Exosomes as Emerging Pro-Tumorigenic Mediators of the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype
Abstract
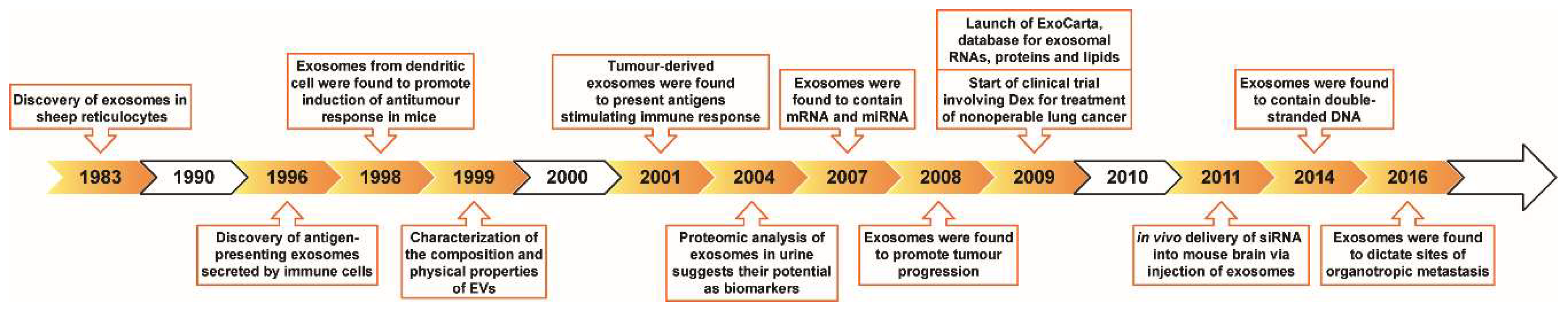
1. Introduction
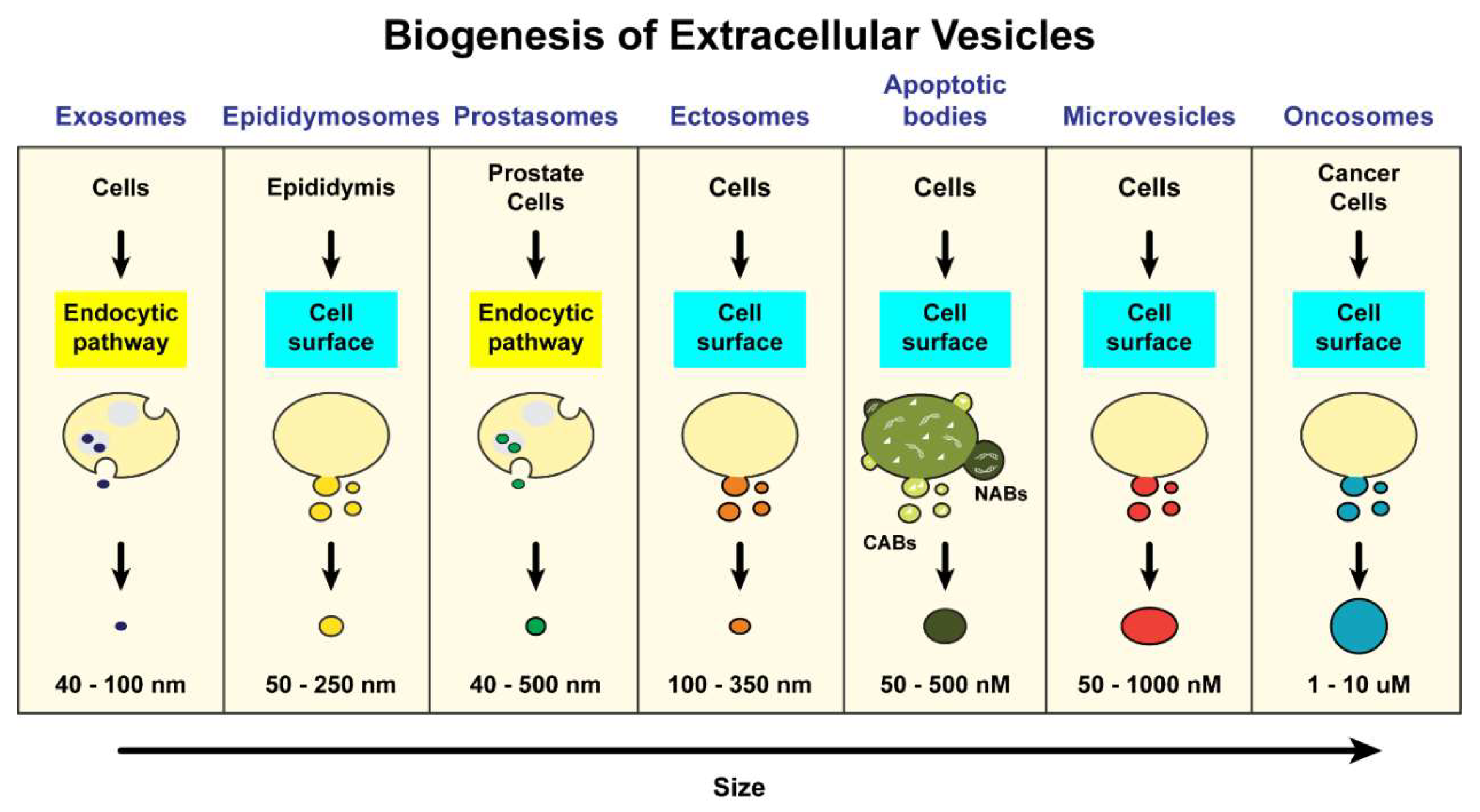
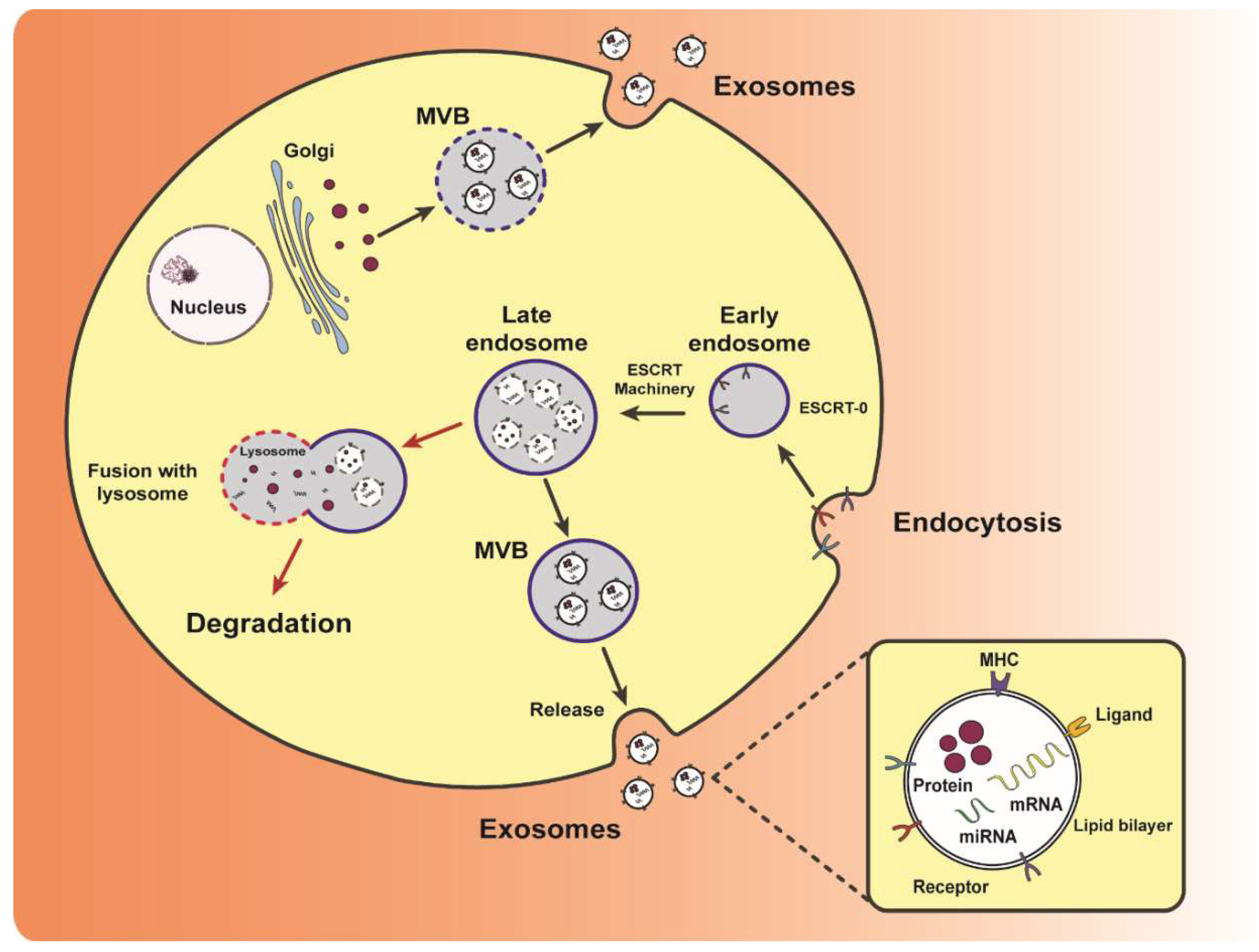
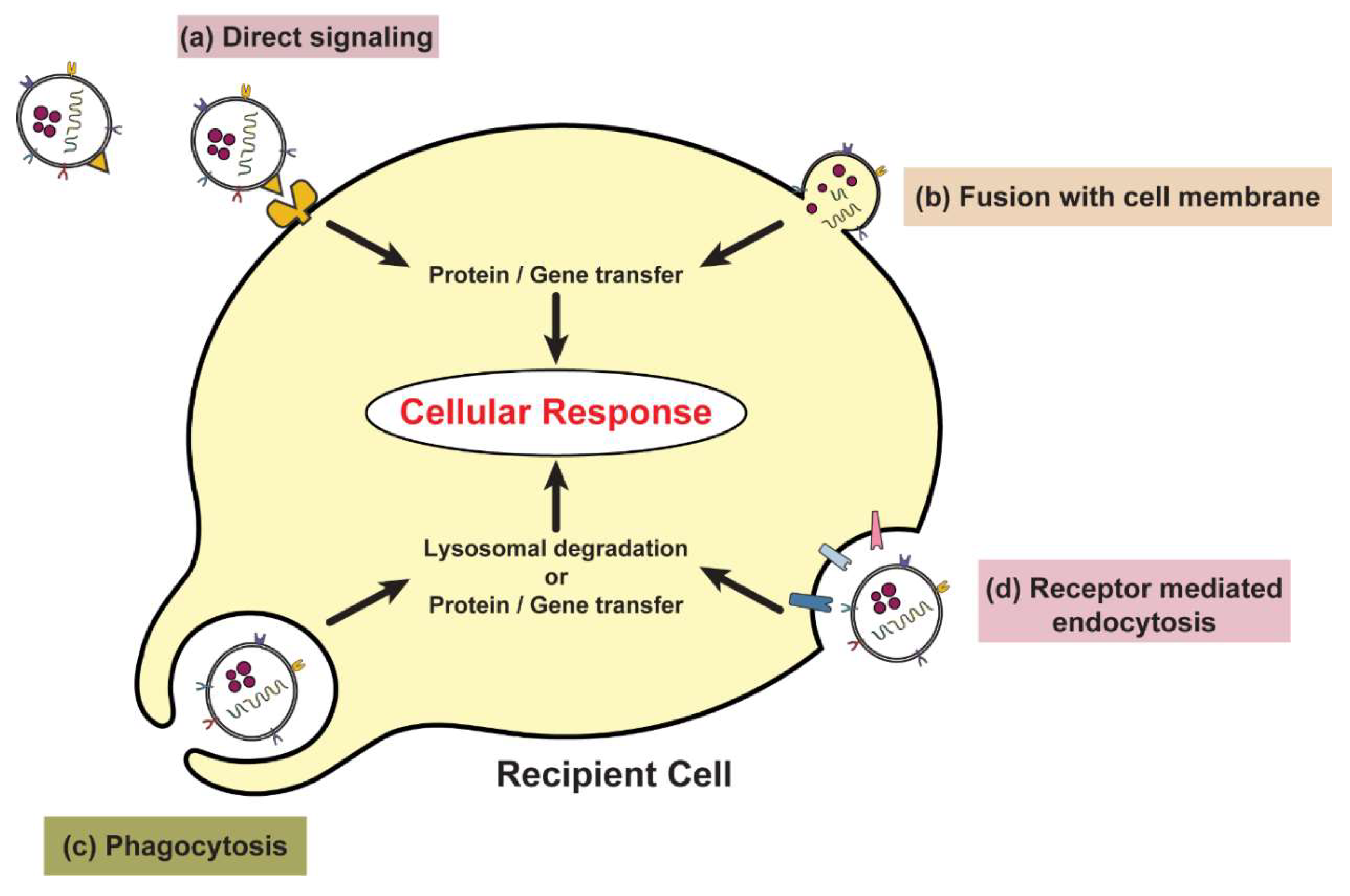
2. Exosome Biogenesis, Composition and Uptake
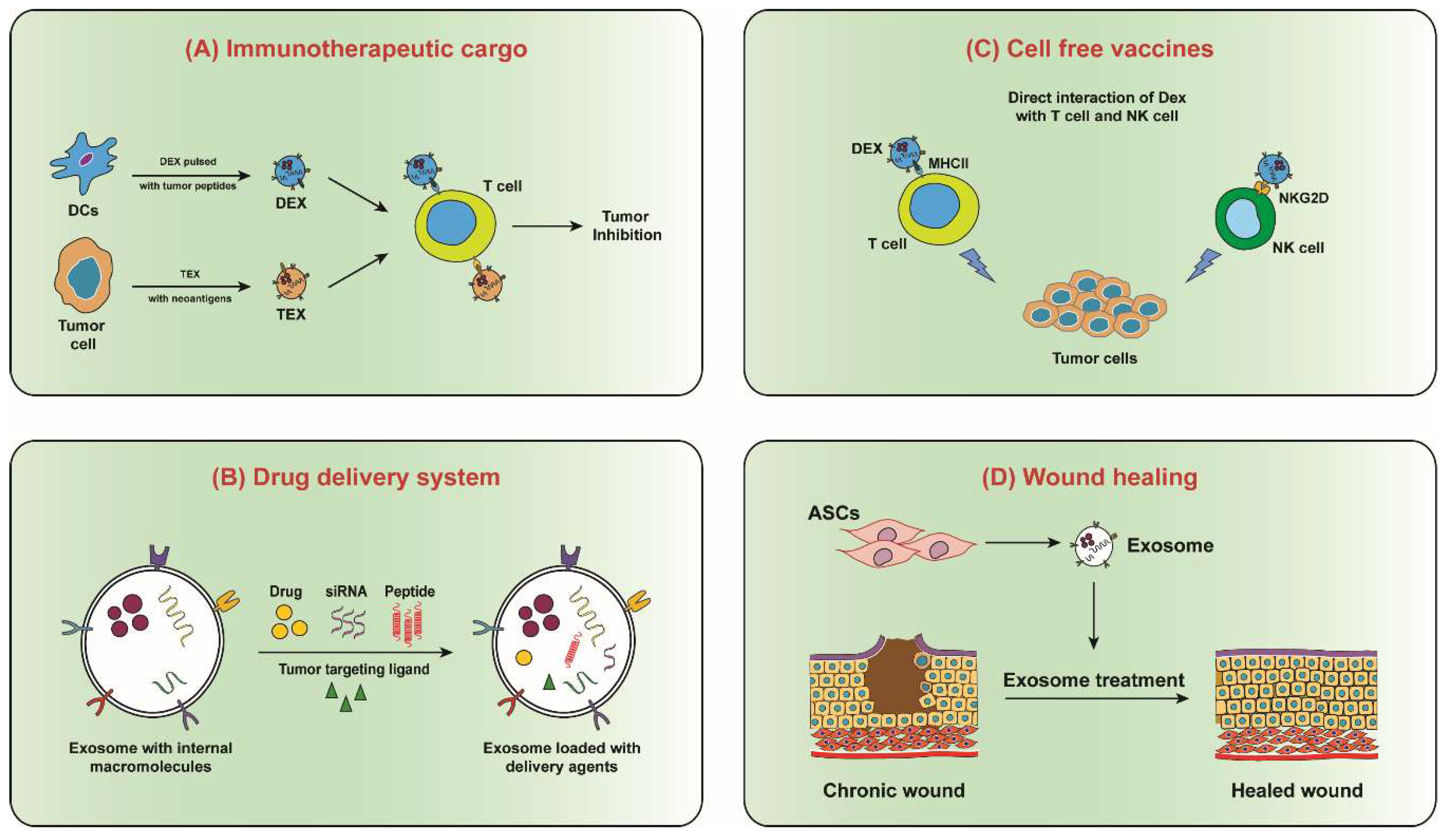
3. Exosomes in the Tumor Microenvironment
3.1. Exosomal Proteins
3.2. Exosomal Messenger RNA
3.3. Exosomal Microrna
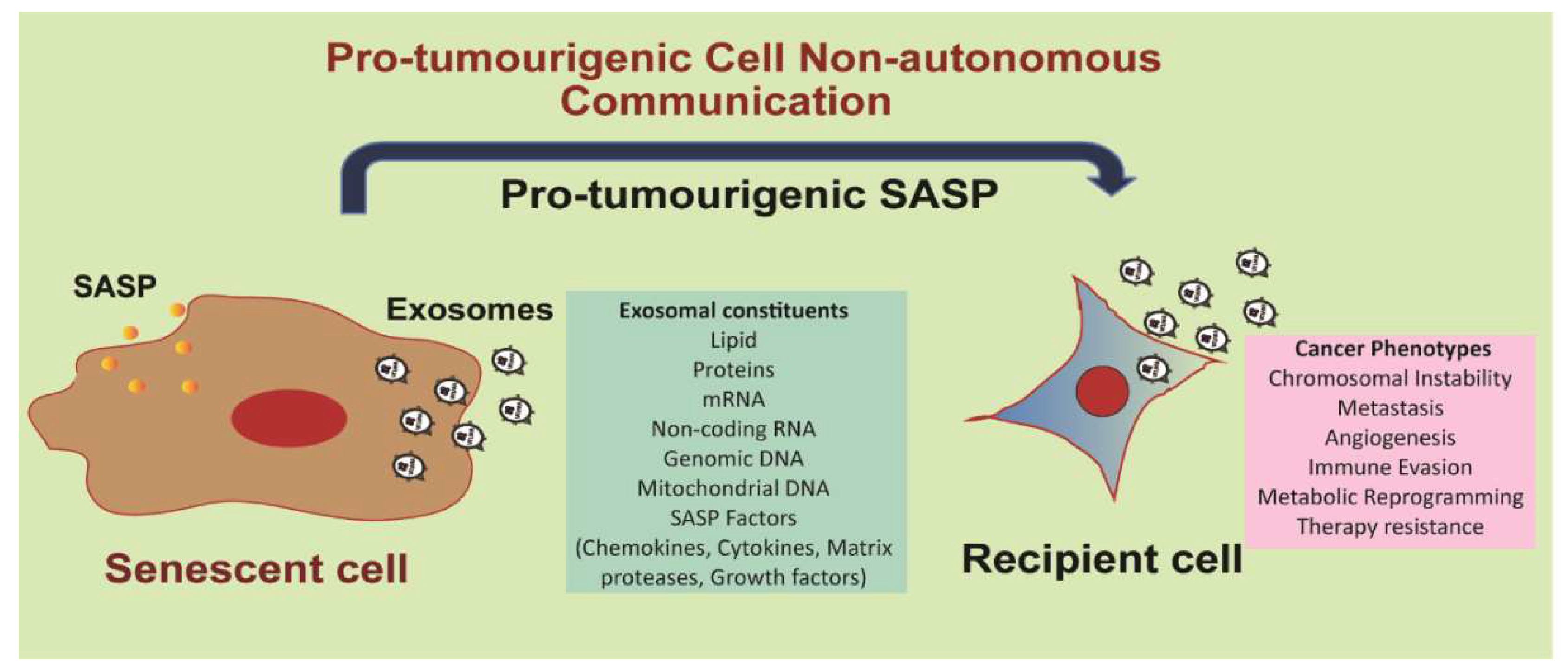
4. Exosomes as Components of the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype
4.1. The Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype
4.2. Exosomes as Pro-Tumorigenic SASP
5. Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campisi, J.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Cellular senescence: When bad things happen to good cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, B.G.; Durik, M.; Baker, D.J.; van Deursen, J.M. Cellular senescence in aging and age-related disease: From mechanisms to therapy. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Paine, M.S.; Brooks, A.M.; McCubrey, J.A.; Renegar, R.H.; Wang, R.; Terrian, D.M. Senescence-associated exosome release from human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7864–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasugi, M.; Okada, R.; Takahashi, A.; Virya Chen, D.; Watanabe, S.; Hara, E. Small extracellular vesicles secreted from senescent cells promote cancer cell proliferation through EphA2. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C. Exosomes: Secreted vesicles and intercellular communications. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: Shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzer, K.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Heijnen, H.F.; Stoorvogel, W.; Geuze, H.J. Exosome: From internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 19, 3365–3374. [Google Scholar]
- Brinton, L.T.; Sloane, H.S.; Kester, M.; Kelly, K.A. Formation and role of exosomes in cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsen, H.; Stenmark, H. Protein secretion: Unconventional exit by exophagy. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, R415–R418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendler, F.; Bota-Rabassedas, N.; Franch-Marro, X. Cancer becomes wasteful: Emerging roles of exosomes(†) in cell-fate determination. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.M.; Fang, Y.; Fallon, J.K.; Yang, J.M.; Hildreth, J.E.K.; Gould, S.J. Exosomes and HIV Gag bud from endosome-like domains of the T cell plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, P.; Shukla, A. Exosomes: Potential in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Medicines 2015, 2, 310–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabouille, C.; Malhotra, V.; Nickel, W. Diversity in unconventional protein secretion. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5251–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusten, T.E.; Vaccari, T.; Stenmark, H. Shaping development with ESCRTs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 14, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henne, W.M.; Buchkovich, N.J.; Emr, S.D. The ESCRT pathway. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baietti, M.F.; Zhang, Z.; Mortier, E.; Melchior, A.; Degeest, G.; Geeraerts, A.; Ivarsson, Y.; Depoortere, F.; Coomans, C.; Vermeiren, E.; et al. Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babst, M. MVB Vesicle Formation: ESCRT-Dependent, ESCRT-Independent and Everything in Between. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; Charrin, S.; Simoes, S.; Romao, M.; Rochin, L.; Saftig, P.; Marks, M.S.; Rubinstein, E.; Raposo, G. The tetraspanin CD63 regulates ESCRT-independent and dependent endosomal sorting during melanogenesis. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brugger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, M.S.; Heijnen, H.F.; Raposo, G. Lysosome-related organelles: Unusual compartments become mainstream. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, S.; Fahner, C.J.; Reid, G.E.; Simpson, R.J. ExoCarta 2012: Database of exosomal proteins, RNA and lipids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1241–D1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borras, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inal, J.M.; Kosgodage, U.; Azam, S.; Stratton, D.; Antwi-Baffour, S.; Lange, S. Blood/plasma secretome and microvesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2317–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P. Interaction of Heat Shock Proteins with Peptides and Antigen Presenting Cells: Chaperoning of the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 395–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.; van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; Manel, N.; Moita, L.F.; Thery, C.; Raposo, G. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, J.D.; Lekutis, C.; Singer, K.L.; Bui, A.; Yuzuki, D.; Srinivasan, U.; Parry, G. cDNA cloning of a mouse mammary epithelial cell surface protein reveals the existence of epidermal growth factor-like domains linked to factor VIII-like sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8417–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Nijman, H.W.; Stoorvogel, W.; Liejendekker, R.; Harding, C.V.; Melief, C.J.; Geuze, H.J. Blymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laulagnier, K.; Motta, C.; Hamdi, S.; Roy, S.; Fauvelle, F.; Pageaux, J.F.; Kobayashi, T.; Salles, J.P.; Perret, B.; Bonnerot, C.; et al. Mast cell- and dendritic cell-derived exosomes display a specific lipid composition and an unusual membrane organization. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubbolts, R.; Leckie, R.S.; Veenhuizen, P.T.; Schwarzmann, G.; Mobius, W.; Hoernschemeyer, J.; Slot, J.W.; Geuze, H.J.; Stoorvogel, W. Proteomic and biochemical analyses of human B cell-derived exosomes. Potential implications for their function and multivesicular body formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10963–10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, A.E.; Larregina, A.T.; Shufesky, W.J.; Sullivan, M.L.; Stolz, D.B.; Papworth, G.D.; Zahorchak, A.F.; Logar, A.J.; Wang, Z.; Watkins, S.C.; et al. Endocytosis, intracellular sorting, and processing of exosomes by dendritic cells. Blood 2004, 104, 3257–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.F.; Schiel, A.E.; Fijnheer, R.; Geuze, H.J.; Sixma, J.J. Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: Microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood 1999, 94, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar]
