Melt Electrospinning Designs for Nanofiber Fabrication for Different Applications
Abstract
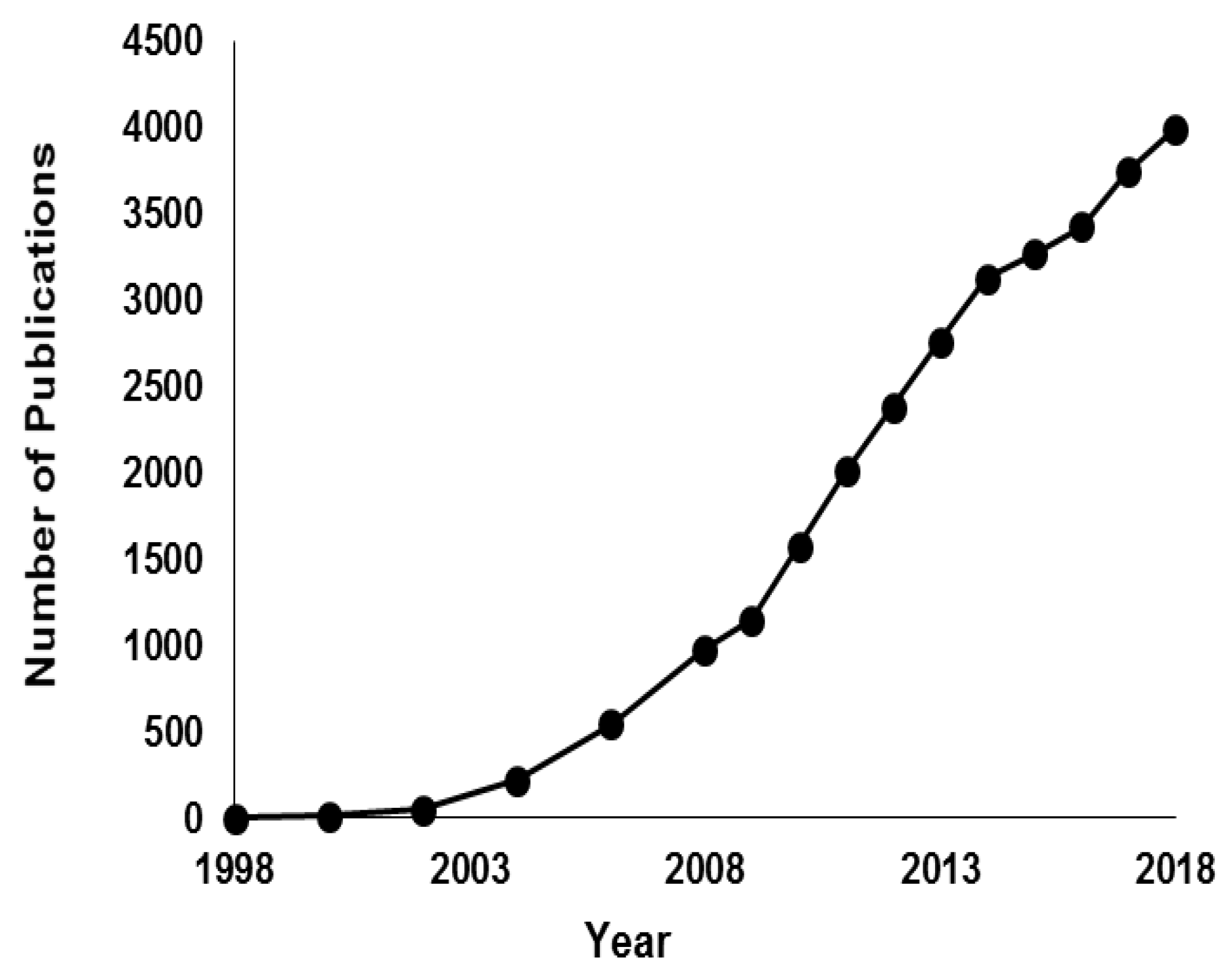
1. Introduction
2. Melt Electrospinning
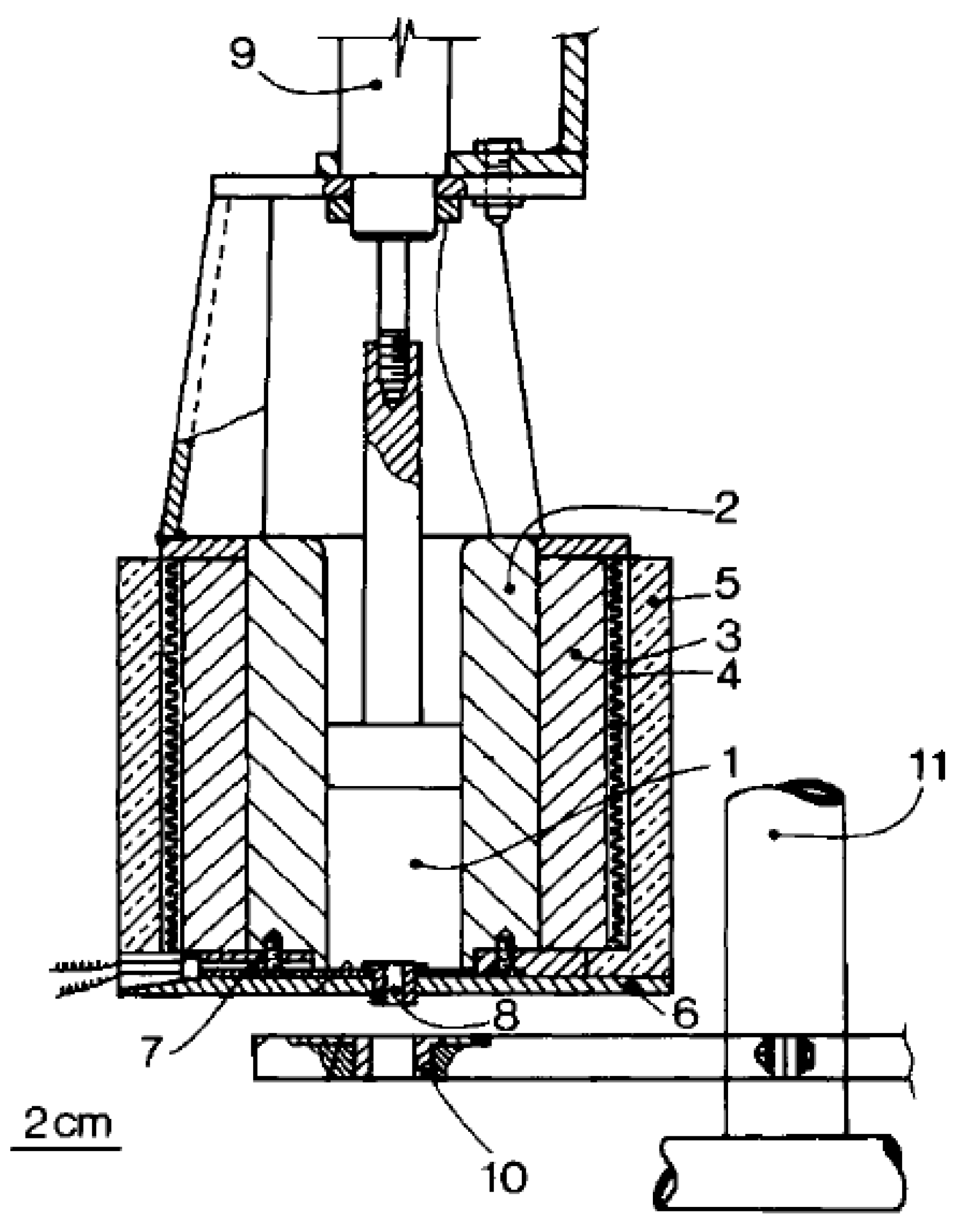
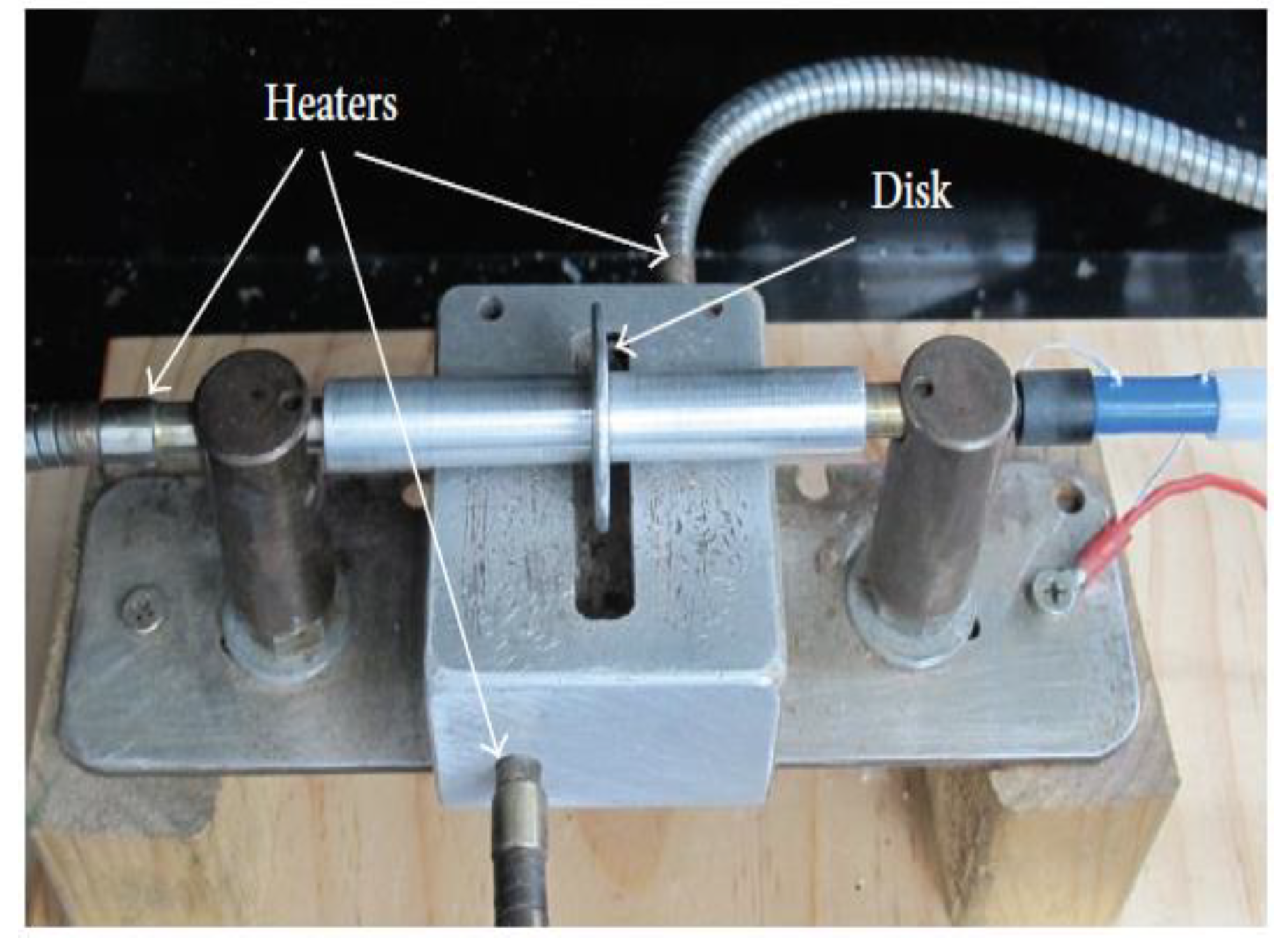
2.1. Multitemperature Control
2.2. Gas Assist
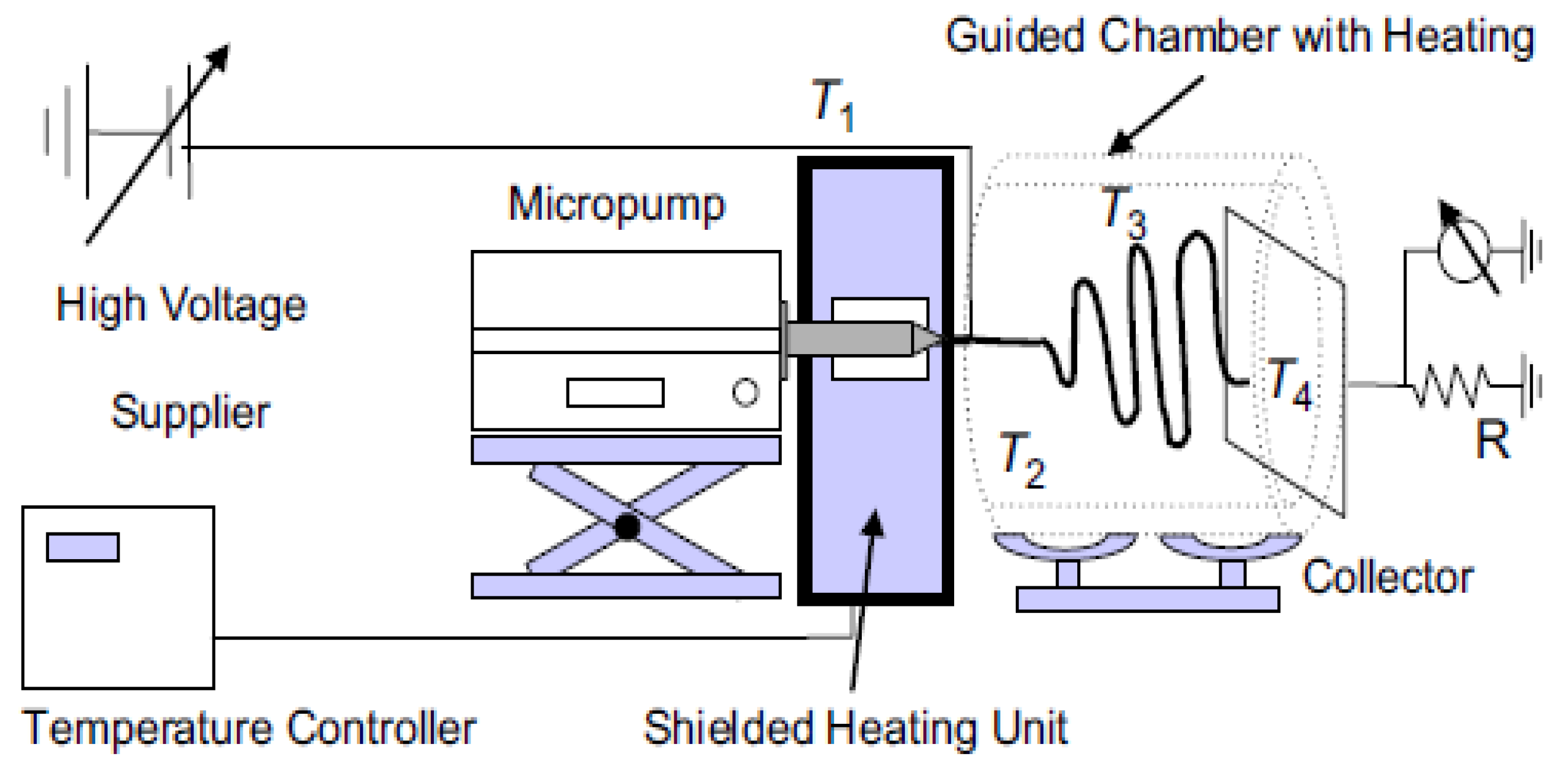
2.3. Laser Melt Electrospinning
2.3.1. Spot Laser Melt Electrospinning
2.3.2. Line Laser Melt Electrospinning
2.4. Coaxial Electrospinning
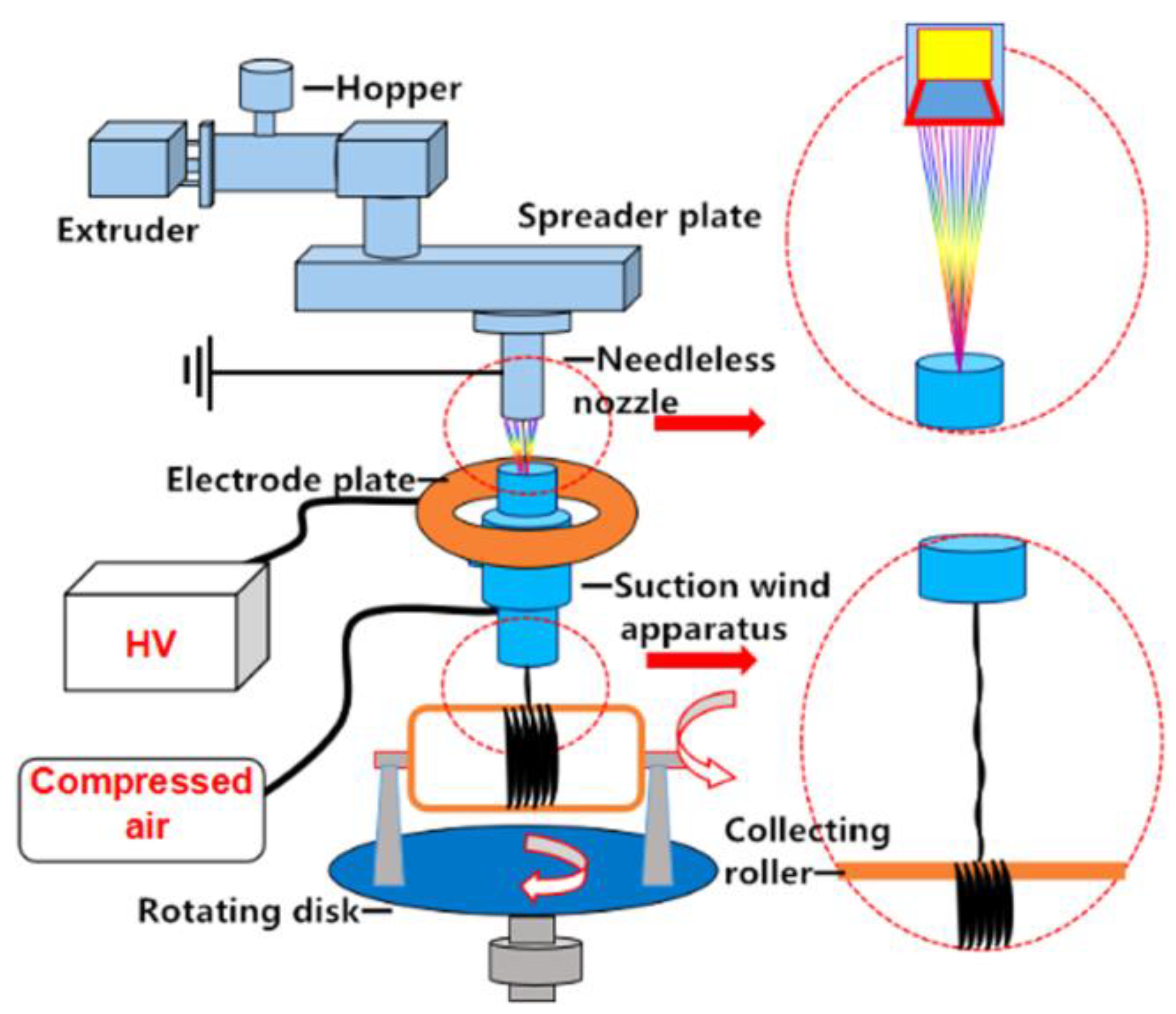
2.5. Needleless Electrospinning
2.6. Other Designs
3. Challenges and Obstacles of Melt Electrospinning
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Wei, Y.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhu, J.H.; Wu, Z.Y. In-Situ Coating of SBA-15 with MgO: Direct Synthesis of Mesoporous Solid Bases from Strong Acidic Systems. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1943–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Yu, X.; Chai, Q.; Ayres, N.; Steckl, A.J. Stimuli-Responsive Self-Immolative Polymer Nanofiber Membranes Formed by Coaxial Electrospinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11858–11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wnek, G.E.; Carr, M.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of Nanofiber Fibrinogen Structures. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Yan, X.; Shen, C.; Guo, Z. Carbon Nanotubes-Adsorbed Electrospun PA66 Nanofiber Bundles with Improved Conductivity and Robust Flexibility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14150–14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Zagho, M.M.; Elzatahry, A.A. Polymer-Based Electrospun Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.K.; Abukmail, A.; Hassiba, A.J.; Mauritz, K.A.; Elzatahry, A.A. PVA/Chitosan/Silver Nanoparticles Electrospun Nanocomposites: Molecular Relaxations Investigated by Modern Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.O.; Huang, X.; Nelson, W.; Kaner, R.B. Polyaniline nanofibers: Broadening applications for conducting polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1510–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thavasi, V.; Singh, G.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers in energy and environmental applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers: New Concepts, Materials, and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrostat. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer (Guildf) 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.B.; Zafar, M.S.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Shah, A.H.; Husain, S.; Rehman, I.U. Electrospinning of chitosan-based solutions for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.-E.; Lim, T.C.; Ma, Z. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers; World Scientific: Singapore, 2005; pp. 23–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chronakis, I.S. Novel nanocomposites and nanoceramics based on polymer nanofibers using electrospinning process—A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 167, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Vazirzadeh, M.; Zohaib, S.; Najeeb, B.; Sefat, F. Potential of electrospun nanofibers for biomedical and dental applications. Materials (Basel) 2016, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fi ber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E. Upward needleless electrospinning of multiple nanofibers. Polymer (Guildf) 2004, 45, 2977–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, S.A.; Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E.; Kroll, E. Multiple jets in electrospinning: Experiment and modeling. Polymer (Guildf) 2005, 46, 2889–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.-H. Bubble Electrospinning for Mass Production of Nanofibers. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2007, 8, 393–396. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaszewski, W.S.M. Investigation of Electrospinning with the Use of a Multi-jet Electrospinning Head. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2005, 13, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dosunmu, O.O.; Chase, G.G.; Kataphinan, W.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibres from multiple jets on a porous tubular surface. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varabhas, J.S.; Chase, G.G.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospun nanofibers from a porous hollow tube. Polymer (Guildf) 2008, 49, 4226–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, C. Method of and Apparatus for Producing Fibrous or Filamentary Material. U.S. Patent 2048651, 21 July 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Yamane, H. Melt electrospinning: Electrodynamics and spinnability. Polymer (Guildf) 2017, 132, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Melt electrospinning today: An opportune time for an emerging polymer process. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 56, 116–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrondo, L.; St. John Manley, R. Electrostatic fiber spinning from polymer melts. I. Experimental observations on fiber formation and properties. J. Polym. Sci. 1981, 19, 909–920. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Green, T.B.; Joo, Y.L. The thermal effects on electrospinning of polylactic acid melts. Polymer (Guildf) 2006, 47, 7497–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.M.; Hohman, M.M.; Brenner, M.P.; Rutledge, G.C. Electrospinning: A whipping fluid jet generates submicron polymer fibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 1149–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.M.; Hohman, M.M.; Brenner, M.P.; Rutledge, G.C. Experimental characterization of electrospinning: The electrically forced jet and instabilities. Polymer (Guildf) 2001, 42, 9955–9967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrikh, S.V.; Yu, J.H.; Brenner, M.P.; Rutledge, G.C. Controlling the Fiber Diameter during Electrospinning. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 144502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohman, M.M.; Shin, M.; Rutledge, G.; Brenner, M.P. Electrospinning and electrically forced jets. II. Applications. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kay Obendorf, S. Developing protective textile materials as barriers to liquid penetration using melt-electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 3430–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.S.; Jo, K.J.; Jo, N.K.; Kim, H.S. Effects of the spin line temperature profile and melt index of poly(propylene) on melt-electrospinning. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Zhou, H.; Cho, Y.; Audus, D.; Lak, Y. Structural properties and superhydrophobicity of electrospun polypropylene fi bers from solution and melt. Polymer (Guildf) 2010, 51, 6005–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Zhmayev, E.; Joo, Y.L. Structural studies of electrospun nylon 6 fibers from solution and melt. Polymer (Guildf) 2011, 52, 4600–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, H.; Ma, X.; Fong, H. Effects of hot air fl ow on macromolecular orientation and crystallinity of melt electrospun poly (l-lactic acid) fi bers. Mater. Lett. 2016, 176, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmayev, E.; Zhou, H.; Joo, Y.L. Modeling of non-isothermal polymer jets in melt electrospinning. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 2008, 153, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmayev, E.; Cho, D.; Joo, Y.L. Modeling of melt electrospinning for semi-crystalline polymers. Polymer (Guildf) 2010, 51, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayadeo, N.; Morikawa, K.; Naraghi, M.; Green, M.J. Modeling of downstream heating in melt electrospinning of polymers. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 55, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmayev, E.; Cho, D.; Joo, Y.L. Nanofibers from gas-assisted polymer melt electrospinning. Polymer (Guildf) 2010, 51, 4140–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armantrout, J.E.; Bryner, M.A.; Spiers, C.B. Electroblowing Fiber Spinning Process. U.S. Patent 7582247, 1 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, B.; Hsaio, B.S.; Fang, D. Apparatus for Electro-Blowing or Blowing-Assisted Electro-Spinning Technology and Process for Post Treatment of Electrospun or Electroblown Membranes. U.S. Patent Application 2009/0123591, 14 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Um, I.C.