The miR396–GRF Regulatory Module Controls the Embryogenic Response in Arabidopsis via an Auxin-Related Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
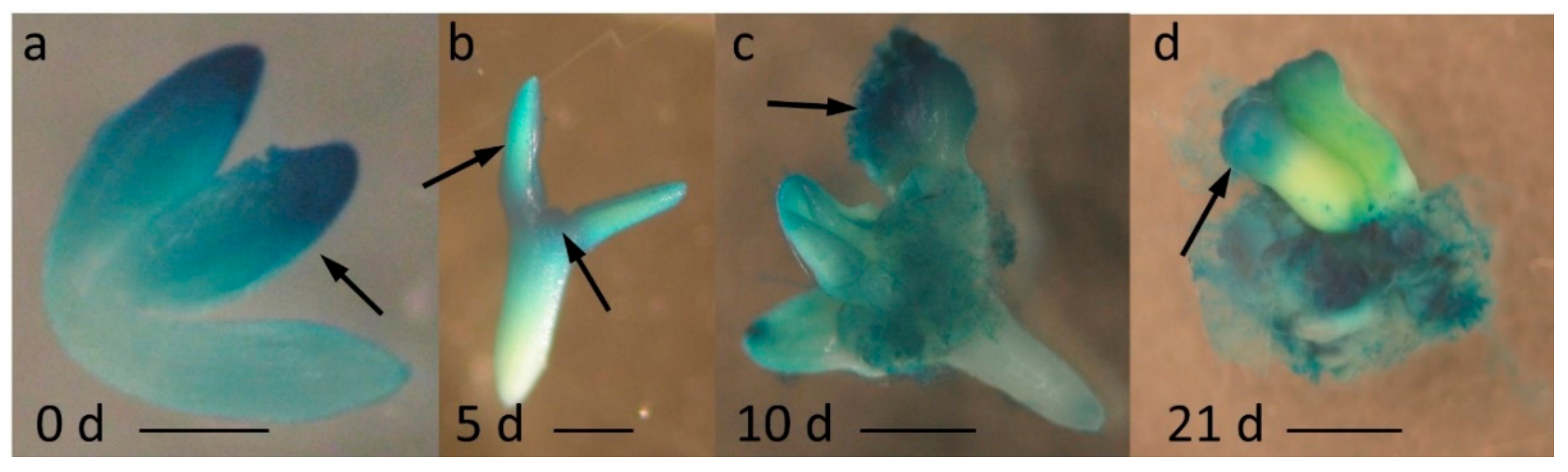
2.1. miR396 Was Expressed Specifically in the SE-Induced Explant Parts
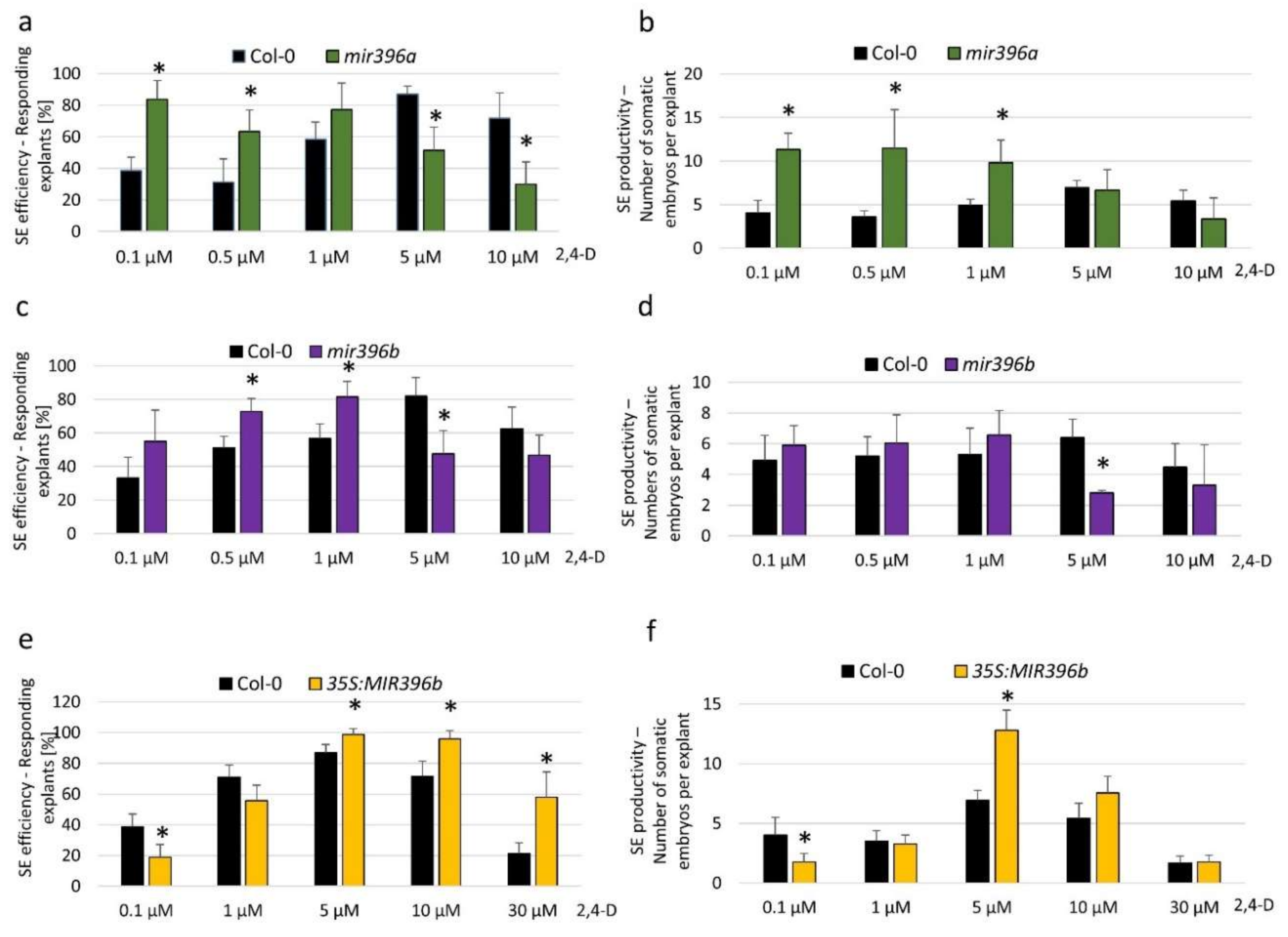
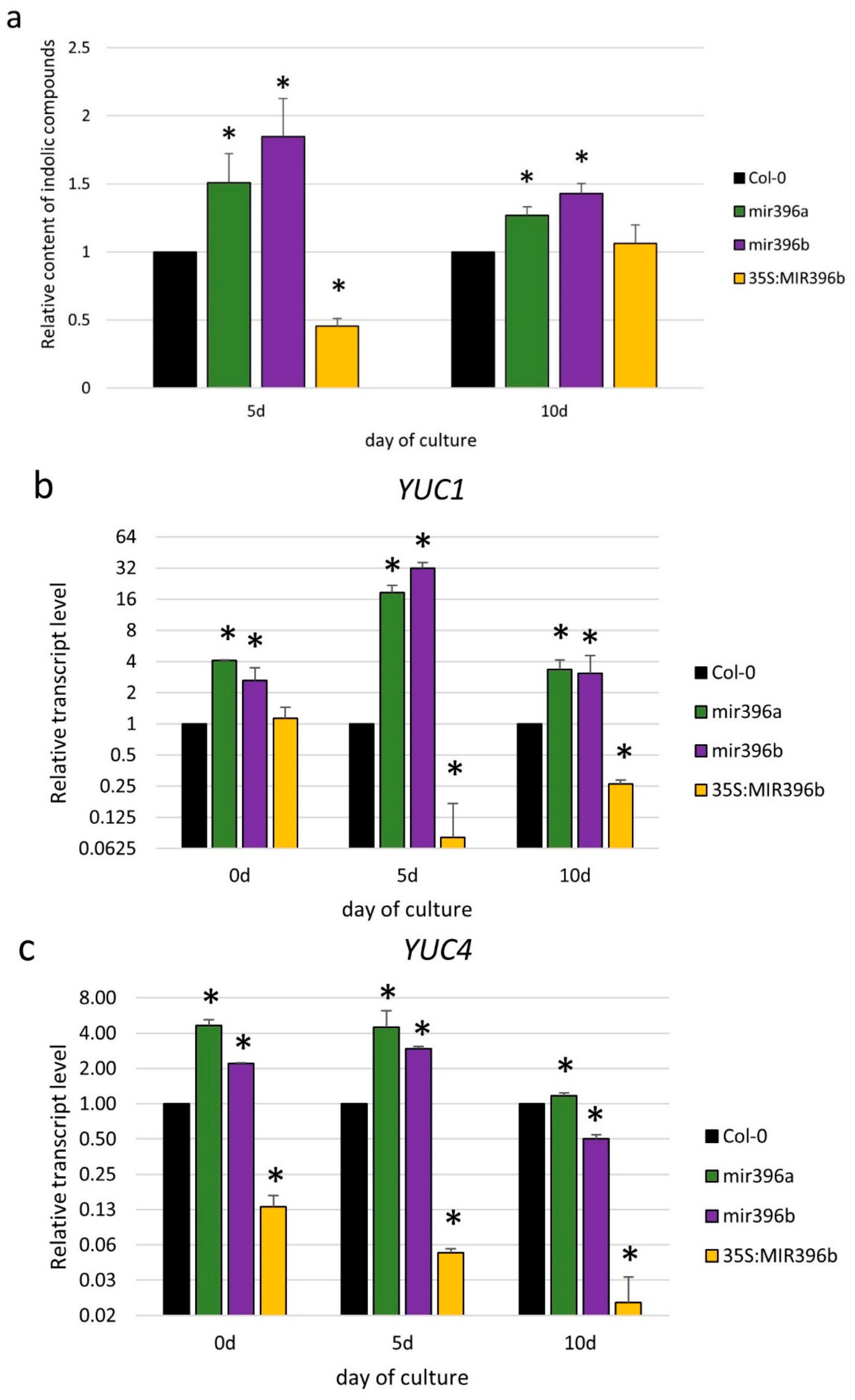
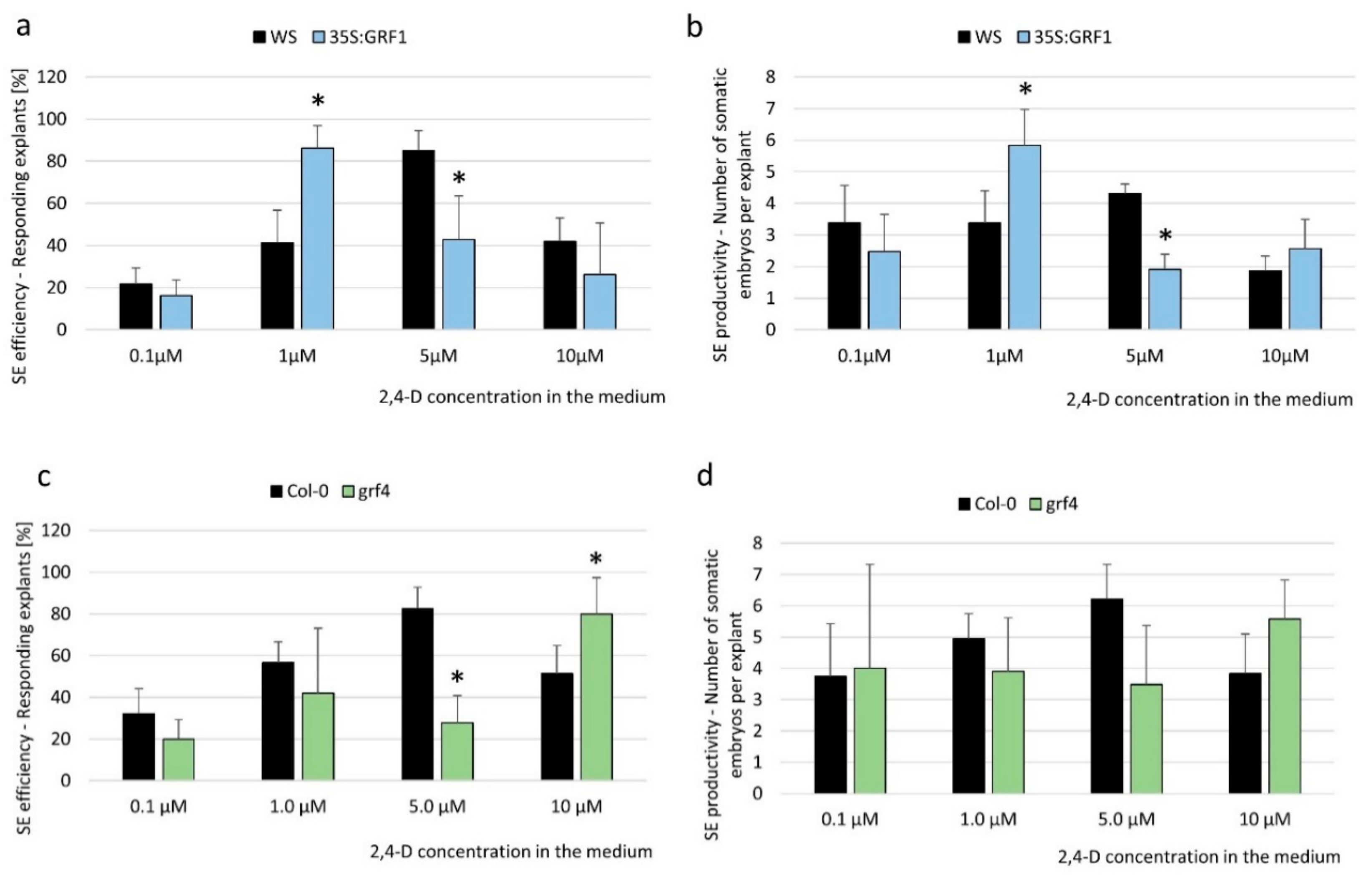
2.2. miR396 Contributed to SE Induction via an Auxin Biosynthesis-Related Pathway
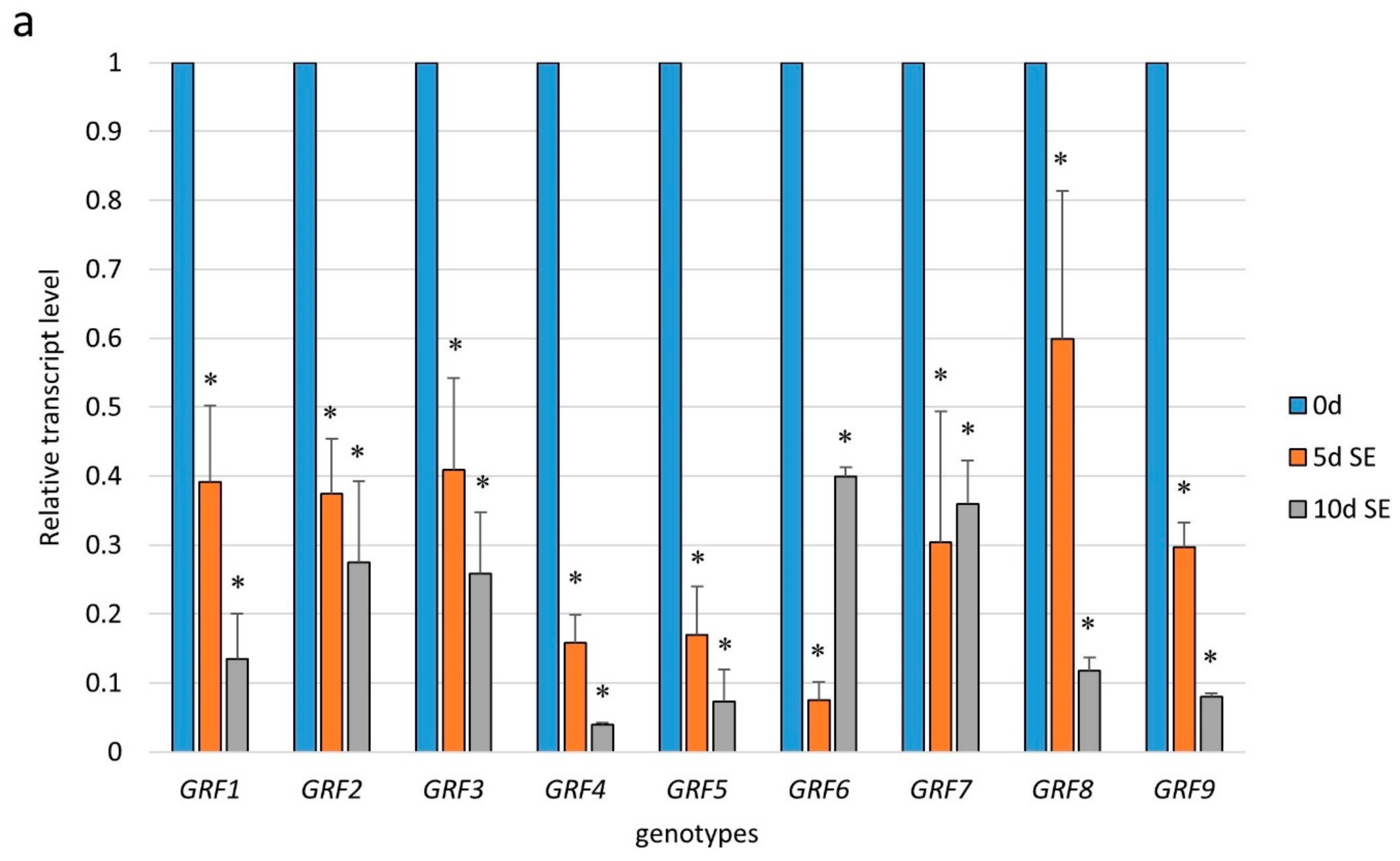
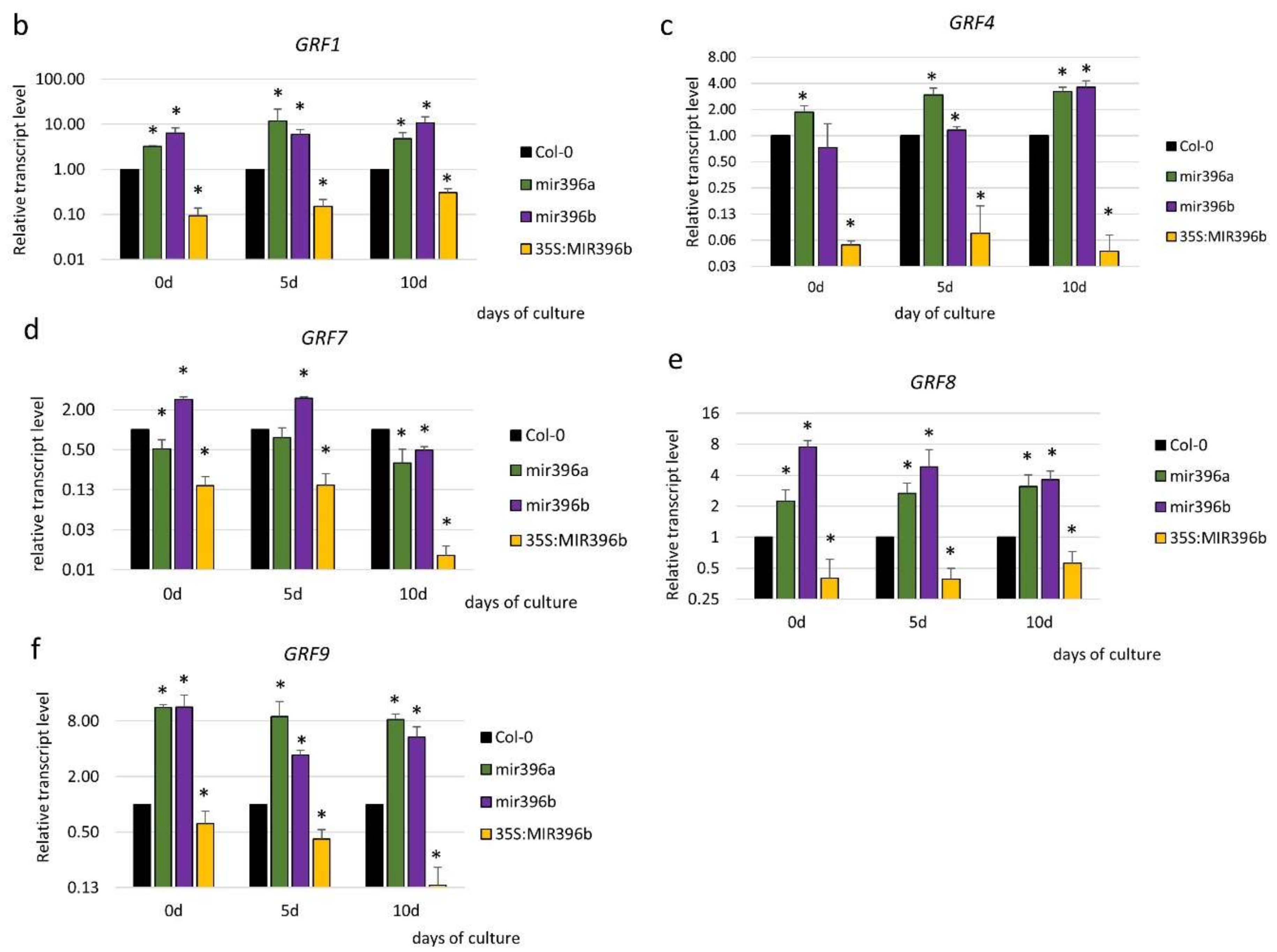
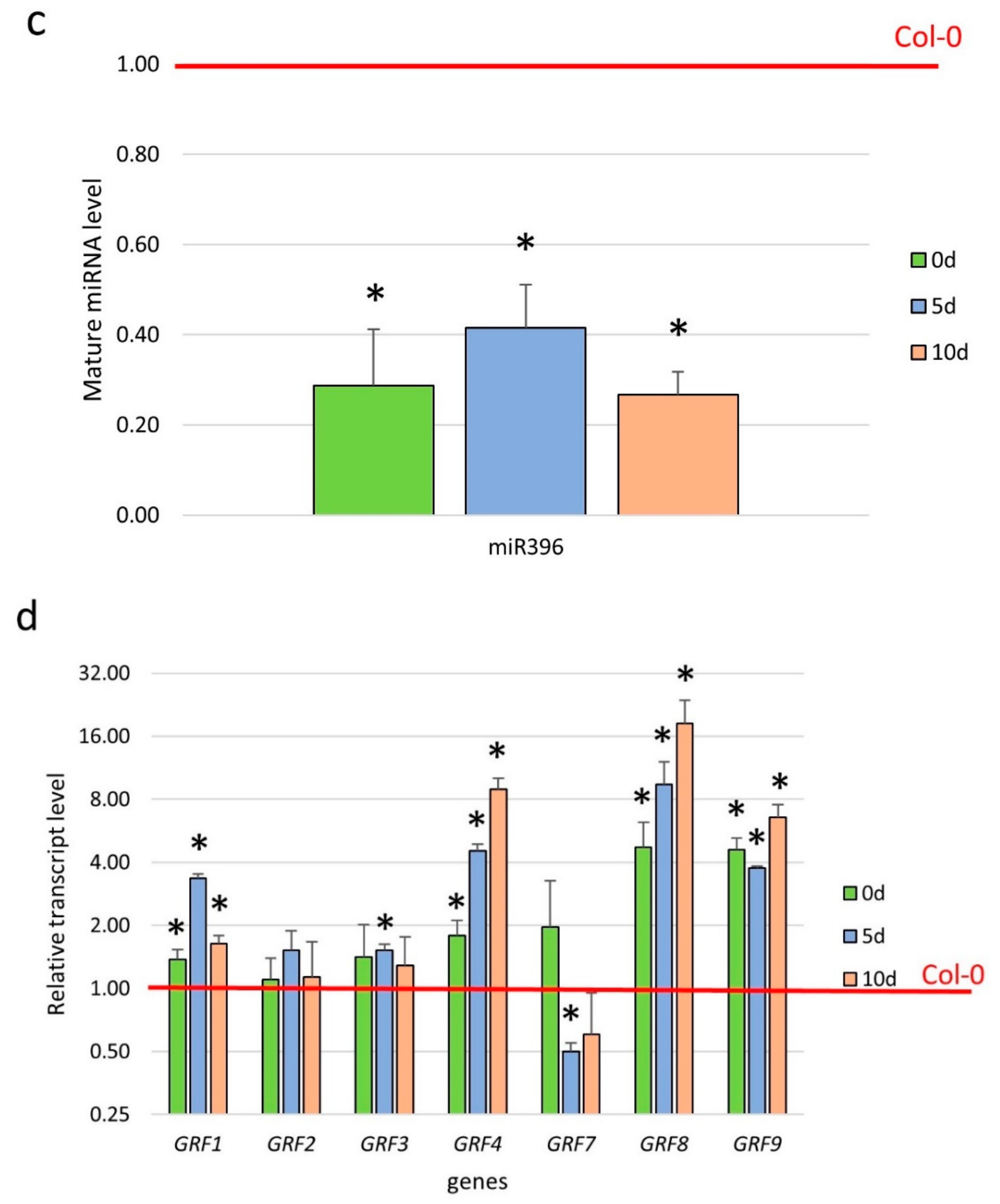
2.3. miR396 Controlled the GRF Genes during SE Induction
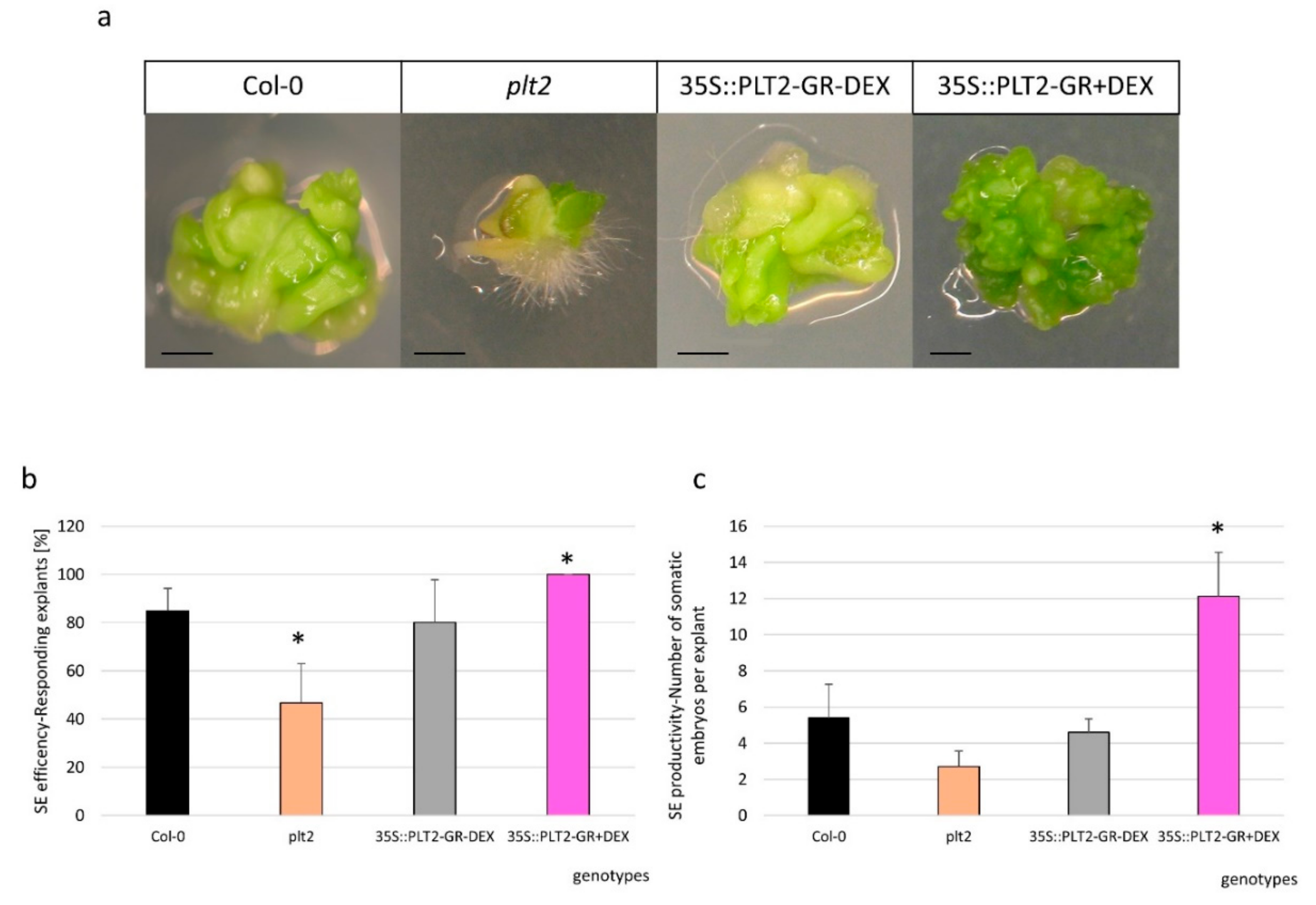
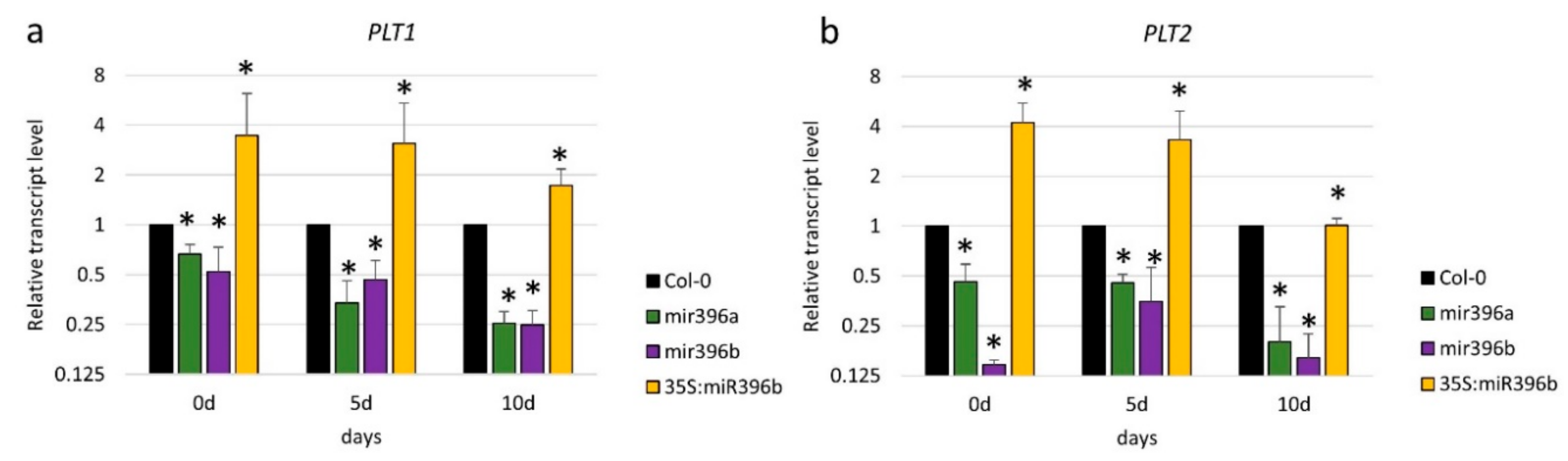
2.4. The Regulatory Relationship between miR396 and PLT1/PLT2 in SE Induction
3. Discussion
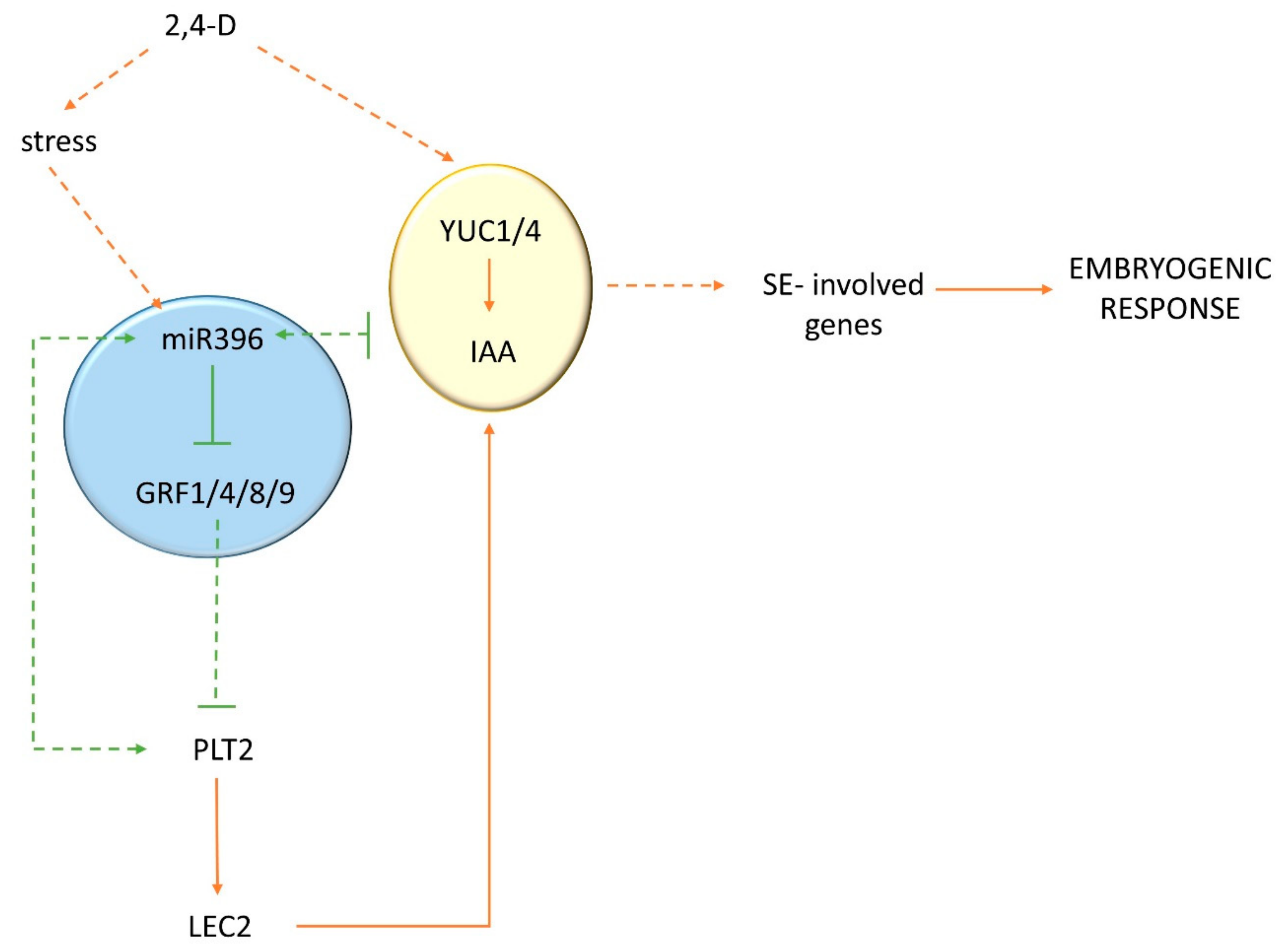
3.1. An Accumulation of miR396 Was Associated with SE Induction
3.2. miR396 Controlled the Embryogenic Response by Modulating the Sensitivity of Tissues to Auxin
3.3. miR396 Regulated SE Induction by Repressing GRFs (GRF1, 4, 7, 8, and 9)
3.4. miR396 Positively Controlled PLT Genes in SE Induction via GRFs
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
4.2. Somatic Embryogenesis Induction
4.3. Content of Indolic Compounds
4.4. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR Analysis
4.5. Stem-Loop RT-PCR for Mature miRNA Detection
4.6. Transcript Level Calculation
4.7. Histochemical Staining of GUS
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2,4-D | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid |
| AGL15 | AGAMOUS-LIKE15 |
| BBM | BABY BOOM |
| DEX | Dexamethasone |
| E5 | Embryogenesis induction medium with auxin |
| GRF | GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR |
| LEC2 | LEAFY COTYLEDON2 |
| MIR | Micro-RNA gene |
| IAA | Indolilic-3-acetic acid |
| IZE | Immature zygotic embryo |
| PLT | PLETHORA |
| SAM | Shoot apical meristem |
| SE | Somatic embryogenesis |
