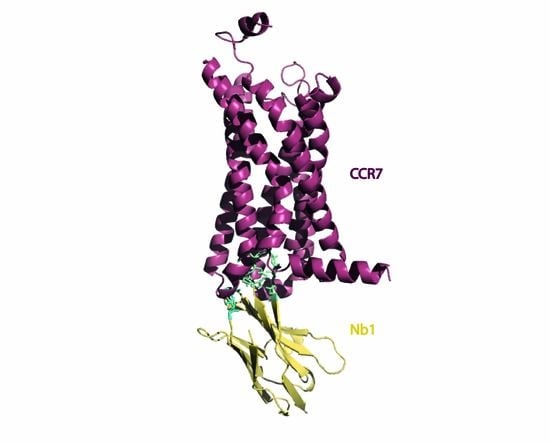
Engineering of Nanobodies Recognizing the Human Chemokine Receptor CCR7
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
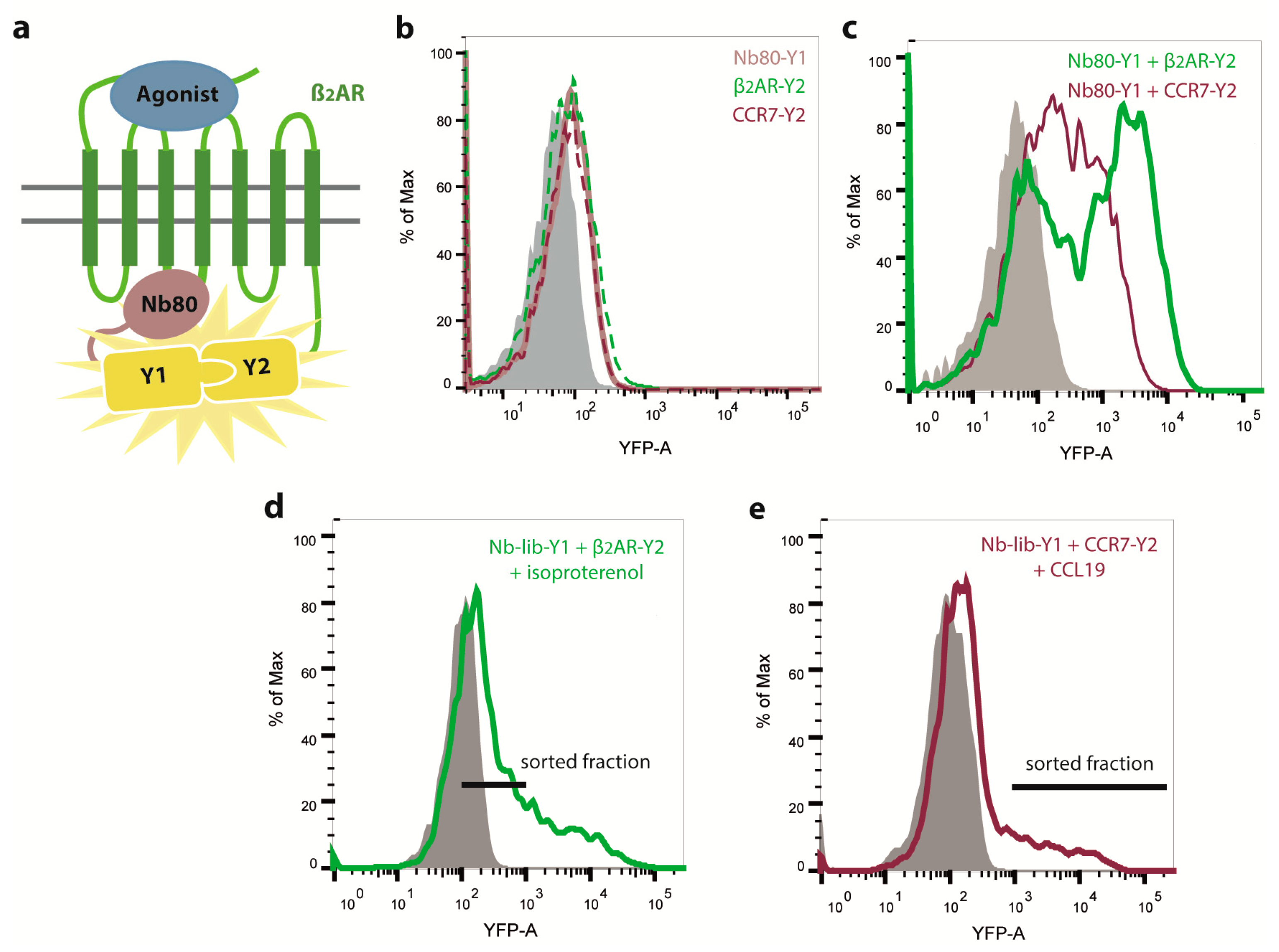
2.1. Engineering of Nbs Recognizing Human CCR7
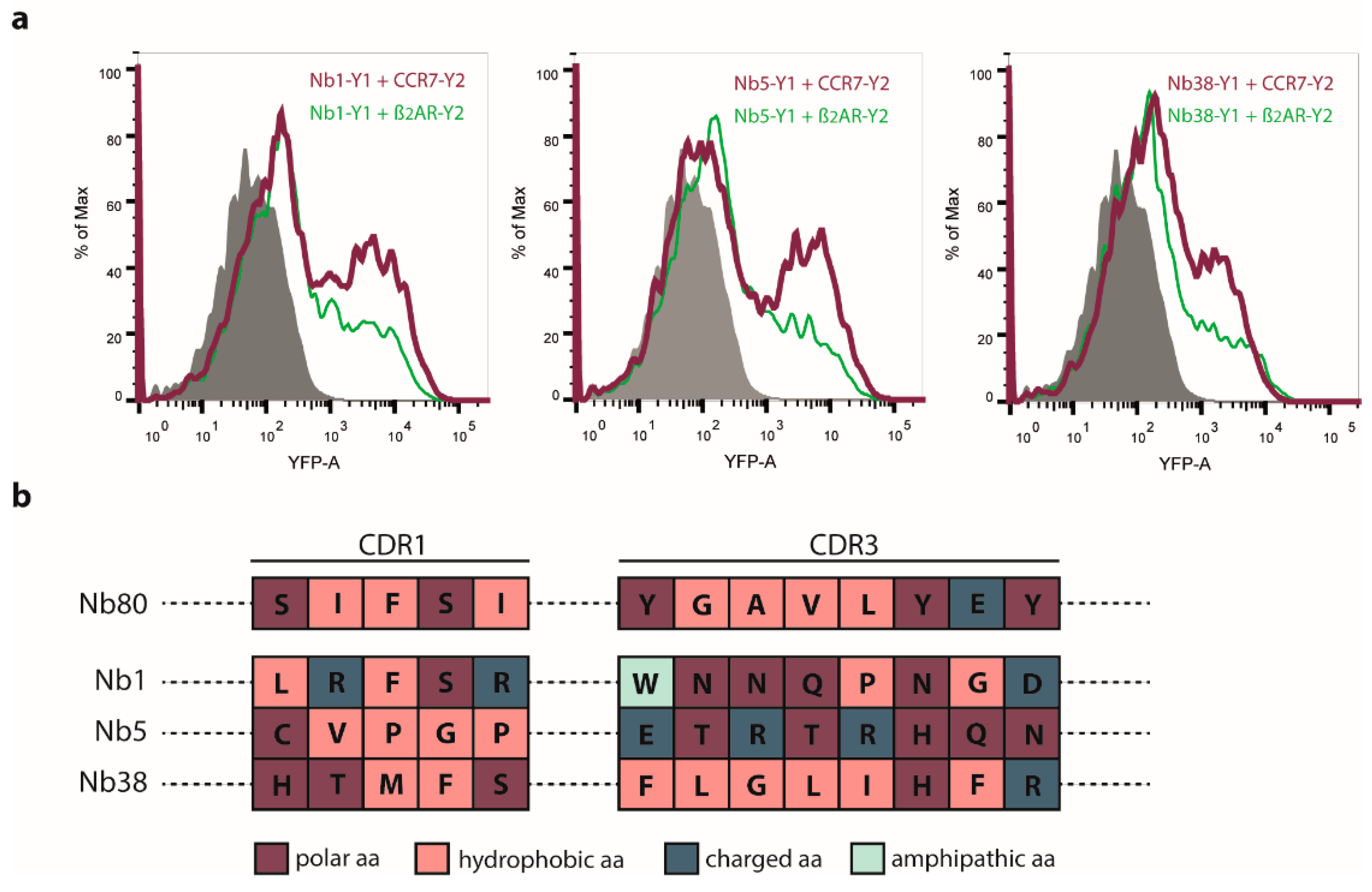
2.2. Nb1, Nb5, and Nb38 Preferentially Recognize CCR7 While Nb80 Preferentially Interacts with β2AR
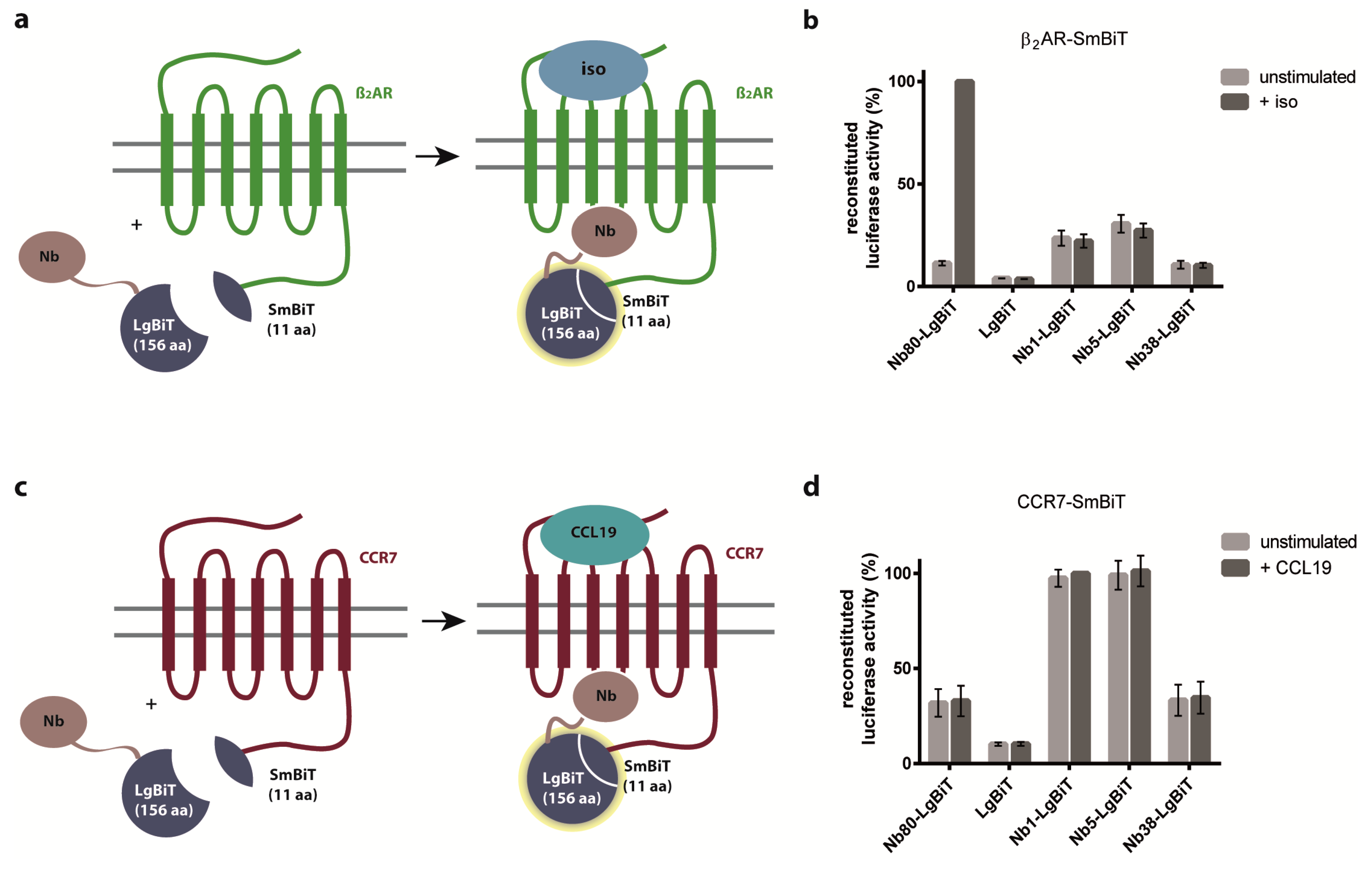
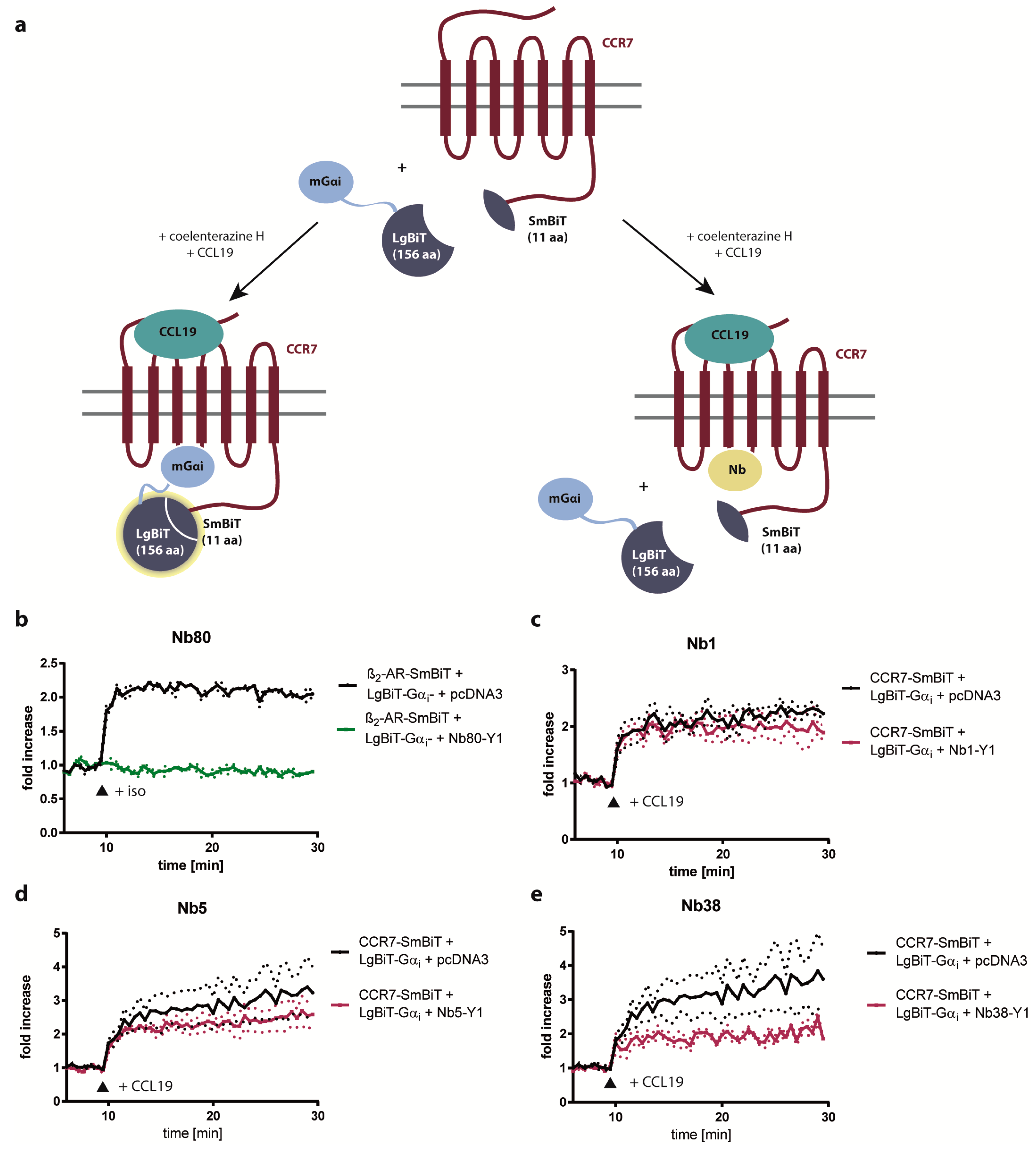
2.3. Nb1, Nb5, and Nb38 Barely Interfere with G-Protein-Coupling to CCR7
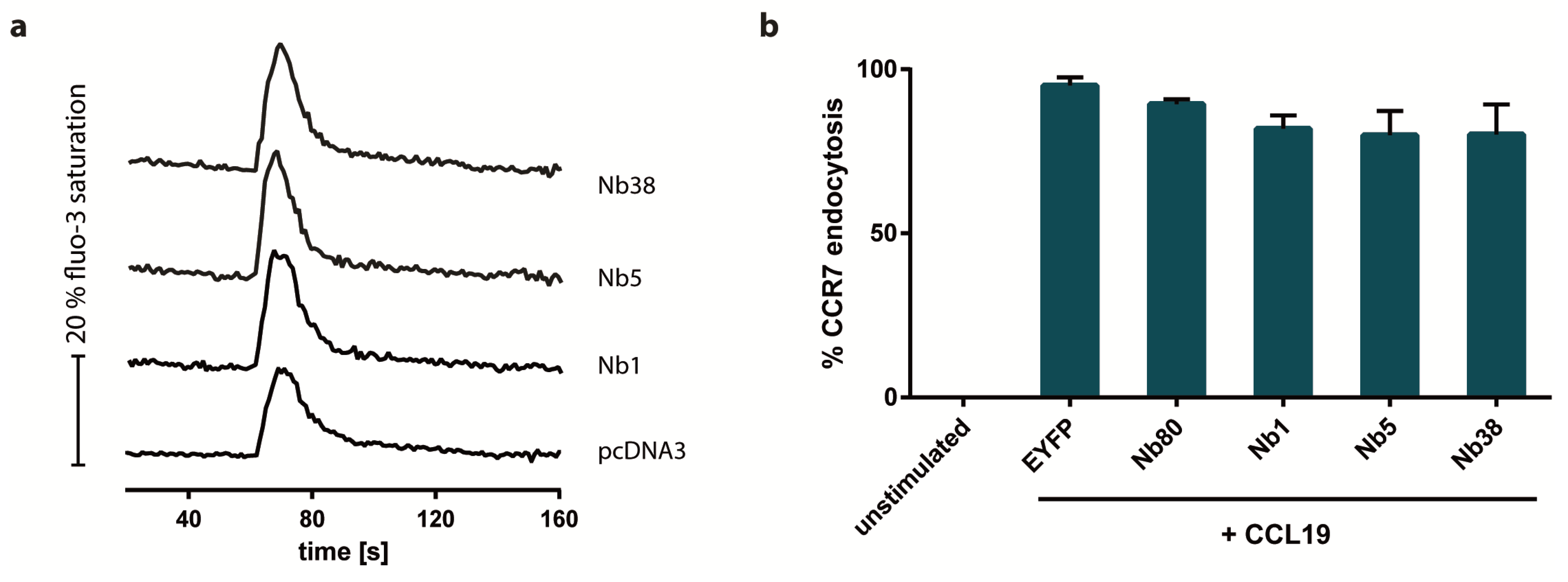
2.4. Nb1, Nb5, or Nb38 do not Impair CCR7-Driven Calcium Mobilization and Receptor Endocytosis
2.5. Monitoring CCL19-induced CCR7 trafficking by Nb1, Nb5, and Nb38
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Lines and Transfection
4.3. Construction of Expression Plasmids
4.4. Synthetic Randomization of Nb80 and Construction of a Nb Library into the BiFC Vector
4.5. Fluorescence Associated Cell Sorting (FACS) Based on BiFC
4.6. Isolation of Nbs Interacting with CCR7
4.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis of CCR7-Recognizing Nbs
4.8. Split-Luciferase Complementation Assay
4.9. G-Protein Competition Assay Based on Split-Luciferase Complementation
4.10. Calcium-Flux
4.11. CCR7 Endocytosis Assay
4.12. Confocal Imaging
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BiFC | bimolecular fluorescence complementation |
| β2AR | β2-adrenergic receptor |
| CCR7 | CC chemokine receptor 7 |
| CCL19 | CC chemokine ligand 19 |
| CCL21 | CC chemokine ligand 21 |
