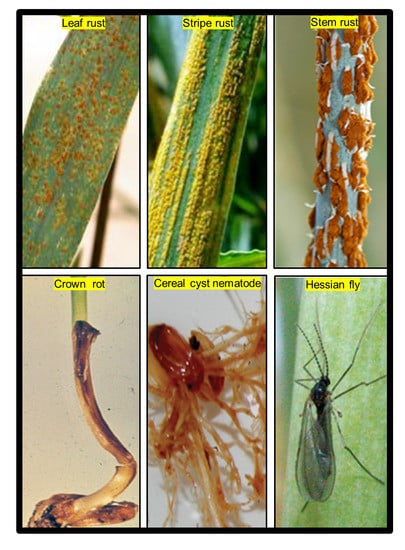
Genome-Wide Association Study for Multiple Biotic Stress Resistance in Synthetic Hexaploid Wheat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
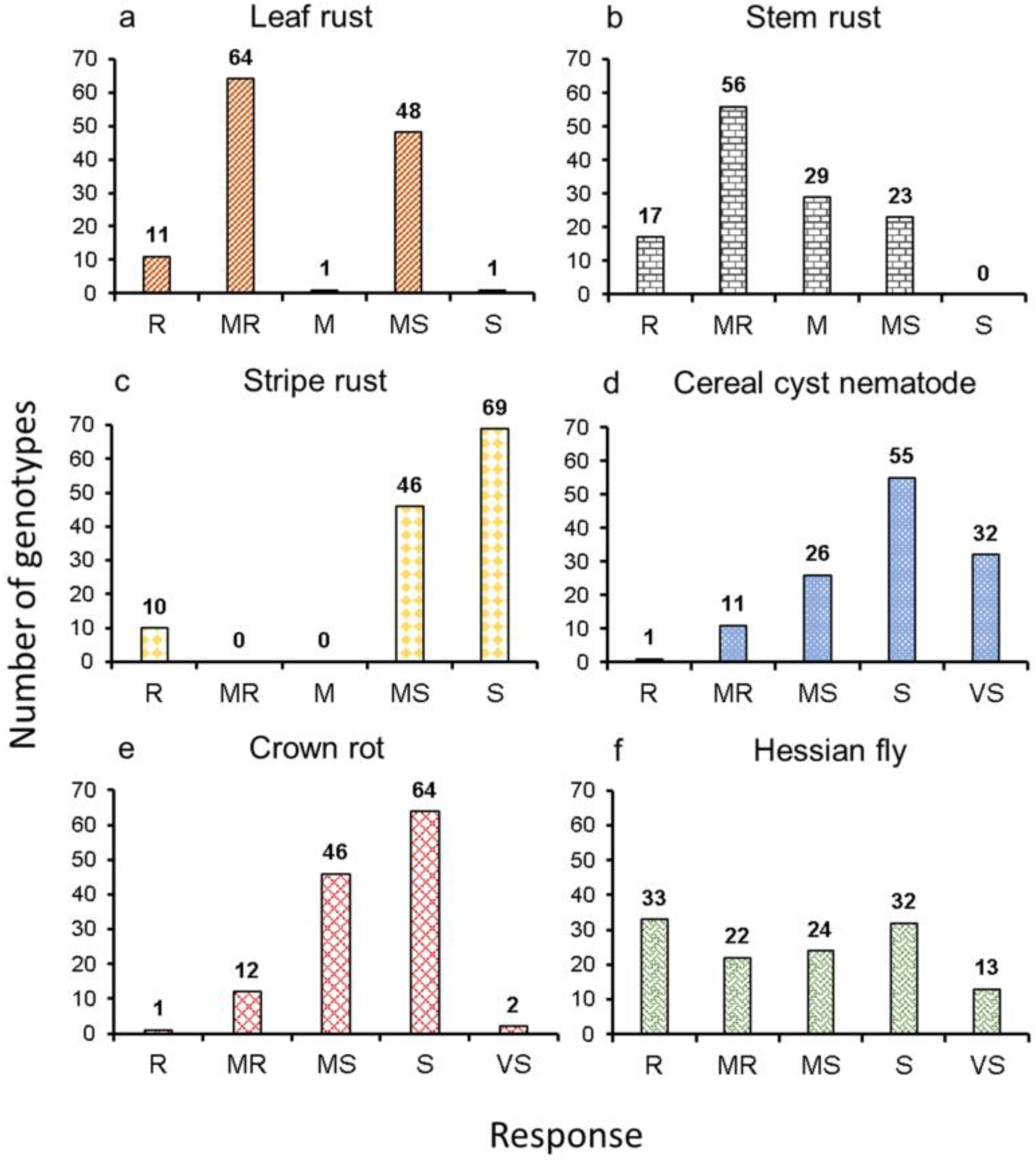
2.1. Phenotypic Distribution of Disease and Pest
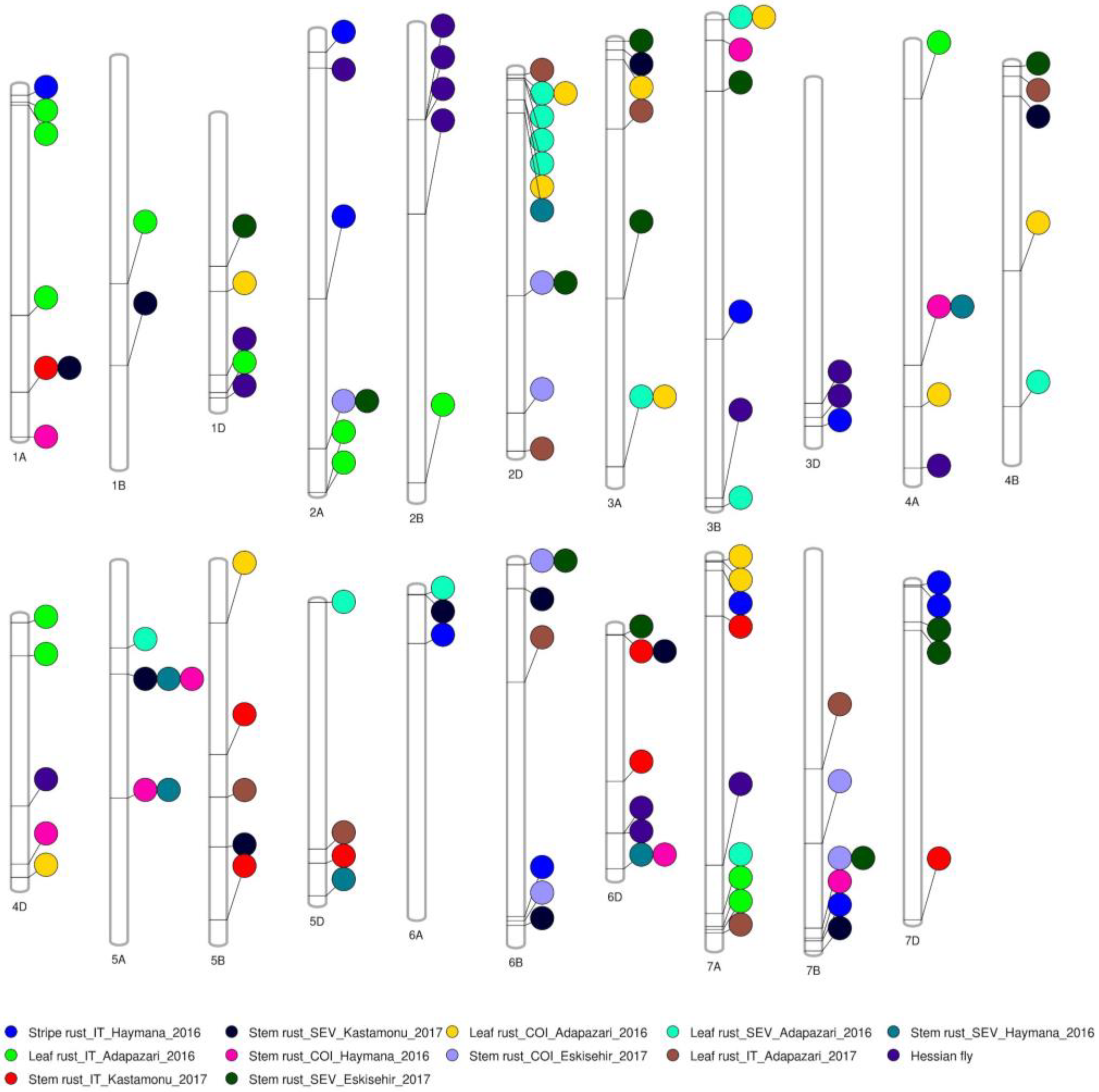
2.2. Genome-Wide Association Study
2.3. Genes Underlying Marker-Trait Associations and Their Functional Annotations
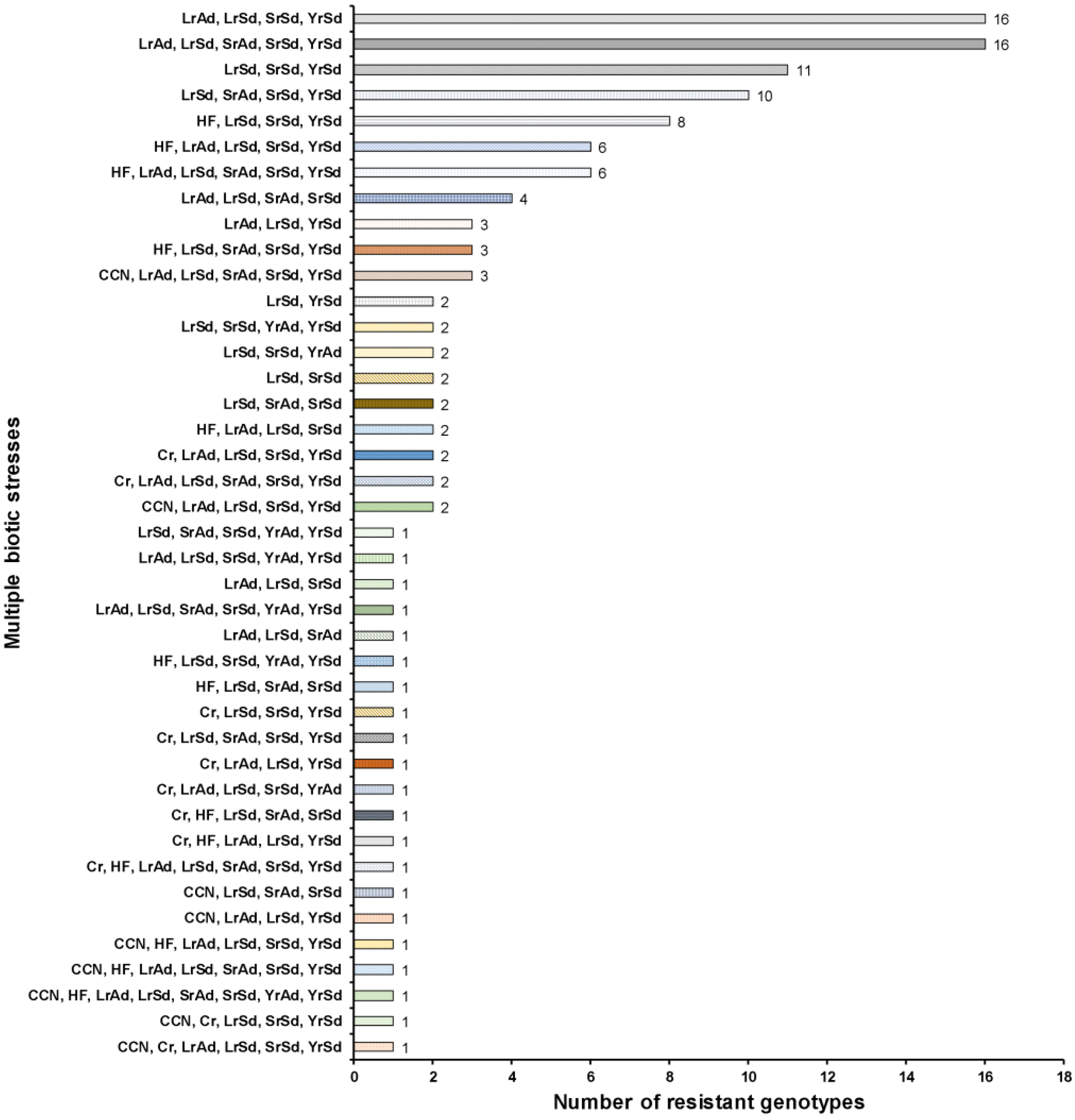
2.4. Multiple Stress Resistant Lines
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Genetic Resources
3.2. Evaluation of Disease and Insect Resistance
3.2.1. Seedling Resistance Screening for Leaf, Stem, and Stripe Rusts
3.2.2. Adult Plant Resistance Screening for Leaf, Stem, and Stripe Rusts
3.2.3. Cereal Cyst Nematode Resistance Screening
3.2.4. Crown Rot Resistance Screening
3.2.5. Hessian Fly Resistance Screening
3.3. Genotyping and SNP Discovery
3.4. Population Structure and Genome-Wide Association Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SHW | Synthetic hexaploid wheat |
| CCN | Cereal cyst nematode |
| Cr | Crown rot |
| HF | Hessian fly |
| Lr | Leaf rust |
| Sr | Stem rust |
| Yr | Stripe rust |
| GBS | Genotyping-by-sequencing |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| MTA | Marker-trait association |
| BLUE | Best linear unbiased estimate |
| PVE | Phenotypic variance explained |
| SEV | Field disease severity |
| COI | Coefficient of infection |
| IT | Infection type |
References
- World Food Situation. Available online: http://www.fao.org/worldfoodsituation/csdb/en/ (accessed on 8 August 2018).
- Poudel, R.; Bhatta, M. Review of Nutraceuticals and Functional Properties of Whole Wheat. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Population Prospects. 2017. Available online: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/Download/Standard/Population/ (accessed on 8 August 2018).
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatta, M.; Regassa, T.; Wegulo, S.N.; Baenziger, P.S. Foliar Fungicide Effects on Disease Severity, Yield, and Agronomic Characteristics of Modern Winter Wheat Genotypes. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, M.; Regassa, T. Seed Treatment Affected Yield and Economic Returns of Nebraska Winter Wheat Genotypes. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 9, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jighly, A.; Alagu, M.; Makdis, F.; Singh, M.; Singh, S.; Emebiri, L.C.; Ogbonnaya, F.C. Genomic regions conferring resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in synthetic hexaploid wheat. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Espino, J.; Singh, R.P.; Germán, S.; McCallum, B.D.; Park, R.F.; Chen, W.Q.; Bhardwaj, S.C.; Goyeau, H. Global status of wheat leaf rust caused by Puccinia triticina. Euphytica 2011, 179, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellings, C.R. Global status of stripe rust: A review of historical and current threats. Euphytica 2011, 179, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Hodson, D.P.; Jin, Y.; Lagudah, E.S.; Ayliffe, M.A.; Bhavani, S.; Rouse, M.N.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Szabo, L.J.; Huerta-Espino, J.; et al. Emergence and Spread of New Races of Wheat Stem Rust Fungus: Continued Threat to Food Security and Prospects of Genetic Control. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.L.; D’Arcy, C.J. Essential Plant Pathology, 2nd ed.; American Phytopathological Society: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nicol, J.M.; Turner, S.J.; Coyne, D.L.; den Nijs, L.; Hockland, S.; Maafi, Z.T. Current Nematode Threats to World Agriculture. In Genomics and Molecular Genetics of Plant-Nematode Interactions; Jones, J., Gheysen, G., Fenoll, C., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 21–43. [Google Scholar]
- Dababat, A.A.; Erginbaş-Orakci, G.; Toktay, H.; Imren, M.; Akin, B.; Braun, H.-J.; Dreisigacker, S.; ElekcioğLu, İ.H.; Morgounov, A. Resistance of winter wheat to Heterodera filipjevi in Turkey. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2014, 38, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dababat, A.A.; Ferney, G.B.H.; Erginbas-Orakci, G.; Dreisigacker, S.; Imren, M.; Toktay, H.; Elekcioglu, H.I.; Mekete, T.; Nicol, J.M.; Ansari, O.; et al. Association analysis of resistance to cereal cyst nematodes (Heterodera avenae) and root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus neglectus and P. thornei) in CIMMYT advanced spring wheat lines for semi-arid conditions. Breed. Sci. 2016, 66, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erginbas-Orakci, G.; Sehgal, D.; Sohail, Q.; Ogbonnaya, F.; Dreisigacker, S.; Pariyar, S.; Dababat, A.; Erginbas-Orakci, G.; Sehgal, D.; Sohail, Q.; et al. Identification of Novel Quantitative Trait Loci Linked to Crown Rot Resistance in Spring Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pan, Y.; Singh, P.K.; He, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, N.; Cheng, S.; Chen, F. Investigation and genome-wide association study for Fusarium crown rot resistance in Chinese common wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunali, B.; Nicol, J.M.; Hodson, D.; Uçkun, Z.; Büyük, O.; Erdurmuş, D.; Hekimhan, H.; Aktaş, H.; Akbudak, M.A.; Bağci, S.A. Root and Crown Rot Fungi Associated with Spring, Facultative, and Winter Wheat in Turkey. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, H.; Ammarellou, A.; Jafary, H. Incidence of crown rot disease of wheat cuased by Fusarium pseudograminearum as a new soil born fungal species in North West Iran. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 3606–3612. [Google Scholar]
- Smiley, R.W.; Gourlie, J.A.; Easley, S.A.; Patterson, L.M. Pathogenicity of Fungi Associated with the Wheat Crown Rot Complex in Oregon and Washington. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.A.; Burgess, L.W.; Ellison, F.W. The incidence and spatial patterns of wheat plants infected by Fusarium graminearum group 1 and the effect of crown rot on yield. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1991, 42, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, I.L.; Lamb, R.J.; McKenzie, R.I.H.; Whistlecraft, J.W. Resistance to Hessian fly (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in a Canadian spring wheat cultivar1. Can. Entomol. 2006, 138, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntin, G.D. Hessian Fly (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) Injury and Loss of Winter Wheat Grain Yield and Quality. J. Econ. Entomol. 1999, 92, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, A.; Bouhssini, M.E.; Lhaloui, S.; Cox, T.S.; Hatchett, J.H. Estimates of yield loss due to the Hessian fly (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) on bread wheat using near-isogenic lines. Al Awamia 1992, 77, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lhaloui, S.; Buschman, L.; Bouhssini’, M.E.; Starks, K.; Kfith, D.; Houssaini, K.E. Control of Mayetiola species (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) with carbofuran in bread wheat, durum wheat and barley with yield loss assessment and its economic analysis. Al Awamia 1992, 77, 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatta, M.; Morgounov, A.; Belamkar, V.; Poland, J.; Baenziger, P.S. Unlocking the novel genetic diversity and population structure of synthetic hexaploid wheat. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbonnaya, F.C.; Abdalla, O.; Mujeeb-Kazi, A.; Kazi, A.G.; Xu, S.S.; Gosman, N.; Lagudah, E.S.; Bonnett, D.; Sorrells, M.E.; Tsujimoto, H. Synthetic Hexaploids: Harnessing Species of the Primary Gene Pool for Wheat Improvement. In Plant Breeding Reviews; Janick, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 35–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatta, M.; Morgounov, A.; Belamkar, V.; Baenziger, P. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Genomic Regions for Grain Yield and Yield-Related Traits in Drought-Stressed Synthetic Hexaploid Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgounov, A.; Abugalieva, A.; Akan, K.; Akın, B.; Baenziger, S.; Bhatta, M.; Dababat, A.A.; Demir, L.; Dutbayev, Y.; Bouhssini, M.E.; et al. High-yielding winter synthetic hexaploid wheats resistant to multiple diseases and pests. Plant Genet. Resour. 2018, 16, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, M.; Morgounov, A.; Belamkar, V.; Yorgancılar, A.; Baenziger, P.S. Genome-wide association study reveals favorable alleles associated with common bunt resistance in synthetic hexaploid wheat. Euphytica 2018, 214, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.K.; Bai, G.; Mujeeb-Kazi, A.; Rajaram, S. Genetic diversity among synthetic hexaploid wheat accessions (Triticum aestivum) with resistance to several fungal diseases. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2016, 63, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbonnaya, F.C.; Imtiaz, M.; Ye, G.; Hearnden, P.R.; Hernandez, E.; Eastwood, R.F.; van Ginkel, M.; Shorter, S.C.; Winchester, J.M. Genetic and QTL analyses of seed dormancy and preharvest sprouting resistance in the wheat germplasm CN10955. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 116, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, H.; Rasheed, A.; Makdis, F.; Badebo, A.; Ogbonnaya, F.C. Genome-Wide Association Mapping for Seedling and Adult Plant Resistance to Stripe Rust in Synthetic Hexaploid Wheat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, R.A.; Dubcovsky, J.; Rogers, J.W.; Morris, C.F.; Appels, R.; Xia, X. Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat: 2013-14 Supplement. Annu. Wheat Newsl. 2014, 58, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Rodriguez-Algaba, J.; Thach, T.; Sørensen, C.K.; Hansen, J.G.; Lassen, P.; Nazari, K.; Hodson, D.P.; Justesen, A.F.; Hovmøller, M.S. Yellow Rust Epidemics Worldwide Were Caused by Pathogen Races from Divergent Genetic Lineages. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.S.; Raupp, W.J.; Gill, B.S. Leaf Rust-Resistance Genes Lr41, Lr42, and Lr43 Transferred from Triticum tauschii to Common Wheat. Crop Sci. 1994, 34, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joukhadar, R.; El-Bouhssini, M.; Jighly, A.; Ogbonnaya, F.C. Genome-wide association mapping for five major pest resistances in wheat. Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Wang, M.; Wan, A.; Xia, C.; See, D.R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X. Virulence and Molecular Characterization of Experimental Isolates of the Stripe Rust Pathogen (Puccinia striiformis) Indicate Somatic Recombination. Phytopathology 2016, 107, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wu, J.; Yan, B.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Lyu, B.; Ni, F.; Caplan, A.; Wu, J.; Fu, D. Remapping of the stripe rust resistance gene Yr10 in common wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Yu, S.; Mu, J.; Huang, S.; Sela, H.; Distelfeld, A.; Huang, L.; et al. SNP-based pool genotyping and haplotype analysis accelerate fine-mapping of the wheat genomic region containing stripe rust resistance gene Yr26. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Bolus, S.; Rouse, M.N.; Dubcovsky, J. Identification and characterization of wheat stem rust resistance gene Sr21 effective against the Ug99 race group at high temperature. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickavelu, A.; Joukhadar, R.; Jighly, A.; Lan, C.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Stanikzai, A.S.; Kilian, A.; Singh, R.P.; Ban, T. Genome wide association mapping of stripe rust resistance in Afghan wheat landraces. Plant Sci. 2016, 252, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.M.I.; Sallam, A.; Belamkar, V.; Wegulo, S.; Bowden, R.; Jin, Y.; Mahdy, E.; Bakheit, B.; El-Wafaa, A.A.; Poland, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study for Identification and Validation of Novel SNP Markers for Sr6 Stem Rust Resistance Gene in Bread Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, O.; Unver, T.; Akkaya, M.S. Genes associated with resistance to wheat yellow rust disease identified by differential display analysis. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 71, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, E.; Achard, P.; Vansiri, A.; Potuschak, T.; Genschik, P. F-box proteins everywhere. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumayla; Sharma, S.; Kumar, R.; Mendu, V.; Singh, K.; Upadhyay, S.K. Genomic Dissection and Expression Profiling Revealed Functional Divergence in Triticum aestivum Leucine Rich Repeat Receptor Like Kinases (TaLRRKs). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1374. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Duan, Y.; Huang, L.; Kang, Z. Cloning and characterization of a calcium binding EF-hand protein gene TaCab1 from wheat and its expression in response to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici and abiotic stresses. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 3857–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliana, P.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, P.K.; Poland, J.A.; Bergstrom, G.C.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Bhavani, S.; Crossa, J.; Sorrells, M.E. Genome-wide association mapping for resistance to leaf rust, stripe rust and tan spot in wheat reveals potential candidate genes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1405–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seevers, P.M.; Daly, J.M.; Catedral, F.F. The Role of Peroxidase Isozymes in Resistance to Wheat Stem Rust Disease 1. Plant Physiol. 1971, 48, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayana, G.T.; Ali, S.; Sidhu, J.S.; Gonzalez Hernandez, J.L.; Turnipseed, B.; Sehgal, S.K. Genome-Wide Association Study for Spot Blotch Resistance in Hard Winter Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, M.; Baenziger, P.S.; Waters, B.M.; Poudel, R.; Belamkar, V.; Poland, J.; Morgounov, A. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Genomic Regions Associated with 10 Grain Minerals in Synthetic Hexaploid Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.A. Identification of Stem Rust Resistance in Three Synthetic Wheat Populations. Master’s Thesis, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, NE, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Stakman, E.C.; Stewart, D.M.; Loegering, W.Q. Identification of Physiologic Races of Puccinia Graminis var. Tritici; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1962; 617, pp. 8–51.
- Roelfs, A.P. Resistance to leaf and stem rusts in wheat. Chapter 2. In Proceedings of the Breeding Strategies for Resistance to the Rusts of Wheat, El Batan, Mexico, 29 June–1 July 1987. [Google Scholar]
- McNeal, F.H.; Konzak, C.F.; Smith, E.P.; Tate, W.S.; Russell, T.S. A Uniform System for Recording and Processing Cereal Research Data; USDA Bulletin Agric. Res. Serv.: Beltsville, MD, USA, 1971; pp. 34–121.
