Antitumor Activity of a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor AIU2001 Due to Abrogation of the DNA Damage Repair in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. AIU2001 Inhibited the Proliferation of Human NSCLC Cells
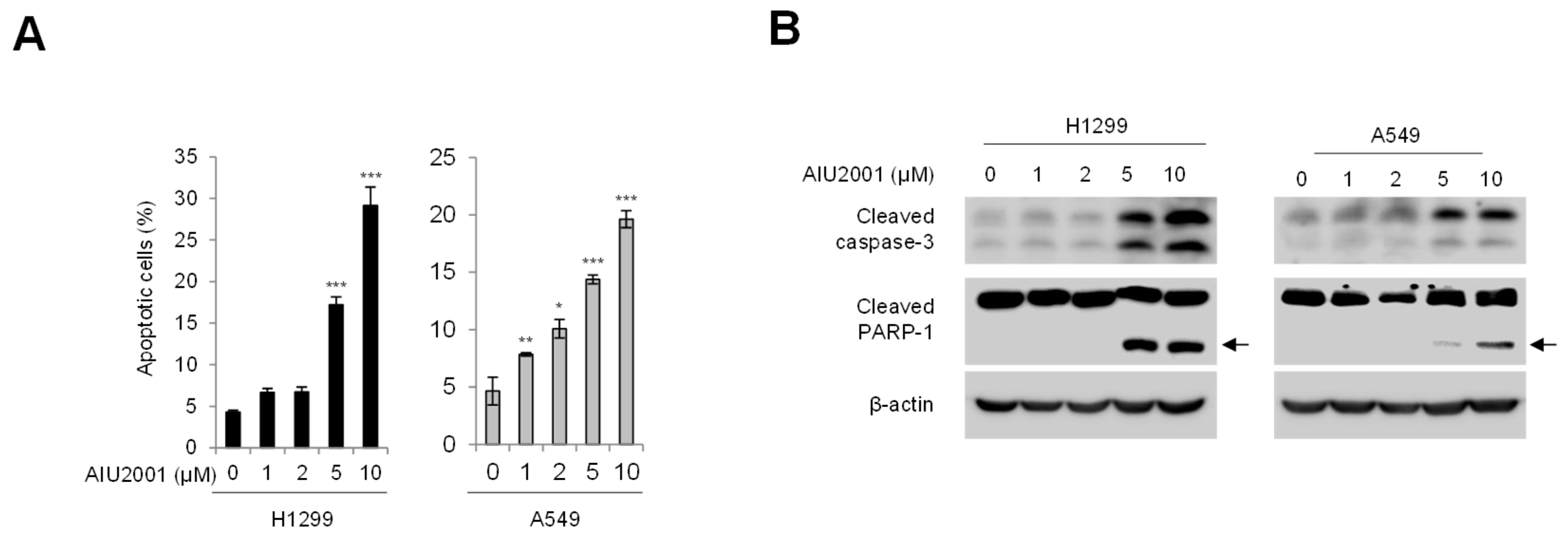
2.2. AIU2001 Increased Apoptotic Cell Death in Human NSCLC Cells
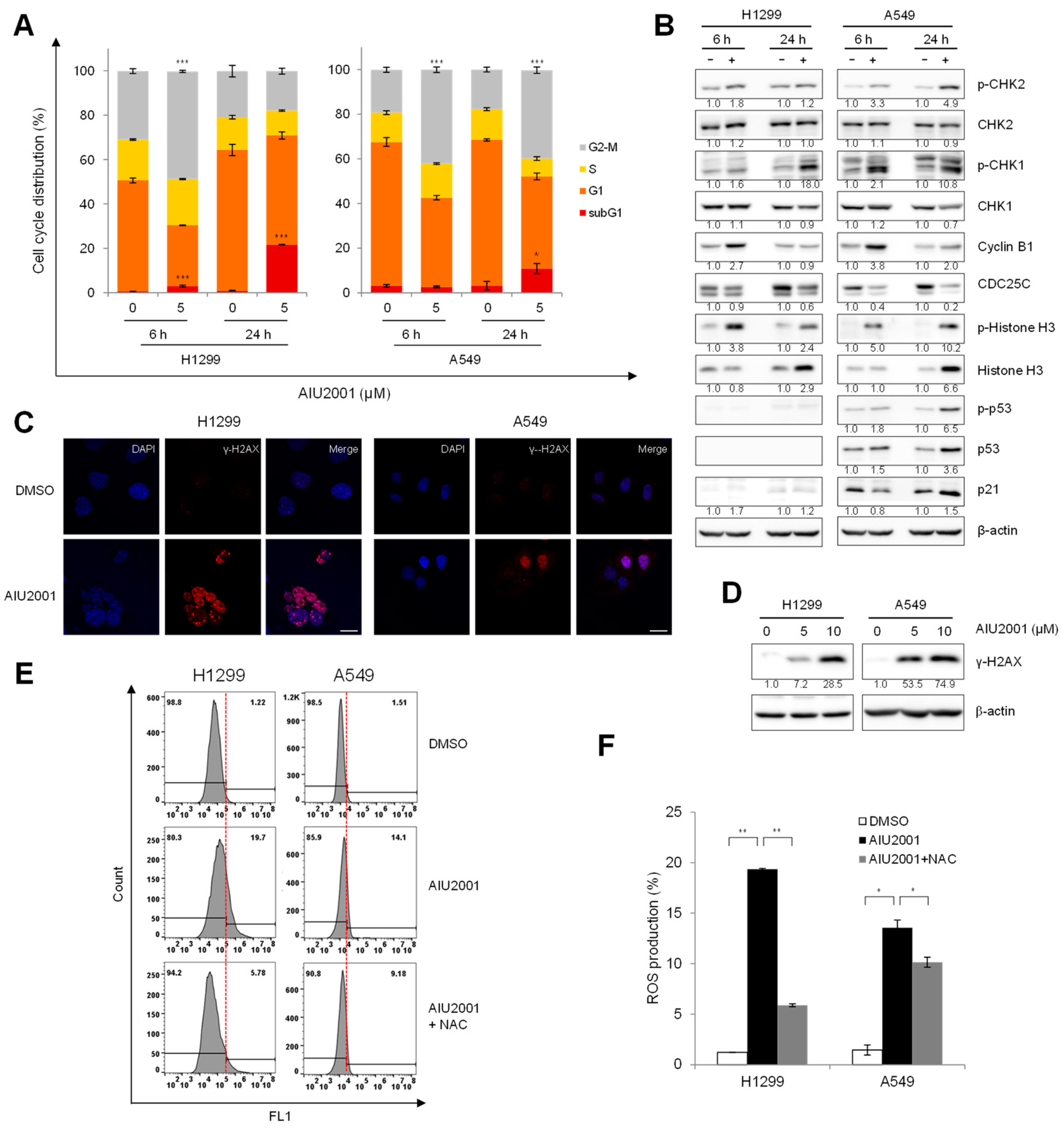
2.3. AIU2001 Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Suppressed DNA Damage Repair
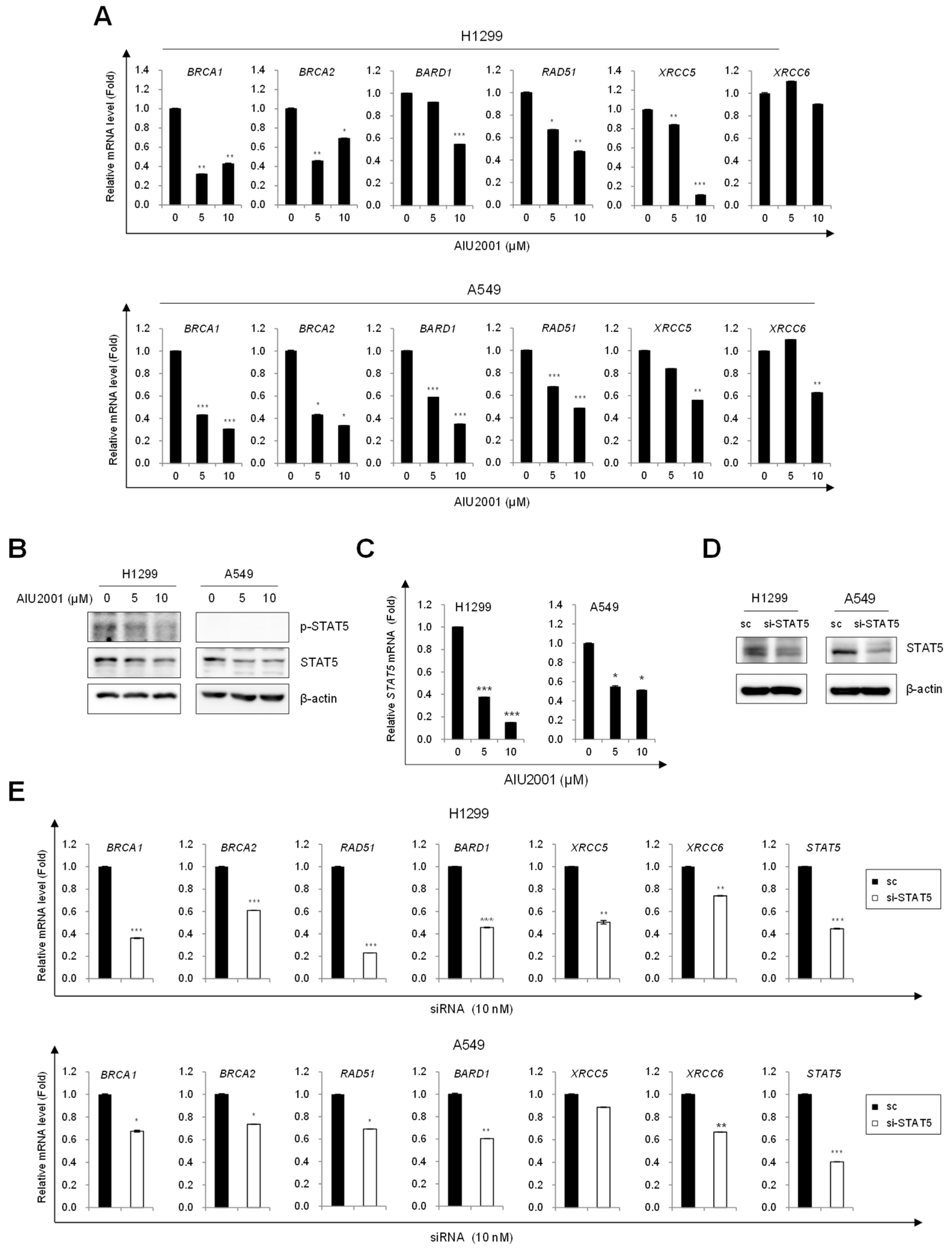
2.4. AIU2001 Induced DNA Damage and Suppressed DNA Damage Repair in NSCLC Cells
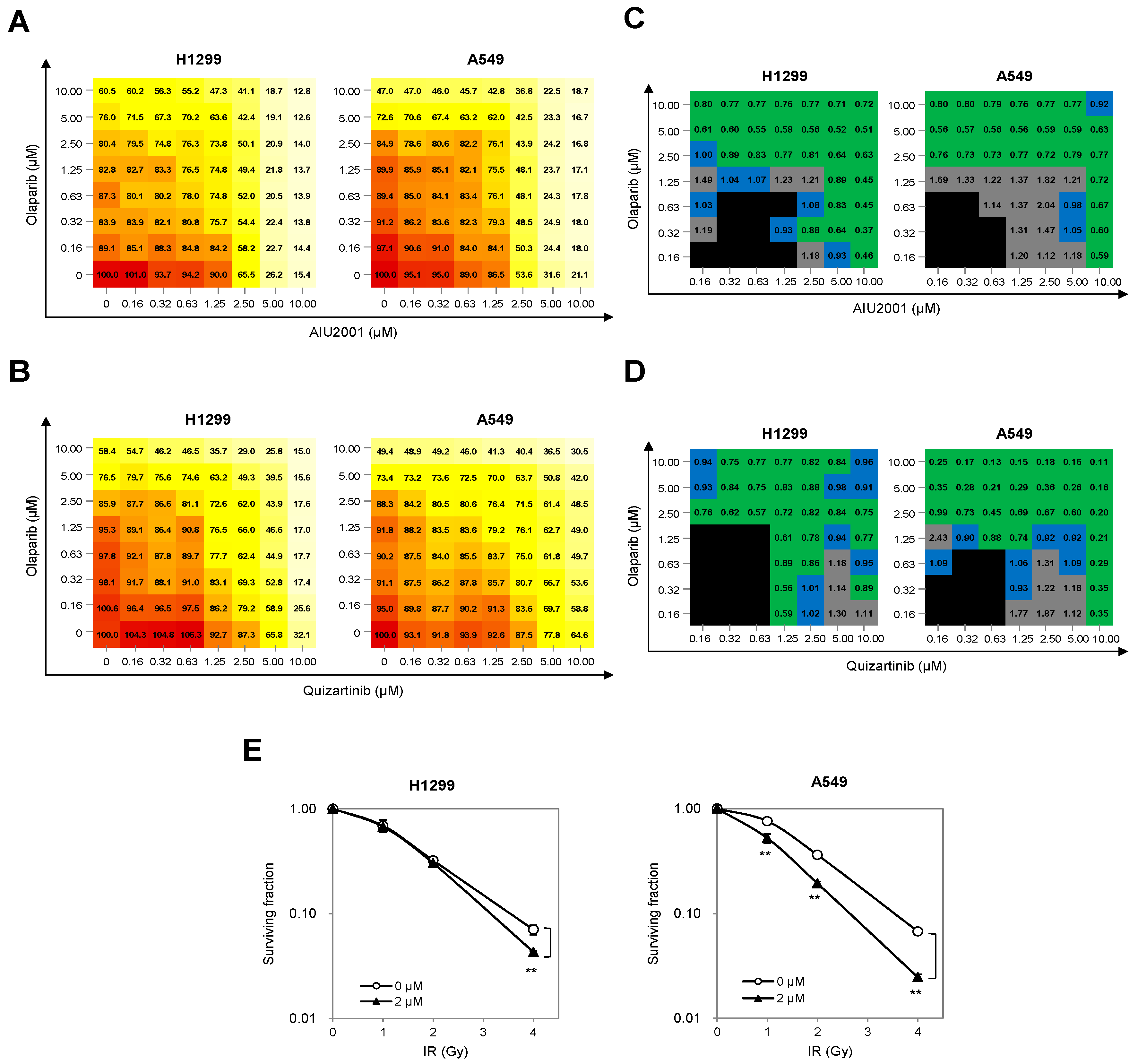
2.5. Combination of AIU2001 and a PARP Inhibitor or IR Synergistically Inhibited the Growth of H1299 and A549 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Synthesis
4.2. Prediction of Drug-Protein Interactions
4.3. Reagents
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. In Vitro Kinase Assay
4.7. Immunoblot Analysis
4.8. Annexin V/PI-Based Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.9. Cell Cycle Analysis
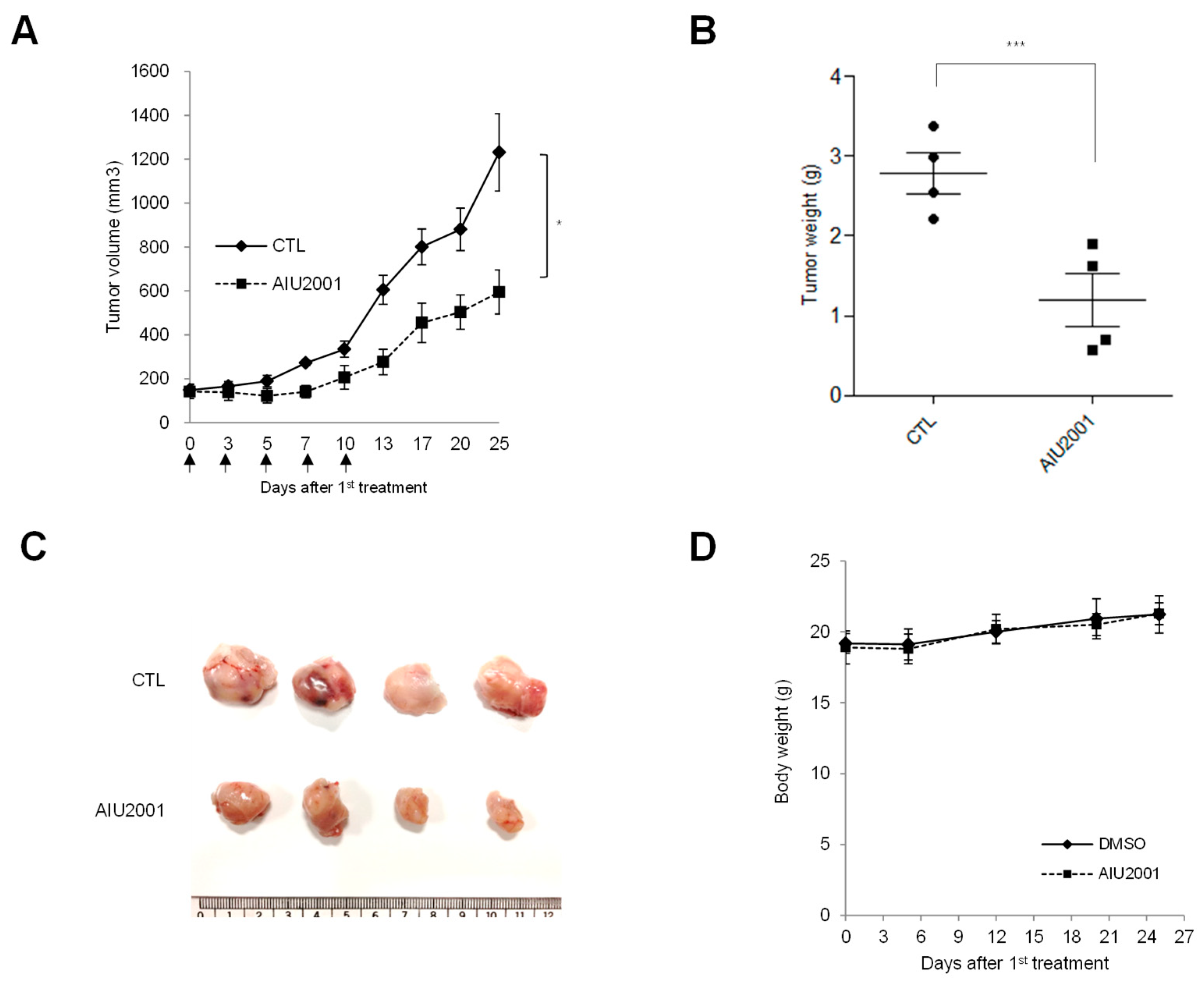
4.10. Tumor Xenograft Mouse Models
4.11. Tumor Measurement
4.12. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
4.13. Immunofluorescence and Foci Assay
4.14. Detection of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
4.15. Combination Index (CI)
4.16. Clonogenic Assay
4.17. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noone, A.M.; Howlader, N.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. (Eds.) SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975–2015; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015/ (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. Ca Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-L.; Li, S.