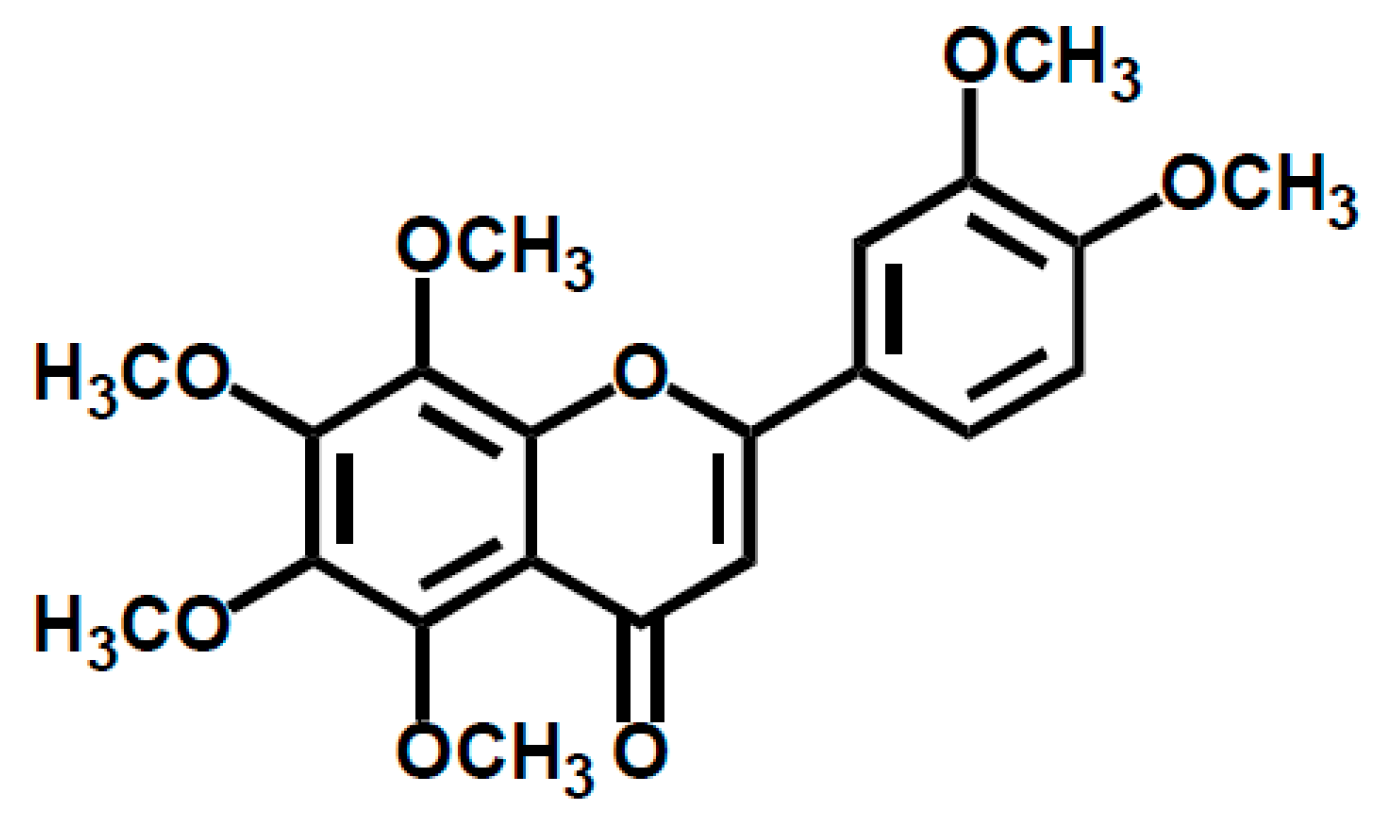
Potential Benefits of Nobiletin, A Citrus Flavonoid, against Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Effects of Nobiletin in Animal Models of AD
2.1. Olfactory-Bulbectomized Mice
2.2. Aβ-infused Rats
2.3. MK-801-Treated Mice
2.4. Senescence-Accelerated Mice
2.5. Amyloid Precursor Protein Tg Mice
2.6. 3XTg-AD Mice
2.7. Animal Models of Cerebral Ischemia
3. Effects of Nobiletin in Animal Models of PD
4. Effects of Nobiletin in Cultured Cells and Slices
4.1. Effects of Nobiletin on the cAMP/PKA/ERK/CREB Signaling Pathway
4.2. Effects of Nobiletin on Oxidative Stress and ER Stress
4.3. Effects of Nobiletin on Neuroinflammation
4.4. Effects of Nobiletin on Aβ Generation and Degradation
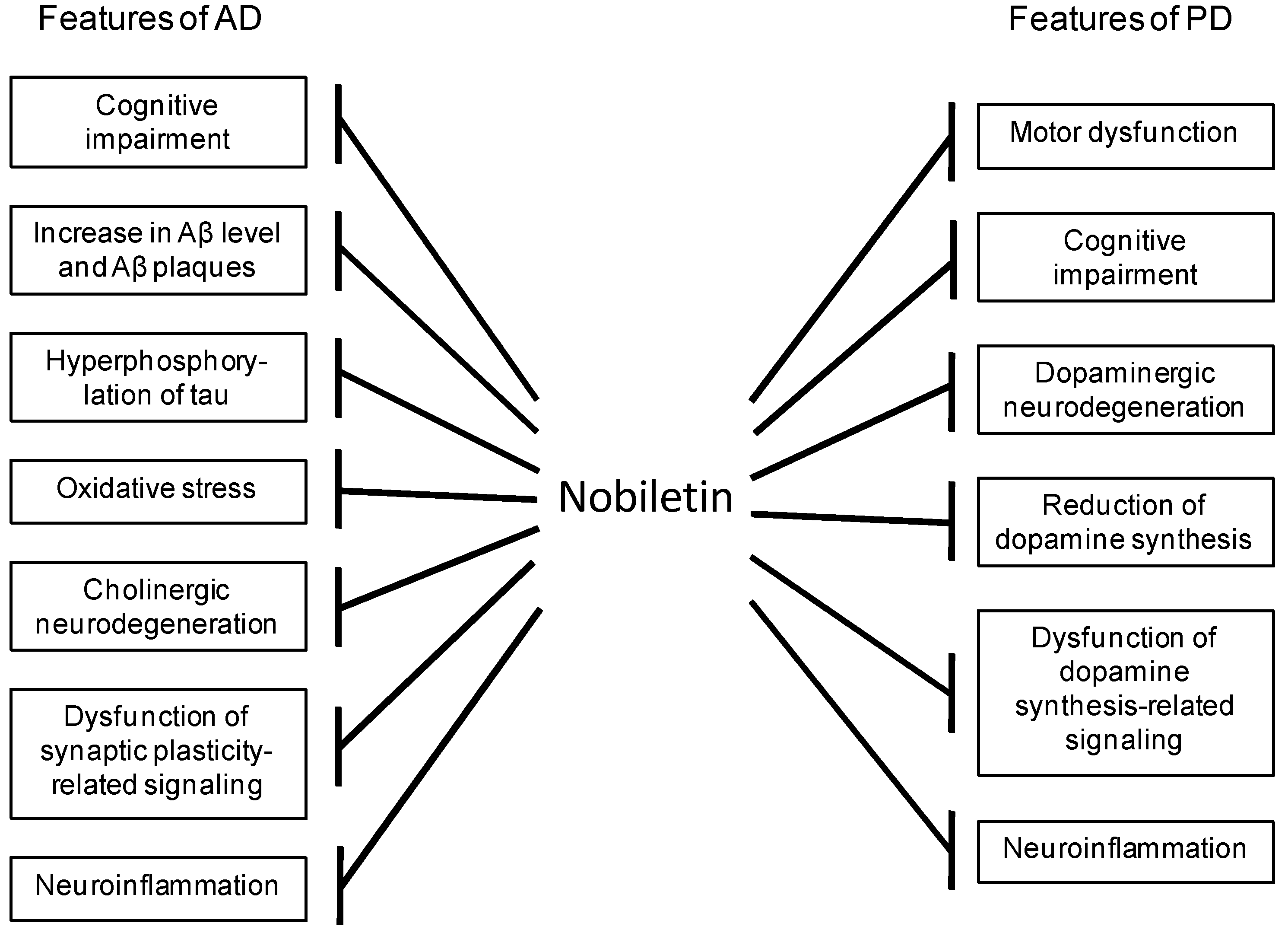
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AMPA | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-D-aspartate |
| Aβ | Amyloid-β |
| APP | Amyloid precursor protein |
| BACE1 | β-secretase |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| BCCAO | Bilateral common carotid artery occlusion |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| CaMKII | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| DARPP-32 | Dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein-32 |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GSSG | Glutathione disulfide |
| HO | Hemeoxygenase |
| IL | Interleukin |
| iPS | Induced pluripotent stem |
| I/R | Ischemia-reperfusion |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| MAP2 | Microtubule-associated protein 2 |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MPP+ | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MPTP | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| OBX | Olfactory-bulbectomized |
| PDE | Phosphodiesterase |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| p-MCAO | Permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| SAMP8 | Senescence-accelerated-prone mouse 8 |
| SNpc | Substantia nigra pars compacta |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TH | Tyrosine hydroxylase |
| t-MCAO | Transient middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| VTA | Ventral tegmental area |
References
- Chen, J.; Montanari, A.M.; Widmer, W.W. Two new polymethoxylated flavones, a class of compounds with potential anticancer activity, isolated from cold pressed Dancy tangerine peel oil solids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogata, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Shiratsuchi, H.; Ishii, T.; Yano, M.; Ohta, H. Flavonoid composition of fruit tissues of citrus species. Biosci. Biotechonol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimizu, N.; Otani, Y.; Saikawa, Y.; Kubota, T.; Yoshida, M.; Furukawa, T.; Kumai, K.; Kameyama, K.; Fujii, M.; Yano, M.; et al. Anti-tumour effects of nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, on gastric cancer include: Antiproliferative effects, induction of apoptosis and cell cycle deregulation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20 (Suppl. 1), 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Yasui, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ohigashi, H.; Murakami, A. Suppressive effects of nobiletin on hyperleptinemia and colitis-related colon carcinogenesis in male ICR mice. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.H.; Deepa, A.; Lam, I.K.; Tsui, S.K.W.; Yang, Z.F.; Lee, M.Y.S. Nobiletin, a polymethoxylated flavonoid from Citrus, shows anti-angiogenic activity in a zebrafish in vivo model and HUVEC in vitro model. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 3313–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Cheng, T.H.; Lee, J.S.; Chen, J.H.; Liao, Y.C.; Fong, Y.; Wu, C.H.; Shih, Y.W. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, suppresses invasion and migration involving FAK/PI3K/Akt and small GTPase signals in human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 347, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Sato, T.; Akimoto, N.; Yano, M.; Ito, A. Prevention of UVB-induced photoinflammation and photoaging by a polymethoxy flavonoid, nobiletin, in human keratinocytes in vivo and in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Ko, H.C.; Park, J.G.; Kim, S.J. Nobiletin from citrus fruit peel inhibits the DNA-binding activity of NF-kappab and ROS production in LPS- activated RAW 264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 113, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, Y.; Masuda, Y.; Kakutani, H.; Higuchi, T.; Takada, K.; Ito, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ishii, H. Sp1 is an essential transcription factor for LPS-induced tissue factor expression in THP-1 monocytic cells, and nobiletin represses the expression through inhibition of NF-kappaB, AP-1, and Sp1 activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, J.; Jung, S.C.; Park, D.B.; Maeng, Y.H.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Anti-neuroinflammatory activity of nobiletin on suppression of microglial activation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Assini, J.M.; Lee, J.K.; Allister, E.M.; Sutherland, B.G.; Koppes, J.B.; Sawyez, C.G.; Edwards, J.Y.; Telford, D.E.; Charbonneau, A.; et al. Nobiletin attenuates VLDL overproduction, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis in mice with diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Cha, B.Y.; Saito, K.; Yamakawa, H.; Choi, S.S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Teruya, T.; Nagai, K.; Woo, J.T. Nobiletin improves hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in obese diabetic ob/ob mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, Y.; Ham, H.; Park, Y.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, J. Nobiletin suppresses adipogenesis by regulating the expression of adipogenic transcription factors and the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12843–12849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, K.; Nishi, K.; Kadota, A.; Nishimoto, S.; Liu, M.C.; Sugahara, T. Nobiletin suppresses adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells by an insulin and IBMX mixture induction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012, 182, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, M.; Wimo, A.; Guerchet, M.; Ali, G.; Wu, Y.; Prina, M. World Alzheimer Report 2015. The Global Impact of Dementia. Alzheimer’s Disease International; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Volpina, O.M.; Samokhin, A.N.; Koroev, D.O.; Nesterova, I.V.; Volkova, T.D.; Medvinskaya, N.I.; Nekrasov, P.V.; Tatarnikova, O.G.; Kamynina, A.V.; Balasanyants, S.M.; et al. Synthetic Fragment of Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products Prevents Memory Loss and Protects Brain Neurons in Olfactory Bulbectomized Mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 61, 1061–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Jin, J.; Watanabe, S. Characteristics of memory dysfunction in olfactory bulbectomized rats and the effects of cholinergic drugs. Behav. Brain Res. 1997, 83, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozumi, S.; Nakagawasai, O.; Tan-No, K.; Niijima, F.; Yamadera, F.; Murata, A.; Arai, Y.; Yasuhara, H.; Tadano, T. Characteristics of changes in cholinergic function and impairment of learning and memory-related behavior induced by olfactory bulbectomy. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 138, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, H.; Omae, N.; Omori, A.; Nakagawasai, O.; Tadano, T.; Yokosuka, A.; Sashida, Y.; Mimaki, Y.; Yamakuni, T.; Ohizumi, Y. Nobiletin and its related flavonoids with CRE-mediated transcription-stimulating and neuritegenic activities. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 337, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Yamakuni, T.; Haraguchi, M.; Omae, N.; Song, S.Y.; Kato, C.; Nakagawasai, O.; Tadano, T.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; et al. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid that improves memory impairment, rescues bulbectomy-induced cholinergic neurodegeneration in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 105, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, D.; De Deyn, P.P. Animal models in the drug discovery pipeline for Alzheimer’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Yamakuni, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Haque, A.M.; Shido, O.; Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y.; Ohizumi, Y. Nobiletin restoring beta-amyloid-impaired CREB phosphorylation rescues memory deterioration in Alzheimer’s disease model rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 400, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; Lin, C.H.; Lane, H.Y.; Tsai, G.E. NMDA Neurotransmission Dysfunction in Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2012, 10, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, G.; Adavastro, G.; Canepa, G.; Capobianco, L.; Conigliaro, C.; Pittaluga, F.; Murri, M.B.; Valchera, A.; De Berardis, D.; Pompili, M.; et al. Abnormalities in Kynurenine Pathway Metabolism in Treatment-Resistant Depression and Suicidality: A Systematic Review. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Berardis, D.; Fornaro, M.; Valchera, A.; Cavuto, M.; Perna, G.; Di Nicola, M.; Serafini, G.; Carano, A.; Pompili, M.; Vellante, F.; et al. Eradicating Suicide at Its Roots: Preclinical Bases and Clinical Evidence of the Efficacy of Ketamine in the Treatment of Suicidal Behaviors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasetti, C.; Montemitro, C.; Fiengo, A.L.C.; Santone, C.; Orsolini, L.; Valchera, A.; Carano, A.; Pompili, M.; Serafini, G.; Perna, G.; et al. Novel Pathways in the Treatment of Major Depression: Focus on the Glutamatergic System. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Yamakuni, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Nakata, N.; Onozuka, H.; Yokosuka, A.; Sashida, Y.; Mimaki, Y.; Ohizumi, Y. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, reverses learning impairment associated with NMDA receptor antagonism by activation of ERK signaling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 321, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, M.; Bevilaqua, L.R.; Ardenghi, P.; Paratcha, G.; Levi de Stein, M.; Izquierdo, I.; Medina, J.H. Learning-associated activation of nuclear MAPK, CREB and Elk-1, along with Fos production, in the rat hippocampus after a one-trial avoidance learning: Abolition by NMDA receptor blockade. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2000, 76, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Viola, H.; Izquierdo, I.; Medina, J.H. Aversive experiences are associated with a rapid and transient activation of ERKs in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2002, 77, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yasuda, T.; Yoshimura, Y.; Yabuki, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Ohsawa, K.; Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y. Urinary metabolites of nobiletin orally administered to rats. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2003, 51, 1426–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Sang, S.; Huang, M.T.; Ho, C.T. Identification of nobiletin metabolites in mouse urine. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 5, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rahim, M.; Nakajima, A.; Saigusa, D.; Tetsu, N.; Maruyama, Y.; Shibuya, M.; Yamakoshi, H.; Tomioka, Y.; Iwabuchi, Y.; Ohizumi, Y.; et al. 4’-Demethylnobiletin, a bioactive metabolite of nobiletin enhancing PKA/ERK/CREB signaling, rescues learning impairment associated with NMDA receptor-antagonism via stimulation of ERK cascade. Biochemistry 2009, 18, 7713–7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Poon, H.F. The senescence-accelerated prone mouse (SAMP8): A model of age-related cognitive decline with relevance to alterations of the gene expression and protein abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2005, 40, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomobe, K.; Nomura, Y. Neurochemistry, neuropathology, and heredity in SAMP8: A mouse model of senescence. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Aoyama, Y.; Nguyen, T.Y.; Shin, E.J.; Kim, H.C.; Yamada, S.; Nakai, T.; Nagai, T.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; et al. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, ameliorates cognitive impairment, oxidative burden, and hyperphosphorylation of tau in senescence-accelerated mouse. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 250, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onozuka, H.; Nakajima, A.; Matsuzaki, K.; Shin, R.W.; Ogino, K.; Saigusa, D.; Tetsu, N.; Yokosuka, A.; Sashida, Y.; Mimaki, Y.; et al. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, improves memory impairment and Aβ pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oddo, S.; Caccamo, A.; Shepherd, J.D.; Murphy, M.P.; Golde, T.E.; Kayed, R.; Metherate, R.; Mattson, M.P.; Akbari, Y.; LaFerla, F.M. Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles: Intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 2003, 39, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, S.; Caccamo, A.; Kitazawa, M.; Tseng, B.P.; LaFerla, F.M. Amyloid deposition precedes tangle formation in a triple transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, M.A.; Bowers, W.J. Detailed immunohistochemical characterization of temporal and spatial progression of Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies in male triple-transgenic mice. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, L.M.; Oddo, S.; Green, K.N.; McGaugh, J.L.; LaFerla, F.M. Intraneuronal Abeta causes the onset of early Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits in transgenic mice. Neuron 2005, 45, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, L.K.; Billings, L.M.; Green, K.N.; Caccamo, A.; Ngo, J.; Oddo, S.; McGaugh, J.L.; LaFerla, F.M. Age-dependent sexual dimorphism in cognition and stress response in the 3xTg-AD mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 28, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietropaolo, S.; Feldon, J.; Yee, B.K.; Pietropaolo, S.; Feldon, J.; Yee, B.K. Age-dependent phenotypic characteristics of a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Behav. Neurosci. 2008, 122, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, T.; Iwashita, H.; Uno, Y.; Kunitomo, J.; Saitoh, M.; Kimura, E.; Fujita, H.; Uchiyama, N.; Kori, M.; Takizawa, M. A novel glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor 2-methyl-5-(3-{4-[(S)-methylsulfinyl]phenyl}-1-benzofuran-5-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole decreases tau phosphorylation and ameliorates cognitive deficits in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filali, M.; Lalonde, R.; Theriault, P.; Julien, C.; Calon, F.; Planel, E. Cognitive and non-cognitive behaviors in the triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease expressing mutated APP, PS1, and Mapt (3xTg-AD). Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 234, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blázquez, G.; Cañete, T.; Tobeña, A.; Giménez-Llort, L.; Fernández-Teruel, A. Cognitive and emotional profiles of aged Alzheimer’s disease (3×TgAD) mice: Effects of environmental enrichment and sexual dimorphism. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 268, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, A.; Aoyama, Y.; Shin, E.J.; Nam, Y.; Kim, H.C.; Nagai, T.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Yokoi, T.; Ohizumi, Y.; et al. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, improves cognitive impairment and reduces soluble Aβ levels in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease (3XTg-AD). Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 289, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Shioda, N.; Han, F.; Moriguchi, S.; Nakajima, A.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y.; Yamakuni, T.; Ohizumi, Y.; et al. Nobiletin improves brain ischemia-induced learning and memory deficits through stimulation of CaMKII and CREB phosphorylation. Brain Res. 2009, 1292, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J. Nobiletin protects against cerebral ischemia via activating the p-Akt, p-CREB, BDNF and Bcl-2 pathway and ameliorating BBB permeability in rat. Brain Res. Bull. 2013, 96, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, C.; Cui, L.; et al. Nobiletin promotes antioxidant and anti-inflammatory responses and elicits protection against ischemic stroke in vivo. Brain Res. 2016, 1636, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, N.; Ishii, T.; Oyama, D.; Fukuta, T.; Agato, Y.; Sato, A.; Shimizu, K.; Asai, T.; Asakawa, T.; Kan, T.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of nobiletin on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in transient middle cerebral artery-occluded rats. Brain Res. 2014, 1559, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Raymick, J.; Imam, S. Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Strategies against Parkinson’s Disease: Recent Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, P.; Joshi, N.; Singh, S. Neurodegenerative signaling factors and mechanisms in Parkinson’s pathology. Toxicol. in Vitro 2017, 43, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuki, Y.; Ohizumi, Y.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Fukunaga, K. Nobiletin treatment improves motor and cognitive deficits seen in MPTP-induced Parkinson model mice. Neuroscience 2014, 259, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinoff, P.B.; Axelrod, J. Biochemistry of catecholamines. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1971, 40, 465–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.H.; Jeon, M.T.; Kim, H.D.; Jung, U.J.; Jang, M.C.; Chu, J.W.; Yang, S.J.; Choi, I.Y.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, S.R. Nobiletin protects dopaminergic neurons in the 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-treated rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Med. Food. 2015, 18, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javitch, J.A.; D’Amato, R.J.; Strittmatter, S.M.; Snyder, S.H. Parkinsonism-inducing neurotoxin, N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6 -tetrahydropyridine: Uptake of the metabolite N-methyl-4-phenylpyridine by dopamine neurons explains selective toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 2173–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossler, M.R.; Yao, H.; York, R.D.; Pan, M.G.; Rim, C.S.; Strok, P.J. cAMP activates MAP kinase and Elk-1 through a B-Raf-and Rap1-dependent pathway. Cell 1997, 89, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwang, W.B.; Arthur, J.S.; Schumacher, A.; Sweatt, J.D. The nuclear kinase mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1 regulates hippocampal chromatin remodeling in memory formation. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12732–12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, U.; Huang, Y.Y.; Kandel, E.R. Effects of cAMP stimulate a late stage LTP in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Science 1993, 260, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impey, S.; Mark, M.; Villacres, E.C.; Poser, S.; Chavkin, C.; Storm, D.R. Induction of CRE-mediated gene expression by stimuli that generate long-lasting LTP in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Neuron 1996, 16, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, T.; Nguyen, P.V.; Barad, M.; Deuel, T.A.; Kandel, E.R.; Bourtchouladze, R. Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell 1997, 88, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweatt, J.D. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in synaptic plasticity and memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandel, E.R. The molecular biology of memory: cAMP, PKA, CRE, CREB-1, CREB-2, and CPEB. Mol. Brain. 2012, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitolo, O.V.; Sant’Angelo, A.; Costanzo, V.; Battaglia, F.; Arancio, O.; Shelanski, M. Amyloid beta-peptide inhibition of the PKA/CREB pathway and long-term potentiation: Reversibility by drugs that enhance cAMP signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13217–13221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.L.; Harris-White, M.E.; Ubeda, O.J.; Simmons, M.; Beech, W.; Lim, G.P.; Teter, B.; Frautschy, S.A.; Cole, G.M. Evidence of Abeta- and transgene-dependent defects in ERK-CREB signaling in Alzheimer’s models. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 1594–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, H.; Yamakuni, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Maruyama, Y.; Kasahara, J.; Hinohara, Y.; Kondo, S.; Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y.; Tank, W.A.; et al. Mechanism of neurotrophic action of nobiletin in PC12D cells. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 13683–13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, J.; Nemoto, K.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Degawa, M.; Ohizumi, Y. 6-demethoxynobiletin, a nobiletin-analog citrus flavonoid, enhances extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation in PC12D cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 1646–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takito, J.; Kimura, J.; Kajima, K.; Uozumi, N.; Watanabe, M.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Ohizumi, Y. Nerve growth factor enhances the CRE-dependent transcriptional activity activated by nobiletin in PC12 cells. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 94, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Miyazaki, K.; Sakai, S.; Yawo, H.; Nakata, N.; Moriguchi, S.; Fukunaga, K.; Yokosuka, A.; Sashida, Y.; Mimaki, Y.; et al. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid with neurotrophic action, augments protein kinase A mediated phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor subunit, GluR1, and the postsynaptic receptor response to glutamate in murine hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 578, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benke, T.A.; Lüthi, A.; Isaac, J.T.; Collingridge, G.L. Modulation of AMPA receptor unitary conductance by synaptic activity. Nature 1998, 393, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, J.A.; Shi, S.H.; Wilson, C.; Nuriya, M.; Huganir, R.L.; Malinow, R. PKA phosphorylation of AMPA receptor subunits controls synaptic trafficking underlying plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakimura, K.; Kutsuwada, T.; Ito, I.; Manabe, T.; Takayama, C.; Kushiya, E.; Yagi, T.; Aizawa, S.; Inoue, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; et al. Reduced hippocampal LTP and spatial learning in mice lacking NMDA receptor epsilon 1 subunit. Nature 1995, 373, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.P.; Shimizu, E.; Dube, G.R.; Rampon, C.; Kerchner, G.A.; Zhuo, M.; Liu, G.; Tsien, J.Z. Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 1999, 401, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Bading, H. Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: Implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, E.M.; Nong, Y.; Almeida, C.G.; Paul, S.; Moran, T.; Choi, E.Y.; Nairn, A.C.; Salter, M.W.; Lombroso, P.J.; Gouras, G.K.; et al. Regulation of NMDA receptor trafficking by amyloid-beta. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishizen-Eberz, A.J.; Rissman, R.A.; Carter, T.L.; Ikonomovic, M.D.; Wolfe, B.B.; Armstrong, D.M. Biochemical and molecular studies of NMDA receptor subunits NR1/2A/2B in hippocampal subregions throughout progression of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 15, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, J.; Nemoto, K.; Degawa, M.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Oku, N.; Ohizumi, Y. Upregulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits and c-Fos expressing genes in PC12D cells by nobiletin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.P.; Sweatt, J.D. Molecular psychology: Roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 135–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Su, M.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Li, L.; Yuan, C.G. Protective effects of the citrus flavanones to PC12 cells against cytotoxicity induced by hydrogen peroxide. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 484, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.D.; Yen, J.H.; Li, S.; Weng, C.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Ho, C.T.; Wu, M.J. 3’,4’-didemethylnobiletin induces phase II detoxification gene expression and modulates PI3K/Akt signaling in PC12 cells. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.W.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, I.Y. Neuroprotective effect of Citrus unshiu immature peel and nobiletin inhibiting hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in HT22 murine hippocampal neuronal cells. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11 (Suppl. 2), S284–S289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, K.; Ikeda, A.; Yoshida, C.; Kimura, J.; Mori, J.; Fujiwara, H.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Ohizumi, Y.; Degawa, M. Characteristics of nobiletin-mediated alteration of gene expression in cultured cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, A.; Nemoto, K.; Yoshida, C.; Miyata, S.; Mori, J.; Soejima, S.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Ohizumi, Y.; Degawa, M. Suppressive effect of nobiletin, a citrus polymethoxyflavonoid that downregulates thioredoxin-interacting protein expression, on tunicamycin-induced apoptosis in SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 549, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, M.R.; St-Pierre, M.K.; Wendeln, A.C.; Makoni, N.J.; Gouwens, L.K.; Garrad, E.C.; Sohrabi, M.; Neher, J.J.; Tremblay, M.E.; Combs, C.K. Inflammatory mechanisms in neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 2019, 149, 562–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bulck, M.; Sierra-Magro, A.; Alarcon-Gil, J.; Perez-Castillo, A.; Morales-Garcia, J.A. Novel Approaches for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.C.; Kuo, C.T. Hesperidin, nobiletin, and tangeretin are collectively responsible for the anti-neuroinflammatory capacity of tangerine peel (Citri reticulatae pericarpium). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 71, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zang, W.; Ji, S.; Cao, J.; Sun, C. Three Polymethoxyflavones Purified from Ougan (Citrus reticulata Cv. Suavissima) Inhibited LPS-Induced NO Elevation in the Neuroglia BV-2 Cell Line via the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway. Nutrients 2019, 11, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Mi, Y.; Fan, R.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Nobiletin Protects against Systemic Inflammation-Stimulated Memory Impairment via MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5122–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seubert, P.; Oltersdorf, T.; Lee, M.G.; Barbour, R.; Blomquist, C.; Davis, D.L.; Bryant, K.; Fritz, L.C.; Galasko, D.; Thal, L.J.; et al. Secretion of beta-amyloid precursor protein cleaved at the amino terminus of the beta-amyloid peptide. Nature 1993, 361, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, N.; Higuchi, M.; Saido, T.C. Metabolism of amyloid-beta peptide and Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 108, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassar, R.; Kuhn, P.H.; Haass, C.; Kennedy, M.E.; Rajendran, L.; Wong, P.C.; Lichtenthaler, S.F. Function, therapeutic potential and cell biology of BACE proteases: Current status and future prospects. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, K.; Yu, Y.; Lee, J.; Jeong, W.S.; Ho, C.T.; Jun, M. Polymethoxyflavones: Novel β-Secretase (BACE1) Inhibitors from Citrus Peels. Nutrients 2017, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Chen, L.; Bennett, D.A.; Dickson, D.W.; Wang, D.S. Expression and functional profiling of neprilysin, insulin-degrading enzyme, and endothelin-converting enzyme in prospectively studied elderly and Alzheimer’s brain. J. Neurochem. 2010, 115, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, H.; Kimura, J.; Sakamoto, M.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Murata, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ohizumi, Y. Nobiletin, a flavone from Citrus depressa, induces gene expression and increases the protein level and activity of neprilysin in SK-N-SH cells. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, J.; Shimizu, K.; Kajima, K.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Oku, N.; Ohizumi, Y. Nobiletin Reduces Intracellular and Extracellular β-Amyloid in iPS Cell-Derived Alzheimer’s Disease Model Neurons. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Kamiya, T.; Furukawa, K.; Azumi, M.; Ishizuka, S.; Takayama, S.; Nagase, S.; Arai, H.; Yamakuni, T.; Yaegashi, N. Nobiletin-rich Citrus reticulata peels, a kampo medicine for Alzheimer’s disease: A case series. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2013, 13, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakajima, A.; Ohizumi, Y. Potential Benefits of Nobiletin, A Citrus Flavonoid, against Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143380
Nakajima A, Ohizumi Y. Potential Benefits of Nobiletin, A Citrus Flavonoid, against Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(14):3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143380
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakajima, Akira, and Yasushi Ohizumi. 2019. "Potential Benefits of Nobiletin, A Citrus Flavonoid, against Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 14: 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143380
APA StyleNakajima, A., & Ohizumi, Y. (2019). Potential Benefits of Nobiletin, A Citrus Flavonoid, against Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143380



