Comparison between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants: In Vivo Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Surface Characterization
2.2. Histological and Histomorhometric Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Implants
4.2. Animals
4.3. Surgical Procedures
4.4. Histological and Histomorphometric Analyses
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berglundh, T.; Persson, L.; Klinge, B. A systematic review of the incidence of biological and technical complications in implant dentistry reported in prospective longitudinal studies of at least 5 years. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2002, 29 (Suppl. 3), 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, N.J.; Zarb, G.A. Long-term treatment outcomes in edentulous patients with implant-fixed prostheses: The Toronto study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Jos, A.; Pato-Mourelo, J.; Cameán, A.M.; Segura-Egea, J.J. In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of a commercial titanium alloy for dental implant logy. Mutat. Res. 2010, 702, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, P.G.; Jimbo, R.; Tovar, N.; Estevam, A.; Bonfante, E.A. Osseointegration: Hierarchical designing encompassing the macrometer, micrometer, and nanometer length scales. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iezzi, G.; Scarano, A.; Di Stefano, D.; Arosio, P.; Doi, K.; Ricci, L.; Piattelli, A.; Perrotti, V. Correlation between the bone density recorded by a computerized implant motor and by a histomorphometric analysis: A preliminary in vitro study on bovine ribs. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraccio, D.; Mussano, F.; Faga, M.G. Biomaterials for dental implants: Current and future trends. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4779–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.J.; Marques, R.G.; Elias, C.N. Influence of acid treatment on surface properties and in vivo performance of Ti6Al4V alloy for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Alfonso-Rodríguez, C.A.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; España-López, A.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Garzón, I.; Alaminos, M.; Gil, F.J. Relevant aspects in the surface properties in titanium dental implants for the cellular viability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Johansson, C.; Lundgren, A.K.; Sul, Y.; Gottlow, J. Experimental studies on oxidized implants. A histomorphometrical and biomechanical analysis. Appl. Osseointegration Res. 2000, 1, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.K.; Kumar, M.A.; Chowdhary, R. Anodized dental implant surface. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2017, 28, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burgos, P.M.; Rasmusson, L.; Meirelles, L.; Sennerby, L. Early bone tissue responses to turned and oxidized implants in the rabbit tibia. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2008, 10, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Choi, S.H.; Ryu, J.J.; Koh, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Lee, I.S. The biocompatibility of SLA-treated titanium implants. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 025011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatt, S.; Pabst, A.M.; Schiegnitz, E.; Hosang, M.; Ziebart, T.; Walter, C.; Al-Nawas, B.; Klein, M.O. Early cell response of osteogenic cells on differently modified implant surfaces: Sequences of cell proliferation, adherence and differentiation. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, B.; Wan, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H. Morphologically modified surface with hierarchical micro-/nano-structures for enhanced bioactivity of titanium implants. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 12679–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasa, C.N.; Rocha, F.A.; Nascimento, A.L.; Coelho, P.G. Influence of implant shape, surface morphology, surgical technique and bone quality on the primary stability of dental implants. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 16, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botticelli, D.; Lang, N.P. Dynamics of osseointegration in various human and animal models—A comparative analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Satorres-Nieto, M.; Aguilar-Salvatierra, A.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Maté-Sánchez de Val, J.E.; Gargallo-Albiol, J.; Gómez-Moreno, G.; Romanos, G.E. Influence of surface treatment on osseointegration of dental implants: Histological, histomorphometric and radiological analysis in vivo. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Yang, I.H.; Kim, S.K.; Yeo, I.S.; Kwon, T.K. In vivo comparison between the effects of chemically modified hydrophilic and anodically oxidized titanium surfaces on initial bone healing. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2015, 45, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, E.