-H.; Hsu, P.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Lin, T.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Fang, Y.-F.; Ko, H.-W.; Yu, C.-T.; et al. The efficacy of 40 mg versus dose de-escalation to less than 40 mg of afatinib (Giotrif) as the first-line therapy for patients with primary lung adenocarcinoma harboring favorable epidermal growth factor mutations. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97602–97612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraete, K.; Savvides, S.N. Extracellular assembly and activation principles of oncogenic class III receptor tyrosine kinases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, M.; Franciosi, V.; Ardizzoni, A. Multi-target inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2006, 17, ii55–ii57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.M. BAY 43-9006 Exhibits Broad Spectrum Oral Antitumor Activity and Targets the RAF/MEK/ERK Pathway and Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Involved in Tumor Progression and Angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7099–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, D.B.; Laird, A.D.; Xin, X.; Louie, S.G.; Christensen, J.G.; Li, G.; Schreck, R.E.; Abrams, T.J.; Ngai, T.J.; Lee, L.B.; et al. In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: Determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Sosman, J.A.; Lawrence, D.P.; McDermott, D.F.; Ramaiya, N.H.; Abbeele, A.D.V.D.; Linette, G.P.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Hodi, F.S. Phase 2 study of sunitinib in patients with metastatic mucosal or acral melanoma. Cancer 2015, 121, 4007–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, A.; Gore, L.; Messersmith, W.A.; Diab, S.; Jimeno, A.; Weekes, C.D.; Lewis, K.D.; Drabkin, H.A.; Flaig, T.W.; Camidge, D.R. A phase I study of sorafenib and vorinostat in patients with advanced solid tumors with expanded cohorts in renal cell carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffalorio, F.; Spitaleri, G.; Catania, C.; Zotto, L.D.; Noberasco, C.; Delmonte, A.; Santarpia, M.; Vecchio, F.; Brunelli, V.; Rampinelli, C.; et al. Phase ib of sorafenib in combination with everolimus in patients with advanced solid tumors, selected on the basis of molecular targets. Oncologist 2014, 19, 344–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, H.C.; Baxter, R.D.; Hunt, K.M.; Agarwal, J.; Elmets, C.A.; Athar, M.; Afaq, F. Fisetin, a phytochemical, potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis and abrogates tumor growth in athymic nude mice implanted with BRAF-mutated melanoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28296–28311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.M.; Mukerji, R.; Timmermann, B.N.; Samadi, A.K.; Cohen, M.S. A novel combination of withaferin A and sorafenib shows synergistic efficacy against both papillary and anaplastic thyroid cancers. Am. J. Surg. 2012, 204, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maifrede, S.; Nieborowska-Skorska, M.; Sullivan-Reed, K.; Dasgupta, Y.; Podszywalow-Bartnicka, P.; Le, B.V.; Solecka, M.; Lian, Z.; Belyaeva, E.A.; Nersesyan, A.; et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor–induced defects in DNA repair sensitize FLT3(ITD)-positive leukemia cells to PARP1 inhibitors. Blood 2018, 132, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Cheung, M.; Hunter, R.N., 3rd; Brown, M.L.; Veal, J.M.; Nolte, R.T.