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Okamoto, A.; Chu, B. Electro-Spinning and Electro-Blowing of Hyaluronic Acid. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, W.; Bubakir, M.; Chen, H.; Zhong, X.; Liu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Yang, W. Polypropylene Fibers Fabricated via a Needleless Melt-Electrospinning Device for Marine Oil-Spill Cleanup. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Yang, W.; An, Y.; Li, H. Efficient preparation of poly (lactic acid) nanofibers by melt differential electrospinning with addition of acetyl tributyl citrate. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 46554, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, L.; Tan, J.; Qin, Y.; Chen, H.; He, W.; Yang, W.; Li, H. Continuous manufacturing of nanofiber yarn with the assistance of suction wind and rotating collection via needleless melt electrospinning. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.-E.; Inai, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Technological advances in electrospinning of nanofibers. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2011, 12, 13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, G.R.; Ranjit, G.S.; Karthikeyan, K.K.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Biji, P. A facile route for controlled alignment of carbon nanotube-reinforced, electrospun nanofibers using slotted collector plates. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuakat, M.N.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Electrospinning of Nanofibre Yarns Using a Novel Ring Collector. In Proceedings of the Fiber Society, Spring Technical Conference, Geelong, Australia, 22–24 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, K.; Nan, N.; You, X.; Shao, W.; Wang, L.; Ding, B.; Cui, S. Highly sensitive, self-powered and wearable electronic skin based on pressure-sensitive nanofiber woven fabric sensor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Shimada, N.; Lu, G.; Iwata, T.; Nakane, K.; Ogihara, T. Poly(lactide) nanofibers produced by a melt-electrospinning system with a laser melting device. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, J.; Li, C.; Ko, F. Melt-electrospinning part I: Processing parameters and geometric properties. Polymer (Guildf) 2004, 45, 7597–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, L.S.; Ugbolue, S.; Jaffe, M.; Patra, P. FY2005 New Project Proposal, No. F05-MD01. Natl. Text. Cent. 2005; pp. 81–84.
