Glucosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb1) as a Biomarker for Monitoring Treated and Untreated Children with Gaucher Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Patients Samples
4.2. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Revel-Vilk, S.; Szer, J.; Mehta, A.; Zimran, A. How we manage Gaucher Disease in the era of choices. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 182, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gary, S.E.; Ryan, E.; Steward, A.M.; Sidransky, E. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of Gaucher disease. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 13, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimran, A.; Elstein, D. Chapter 72: Gaucher disease and related Lysosomal Storage Diseases. In Williams’ Hematology; Kaushansky, K., Lichtman, M.A., Prchal, J.T., Levi, M.M., Press, O.W., Burns, L.J., Caligiuri, M.L., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, N.W.; Brady, R.O.; Dambrosia, J.M.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Doppelt, S.H.; Hill, S.C.; Mankin, H.J.; Murray, G.J.; Parker, R.I.; Argoff, C.E.; et al. Replacement therapy for inherited enzyme deficiency--macrophage-targeted glucocerebrosidase for Gaucher's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, H.; Kaplan, P.; Kacena, K.; Yee, J. Eight-year clinical outcomes of long-term enzyme replacement therapy for 884 children with Gaucher disease type 1. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elstein, D.; Altarescu, G.; Abrahamov, A.; Zimran, A. Children with type 1 Gaucher disease: Changing profiles in the 21st century. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2018, 68, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.C.; Bier, L.; Overbey, J.R.; Cohen-Pfeffer, J.; Desai, K.; Desnick, R.J.; Balwani, M. Early manifestations of type 1 Gaucher disease in presymptomatic children diagnosed after parental carrier screening. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfs, A.; Giese, A.K.; Grittner, U.; Mascher, D.; Elstein, D.; Zimran, A.; Bottcher, T.; Lukas, J.; Hubner, R.; Golnitz, U.; et al. Glucosylsphingosine is a highly sensitive and specific biomarker for primary diagnostic and follow-up monitoring in Gaucher disease in a non-Jewish, Caucasian cohort of Gaucher disease patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elstein, D.; Mellgard, B.; Dinh, Q.; Lan, L.; Qiu, Y.; Cozma, C.; Eichler, S.; Bottcher, T.; Zimran, A. Reductions in glucosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb1) in treatment-naive and previously treated patients receiving velaglucerase alfa for type 1 Gaucher disease: Data from phase 3 clinical trials. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, V.; Chuang, W.L.; Liu, J.; Lischuk, A.; Kacena, K.; Lin, H.; Pastores, G.M.; Yang, R.; Keutzer, J.; Zhang, K.; et al. Glucosylsphingosine is a key biomarker of Gaucher disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, B.A.; Hassan, S.; Garcia, E.J.; Tayebi, N.; Sidransky, E. Exploring genetic modifiers of Gaucher disease: The next horizon. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, N.; van Dussen, L.; Hollak, C.E.; Overkleeft, H.; Scheij, S.; Ghauharali, K.; van Breemen, M.J.; Ferraz, M.J.; Groener, J.E.; Maas, M.; et al. Elevated plasma glucosylsphingosine in Gaucher disease: Relation to phenotype, storage cell markers, and therapeutic response. Blood 2011, 118, e118–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, G.A.; Kacena, K.; Cole, J.A.; Hollak, C.E.; Zhang, L.; Yee, J.; Mistry, P.K.; Zimran, A.; Charrow, J.; vom Dahl, S. Dose-response relationships for enzyme replacement therapy with imiglucerase/alglucerase in patients with Gaucher disease type 1. Genet. Med. 2009, 11, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkadir, D.; Dinur, T.; Revel-Vilk, S.; Becker Cohen, M.; Cozma, C.; Hovakimyan, M.; Eichler, S.; Rolfs, A.; Zimran, A. Glucosylsphingosine is a reliable response biomarker in Gaucher disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, E140–E142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, P.K.; Lukina, E.; Ben Turkia, H.; Shankar, S.P.; Baris, H.; Ghosn, M.; Mehta, A.; Packman, S.; Pastores, G.; Petakov, M.; et al. Outcomes after 18 months of eliglustat therapy in treatment-naive adults with Gaucher disease type 1: The phase 3 ENGAGE trial. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brautbar, A.; Abrahamov, A.; Hadas-Halpern, I.; Elstein, D.; Zimran, A. Gaucher disease in Arab patients at an Israeli referral clinic. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2008, 10, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abrahamov, A.; Elstein, D.; Gross-Tsur, V.; Farber, B.; Glaser, Y.; Hadas-Halpern, I.; Ronen, S.; Tafakjdi, M.; Horowitz, M.; Zimran, A. Gaucher’s disease variant characterised by progressive calcification of heart valves and unique genotype. Lancet 1995, 346, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.K. Genotype/phenotype correlations in Gaucher’s disease. Lancet 1995, 346, 982–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimran, A.; Gross, E.; West, C.; Sorge, J.; Kubitz, M.; Beutler, E. Prediction of severity of Gaucher’s disease by identification of mutations at DNA level. Lancet 1989, 2, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetter, E.M.; Acosta, K.B.; Olson, M.C.; Blundell, K. Estimating Splenic Volume: Sonographic Measurements Correlated with Helical CT Determination. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 181, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elstein, D.; Hadas-Halpern, I.; Azuri, Y.; Abrahamov, A.; Bar-Ziv, Y.; Zimran, A. Accuracy of ultrasonography in assessing spleen and liver size in patients with Gaucher disease: Comparison to computed tomographic measurements. J. Ultrasound Med. 1997, 16, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
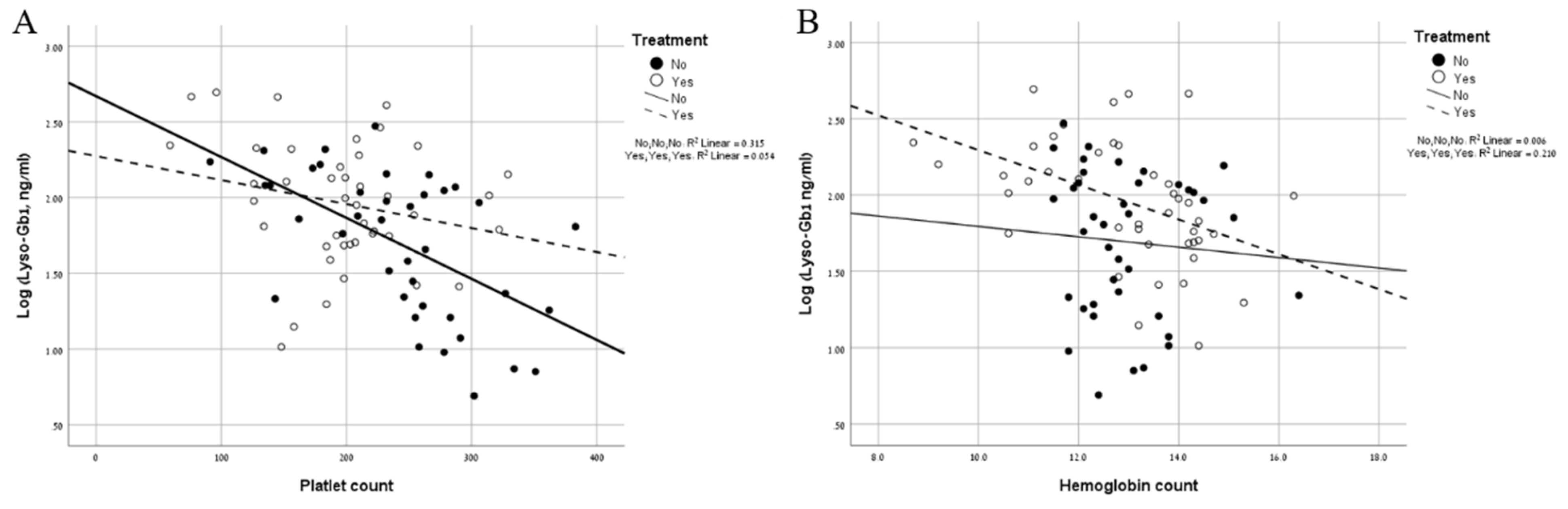
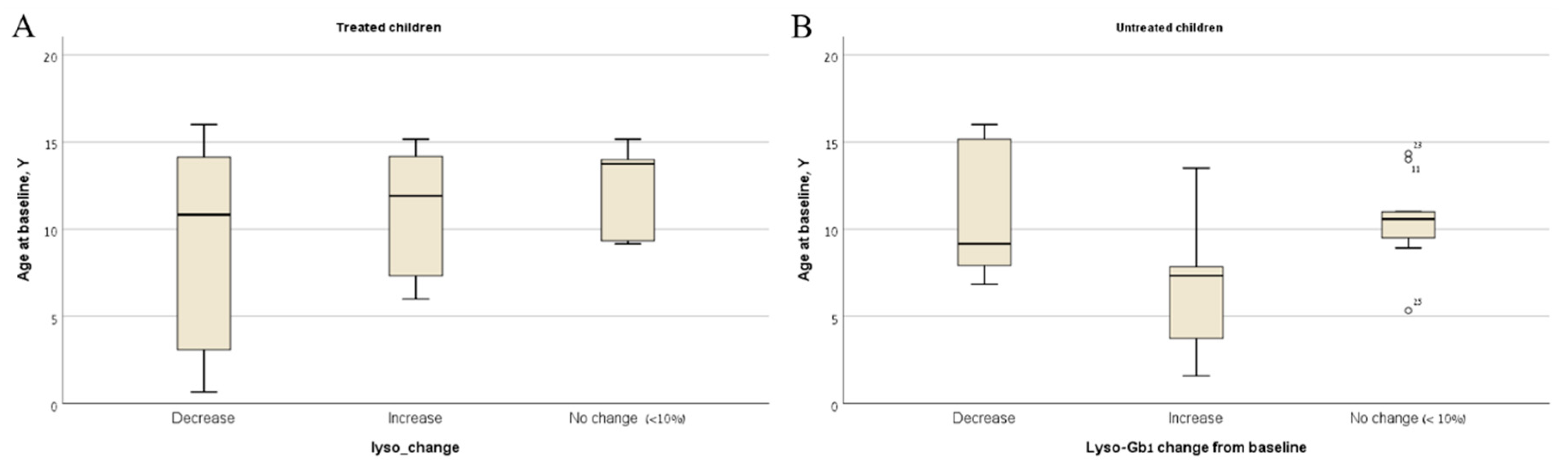
| Total | Mild Type 1 | Severe Type 1 | Type 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 81 | 35 | 34 | 12 |
| Age, years* | 11 (1–18) | 11 (4–18) | 12 (2–16) | 9.5 (1–18) |
| Male, % | 38 (47%) | 16 (38%) | 18 (52%) | 4 (33%) |
| ERT* | 42 (51%) | 2 (5.7%) | 30 (88%) | 10 (83%) |
| Platelet count, ×103/mL | 214 (59–383) | 251 (134–383) | 209 (76–334) | 190 (59–322) |
| Hemoglobin, mg/dl | 12.9 (8.7–16.4) | 12.8(11.5–16.4) | 13.15 (9.2–15.3) | 12.4 (8.7–16.3) |
| Spleen (MN)* | 1.3 (0–16.7) | 1.3 (0.5–4.7) | 1.3 (0.6–10.3) | 3.4 (1.2–16.7) |
| Liver (MN)* | 1.4 (0.3–3.6) | 1.4 (1–2.3) | 1.3 (0.3–2.8) | 2.3 (1.3–3.5) |
| Lyso-Gb1 level, ng/mL* | 76.3 (4.9–495) | 64 (4.9–208) | 98 (7.3–495) | 100.4 (21.4–210) |
| Weight, Kg* | 37.8 (10.1–76) | 34.1 (14.7–70.9) | 49 (15.4–76) | 29.8 (10.1–52.2) |
| Pre-Treatment | Un-Treated | |
|---|---|---|
| N | 10 | 28 |
| Age, years | 5.5 (2–14) | 8.5 (1–16) |
| Male, % | 5 (55%) | 11 (37%) |
| Platelet count, ×103/mL | 82.5 (68–228) | 236.5 (117–339) |
| Hemoglobin, mg/dl | 11.1 (6.7–12.4) | 12.7 (11.1–15.7) |
| Spleen (MN)* | 3.9 (1.1–22.9) | 1.35 (0.5–5.2) |
| Liver (MN)* | 2.4 (1.2–4.5) | 1.7 (1–3) |
| Lyso-Gb1 level, ng/mL* | 262.5 (101–1270) | 61.45 (6.1–157) |
| Untreated | Treated, Pretreatment Baseline | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | ||
| N | 28 | 10 | 30 |
| Male | 11 | 5 | 16 |
| Age, years* | 12 (4–18) | 8.5 (3–18) | 16 (3–19) |
| Months of follow-up* | 31.85 ( 6.7–45) | 27.6 (6.7–44) | 28.75 (9.3–49.9) |
| Number of visits | 3 (2–6) | 4 (3-6) | 4 (2–9) |
| Unchanged** (n) | 9 (32%) | 1 (10%) | 5 (16%) |
| Increased (n) | 13 (46%) | 0 (0%) | 8 (26%) |
| Increase change* | 12 (1.29–128) | 67.4 (5.7–368) | |
| Decreased (n) | 6 (21%) | 9 (90%) | 17 (56%) |
| Decrease change* | 11.2 (4–50.4) | 143.6 (13–1207.7) | 32.7 (4.2–172) |