- Peterson, R.F.; Campbell, A.B.; Hannah, A.E. A Diagrammatic Scale for Estimating Rust Intensity on Leaves and Stems of Cereals. Can. J. Res. 1948, 26, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erginbas-Orakci, G.; Poole, G.; Nicol, J.M.; Paulitz, T.; Dababat, A.A.; Campbell, K. Assessment of inoculation methods to identify resistance to Fusarium crown rot in wheat. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2016, 123, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouhssini, M.; Chen, M.; Lhaloui, S.; Zharmukhamedova, G.; Rihawi, F. Virulence of Hessian fly (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in the Fertile Crescent. J. Appl. Entomol. 2009, 133, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaubitz, J.C.; Casstevens, T.M.; Lu, F.; Harriman, J.; Elshire, R.J.; Sun, Q.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL-GBS: A High Capacity Genotyping by Sequencing Analysis Pipeline. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium. Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 2018, 361, 7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of Population Structure Using Multilocus Genotype Data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huang, M.; Fan, B.; Buckler, E.S.; Zhang, Z. Iterative Usage of Fixed and Random Effect Models for Powerful and Efficient Genome-Wide Association Studies. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Trait a | SNP_ID b | PVE c | Allele d | Effect | −Log10(p) | Gene-ID | Potential Candidate Gene | Trait e | References f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yr | S3B_544810753 | 6.4 | G/A | −0.09 | 8.21 | TraesCS3B01G338200 | Calcium-binding protein | Yr | [46] |
| Lr | S4D_73425349 | 18.5 | C/T | 0.27 | 10.14 | TraesCS4D01G096900 | Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane neuronal protein 3 | Yr, Sr | [38,39,40] |
| Sr | S7B_706787545 | 15.1 | A/G | 15.54 | 7.95 | TraesCS7B01G441400 | ARM repeat superfamily protein | Tanspot | [47] |
| Yr | S2A_34483654 | 12.4 | T/G | −0.13 | 9.63 | TraesCS2A01G076700 | Elongation factor 1 alpha a | Yr | [43] |
| Yr | S2A_34483654 | 12.4 | T/G | −0.13 | 9.63 | TraesCS2A01G076800 | F-box protein | Lr, Sr, Yr | [41,42,43] |
| Yr | S7B_730117633 | 3.8 | C/A | −0.09 | 7.54 | TraesCS7B01G473300 | F-box protein | Lr, Sr, Yr | [41,42,43] |
| Sr | S1A_516079891 | 9.9 | G/C | −0.09 | 6.29 | TraesCS1A01G325300 | F-box protein | Lr, Sr, Yr | [41,42,43] |
| Yr | S6B_669910684 | 0.9 | C/G | 0.15 | 8.03 | TraesCS6B01G394600 | F-box protein | Lr, Sr, Yr | [41,42,43] |
| Sr | S5B_360428982 | 10.8 | T/C | −0.07 | 6.95 | TraesCS5B01G199700 | F-box protein | Lr, Sr, Yr | [41,42,43] |
| Lr | S5A_158912458 | 8.7 | G/A | −5.51 | 4.96 | TraesCS5A01G103000 | F-box protein | Lr, Sr, Yr | [41,42,43] |