- Ogata, N.; Lu, G.; Iwata, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nakane, K.; Ogihara, T. Effects of ethylene content of poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) on diameter of fibers produced by melt-electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, N.; Shimada, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nakane, K.; Ogihara, T. Melt-electrospinning of poly(ethylene terephthalate) and polyalirate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Ogata, N.; Shimada, N.; Nakane, K.; Ogihara, T.; Yu, M. Melt electrospinning from poly(L-lactide) rods coated with poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, N.; Ogata, N.; Nakane, K.; Ogihara, T. Spot laser melt electrospinning of a fiber bundle composed of poly(lactide)/poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) pie wedge fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, E384–E389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, C. Preparation and properties of PET/SiO2 composite micro/nanofibers by a laser melt-electrospinning system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, C. Preparation and characterization of poly(ε-caprolactone) nonwoven mats via melt electrospinning. Polymer (Guildf) 2012, 53, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, C. Preparation and characterization of PLLA/nHA nonwoven mats via laser melt electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2012, 73, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, C. Preparation and experimental parameters analysis of laser melt electrospun poly(l-lactide) fibers via orthogonal design. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 52, 1964–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, C. Preparation and properties of TPU micro/nanofibers by a laser melt-electrospinning system. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
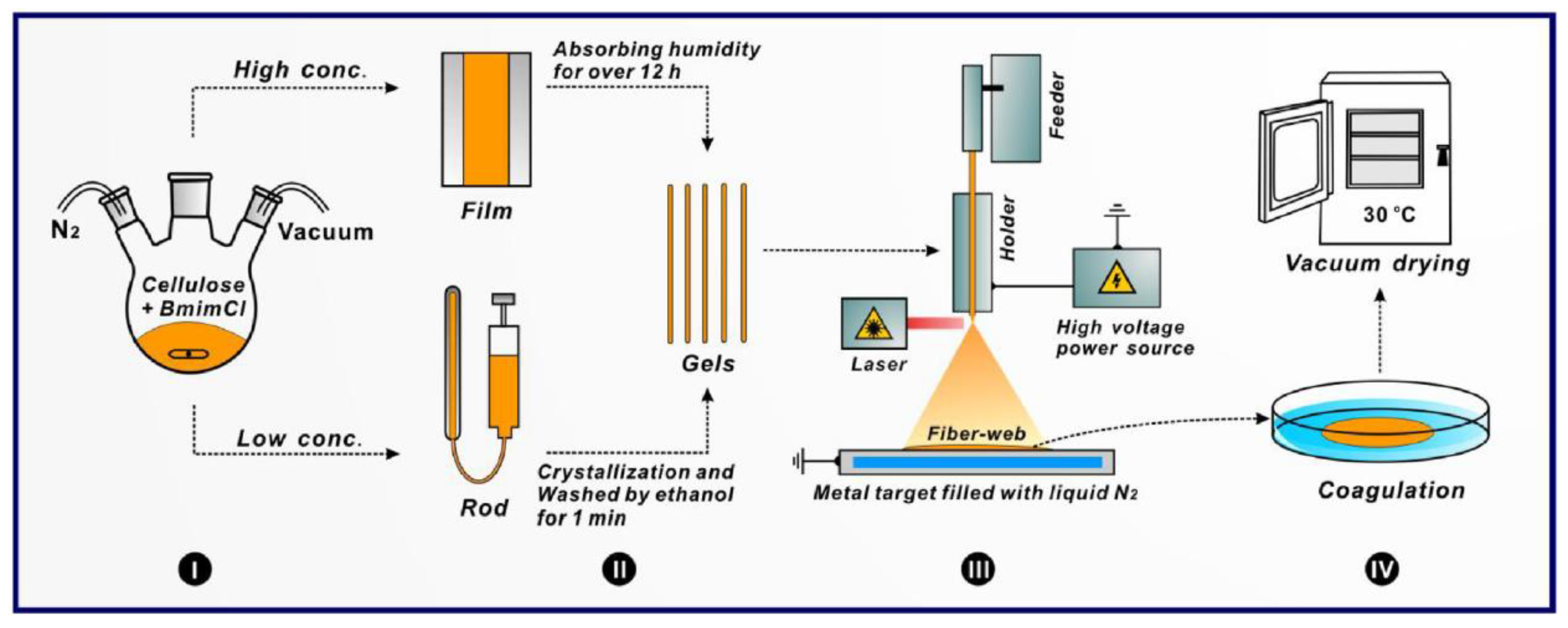
- Xu, H.; Bronner, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Yamane, H. Regeneration of cellulose dissolved in ionic liquid using laser-heated melt-electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, M.; Kengo, M.; Ohkoshi, Y.; Hirai, T. Effects of Laser Beam Width on the Diameter and Molecular Weight of Laser-Electrospun Polylactide Fiber. Sen’i Gakkaishi 2015, 71, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, N.; Tsutsumi, H.; Nakane, K.; Ogihara, T.; Ogata, N. Poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) and Nylon 6/12 nanofibers produced by melt electrospinning system equipped with a line-like laser beam melting device. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2998–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Deng, B.; Yao, P.; Xia, S. Experimental study and prediction of the diameter of melt-electrospinning polypropylene fiber. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Mizutani, Y.; Nakane, K. Melt-electrospun fibers obtained from polypropylene/poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol)/polypropylene three-layer films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, J.T.; Marquez, M.; Xia, Y. Melt Coaxial Electrospinning: A Versatile Method for the Encapsulation of Solid Materials and Fabrication of Phase Change Nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2868–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
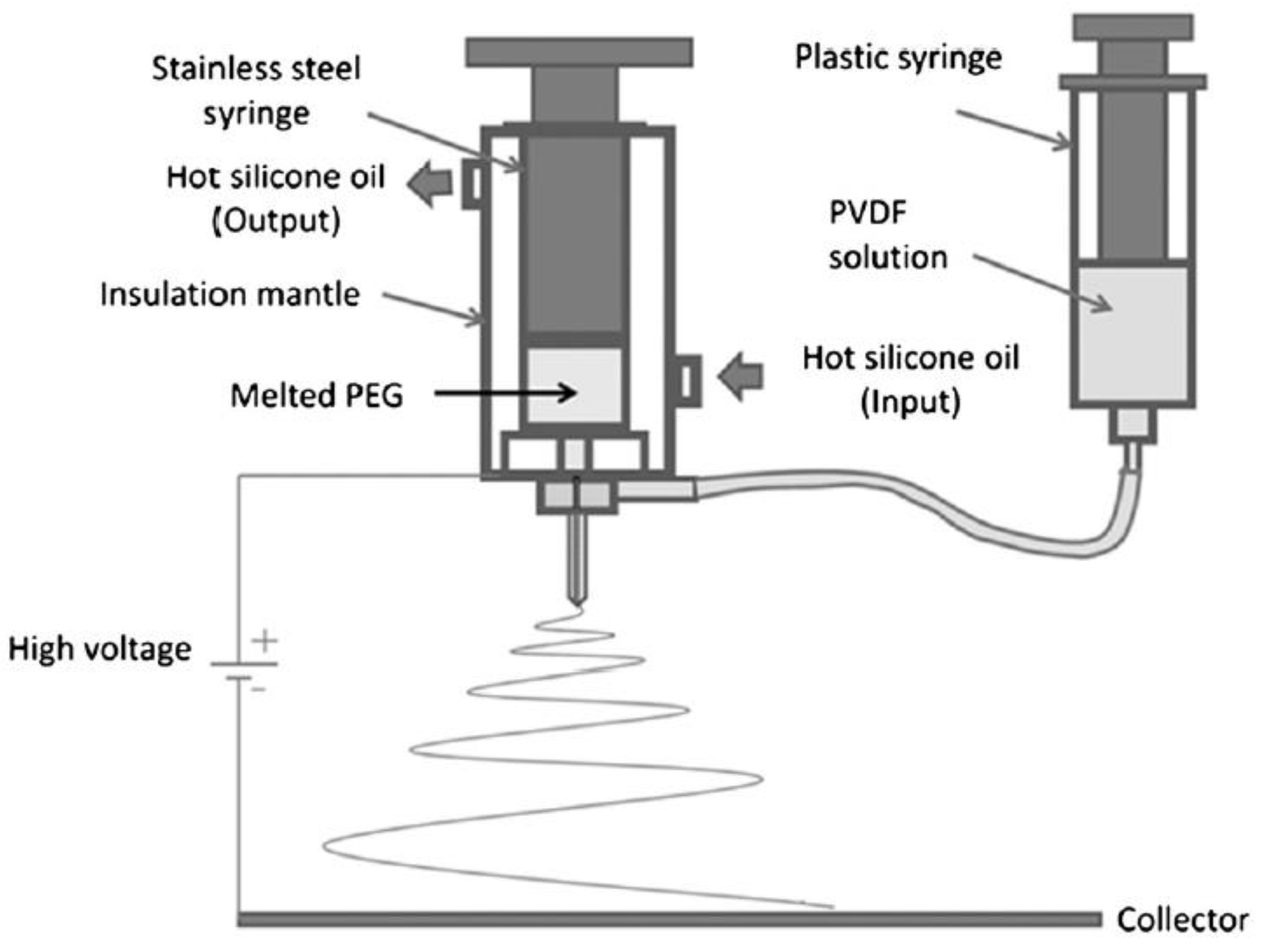
