Directed Evolution of Clostridium thermocellum β-Glucosidase A Towards Enhanced Thermostability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
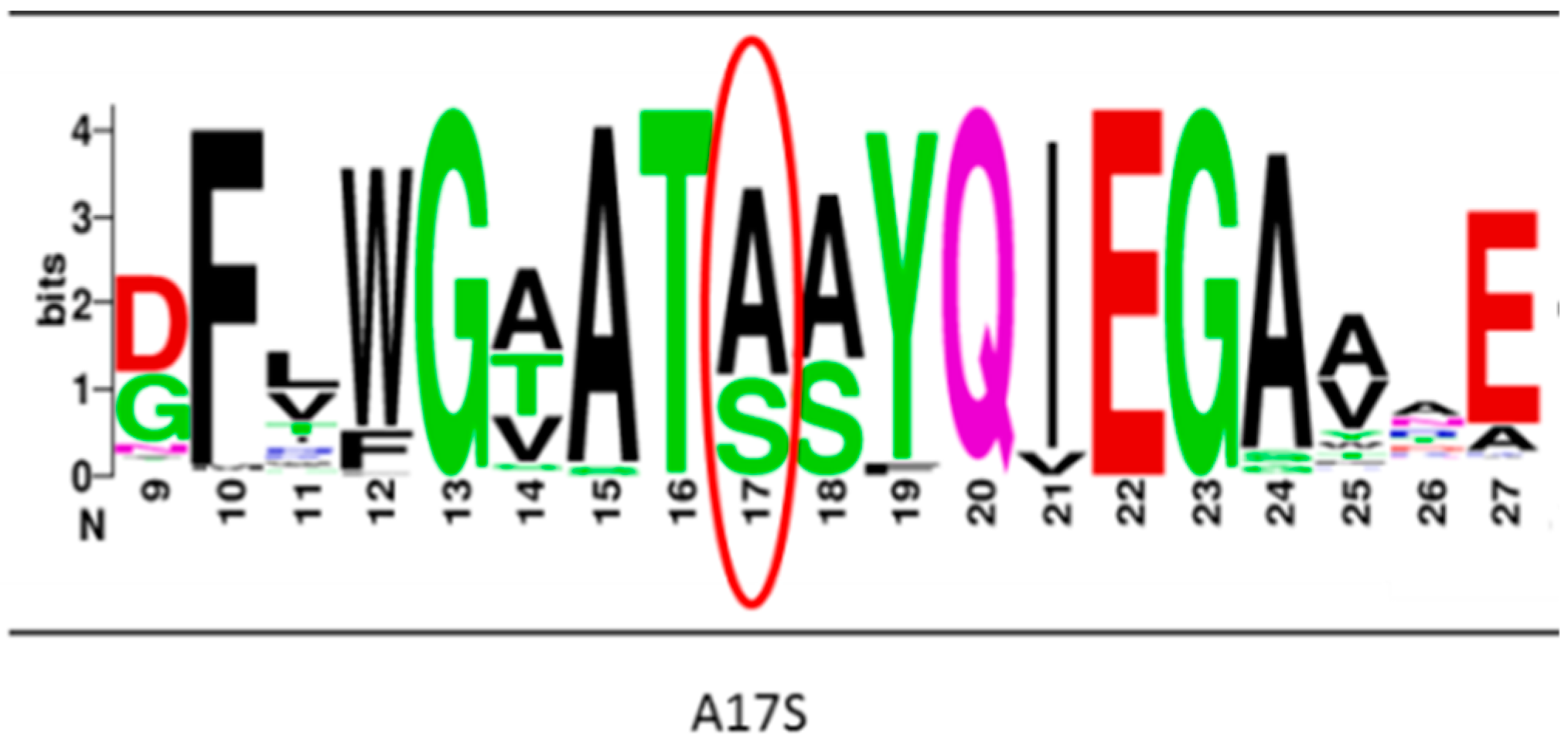
2.1. Construction and Screening of C. Thermocellum BglA Clones Library
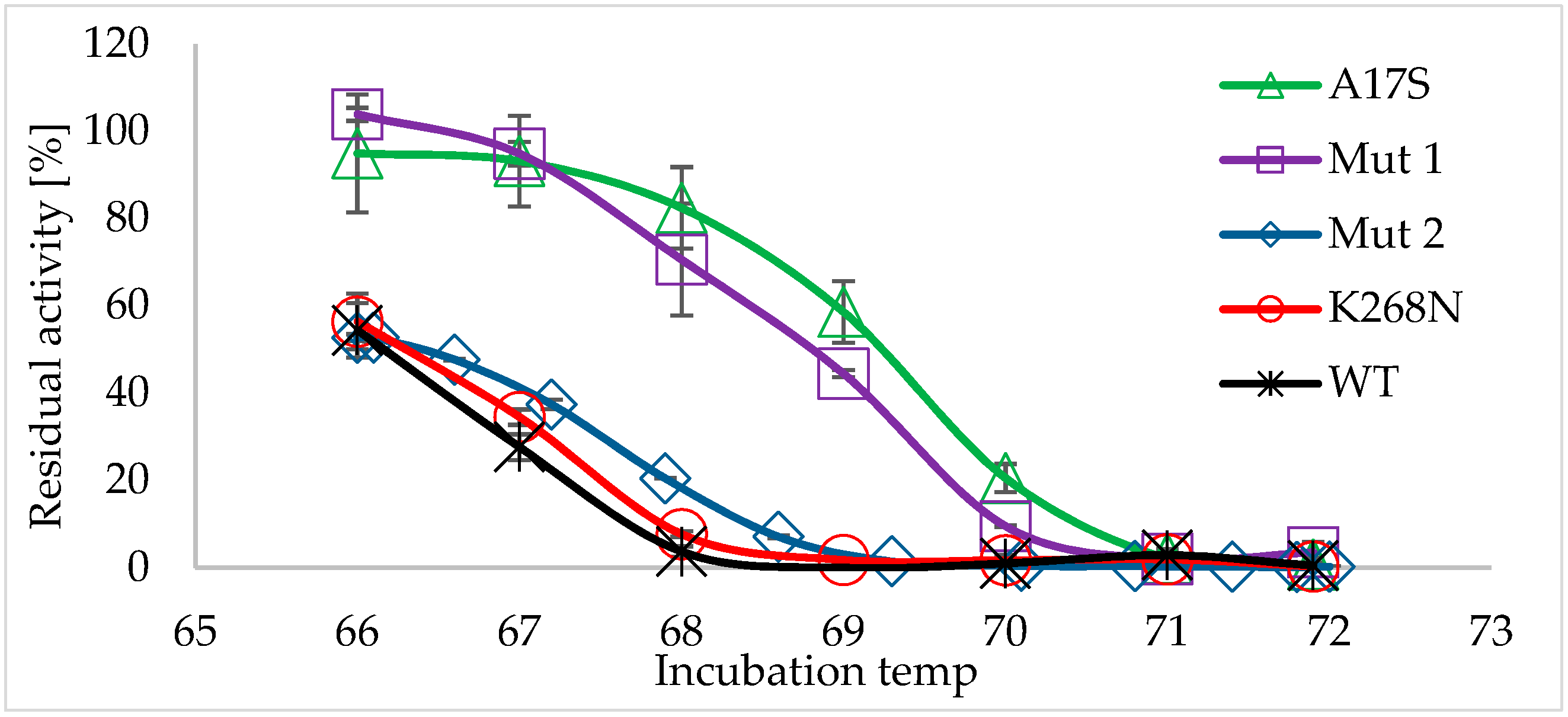
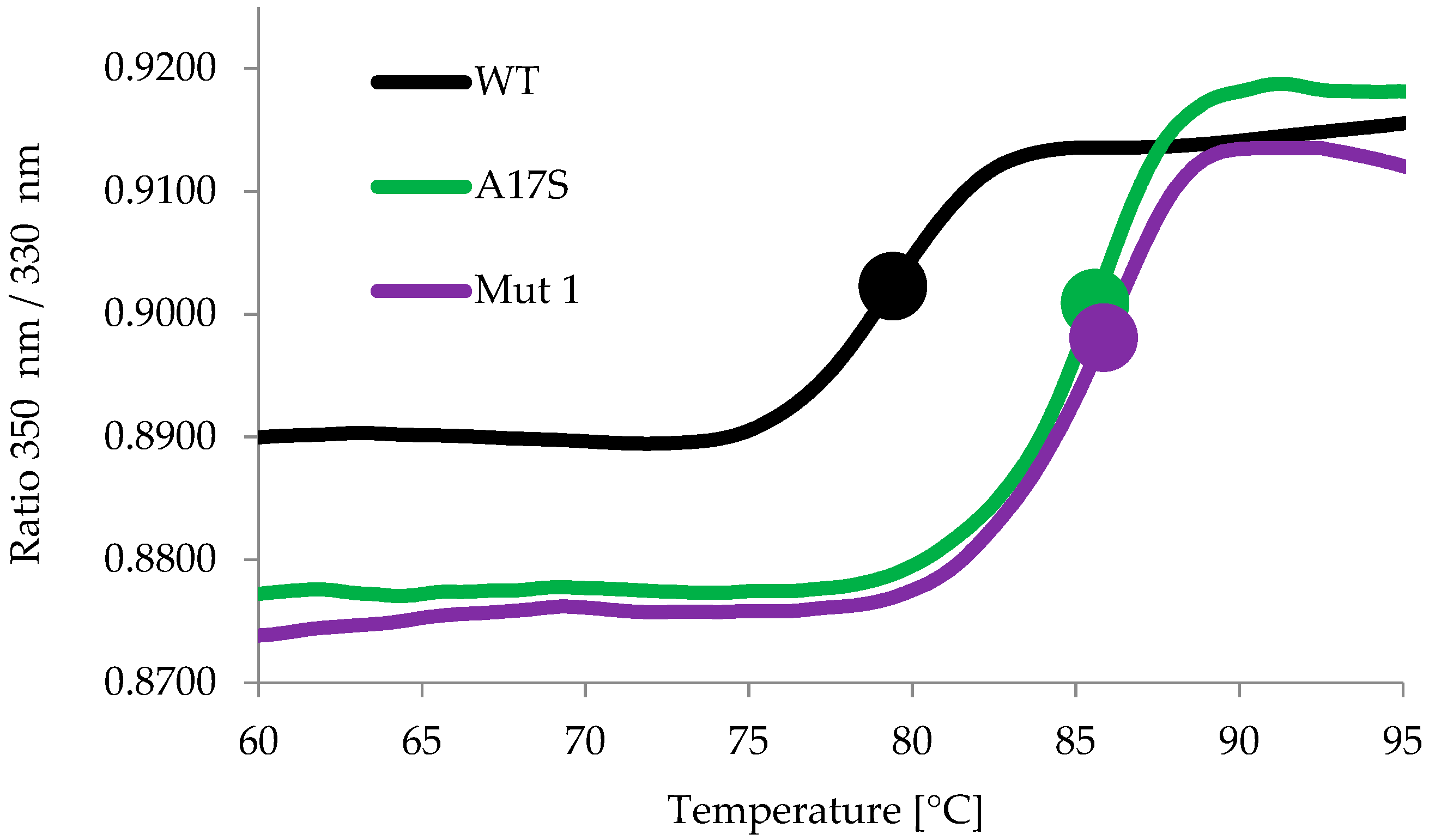
2.2. Characterization of the Thermostable Mutants
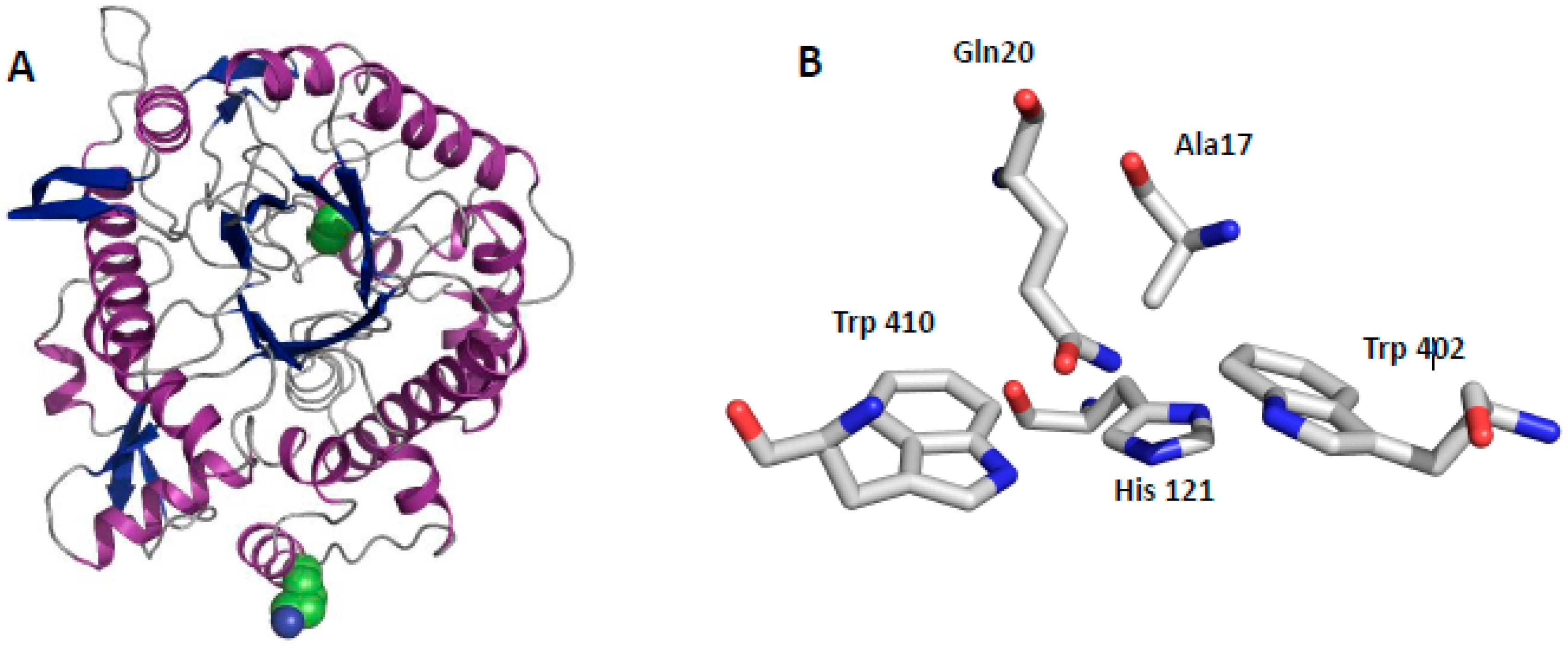
2.3. Structural Aspects of BglA
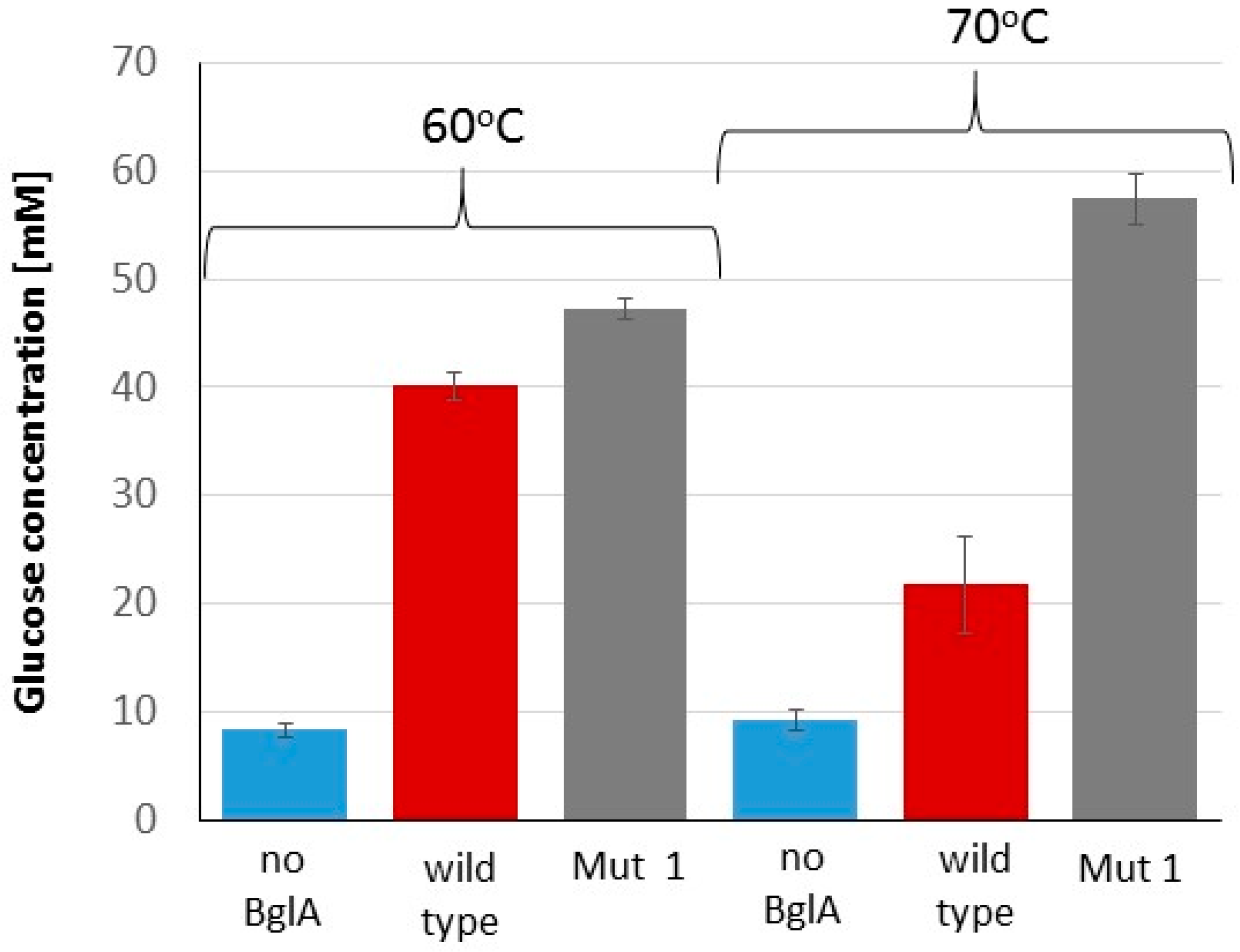
2.4. Advantage of Thermostable BglA in the Cellulose Hydrolysis Process
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Random Mutagenesis and Library Construction
4.2. Screening for Thermostable Clones
4.3. Residual Activity of Overexpressing BglA Colonies
4.4. Protein Expression and Purification
4.5. Stability Assay
4.6. Kinetic Parameters Measurements
4.7. Sequence Analysis
4.8. Purification of the C. Thermocellum Secretome
4.9. Cellulose Hydrolysis Assay
4.10. Ti Measurements
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BglA | β-glucosidase A |
| pNPG | p-nitrophenyl-β-d-glucopyranoside |
| CBM | cellulose binding module |
References
- Bayer, E.A.; Shoham, Y.; Lamed, R. Lignocellulose-decomposing bacteria and their enzyme system. In The Prokaryotes, 4th ed.; Rosenberg, E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 216–266. [Google Scholar]
- Varrot, A.; Frandsen, T.P.; Von Ossowski, I.; Boyer, V.; Cottaz, S.; Driguez, H.; Schülein, M.; Davies, G.J. Structural Basis for Ligand Binding and Processivity in Cellobiohydrolase Cel6A from Humicola insolens. Structure 2003, 11, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viikari, L.; Vehmaanperä, J.; Koivula, A. Lignocellulosic ethanol: from science to industry. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 46, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Marcuschamer, D.