, J.J.; Borger, M.A.; Brotons, C.; Chew, D.P.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting Without Persistent ST-segment Elevation. Revista Española Cardiología 2015, 68, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.F.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Hear. J. 2019, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Stroke, O.; Tendera, M.; Aboyans, V.; Bartelink, M.-L.; Baumgartner, I.; Clément, D.; Collet, J.-P.; Cremonesi, A.; De Carlo, M.; Erbel, R.; et al. ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral artery diseases: Document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral, mesenteric, renal, upper and lower extremity arteries * The Task Force on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Artery Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Hear. J. 2011, 32, 2851–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukema, J.W.; Verschuren, J.J.W.; Ahmed, T.A.N.; Quax, P.H.A. Restenosis after PCI. Part 1: Pathophysiology and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 9, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; David, E.M.; Makkar, R.; Wilentz, J.R. Molecular and cellular basis of restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention: The intertwining roles of platelets, leukocytes, and the coagulation–fibrinolysis system. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, J.; Leon, M.B.; Popma, J.J.; Fitzgerald, P.J.; Holmes, D.R.; O’Shaughnessy, C.; Caputo, R.P.; Kereiakes, D.J.; Williams, D.O.; Teirstein, P.S.; et al. Sirolimus-Eluting Stents versus Standard Stents in Patients with Stenosis in a Native Coronary Artery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, G.W.; Ellis, S.G.; Cox, D.A.; Hermiller, J.; O’Shaughnessy, C.; Mann, J.T.; Turco, M.; Caputo, R.; Bergin, P.; Greenberg, J.; et al. A Polymer-Based, Paclitaxel-Eluting Stent in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, E.; Hong, M.-K. Drug-eluting stents to prevent stent thrombosis and restenosis. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2015, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kopia, G.; Hayashi, S.-I.; Bailey, L.R.; Llanos, G.; Wilensky, R.; Klugherz, B.D.; Papandreou, G.; Narayan, P.; Leon, M.B.; et al. Stent-based delivery of sirolimus reduces neointimal formation in a porcine coronary model. Circulation 2001, 104, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, P.E.; Machan, L.S.; Jackson, J.K.; Burt, H.; Bromley, P.; Wilson, J.E.; McManus, B.M. Complete inhibition of intimal hyperplasia by perivascular delivery of paclitaxel in balloon-injured rat carotid arteries. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.M.; Eefting, D.; De Vries, M.R.; Quax, P.H.A.; Jukema, J.W. Sirolimus and paclitaxel provoke different vascular pathological responses after local delivery in a murine model for restenosis on underlying atherosclerotic arteries. Heart 2007, 93, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, L.; Byrne, R.A.; Mehilli, J.; Schömig, A.; Kastrati, A.; Pache, J. Five-year clinical outcomes of a polymer-free sirolimus-eluting stent versus a permanent polymer paclitaxel-eluting stent: Final results of the intracoronary stenting and angiographic restenosis - test equivalence between two drug-eluting stents (ISAR-TES. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 81, E23–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherron, A.; Lawler, A.M.; Lee, S.-J. Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-p superfamily member. Nature 1997, 387, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmers, T.A.; Davies, M.V.; Koniaris, L.G.; Haynes, P.A.; Esquela, A.F.; Tomkinson, K.N.; McPherron, A.; Wolfman, N.M.; Lee, S.-J. Induction of Cachexia in Mice by Systemically Administered Myostatin. Science 2002, 296, 1486–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kambadur, R.; Matthews, K.G.; Somers, W.G.; Devlin, G.P.; Conaglen, J.V.; Fowke, P.J.; Bass, J.J. Myostatin, a transforming growth factor-beta superfamily member, is expressed in heart muscle and is upregulated in cardiomyocytes after infarct. J. Cell. Physiol. 1999, 180, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzola, D.; Milanesi, S.; Bertolotto, M.; Garibaldi, S.; Villaggio, B.; Brunelli, C.; Balbi, M.; Ameri, P.; Montecucco, F.; Palombo, D.; et al. Myostatin mediates abdominal aortic atherosclerosis progression by inducing vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction and monocyte recruitment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, K.; Nakatani, M.; Uezumi, A.; Murakami, T.; Cui, X. Signal Transduction Pathway through Activin Receptors as a Therapeutic Target of Musculoskeletal Diseases and Cancer. Endocr. J. 2008, 55, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitachi, K.; Tsuchida, K. Myostatin-deficiency in mice increases global gene expression at the Dlk1-Dio3 locus in the skeletal muscle. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 5943–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, D.A.; Berry, D.P.; Berkowicz, E.W.; Sikora, K.M.; Howard, D.J.; Mullen, M.P.; Evans, R.D.; Spillane, C.; MacHugh, D.E. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms within the Bovine DLK1-DIO3 Imprinted Domain Are Associated with Economically Important Production Traits in Cattle. J. Hered. 