- Denzer, K.; van Eijk, M.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Jakobson, E.; de Groot, C.; Geuze, H.J. Follicular dendritic cells carry MHC class II-expressing microvesicles at their surface. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gassart, A.; Geminard, C.; Fevrier, B.; Raposo, G.; Vidal, M. Lipid raft-associated protein sorting in exosomes. Blood 2003, 102, 4336–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janas, T.; Janas, M.M.; Sapoń, K.; Janas, T. Mechanisms of RNA loading into exosomes. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Yue, S.; Stadel, D.; Zoller, M. Toward tailored exosomes: The exosomal tetraspanin web contributes to target cell selection. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhu, Y.L.; Hu, F.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, N.P.; Xiao, Z.D. Dynamics of exosome internalization and trafficking. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zhao, W.L.; Ye, Y.Y.; Bai, X.C.; Liu, R.Q.; Chang, L.F.; Zhou, Q.; Sui, S.F. Cellular internalization of exosomes occurs through phagocytosis. Traffic 2010, 11, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellos-Hoff, M.H.; Lyden, D.; Wang, T.C. The evolution of the cancer niche during multistage carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Rana, S.; Zoller, M. Host matrix modulation by tumor exosomes promotes motility and invasiveness. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.W.; Michael, M.Z.; Gleadle, J.M. Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Hung, J.Y.; Chang, W.A.; Lin, Y.S.; Pan, Y.C.; Tsai, P.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Kuo, P.L. Hypoxic lung cancer-secreted exosomal miR-23a increased angiogenesis and vascular permeability by targeting prolyl hydroxylase and tight junction protein ZO-1. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4929–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, A.; Ting, H.; Agarwal, C.; Mateen, S.; Somasagara, R.; Hussain, A.; Graner, M.; Frederick, B.; Agarwal, R.; Deep, G. Exosomes secreted under hypoxia enhance invasiveness and stemness of prostate cancer cells by targeting adherens junction molecules. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Aleckovic, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; Garcia-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demory Beckler, M.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Franklin, J.L.; Ham, A.J.; Halvey, P.J.; Imasuen, I.E.; Whitwell, C.; Li, M.; Liebler, D.C.; Coffey, R.J. Proteomic analysis of exosomes from mutant KRAS colon cancer cells identifies intercellular transfer of mutant KRAS. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.; Thomas, R.; Ranjan, M.; Mondal, D.; Moroz, K.; Fang, Z.; Rezk, B.M.; Moparty, K.; Sikka, S.C.; et al. Neoplastic reprogramming of patient-derived adipose stem cells by prostate cancer cell-associated exosomes. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luga, V.; Zhang, L.; Viloria-Petit, A.M.; Ogunjimi, A.A.; Inanlou, M.R.; Chiu, E.; Buchanan, M.; Hosein, A.N.; Basik, M.; Wrana, J.L. Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell 2012, 151, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Tan, H.S.; Datta, A.; Lai, R.C.; Zhang, H.; Meng, W.; Lim, S.K.; Sze, S.K. Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by secretion of proteins and exosomes. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzewska, P.; Christianson, H.C.; Welch, J.E.; Svensson, K.J.; Fredlund, E.; Ringner, M.; Morgelin, M.; Bourseau-Guilmain, E.; Bengzon, J.; Belting, M. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7312–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko, I.; Rana, S.; Baumann, A.; McAlear, J.; Hellwig, A.; Trendelenburg, M.; Lochnit, G.; Preissner, K.T.; Zoller, M. Cell surface tetraspanin Tspan8 contributes to molecular pathways of exosome-induced endothelial cell activation. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nedawi, K.; Meehan, B.; Kerbel, R.S.; Allison, A.C.; Rak, J. Endothelial expression of autocrine VEGF upon the uptake of tumor-derived microvesicles containing oncogenic EGFR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3794–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, F.; Schartz, N.E.; Chaput, N.; Flament, C.; Raposo, G.; Amigorena, S.; Angevin, E.; Zitvogel, L. Tumor-derived exosomes: A new source of tumor rejection antigens. Vaccine 2002, 20 (Suppl. 4), A28–A31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skokos, D.; Botros, H.G.; Demeure, C.; Morin, J.; Peronet, R.; Birkenmeier, G.; Boudaly, S.; Mecheri, S. Mast cell-derived exosomes induce phenotypic and functional maturation of dendritic cells and elicit specific immune responses in vivo. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Shen, X.; Sprent, J. Direct stimulation of naive T cells by membrane vesicles from antigen-presenting cells: Distinct roles for CD54 and B7 molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6670–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfers, J.; Lozier, A.; Raposo, G.; Regnault, A.; Thery, C.; Masurier, C.; Flament, C.; Pouzieux, S.; Faure, F.; Tursz, T.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, A.; Mitchell, J.P.; Court, J.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z. Human tumor-derived exosomes selectively impair lymphocyte responses to interleukin-2. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 7458–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, M.; Schroder, M.; Nagaeva, O.; Baranov, V.; Widmark, A.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; Wikstrom, P. Prostate tumor-derived exosomes down-regulate NKG2D expression on natural killer cells and CD8+ T cells: Mechanism of immune evasion. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreola, G.; Rivoltini, L.; Castelli, C.; Huber, V.; Perego, P.; Deho, P.; Squarcina, P.; Accornero, P.; Lozupone, F.; Lugini, L.; et al. Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion of FasL-bearing microvesicles. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T., Jr.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.S.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, E.J.; Rho, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Hwang, D.; et al. Colorectal cancer cell-derived microvesicles are enriched in cell cycle-related mRNAs that promote proliferation of endothelial cells. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutkin, A.; Uziel, O.; Beery, E.; Nordenberg, J.; Pinchasi, M.; Goldvaser, H.; Henick, S.; Goldberg, M.; Lahav, M. Tumor cells derived exosomes contain hTERT mRNA and transform nonmalignant fibroblasts into telomerase positive cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59173–59188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldevilla, B.; Rodriguez, M.; San Millan, C.; Garcia, V.; Fernandez-Perianez, R.; Gil-Calderon, B.; Martin, P.; Garcia-Grande, A.; Silva, J.; Bonilla, F.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes are enriched in DeltaNp73, which promotes oncogenic potential in acceptor cells and correlates with patient survival. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, L.; Muller-Haegele, S.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Gooding, W.; Okada, H.; Whiteside, T.L. Exosomes isolated from plasma of glioma patients enrolled in a vaccination trial reflect antitumor immune activity and might predict survival. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1008347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.; Bajracharya, S.D.; Yuen, P.S.; Zhou, H.; Star, R.A.; Illei, G.G.; Alevizos, I. Exosomes from human saliva as a source of microRNA biomarkers. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids--the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata-Kawata, H.; Izumiya, M.; Kurioka, D.; Honma, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Furuta, K.; Gunji, T.; Ohta, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sonoda, H.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, T.; Sugimachi, K.; Iinuma, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Kurashige, J.; Sawada, G.; Ueda, M.; Uchi, R.; Ueo, H.; Takano, Y.; et al. Exosomal microRNA in serum is a novel biomarker of recurrence in human colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowits, G.; Gercel-Taylor, C.; Day, J.M.; Taylor, D.D.; Kloecker, G.H. Exosomal microRNA: A diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2009, 10, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejima, H.; Iinuma, H.; Kanaoka, R.; Matsutani, N.; Kawamura, M. Exosomal microRNA in plasma as a non-invasive biomarker for the recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.D.; Gercel-Taylor, C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 110, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Exosomal miRNAs as Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kamohara, H.; Kinoshita, K.; Kurashige, J.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; Watanabe, M.; Baba, H. Clinical impact of serum exosomal microRNA-21 as a clinical biomarker in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2013, 119, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Fong, M.Y.; Min, Y.; Somlo, G.; Liu, L.; Palomares, M.R.; Yu, Y.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezu, T.; Ohyashiki, K.; Kuroda, M.; Ohyashiki, J.H. Leukemia cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miRNAs. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, K.; Inoue, K.; Fujiwara, A.; Hatakeyama, K.; Kanto, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Muramatsu, K.; Fukuda, Y.; Ogura, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Let-7 microRNA family is selectively secreted into the extracellular environment via exosomes in a metastatic gastric cancer cell line. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, S.A.; Sugimoto, H.; O’Connell, J.T.; Kato, N.; Villanueva, A.; Vidal, A.; Qiu, L.; Vitkin, E.; Perelman, L.T.; Melo, C.A.; et al. Cancer exosomes perform cell-independent microRNA biogenesis and promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppe, J.P.; Desprez, P.Y.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: The dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2010, 5, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuilman, T.; Peeper, D.S. Senescence-messaging secretome: SMS-ing cellular stress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, J.C.; O’Loghlen, A.; Banito, A.; Guijarro, M.V.; Augert, A.; Raguz, S.; Fumagalli, M.; Da Costa, M.; Brown, C.; Popov, N.; et al. Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell 2008, 133, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuilman, T.; Michaloglou, C.; Vredeveld, L.C.; Douma, S.; van Doorn, R.; Desmet, C.J.; Aarden, L.A.; Mooi, W.J.; Peeper, D.S. Oncogene-induced senescence relayed by an interleukin-dependent inflammatory network. Cell 2008, 133, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Xu, Q.; Martin, T.D.; Li, M.Z.; Demaria, M.; Aron, L.; Lu, T.; Yankner, B.A.; Campisi, J.; Elledge, S.J. The DNA damage response induces inflammation and senescence by inhibiting autophagy of GATA4. Science 2015, 349, aaa5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppe, J.P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Munoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 2853–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.C.; Banito, A.; Wuestefeld, T.; Georgilis, A.; Janich, P.; Morton, J.P.; Athineos, D.; Kang, T.W.; Lasitschka, F.; Andrulis, M.; et al. A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, S.; Coppe, J.P.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. Stromal-epithelial interactions in aging and cancer: Senescent fibroblasts alter epithelial cell differentiation. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppe, J.P.; Kauser, K.; Campisi, J.; Beausejour, C.M. Secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor by primary human fibroblasts at senescence. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29568–29574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos, A.R.; Coppe, J.P.; Campisi, J.; Desprez, P.Y. Senescent cells as a source of inflammatory factors for tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krtolica, A.; Parrinello, S.; Lockett, S.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Senescent fibroblasts promote epithelial cell growth and tumorigenesis: A link between cancer and aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12072–12077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavik, C.; Coleman, I.; Dean, J.P.; Knudsen, B.; Plymate, S.; Nelson, P.S. The gene expression program of prostate fibroblast senescence modulates neoplastic epithelial cell proliferation through paracrine mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toso, A.; Revandkar, A.; Di Mitri, D.; Guccini, I.; Proietti, M.; Sarti, M.; Pinton, S.; Zhang, J.; Kalathur, M.; Civenni, G.; et al. Enhancing chemotherapy efficacy in Pten-deficient prostate tumors by activating the senescence-associated antitumor immunity. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhland, M.K.; Loza, A.J.; Capietto, A.H.; Luo, X.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Flanagan, K.C.; Belt, B.A.; Alspach, E.; Leahy, K.; Luo, J.; et al. Stromal senescence establishes an immunosuppressive microenvironment that drives tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimonti, A.; Carracedo, A.; Clohessy, J.G.; Trotman, L.C.; Nardella, C.; Egia, A.; Salmena, L.; Sampieri, K.; Haveman, W.J.; Brogi, E.; et al. Subtle variations in Pten dose determine cancer susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlecki-Zaniewicz, L.; Lammermann, I.; Latreille, J.; Bobbili, M.R.; Pils, V.; Schosserer, M.; Weinmullner, R.; Dellago, H.; Skalicky, S.; Pum, D.; et al. Small extracellular vesicles and their miRNA cargo are anti-apoptotic members of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Aging 2018, 10, 1103–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadota, T.; Fujita, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Araya, J.; Kuwano, K.; Ochiya, T. Emerging role of extracellular vesicles as a senescence-associated secretory phenotype: Insights into the pathophysiology of lung diseases. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atienzar-Aroca, S.; Flores-Bellver, M.; Serrano-Heras, G.; Martinez-Gil, N.; Barcia, J.M.; Aparicio, S.; Perez-Cremades, D.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Diaz-Llopis, M.; Romero, F.J.; et al. Oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelium cells increases exosome secretion and promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Harris, S.L.; Levine, A.J. The regulation of exosome secretion: A novel function of the p53 protein. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4795–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.; Serrano, M. The power and the promise of oncogene-induced senescence markers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi, M. Emerging roles of extracellular vesicles in cellular senescence and aging. Aging Cell 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, E.L.; Lindsay, S.; Halasz, M.; Gubbins, L.C.; Weiner-Gorzel, K.; Guang, M.H.Z.; McGoldrick, A.; Collins, E.; Henry, M.; Blanco-Fernandez, A.; et al. Protein and chemotherapy profiling of extracellular vesicles harvested from therapeutic induced senescent triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effenberger, T.; von der Heyde, J.; Bartsch, K.; Garbers, C.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Chalaris, A.; Murphy, G.; Rose-John, S.; Rabe, B. Senescence-associated release of transmembrane proteins involves proteolytic processing by ADAM17 and microvesicle shedding. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4847–4856. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, N.; Meyer, D.; Mauermann, A.; von der Heyde, J.; Wolf, J.; Schwarz, J.; Knittler, K.; Murphy, G.; Michalek, M.; Garbers, C.; et al. Shedding of Endogenous Interleukin-6 Receptor (IL-6R) Is Governed by A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase (ADAM) Proteases while a Full-length IL-6R Isoform Localizes to Circulating Microvesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26059–26071. [Google Scholar]
