The Crosstalk between Acetylation and Phosphorylation: Emerging New Roles for HDAC Inhibitors in the Heart
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)
3. HDAC Inhibitors in the Heart
4. Protein Phosphorylation-Acetylation
5. HDAC Inhibition, Protein Phosphorylation, and Heart Failure
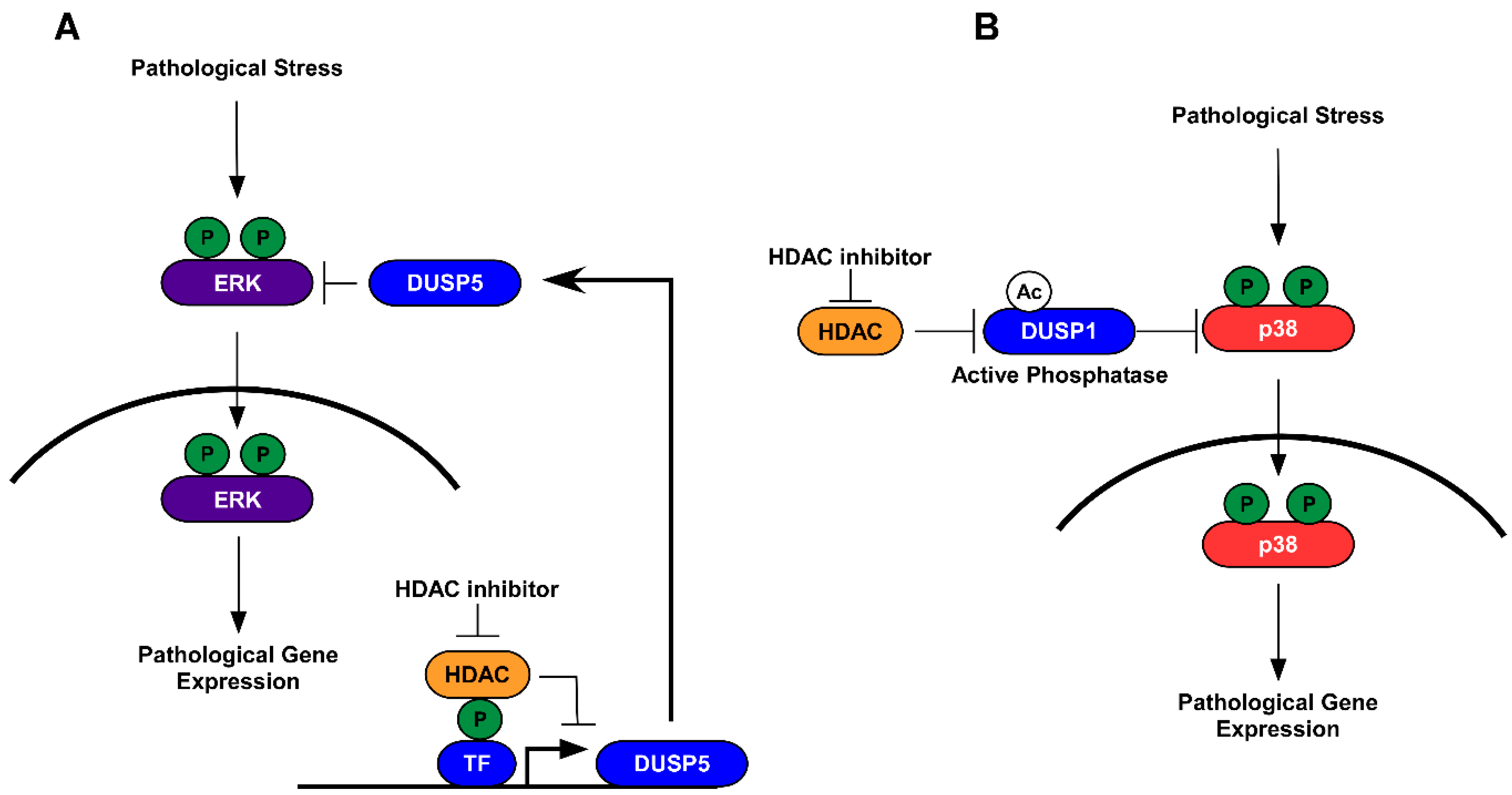
5.1. HDAC Inhibition and Protein Dephosphorylation
5.2. HDAC Inhibition and Protein Kinases
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; de Ferranti, S.; Despres, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; Howard, V.J.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2015 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, e29–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamdar, A.A.; Inamdar, A.C. Heart Failure: Diagnosis, Management and Utilization. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinsey, T.A. Targeting inflammation in heart failure with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, B.S.; McKinsey, T.A. Non-sirtuin histone deacetylases in the control of cardiac aging. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 83, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.M.; Golden-Mason, L.; Ferguson, B.S.; Schuetze, K.B.; Cavasin, M.A.; Demos-Davies, K.; Yeager, M.E.; Stenmark, K.R.; McKinsey, T.A. Class I HDACs regulate angiotensin II-dependent cardiac fibrosis via fibroblasts and circulating fibrocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 67, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demos-Davies, K.M.; Ferguson, B.S.; Cavasin, M.A.; Mahaffey, J.H.; Williams, S.M.; Spiltoir, J.I.; Schuetze, K.B.; Horn, T.R.; Chen, B.; Ferrara, C.; et al. HDAC6 contributes to pathological responses of heart and skeletal muscle to chronic angiotensin-II signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 307, H252–H258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLendon, P.M.; Ferguson, B.S.; Osinska, H.; Bhuiyan, M.S.; James, J.; McKinsey, T.A.; Robbins, J. Tubulin hyperacetylation is adaptive in cardiac proteotoxicity by promoting autophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5178–E5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey, T.A. Therapeutic potential for HDAC inhibitors in the heart. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, C.R.; Li, D.L.; Pedrozo, Z.; May, H.I.; Jiang, N.; Kyrychenko, V.; Cho, G.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Wang, Z.V.; Rotter, D.; et al. Inhibition of class I histone deacetylases blunts cardiac hypertrophy through TSC2-dependent mTOR repression. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Kong, Y.; Tan, W.; May, H.; Battiprolu, P.K.; Pedrozo, Z.; Wang, Z.V.; Morales, C.; Luo, X.; Cho, G.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition blunts ischemia/reperfusion injury by inducing cardiomyocyte autophagy. Circulation 2014, 129, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Tannous, P.; Lu, G.; Berenji, K.; Rothermel, B.A.; Olson, E.N.; Hill, J.A. Suppression of class I and II histone deacetylases blunts pressure-overload cardiac hypertrophy. Circulation 2006, 113, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradner, J.E.; West, N.; Grachan, M.L.; Greenberg, E.F.; Haggarty, S.J.; Warnow, T.; Mazitschek, R. Chemical phylogenetics of histone deacetylases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, M.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Wennersten, S.A.; Demos-Davies, K.M.; Cavasin, M.A.; Mahaffey, J.H.; Monzani, V.; Saripalli, C.; Mascagni, P.; Reece, T.B.; et al. Histone deacetylase activity governs diastolic dysfunction through a nongenomic mechanism. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaao0144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakeslee, W.W.; Wysoczynski, C.L.; Fritz, K.S.; Nyborg, J.K.; Churchill, M.E.; McKinsey, T.A. Class I HDAC inhibition stimulates cardiac protein SUMOylation through a post-translational mechanism. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 2912–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, B.S.; Harrison, B.C.; Jeong, M.Y.; Reid, B.G.; Wempe, M.F.; Wagner, F.F.; Holson, E.B.; McKinsey, T.A. Signal-dependent repression of DUSP5 by class I HDACs controls nuclear ERK activity and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9806–9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryson, B.D.; White, F.M. Quantitative Profiling of Lysine Acetylation Reveals Dynamic Crosstalk between Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and Lysine Acetylation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henikoff, S. Mechanisms of Nucleosome Dynamics In Vivo. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, T.C.; Hager, G.L. Dynamic regulation of transcriptional states by chromatin and transcription factors. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberharter, A.; Becker, P.B. Histone acetylation: A switch between repressive and permissive chromatin. Second in review series on chromatin dynamics. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoretti, I.V.; Lee, Y.M.; Goodson, H.V. Molecular evolution of the histone deacetylase family: Functional implications of phylogenetic analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, D.J.; Baarine, M.; Aune, S.E.; Li, X.; Ball, L.E.; Lemasters, J.J.; Beeson, C.C.; Chou, J.C.; Menick, D.R. HDAC1 localizes to the mitochondria of cardiac myocytes and contributes to early cardiac reperfusion injury. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 114, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nural-Guvener, H.F.; Zakharova, L.; Nimlos, J.; Popovic, S.; Mastroeni, D.; Gaballa, M.A. HDAC class I inhibitor, Mocetinostat, reverses cardiac fibrosis in heart failure and diminishes CD90+ cardiac myofibroblast activation. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2014, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.H.; Liou, J.P.; Chung, C.C.; Lien, G.S.; Kuo, C.C.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Histone deacetylase inhibition improved cardiac functions with direct antifibrotic activity in heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 4178–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, A.; Fenning, A.; Lim, J.; Le, G.T.; Reid, R.C.; Halili, M.A.; Fairlie, D.P.; Brown, L. Antifibrotic activity of an inhibitor of histone deacetylases in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, H.J.; Sohn, I.S.; Nam, K.I.; Park, J.E.; Qian, Y.R.; Yin, Z.; Ahn, Y.; Jeong, M.H.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, N.; et al. Inhibition of histone deacetylation blocks cardiac hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II infusion and aortic banding. Circulation 2006, 113, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antos, C.L.; McKinsey, T.A.; Dreitz, M.; Hollingsworth, L.M.; Zhang, C.L.; Schreiber, K.; Rindt, H.; Gorczynski, R.J.; Olson, E.N. Dose-dependent blockade to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28930–28937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, T.E.; Hsieh, J.H.; Sung, T.Y.; Tseng, H.J.; Yang, J.M.; Huang, W.J. Novel Class IIa-Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Discovered Using an in Silico Virtual Screening Approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of histone acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, R.A.; Ferguson, B.S.; Stratton, M.S.; Hu, T.; Cavasin, M.A.; Sun, L.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, D.; Londono, P.; Song, K.; et al. HDAC11 suppresses the thermogenic program of adipose tissue via BRD2. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey, T.A. Derepression of pathological cardiac genes by members of the CaM kinase superfamily. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; McKinsey, T.A.; Chang, S.; Antos, C.L.; Hill, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Class II histone deacetylases act as signal-responsive repressors of cardiac hypertrophy. Cell 2002, 110, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey, T.A.; Zhang, C.L.; Olson, E.N. MEF2: A calcium-dependent regulator of cell division, differentiation and death. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey, T.A.; Zhang, C.L.; Olson, E.N. Identification of a signal-responsive nuclear export sequence in class II histone deacetylases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 6312–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinsey, T.A.; Zhang, C.L.; Olson, E.N. Activation of the myocyte enhancer factor-2 transcription factor by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-stimulated binding of 14-3-3 to histone deacetylase 5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14400–14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinsey, T.A.; Zhang, C.L.; Lu, J.; Olson, E.N. Signal-dependent nuclear export of a histone deacetylase regulates muscle differentiation. Nature 2000, 408, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; McKinsey, T.A.; Zhang, C.L.; Olson, E.N. Regulation of skeletal myogenesis by association of the MEF2 transcription factor with class II histone deacetylases. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; McKinsey, T.A.; Nicol, R.L.; Olson, E.N. Signal-dependent activation of the MEF2 transcription factor by dissociation from histone deacetylases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4070–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gong, N.L.; Bodi, I.; Aronow, B.J.; Backx, P.H.; Molkentin, J.D. Myocyte enhancer factors 2A and 2C induce dilated cardiomyopathy in transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9152–9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, E.N.; Williams, R.S. Remodeling muscles with calcineurin. Bioessays 2000, 22, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passier, R.; Zeng, H.; Frey, N.; Naya, F.J.; Nicol, R.L.; McKinsey, T.A.; Overbeek, P.; Richardson, J.A.; Grant, S.R.; Olson, E.N. CaM kinase signaling induces cardiac hypertrophy and activates the MEF2 transcription factor in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; McKinsey, T.A.; Zhang, C.L.; Richardson, J.A.; Hill, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Histone deacetylases 5 and 9 govern responsiveness of the heart to a subset of stress signals and play redundant roles in heart development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 8467–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nural-Guvener, H.; Zakharova, L.; Feehery, L.; Sljukic, S.; Gaballa, M. Anti-Fibrotic Effects of Class I HDAC Inhibitor, Mocetinostat Is Associated with IL-6/Stat3 Signaling in Ischemic Heart Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 11482–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternson, S.M.; Wong, J.C.; Grozinger, C.M.; Schreiber, S.L. Synthesis of 7200 small molecules based on a substructural analysis of the histone deacetylase inhibitors trichostatin and trapoxin. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 4239–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, F.F.; Weiwer, M.; Steinbacher, S.; Schomburg, A.; Reinemer, P.; Gale, J.P.; Campbell, A.J.; Fisher, S.L.; Zhao, W.N.; Reis, S.A.; et al. Kinetic and structural insights into the binding of histone deacetylase 1 and 2 (HDAC1, 2) inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4008–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qian, L.B.; Chen, S.Y.; Sun, J.; Cai, L. Inhibition of HDAC3 prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy in OVE26 mice via epigenetic regulation of DUSP5-ERK1/2 pathway. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2017, 131, 1841–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, J.Y.; Tuano, N.K.; Rafehi, H.; Gao, X.M.; Ziemann, M.; Du, X.J.; El-Osta, A. HDAC inhibition attenuates cardiac hypertrophy by acetylation and deacetylation of target genes. Epigenetics 2015, 10, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Du, J.; Zhao, Y.T.; Zhang, L.; Lv, G.; Zhuang, S.; Qin, G.; Zhao, T.C. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition improves myocardial function and prevents cardiac remodeling in diabetic mice. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2015, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, L.; Harris, L.G.; Mani, S.K.; Kasiganesan, H.; Chou, J.C.; Baicu, C.F.; Van Laer, A.; Akerman, A.W.; Stroud, R.E.; Jones, J.A.; et al. HDACs Regulate miR-133a Expression in Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biernacka, A.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Aging and Cardiac Fibrosis. Aging Dis. 2011, 2, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stratton, M.S.; McKinsey, T.A. Epigenetic regulation of cardiac fibrosis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 92, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetze, K.B.; McKinsey, T.A.; Long, C.S. Targeting cardiac fibroblasts to treat fibrosis of the heart: Focus on HDACs. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 70, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey, T.A. Isoform-selective HDAC inhibitors: Closing in on translational medicine for the heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, V.B.; Sundaresan, N.R.; Samant, S.A.; Wolfgeher, D.; Trivedi, C.M.; Gupta, M.P. Acetylation of a conserved lysine residue in the ATP binding pocket of p38 augments its kinase activity during hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 31, 2349–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Cao, C. Sulforaphane induces autophagy by inhibition of HDAC6-mediated PTEN activation in triple negative breast cancer cells. Life Sci. 2018, 213, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Walther, D. The roles of post-translational modifications in the context of protein interaction networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.J.; Seto, E. Lysine acetylation: Codified crosstalk with other posttranslational modifications. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.T.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S.; Gatto, G.J., Jr. Protein posttranslational modifications: The chemistry of proteome diversifications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 7342–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardito, F.; Giuliani, M.; Perrone, D.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in Cell Signal.ing and its use as targeted therapy (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, K.I.; Brummer, T.; O’Brien, P.M.; Daly, R.J. Dual-specificity phosphatases: Critical regulators with diverse cellular targets. Biochem. J. 2009, 418, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, K.L.; Camps, M.; Rommel, C.; Mackay, C.R. Targeting dual-specificity phosphatases: Manipulating MAP kinase signalling and immune responses. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondoh, K.; Nishida, E. Regulation of MAP kinases by MAP kinase phosphatases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, T.W.; Hauck, L.; Grothe, D.; Billia, F. p53 regulates the cardiac transcriptome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2331–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.A.; Kim, M.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Mishra, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, J.H.; Xiang, Y.K.; Jung, Y.S. Gadd45beta is transcriptionally activated by p53 via p38alpha-mediated phosphorylation during myocardial ischemic injury. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2013, 91, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, T.G.; Moller, A.; Sirma, H.; Zentgraf, H.; Taya, Y.; Droge, W.; Will, H.; Schmitz, M.L. Regulation of p53 activity by its interaction with homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, K.; Herrera, J.E.; Saito, S.; Miki, T.; Bustin, M.; Vassilev, A.; Anderson, C.W.; Appella, E. DNA damage activates p53 through a phosphorylation-acetylation cascade. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley-Hasnain, S.; Hauck, L.; Grothe, D.; Aschar-Sobbi, R.; Beca, S.; Butany, J.; Backx, P.H.; Mak, T.W.; Billia, F. p53 and Mdm2 act synergistically to maintain cardiac homeostasis and mediate cardiomyocyte cell cycle arrest through a network of microRNAs. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundby, A.; Lage, K.; Weinert, B.T.; Bekker-Jensen, D.B.; Secher, A.; Skovgaard, T.; Kelstrup, C.D.; Dmytriyev, A.; Choudhary, C.; Lundby, C.; et al. Proteomic analysis of lysine acetylation sites in rat tissues reveals organ specificity and subcellular patterns. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.W.; Yang, X.J. Comprehensive lysine acetylomes emerging from bacteria to humans. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, B.T.; Wagner, S.A.; Horn, H.; Henriksen, P.; Liu, W.R.; Olsen, J.V.; Jensen, L.J.; Choudhary, C. Proteome-wide mapping of the Drosophila acetylome demonstrates a high degree of conservation of lysine acetylation. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, C.; Kumar, C.; Gnad, F.; Nielsen, M.L.; Rehman, M.; Walther, T.C.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science 2009, 325, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sprung, R.; Pei, J.; Tan, X.; Kim, S.; Zhu, H.; Liu, C.F.; Grishin, N.V.; Zhao, Y. Lysine acetylation is a highly abundant and evolutionarily conserved modification in Escherichia coli. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2009, 8, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Sprung, R.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ball, H.; Pei, J.; Cheng, T.; Kho, Y.; Xiao, H.; Xiao, L.; et al. Substrate and functional diversity of lysine acetylation revealed by a proteomics survey. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanick, S.S.; Ulrich, C.; Schlauch, K.; Hostler, A.; Payne, J.; Woolsey, R.; Quilici, D.; Feng, Y.; Ferguson, B.S. Obesity-mediated regulation of cardiac protein acetylation: Parallel analysis of total and acetylated proteins via TMT-tagged mass spectrometry. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, D.B.; Liu, T.; Rucker, J.; O’Meally, R.N.; Devine, L.R.; Cole, R.N.; O’Rourke, B. The cardiac acetyl-lysine proteome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharathi, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Mohsen, A.W.; Uppala, R.; Balasubramani, M.; Schreiber, E.; Uechi, G.; Beck, M.E.; Rardin, M.J.; Vockley, J.; et al. Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) protein regulates long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase by deacetylating conserved lysines near the active site. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33837–33847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sack, M.N. Emerging characterization of the role of SIRT3-mediated mitochondrial protein deacetylation in the heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H2191–H2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Weddle, A.; Kinter, C.S.; Humphries, K.M.; Mather, T.; Szweda, L.I.; Kinter, M. Lysine Acetylation Activates Mitochondrial Aconitase in the Heart. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 4008–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, C.; Weinert, B.T.; Nishida, Y.; Verdin, E.; Mann, M. The growing landscape of lysine acetylation links metabolism and cell signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufi, B.; Soares, N.C.; Ravikumar, V.; Macek, B. Proteomics reveals evidence of cross-talk between protein modifications in bacteria: Focus on acetylation and phosphorylation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Noort, V.; Seebacher, J.; Bader, S.; Mohammed, S.; Vonkova, I.; Betts, M.J.; Kuhner, S.; Kumar, R.; Maier, T.; O’Flaherty, M.; et al. Cross-talk between phosphorylation and lysine acetylation in a genome-reduced bacterium. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2012, 8, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Bao, H.; Zhang, X.P.; Liu, F.; Wang, W. Regulation of Tip60-dependent p53 acetylation in cell fate decision. FEBS Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, W. Acetylation is indispensable for p53 activation. Cell 2008, 133, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, W.; Gu, W. Tip60-dependent acetylation of p53 modulates the decision between cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, S.M.; Mellert, H.S.; Holbert, M.A.; Li, K.; Marmorstein, R.; Lane, W.S.; McMahon, S.B. Acetylation of the p53 DNA-binding domain regulates apoptosis induction. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Koh, X.Y.; Goh, H.C.; Rahmat, S.A.B.; Hwang, L.A.; Lane, D.P. Inhibiting p53 Acetylation Reduces Cancer Chemotoxicity. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4342–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogna, R.; Madan, E.; Khan, M.; Pati, U.; Kuppusamy, P. p53’s choice of myocardial death or survival: Oxygen protects infarct myocardium by recruiting p53 on NOS3 promoter through regulation of p53-Lys(118) acetylation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1662–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appella, E.; Anderson, C.W. Signaling to p53: Breaking the posttranslational modification code. Pathol. Biol. (Paris) 2000, 48, 227–245. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, J.M.; Pasupuleti, R.; Xu, L.; McDonagh, T.; Curtis, R.; DiStefano, P.S.; Huber, L.J. Inhibition of SIRT1 catalytic activity increases p53 acetylation but does not alter cell survival following DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Lai, C.H.; Kovacs, J.J.; Higashimoto, Y.; Appella, E.; Yao, T.P. MDM2-HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of p53 is required for its degradation. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6236–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaub, P.; Tedeschi, A.; Puttagunta, R.; Nguyen, T.; Schmandke, A.; Di Giovanni, S. HDAC inhibition promotes neuronal outgrowth and counteracts growth cone collapse through CBP/p300 and P/CAF-dependent p53 acetylation. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 1392–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakhrusheva, O.; Smolka, C.; Gajawada, P.; Kostin, S.; Boettger, T.; Kubin, T.; Braun, T.; Bober, E. Sirt7 increases stress resistance of cardiomyocytes and prevents apoptosis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy in mice. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakeslee, W.W.; Lin, Y.H.; Stratton, M.S.; Tatman, P.D.; Hu, T.; Ferguson, B.S.; McKinsey, T.A. Class I HDACs control a JIP1-dependent pathway for kinesin-microtubule binding in cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2017, 112, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liang, Y.Y.; Feng, X.H.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; O’Malley, B.W. Essential phosphatases and a phospho-degron are critical for regulation of SRC-3/AIB1 coactivator function and turnover. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Bao, C.; Padalko, E.; Lowenstein, C.J. Acetylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 inhibits Toll-like receptor signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, S.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, S.J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, R.P. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates a negative inotropic effect in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, W.; Kihara, Y.; Yasaka, A.; Inagaki, K.; Iwanaga, Y.; Sasayama, S. Stage-specific differential activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in hypertrophied and failing rat hearts. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, S.; Choukroun, G.; Lim, H.; Tymitz, K.M.; del Monte, F.; Gwathmey, J.; Grazette, L.; Michael, A.; Hajjar, R.; Force, T.; et al. Differential activation of signal transduction pathways in human hearts with hypertrophy versus advanced heart failure. Circulation 2001, 103, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Sah, V.P.; Ross, J., Jr.; Brown, J.H.; Han, J.; Chien, K.R. Cardiac muscle cell hypertrophy and apoptosis induced by distinct members of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase family. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crackower, M.A.; Oudit, G.Y.; Kozieradzki, I.; Sarao, R.; Sun, H.; Sasaki, T.; Hirsch, E.; Suzuki, A.; Shioi, T.; Irie-Sasaki, J.; et al. Regulation of myocardial contractility and cell size by distinct PI3K-PTEN signaling pathways. Cell 2002, 110, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Keitany, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ball, H.L.; Goldsmith, E.J.; Orth, K. Yersinia YopJ acetylates and inhibits kinase activation by blocking phosphorylation. Science 2006, 312, 1211–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martindale, J.J.; Wall, J.A.; Martinez-Longoria, D.M.; Aryal, P.; Rockman, H.A.; Guo, Y.; Bolli, R.; Glembotski, C.C. Overexpression of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 in the heart improves functional recovery from ischemia in vitro and protects against myocardial infarction in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braz, J.C.; Bueno, O.F.; Liang, Q.; Wilkins, B.J.; Dai, Y.S.; Parsons, S.; Braunwart, J.; Glascock, B.J.; Klevitsky, R.; Kimball, T.F.; et al. Targeted inhibition of p38 MAPK promotes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy through upregulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, R.; Larkin, A.; Mingo, A.M.; Thuerauf, D.J.; Andrews, C.; McDonough, P.M.; Glembotski, C.C. p38 MAPK and NF-kappa B collaborate to induce interleukin-6 gene expression and release. Evidence for a cytoprotective autocrine signaling pathway in a cardiac myocyte model system. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23814–23824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itzen, F.; Greifenberg, A.K.; Bosken, C.A.; Geyer, M. Brd4 activates P-TEFb for RNA polymerase II CTD phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7577–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparidis, N.F.; Durvale, M.C.; Canduri, F. The emerging picture of CDK9/P-TEFb: More than 20 years of advances since PITALRE. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 246–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo, A.; Lusic, M.; Cereseto, A.; Giacca, M. Acetylation of conserved lysines in the catalytic core of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 inhibits kinase activity and regulates transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, R.; Ai, N.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, B.