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Crosby, R.M.; Johnson, J.H.; et al. Discovery and evaluation of 2-anilino-5-aryloxazoles as a novel class of VEGFR2 kinase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorn, J.A.; Wang, Q.; Fujimura, E.; Barros, T.; Kuriyan, J. Crystal Structure of the FLT3 Kinase Domain Bound to the Inhibitor Quizartinib (AC220). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettle, J.G.; Anjum, R.; Barry, E.; Bhavsar, D.; Brown, C.; Boyd, S.; Campbell, A.; Goldberg, K.; Grondine, M.; Guichard, S.; et al. Discovery of N-(4-{[5-Fluoro-7-(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-yl]amino}phenyl)-2-[4-(propan-2-y l)-1 H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl]acetamide (AZD3229), a potent pan-KIT mutant inhibitor for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8797–8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik, T.M.; Keyomarsi, K. Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 59, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, G.R.; Taylor, W.R. Control of the G2/M transition. Mol. Biotechnol. 2006, 32, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.R.; Stark, G.R. Regulation of the G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinhardt, H.C.; Yaffe, M.B. Kinases that control the cell cycle in response to DNA damage: Chk1, Chk2, and MK2. Curr. Opin. Cell Boil. 2009, 21, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.J.; Fukui, M.; Zhu, B.T. Role of Cyclin B1/Cdc2 Up-Regulation in the Development of Mitotic Prometaphase Arrest in Human Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Nocodazole. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Ren, H.; Xiao, W.; Chu, Z.; Lee, J.J.; Mao, L. Antitumor activity of AZ64 via G2/M arrest in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1798–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ling, Y.