Bioinformatics Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Radish (Raphanus sativus) and Functional Characterization in Response to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
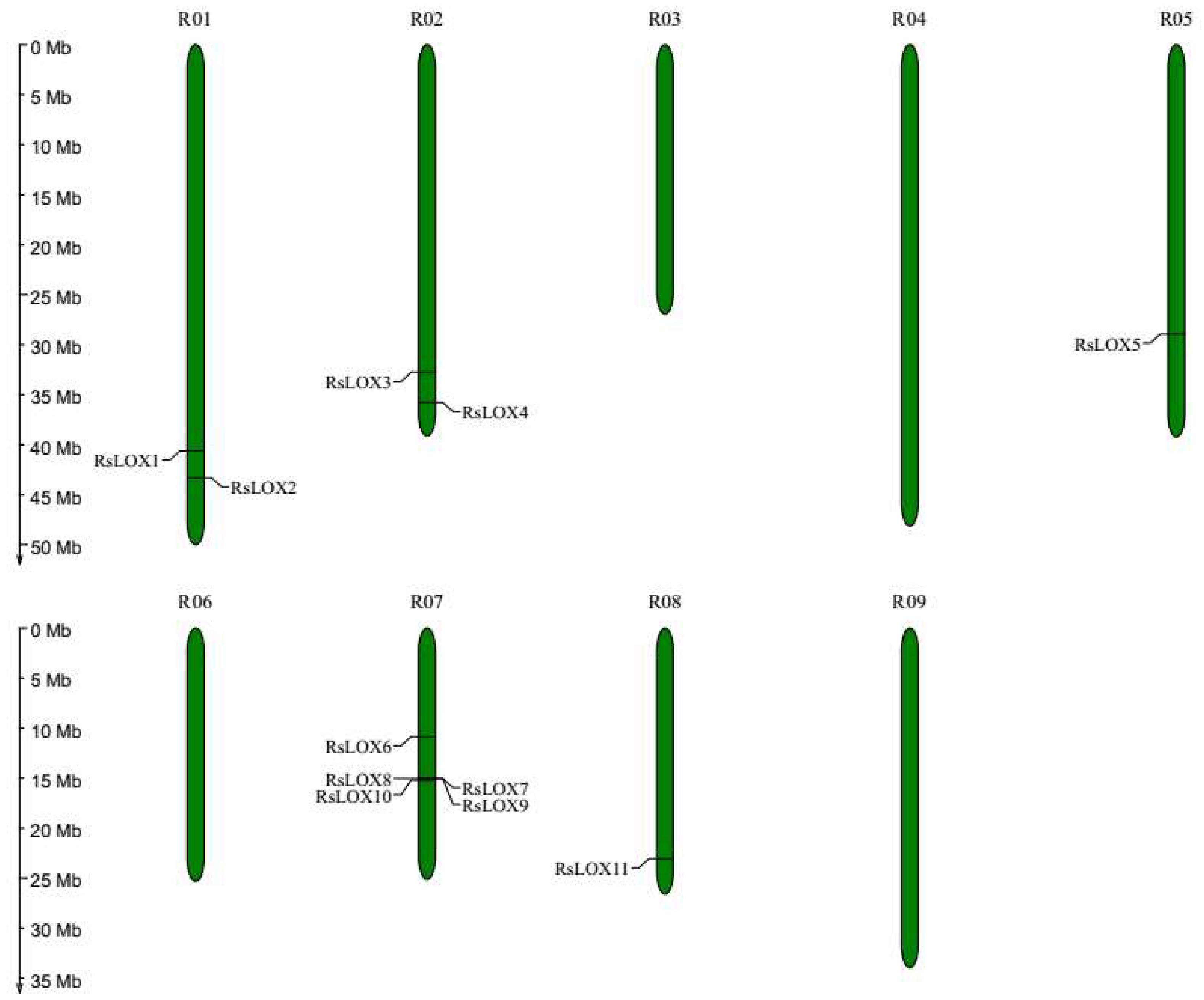
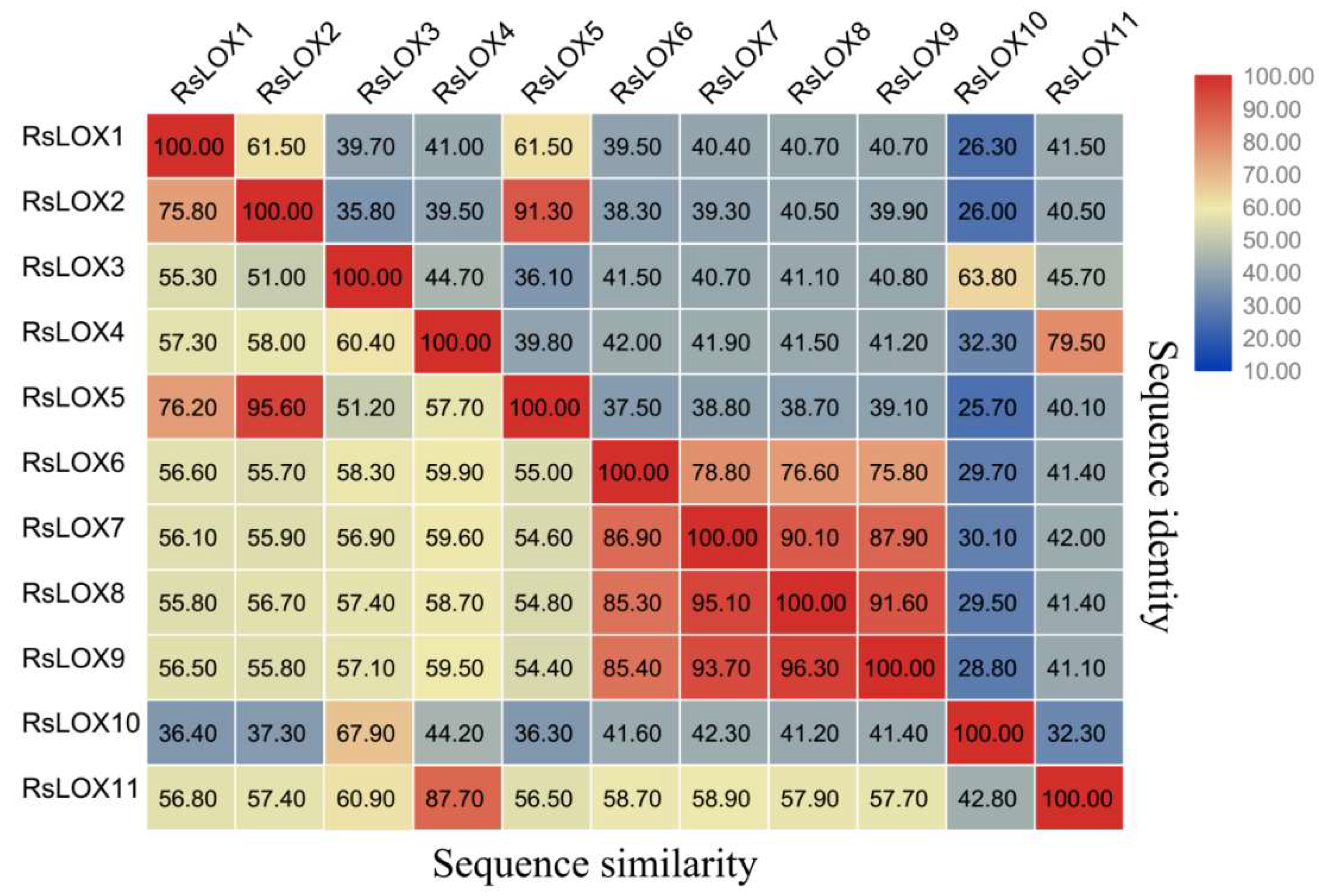
2.1. Identification and Characterization of LOX Gene Family Members
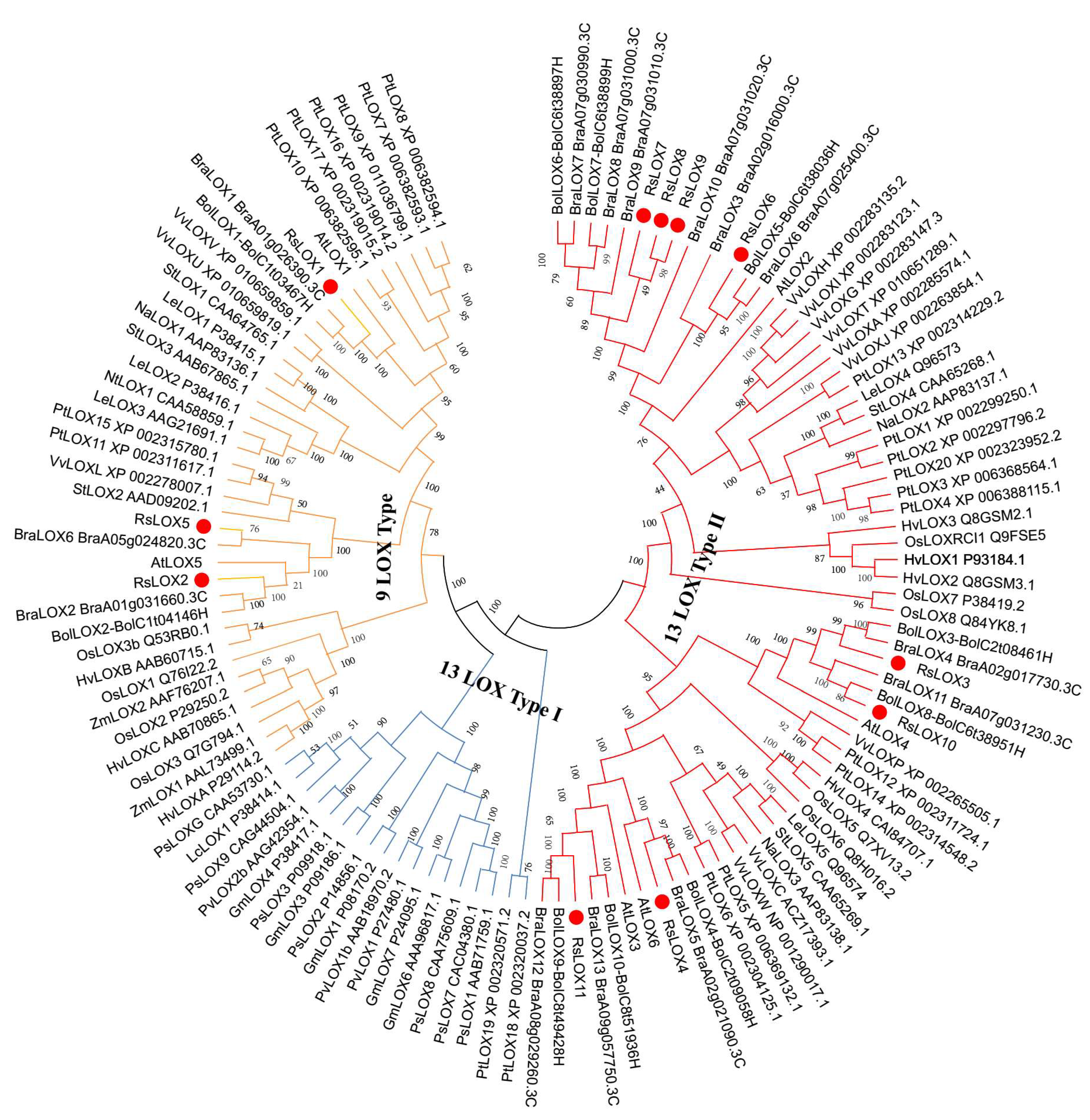
2.2. Phylogenetic Relationships among LOX Family Members from Diverse Plant Species
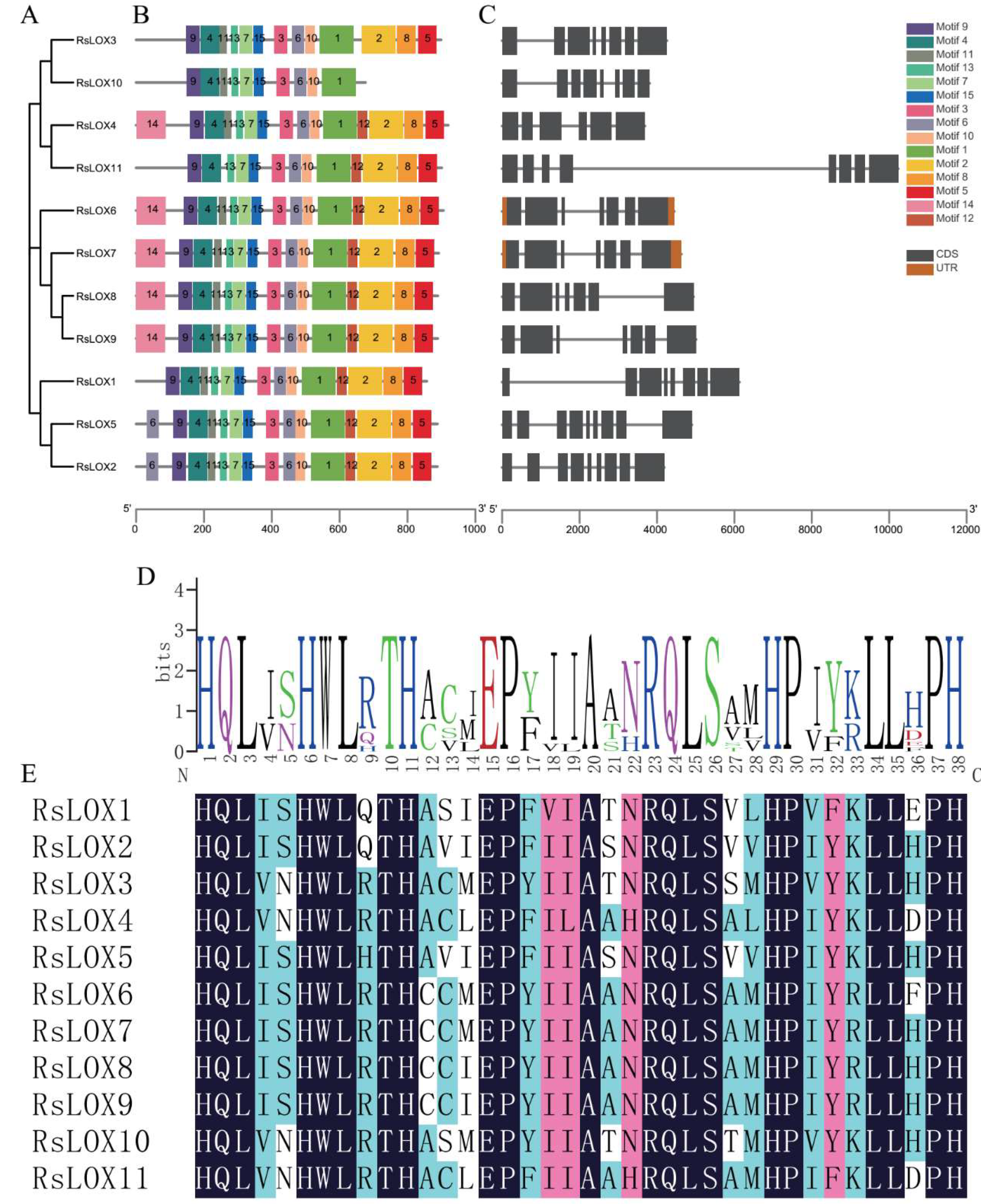
2.3. Conserved Domain and Structural Analyses of R. sativus LOXs
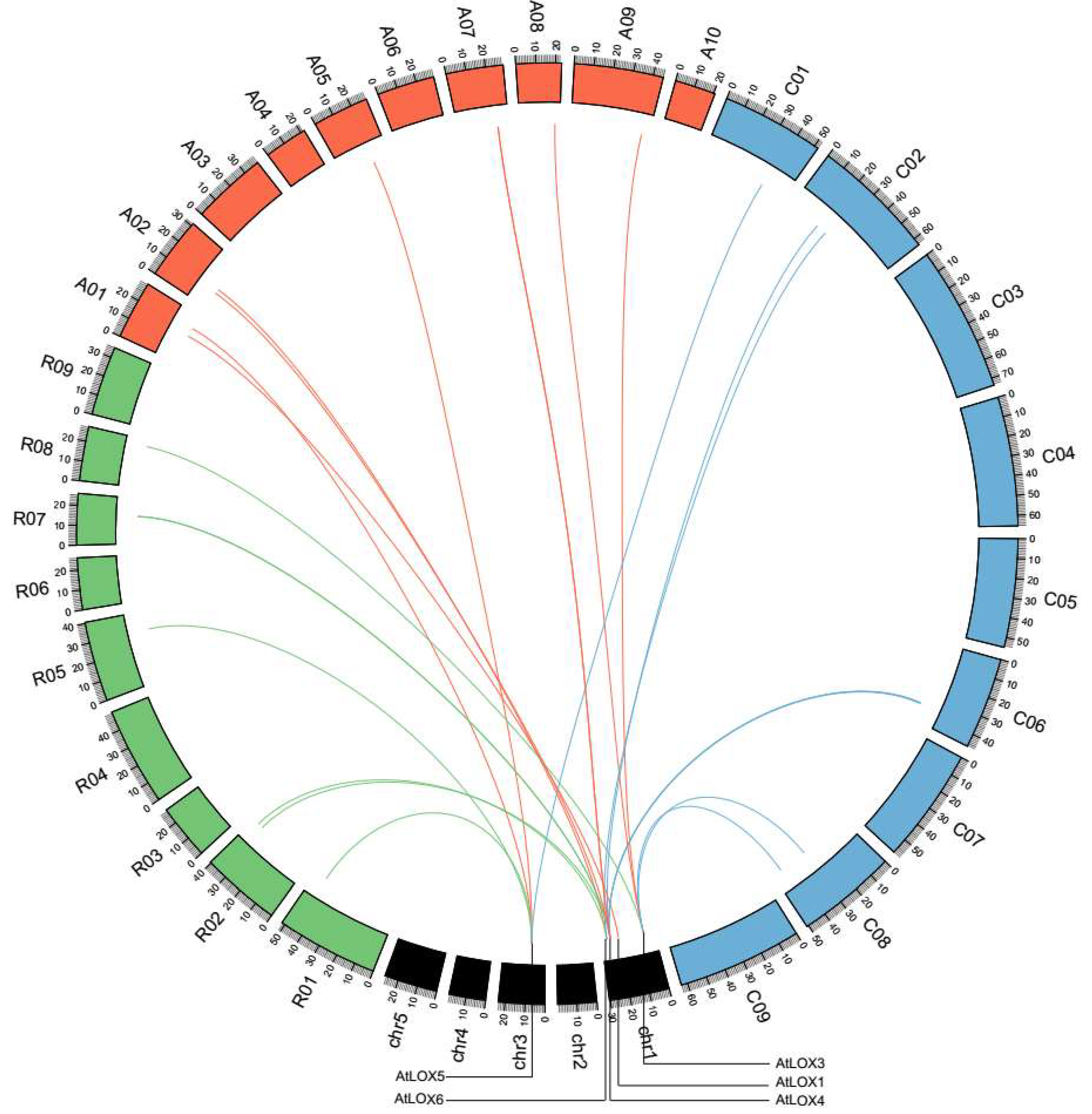
2.4. Tandem Duplications and Synteny of LOX Genes
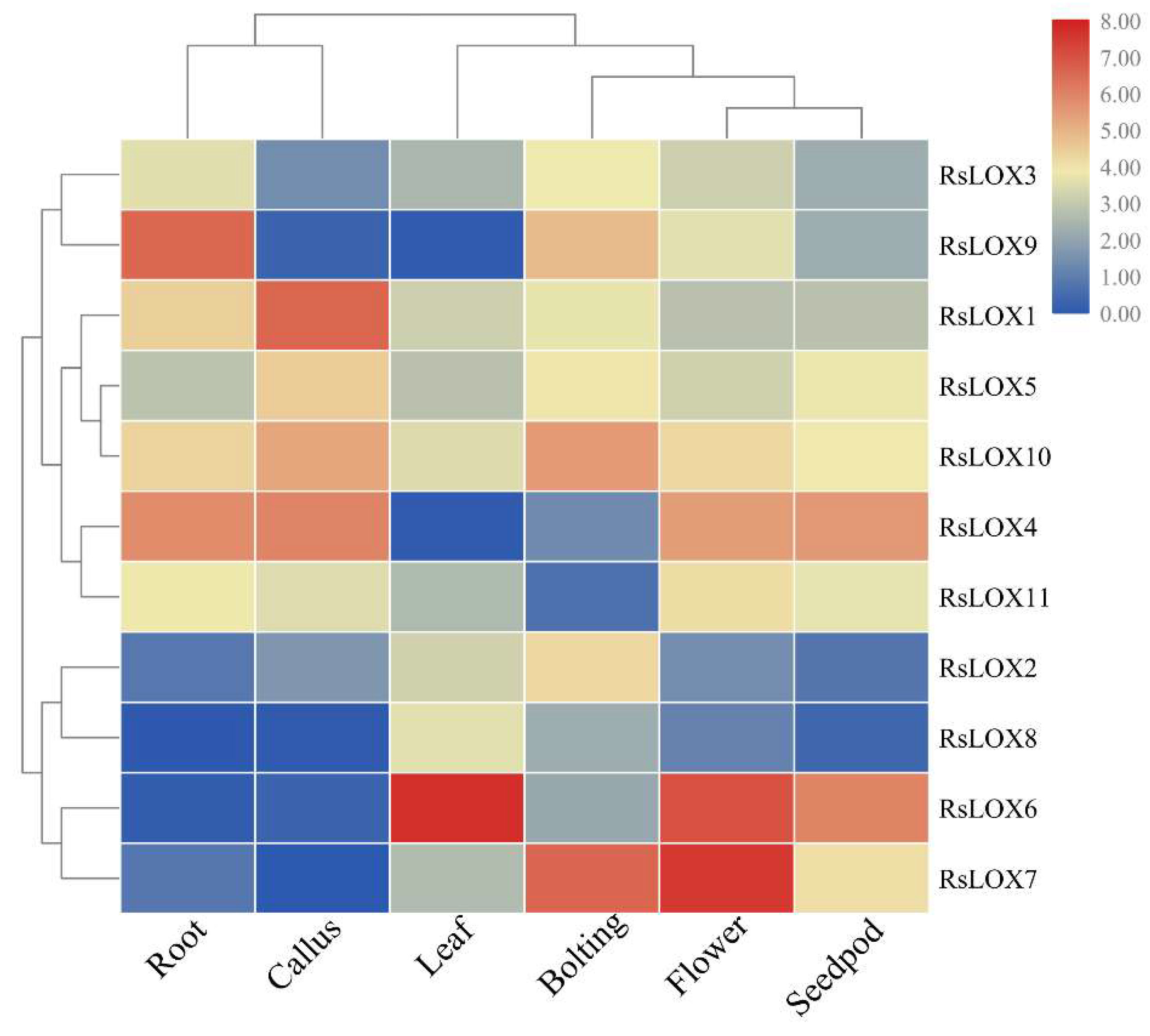
2.5. Expression Profiles of R. sativus LOX Genes in Various Tissues
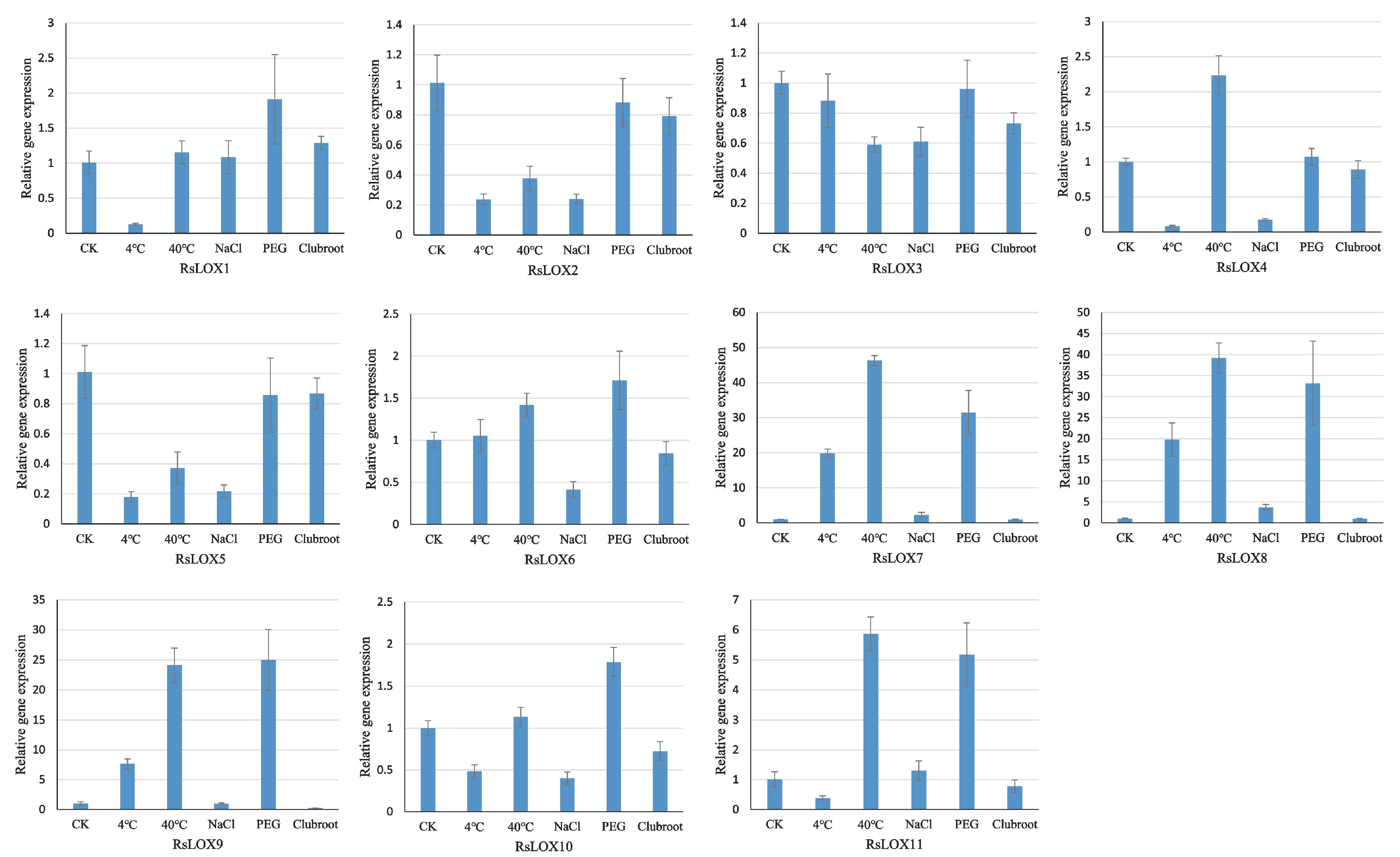
2.6. Analysis of RsLOX Expression in Response to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Acquisition and Identification of LOX Genes
4.2. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Construction
4.3. Analyses of Conserved Motifs, Gene Structures, and Subcellular Localizations
4.4. Analyses of Tandem Duplications and Synteny
4.5. Transcriptional Profile Analysis
4.6. Plant Materials and Stress Treatments
4.7. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LOXs | Lipoxygenases |
| PLAT | Polycystin-1, lipoxygenase, alpha-toxin |
| His | Histidine |
| 9-HPOD | 9s-hydroperoxyoctadecadienoic acid |
| 13-HPOD | 13s-hydroperoxyoctadecadienoic acid |
| JA | Jasmonic acid |
| WGT | Genome triplication |
| SD | Segmental duplication |
| TD | Tandem duplication |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| FPKM | Fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads |
References
- Hildebrand, D.F. Lipoxygenases. Physiol. Plant. 1989, 76, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feussner, I.; Wasternack, C. The lipoxygenase pathway. Plant Biol. 2003, 53, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, L.; Han, W.; Fan, X.; Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Dittami, S.M.; Ye, N. Evolution and expansion of the prokaryote-like lipoxygenase family in the brown alga Saccharina japonica. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 28, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minor, W.; Steczko, J.; Stec, B.; Otwinowski, Z.; Bolin, J.T.; Walter, R.; Axelrod, B. Crystal structure of soybean lipoxygenase L-1 at 1.4 A resolution. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 10687–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, A.; Sandford, R. The PLAT domain: A new piece in the PKD1 puzzle. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, R588–R590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomchick, D.R.; Phan, P.; Cymborowski, M.; Minor, W.; Holman, T.R. Structural and functional characterization of second-coordination sphere mutants of soybean lipoxygenase-1. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 7509–7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brash, A.R. Lipoxygenases: Occurrence, functions, catalysis, and acquisition of substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 23679–23682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, H.; Rochasosa, M. Plant lipoxygenases. physiological and molecular features. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C.; Bogatekleszczynska, R.; Come, D.; Corbineau, F. Changes in activities of antioxidant enzymes and lipoxygenase during growth of sunflower seedlings from seeds of different vigour. Seed Sci. Res. 2002, 12, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolomiets, M.V.; Hannapel, D.J.; Chen, H.; Tymeson, M.; Gladon, R.J. Lipoxygenase is involved in the control of potato tuber development. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, C.S.; Giovannoni, J.J. Ethylene and fruit ripening. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2007, 26, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuck, G. Molecular mechanisms of sex determination in monoecious and dioecious plants. Adv. Bot. Res. 2010, 54, 53–83. [Google Scholar]