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P.; Simmons, B.A.; Blanch, H.W. The challenge of enzyme cost in the production of lignocellulosic biofuels. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettolino, F.A.; Walsh, C.; Fincher, G.B.; Bacic, A. Determining the polysaccharide composition of plant cell walls. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1590–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauly, M.; Keegstra, K. Cell-wall carbohydrates and their modification as a resource for biofuels. Plant J. 2008, 54, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmel, M.E.; Xu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Ding, S.-Y.; Lamed, R.; Bayer, E.A. Microbial enzyme systems for biomass conversion: emerging paradigms. Biofuels 2010, 1, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, V.; Ramulu, H.G.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database ( CAZy ) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, S.J.; Vaaje-Kolstad, G.; Westereng, B.; Eijsink, V.G. Novel enzymes for the degradation of cellulose. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2012, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, H.J. Growth of the thermophilic bacterium Clostridium thermocellum in continuous culture. Curr. Microbiol. 1995, 31, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamed, R.; Kenig, R.; Setter, E.; Bayer, E.A. Major characteristics of the cellulolytic system of Clostridium thermocellum coincide with those of the purified cellulosome. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1985, 7, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrić, P.; Meyer, A.S.; Jensen, P.A.; Dam-Johansen, K. Effect and modeling of glucose inhibition and in situ glucose removal during enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated wheat straw. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, S.K.; Demain, A.L. Addition of cloned β-glucosidase enhances the degradation of crystalline cellulose by the Clostridium thermocellum cellulase complex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 161, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamed, R.; Kenig, R.; Morgenstern, E.; Calzada, J.F.; De Micheo, F.; Bayer, E.A. Efficient cellulose solubilization by a combined cellulosome-β-glucosidase system. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1991, 27, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, M.L.; Armstrong, L.; Leung, K.T.; Qin, W. Increased expression of β-glucosidase A in Clostridium thermocellum 27405 significantly increases cellulase activity. Bioengineered 2013, 4, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Decker, S.R. Special issue: Application of biotechnology for biofuels: transforming biomass to biofuels. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.P.; Lynd, L.R. A functionally based model for hydrolysis of cellulose by fungal cellulase. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 94, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzelman, P.; Snow, C.D.; Wu, I.; Nguyen, C.; Villalobos, A.; Govindarajan, S.; Minshull, J.; Arnold, F.H. A family of thermostable fungal cellulases created by structure-guided recombination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5610–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, R.H.; Kosugi, A. Cellulosomes: plant-cell-wall-degrading enzyme complexes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer-Schuette, S.E.; Brown, S.D.; Sander, K.B.; Bayer, E.A.; Kataeva, I.; Zurawski, J.V.; Conway, J.M.; Adams, M.W.W.; Kelly, R.M. Thermophilic lignocellulose deconstruction. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 393–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, A.; Felby, C.; Gama, M. Cellulase stability, adsorption/desorption profiles and recycling during successive cycles of hydrolysis and fermentation of wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 156, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Skovgaard, P.A.; Jørgensen, H. Influence of high temperature and ethanol on thermostable lignocellulolytic enzymes. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-banat, B.M.A.; Hoshida, H.; Ano, A.; Nonklang, S.; Akada, R. High-temperature fermentation: How can processes for ethanol production at high temperatures become superior to the traditional process using mesophilic yeast? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, I.; Arnold, F.H. Engineered thermostable fungal Cel6A and Cel7A cellobiohydrolases hydrolyze cellulose efficiently at elevated temperatures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, H.; Okada, K.; Onodera, T.; Ogasawara, W.; Okada, H.; Morikawa, Y. Directed evolution of endoglucanase III (Cel12A) from Trichoderma reesei. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.P. Engineering of Clostridium phytofermentans endoglucanase Cel5A for improved thermostability. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4914–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voutilainen, S.P.; Boer, H.; Alapuranen, M.; Jänis, J.; Vehmaanperä, J.; Koivula, A. Improving the thermostability and activity of Melanocarpus albomyces cellobiohydrolase Cel7B. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, D.L.; Lee, T.M.; Arnold, F.H. Engineered thermostable fungal cellulases exhibit efficient synergistic cellulose hydrolysis at elevated temperatures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 2390–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, E.A.; Belaich, J.P.; Shoham, Y.; Lamed, R. The cellulosomes: multienzyme machines for degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 58, 