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Jiménez, A.; Ortiz, I.; Moreno-Muñoz, J.; Nuñez-Marquez, E.; Pegueroles, M.; Pérez, R.A.; Gil, F.J. Importance of the roughness and residual stresses of dental implants on fatigue and osseointegration behavior. In vivo study in rabbits. J. Oral Implantol. 2016, 42, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Padros, A.; Aparico, C. The effect of shot blasting and heat treatment on the fatigue behavior of titanium for dental implant applications. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 486–491. [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio, C.; Padros, A.; Gil, F.J. In vivo evaluation of micro-rough and bioactive titanium dental implants using histometry and pull-out tests. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, H.J.; Hsu, H.J.; Peng, P.W.; Wu, C.Z.; Ou, K.L.; Cheng, H.Y.; Walinski, C.J.; Sugiatno, E. Early bone response to machined, sandblasting acid etching (SLA) and novel surface-functionalization (SLAffinity) titanium implants: Characterization, biomechanical analysis and histological evaluation in pigs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2016, 104, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salou, L.; Hoornaert, A.; Louarn, G.; Layrolle, P. Enhanced osseointegration of titanium implants with nanostructured surfaces: An experimental study in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T.S.; Johansson, C.; Wennerberg, A.; Cho, L.R.; Chang, B.S.; Albrektsson, T. Optimum surface properties of oxidized implants for reinforcement of osseointegration: Surface chemistry, oxide thickness, porosity, roughness, and crystal structure. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2005, 20, 349–359. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, N.P.; Salvi, G.E.; Huynh-Ba, G.; Ivanovski, S.; Donos, N.; Bosshardt, D.D. Early osseointegration to hydrophilic and hydrophobic implant surfaces in humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Suggested guidelines for the topographic evaluation of implant surfaces. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 331–344. [Google Scholar]
- Donath, K.; Breuner, G. A method for the study of undecalcified bones and teeth with attached soft tissues. The Säge-Schliff (sawing and grinding) technique. J. Oral Pathol. 1982, 11, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszko, J.; Levai, G. A simple differential staining method for semithin sections of ossifying cartilage and bone tissues embedded in epoxy resin. Mikroskopie 1975, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