| Age (Y)* | Gender | Genotype | Mo. on Tx* | Dosa u/kg/mo* | Follow Up (mo) | Baseline Lyso- Gb1 | Change from Baseline | Possible Explanation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lyso-Gb1 | PLT | Hb | Spleen MN | Liver MN | ||||||||
| 9 | male | Severe GD1 | 72 | 36.7 | 140 | 79↑ | 9↓ | 0.5≈ | 0.5≈ | 0.4≈ | ||
| 9 | male | Severe GD1 | 81.2 | 52 | 23.6 | 168 | 18↑ | 31↓ | 0.4≈ | Weight gain** | ||
| 18 | male | Severe GD1 | 92.3 | 42 | 18.6 | 95 | 368↑ | 24↓ | 1.1↓ | 1.8↑ | 0.3≈ | Compliance |
| 18 | female | Severe GD1 | 130.9 | 35 | 36.9 | 281 | 180↑ | 18↓ | 0.5≈ | 0.6↓ | 0.1≈ | |
| 10 | male | Severe GD1 | 90.3 | 42 | 40.0 | 164 | 48↑ | 56↓ | 1.1↑ | 1.4↓ | 0.2≈ | |
| 14 | male | Severe GD1 | 113.7 | 114 | 38.3 | 45 | 6↑ | 4≈ | 1.3↓ | 6.4↑ | 1.2↓ | Weight gain** |
| 16 | male | Severe GD1 | 137.0 | 50 | 30.2 | 124 | 77↑ | 20↑ | 2.5↓ | 0.6↓ | 0.3≈ | Weight gain** |
| 17 | male | GD3 | 124.8 | 60 | 18.6 | 32 | 13↑ | 20↓ | 1.3↑ | 0.5↑ | 0.8↑ | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hurvitz, N.; Dinur, T.; Becker-Cohen, M.; Cozma, C.; Hovakimyan, M.; Oppermann, S.; Demuth, L.; Rolfs, A.; Abramov, A.; Zimran, A.; et al. Glucosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb1) as a Biomarker for Monitoring Treated and Untreated Children with Gaucher Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20123033
Hurvitz N, Dinur T, Becker-Cohen M, Cozma C, Hovakimyan M, Oppermann S, Demuth L, Rolfs A, Abramov A, Zimran A, et al. Glucosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb1) as a Biomarker for Monitoring Treated and Untreated Children with Gaucher Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(12):3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20123033
Chicago/Turabian StyleHurvitz, Noa, Tama Dinur, Michal Becker-Cohen, Claudia Cozma, Marina Hovakimyan, Sebastian Oppermann, Laura Demuth, Arndt Rolfs, Aya Abramov, Ari Zimran, and et al. 2019. "Glucosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb1) as a Biomarker for Monitoring Treated and Untreated Children with Gaucher Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 12: 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20123033
APA StyleHurvitz, N., Dinur, T., Becker-Cohen, M., Cozma, C., Hovakimyan, M., Oppermann, S., Demuth, L., Rolfs, A., Abramov, A., Zimran, A., & Revel-Vilk, S. (2019). Glucosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb1) as a Biomarker for Monitoring Treated and Untreated Children with Gaucher Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(12), 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20123033







