Multiple Functions of B Cells in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
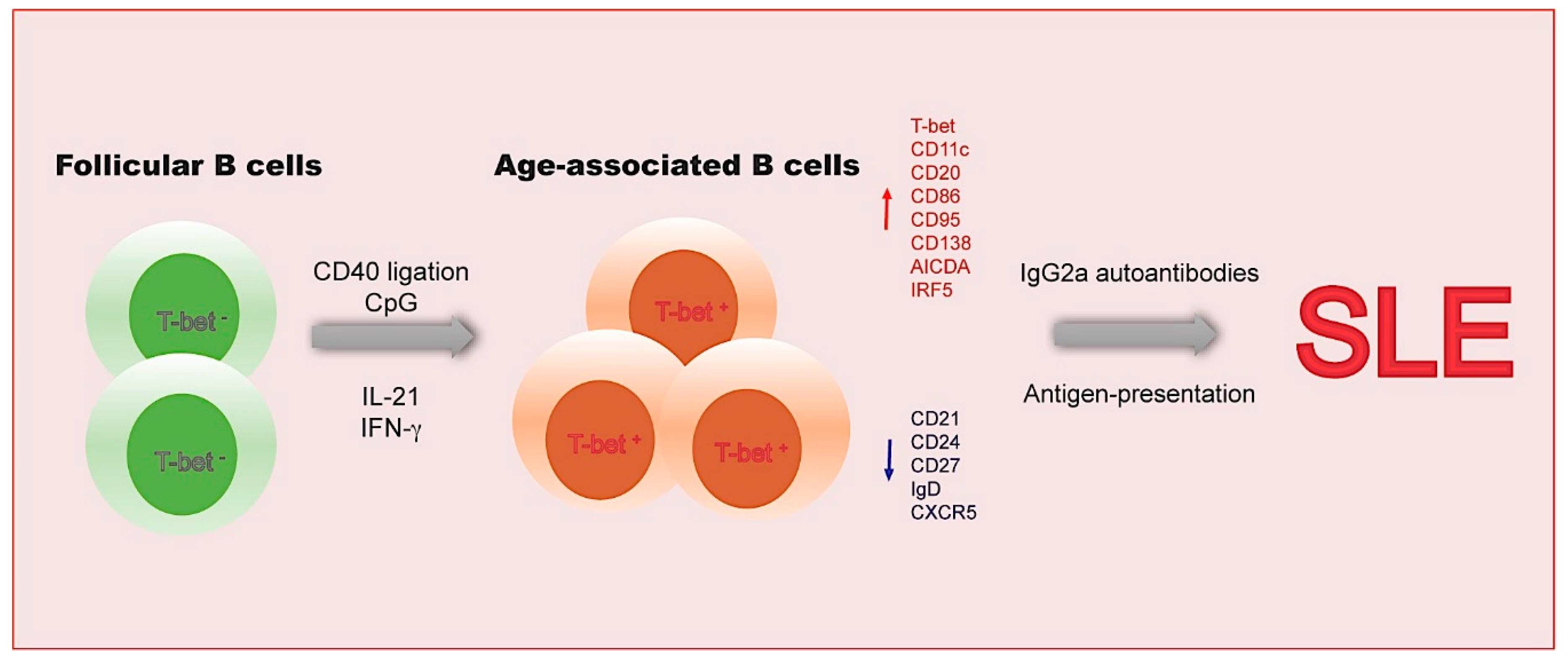
2. Age-Associated B Cells
2.1. The Functional Features of ABCs
2.2. The Transcriptional Network in ABCs
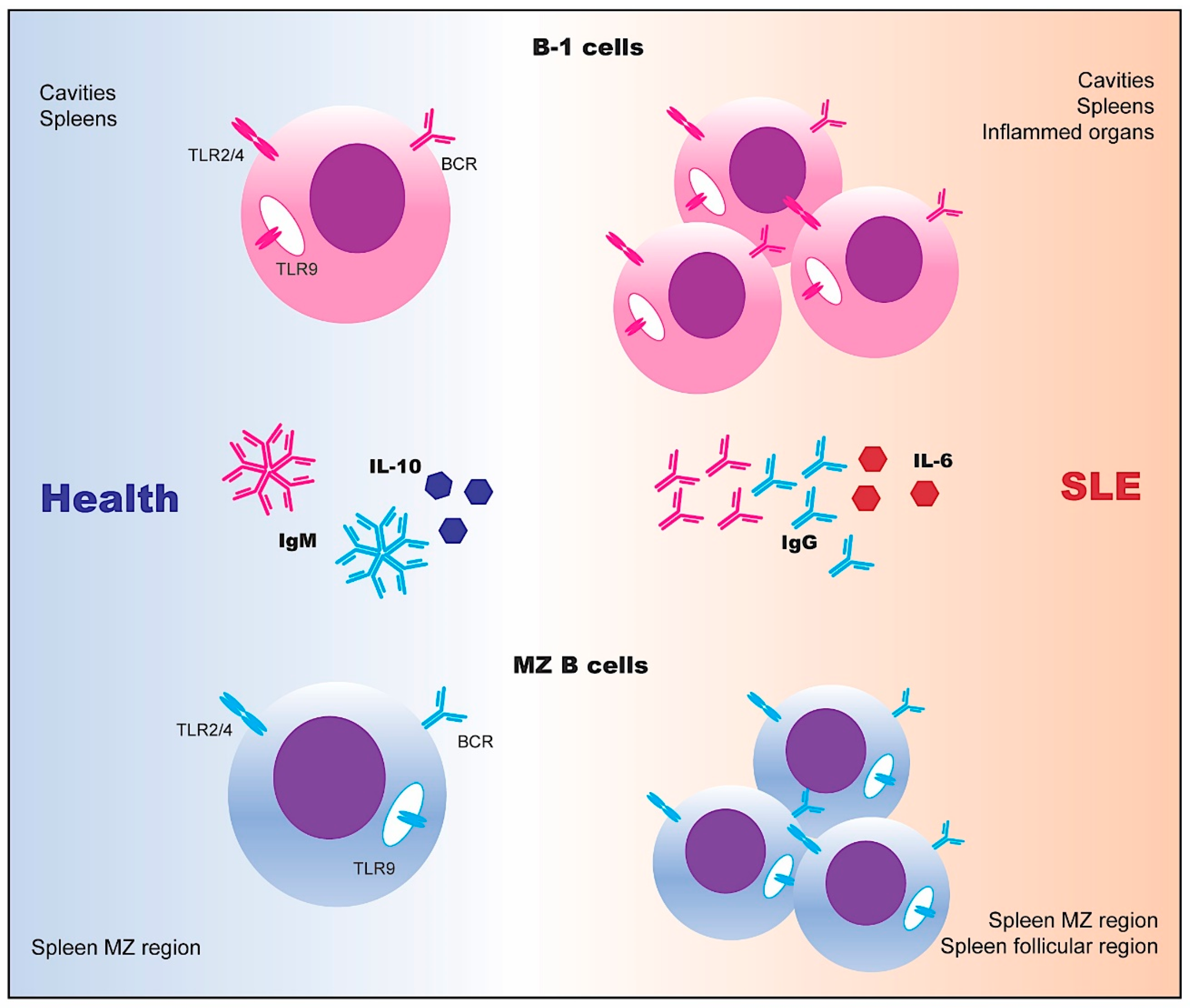
3. Innate-Like B Cells
3.1. The Functional Features of Innate-Like B Cells
3.2. The Transcriptional Network of Innate-Like B Cells
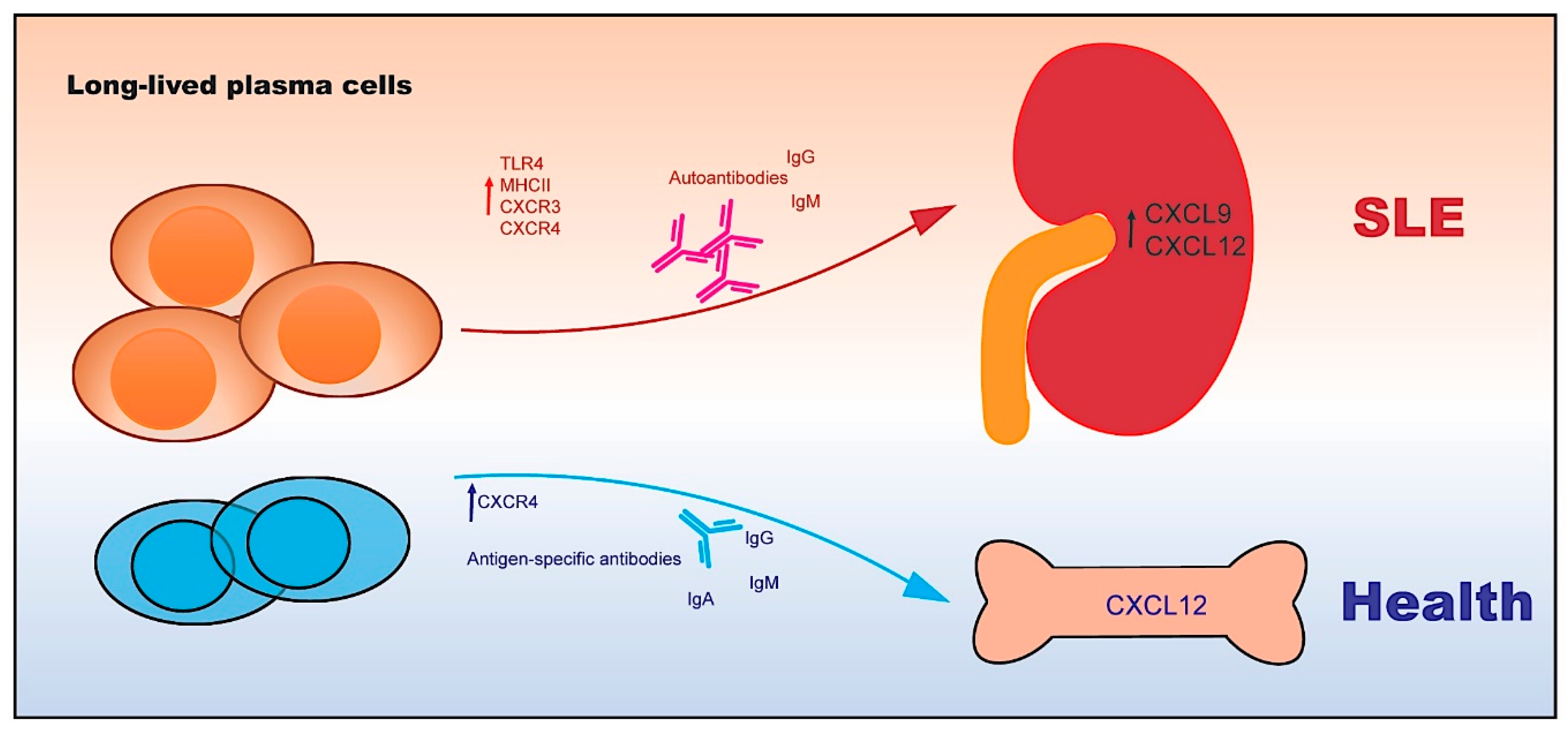
4. Autoreactive Plasma Cells
4.1. The Functional Features of Plasma Cells
4.2. The Transcriptional Network of Plasma Cells
5. Regulatory B Cells
5.1. The Functional Features of Bregs
5.2. The Regulation of Bregs
5.2.1. B Cell Receptor (BCR)
5.2.2. Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs)
5.2.3. Co-stimulatory Molecules
5.2.4. Cytokines
6. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medzhitov, R.; Janeway, C.A., Jr. Decoding the patterns of self and nonself by the innate immune system. Science 2002, 296, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pani, G.; Piastra, M.; Ria, F. Failure of presented, non-dominant self epitope to induce tolerance: Implications for autoimmune diseases. Immunol. Investig. 1994, 23, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, A.A.; Lopez, M.T.; McDevitt, H.O. Autoimmune diseases: The failure of self tolerance. Science 1990, 248, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbuckle, M.R.; McClain, M.T.; Rubertone, M.V.; Scofield, R.H.; Dennis, G.J.; James, J.A.; Harley, J.B. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurasov, S.; Wardemann, H.; Hammersen, J.; Tsuiji, M.; Meffre, E.; Pascual, V.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Defective b cell tolerance checkpoints in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipton, C.M.; Fucile, C.F.; Darce, J.; Chida, A.; Ichikawa, T.; Gregoretti, I.; Schieferl, S.; Hom, J.; Jenks, S.; Feldman, R.J.; et al. Diversity, cellular origin and autoreactivity of antibody-secreting cell population expansions in acute systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumet, F.C.; Coukell, A.; Bodmer, J.G.; Bodmer, W.F.; McDevitt, H.O. Histocompatibility (hl-a) antigens associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. A possible genetic predisposition to disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, T.H.; Fehr, H.; Kalden, J.R. Analysis of immunoglobulin variable region genes from human igg anti-DNA hybridomas. Eur. J. Immunol. 1992, 22, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naradikian, M.S.; Hao, Y.; Cancro, M.P. Age-associated b cells: Key mediators of both protective and autoreactive humoral responses. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 269, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsova, K.; Rubtsov, A.V.; Cancro, M.P.; Marrack, P. Age-associated b cells: A t-bet-dependent effector with roles in protective and pathogenic immunity. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancro, M.P. Expanding roles for the tbet+ b cell subset in health and disease. Cell Immunol. 2017, 321, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.; Oliver, A.M.; Kearney, J.F. Marginal zone and b1 b cells unite in the early response against t-independent blood-borne particulate antigens. Immunity 2001, 14, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Morel, L. Role of b-1a cells in autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2006, 5, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Carvalho, T.; Kearney, J.F. Development and selection of marginal zone b cells. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 197, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecino-Rodriguez, E.; Dorshkind, K. B-1 b cell development in the fetus and adult. Immunity 2012, 36, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, Y.; Uchida, J.; Cain, D.W.; Venturi, G.M.; Poe, J.C.; Haas, K.M.; Tedder, T.F. The peritoneal cavity provides a protective niche for b1 and conventional b lymphocytes during anti-cd20 immunotherapy in mice. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4389–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiepe, F.; Dorner, T.; Hauser, A.E.; Hoyer, B.F.; Mei, H.; Radbruch, A. Long-lived autoreactive plasma cells drive persistent autoimmune inflammation. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duddy, M.E.; Alter, A.; Bar-Or, A. Distinct profiles of human b cell effector cytokines: A role in immune regulation? J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3422–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C. Current role of rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 18, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, D.; Dunham, J.; Khan, S.; Stansberry, J.; Kolasinski, S.; Tsai, D.; Pullman-Mooar, S.; Barnack, F.; Striebich, C.; Looney, R.J.; et al. Variability in the biological response to anti-cd20 b cell depletion in systemic lupus erythaematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.G.; Jones, R.B.; Burns, S.M.; Jayne, D.R. Long-term comparison of rituximab treatment for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis: Remission, relapse, and re-treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2970–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, V.S.; Tsang, H.H.; Tam, R.C.; Lu, L.; Lau, C.S. B-cell-targeted therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagaki, T. Regulatory b cells in human autoimmune diseases. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi 2015, 38, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadasz, Z.; Peri, R.; Eiza, N.; Slobodin, G.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Toubi, E. The expansion of cd25 high il-10 high foxp3 high b regulatory cells is in association with sle disease activity. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 254245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T. Regulatory b cells in mouse models of systemic lupus erythematosus (sle). Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1190, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Dambuza, I.M.; He, C.; Choi, J.K.; Yu, C.R.; Wang, R.; Mattapallil, M.J.; Wingfield, P.T.; Caspi, R.R.; Egwuagu, C.E. Il-12p35 induces expansion of il-10 and il-35-expressing regulatory b cells and ameliorates autoimmune disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, P.R.; Gordon, C. B-cell targeted therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus: Successes and challenges. BioDrugs 2013, 27, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A., 3rd; Kahler, D.J.; Baban, B.; Chandler, P.R.; Kang, B.; Shimoda, M.; Koni, P.A.; Pihkala, J.; Vilagos, B.; Busslinger, M.; et al. B-lymphoid cells with attributes of dendritic cells regulate t cells via indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10644–10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsov, A.V.; Rubtsova, K.; Fischer, A.; Meehan, R.T.; Gillis, J.Z.; Kappler, J.W.; Marrack, P. Toll-like receptor 7 (tlr7)-driven accumulation of a novel cd11c(+) b-cell population is important for the development of autoimmunity. Blood 2011, 118, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; O’Neill, P.; Naradikian, M.S.; Scholz, J.L.; Cancro, M.P. A b-cell subset uniquely responsive to innate stimuli accumulates in aged mice. Blood 2011, 118, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehr, C.; Eibel, H.; Masilamani, M.; Illges, H.; Schlesier, M.; Peter, H.H.; Warnatz, K. A new cd21low b cell population in the peripheral blood of patients with sle. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.O.; Rothstein, T.L. A small cd11b(+) human b1 cell subpopulation stimulates t cells and is expanded in lupus. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2591–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenks, S.A.; Cashman, K.S.; Zumaquero, E.; Marigorta, U.M.; Patel, A.V.; Wang, X.; Tomar, D.; Woodruff, M.C.; Simon, Z.; Bugrovsky, R.; et al. Distinct effector b cells induced by unregulated toll-like receptor 7 contribute to pathogenic responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 2018, 49, 725–739 e726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Qian, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Dai, D.; Dai, M.; Wu, L.; Liao, Z.; Xue, Z.; et al. T-bet(+)cd11c(+) b cells are critical for antichromatin immunoglobulin g production in the development of lupus. Arthritis Res. 2017, 19, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Fu, Q.; Guo, Q.; Chen, S.; Goswami, S.; Sun, S.; Li, T.; Cao, X.; Chu, F.; Chen, Z.; et al. Lupus-associated atypical memory b cells are mtorc1-hyperactivated and functionally dysregulated. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnell, J.L.; Kumar, V.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Voynova, E.; Ettinger, R. Role of cd11c(+) t-bet(+) b cells in human health and disease. Cell Immunol. 2017, 321, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.W.; Arkatkar, T.; Jacobs, H.M.; Rawlings, D.J.; Jackson, S.W. Generation of functional murine cd11c(+) age-associated b cells in the absence of b cell t-bet expression. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsov, A.V.; Rubtsova, K.; Kappler, J.W.; Jacobelli, J.; Friedman, R.S.; Marrack, P. Cd11c-expressing b cells are located at the t cell/b cell border in spleen and are potent apcs. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arazi, A.; Rao, D.A.; Berthier, C.C.; Davidson, A.; Liu, Y.; Hoover, P.J.; Chicoine, A.; Eisenhaure, T.M.; Jonsson, A.H.; Li, S.; et al. The immune cell landscape in kidneys of patients with lupus nephritis. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsova, K.; Rubtsov, A.V.; Thurman, J.M.; Mennona, J.M.; Kappler, J.W.; Marrack, P. B cells expressing the transcription factor t-bet drive lupus-like autoimmunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naradikian, M.S.; Myles, A.; Beiting, D.P.; Roberts, K.J.; Dawson, L.; Herati, R.S.; Bengsch, B.; Linderman, S.L.; Stelekati, E.; Spolski, R.; et al. Cutting edge: Il-4, il-21, and ifn-gamma interact to govern t-bet and cd11c expression in tlr-activated b cells. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Lu, L. Roles of b cell-intrinsic tlr signals in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13084–13105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, J.J.; Buggert, M.; Kardava, L.; Seaton, K.E.; Eller, M.A.; Canaday, D.H.; Robb, M.L.; Ostrowski, M.A.; Deeks, S.G.; Slifka, M.K.; et al. T-bet+ b cells are induced by human viral infections and dominate the hiv gp140 response. JCI Insight 2017, 2, 92943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindhava, V.J.; Oropallo, M.A.; Moody, K.; Naradikian, M.; Higdon, L.E.; Zhou, L.; Myles, A.; Green, N.; Nundel, K.; Stohl, W.; et al. A tlr9-dependent checkpoint governs b cell responses to DNA-containing antigens. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1651–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighvani, A.A.; Frucht, D.M.; Jankovic, D.; Yamane, H.; Aliberti, J.; Hissong, B.D.; Nguyen, B.V.; Gadina, M.; Sher, A.; Paul, W.E.; et al. T-bet is rapidly induced by interferon-gamma in lymphoid and myeloid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15137–15142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, A.; Gearhart, P.J.; Cancro, M.P. Signals that drive t-bet expression in b cells. Cell Immunol. 2017, 321, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Kumar, V.; Karnell, J.L.; Naiman, B.; Gross, P.S.; Rahman, S.; Zerrouki, K.; Hanna, R.; Morehouse, C.; et al. Il-21 drives expansion and plasma cell differentiation of autoreactive cd11c(hi)t-bet(+) b cells in sle. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wei, Y.; Fonseca, V.R.; Graca, L.; Yu, D. T follicular helper cells and t follicular regulatory cells in rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T.R.; Sad, S. The expanding universe of t-cell subsets: Th1, th2 and more. Immunol. Today 1996, 17, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A.G.; Gray, C.W.; Pearson, J.F.; Greenwood, J.M.; During, M.J.; Dragunow, M. Atf3 enhances c-jun-mediated neurite sprouting. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 120, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.C.; Choi, S.J.; Ji, J.D.; Song, G.G. Genome-wide pathway analysis of genome-wide association studies on systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 10627–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borggrefe, T.; Keshavarzi, S.; Gross, B.; Wabl, M.; Jessberger, R. Impaired ige response in swap-70-deficient mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Molineros, J.E.; Looger, L.L.; Zhou, X.J.; Kim, K.; Okada, Y.; Ma, J.; Qi, Y.Y.; Kim-Howard, X.; Motghare, P.; et al. High-density genotyping of immune-related loci identifies new sle risk variants in individuals with asian ancestry. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanzo, J.C.; Yang, W.; Jang, S.Y.; Gupta, S.; Chen, Q.; Siddiq, A.; Greenberg, S.; Pernis, A.B. Loss of irf-4-binding protein leads to the spontaneous development of systemic autoimmunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, M.; Chacon-Martinez, C.A.; Jessberger, R. Fine tuning of irf-4 expression by swap-70 controls the initiation of plasma cell development. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 3063–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, W.; Gupta, S.; Biswas, P.; Smith, P.; Bhagat, G.; Pernis, A.B. Irf-4-binding protein inhibits interleukin-17 and interleukin-21 production by controlling the activity of irf-4 transcription factor. Immunity 2008, 29, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Cannons, J.L.; Klauschen, F.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Germain, R.N. Sap-controlled t-b cell interactions underlie germinal centre formation. Nature 2008, 455, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, F.Y.; Manzi, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Minster, R.L.; Kenney, M.; Shaw, P.S.; Dunlop-Thomas, C.M.; Kao, A.H.; Rhew, E.; Bontempo, F.; et al. Association of a common interferon regulatory factor 5 (irf5) variant with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus (sle). Ann. Hum. Genet. 2007, 71, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, M.; Gupta, S.; Ricker, E.; Chinenov, Y.; Park, S.H.; Shi, M.; Pannellini, T.; Jessberger, R.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Pernis, A.B. Regulation of age-associated b cells by irf5 in systemic autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deenick, E.K.; Chan, A.; Ma, C.S.; Gatto, D.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Brink, R.; Tangye, S.G. Follicular helper t cell differentiation requires continuous antigen presentation that is independent of unique b cell signaling. Immunity 2010, 33, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisand, K.; Link, M.; Wolff, A.S.; Meager, A.; Tserel, L.; Org, T.; Murumagi, A.; Uibo, R.; Willcox, N.; Trebusak Podkrajsek, K.; et al. Interferon autoantibodies associated with aire deficiency decrease the expression of ifn-stimulated genes. Blood 2008, 112, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecino-Rodriguez, E.; Dorshkind, K. New perspectives in b-1 b cell development and function. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berland, R.; Wortis, H.H. Origins and functions of b-1 cells with notes on the role of cd5. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 253–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnrot, C.; Prokopec, K.E.; Rasbo, K.; Karlsson, M.C.; Kleinau, S. Marginal zone b cells are naturally reactive to collagen type ii and are involved in the initiation of the immune response in collagen-induced arthritis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Z.; Hou, B. Tlr signaling in b-cell development and activation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, C.G.; Chang, P.P. Innate b cell helpers reveal novel types of antibody responses. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, H.; Mota-Santos, T.; Huetz, F.; Coutinho, A.; Cazenave, P.A. All t15 id-positive antibodies (but not the majority of vht15+ antibodies) are produced by peritoneal cd5+ b lymphocytes. Int. Immunol. 1990, 2, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ye, C.; Lin, X.; Ma, K.; Xiao, F.; Dong, L.; Lu, L. New insights into the significance of the bcr repertoire in b-1 cell development and function. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, M.; Martin, F.; Zhou, T.; Kearney, J. Blood dendritic cells interact with splenic marginal zone b cells to initiate t-independent immune responses. Immunity 2002, 17, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenert, P.; Brummel, R.; Field, E.H.; Ashman, R.F. Tlr-9 activation of marginal zone b cells in lupus mice regulates immunity through increased il-10 production. J. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 25, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, T.A.; Shen, P.; Brown, S.; Lampropoulou, V.; Roch, T.; Lawrie, S.; Fan, B.; O’Connor, R.A.; Anderton, S.M.; Bar-Or, A.; et al. B cell depletion therapy ameliorates autoimmune disease through ablation of il-6-producing b cells. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wofsy, D.; Chiang, N.Y. Proliferation of ly-1 b cells in autoimmune nzb and (nzb x nzw)f1 mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1987, 17, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Butfiloski, E.J.; Sobel, E.S.; Morel, L. Mechanisms of peritoneal b-1a cells accumulation induced by murine lupus susceptibility locus sle2. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 6050–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.O.; Holodick, N.E.; Rothstein, T.L. Human b1 cells in umbilical cord and adult peripheral blood express the novel phenotype cd20+ cd27+ cd43+ cd70. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atencio, S.; Amano, H.; Izui, S.; Kotzin, B.L. Separation of the new zealand black genetic contribution to lupus from new zealand black determined expansions of marginal zone b and b1a cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4159–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzler, T.; Bonizzi, G.; Silverman, G.J.; Otero, D.C.; Widhopf, G.F.; Anzelon-Mills, A.; Rickert, R.C.; Karin, M. Alternative and classical nf-kappa b signaling retain autoreactive b cells in the splenic marginal zone and result in lupus-like disease. Immunity 2006, 25, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Niu, H.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Morel, L. Autoreactive marginal zone b cells enter the follicles and interact with cd4+ t cells in lupus-prone mice. BMC Immunol. 2011, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.; Miles, K.; Salter, D.; Gray, D.; Savill, J. Apoptotic cells protect mice from autoimmune inflammation by the induction of regulatory b cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14080–14085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ramirez, S.; Navarro-Hernandez, I.C.; Cervantes-Diaz, R.; Sosa-Hernandez, V.A.; Acevedo-Ochoa, E.; Kleinberg-Bild, A.; Valle-Rios, R.; Meza-Sanchez, D.E.; Hernandez-Hernandez, J.M.; Maravillas-Montero, J.L. Innate-like b cell subsets during immune responses: Beyond antibody production. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellusova, J.; Wellmann, U.; Amann, K.; Winkler, T.H.; Nitschke, L. Cd22 x siglec-g double-deficient mice have massively increased b1 cell numbers and develop systemic autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3618–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Kerr, S.; Jellusova, J.; Zhang, J.; Weisel, F.; Wellmann, U.; Winkler, T.H.; Kneitz, B.; Crocker, P.R.; Nitschke, L. Siglec-g is a b1 cell-inhibitory receptor that controls expansion and calcium signaling of the b1 cell population. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weil, R.; Israel, A. T-cell-receptor- and b-cell-receptor-mediated activation of nf-kappab in lymphocytes. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.S.; Gottschalk, R.A.; Lounsbury, N.W.; Sun, J.; Dorrington, M.G.; Baek, S.; Sun, G.; Wang, Z.; Krauss, K.S.; Milner, J.D.; et al. Dual roles for ikaros in regulation of macrophage chromatin state and inflammatory gene expression. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias-Garcia, A.; Heizmann, B.; Sellars, M.; Marchal, P.; Dali, H.; Pasquali, J.L.; Muller, S.; Kastner, P.; Chan, S. Ikaros is a negative regulator of b1 cell development and function. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 9073–9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizar, J.; Tan, C.; Noviski, M.; Mueller, J.L.; Zikherman, J. Nur77 is upregulated in b-1a cells by chronic self-antigen stimulation and limits generation of natural igm plasma cells. Immunohorizons 2017, 1, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlinton, D.; Radbruch, A.; Hiepe, F.; Dorner, T. Plasma cell differentiation and survival. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorner, T.; Giesecke, C.; Lipsky, P.E. Mechanisms of b cell autoimmunity in sle. Arthritis Res. 2011, 13, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, K.; Tokoyoda, K.; Radbruch, A.; MacLennan, I.; Manz, R.A. Stromal niches, plasma cell differentiation and survival. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espeli, M.; Bokers, S.; Giannico, G.; Dickinson, H.A.; Bardsley, V.; Fogo, A.B.; Smith, K.G. Local renal autoantibody production in lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.J., 3rd; Cole, L.J. Resistance of long-lived lymphocytes and plasma cells in rat lymph nodes to treatment with prednisone, cyclophosphamide, 6 mercaptopurine and actinomycin d. Usnrdl-tr-67-24. Res. Dev. Tech. Rep. 1967, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, E.J.; Butcher, E.C. Plasma-cell homing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddeo, A.; Khodadadi, L.; Voigt, C.; Mumtaz, I.M.; Cheng, Q.; Moser, K.; Alexander, T.; Manz, R.A.; Radbruch, A.; Hiepe, F.; et al. Long-lived plasma cells are early and constantly generated in new zealand black/new zealand white f1 mice and their therapeutic depletion requires a combined targeting of autoreactive plasma cells and their precursors. Arthritis Res. 2015, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahevas, M.; Michel, M.; Weill, J.C.; Reynaud, C.A. Long-lived plasma cells in autoimmunity: Lessons from b-cell depleting therapy. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, O.; Musiol, S.; Schablowsky, M.; Cheng, Q.; Khodadadi, L.; Hiepe, F. Analyzing pathogenic (double-stranded (ds) DNA-specific) plasma cells via immunofluorescence microscopy. Arthritis Res. 2015, 17, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnhorst, J.; Rasmussen, T.; Moen, S.H.; Flottum, M.; Knudsen, L.; Borset, M.; Espevik, T.; Sundan, A. Toll-like receptors mediate proliferation and survival of multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia 2006, 20, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, M.; Brandt, S.; Tinguely, M.; Zucol, F.; Bourquin, J.P.; Zauner, L.; Berger, C.; Bernasconi, M.; Speck, R.F.; Nadal, D. Plasma cell toll-like receptor (tlr) expression differs from that of b cells, and plasma cell tlr triggering enhances immunoglobulin production. Immunology 2009, 128, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Du, W.; Yang, X.; Mou, F.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hong, X.; et al. Tlr4(+)cxcr4(+) plasma cells drive nephritis development in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.Y.; Becker, A.M.; Kennerly, K.M.; Wong, R.; Curtis, J.D.; Llufrio, E.M.; McCommis, K.S.; Fahrmann, J.; Pizzato, H.A.; Nunley, R.M.; et al. Mitochondrial pyruvate import promotes long-term survival of antibody-secreting plasma cells. Immunity 2016, 45, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.I.; Tunyaplin, C.; Calame, K. Transcriptional regulatory cascades controlling plasma cell differentiation. Immunol. Rev. 2003, 194, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomchik, M.J.; Weisel, F. Germinal center selection and the development of memory b and plasma cells. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 247, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro-Shelef, M.; Calame, K. Regulation of plasma-cell development. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimold, A.M.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Manis, J.; Vallabhajosyula, P.; Szomolanyi-Tsuda, E.; Gravallese, E.M.; Friend, D.; Grusby, M.J.; Alt, F.; Glimcher, L.H. Plasma cell differentiation requires the transcription factor xbp-1. Nature 2001, 412, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, U.; Casola, S.; Cattoretti, G.; Shen, Q.; Lia, M.; Mo, T.; Ludwig, T.; Rajewsky, K.; Dalla-Favera, R. Transcription factor irf4 controls plasma cell differentiation and class-switch recombination. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, A.L.; Lin, K.I.; Kuo, T.C.; Yu, X.; Hurt, E.M.; Rosenwald, A.; Giltnane, J.M.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H.; Calame, K.; et al. Blimp-1 orchestrates plasma cell differentiation by extinguishing the mature b cell gene expression program. Immunity 2002, 17, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oracki, S.A.; Walker, J.A.; Hibbs, M.L.; Corcoran, L.M.; Tarlinton, D.M. Plasma cell development and survival. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 237, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahevas, M.; Patin, P.; Huetz, F.; Descatoire, M.; Cagnard, N.; Bole-Feysot, C.; Le Gallou, S.; Khellaf, M.; Fain, O.; Boutboul, D.; et al. B cell depletion in immune thrombocytopenia reveals splenic long-lived plasma cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, F.J.; Zuccarino-Catania, G.V.; Chikina, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. A temporal switch in the germinal center determines differential output of memory b and plasma cells. Immunity 2016, 44, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Lu, X.L.; Lv, J.C.; Yang, H.Z.; Qin, L.X.; Zhao, M.H.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.G.; Zhang, H. Genetic association of prdm1-atg5 intergenic region and autophagy with systemic lupus erythematosus in a chinese population. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, T.; Sarfert, R.; Klotsche, J.; Kuhl, A.A.; Rubbert-Roth, A.; Lorenz, H.M.; Rech, J.; Hoyer, B.F.; Cheng, Q.; Waka, A.; et al. The proteasome inhibitior bortezomib depletes plasma cells and ameliorates clinical manifestations of refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, K.; Meister, S.; Moser, K.; Weisel, F.; Maseda, D.; Amann, K.; Wiethe, C.; Winkler, T.H.; Kalden, J.R.; Manz, R.A.; et al. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib depletes plasma cells and protects mice with lupus-like disease from nephritis. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Rui, K.; Wang, S.; Lu, L. Regulatory b cells in autoimmune diseases. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillatreau, S.; Sweenie, C.H.; McGeachy, M.J.; Gray, D.; Anderton, S.M. B cells regulate autoimmunity by provision of il-10. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanaba, K.; Bouaziz, J.D.; Haas, K.M.; Poe, J.C.; Fujimoto, M.; Tedder, T.F. A regulatory b cell subset with a unique cd1dhicd5+ phenotype controls t cell-dependent inflammatory responses. Immunity 2008, 28, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, T.; Yanaba, K.; Bouaziz, J.D.; Fujimoto, M.; Tedder, T.F. Regulatory b cells inhibit eae initiation in mice while other b cells promote disease progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3420–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Fujimoto, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Komura, K.; Takehara, K.; Tedder, T.F.; Sato, S. Inhibitory role of cd19 in the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating cytokine response. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.G.; Chavez-Rueda, K.A.; Eddaoudi, A.; Meyer-Bahlburg, A.; Rawlings, D.J.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Mauri, C. Novel suppressive function of transitional 2 b cells in experimental arthritis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7868–7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Baba, A.; Yokota, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Ohkawa, Y.; Kayama, H.; Kallies, A.; Nutt, S.L.; Sakaguchi, S.; Takeda, K.; et al. Interleukin-10-producing plasmablasts exert regulatory function in autoimmune inflammation. Immunity 2014, 41, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, P.; Lampropoulou, V.; Calderon-Gomez, E.; Roch, T.; Stervbo, U.; Shen, P.; Kuhl, A.A.; Loddenkemper, C.; Haury, M.; Nedospasov, S.A.; et al. Signaling via the myd88 adaptor protein in b cells suppresses protective immunity during salmonella typhimurium infection. Immunity 2010, 33, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.X.; Yu, C.R.; Dambuza, I.M.; Mahdi, R.M.; Dolinska, M.B.; Sergeev, Y.V.; Wingfield, P.T.; Kim, S.H.; Egwuagu, C.E. Interleukin-35 induces regulatory b cells that suppress autoimmune disease. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Brooks, C.R.; Sobel, R.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. Tim-1 is essential for induction and maintenance of il-10 in regulatory b cells and their regulation of tissue inflammation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Hams, E.; Floudas, A.; Sparwasser, T.; Weaver, C.T.; Fallon, P.G. Pd-l1hi b cells are critical regulators of humoral immunity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, L.; Qian, T.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Huang, E.; Xu, F.; Wang, J.Y.; et al. B cells expressing cd11b effectively inhibit cd4+ t-cell responses and ameliorate experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Pefanis, E.; Chao, J.; Rothschild, G.; Tachibana, I.; Chen, J.K.; Ivanov, I.I.; Rabadan, R.; Takeda, Y.; et al. Transcriptomics identify cd9 as a marker of murine il-10-competent regulatory b cells. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giang, S.; La Cava, A. Regulatory t cells in sle: Biology and use in treatment. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, P.A.; Norena, L.Y.; Flores-Borja, F.; Rawlings, D.J.; Isenberg, D.A.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Mauri, C. Cd19(+)cd24(hi)cd38(hi) b cells exhibit regulatory capacity in healthy individuals but are functionally impaired in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Immunity 2010, 32, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Seo, H.B.; Ryu, J.G.; Jung, K.; Choi, J.W.; Jhun, J.; Park, J.S.; Kwon, J.Y.; Kwok, S.K.; et al. Inhibition of il-17 ameliorates systemic lupus erythematosus in roquin(san/san) mice through regulating the balance of tfh cells, gc b cells, treg and breg. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Ko, K.H.; Wang, X.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, S.; Hua, Z.; Sun, L.; Srivastava, G.; et al. Il-10-producing regulatory b10 cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis via suppressing th17 cell generation. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 2375–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Xiao, F.; Ma, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, F.; Shi, X.; Liu, D.; et al. Il-10-producing regulatory b cells restrain the t follicular helper cell response in primary sjogren’s syndrome. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Chu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Xuan, D.; Zheng, S.; Zou, H. T follicular helper cells and regulatory b cells dynamics in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Chen, G.; Hou, C.; Zhang, L.; Ma, N.; et al. Pre-existing cd19-independent gl7(-) breg cells are expanded during inflammation and in mice with lupus-like disease. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 71, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Roch, T.; Lampropoulou, V.; O’Connor, R.A.; Stervbo, U.; Hilgenberg, E.; Ries, S.; Dang, V.D.; Jaimes, Y.; Daridon, C.; et al. Il-35-producing b cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature 2014, 507, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagaki, T.; Fujimoto, M.; Sato, S. Regulatory b cells in human inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: From mouse models to clinical research. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.I.; Rothstein, D.M.; Markmann, J.F. Role of b cells in tolerance induction. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2015, 20, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernasconi, N.L.; Onai, N.; Lanzavecchia, A. A role for toll-like receptors in acquired immunity: Up-regulation of tlr9 by bcr triggering in naive b cells and constitutive expression in memory b cells. Blood 2003, 101, 4500–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, M.; Fujii, Y.; Baba, A.; Hikida, M.; Kurosaki, T.; Baba, Y. The calcium sensors stim1 and stim2 control b cell regulatory function through interleukin-10 production. Immunity 2011, 34, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.M.; Marshak-Rothstein, A. Toll-like receptor driven b cell activation in the induction of systemic autoimmunity. Semin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zekzer, D.; Hanssen, L.; Lu, Y.; Olcott, A.; Kaufman, D.L. Lipopolysaccharide-activated b cells down-regulate th1 immunity and prevent autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, D.; Kuo, C.H.; Tominaga, T.; Inoue, Y.; Ono, S.J. Regulatory function of cpg-activated b cells in late-phase experimental allergic conjunctivitis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Hasegawa, N.; Noguchi, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Touma, M. The atypical ikappab protein ikappab(ns) is important for toll-like receptor-induced interleukin-10 production in b cells. Immunology 2016, 147, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Takeda, K. Role of adapters in toll-like receptor signalling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, P.A.; Chavez-Rueda, K.A.; Evans, J.G.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Eddaoudi, A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Mauri, C. Selective targeting of b cells with agonistic anti-cd40 is an efficacious strategy for the generation of induced regulatory t2-like b cells and for the suppression of lupus in mrl/lpr mice. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3492–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noelle, R.J.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Aruffo, A. Cd40 and its ligand, an essential ligand-receptor pair for thymus-dependent b-cell activation. Immunol. Today 1992, 13, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, S.E.; Lee, W.L.; McIntire, J.J.; Downey, L.; Sanjanwala, B.; Akbari, O.; Berry, G.J.; Nagumo, H.; Freeman, G.J.; Umetsu, D.T.; et al. Tim-1 induces t cell activation and inhibits the development of peripheral tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Davidson, A. Baff and selection of autoreactive b cells. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.; Blair, P.A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Mauri, C. A regulatory feedback between plasmacytoid dendritic cells and regulatory b cells is aberrant in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 2016, 44, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, E.C.; Oleinika, K.; Tonon, S.; Doyle, R.; Bosma, A.; Carter, N.A.; Harris, K.A.; Jones, S.A.; Klein, N.; Mauri, C. Regulatory b cells are induced by gut microbiota-driven interleukin-1beta and interleukin-6 production. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, S.; Ling, G.S.; Xu, D.; Hussaarts, L.; Romaine, A.; Zhao, H.