| CDR | complementarity determining region |
| DC | dendritic cell |
| ERK | extracellular signaling regulated kinase |
| FACS | fluorescence associated cell sorting |
| GDP | guanosine diphosphate |
| GFP | green fluorescent protein |
| GPCR | G-protein-coupled receptor |
| GRKs | G-protein-coupled receptor kinases |
| GTP | guanosine triphosphate |
| LgBiT | Large BiT |
| mG-protein | mini-G-protein |
| Nb | nanobody |
| Nbs | nanobodies |
| NLUc | NanoLuc |
| SEM | standard error of the mean |
| SmBiT | Small BiT |
| YFP | yellow fluorescent protein |
References
- Griffith, J.W.; Sokol, C.L.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors: Positioning Cells for Host Defense and Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 659–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legler, D.; Thelen, M. Chemokines: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Biological Function. Chim. Int. J. Chem. 2016, 70, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laufer, J.M.; Legler, D.F. Beyond migration—Chemokines in lymphocyte priming, differentiation, and modulating effector functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuzzi, E.; Angioni, R.; Molon, B.; Cal, B. Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors: Orchestrating Tumor Metastasization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufareva, I.; Salanga, C.L.; Handel, T.M.; Diego, S.; Jolla, L. Chemokine and chemokine receptor structure and interactions: implications for therapeutic strategies. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comerford, I.; Harata-Lee, Y.; Bunting, M.D.; Gregor, C.; Kara, E.E.; McColl, S.R. A myriad of functions and complex regulation of the CCR7/CCL19/CCL21 chemokine axis in the adaptive immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, R.; Davalos-Misslitz, A.C.; Rot, A. CCR7 and its ligands: balancing immunity and tolerance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Hauschild, R.; Schwarz, J.; Moussion, C.; de Vries, I.; Legler, D.F.; Luther, S.A.; Bollenbach, T.; Sixt, M. Interstitial dendritic cell guidance by haptotactic chemokine gradients. Science 2013, 339, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos-misslitz, A.C.M.; Rieckenberg, J.; Willenzon, S.; Worbs, T.; Kremmer, E.; Bernhardt, G.; Förster, R. Generalized multi-organ autoimmunity in CCR7- deficient mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschovakis, G.L.; Förster, R. Multifaceted activities of CCR7 regulate T-cell homeostasis in health and disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1949–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legler, D.F.; Uetz-von Allmen, E.; Hauser, M.A. CCR7: Roles in cancer cell dissemination, migration and metastasis formation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 54, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legler, D.F.; Thelen, M. New insights in chemokine signaling. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legler, D.F.; Matti, C.; Laufer, J.M.; Jakobs, B.D.; Purvanov, V.; Allmen, E.U.; Thelen, M. Modulation of Chemokine Receptor Function by Cholesterol: New Prospects for Pharmacological Intervention. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauser, M.A.; Legler, D.F. Common and biased signaling pathways of the chemokine receptor CCR7 elicited by its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 in leukocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvanov, V.; Matti, C.; Samson, G.P.B.; Kindinger, I.; Legler, D.F. Fluorescently Tagged CCL19 and CCL21 to Monitor CCR7 and ACKR4 Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, M.A.; Schaeuble, K.; Kindinger, I.; Impellizzieri, D.; Krueger, W.A.; Hauck, C.R.; Boyman, O.; Legler, D.F. Inflammation-Induced CCR7 Oligomers Form Scaffolds to Integrate Distinct Signaling Pathways for Efficient Cell Migration. Immunity 2016, 44, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laufer, J.M.; Kindinger, I.; Artinger, M.; Pauli, A.; Legler, D.F. CCR7 Is Recruited to the Immunological Synapse, Acts as Co-stimulatory Molecule and Drives LFA-1 Clustering for Efficient T Cell Adhesion Through ZAP70. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesmer, J.J.G. Hitchhiking on the heptahelical highway: structure and function of 7 TM receptor complexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Fenalti, G.; Wu, H.; Han, G.W.; Cherezov, V. Crystal structure of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in complex with a viral chemokine. Sience 2015, 347, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Han, G.W.; Abagyan, R.; Cherezov, V.; Kufareva, I.; Handel, T.M.; Zheng, Y.; Han, G.W.; Abagyan, R.; Wu, B.; et al. Structure of CC Chemokine Receptor 5 with a Potent Chemokine Antagonist Reveals Mechanisms of Chemokine