-H.; Liebes, L.; Jiang, J.-D.; Holland, J.F.; Elliott, P.J.; Adams, J.; Muggia, F.M.; Perez-Soler, R. Mechanisms of proteasome inhibitor PS-341-induced G(2)-M-phase arrest and apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug Combination Studies and Their Synergy Quantification Using the Chou-Talalay Method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokota, S.; Kiyoi, H.; Nakao, M.; Iwai, T.; Misawa, S.; Okuda, T.; Sonoda, Y.; Abe, T.; Kahsima, K.; Matsuo, Y.; et al. Internal tandem duplication of the FLT3 gene is preferentially seen in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome among various hematological malignancies. A study on a large series of patients and cell lines. Leukemia 1997, 11, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohl, T.M.; Schnittger, S.; Ellwart, J.W.; Hiddemann, W.; Spiekermann, K. KIT exon 8 mutations associated with core-binding factor (CBF)-acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cause hyperactivation of the receptor in response to stem cell factor. Blood 2005, 105, 3319–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissel, N.; Leroy, H.; Brethon, B.; Philippe, N.; de Botton, S.; Auvrignon, A.; Raffoux, E.; Leblanc, T.; Thomas, X.; Hermine, O.; et al. Incidence and prognostic impact of c-Kit, FLT3, and Ras gene mutations in core binding factor acute myeloid leukemia (CBF-AML). Leukemia 2006, 20, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadopoulos, K.P.; Ben-Ami, E.; Patnaik, A.; Trone, D.; Li, J.; Demetri, G.D. Safety and tolerability of quizartinib, a FLT3 inhibitor, in advanced solid tumors: A phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Bmc Cancer 2018, 18, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallmyr, A.; Fan, J.; Datta, K.; Kim, K.