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Malik, T.; Cook, H.T.; Botto, M.; et al. Il-10-producing regulatory b cells induced by il-33 (breg(il-33)) effectively attenuate mucosal inflammatory responses in the gut. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 50, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, M.; Saito, K.; Kawabata, D.; Imura, Y.; Fujii, T.; Nakayamada, S.; Tsujimura, S.; Nawata, M.; Iwata, S.; Azuma, T.; et al. Efficacy of rituximab (anti-cd20) for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus involving the central nervous system. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaani, S.; Rovin, B.H. B-cell therapy in lupus nephritis: An overview. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabahi, R.; Anolik, J.H. B-cell-targeted therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. Drugs 2006, 66, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Foote, S.; Jones, G. B-cell-targeted therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus: An update. BioDrugs 2008, 22, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, K.; Clauder, A.K.; Manz, R.A. Targeting b cells and plasma cells in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlinton, D.M.; Hodgkin, P.D. Targeting plasma cells in autoimmune diseases. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odendahl, M.; Jacobi, A.; Hansen, A.; Feist, E.; Hiepe, F.; Burmester, G.R.; Lipsky, P.E.; Radbruch, A.; Dorner, T. Disturbed peripheral b lymphocyte homeostasis in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5970–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Lin, X.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Rui, K.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. Proteasome inhibition suppresses th17 cell generation and ameliorates autoimmune development in experimental sjogren’s syndrome. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Moisini, I.; Bethunaickan, R.; Sahu, R.; Akerman, M.; Eilat, D.; Lesser, M.; Davidson, A. Baff/april inhibition decreases selection of naive but not antigen-induced autoreactive b cells in murine systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6571–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, S.; Bai, B.; Zhang, L.; Xue, L.; Lin, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhu, F.; He, P.; Tang, W.; et al. Therapeutic effects of the artemisinin analog sm934 on lupus-prone mrl/lpr mice via inhibition of tlr-triggered b-cell activation and plasma cell formation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, T.; Lipsky, P.E. Beyond pan-b-cell-directed therapy—New avenues and insights into the pathogenesis of sle. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Guilpain, P.; Chong, B.F.; Chouzenoux, S.; Guillevin, L.; Du, Y.; Zhou, X.J.; Lin, F.; Fairhurst, A.M.; Boudreaux, C.; et al. Dysregulated expression of cxcr4/cxcl12 in subsets of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3436–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoura, Z.; Combadiere, C.; Faure, S.; Parizot, C.; Miyara, M.; Raphael, D.; Ghillani, P.; Debre, P.; Piette, J.C.; Gorochov, G. Roles of ccr2 and cxcr3 in the t cell-mediated response occurring during lupus flares. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3487–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Deng, Y.; Feng, Y.; Long, D.; Ma, K.; Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Lu, L.; Lu, Q. Epigenetic regulation in b-cell maturation and its dysregulation in autoimmunity. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Mei, Y.; Li, Z. Research progress on regulatory b cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7948687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, C.; Menon, M. Human regulatory b cells in health and disease: Therapeutic potential. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gao, D.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Wan, L.; Li, M. Th17 and natural treg cell population dynamics in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.M.; Stockinger, B. Effector t cell plasticity: Flexibility in the face of changing circumstances. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, K.; Du, W.; Wang, X.; Yuan, S.; Cai, X.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Lu, L. Multiple Functions of B Cells in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236021
Ma K, Du W, Wang X, Yuan S, Cai X, Liu D, Li J, Lu L. Multiple Functions of B Cells in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(23):6021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236021
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Kongyang, Wenhan Du, Xiaohui Wang, Shiwen Yuan, Xiaoyan Cai, Dongzhou Liu, Jingyi Li, and Liwei Lu. 2019. "Multiple Functions of B Cells in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 23: 6021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236021
APA StyleMa, K., Du, W., Wang, X., Yuan, S., Cai, X., Liu, D., Li, J., & Lu, L. (2019). Multiple Functions of B Cells in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 6021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236021