Recognition and Molecular Mimicry by HIV Article Structure of CC Chemokine Receptor 5 with a Potent Chemokine Antagonist Reveals Mechanisms of Chemokin. Immunity 2017, 46, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Choi, H.; Fung, J.J.; Pardon, E.; Casarosa, P.; Chae, P.S.; Devree, B.T.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Thian, F.S.; Kobilka, T.S.; et al. Structure of a nanobody-stabilized active state of the b 2 adrenoceptor. Nature 2011, 469, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannejad, R.; Tomshine, J.C.; Tomshine, J.R.; Chevalier, M.; Mahoney, J.P.; Steyaert, J.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Sunahara, R.K.; El-Samad, H.; Huang, B.; et al. Conformational biosensors reveal GPCR signalling from endosomes. Nature 2013, 495, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manglik, A.; Kobilka, B.K.; Steyaert, J. Nanobodies to Study G Protein – Coupled Receptor Structure and Function. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 57, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heukers, R.; De Groof, T.W.M.; Smit, M.J. ScienceDirect Nanobodies detecting and modulating GPCRs outside in and inside out. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2019, 57, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revets, H.; De Baetselier, P.; Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies as novel agents for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2005, 5, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyaert, J.; Kobilka, B.K. Nanobody stabilization of G protein-coupled receptor conformational states. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Wit, R.H.; Verkaar, F.; Smit, M.J.; Mujic, A. GPCR-targeting nanobodies: attractive research tools, diagnostics, and therapeutics. CellPress 2014, 35, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Nyfeler, B.; Michnick, S.W.; Hauri, H.-P. Capturing protein interactions in the secretory pathway of living cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2005, 102, 6350–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staus, D.P.; Wingler, L.M.; Strachan, R.T.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Pardon, E.; Ahn, S.; Steyaert, J.; Kobilka, B.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Regulation of β2-adrenergic receptor function by conformationally selective single-domain intrabodies. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Okashah, N.; Inoue, A.; Nehme, R.; Carpenter, B.; Tate, C.G.; Lambert, N.A. Mini G protein probes for active G protein– coupled receptors (GPCRs) in live cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 7466–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeuble, K.; Hauser, M.A.; Rippl, A.V.; Bruderer, R.; Otero, C.; Groettrup, M.; Legler, D.F. Ubiquitylation of the chemokine receptor CCR7 enables efficient receptor recycling and cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4463–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerbini, T.; Funahashi, R.; Luo, Y.; Liu, C.; Park, K.; Rao, M.; Malik, N.; Zou, J. Transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN)-mediated CLYBL targeting enables enhanced transgene expression and one-step generation of dual reporter human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) and neural stem cell (NSC) lines. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, C.; Groettrup, M.; Legler, D.F. Opposite fate of endocytosed CCR7 and its ligands: recycling versus degradation. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2314–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, C.; Eisele, P.S.; Schaeuble, K.; Groettrup, M.; Legler, D.F. Distinct motifs in the chemokine receptor CCR7 regulate signal transduction, receptor trafficking and chemotaxis. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jakobs, B.D.; Spannagel, L.; Purvanov, V.; Uetz-von Allmen, E.; Matti, C.; Legler, D.F. Engineering of Nanobodies Recognizing the Human Chemokine Receptor CCR7. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102597
Jakobs BD, Spannagel L, Purvanov V, Uetz-von Allmen E, Matti C, Legler DF. Engineering of Nanobodies Recognizing the Human Chemokine Receptor CCR7. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102597
Chicago/Turabian StyleJakobs, Barbara D., Lisa Spannagel, Vladimir Purvanov, Edith Uetz-von Allmen, Christoph Matti, and Daniel F. Legler. 2019. "Engineering of Nanobodies Recognizing the Human Chemokine Receptor CCR7" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102597
APA StyleJakobs, B. D., Spannagel, L., Purvanov, V., Uetz-von Allmen, E., Matti, C., & Legler, D. F. (2019). Engineering of Nanobodies Recognizing the Human Chemokine Receptor CCR7. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102597