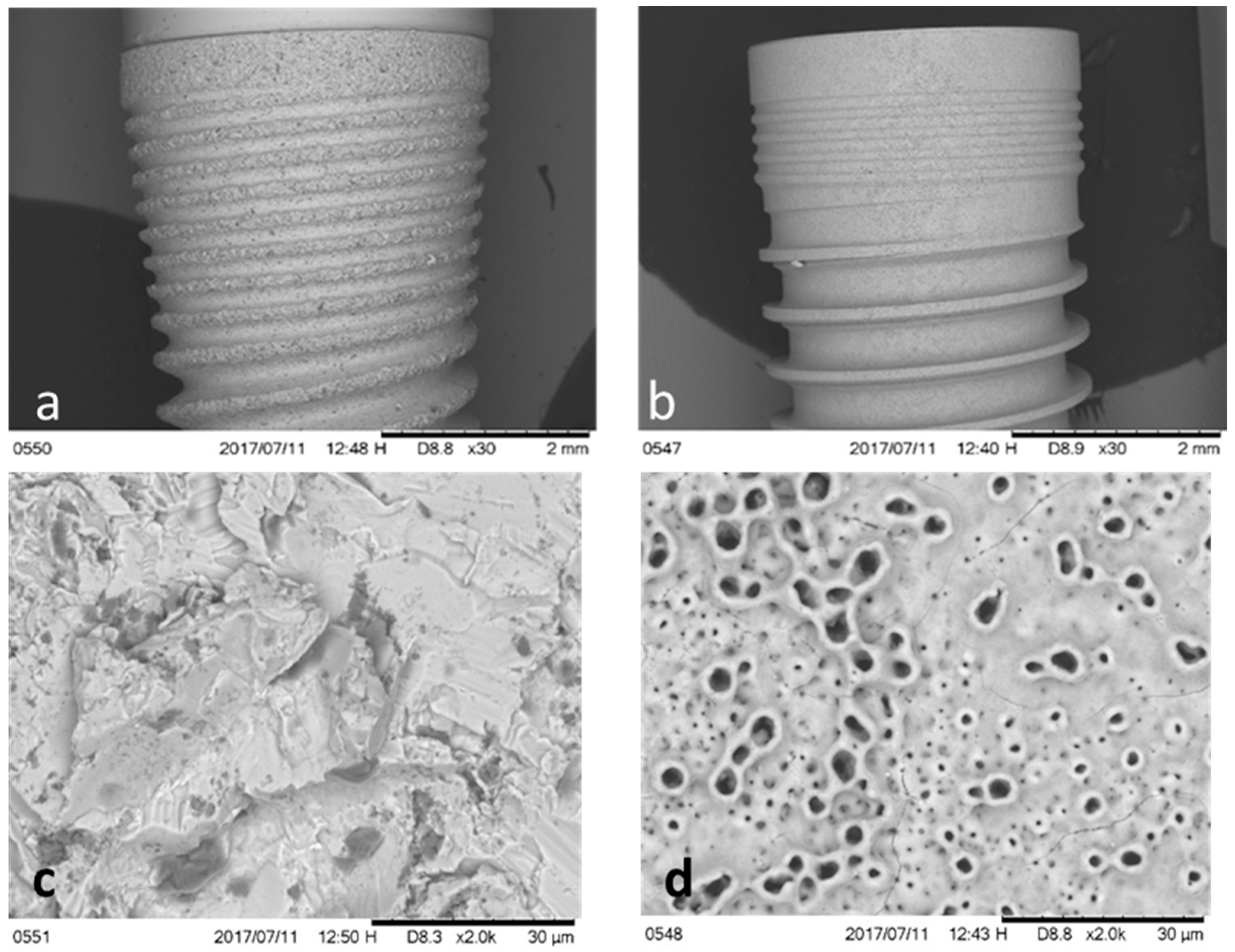
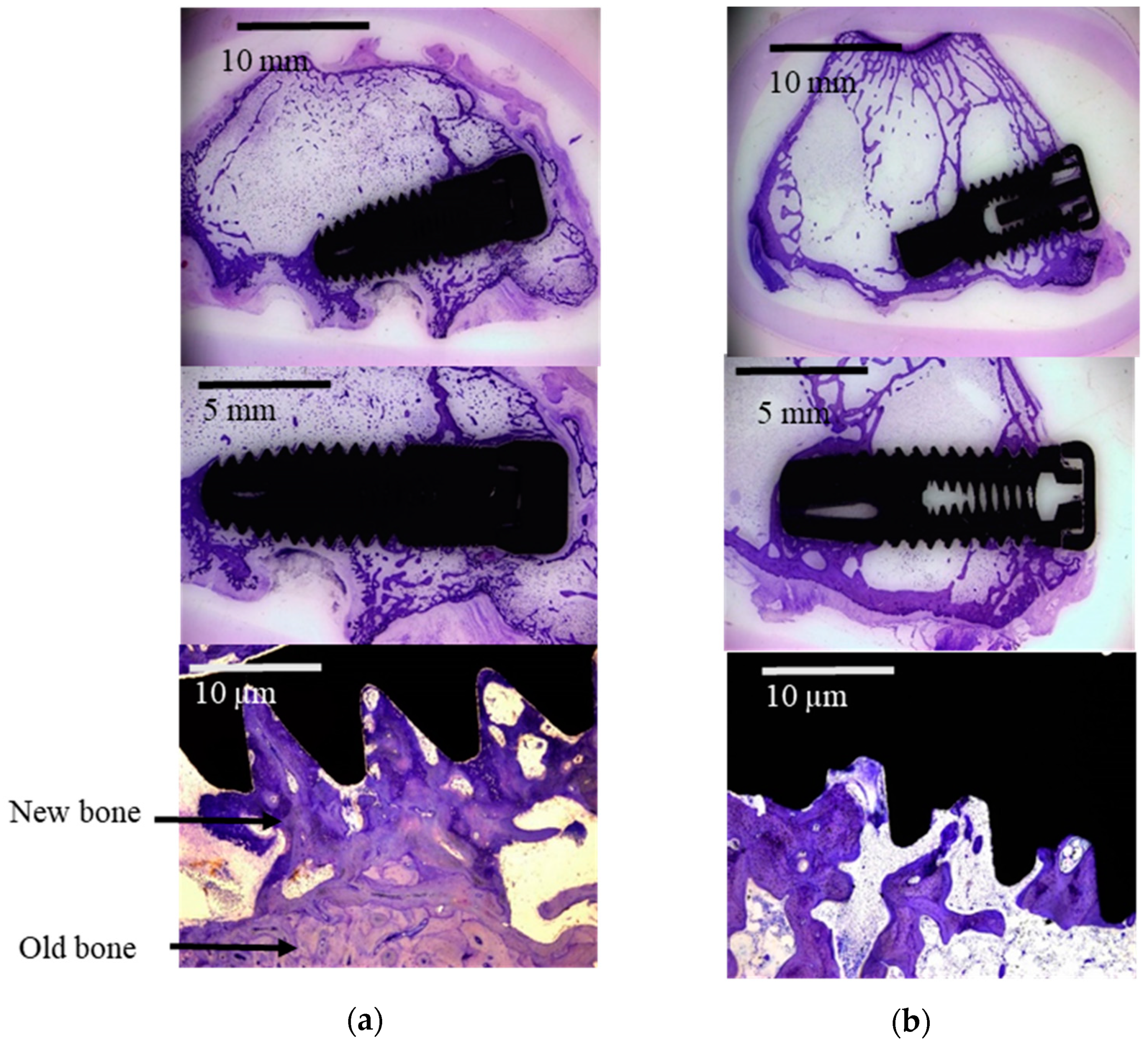
| Parameter | SA | OS | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ra | 1.76 ± 0.21 | 1.37 ± 0.11 | 0.0008 |
| Rt | 31.37 ± 2.30 | 24.21± 2.89 | 0.0002 |
| Rq | 2.37± 0.12 | 1.50 ± 0.13 | 0.0003 |
| Rz | 22.80 ± 3.30 | 20.77± 4.00 | 0.0001 |
| Residual stress | −213.3 ± 3.6 | −71.0 ± 5.1 | 0.0001 |
| Animal | SA | OS | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 62.74 ± 8.01 | 30.01 ± 15.88 | 0.02 |
| 2 | 46.04 ± 7.56 | 71.77 ± 20.22 | 0.33 |
| 3 | 64.11 ± 8.43 | 42.80 ± 18.13 | 0.28 |
| 4 | 47.33 ± 8.67 | 32.03 ± 14.34 | 0.04 |
| 5 | 56.14 ± 7.56 | 41.03 ± 21.10 | 0.03 |
| 6 | 45.76 ± 10.53 | 37.98 ± 8.85 | 0.03 |
| Mean ± SD | 53.49 ± 8.46 | 50.94 ± 16.42 |
| Region | SA | OS |
|---|---|---|
| Cervical | 41.22 ± 5.12 | 38.54 ± 4.56 |
| Medial | 29.97 ± 3.21 | 19.97 ± 3.99 |
| Apical | 41.61 ± 4.23 | 47.67 ± 5.67 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velasco-Ortega, E.; Ortiz-García, I.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Muñoz-Guzón, F.; Perez, R.A.; Gil, F.J. Comparison between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants: In Vivo Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133267
Velasco-Ortega E, Ortiz-García I, Jiménez-Guerra A, Monsalve-Guil L, Muñoz-Guzón F, Perez RA, Gil FJ. Comparison between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants: In Vivo Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(13):3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133267
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelasco-Ortega, Eugenio, Ivan Ortiz-García, Alvaro Jiménez-Guerra, Loreto Monsalve-Guil, Fernando Muñoz-Guzón, Roman A. Perez, and F. Javier Gil. 2019. "Comparison between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants: In Vivo Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 13: 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133267
APA StyleVelasco-Ortega, E., Ortiz-García, I., Jiménez-Guerra, A., Monsalve-Guil, L., Muñoz-Guzón, F., Perez, R. A., & Gil, F. J. (2019). Comparison between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants: In Vivo Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(13), 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133267