2010, 102, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welten, S.M.; De Jong, R.C.; Wezel, A.; De Vries, M.R.; Boonstra, M.C.; Parma, L.; Jukema, J.W.; Van Der Sluis, T.; Arens, R.; Bot, I.; et al. Inhibition of 14q32 microRNA miR-495 reduces lesion formation, intimal hyperplasia and plasma cholesterol levels in experimental restenosis. Atherosclerosis 2017, 261, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nossent, A.Y.; Eskildsen, T.V.; Andersen, L.B.; Bie, P.; Brønnum, H.; Schneider, M.; Andersen, D.C.; Welten, S.M.J.; Jeppesen, P.L.; Hamming, J.F.; et al. The 14q32 MicroRNA-487b Targets the Antiapoptotic Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 in Hypertension-Induced Remodeling of the Aorta. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welten, S.M.; Bastiaansen, A.J.; De Jong, R.C.M.; De Vries, M.R.; Peters, E.A.; Boonstra, M.C.; Sheikh, S.P.; La Monica, N.; Kandimalla, E.R.; Quax, P.H.A.; et al. Inhibition of 14q32 MicroRNAs miR-329, miR-487b, miR-494, and miR-495 Increases Neovascularization and Blood Flow Recovery After Ischemia. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welten, S.; Goossens, E.; Quax, P.H.A.; Nossent, A.Y. The multifactorial nature of microRNAs in vascular remodelling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wezel, A.; Welten, S.M.J.; Razawy, W.; Lagraauw, H.M.; De Vries, M.R.; Goossens, E.; Boonstra, M.C.; Hamming, J.F.; Kandimalla, E.R.; Kuiper, J.; et al. Inhibition of MicroRNA-494 Reduces Carotid Artery Atherosclerotic Lesion Development and Increases Plaque Stability. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, N.M.; Vanderhoeven, B.; Devries, M.; Havekes, L.; Vanvlijmen, B.; Hennink, W.; Quax, P.H.A.; Jukema, J.W. Local perivascular delivery of anti-restenotic agents from a drug-eluting poly(-caprolactone) stent cuff. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5386–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.M.; Schepers, A.; Van Der Hoeven, B.L.; De Vries, M.R.; Boesten, L.S.; Jukema, J.W.; Quax, P.H.A. Histopathologic alterations following local delivery of dexamethasone to inhibit restenosis in murine arteries. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 68, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eefting, D.; Schepers, A.; De Vries, M.R.; Pires, N.M.; Grimbergen, J.M.; Lagerweij, T.; Nagelkerken, L.M.; Monraats, P.S.; Jukema, J.W.; Van Bockel, J.H.; et al. The effect of interleukin-10 knock-out and overexpression on neointima formation in hypercholesterolemic APOE*3-Leiden mice. Atherosclerosis 2007, 193, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, R.C.M.; Ewing, M.M.; De Vries, M.R.; Karper, J.C.; Bastiaansen, A.J.N.M.; Peters, H.A.B.; Baghana, F.; Elsen, P.J.V.D.; Gongora, C.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. The epigenetic factor PCAF regulates vascular inflammation and is essential for intimal hyperplasia development. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroi, M.; Zhang, L.; Yasuda, T.; Virmani, R.; Gold, H.K.; Fishman, M.C.; Huang, P. Interaction of genetic deficiency of endothelial nitric oxide, gender, and pregnancy in vascular response to injury in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.J.; Lloyd, D.J.; Gekakis, N. Loss-of-Function Mutation in Myostatin Reduces Tumor Necrosis Factor α Production and Protects Liver Against Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lardenoye, J.H.P.; Delsing, D.J.M.; De Vries, M.R.; Deckers, M.M.L.; Princen, H.M.G.; Havekes, L.M.; Van Hinsbergh, V.W.M.; Van Bockel, J.H.; Quax, P.H.A. Accelerated atherosclerosis by placement of a perivascular cuff and a cholesterol-rich diet in ApoE*3Leiden transgenic mice. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, E.; De Vries, M.R.; Simons, K.H.; Putter, H.; Quax, P.H.A.; Nossent, A.Y. miRMap: Profiling 14q32 microRNA Expression and DNA Methylation Throughout the Human Vasculature. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogg, E.-M.; Abplanalp, W.T.; Bischof, C.; John, D.; Schulz, M.H.; Krishnan, J.; Fischer, A.; Poluzzi, C.; Schaefer, L.; Bonauer, A.; et al. Analysis of Cell Type-Specific Effects of MicroRNA-92a Provides Novel Insights Into Target Regulation and Mechanism of Action. Circulation 2018, 138, 2545–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, W.K.D.; Tempel, D.; Bot, I.; Biessen, E.A.; Joosten, L.A.; Netea, M.G.; Van Der Meer, J.W.M.; Cheng, C.; Duckers, H.J. Mast Cells Induce Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis via a Toll-Like Receptor 4 Activation Pathway. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2012, 32, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goossens, E.A.C.; de Vries, M.R.; Jukema, J.W.; Quax, P.H.A.; Nossent, A.Y. Myostatin Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Local 14q32 microRNA Expression, But Not Systemic Inflammation or Restenosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103508
Goossens EAC, de Vries MR, Jukema JW, Quax PHA, Nossent AY. Myostatin Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Local 14q32 microRNA Expression, But Not Systemic Inflammation or Restenosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103508
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoossens, Eveline A.C., Margreet R. de Vries, J. Wouter Jukema, Paul H.A. Quax, and A. Yaël Nossent. 2020. "Myostatin Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Local 14q32 microRNA Expression, But Not Systemic Inflammation or Restenosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 10: 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103508
APA StyleGoossens, E. A. C., de Vries, M. R., Jukema, J. W., Quax, P. H. A., & Nossent, A. Y. (2020). Myostatin Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Local 14q32 microRNA Expression, But Not Systemic Inflammation or Restenosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10), 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103508