| TF | Transcription factor |
References
- Gordon-Kamm, B.; Sardesai, N.; Arling, M.; Lowe, K.; Hoerster, G.; Betts, S.; Jones, T. Using Morphogenic Genes to Improve Recovery and Regeneration of Transgenic Plants. Plants 2019, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliwicka, M.; Nowak, K.; Balazadeh, S.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Gaj, M.D. Extensive Modulation of the Transcription Factor Transcriptome during Somatic Embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plos One 2013, 8, e69261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramasuriya, A.M.; Dunwell, J.M. Global Scale Transcriptome Analysis of Arabidopsis Embryogenesis In Vitro. Bmc Genom. 2015, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutilier, K. Ectopic Expression of BABY BOOM Triggers a Conversion from Vegetative to Embryonic Growth. Plant Cell Online 2002, 14, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, M.D.; Zhang, S.; Harada, J.J.; Lemaux, P.G. Leafy Cotyledon Genes Are Essential for Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis of Arabidopsis. Planta 2005, 222, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Niu, Q.-W.; Frugis, G.; Chua, N.-H. The WUSCHEL Gene Promotes Vegetative-to-Embryonic Transition in Arabidopsis. Plant. J. 2002, 30, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, E.W. Expression and Maintenance of Embryogenic Potential Is Enhanced through Constitutive Expression of AGAMOUS-Like 15. Plant. Physiol. 2003, 133, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, Q.-W.; Teng, C.; Li, C.; Mu, J.; Chua, N.-H.; Zuo, J. Overexpression of PGA37/MYB118 and MYB115 Promotes Vegetative-to-Embryonic Transition in Arabidopsis. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuwamoto, R.; Yokoi, S.; Takahata, Y. Arabidopsis EMBRYOMAKER Encoding an AP2 Domain Transcription Factor Plays a Key Role in Developmental Change from Vegetative to Embryonic Phase. Plant. Mol. Biol. 2010, 73, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobert, O. Common Logic of Transcription Factor and MicroRNA Action. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNAs and Their Regulatory Roles in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2006, 57, 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szyrajew, K.; Bielewicz, D.; Dolata, J.; Wójcik, A.M.; Nowak, K.; Szczygieł-Sommer, A.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z.; Jarmolowski, A.; Gaj, M.D. MicroRNAs Are Intensively Regulated during Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Qu, L.-H.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Gautheret, D. Genome-Wide Discovery and Analysis of MicroRNAs and Other Small RNAs from Rice Embryogenic Callus. Rna Biol. 2011, 8, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chen, J.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Lu, Y.; Shi, J. Deep Sequencing and Microarray Hybridization Identify Conserved and Species-Specific MicroRNAs during Somatic Embryogenesis in Hybrid Yellow Poplar. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Han, S.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Qi, L. Genome-Wide Identification of MicroRNAs in Larch and Stage-Specific Modulation of 11 Conserved MicroRNAs and Their Targets during Somatic Embryogenesis. Planta 2012, 236, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Yuan, D.; Lindsey, K.; Zhang, X. Small RNA and Degradome Sequencing Reveal Complex MiRNA Regulation during Cotton Somatic Embryogenesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1521–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Hernández, E.C.; Alejandri-Ramírez, N.D.; Juárez-González, V.T.; Dinkova, T.D. Maize MiRNA and Target Regulation in Response to Hormone Depletion and Light Exposure during Somatic Embryogenesis. Front. Plant. Sci. 2015, 6, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongomake, K.; Doungous, O.; Khatabi, B.; Fondong, V.N. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration of Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) Landraces from Cameroon. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, A.M.; Nodine, M.D.; Gaj, M.D. miR160 and miR166/165 Contribute to the LEC2-Mediated Auxin Response Involved in the Somatic Embryogenesis Induction in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.H.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhou, C.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, X.S. The microRNA167 Controls Somatic Embryogenesis in Arabidopsis Through Regulating Its Target Genes ARF6 and ARF8. Plant. Cell Tiss. Organ. Cult. 2016, 124, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, A.M.; Gaj, M.D. miR393 Contributes to the Embryogenic Transition Induced In Vitro in Arabidopsis via the Modification of the Tissue Sensitivity to Auxin Treatment. Planta 2016, 244, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.-M.; Liu, C.-Y.; Feng, M.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.-M.; Guo, W.-W. miR156-SPL Modules Regulate Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Citrus Callus. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2979–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.E.; Mecchia, M.A.; Debernardi, J.M.; Schommer, C.; Weigel, D.; Palatnik, J.F. Control of Cell Proliferation in Arabidopsis thaliana by microRNA miR396. Development 2010, 137, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.E.; Schommer, C.; Palatnik, J.F. Control of Cell Proliferation by microRNAs in Plants. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2016, 34, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.E.; Ercoli, M.F.; Debernardi, J.M.; Breakfield, N.W.; Mecchia, M.A.; Sabatini, M.; Cools, T.; De Veylder, L.; Benfey, P.N.; Palatnik, J.F. MicroRNA miR396 Regulates the Switch between Stem Cells and Transit-Amplifying Cells in Arabidopsis Roots. Plant. Cell 2015, 27, 3354–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P. Computational Identification of Plant MicroRNAs and Their Targets, Including a Stress-Induced miRNA. Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.; Kende, H. The AtGRF Family of Putative Transcription Factors is Involved in Leaf and Cotyledon Growth in Arabidopsis. Plant. J. 2003, 36, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidbakhshfard, M.A.; Proost, S.; Fujikura, U.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Growth-Regulating Factors (GRFs): A Small Transcription Factor Family with Important Functions in Plant Biology. Mol. Plant. 2015, 8, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, A.; Li, M.; Heidmann, I.; Weemen, M.; Chen, B.; Muiño, J.M.; Angenent, G.C.; Boutilier, K. The BABY BOOM Transcription Factor Activates the LEC1-ABI3-FUS3-LEC2 Network to Induce Somatic Embryogenesis. Plant. Physiol. 2017, 175, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, A. Somatic embryogenesis — Stress-Induced Remodeling of Plant Cell Fate. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (Bba) – Gene. Regul. Mech. 2015, 1849, 358–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadevall, R.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Debernardi, J.M.; Palatnik, J.F.; Casati, P. Repression of Growth Regulating Factors by the MicroRNA396 Inhibits Cell Proliferation by UV-B Radiation in Arabidopsis Leaves. Plant. Cell 2013, 25, 3570–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-H.; Tian, X.; Li, Y.-J.; Wu, C.-A.; Zheng, C.-C. Microarray-Based Analysis of Stress-Regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA 2008, 14, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcikowska, B.; Jaskóła, K.; Gąsiorek, P.; Meus, M.; Nowak, K.; Gaj, M.D. LEAFY COTYLEDON2 (LEC2) Promotes Embryogenic Induction in Somatic Tissues of Arabidopsis, via YUCCA-Mediated Auxin Biosynthesis. Planta 2013, 238, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavattieri, M.A.; Frederico, A.M.; Lima, M.; Sabino, R.; Arnholdt-Schmitt, B. Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis as an Example of Stress-Related Plant Reactions. Electro. J. Biotech. 2010, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurczyńska, E.U.; Gaj, M.D.; Ujczak, A.; Mazur, E. Histological Analysis of Direct Somatic Embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Planta 2007, 226, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, M.D. Factors Influencing Somatic Embryogenesis Induction and Plant Regeneration with Particular Reference to Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant. Growth Regul. 2004, 43, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, W. Ethylene-Responsive miRNAs in Roots of Medicago truncatula Identified by High-Throughput Sequencing at Whole Genome Level. Plant. Sci. 2012, 184, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Chong, K.; Xu, Y. OsmiR396d Affects Gibberellin and Brassinosteroid Signaling to Regulate Plant Architecture in Rice. Plant. Physiol. 2018, 176, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; Shi, Z.; Luo, J.; Jiang, D.; Fan, F.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Blocking miR396 Increases Rice Yield by Shaping Inflorescence Architecture. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 15196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chu, J.; Yu, T.; Xu, Q.; Sun, X.; Yuan, J.; Xiong, G.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Tryptophan-Independent Auxin Biosynthesis Contributes to Early Embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. Usa 2015, 112, 4821–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Shi, B.; Hou, N.; Cao, Y.; Meng, Y.; Bian, H.; Zhu, M.; Han, N. MicroRNAs Participate in Gene Expression Regulation and Phytohormone Cross-Talk in Barley Embryo during Seed Development and Germination. Bmc Plant. Biol. 2017, 17, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Liu, Z.; Xing, L.; Wei, Y.; Mao, J.; Meng, Y.; Bao, L.; Han, M.