- Blee, E. Impact of phyto-oxylipins in plant defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.J.; Thompson, G.A. Molecular responses to aphid feeding in Arabidopsis in relation to plant defense pathways. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 1074–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhai, Q.; Wei, J.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Huang, T.; Du, M.; Sun, J.; Kang, L.; Li, C.B. Role of tomato lipoxygenase D in wound-induced jasmonate biosynthesis and plant immunity to insect herbivores. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browse, J. Jasmonate passes muster: A receptor and targets for the defense hormone. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.N.; Zainal, Z.; Ismail, I. Green leaf volatiles: Biosynthesis, biological functions and their applications in biotechnology. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.A.; Huffaker, A.; Kaplan, F.; Sims, J.; Ziemann, S.; Doehlemann, G.; Ji, L.; Schmitz, R.J.; Kolomiets, M.V.; Alborn, H.T. Maize death acids, 9-lipoxygenase–derived cyclopente(a)nones, display activity as cytotoxic phytoalexins and transcriptional mediators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11407–11412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.A.; Huffaker, A.; Hunter, C.T.; Alborn, H.T.; Schmelz, E.A. A maize death acid, 10-oxo-11-phytoenoic acid, is the predominant cyclopentenone signal present during multiple stress and developmental conditions. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016, 11, e1120395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umate, P. Genome-wide analysis of lipoxygenase gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melan, M.A.; Dong, X.; Endara, M.E.; Davis, K.; Ausubel, F.M.; Peterman, T.K. An Arabidopsis thaliana lipoxygenase gene can be induced by pathogens, abscisic acid, and methyl jasmonate. Plant Physiol. 1993, 101, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellosillo, T.; Martinez, M.; Lopez, M.A.; Vicente, J.; Cascon, T.; Dolan, L.; Hamberg, M.; Castresana, C. Oxylipins produced by the 9-lipoxygenase pathway in Arabidopsis regulate lateral root development and defense responses through a specific signaling cascade. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.; Creelman, R.A.; Mullet, J.E. A chloroplast lipoxygenase is required for wound-induced jasmonic acid accumulation in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8675–8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebner, W.; Stingl, N.; Oenel, A.; Mueller, M.J.; Berger, S. Lipoxygenase6-dependent oxylipin synthesis in roots is required for abiotic and biotic stress resistance of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayko, H.; Baldwin, I.T. Antisense LOX expression increases herbivore performance by decreasing defense responses and inhibiting growth-related transcriptional reorganization in Nicotiana attenuata. Plant J. 2010, 36, 794–807. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, A.; Halitschke, R.; Baldwin, I.T. Silencing the jasmonate cascade: Induced plant defenses and insect populations. Science 2004, 305, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo, J.; Vancanneyt, G.; Pérez, A.G.; Sanz, C.; Störmann, K.; Rosahl, S.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.J. Characterization of three potato lipoxygenases with distinct enzymatic activities and different organ-specific and wound-regulated expression patterns. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 21012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmann, S.; Halitschke, R.; Schuurink, R.C.; Baldwin, I.T. Oxylipin channelling in Nicotiana attenuata: Lipoxygenase 2 supplies substrates for green leaf volatile production. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 2028–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- José, L.; Joaquín, R.; Guy, V.; Carlos, S.; Helena, S.; Gareth, G.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.J. Lipoxygenase H1 gene silencing reveals a specific role in supplying fatty acid hydroperoxides for aliphatic aldehyde production. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 416–423. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, C.W.; Han, S.; Hwang, I.S.; Kim, D.S.; Hwang, B.K.; Lee, S.C. The pepper lipoxygenase CaLOX1 plays a role in osmotic, drought and high salinity stress response. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Meng, K.; Han, Y.; Ban, Q.; Wang, B.; Suo, J.; Lv, J.; Rao, J. The persimmon 9-lipoxygenase gene DkLOX3 plays positive roles in both promoting senescence and enhancing tolerance to abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannenberg, G.; Martinez, M.; Hamberg, M.; Castresana, C. Diversity of the enzymatic activity in the lipoxygenase gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Lipids 2009, 44, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Sun, H.; Ullah, A.; Zhu, L. Genome-wide identification of lipoxygenase gene family in cotton and functional characterization in response to abiotic stresses. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunola, O.; Hawkins, L.K.; Mylroie, E.; Kolomiets, M.V.; Borrego, E.J.; Tang, J.D.; Williams, W.P.; Warburton, M.L. Characterization of the maize lipoxygenase gene family in relation to aflatoxin accumulation resistance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Liu, X.H.; Jiang, L.W. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of the lipoxygenase gene family in cucumber. Gen. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 2613–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Yan, H.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Cai, R.; Xiang, Y. The lipoxygenase gene family in poplar: Identifcation, classifcation, and expression in response to MeJA treatment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Liao, B.; King, G.; Zhang, X. Genome evolutionary dynamics followed by diversifying selection explains the complexity of the Sesamum indicum genome. BMC Genom. 2015, 18, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yue, Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Shen, D.; Wang, H.; Song, J. Insights into the species-specific metabolic engineering of glucosinolates in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) based on comparative genomic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Force, A.; Lynch, M.; Pickett, F.B.; Amores, A.; Yan, Y.; Postlethwait, J.H. Preservation of duplicate genes by complementary, degenerative mutations. Genetics 1999, 151, 1531–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, A.H.; Chapman, B.; Kissinger, J.C.; Bowers, J.E.; Feltus, F.A.; Estill, J.C. Many gene and domain families have convergent fates following independent whole-genome duplication events in Arabidopsis, Oryza, Saccharomyces and Tetraodon. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Tan, X.; Ficklin, S.P.; Feltus, F.A.; Paterson, A.H. Modes of gene duplication contribute differently to genetic novelty and redundancy, but show parallels across divergent angiosperms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. Locally duplicated ohnologs evolve faster than nonlocally duplicated ohnologs in Arabidopsis and Rice. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beilstein, M.A.; Alshehbaz, I.A.; Kellogg, E.A. Brassicaceae phylogeny and trichome evolution. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysak, M.A.; Koch, M.A.; Pecinka, A.; Schubert, I. Chromosome triplication found across the tribe Brassiceae. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Bowers, J.E.; Wang, X.; Ming, R.R.; Alam, M.; Paterson, A.H. Synteny and collinearity in plant genomes. Science 2008, 320, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchler, J.A.; Veitia, R.A. The Gene Balance Hypothesis: From classical genetics to modern genomics. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarde, S.J.; Kumar, A.; Remme, R.N.; Dicke, M. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression of lipoxygenase gene family in pepper. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 98, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahouachi, J.; Argamasilla, R.; Gomezcadenas, A. Influence of exogenous glycine betaine and abscisic acid on papaya in responses to water-deficit stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jian, G.; Qi, F. Chilling stress--the key predisposing factor for causing Alternaria alternata infection and leading to cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) leaf senescence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creelman, R.A.; Mullet, J.E. Jasmonic acid distribution and action in plants: Regulation during development and response to biotic and abiotic stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4114–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huala, E.; Dickerman, A.W.; Garciahernandez, M.; Weems, D.; Reiser, L.; Lafond, F.; Hanley, D.; Kiphart, D.; Zhuang, M.; Huang, W. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): A comprehensive database and web-based information retrieval, analysis, and visualization system for a model plant. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaohui, Z.; Zhen, Y.; Shiyong, M.; Yang, Q.; Xinhua, Y.; Xiaohua, C.; Feng, C.; Zhangyan, W.; Yuyan, S.; Yi, J. A de novo genome of a chinese radish cultivar. Hortic. Plant J. 2015, 1, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mun, J.; Bancroft, I.; Cheng, F. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Fang, L.; Sun, S.; Liu, B.; Li, P.; Hua, W.; Wang, X. BRAD, the genetics and genomics database for Brassica plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belser, C.; Istace, B.; Denis, E.; Dubarry, M.; Baurens, F.; Falentin, C.; Genete, M.; Berrabah, W.; Chevre, A.; Delourme, R. Chromosome-scale assemblies of plant genomes using nanopore long reads and optical maps. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: Interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangtao, C.; Yingzhen, K.; Qian, W.; Yuhe, S.; Daping, G.; Jing, L.; Guanshan, L. MapGene2Chrom, a tool to draw gene physical map based on Perl and SVG languages. Hereditas 2015, 37, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, P.M.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A.J. EMBOSS: The european molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Li, F.; Yan, X.; Liu, S.; Wei, C. Characterization and alternative splicing profiles of the lipoxygenase gene family in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1765–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.C.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME Suite: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xia, R.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various HTS-data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.C.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuelsson, O.; Nielsen, H.; Von Heijne, G. ChloroP, a neural network-based method for predicting chloroplast transit peptides and their cleavage sites. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.P.; Wu, J.; Fang, L.; Wang, X. Syntenic gene analysis between Brassica rapa and other Brassicaceae species. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.E.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.M.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.M.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Song, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, X. Identification of optimal reference genes for expression analysis in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) and its relatives based on expression stability. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, W.; Hu, H.; Wei, Q.; Wei, X.; Bao, C. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Radish (Raphanus sativus) and Functional Characterization in Response to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236095
Wang J, Hu T, Wang W, Hu H, Wei Q, Wei X, Bao C. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Radish (Raphanus sativus) and Functional Characterization in Response to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(23):6095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236095
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jinglei, Tianhua Hu, Wuhong Wang, Haijiao Hu, Qingzhen Wei, Xiaochun Wei, and Chonglai Bao. 2019. "Bioinformatics Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Radish (Raphanus sativus) and Functional Characterization in Response to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 23: 6095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236095
APA StyleWang, J., Hu, T., Wang, W., Hu, H., Wei, Q., Wei, X., & Bao, C. (2019). Bioinformatics Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Radish (Raphanus sativus) and Functional Characterization in Response to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 6095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236095