- Van Do, C.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Park, J.S. Fabrication of polyethylene glycol/polyvinylidene fluoride core/shell nanofibers via melt electrospinning and their characteristics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 104, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Lee, J.G.; Park, J.S. Fabrication and characterization of coaxial electrospun polyethylene glycol/polyvinylidene fluoride (Core/Sheath) composite non-woven mats. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y. Electrospinning of thermo-regulating ultrafine fibers based on polyethylene glycol/cellulose acetate composite. Polymer (Guildf) 2007, 48, 5202–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y. A novel shape-stabilized PCM: Electrospun ultrafine fibers based on lauric acid/polyethylene terephthalate composite. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3515–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y. Ultrafine electrospun fibers based on stearyl stearate/polyethylene terephthalate composite as form stable phase change materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Jiang, L.; Song, Y. Thermochromic core–shell nanofibers fabricated by melt coaxial electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, L.; Sutton, D.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Needleless Melt-Electrospinning of Polypropylene Nanofibres. Nanomaterials 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detta, N.; Brown, T.D.; Edin, F.K.; Albrecht, K.; Chiellini, F.; Chiellini, E.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Melt electrospinning of polycaprolactone and its blends with poly(ethylene glycol). Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 1558–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xie, P.; Luo, L.; Yang, W. Melt electrospinning of low-density polyethylene having a low-melt flow index. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, H.; Zhong, X.; Wu, W.; Ding, Y.; Yang, W. Interjet Distance in Needleless Melt Differential Electrospinning with Umbellate Nozzles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 40515, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Disintegration of water drops in an electric field. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1964, 280, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinov, L.; Komarek, M. Design And Evaluation of Melt-Electrospinning Electrodes. NANOCON 2010, 10, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.-M.; Wang, X.-X.; Yu, S.-X.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Yan, X.; Zheng, J.; Yu, M.; Yan, S.-Y.; Long, Y.-Z. Bubble Melt Electrospinning for Production of Polymer Microfibers. Polymers (Basel) 2018, 10, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangkupan, R.; RENEKER, D.H. Electrospinning Process of Molten Polypropylene in Vacuum. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2003, 12, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, P.; Lleixà Calvet, J.; Ahmed, M.; Klee, D.; Möller, M. Melt electrospinning of poly-(ethylene glycol-block-ϵ-caprolactone). Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, K.; Vashisth, A.; Grimme, C.J.; Green, M.J. Wire Melt Electrospinning of Thin Polymeric Fibers via Strong Electrostatic Field Gradients. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 1800417, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgarten, P.K. Electrostatic spinning of acrylic microfibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1971, 36, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Reneker, D.H. DNA fibers by electrospinning. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 1997, 36, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.; BeckTan, N.C.; Kleinmeyer, J.D.; Rehrmann, J.; Tevault, D. Generation of Polymer Nanofibers Through Electrospinning. Army Res. Lab. 1999, 41, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Gong, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, D.; Liu, Y. Pulsed Electric Fields on Poly—l-(lactic acid) Melt Electrospun Fibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 7116–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, R. Design of an IGBT-Based Pulsed Power Supply for Non-Continuous-Mode Electrospinning. Master’s Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2010; pp. 