| Lr | S7A_701569874 | 8.5 | A/G | 0.15 | 8.60 | TraesCS7A01G517300 | Leucine-rich repeat protein kinase family protein | Lr, Sr, Yr | [41,42,43] |
| Sr | S4B_4791631 | 3.0 | G/C | −6.10 | 7.43 | TraesCS4B01G007000 | Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase family protein | Sr, Yr | [38,39,40] |
| Sr | S2D_381953220 | 8.4 | G/T | 8.33 | 7.48 | TraesCS2D01G299700 | Peroxidase | Sr, Tanspot | [47,48] |
| Lr | S3A_721353764 | 14.6 | G/T | 3.51 | 7.78 | TraesCS3A01G495400 | Leucine rich repeat N-terminal domain | Sr, Yr | [38,39,40] |
| Sr | S1A_592532938 | 6.4 | G/A | −7.50 | 5.54 | TraesCS1A01G444500 | Leucine rich repeat N-terminal domain | Sr, Yr | [38,39,40] |
| Lr | S2D_644835165 | 1.4 | G/T | 0.07 | 5.89 | TraesCS2D01G586500 | WAT1-related protein/EamA-like transporter family | Fungal pathogen | [49] |
| Lr | S7A_708435571 | 19.4 | T/C | −0.18 | 8.20 | TraesCS7A01G526900 | WAT1-related protein/EamA-like transporter family | Fungal pathogen | [49] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhatta, M.; Morgounov, A.; Belamkar, V.; Wegulo, S.N.; Dababat, A.A.; Erginbas-Orakci, G.; Bouhssini, M.E.; Gautam, P.; Poland, J.; Akci, N.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study for Multiple Biotic Stress Resistance in Synthetic Hexaploid Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153667
Bhatta M, Morgounov A, Belamkar V, Wegulo SN, Dababat AA, Erginbas-Orakci G, Bouhssini ME, Gautam P, Poland J, Akci N, et al. Genome-Wide Association Study for Multiple Biotic Stress Resistance in Synthetic Hexaploid Wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(15):3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153667
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhatta, Madhav, Alexey Morgounov, Vikas Belamkar, Stephen N. Wegulo, Abdelfattah A. Dababat, Gül Erginbas-Orakci, Mustapha El Bouhssini, Pravin Gautam, Jesse Poland, Nilüfer Akci, and et al. 2019. "Genome-Wide Association Study for Multiple Biotic Stress Resistance in Synthetic Hexaploid Wheat" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 15: 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153667
APA StyleBhatta, M., Morgounov, A., Belamkar, V., Wegulo, S. N., Dababat, A. A., Erginbas-Orakci, G., Bouhssini, M. E., Gautam, P., Poland, J., Akci, N., Demir, L., Wanyera, R., & Baenziger, P. S. (2019). Genome-Wide Association Study for Multiple Biotic Stress Resistance in Synthetic Hexaploid Wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(15), 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153667