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.; et al. Histone cross-talk connects protein phosphatase 1alpha (PP1alpha) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) pathways to regulate the functional transition of bromodomain-containing 4 (BRD4) for inducible gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 23154–23167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covington, J.D.; Bajpeyi, S. The sirtuins: Markers of metabolic health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, S.; Sadoshima, J. The role of sirtuins in cardiac disease. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1375–H1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.; Stein, L.; Imai, S. The role of mammalian sirtuins in the regulation of metabolism, aging, and longevity. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 206, 125–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lombard, D.B.; Tishkoff, D.X.; Bao, J. Mitochondrial sirtuins in the regulation of mitochondrial activity and metabolic adaptation. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 206, 163–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alcendor, R.R.; Gao, S.; Zhai, P.; Zablocki, D.; Holle, E.; Yu, X.; Tian, B.; Wagner, T.; Vatner, S.F.; Sadoshima, J. Sirt1 regulates aging and resistance to oxidative stress in the heart. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcendor, R.R.; Kirshenbaum, L.A.; Imai, S.; Vatner, S.F.; Sadoshima, J. Silent information regulator 2alpha, a longevity factor and class III histone deacetylase, is an essential endogenous apoptosis inhibitor in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, T.; Inuzuka, Y.; Okuda, J.; Kato, T.; Niizuma, S.; Tamaki, Y.; Iwanaga, Y.; Kawamoto, A.; Narazaki, M.; Matsuda, T.; et al. Constitutive SIRT1 overexpression impairs mitochondria and reduces cardiac function in mice. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaresan, N.R.; Pillai, V.B.; Wolfgeher, D.; Samant, S.; Vasudevan, P.; Parekh, V.; Raghuraman, H.; Cunningham, J.M.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, M.P. The deacetylase SIRT1 promotes membrane localization and activation of Akt and PDK1 during tumorigenesis and cardiac hypertrophy. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiattarella, G.G.; Sannino, A.; Toscano, E.; Cattaneo, F.; Trimarco, B.; Esposito, G.; Perrino, C. Cardiovascular effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors epigenetic therapies: Systematic review of 62 studies and new hypotheses for future research. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 219, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, R.L.; Crichton, S.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Yi, Q.; Li, L.; Hankey, G.J.; Rothwell, P.M.; Markus, H.S. Sodium Valproate, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Is Associated With Reduced Stroke Risk After Previous Ischemic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Stroke 2018, 49, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HDAC Inhibitor | HDAC Class | Known Actions in the Heart |
|---|---|---|
| Scriptaid | Pan- HDAC inhibitor |
|
| MGCD0103 (Mocetinostat) | Class I HDAC selective inhibitor | |
| Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic acid (SAHA) | Pan-HDAC inhibitor |
|
| ITF | Pan-HDAC inhibitor |
|
| SK-7041 | Pan-HDAC inhibitor |
|
| TSA | Class I and II HDAC inhibitor | |
| RGFP966 | HDAC3 (class I HDAC) inhibitor | |
| Sulforaphane | Class I and II HDAC inhibitor |
|
| Tubastatin A | HDAC6 (Class IIb HDAC) inhibitor |
|
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habibian, J.; Ferguson, B.S. The Crosstalk between Acetylation and Phosphorylation: Emerging New Roles for HDAC Inhibitors in the Heart. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010102
Habibian J, Ferguson BS. The Crosstalk between Acetylation and Phosphorylation: Emerging New Roles for HDAC Inhibitors in the Heart. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabibian, Justine, and Bradley S. Ferguson. 2019. "The Crosstalk between Acetylation and Phosphorylation: Emerging New Roles for HDAC Inhibitors in the Heart" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010102
APA StyleHabibian, J., & Ferguson, B. S. (2019). The Crosstalk between Acetylation and Phosphorylation: Emerging New Roles for HDAC Inhibitors in the Heart. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010102