-T.; Grosu, D.; Shapiro, P.; Small, D.; Rassool, F. Internal tandem duplication of FLT3 (FLT3/ITD) induces increased ROS production, DNA damage, and misrepair: Implications for poor prognosis in AML. Blood 2008, 111, 3173–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, R.V.N.; Brabender, J.; Gandara, D.; Alberola, V.; Camps, C.; Domine, M.; Cardenal, F.; Sánchez, J.M.; Gumerlock, P.H.; Tarón, M.; et al. Low ERCC1 expression correlates with prolonged survival after cisplatin plus gemcitabine chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar]
- Rosell, R.; Lord, R.V.N.; Taron, M.; Reguart, N. DNA repair and cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2002, 38, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Velculescu, V.E.; Zhou, S.; Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Kinzler, K.W. Cancer genome landscapes. Science 2013, 339, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating Mutations in the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Underlying Responsiveness of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer to Gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riely, G.J.; Marks, J.; Pao, W. KRAS Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2009, 6, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimutho, M.; Bain, A.L.A.L.; Mukherjee, B.; Nag, P.; Nanayakkara, D.M.; Harten, S.K.; Harris, J.L.; Subramanian, G.N.; Sinha, D.; Shirasawa, S.; et al. Enhanced dependency of KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer cells on RAD51-dependent homologous recombination repair identified from genetic interactions inSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 470–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulany, M.; Kehlbach, R.; Florczak, U.; Sak, A.