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, D. MiRNAs Associated with Auxin Signaling, Stress Response, and Cellular Activities Mediate Adventitious Root Formation in Apple Rootstocks. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xue, B.; Gai, M.; Song, S.; Jia, N.; Sun, H. Small RNA and Transcriptome Sequencing Reveal a Potential miRNA-Mediated Interaction Network That Functions during Somatic Embryogenesis in Lilium pumilum DC. Fisch. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, B.H. GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR4 of Arabidopsis thaliana Is Required for Development of Leaves, Cotyledons, and Shoot Apical Meristem. J. Plant. Biol. 2006, 49, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewezi, T.; Maier, T.R.; Nettleton, D.; Baum, T.J. The Arabidopsis MicroRNA396-GRF1/GRF3 Regulatory Module Acts as a Developmental Regulator in the Reprogramming of Root Cells during Cyst Nematode Infection. Plant. Physiol. 2012, 159, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.-H.; Chiang-Hsieh, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-A.; Chow, C.-N.; Wu, N.-Y.; Hou, P.-F.; Chang, W.-C. AtmiRNET: A Web-Based Resource for Reconstructing Regulatory Networks of Arabidopsis microRNAs. Database 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ren, N.; Wang, H.; Stromberg, A.J.; Perry, S.E. Global Identification of Targets of the Arabidopsis MADS Domain Protein AGAMOUS-Like15. Plant. Cell Online 2009, 21, 2563–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Mejia-Guerra, M.K.; Kurz, K.; Liang, X.; Welch, L.; Grotewold, E. AGRIS: The Arabidopsis Gene Regulatory Information Server, an update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D1118–D1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.L.; Kwong, L.W.; Yee, K.M.; Pelletier, J.; Lepiniec, L.