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Direct Writing By Way of Melt Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5651–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutmacher, D.W.; Dalton, P.D. Melt Electrospinning. Chemistry 2011, 6, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochleitner, G.; Jüngst, T.; Brown, T.D.; Hahn, K.; Moseke, C.; Jakob, F.; Dalton, P.D.; Groll, J. Additive manufacturing of scaffolds with sub-micron filaments via melt electrospinning writing. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 35002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, C.B.; Afghah, F.; Okan, B.S.; Yıldız, M.; Menceloglu, Y.; Culha, M.; Koc, B. Modeling 3D melt electrospinning writing by response surface methodology. Mater. Des. 2018, 148, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.; Hollister, S.J.; Dalton, P.D. Additive manufacturing of polymer melts for implantable medical devices and scaffolds. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, B.L.; Brown, T.D.; Upton, Z.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Dalton, P.D.; Dargaville, T.R. Dermal fibroblast infiltration of poly(upepsilon-caprolactone) scaffolds fabricated by melt electrospinning in a direct writing mode. Biofabrication 2013, 5, 25001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muerza-Cascante, M.L.; Shokoohmand, A.; Khosrotehrani, K.; Haylock, D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Loessner, D. Endosteal-like extracellular matrix expression on melt electrospun written scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2017, 52, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, J.G.; Wagner, F.; Martine, L.C.; Holzapfel, B.M.; Theodoropoulos, C.; Bas, O.; Savi, F.M.; Werner, C.; De-Juan-Pardo, E.M.; Hutmacher, D.W. Periosteum tissue engineering in an orthotopic in vivo platform. Biomaterials 2017, 121, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertlein, S.; Hikimoto, D.; Hochleitner, G.; Hümmer, J.; Jungst, T.; Matsusaki, M.; Akashi, M.; Groll, J. Development of Endothelial Cell Networks in 3D Tissues by Combination of Melt Electrospinning Writing with Cell-Accumulation Technology. Small 2018, 14, 1701521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, M.; Feyen, D.; Flandes-Iparraguirre, M.; Hochleitner, G.; Groll, J.; Doevendans, P.A.F.; Vermonden, T.; Ito, K.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Malda, J. Melt Electrospinning Writing of Poly-Hydroxymethylglycolide-co-ε-Caprolactone-Based Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichholz, K.F.; Hoey, D.A. Mediating human stem cell behaviour via defined fibrous architectures by melt electrospinning writing. Acta Biomater. 2018, 75, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbolaghi, S.; Abbaspoor, S.; Abbasi, F. A comprehensive review on polymer single crystals-From fundamental concepts to applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, P.; Grafahrend, D.; Klinkhammer, K.; Klee, D.; Möller, M. Electrospinning of polymer melts: Phenomenological observations. Polymer 2007, 48, 6823–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, M.; Fu, H.; Nakata, K.; Ohkoshi, Y.; Hirai, T. Ultra-Fine Fibers Produced by Laser-Electrospinning. Sen’i Gakkaishi 2008, 64, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhmayev, E.; Cho, D.; Lak Joo, Y. Electrohydrodynamic quenching in polymer melt electrospinning. Phys. Fluids 2011, 23, 73102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, P.D.; Klinkhammer, K.; Salber, J.; Klee, D.; Moller, M. Direct in vitro electrospinning with polymer melts. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Bubakir, M.M.; Xia, T.; Zhong, X.F.; Ding, Y.M.; Yang, W.M. Mass production of ultra-fine fibre by melt electrospinning method using umbellate spinneret. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, S4-921–S4-925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisken, C.; Kalyon, D.M.; Wang, H. A hybrid twin screw extrusion/electrospinning method to process nanoparticle-incorporated electrospun nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 165302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.