Leptin and Immunological Profile in Obesity and Its Associated Diseases in Dogs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physiological Role of Leptin and Its Relationship with Obesity
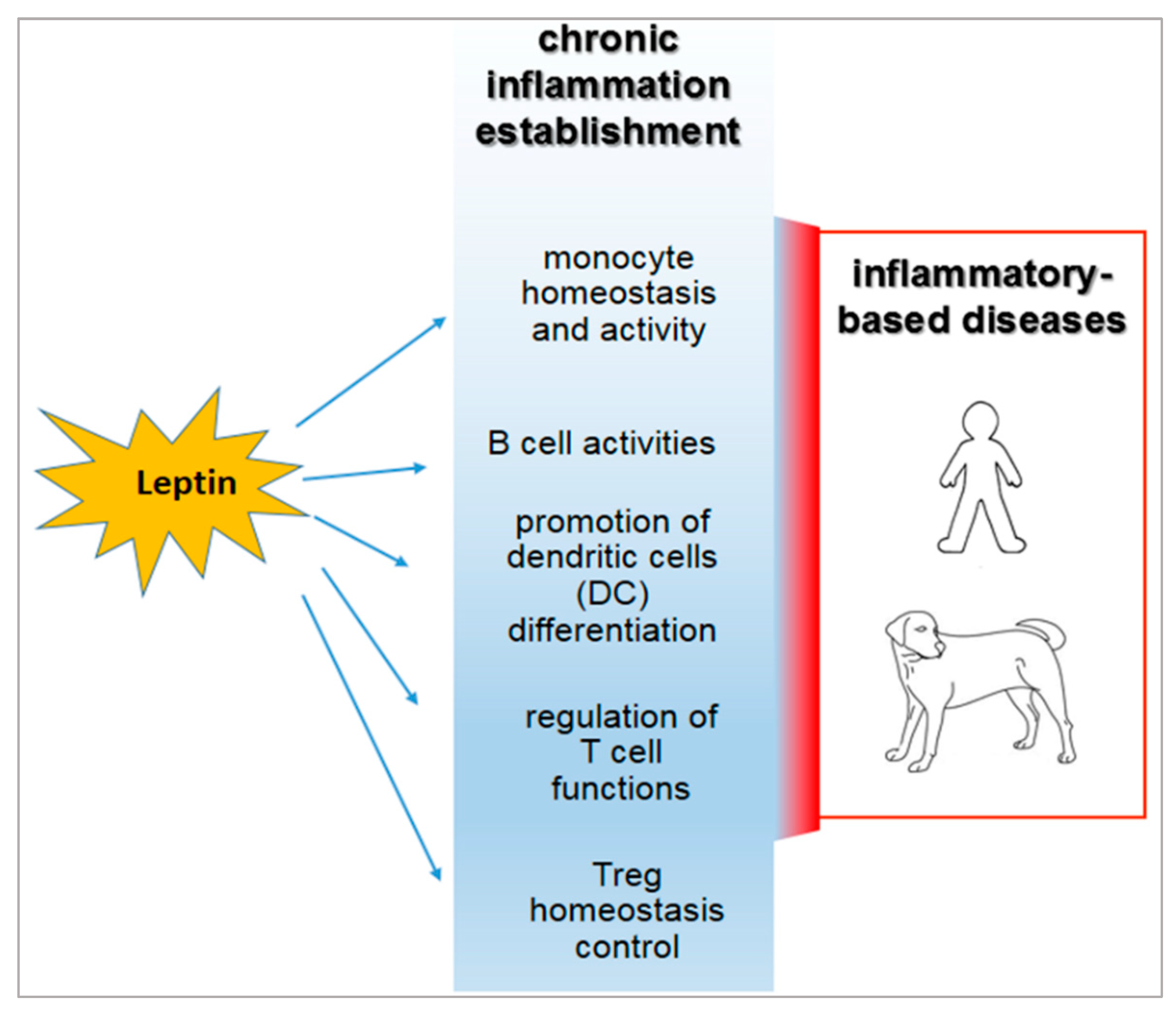
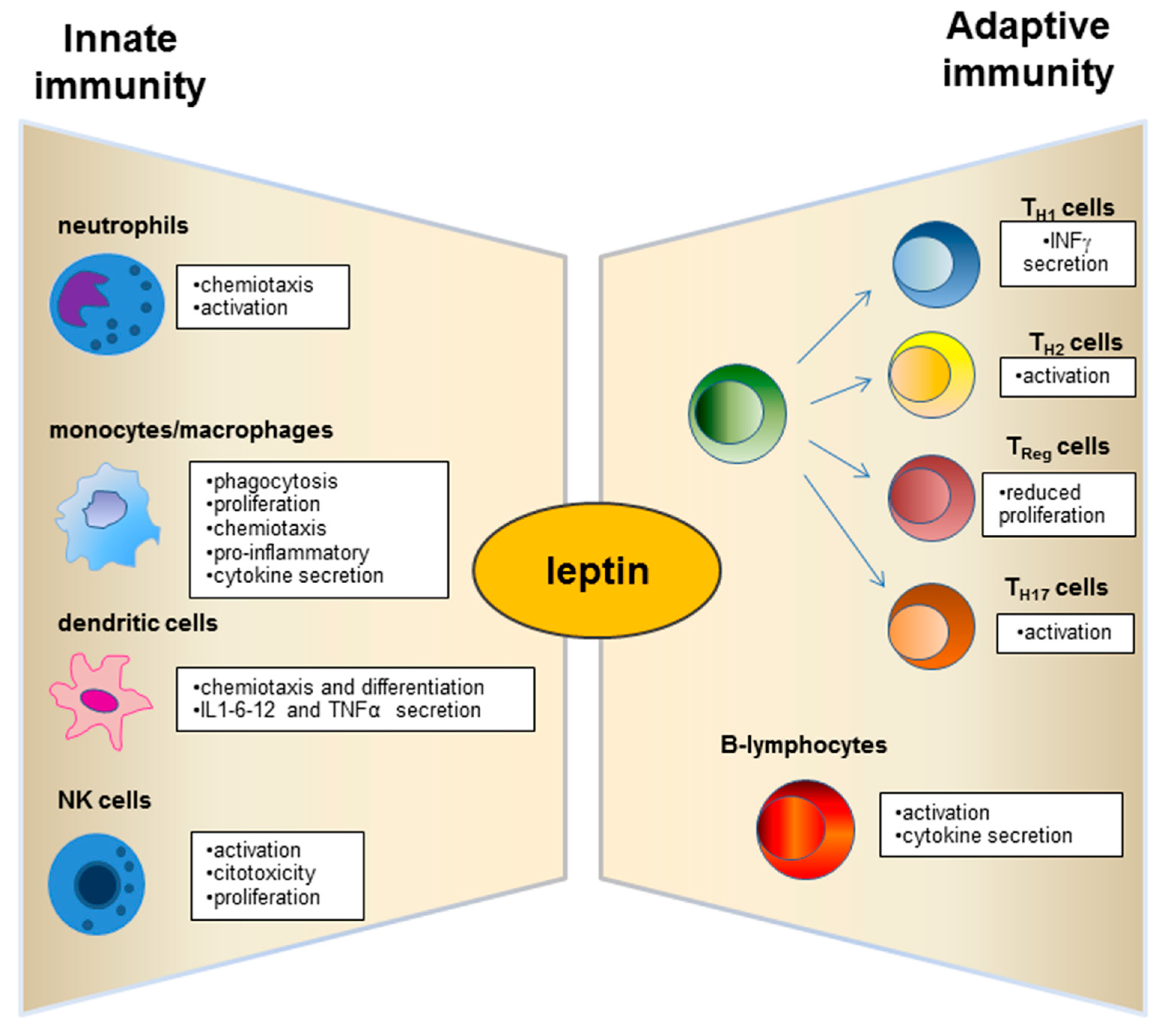
3. Role of Leptin in the Relationship between Obesity and Immune-Modulation.
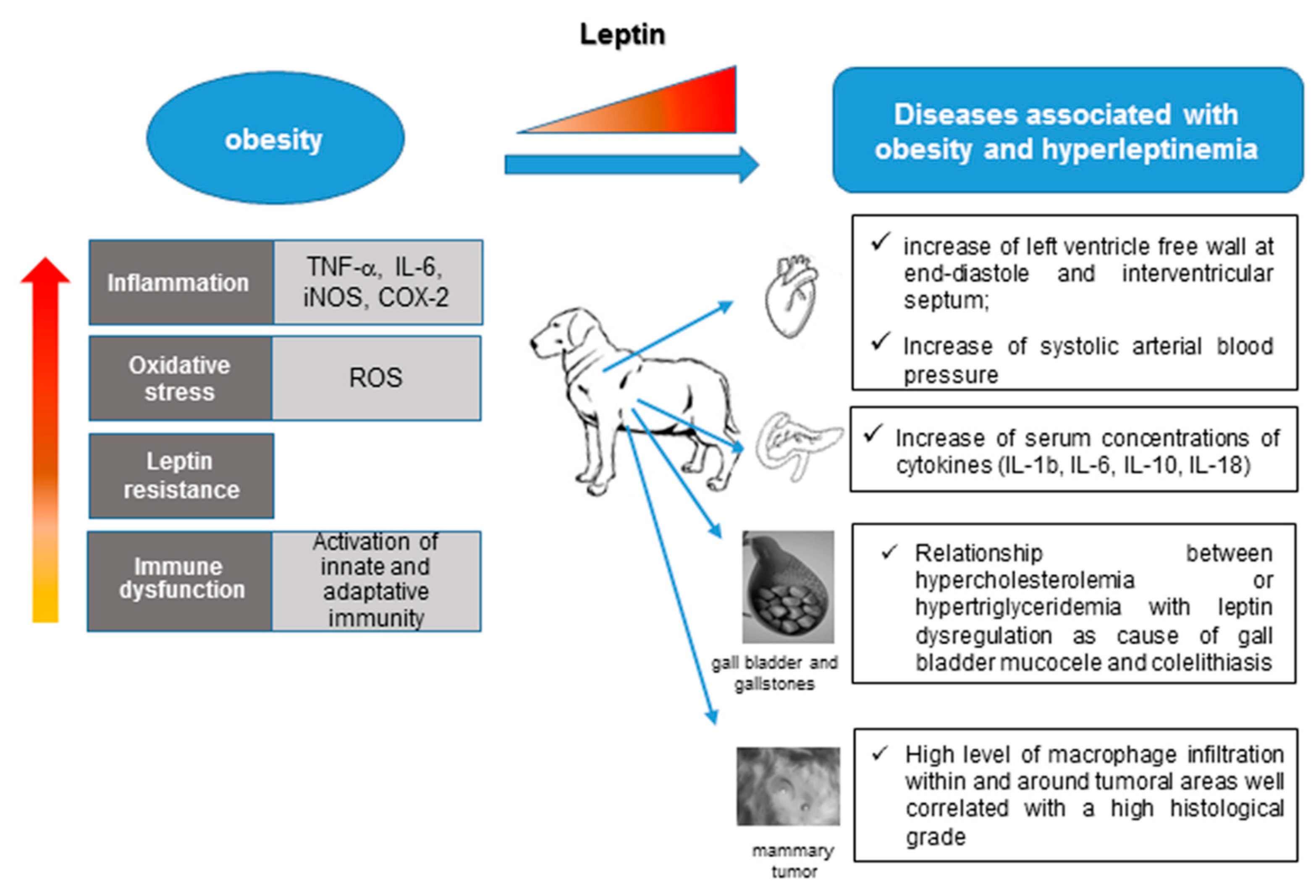
4. Leptin and Associated Diseases in Humans and Dogs
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| apoE | Apolipoprotein E |
| AP | Acute pancreatitis |
| BCS | Body condition score |
| CDi | Cardiac disease |
| CHF | Congestive heart failure |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DC | Dendritic cells |
| GBM | Gallbladder mucocele |
| HF | Heart failure |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IL | Interleukin |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| LEPR | Leptin receptor |
| LVH | Left ventricle hypertrophy |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MC | Mammary carcinoma |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MS | Metabolic Syndrome |
| VEGF | Vascular growth factor |
| VL | Visceral Leishmaniasis |
| ROR | Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TNF | Tumour necrosis factor |
| Treg cells | Regulatory T cells |
| VSMCs | Vascular smooth muscle cells |
References
- Tremmel, M.; Gerdtham, U.G.; Nilsson, P.M.; Saha, S. Economic burden of obesity: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes: Inflammatory basis of glucose metabolic disorders. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, S152–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihalko, W.M.; Bergin, P.F.; Kelly, F.B.; Canale, S.T. Obesity, orthopaedics, and outcomes. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 22, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammit, C.; Liddicoat, H.; Moonsie, I.; Makker, H. Obesity and respiratory diseases. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2010, 3, 335–343. [Google Scholar]
- Câmara, N.O.; Iseki, K.; Kramer, H.; Liu, Z.H.; Sharma, K. Kidney disease and obesity: Epidemiology, mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, A.J. The growing problem of obesity in dogs and cats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1940S–1946S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cava, A. Leptin in inflammation and autoimmunity. Cytokine 2017, 98, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abella, V.; Scotece, M.; Conde, J.; Pino, J.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Mera, A.; Lago, F.; Gómez, R.; Gualillo, O. Leptin in the interplay of inflammation, metabolism and immune system disorders. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, F.; Dieguez, C.; Gómez-Reino, J.; Gualillo, O. Adipokines as emerging mediators of immune response and inflammation. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2007, 3, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, F.; Dieguez, C.; Gómez-Reino, J.; Gualillo, O. The emerging role of adipokines as mediators of inflammation and immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007, 18, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, F.; Gómez, R.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Dieguez, C.; Gualillo, O. Adipokines as novel modulators of lipid metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Flier, J.S. Leptin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000, 62, 413–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Ahima, R.S. Physiology of leptin: Energy homeostasis, neuroendocrine function and metabolism. Metabolism 2015, 64, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J. The long road to leptin. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4727–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havel, P.J. Role of adipose tissue in body-weight regulation: Mechanisms regulating leptin production and energy balance. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2000, 59, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Proenca, R.; Montez, J.M.; Carroll, K.M.; Darvishzadeh, J.G.; Lee, J.I.; Friedman, J.M. Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature 1996, 379, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armağan, C.; Yılmaz, C.; Koç, A.; Abac, A.; Ülgenalp, A.; Böber, E.; Erçal, D.; Demir, K. A toddler with a novel LEPR mutation. Hormones 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasim, M.; Awan, F.R.; Najam, S.S.; Khan, A.R.; Khan, H.N. Role of Leptin Deficiency, Inefficiency, and Leptin Receptors in Obesity. Biochem. Genet. 2016, 54, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, L.A. The leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6093–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska, E.; Popko, K.; Stelmaszczyk-Emmel, A.; Ciepiela, O.; Kucharska, A.; Wasik, M. Leptin receptors. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2010, 15, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, H.; Okano, H.J.; Li, C.; Lee, G.H.; Zhao, C.; Darnell, R.; Friedman, J.M. Anatomic localization of alternatively spliced leptin receptors (Ob-R) in mouse brain and other tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7001–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Murakami, T.; Otani, S.; Kuwajima, M.; Shima, K. Leptin receptor signal transduction: OBRa and OBRb of fa type. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 246, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margetic, S.; Gazzola, C.; Pegg, G.G.; Hill, R.A. Leptin: A review of its peripheral actions and interactions. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 1407–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G. Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin. Biochem. J. 2006, 393, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Katsuura, G.; Numata, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Hayase, M.; Ebihara, K.; Masuzaki, H.; Hosoda, K.; Yoshimasa, Y.; et al. Sympathetic activation of leptin via the ventromedial hypothalamus: Leptin-induced increase in catecholamine secretion. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalamaga, M.; Chou, S.H.; Shields, K.; Papageorgiou, P.; Polyzos, S.A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin at the intersection of neuroendocrinology and metabolism: Current evidence and therapeutic perspectives. Cell Metabol. 