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Harada, J.J. LEAFY COTYLEDON2 Encodes a B3 Domain Transcription Factor that Induces Embryo Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2001, 98, 11806–11811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, M.D. Direct Somatic Embryogenesis as a Rapid and Efficient System for In Vitro Regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant. Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2001, 64, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamborg, O.L.; Miller, R.A.; Ojima, K. Nutrient Requirements of Suspension Cultures of Soybean Root Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1968, 50, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bric, J.M.; Bostock, R.M.; SILVERSTONEt, S.E. Rapid In Situ Assay for Indoleacetic Acid Production by Bacteria Immobilized on a Nitrocellulose Membrane. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 535–538. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szczygieł-Sommer, A.; Gaj, M.D. The miR396–GRF Regulatory Module Controls the Embryogenic Response in Arabidopsis via an Auxin-Related Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205221
Szczygieł-Sommer A, Gaj MD. The miR396–GRF Regulatory Module Controls the Embryogenic Response in Arabidopsis via an Auxin-Related Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(20):5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205221
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzczygieł-Sommer, Aleksandra, and Małgorzata D. Gaj. 2019. "The miR396–GRF Regulatory Module Controls the Embryogenic Response in Arabidopsis via an Auxin-Related Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 20: 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205221
APA StyleSzczygieł-Sommer, A., & Gaj, M. D. (2019). The miR396–GRF Regulatory Module Controls the Embryogenic Response in Arabidopsis via an Auxin-Related Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(20), 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205221