-C.; Duan, X.-P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.-H.; Yu, M.; Dong, R.-H.; Yan, X.; He, H.-W.; Long, Y.-Z. Melt electrospinning of poly(lactic acid) and polycaprolactone microfibers by using a hand-operated Wimshurst generator. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16611–16615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Design Method | Polymer | Process Parameters | Fiber Diameter | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | PE | T1 = 200–220 °C | ND = 2.2 mm, V = 6 kV/cm & Cd = 1–3 cm | - | [28] | |
| PP | T1 = 220–240 °C | - | ||||
| Multitemperature control | PLA | T1 = 200 °C, T2 = 255 °C, T3 = 80 °C & T4 = 25 °C F = 0.001 mL/min, V = 20 kV, Cd = 10 cm & ND = 0.16 mm | 800 nm | [29] | ||
| PP | T1 = 230 °C, T2 = 280–290 °C, T3 = 100–140 °C, T4 = 85–95 °C, V = 10–20 kV, F = 0.002–0.008 mL/min & Cd = 5–7 cm | – | [34] | |||
| PP | T1 = 330–390 °C, T2 = 100–150 °C, T3 = 25 °C, V = 35 kV & Cd = 10–18 cm | ~20 µm | [35] | |||
| iPP | T1 = 240 °C, T2 = 180 °C, T3 = room temp, Cd = 2 inch, Cv = 28 kV, Nv = −5 kv & F = 0.001 mL/min | 2.4 µm | [36] | |||
| N6 | T1 = 270 °C, T2 = 280 °C, T3 = 210–220 °C, F = 0.03 mL/h, Cd = 90 mm, Cv = 29 kV & Nd = 0.26 mm | 0.9 µm | [37] | |||
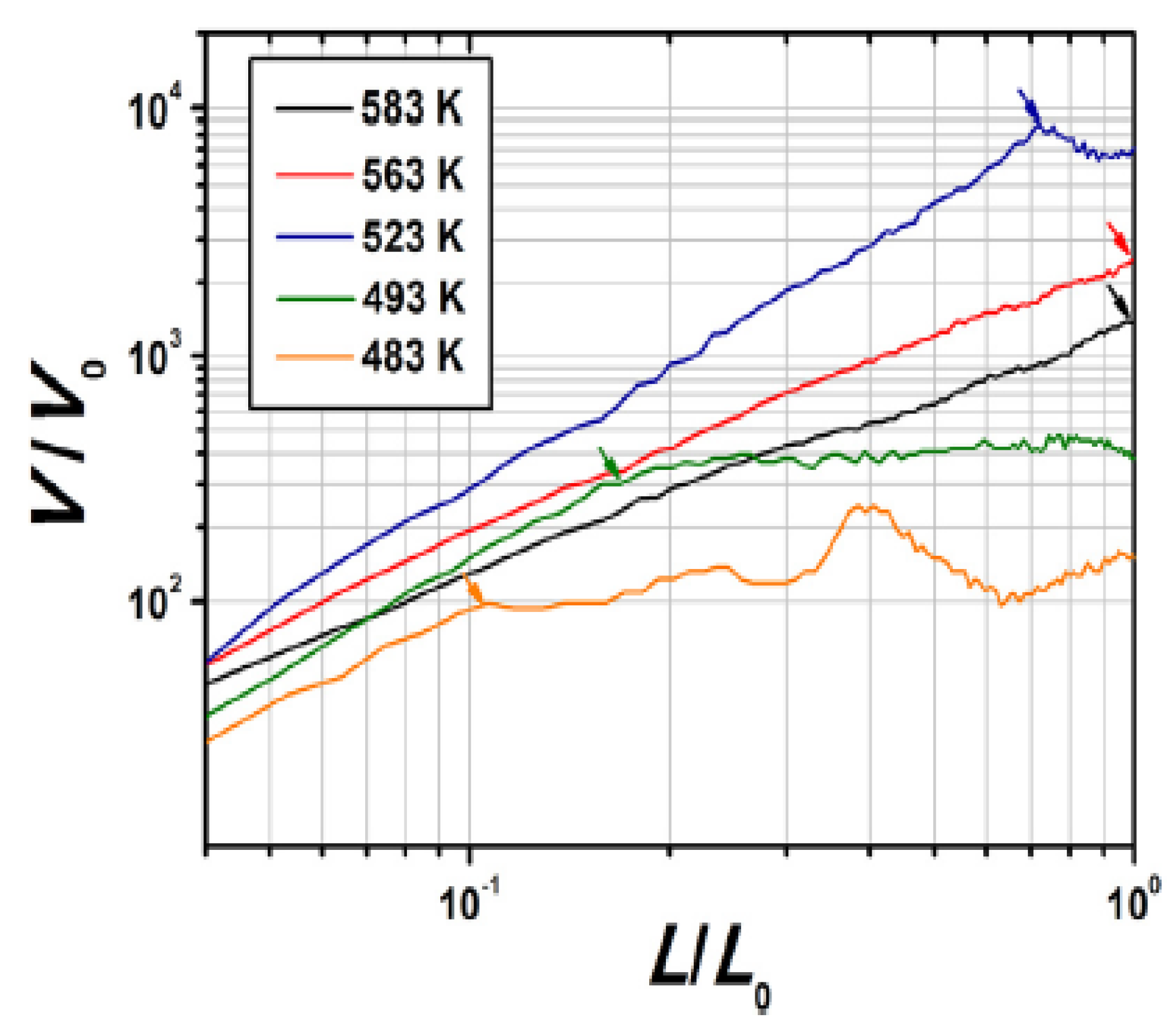
| Gas assist | PLA | TM&A = 483 K, Av = 300 m/s, F = 1.67 × 10–10 m3/s & Cd = 0.09 m | 0.18 µm | [42] | ||
| PP | T2 = 260 °C, Av = 30 m/s, nozzle to electrode = 10 cm, V = 35 kV, Cd = 200 nm & RDs = 0–500 rpm | 400 nm | [48] | |||
| PLA + 6 wt% ATBC | FA = 25 m/s, V = 40 kV, T = 240 °C & Cd = 9 cm | 236 nm | [47] | |||
| Laser | spot | PLA | V = 26–30 kV, PL = 13–17 W, Cd = 20 mm & λ = 10.6 µm | 712–804 nm | [53] | |
| EVAL | F = 2–4 mm/s, V = 18–20 kV, Cd = 25 mm, PL = 8–22 W & λ = 10.6 µm | 740 nm–2.842 µm | [56] | |||
| PLLA coated with EVOH | F = 10 mm/min, V = 25 kV, PL = 12 w, CD = 5 cm, λ = 10.6 µm & T3 = 40 °C | 845 ± 500 nm | [58] | |||
| line | EVOH/Nylon 6/12 sheets | V = 40 kV, PL = 45 W, F = 0.25 mm/min & Cd = 10 mm | 800 nm | [67] | ||
| PP/EVOH/PP | Cd = 100 mm, V = 20–70 kV, λ = 10.6 µm & F = 4 mm/min | 0.64–1.08 µm | [69] | |||
| Coaxial | PEG/PVDF | V = 12 kV, Cd = 17 cm, N1ID = 0.35, N1OD = 0.65 mm, N2ID = 1.05, N2OD = 1.2 mm, FN2 = 1.5 mL/h & FN1 = 0.09–0.24 mL/h | 637–911 nm | [71] | ||
| Needleless | PP | T = 320 °C, V = 75 kV, Cd = 16 cm | 3.31 µm | [77] | ||
| Pp | T = 260 °C, V = 39–63 kV, Cd = 11 cm & ND = 16 mm | 14.6–5.3 µm | [80] | |||
| TPU | T = 240 °C | V = 18–25 kV | 20 µm | [83] | ||
| PLA | T = 200–250 °C | 30 µm | ||||
| Others | Pp | T = 300 °C, V = 200 kV/m & vacuum pressure | 300 nm–30 µm | [84] | ||
| PEG-b-PCL | V = 20 kV, F = 0.02–5 mL/h & T = 80–90 °C | 560 ± 90 nm–16 ± 10.7 µm | [85] | |||
| PCL | T = 100, Cd = 5 cm, Csp = 270 rpm & V = 15–17 kV | 1 ± 0.9 µm | [86] | |||
| PCL | Csp = 310–400 mm/min, Cd = 7–13 mm, P = 0.6–1 bar, V = 5.5–7 kV | 48.31–75.12 µm | [95] | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, Y.S.; Hussein, E.A.; Zagho, M.M.; Abdo, G.G.; Elzatahry, A.A. Melt Electrospinning Designs for Nanofiber Fabrication for Different Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102455
Ibrahim YS, Hussein EA, Zagho MM, Abdo GG, Elzatahry AA. Melt Electrospinning Designs for Nanofiber Fabrication for Different Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102455
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Yasseen S., Essraa A. Hussein, Moustafa M. Zagho, Ghada G. Abdo, and Ahmed A. Elzatahry. 2019. "Melt Electrospinning Designs for Nanofiber Fabrication for Different Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102455
APA StyleIbrahim, Y. S., Hussein, E. A., Zagho, M. M., Abdo, G. G., & Elzatahry, A. A. (2019). Melt Electrospinning Designs for Nanofiber Fabrication for Different Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102455





