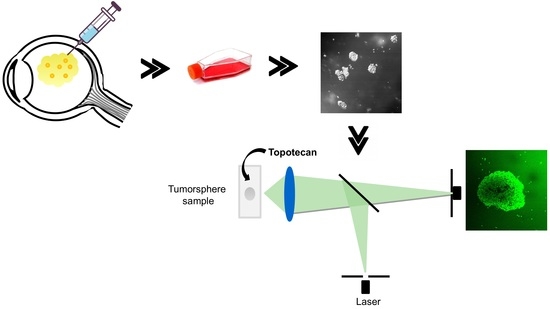
Tridimensional Retinoblastoma Cultures as Vitreous Seeds Models for Live-Cell Imaging of Chemotherapy Penetration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
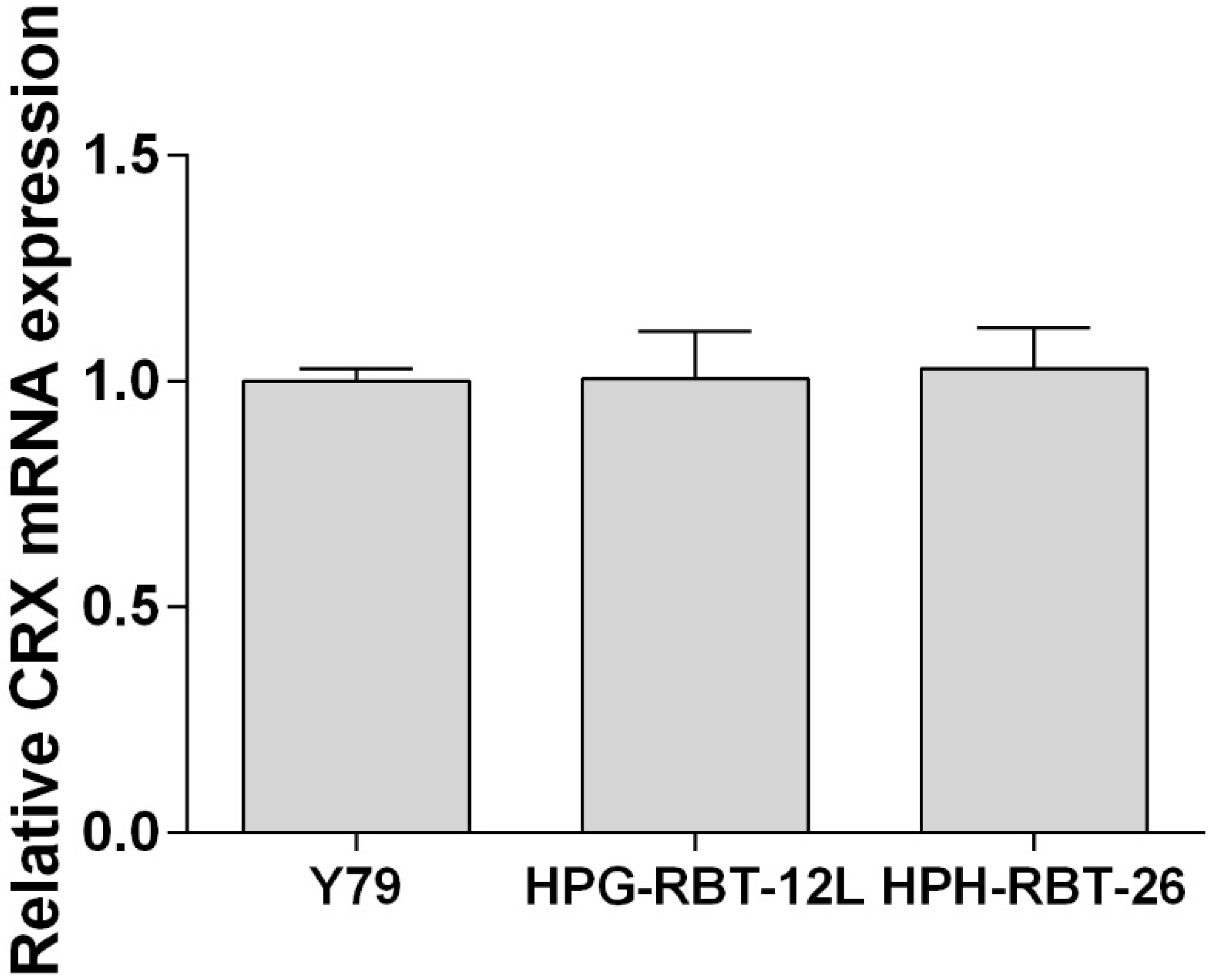
2.1. Patient-Derived Tumorspheres Resemble the Original Tumor
2.2. Topotecan Penetration and Live-Cell Imaging
2.3. Topotecan Cytotoxicity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Retinoblastoma Cell Line
4.3. Establishment of Patient-Derived Cell Cultures
4.4. Cell Authentication and Retinal Lineage Markers
4.5. Live-Cell Confocal Microscopy
4.6. Topotecan Cytotoxicity and Cell Viability Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abramson, D.H. Retinoblastoma: Saving life with vision. Annu. Rev. Med. 2014, 65, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PDQ® Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Retinoblastoma Treatment; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/retinoblastoma/hp/retinoblastoma-treatment-pdq (accessed on 23 November 2018).
- Chantada, G.; Schaiquevich, P. Management of retinoblastoma in children: Current status. Paediatr. Drugs 2015, 17, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.H.; Levin, A.M.; Zabor, E.C.; Gobin, Y.P.; Abramson, D.H. Ten-year experience with ophthalmic artery chemosurgery: Ocular and recurrence-free survival. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, D.H.; Shields, C.L.; Munier, F.L.; Chantada, G.L. Treatment of Retinoblastoma in 2015: Agreement and Disagreement. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015, 133, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munier, F.L.; Gaillard, M.C.; Soliman, S.; Balmer, A.; Moulin, A.; Podilsky, G. Intravitreal chemotherapy for vitreous disease in retinoblastoma revisited: From prohibition to conditional indications. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munier, F.L. Classification and management of seeds in retinoblastoma. Ellsworth Lecture Ghent August 24th 2013. Ophthalmic Genet. 2014, 35, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.H.; Abramson, D.H.; Gaillard, M.C.; Marr, B.P.; Beck-Popovic, M.; Munier, F.L. The classification of vitreous seeds in retinoblastoma and response to intravitreal melphalan. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.H.; Marr, B.P.; Abramson, D.H. Classification of Vitreous Seeds in Retinoblastoma: Correlations with Patient, Tumor, and Treatment Characteristics. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, J.L.; Bechtold, M.; Shah, S.; Zolfaghari, E.; Reid, M.; Jubra, R.; Kim, J.W. Not All Seeds Are Created Equal: Seed Classification Is Predictive of Outcomes in Retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amram, A.L.; Rico, G.; Kim, J.W.; Chintagumpala, M.; Herzog, C.E.; Gombos, D.S.; Chévez-Barrios, P. Vitreous Seeds in Retinoblastoma: Clinicopathologic Classification and Correlation. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaiquevich, P.; Carcaboso, A.M.; Buitrago, E.; Taich, P.; Opezzo, J.; Bramuglia, G.; Chantada, G.L. Ocular pharmacology of topotecan and its activity in retinoblastoma. Retina 2014, 34, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.H.; Marr, B.P.; Schaiquevich, P.; Kellick, M.G.; Abramson, D.H. Properties and clinical utility of topotecan fluorescence: Uses for retinoblastoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 99, 1320–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beijnen, J.H.; Rosing, H. Bioanalytical methods for anticancer drugs. In Cancer Clinical Pharmacology; Schellens, J.H., McLeod, H.L., Newell, D.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pawley, J. (Ed.) Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, S.; Devi, G.R. Three-dimensionalculturesystems in cancer research: Focus on tumorspheroidmodel. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 163, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfter, K.; Mayer, B. Bringing 3D tumor models to the clinic—Predictive value for personalized medicine. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, W.S.; Akinfenwa, P.Y.; Perlaky, L.; Hurwitz, M.Y.; Hurwitz, R.L.; Chévez-Barrios, P. Tumorspheres but not adherent cells derived from retinoblastoma tumors are of malignant origin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Pasto, G.; Olaciregui, N.G.; Vila-Ubach, M.; Paco, S.; Monterrubio, C.; Rodriguez, E.; Winter, U.; Batalla-Vilacis, M.; Catala, J.; Salvador, H.; et al. Preclinical platform of retinoblastoma xenografts recapitulating human disease and molecular markers of dissemination. Cancer Lett. 2016, 38, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurie, N.A.; Gray, J.K.; Zhang, J.; Leggas, M.; Relling, M.; Egorin, M.; Stewart, C.; Dyer, M.A. Topotecan combination chemotherapy in two new rodent models of retinoblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7569–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, A.C.; Bottiroli, G.; Supino, R.; Favini, E.; Zuco, V.; Zuino, F. Subcellularlocalization of the camptothecin analogues, topotecan and gimatecan. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugit, K.D.; Jyoti, A.; Upreti, M.; Anderson, B.D. Insights into accelerated liposomal release of topotecan in plasma monitored by a non-invasive fluorescence spectroscopic method. J. Control. Release 2015, 197, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centelles, M.N.; Wright, M.; So, P.W.; Amrahli, M.; Xu, X.Y.; Stebbing, J.; Miller, A.D.; Gedroyc, W.; Thanou, M. Image-guided thermosensitive liposomes for focused ultrasound drug delivery: Using NIRF-labelled lipids and topotecan to visualize the effects of hyperthermia in tumours. J. Control. Release 2018, 280, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyoti, A.; Fugit, K.D.; Sethi, P.; McGarry, R.C.; Anderson, B.D.; Upreti, M. An in vitro assessment of liposomal topotecan simulating metronomic chemotherapy in combination with radiation in tumor-endothelial spheroids. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foty, R. A simple hanging drop cell culture protocol for generation of 3D spheroids. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, M.; Mohanty, C.; Harilal, A.; Maheswari, U.K.; Sahoo, S.K.; Krishnakumar, S. A novel in vitro three-dimensional retinoblastoma model for evaluating chemotherapeutic drugs. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 1361–1378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winter, U.; Mena, H.A.; Negrotto, S.; Arana, E.; Pascual-Pasto, G.; Laurent, V.; Suñol, M.; Chantada, G.L.; Carcaboso, A.M.; Schaiquevich, P. Schedule-Dependent Antiangiogenic and Cytotoxic Effects of Chemotherapy on Vascular Endothelial and Retinoblastoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledur, P.F.; Onzi, G.R.; Zong, H.; Lenz, G. Culture conditions defining glioblastoma cells behavior: What is the impact for novel discoveries? Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69185–69197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi-Baig, K.; Ullmann, P.; Rodriguez, F.; Frasquilho, S.; Nazarov, P.V.; Haan, S.; Letellier, E. What Do We Learn from Spheroid Culture Systems? Insights from Tumorspheres Derived from Primary Colon Cancer Tissue. PLoS ONE 2016, 8, e0146052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Shin, D.; Roh, J.L. Development of an in vitro cell-sheet cancer model for chemotherapeutic screening. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3964–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaiquevich, P.; Fabius, A.W.; Francis, J.H.; Chantada, G.L.; Abramson, D.H. Ocular pharmacology of chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. Retina 2017, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parma, D.; Ferrer, M.; Luce, L.; Giliberto, F.; Szijan, I. RB1 gene mutations in Argentine retinoblastoma patients. Implications for genetic counseling. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbidoni, A.V.; Laurent, V.E.; Sampor, C.; Ottaviani, D.; Vazquez, V.; Gabri, M.R.; Rossi, J.; de Dávila, M.T.; Alonso, C.; Alonso, D.F.; et al. Association of cone-rod homeobox transcription factor messenger RNA with pediatric metastatic retinoblastoma. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015, 133, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.; Honavar, S.G.; Sharma, V.; Reddy, V.A.P. Intravitreal topotecan in the management of refractory and recurrent vitreous seeds in retinoblastoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.H.; Gobin, Y.P.; Dunkel, I.J.; Marr, B.P.; Brodie, S.E.; Jonna, G.; Abramson, D.H. Carboplatin +/− topotecan ophthalmic artery chemosurgery for intraocular retinoblastoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perona, J.; Malik, J. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1990, 12, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histogram. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 19, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Karl, W.C. Real-time Tracking Using Level Sets. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2008, 17, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Marker | Cell Line | Tumor | Cell Line | Tumor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPG-RBT-12L | HPG-RBT-12T | HPG-RBT-26 | HPG-RBT-26T | |
| Amelogenin | X | X | X | X |
| D3S1358 | 14–17 | 14–17 | 17–18 | 17–18 |
| D13S317 | 12 | 12 | 14 | 14 |
| Penta E | 6–13 | 6–13 | 11–14 | 11–14 |
| D16S539 | 10–13 | 10–13 | 12 | 12 |
| D18S51 | 12–15 | 12–15 | 12–15 | 12–15 |
| CSF1PO | 12 | 12 | 12–14 | 12–14 |
| Penta D | 10–12 | 10–12 | 8–14 | 8–14 |
| TH01 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 6 |
| VWA | 15–16 | 15–16 | 15–19 | 15–19 |
| D21S11 | 29–31 | 29–31 | 29–33.2 | 29–33.2 |
| D7S820 | 10–11 | 10–11 | 10–11 | 10–11 |
| D5S818 | 11–13 | 11–13 | 11–13 | 11–13 |
| TPOX | 11–12 | 11–12 | 8 | 8 |
| D8S1179 | 14 | 14 | 8 | 8 |
| FGA | 21–25 | 21–25 | 22–23 | 22–23 |
| tmax (min) HPG-RBT-12L | tmax (min) HPG-RBT-26 | P Value (t Test) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small spheres | 1.50 (0.29) | 1.62 (0.12) | 0.677 |
| Large spheres | 2.75 (0.14) | 2.67 (0.17) | 0.721 |
| p-value (t test) | 0.008 | 0.004 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Winter, U.; Aschero, R.; Fuentes, F.; Buontempo, F.; Zugbi, S.; Sgroi, M.; Sampor, C.; Abramson, D.H.; Carcaboso, A.M.; Schaiquevich, P. Tridimensional Retinoblastoma Cultures as Vitreous Seeds Models for Live-Cell Imaging of Chemotherapy Penetration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051077
Winter U, Aschero R, Fuentes F, Buontempo F, Zugbi S, Sgroi M, Sampor C, Abramson DH, Carcaboso AM, Schaiquevich P. Tridimensional Retinoblastoma Cultures as Vitreous Seeds Models for Live-Cell Imaging of Chemotherapy Penetration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051077
Chicago/Turabian StyleWinter, Ursula, Rosario Aschero, Federico Fuentes, Fabian Buontempo, Santiago Zugbi, Mariana Sgroi, Claudia Sampor, David H. Abramson, Angel M. Carcaboso, and Paula Schaiquevich. 2019. "Tridimensional Retinoblastoma Cultures as Vitreous Seeds Models for Live-Cell Imaging of Chemotherapy Penetration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051077
APA StyleWinter, U., Aschero, R., Fuentes, F., Buontempo, F., Zugbi, S., Sgroi, M., Sampor, C., Abramson, D. H., Carcaboso, A. M., & Schaiquevich, P. (2019). Tridimensional Retinoblastoma Cultures as Vitreous Seeds Models for Live-Cell Imaging of Chemotherapy Penetration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051077