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Lobrich, M.; Rodemann, H.P. Targeting of AKT1 enhances radiation toxicity of human tumor cells by inhibiting DNA-PKcs-dependent DNA double-strand break repair. Mol. Cancer 2008, 7, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueck, K.; Rebholz, S.; Harati, M.D.; Rodemann, H.P.; Toulany, M. Akt1 Stimulates Homologous Recombination Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in a Rad51-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liccardi, G.; Hartley, J.A.; Hochhauser, D. EGFR nuclear translocation modulates DNA repair following cisplatin and ionizing radiation treatment. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, K.; Mayer, C.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; Raju, U.; Milas, L.; Chen, D.J.; Kehlbach, R.; Rodemann, H.P. Radiation-induced Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Nuclear Import Is Linked to Activation of DNA-dependent Protein Kinase. J. Boil. Chem. 2005, 280, 31182–31189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Blais, N.; Mazieres, J.; Reck, M.; Jones, C.M.; Juhasz, E.; Urban, L.; Orlov, S.; Barlesi, F.; Kio, E.; et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II study of veliparib in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel for advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseright, T.; Mackey, M.; Rose, S.; Vinter, A. Molecular Field Extrema as Descriptors of Biological Activity: Definition and Validation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2006, 46, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
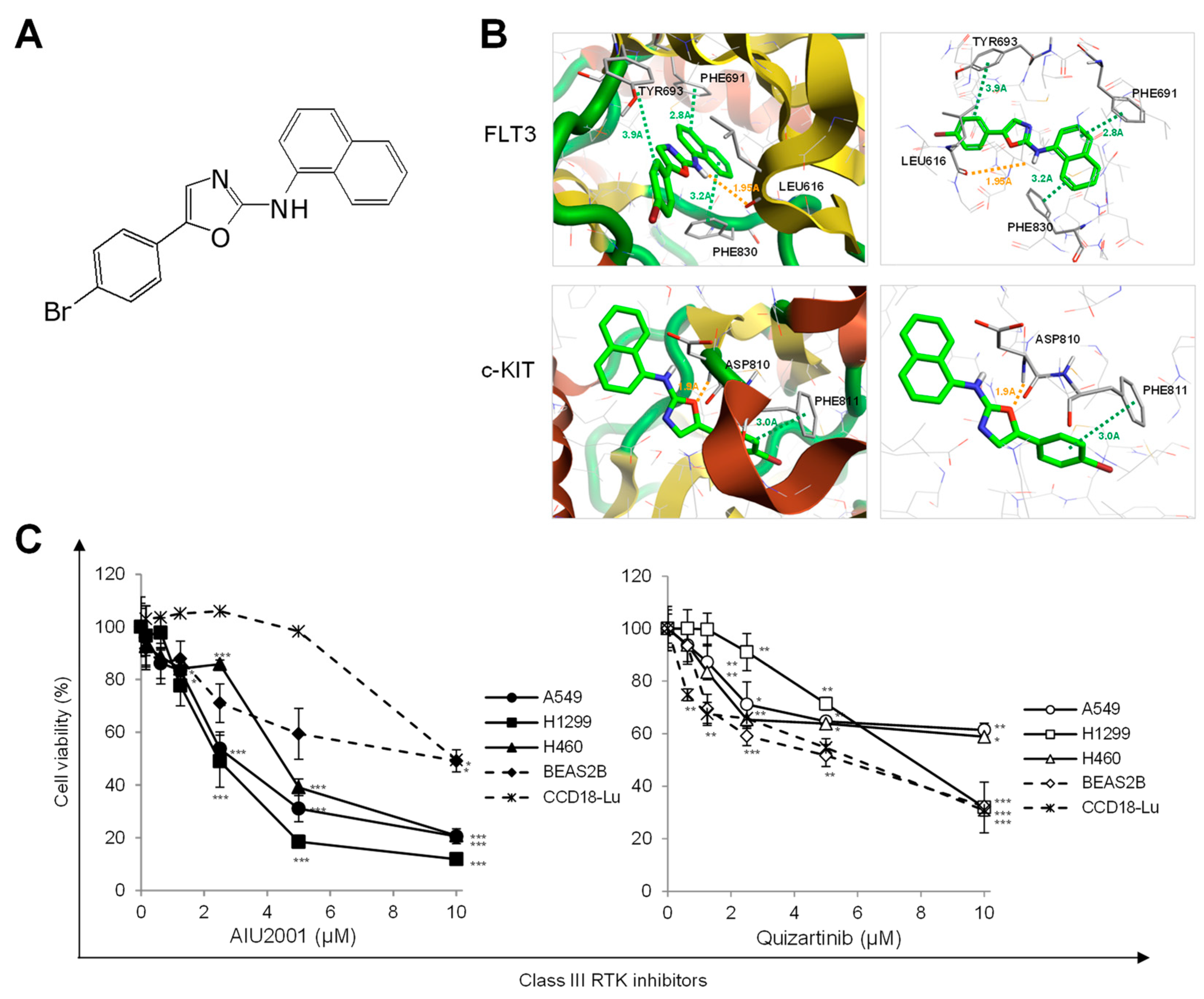
| Kinase | IC50 (nM) | Inhibitory Activity at 10 μM (%) |
|---|---|---|
| FLT3 | 206.4 | 92 |
| FLT3 (D835Y) | 108.1 | 75 |
| FLT3 (ITD) | 63.2 | 98 |
| FLT4 | 785.5 | 81 |
| c-KIT | 223.3 | 88 |
| c-KIT (V560G) | 53.4 | 91 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, H.; Choi, H.-K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, A.-Y.; Song, J.-Y.; Hwang, S.-G.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, D.-U.; Kim, E.-H.; Kim, J.; et al. Antitumor Activity of a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor AIU2001 Due to Abrogation of the DNA Damage Repair in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194728
Ryu H, Choi H-K, Kim HJ, Kim A-Y, Song J-Y, Hwang S-G, Kim J-S, Kim D-U, Kim E-H, Kim J, et al. Antitumor Activity of a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor AIU2001 Due to Abrogation of the DNA Damage Repair in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194728
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Hwani, Hyun-Kyung Choi, Hyo Jeong Kim, Ah-Young Kim, Jie-Young Song, Sang-Gu Hwang, Jae-Sung Kim, Da-Un Kim, Eun-Ho Kim, Joon Kim, and et al. 2019. "Antitumor Activity of a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor AIU2001 Due to Abrogation of the DNA Damage Repair in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194728
APA StyleRyu, H., Choi, H.-K., Kim, H. J., Kim, A.-Y., Song, J.-Y., Hwang, S.-G., Kim, J.-S., Kim, D.-U., Kim, E.-H., Kim, J., & Ahn, J. (2019). Antitumor Activity of a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor AIU2001 Due to Abrogation of the DNA Damage Repair in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194728