521–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbar, M.; Gul, O.; Lamed, R.; Sezerman, U.O.; Bayer, E.A. Improved thermostability of Clostridium thermocellum endoglucanase Cel8A by using consensus-guided mutagenesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3458–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbar, M.; Lamed, R.; Bayer, E.A. Thermostability enhancement of Clostridium thermocellum cellulosomal endoglucanase Cel8A by a single glycine substitution. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Pei, X.; Wu, Z. Introduction of glycine and proline residues onto protein surface increases the thermostability of endoglucanase CelA from Clostridium thermocellum. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3636–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Rentmeister, A.; Snow, C.D.; Wu, T.; Farrow, M.F.; Mingardon, F.; Arnold, F.H. A diverse set of family 48 bacterial glycoside hydrolase cellulases created by structure-guided recombination. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 4453–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataf, Y.; Yaron, S.; Stahl, F.; Lamed, R.; Bayer, E.A.; Scheper, T.; Sonenshein, A.; Shoham, Y. Cellodextrin and laminaribiose ABC transporters in Clostridium thermocellum. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, Y.; Huang, J.; Song, H.; Xu, J. Factors influencing cellulosome activity in Consolidated Bioprocessing of cellulosic ethanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9560–9569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Hong, J.; Bevan, D.R.; Zhang, Y.-H.P. Fast identification of thermostable beta-glucosidase mutants on cellobiose by a novel combinatorial selection/screening approach. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, R.E.; Sun, N.; Zhao, H. Directed evolution as a powerful synthetic biology tool. Methods 2013, 60, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J.K.; Uzelac, A.; Davis, D.F.; Eveleigh, D.E. Improved catalytic efficiency and active site modification of 1,4-beta-D-glucan glucohydrolase A from Thermotoga neapolitana by directed evolution. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11495–11502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrizubieta, M.J. Increased thermal resistance and modification of the catalytic properties of a beta -glucosidase by random mutagenesis and in vitro recombination. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28843–28848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierla, M.; Hõrak, H.; Overmyer, K.; Waszczak, C.; Yarmolinsky, D.; Maierhofer, T.; Vainonen, J.P.; Salojärvi, J.; Denessiouk, K.; Laanemets, K.; et al. The Receptor-like Pseudokinase GHR1 Is Required for Stomatal Closure[OPEN]. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 2813–2837. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen, J.; Bern, M.; Sand, K.M.K.; Grevys, A.; Dalhus, B.; Sandlie, I.; Andersen, J.T. Human and mouse albumin bind their respective neonatal Fc receptors differently. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, M.; Tschammer, N.; Breitsprecher, D. Quick protein binding analysis by label-free thermal shift analysis on the Tycho NT. 6. Available online: https://www.accela.eu/files/produc (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Moraïs, S.; Stern, J.; Kahn, A.; Galanopoulou, A.P.; Yoav, S.; Shamshoum, M.; Smith, M.A.; Hatzinikolaou, D.G.; Arnold, F.H.; Bayer, E.A. Enhancement of cellulosome-mediated deconstruction of cellulose by improving enzyme thermostability. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodina, A.; Godson, G.N. Role of conserved amino acids in the catalytic activity of Escherichia coli primase. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3614–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dokholyan, N.V.; Mirny, L.A.; Shakhnovich, E.I. Understanding conserved amino acids in proteins. Physica 2002, 314, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Daniel, R.M.; Dines, M.; Petach, H.H. The denaturation and degradation of stable enzymes at high temperatures. Biochem. J. 1996, 317, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzelman, P.; Snow, C.D.; Smith, M.A.; Yu, X.; Kannan, A.; Boulware, K.; Villalobos, A.; Govindarajan, S.; Minshull, J.; Arnold, F.H. SCHEMA Recombination of a Fungal Cellulase Uncovers a Single Mutation That Contributes Markedly to Stability*. J. Boil. Chem. 2009, 284, 26229–26233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, P.J.; Badger, J.H.; Buldak, G.L.; Reich, C.I.; Woese, C.R.; Olsen, G.J. Thermal adaptation analyzed by comparison of protein sequences from mesophilic and extremely thermophilic Methanococcus species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3578–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Aparicio, J.; Hermoso, J.A.; Martínez-Ripoll, M.; Lequerica, J.L.; Polaina, J. Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase A from Bacillus polymyxa: insights into the catalytic activity in family 1 glycosyl hydrolases. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 275, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Candelas, L.; Aristoy, M.C.; Polaina, J.; Flors, A. Cloning and characterization of two genes from Bacillus polymyxa expressing beta-glucosidase activity in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 3173–3177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Chadha, B.S.; Kumar, B.A.; Ghatora, S.K.; Saini, H.S. Purification and characterization of ß-glucosidase from Melanocarpus sp. MTCC 3922. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 10, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, G.; Anbar, M.; Morag, E.; Lamed, R.; Bayer, E.A. Enhanced cellulose degradation by targeted integration of a cohesin-fused β-glucosidase into the Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10298–10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbar, M.; Bayer, E.A. Approaches for improving thermostability characteristics in cellulases. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 510, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 48–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Title | Wild Type | Mut 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Vmax [M·s−1] | 9.92 × 10−7 ± 6.57 × 10−8 | 9.1 × 10−7 ± 3.97 × 10−8 |
| Kcat [s−1] | 76 ± 5.036 | 70 ± 3.05 |
| Km [mM] | 6.7 ± 1.111 | 5 ± 0.59 |
| Kcat/Km [s−1·M−1] | 11,282 ± 900 | 14,018 ± 867 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoav, S.; Stern, J.; Salama-Alber, O.; Frolow, F.; Anbar, M.; Karpol, A.; Hadar, Y.; Morag, E.; Bayer, E.A. Directed Evolution of Clostridium thermocellum β-Glucosidase A Towards Enhanced Thermostability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194701
Yoav S, Stern J, Salama-Alber O, Frolow F, Anbar M, Karpol A, Hadar Y, Morag E, Bayer EA. Directed Evolution of Clostridium thermocellum β-Glucosidase A Towards Enhanced Thermostability. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194701
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoav, Shahar, Johanna Stern, Orly Salama-Alber, Felix Frolow, Michael Anbar, Alon Karpol, Yitzhak Hadar, Ely Morag, and Edward A. Bayer. 2019. "Directed Evolution of Clostridium thermocellum β-Glucosidase A Towards Enhanced Thermostability" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194701
APA StyleYoav, S., Stern, J., Salama-Alber, O., Frolow, F., Anbar, M., Karpol, A., Hadar, Y., Morag, E., & Bayer, E. A. (2019). Directed Evolution of Clostridium thermocellum β-Glucosidase A Towards Enhanced Thermostability. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194701