2013, 18, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuzzi, G.; Faggioni, R. Leptin in the regulation of immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 68, 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Fernández-Riejos, P.; Martín-González, J.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of leptin as a link between metabolism and the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 35, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainsford, T.; Willson, T.A.; Metcalf, D.; Handman, E.; McFarlane, C.; Nq, A.; Nicola, N.A.; Alexander, W.S.; Hilton, D.J. Leptin can induce proliferation, differentiation, and functional activation of hemopoietic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14564–14568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.D.; Solar, G.P.; Yuan, J.Q.; Mathias, J.; Thomas, G.R.; Matthews, W. A role for leptin and its cognate receptor in hematopoiesis. Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claycombe, K.; King, L.E.; Fraker, P.J. A role for leptin in sustaining lymphopoiesis and myelopoiesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.J.; Wang, X. Leptin and its receptor in hematologic malignancies. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 19840–19849. [Google Scholar]
- Ahima, R.S.; Prabakaran, D.; Mantzoros, C.; Qu, D.; Lowell, B.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Flier, J.S. Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature 1996, 382, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G., Jr.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Haft, C.; Kahn, B.B.; Laughlin, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Tschöp, M.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Challenges and opportunities of defining clinical leptin resistance. Cell Metabol. 2012, 15, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.H.; Kim, M.S. Molecular mechanisms of central leptin resistance in obesity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoran, D.L. Obesity in dogs and cats: A metabolic and endocrine disorder. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Epicardial adipose tissue may mediate deleterious effects of obesity and inflammation on the myocardium. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2360–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, I. The prothrombotic tendency in metabolic syndrome: Focus on the potential mechanisms involved in impaired haemostasis and fibrinolytic balance. Scientifica 2012, 2012, 525374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Ferreira, J.M.; Fernandes, F.; Dabarian, A.; Mady, C. Leptin in heart failure. Expert. Opin. Med. Diagn. 2013, 7, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Shinozaki, S.; Nakazawa, T.; Kawakami, A.; Ai, M.; Kaneko, E.; Kitagawa, M.; Kondo, K.; Chait, A.; Shimokado, K. Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Folmes, C.D.; Stanley, W.C. Cardiac energy metabolism in obesity. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tune, J.D.; Considine, R.V. Effects of leptin on cardiovascular physiology. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2007, 1, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Hall, D.; Subramanian, M. Sympathetic nervous system as a target for aging and obesity-related cardiovascular diseases. Geroscience 2019, 41, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Yokoyama, M. Leptin stimulates rat aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Kobe J. Med. Sci. 2001, 47, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuño, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Muñiz, P.; Salvador, J.; Díez, J.; Frühbeck, G. Leptin inhibits angiotensin II-induced intracellular calcium increase and vasoconstriction in the rat aorta. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 3555–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganami, T.; Mukoyama, M.; Mori, K.; Yokoi, H.; Koshikawa, M.; Sawai, K.; Hidaka, S.; Ebihara, K.; Tanaka, T.; Sugawara, A.; et al. Prevention and reversal of renal injury by leptin in a new mouse model of diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Ruiz, M.; Fulton, D.; Sowa, G.; Languino, L.R.; Fujio, Y.; Walsh, K.; Sessa, W.C. Vascular endothelial growth factor-stimulated actin reorganization and migration of endothelial cells is regulated via the serine/threonine kinase Akt. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, P.C.; Jaworek, J.; Maniatoglou, A.; Bonior, J.; Meixner, H.; Konturek, S.J.; Hahn, E.G. Leptin modulates the inflammatory response in acute pancreatitis. Digestion 2002, 65, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossard, J.L.; Lescuyer, P.; Pastor, C.M. Experimental evidence of obesity as a risk factor for severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 5260–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpavicius, A.; Dambrauskas, Z.; Sileikis, A.; Vitkus, D.; Strupas, K. Value of adipokines in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis: Comprehensive review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 6620–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konturek, P.C.; Konturek, S.J.; Brzozowski, T.; Jaworek, J.; Hahn, E.G. Role of leptin in the stomach and the pancreas. J. Physiol. 2001, 95, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warzecha, Z.; Dembiński, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Jaworek, J.; Konturek, P.C.; Dembiński, M.; Bilskl, J.; Konturek, S.J. Influence of leptin administration on the course of acute ischemic pancreatitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2002, 53, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gultekin, F.A.; Kerem, M.; Tatlicioglu, E.; Aricioglu, A.; Unsal, C.; Bukan, N. Leptin treatment ameliorates acute lung injury in rats with cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; La Rocca, C.; De Candia, P.; Procaccini, C.; Colamatteo, A.; Micillo, T.; De Rosa, V.; Matarese, G. Metabolic control of immune tolerance in health and autoimmunity. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, G.; Vera-Lastra, O.; Peralta-Amaro, A.L.; Jiménez-Arellano, M.P.; Saavedra, M.A.; Cruz-Domínguez, M.P.; Jara, L.J. Metabolic syndrome, autoimmunity and rheumatic diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 133, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, P.; Katona-Apte, J. The interaction between nutrition and infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadi, S.; Ovchinnikov, R.S. The relationship between nutrition and infectious diseases: A review. Biomed. Biotechnol. Res. J. 2018, 2, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Hennig, B.; Petriello, M.C.; Gamble, M.V.; Surh, Y.J.; Kresty, L.A.; Frank, N.; Rangkadilok, N.; Ruchirawat, M.; Suk, W.A. The role of nutrition in influencing mechanisms involved in environmentally mediated diseases. Rev. Environ. Health 2018, 33, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, R.; Bhattacharya, P.; Dey, R.; Nakhasi, H.L. Leptin Functions in Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, C.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Leptin regulation of immune responses. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Ruiz, R.; Fuentes-Mera, L.; Camacho, A. Central modulation of neuroinflammation by neuropeptides and energy-sensing hormones during obesity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7949582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, E.V.; Liu, A.; Matarese, G.; La Cava, A. Leptin promotes systemic lupus erythematosus by increasing autoantibody production and inhibiting immune regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10637–10642. [Google Scholar]
- Palatucci, A.T.; Piantedosi, D.; Rubino, V.; Giovazzino, A.; Guccione, J.; Pernice, V.; Ruggiero, G.; Cortese, L.; Terrazzano, G. Circulating regulatory T cells (Treg), leptin and induction of proinflammatory activity in obese Labrador Retriever dogs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2018, 202, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawauchi, I.M.; Jeremias, J.T.; Takeara, P.; de Souza, D.F.; Balieiro, J.C.C.; Pfrimer, K.; Brunetto, M.A.; Pontieri, C.F.F. Effect of dietary protein intake on the body composition and metabolic parameters of neutered dogs. J. Nutr. Sci. 2017, 6, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; Yang, M.P. Serum adipokine concentrations in dogs with diabetes mellitus: A pilot study. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 16, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lam, Q.L.; Lu, L. Role of leptin in immunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Francisco, V.; Pino, J.; Campos-Cabaleiro, V.; Ruiz-Fernández, C.; Mera, A.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Gómez, R.; Gualillo, O. Obesity, fat mass and immune system: Role for leptin. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.M.; Halaas, J.L. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1998, 395, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, L.A.; Dembski, M.; Weng, X.; Deng, N.; Culpepper, J.; Devos, R.; Richards, G.J.; Campfield, L.A.; Clark, F.T.; Deeds, J.; et al. Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell 1995, 83, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarese, G.; La Cava, A. The intricate interface between immune system and metabolism. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.L.; Matarese, G.; Shetty, G.K.; Raciti, P.; Kelesidis, I.; Aufiero, D.; De Rosa, V.; Perna, F.; Fontana, S.; Mantzoros, C.S. Differential regulation of metabolic, neuroendocrine, and immune function by leptin in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8481–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccini, C.; Jirillo, E.; Matarese, G. Leptin as an immunomodulator. Mol. Aspects Med. 2012, 33, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. The weight of leptin in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernotiene, E.; Palmer, G.; Gabay, C. The role of leptin in innate and adaptive immune responses. Arthritis. Res. Ther. 2006, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hsu, A.; Aronoff, D.M.; Phipps, J.; Goel, D.; Mancuso, P. Leptin improves pulmonary bacterial clearance and survival in ob/ob mice during pneumococcal pneumonia. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 150, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruen, M.L.; Hao, M.; Piston, D.W.; Hasty, A.H. Leptin requires canonical migratory signaling pathways for induction of monocyte and macrophage chemotaxis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 293, C1481–C1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, L.H.; Ortega, M.T.; Fleming, S.D.; Chapes, S.K.; Melgarejo, T. Bone marrow leptin signaling mediates obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation in male mice. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, J.; Scotece, M.; Gómez, R.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Lago, F.; Gualillo, O. At the crossroad between immunity and metabolism: Focus on leptin. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pozo, C.; Rodriguez-Baño, J.; Domínguez-Castellano, A.; Muniain, M.A.; Goberna, R.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Leptin stimulates the oxidative burst in control monocytes but attenuates the oxidative burst in monocytes from HIV-infected patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 134, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohchi, C.; Inagawa, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Soma, G. ROS and innate immunity. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 817–821. [Google Scholar]
- Najib, S.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Human leptin promotes survival of human circulating blood monocytes prone to apoptosis by activation of p42/44 MAPK pathway. Cell Immunol. 2002, 220, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggioni, R.; Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Leptin regulation of the immune response and the immunodeficiency of malnutrition. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, A.; Conus, S.; Schmid, I.; Simon, H.U. Apoptotic pathways are inhibited by leptin receptor activation in neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 8090–8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarkesh-Esfahani, H.; Pockley, A.G.; Wu, Z.; Hellewell, P.G.; Weetman, A.P.; Ross, R.J. Leptin indirectly activates human neutrophils via induction of TNF-alpha. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, B.; Straface, E.; Quaranta, M.G.; Giordani, L.; Viora, M. Leptin promotes differentiation and survival of human dendritic cells and licenses them for Th1 priming. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6820–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Q.L.K.; Liu, S.; Cao, X.; Lu, L. Involvement of leptin signaling in the survival and maturation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 3118–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laue, T.; Wrann, C.D.; Hoffmann-Castendiek, B.; Pietsch, D.; Hübner, L.; Kielstein, H. Altered NK cell function in obese healthy humans. BMC Obes. 2015, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, J.; Spielau, M.; Brandsch, C.; Stangl, G.I.; Delank, K.S.; Bähr, I.; Berreis, T.; Wrann, C.D.; Kielstein, H. Decreased NK cell functions in obesity can be reactivated by fat mass reduction. Obesity 2015, 23, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Gao, B. Impaired natural killer (NK) cell activity in leptin receptor deficient mice: Leptin as a critical regulator in NK cell development and activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 298, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.K.; Lord, G.M.; Matarese, G.; Vendetti, S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Ritter, M.A.; Lechler, R.I.; Bloom, S.R. Leptin protects mice from starvation-induced lymphoid atrophy and increases thymic cellularity in ob/ob mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Margalet, V.; Martín-Romero, C.; González-Yanes, C.; Goberna, R.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Muniain, M.A. Leptin receptor (Ob-R) expression is induced in peripheral blood mononuclear cells by in vitro activation and in vivo in HIV-infected patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 129, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Romero, C.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Goberna, R.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Human leptin enhances activation and proliferation of human circulating T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 2000, 199, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, G.M.; Matarese, G.; Howard, J.K.; Baker, R.J.; Bloom, S.R.; Lechler, R.I. Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature 1998, 394, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, A.; Okur, B.; Glauben, R.; Erben, U.; Ihbe, J.; Stroh, T.; Fedke, I.; Chang, H.D.; Zeitz, M.; Siegmund, B. Leptin: A critical regulator of CD4+ T-cell polarization in vitro and in vivo. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Ko, K.H.; Hua, Z.; Sun, L.; Cao, X.; et al. Leptin exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis via enhancement of Th17 cell response. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3564–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, B.S.; Lee, K.; Fanok, M.H.; Mascaraque, C.; Amoury, M.; Cohn, L.B.; Rogoz, A.; Dallner, O.S.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Domingos, A.I.; et al. Leptin receptor signaling in T cells is required for Th17 differentiation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5253–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Q.L.K.; Wang, S.; Ko, O.K.H.; Kincade, P.W.; Lu, L. Leptin signaling maintains B-cell homeostasis via induction of Bcl-2 and Cyclin D1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13812–13817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, S. The origin of FOXP3-expressing CD4+ regulatory T cells: Thymus or periphery. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1310–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, V.; Procaccini, C.; Calì, G.; Pirozzi, G.; Fontana, S.; Zappacosta, S.; La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. A key role of leptin in the control of regulatory T cell proliferation. Immunity 2007, 26, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Morales, M.; Mueller, D. Anergy into T regulatory cells: An integration of metabolic cues and epigenetic changes at the Foxp3 conserved non-coding sequence 2. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Bhattacharya, P.; Prabhakar, B.S. A comprehensive review on the role of co-signaling receptors and Treg homeostasis in autoimmunity and tumor immunity. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 95, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarese, G.; Procaccini, C.; De Rosa, V.; Horvath, T.L. La Cava, A. Regulatory T cells in obesity: The leptin connection. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, J.E.; Torgerson, T.R.; Schubert, L.A.; Anover, S.D.; Ocheltree, E.L.; Ochs, H.D.; Ziegler, S.F. Analysis of FOXP3 reveals multiple domains required for its function as a transcriptional repressor. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 3133–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Hanabuchi, S.; Wang, Y.H.; Park, W.R.; Arima, K.; Bover, L.; Qin, F.X.; Gilliet, M.; Liu, Y.J. Two functional subsets of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in human thymus and periphery. Immunity 2008, 28, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Huang, C.; Zhou, B.; Ziegler, S.F. Isoform-specific inhibition of ROR alpha-mediated transcriptional activation by human FOXP3. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4785–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lopes, J.E.; Chong, M.M.; Ivanov, I.I.; Min, R.; Victora, G.D.; Shen, Y.; Du, J.; Rubtsov, Y.P.; Rudensky, A.Y.; et al. TGF-beta-induced Foxp3 inhibits T(H)17 cell differentiation by antagonizing RORgammat function. Nature 2008, 453, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambucci, M.; Gargano, F.; De Rosa, V.; De Bardi, M.; Picozza, M.; Placido, R.; Ruggieri, S.; Capone, A.; Gasperini, C.; Matarese, G.; et al. FoxP3 isoforms and PD-1 expression by T regulatory cells in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Porcellini, A.; Colamatteo, A.; Santopaolo, M.; Zuchegna, C.; Romano, A.; De Simone, S.; Procaccini, C.; La Rocca, C.; et al. Glycolysis controls the induction of human regulatory T cells by modulating the expression of FOXP3 exon 2 splicing variants. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailer, R.K.; Joly, A.L.; Liu, S.; Elias, S.; Tegner, J.; Andersson, J. IL-1β promotes Th17 differentiation by inducing alternative splicing of FOXP3. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, L.E.; Proud, C.G. ATP depletion increases phosphorylation of elongation factor eEF2 in adult cardiomyocytes independently of inhibition of mTOR signalling. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling at a glance. J. Cell. Sci. 2009, 122, 3589–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgani, M.; Procaccini, C.; De Rosa, V.; Carbone, F.; Chieffi, P.; La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. Leptin modulates the survival of autoreactive CD4+ T cells through the nutrient/energy-sensing mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7474–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Yang, K.; Cloer, C.; Neale, G.; Vogel, P.; Chi, H. mTORC1 couples immune signals and metabolic programming to establish T(reg)-cell function. Nature 2013, 499, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Dillon, C.P.; Shi, L.Z.; Milasta, S.; Carter, R.; Finkelstein, D.; McCormick, L.L.; Fitzgerald, P.; Chi, H.; Munger, J.; et al. The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity 2011, 35, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.P.; Finlay, D.K. Glucose, glycolysis and lymphocyte responses. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 68, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagih, J.; Coulombe, F.; Vincent, E.E.; Dupuy, F.; Galicia-Vázquez, G.; Yurchenko, E.; Raissi, T.C.; van der Windt, G.J.; Viollet, B.; Pearce, E.L.; et al. The energy sensor AMPK regulates T cell metabolic adaptation and effector responses in vivo. Immunity 2015, 42, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, R.M.; Finlay, D.K. Immunometabolism: Cellular metabolism turns immune regulator. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerriets, V.A.; Rathmell, J.C. Metabolic pathways in T cell fate and function. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccini, C.; Carbone, F.; Galgani, M.; La Rocca, C.; De Rosa, V.; Cassano, S.; Matarese, G. Obesity and susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Lee, J. Cellular and molecular players in adipose tissue inflammation in the development of obesity-induced insulin resistance. Biochim. Biophys Acta 2014, 1842, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Q.; Shao, S. Th17 and Treg lymphocytes in obesity and Type 2 diabetic patients. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 197, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.M.; Jialal, I.; Devaraj, S. Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on regulatory T cell number and function in obese v. lean volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wagner, N.M.; Brandhorst, G.; Czepluch, F.; Lankeit, M.; Eberle, C.; Herzberg, S.; Faustin, V.; Riggert, J.; Oellerich, M.; Hasenfuss, G.; et al. Circulating regulatory T cells are reduced in obesity and may identify iubjects at increased metabolic and cardiovascular risk. Obesity 2013, 2, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiuliis, J.; Shah, Z.; Shah, N.; Needleman, B.; Mikami, D.; Narula, V.; Perry, K.; Hazey, J.; Kampfrath, T.; Kollengode, M.; et al. Visceral adipose inflammation in obesity is associated with critical alterations in T regulatory cell numbers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, S.; Herbin, O.; Ait-Oufella, H.; Verreth, W.; Gourdy, P.; Barateau, V.; Merval, R.; Esposito, B.; Clément, K.; Holvoet, P.; et al. Defective leptin/leptin receptor signaling improves regulatory T cell immune response and protects mice from atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2691–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuna-Puente, B.; Feve, B.; Fellahi, S.; Bastard, J.P. Adipokines: The missing link between insulin resistance and obesity. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 34, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Tecles, F.; Martinez-Subiela, S.; Ceron, J.J. Effect of weight loss on inflammatory biomarkers in obese dogs. Vet. J. 2012, 193, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakshlag, J.J.; Struble, A.M.; Levine, C.B.; Bushey, J.J.; Laflamme, D.P.; Long, G.M. The effects of weight loss on adipokines and markers of inflammation in dogs. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, S11–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastien, B.C.; Patil, A.; Satyaraj, E. The impact of weight loss on circulating cytokines in Beagle dogs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 163, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagawa, M.M.; Nakadomo, F.; Honjoh, T.; Ishioka, K.; Saito, M. Correlation between plasma leptin concentration and body fat content in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 63, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishioka, K.; Soliman, M.M.; Sagawa, M.; Nakadomo, F.; Shibata, H.; Honjoh, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Kitamura, H.; Kimura, K.; Saito, M. Experimental and clinical studies on plasma leptin in obese dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2002, 64, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishioka, K.; Hosoya, K.; Kitagawa, H.; Shibata, H.; Honjoh, T.; Kimura, K.; Saito, M. Plasma leptin concentration in dogs: Effects of body condition score, age, gender and breeds. Res. Vet. Sci. 2007, 82, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeusette, I.C.; Detilleux, J.; Shibata, H.; Saito, M.; Honjoh, T.; Delobel, A.; Istasse, L.; Diez, M. Effects of chronic obesity and weight loss on plasma ghrelin and leptin concentrations in dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2005, 79, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, K.R.; Landt, M.; Klein, S. Relationship between insulin sensitivity and plasma leptin concentration in lean and obese men. Diabetes 1996, 45, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayet, C.; Bailhache, E.; Dumon, H.; Martin, L.; Siliart, B.; Nguyen, P. Insulin resistance and changes in plasma concentration of TNFalpha, IGF1, and NEFA in dogs during weight gain and obesity. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2004, 88, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, A.P.M.; Price, C.A.; de Oliveira, S.T.; dos Santos, A.P.; Campos, R.; Barbosa, P.R.; Gonzalez, F.H.D. Association of canine obesity with reduced serum levels of C-reactive protein. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2008, 20, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, H.; Janssens, G.P.; Stuyven, E.; Cox, E.; Buyse, J.; Hesta, M. Short-term increase of body weight triggers immunological variables in dogs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 145, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, H.; Janssens, G.P.; Rochus, K.; Duchateau, L.; Scharek-Tedin, L.; Zentek, J.; Nguyen, P.; Cox, E.; Buyse, J.; Biourge, V.; et al. Proliferation capacity of T-lymphocytes is affected transiently after a long-term weight gain in Beagle dogs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 152, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.; Mann, S.; Levine, C.B.; Cummings, B.P.; Wakshlag, J.J. Increasing body condition score is positively associated interleukin-6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in Labrador retrievers. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 167, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piantedosi, D.; Di Loria, A.; Guccione, J.; De Rosa, A.; Fabbri, S.; Cortese, L.; Carta, S.; Ciaramella, P. Serum biochemistry profile, inflammatory cytokines, adipokines and cardiovascular findings in obese dogs. Vet. J. 2016, 216, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, C.W.; Florquin, S.; Chan, E.D.; Leemans, J.C.; Weijer, S.; Verbon, A.; Fantuzzi, G.; van der Poll, T. Pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in leptin deficient ob/ob mice. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedantama, G.; Viswanathana, V.K. Leptin signaling protects the gut from Entamoeba histolytica infection. Gut Microbes. 2012, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Madan, R.; Guo, X.; Naylor, C.; Buonomo, E.L.; Mackay, D.; Noor, Z.; Concannon, P.; Scully, K.W.; Pramoonjago, P.; Kolling, G.L.; et al. Role of leptin-mediated colonic inflammation in defense against Clostridium difficile Colitis. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivahare, R.; Ali, W.; Vishwakarma, P.; Natu, S.M.; Puri, S.K.; Gupta, S. Leptin augments protective immune responses in murine macrophages and enhances potential of miltefosine against experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Acta. Tropica 2015, 150, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayakar, A.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Veronica, J. Maurya, R.S. Leptin induces the phagocytosis and protective immune response in Leishmania donovani infected THP-1 cell line and human PBMCs. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 160, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, L.; Graniel, J.; Ortiz, R. Effect of leptin on activation and cytokine synthesis in peripheral blood lymphocytes of malnourished infected children. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 148, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, A.; Moreno Castilho, T.; Goldsmith-Pestana, K.; Chae, W.J.; Bothwell, A.L.; Sparwasser, T.; McMahon-Pratt, D. The immunotherapeutic role of regulatory T cells in Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis infection. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2961–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, L.; Annunziatella, M.; Palatucci, A.T.; Rubino, V.; Piantedosi, D.; Di Loria, A.; Ruggiero, G.; Ciaramella, P.; Terrazzano, G. Regulatory T cells, Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and a T(H)1 cytokine profile in dogs naturally infected by Leishmania infantum. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalid-Peralta, L.; Fragoso, G.; Fleury, A.; Sciutto, E. Mechanisms underlying the induction of regulatory T cells and its relevance in the adaptive immune response in parasitic infections. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 1412–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Loria, A.; Squillacioti, C.; De Luca, A.; Veneziano, V.; Mirabella, N.; Guccione, J.; Santoro, D. Increased leptin mRNA expression in the blood of dogs naturally infected by Leishmania infantum. Vet. J. 2014, 202, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Buzdar, A.U.; Hursting, S.D. Inflammatory breast cancer and body mass index. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 3731–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconato, L.; Romanelli, G.; Stefanello, D.; Giacoboni, C.; Bonfanti, U.; Bettini, G.; Finotello, R.; Verganti, S.; Valenti, P.; Ciaramella, L. Prognostic factors for dogs with mammary inflammatory carcinoma: 43 cases (2003–2008). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2009, 235, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.S.; Vieira, A.R.; Aune, D.; Bandera, E.V.; Greenwood, D.C.; McTiernan, A.; Navarro Rosenblatt, D.; Thune, I.; Vieira, R.; Norat, T. Body mass index and survival in women with breast cancer-systematic literature review and meta-analysis of 82 follow-up studies. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.Y.; Im, K.S.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.W.; Shin, J.I.; Yhee, J.Y.; Sur, J.H. Effects of obesity and obesity-related molecules on canine mammary gland tumors. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 52, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorincz, A.M.; Sukumar, S. Molecular links between obesity and breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laud, K.; Gourdou, I.; Pessemesse, L.; Peyrat, J.; Djiane, J. Identification of leptin receptors in human breast cancer: Functional activity in the T47-D breast cancer cell line. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 188, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardé, T.; Caldefie-Chezet, F.; Damez, M.; Mishellany, F.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Guillot, J.; Vasson, M.P. Leptin and leptin receptor involvement in cancer development: A study on human primary breast carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardé, T.; Perrier, S.; Vasson, M.P.; Caldefie-Chézet, F. Molecular mechanisms of leptin and adiponectin in breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. 2011, 47, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A. Cancer and comorbidity: The role of leptin in breast cancer and associated pathologies. World J. Clin. Cases. 2018, 6, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.P.; Gilhooly, E.M.; Nixon, D.W. Adverse effects of obesity on breast cancer prognosis, and the biological actions of leptin. Int. J. Oncol. 