- van Balkom, B.W.; de Jong, O.G.; Smits, M.; Brummelman, J.; den Ouden, K.; de Bree, P.M.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Pegtel, D.M.; Stoorvogel, W.; Wurdinger, T.; et al. Endothelial cells require miR-214 to secrete exosomes that suppress senescence and induce angiogenesis in human and mouse endothelial cells. Blood 2013, 121, 3997–4006. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner-Gorzel, K.; Dempsey, E.; Milewska, M.; McGoldrick, A.; Toh, V.; Walsh, A.; Lindsay, S.; Gubbins, L.; Cannon, A.; Sharpe, D.; et al. Overexpression of the microRNA miR-433 promotes resistance to paclitaxel through the induction of cellular senescence in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 745–758. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, A.; Okada, R.; Nagao, K.; Kawamata, Y.; Hanyu, A.; Yoshimoto, S.; Takasugi, M.; Watanabe, S.; Kanemaki, M.T.; Obuse, C.; et al. Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15287. [Google Scholar]
- van Deursen, J.M. The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature 2014, 509, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhashi, M.; Taub, D.D.; Kapogiannis, D.; Eitan, E.; Zukley, L.; Mattson, M.P.; Ferrucci, L.; Schwartz, J.B.; Goetzl, E.J. Aging enhances release of exosomal cytokine mRNAs by Abeta1-42-stimulated macrophages. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 5141–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhar, R.; Luijten, M.N.H.; Wong, A.X.F.; Cheng, B.; Guo, K.; Neo, S.P.; Au, B.; Kulkarni, M.; Lim, K.J.; Maimaiti, J.; et al. Autophagy Governs Protumorigenic Effects of Mitotic Slippage-induced Senescence. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crasta, K.; Ganem, N.J.; Dagher, R.; Lantermann, A.B.; Ivanova, E.V.; Pan, Y.; Nezi, L.; Protopopov, A.; Chowdhury, D.; Pellman, D. DNA breaks and chromosome pulverization from errors in mitosis. Nature 2012, 482, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.M.; Baker, D.J.; van Deursen, J.M. Senescent cells: A novel therapeutic target for aging and age-related diseases. Clin Pharm. 2013, 93, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.C.; Yeo, R.W.; Tan, K.H.; Lim, S.K. Exosomes for drug delivery—A novel application for the mesenchymal stem cell. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, K.C.; Remaley, A.T. Lipid-based carriers of microRNAs and intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2012, 23, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jakhar, R.; Crasta, K. Exosomes as Emerging Pro-Tumorigenic Mediators of the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102547
Jakhar R, Crasta K. Exosomes as Emerging Pro-Tumorigenic Mediators of the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102547
Chicago/Turabian StyleJakhar, Rekha, and Karen Crasta. 2019. "Exosomes as Emerging Pro-Tumorigenic Mediators of the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102547
APA StyleJakhar, R., & Crasta, K. (2019). Exosomes as Emerging Pro-Tumorigenic Mediators of the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102547