2002, 21, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, H.; Aljada, A.; Hofmeyer, D.; Syed, T.; Mohanty, P.; Dandona, P. Circulating mononuclear cells in the obese are in a proinflammatory state. Circulation 2004, 110, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, A.; Carpi, A.; Rossi, G. Cytokines in breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, P.G.; Hudis, C.A.; Giri, D.; Morrow, M.; Falcone, D.J.; Zhou, X.K.; Du, B.; Brogi, E.; Crawford, C.B.; Kopelovich, L. Inflammation and increased aromatase expression occur in the breast tissue of obese women with breast cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, L.M.; McCready, J.; Keller, P.J.; Baker, D.D.; Naber, S.P.; Seewaldt, V.; Kuperwasser, C. Obesity promotes breast cancer by CCL2-mediated macrophage recruitment and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6080–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Kitamura, T.; Zhang, J.; Campion, L.R.; Kaiser, E.A.; Snyder, L.A.; Pollard, J.W. CCL2 recruits inflammatory monocytes to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis. Nature 2011, 475, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Du, B.; Zhou, X.K.; Sue, E.; Harbus, M.D.; Falcone, D.J.; Giri, D.; Hudis, C.A.; Kopelovich, L.; Subbaramaiah, K. Caloric restriction reverses obesity- induced mammary gland inflammation in mice. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlman, E.; Bright, J.M.; Jeckel, K.; Porsche, C.; Veeramachaneni, D.N.; Frye, M. Echocardiographic evidence of left ventricular hypertrophy in obese dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolphe, J.L.; Silver, T.I.; Childs, H.; Drew, M.D.; Weber, L.P. Short-term obesity results in detrimental metabolic and cardiovascular changes that may not be reversed with weight loss in an obese dog model. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropf, M.; Nelson, O.L.; Lee, P.M.; Weng, H.Y. Cardiac and metabolic variables in obese dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonfara, S.; Hetzel, U.; Tew, S.R.; Dukes-McEwan, J.; Cripps, P.; Clegg, P.D. Leptin expression in dogs with cardiac disease and congestive heart failure. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; Jeung, E.B.; Yang, M.P. Serum concentrations of leptin and adiponectin in dogs with myxomatous mitral valve disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuspidi, C.; Rescaldani, M.; Sala, C.; Grassi, G. Left-ventricular hypertrophy and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of echocardiographic studies. J. Hypertens. 2014, 32, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdolo, G.; Angeli, F.; Reboldi, G.; Di Giacomo, L.; Aita, A.; Bartolini, C.; Vedecchia, P. Left ventricular hypertrophy and obesity: Only a matter of fat? High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2015, 22, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, A.P.; Del-Angel-Caraza, J.; Quijano-Hernández, I.A.; Barbosa-Mireles, M.A. Obesity-hypertension and its relation to other diseases in dogs. Vet. Res. Commun. 2015, 39, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwaerde, P.; Sénard, J.M.; Galinier, M.; Rougé, P.; Massabuau, P.; Galitzky, J.; Berlan, M.; Lafontan, M.; Montastruc, J.L. Changes in short-term variability of blood pressure and heart rate during the development of obesity-associated hypertension in high-fat fed dogs. J. Hypertens. 1999, 17, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.A.; Morris, P.J.; Bautista, I.; Juste, M.C.; Suarez, L.; Peña, C.; Hackett, R.M.; Rawlings, J. Hypertension: A risk factor associated with weight status in dogs. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2011S–2013S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, P.C.; Kratzsch, J. Leptin as a new diagnostic tool in chronic heart failure. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 362, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdham, D.M.; Zou, M.X.; Rajapurohitam, V. Rat heart is a site of leptin production and action. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H2877–H2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmazyn, M.; Purdham, D.M.; Rajapurohitam, V.; Zeidan, A. Leptin as a cardiac hypertrophic factor: A potential target for therapeutics. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 17, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Honigmann, M.R.; Nath, A.K.; Murakami, C.; García-Cardeña, G.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Sessa, W.C.; Madge, L.A.; Schechner, J.S.; Schwabb, M.B.; Polverini, P.J.; et al. Biological action of leptin as an angiogenic factor. Science 1998, 281, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, G. Cardiovascular effects of leptin. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010, 7, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; McNeill, J.H. The emerging roles of leptin and ghrelin in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2005, 3, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.H.; Chu, C.S.; Lee, K.T.; Lin, T.H.; Hsieh, C.C.; Chiu, C.C.; Voon, W.C.; Sheu, S.H.; Lai, W.T. Adipocytokines and proinflammatory mediators from abdominal and epicardial adipose tissue in patients with coronary artery disease. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudson, J.D.; Payne, G.A.; Borbouse, L.; Tune, J.D. Leptin and mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2008, 10, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Chua, T.P.; Ponikowski, P.; Hrrington, D.; Swan, J.W.; Kox, W.J.; Poole-Wilson, P.A.; Coats, A.J. Hormonal changes and catabolic/anabolic imbalance in chronic heart failure and their importance for cardiac cachexia. Circulation 1997, 96, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehner, W.; Pflaum, C.D.; Rauchhaus, M.; Godsland, I.F.; Egerer, K.; Cicoira, M.; Florea, V.G.; Sharma, R.; Bolger, A.P.; Coats, A.J.; et al. Leptin, insulin sensitivity and growth hormone binding protein in chronic heart failure with and without cardiac cachexia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 145, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Haynes, W.G.; Morgan, D.A.; Walsh, S.A.; Mark, A.L.; Sivitz, W.I. Receptor- mediated regional sympathetic nerve activation by leptin. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, L.L.; Fischer, M.A.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Leptin activates cardiac fatty acid oxidation independent of changes in the AMP-activated protein kinase-acetyl-CoA carboxylase-malonyl- CoA axis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 29424–29430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, K.; De Girolamo, S.; Madani, S.; Munoz, D.; Thong, F.; Sweeney, G. Leptin regulates MMP-2, TIMP-1 and collagen synthesis via p38 MAPK in HL-1 murine cardiomyocytes. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2010, 15, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barouch, L.A.; Gao, D.; Chen, L.; Miller, K.L.; Xu, W.; Phan, A.C.; Kittleson, M.M.; Minhas, K.M.; Berkowitz, D.E.; Wei, C.; et al. Cardiac myocyte apoptosis is associated with increased DNA damage and decreased survival in murine models of obesity. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaffin, K.R.; Witham, W.G.; Yester, K.A.; Romano, L.C.; O’Doherty, R.M.; McTiernan, C.F.; O’Donnell, C.P. Cardiac-specific leptin receptor deletion exacerbates ischaemic heart failure in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazaki-Tovi, M.; Feuermann, Y.; Segev, G.; Klement, E.; Yas-Natan, E.; Farkas, A.; Kol, A.; Shamay, A. Increased serum leptin and insulin concentrations in canine hypothyroidism. Vet. J. 2010, 183, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, V.R.; Wilson, H.; Pfent, C.; Roethele, J.; Carwile, J.; Qin, Y.; Grimm, E.; Ellerhorst, J.A. Expression of leptin and iNOS in oral melanomas in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffler, A.; Landfried, K.; Volk, M.; Fürst, A.; Büchler, C.; Schölmerich, J.; Herfarth, H. Potential of adipocytokines in predicting peripancreatic necrosis and severity in acute pancreatitis: Pilot study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Muddana, V.; Lamb, J.; Greer, J.; Papachristou, G.I.; Whitcomb, D.C. Low serum adiponectin levels are associated with systemic organ failure in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2009, 38, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffler, A.; Hamer, O.; Dickopf, J.; Goetz, A.; Landfried, K.; Voelk, M.; Herfarth, H.; Kopp, A.; Büchler, C.; Schölmerich, J.; et al. Admission resistin levels predict peripancreatic necrosis and clinical severity in acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2474–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffler, A.; Hamer, O.W.; Dickopf, J.; Goetz, A.; Landfried, K.; Voelk, M.; Herfarth, H.; Kopp, A.; Buechler, C.; Schölmerich, J.; et al. Admission visfatin levels predict pancreatic and peripancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis and correlate with clinical severity. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerem, M.; Bedirli, A.; Pasaoglu, H.; Unsal, C.; Yilmaz, T.U.; Ofluoglu, E.; Sahin, T.T. Role of ghrelin and leptin in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyromski, N.J.; Mathur, A.; Pitt, H.A.; Lu, D.; Gripe, J.T.; Walker, J.J.; Yancey, K.; Wade, T.E.; Swartz-Basile, D.A. A murine model of obesity implicates the adipokine milieu in the pathogenesis of severe acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G552–G558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Franco-Pons, N.; Gea-Sorlì, S.; Closa, D. Release of inflammatory mediators by adipose tissue during acute pancreatitis. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, J.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, I.; Seo, K.W.; Yang, M.P. Serum adipokine concentrations in dogs with acute pancreatitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, A.; Kweon, O.K.; Kim, W.H. Presence and distribution of leptin and leptin receptor in the canine gallbladder. Acta Histochem. 2016, 118, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Kweon, O.K.; Kim, W.H. Increased leptin and leptin receptor expression in dogs with gallbladder mucocele. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haluzík, M.; Fiedler, J.; Nedvidkova, J.; Ceska, R. Serum leptin concentrations in patients with combined hyperlipidemia: Relationship to serum lipids and lipoproteins. Physiol. Res. 1998, 48, 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Haluzík, M.; Fiedler, J.; Nedvídkova, J.; Ceska, R. Serum leptin levels in patients with hyperlipidemias. Nutrition 2000, 16, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, S.E.; Oh, J.H.; Seo, K.W.; Song, K.H. Leptin, adiponectin and serotonin levels in lean and obese dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzaga, N.C.; Medeiros, C.C.; de Carvalho, D.F.; Alves, J.G. Leptin and cardiometabolic risk factors in obese children and adolescents. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2014, 50, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.; Miquel, J.F.; Reyes, M.S.; Zanlungo, S.; Nervi, F. Diet as a risk factor for cholesterol gallstone disease. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Lee, H.L.; Moon, W.; Koh, D.H.; Lee, O.Y.; Yoon, B.C.; Choi, H.S.; Hahm, J.S.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Association between insulin, insulin resistance, and gallstone disease in Korean general population. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 50, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kweon, O.K.; Kim, W.H. Associations between serum leptin levels, hyperlipidemia, and cholelithiasis in dogs. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, L.; Trayhurn, P.; Abramovich, D.; Fowler, P. Circulating leptin in women: A longitudinal study in the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy. Clin. Endocrinol. 1997, 47, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amico, J.A.; Thomas, A.; Crowley, R.S.; Burmeister, L.A. Concentrations of leptin in the serum of pregnant, lactating, and cycling rats and of leptin messenger ribonucleic acid in rat placental tissue. Life Sci. 1998, 63, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, O.; Staub, L.P.; Gram, A.; Boos, A.; Kowalewski, M.P.; Reichler, I.M. Leptin in the canine uterus and placenta: Possible implications in pregnancy. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2015, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, M.; Cojocaru, I.M.; Silosi, I.; Rogoz, S. Role of Leptin in Autoimmune Diseases. Maedica J. Clin. Med. 2013, 8, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortese, L.; Terrazzano, G.; Pelagalli, A. Leptin and Immunological Profile in Obesity and Its Associated Diseases in Dogs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102392
Cortese L, Terrazzano G, Pelagalli A. Leptin and Immunological Profile in Obesity and Its Associated Diseases in Dogs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102392
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortese, Laura, Giuseppe Terrazzano, and Alessandra Pelagalli. 2019. "Leptin and Immunological Profile in Obesity and Its Associated Diseases in Dogs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102392
APA StyleCortese, L., Terrazzano, G., & Pelagalli, A. (2019). Leptin and Immunological Profile in Obesity and Its Associated Diseases in Dogs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102392





