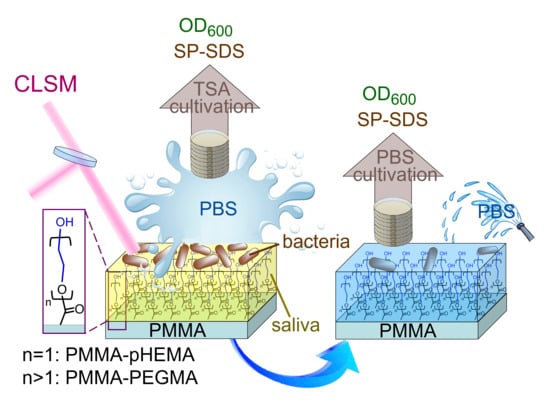
Comparison of Antibacterial Adhesion When Salivary Pellicle Is Coated on Both Poly(2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate)- and Polyethylene-glycol-methacrylate-grafted Poly(methyl methacrylate)
Abstract
1. Introduction
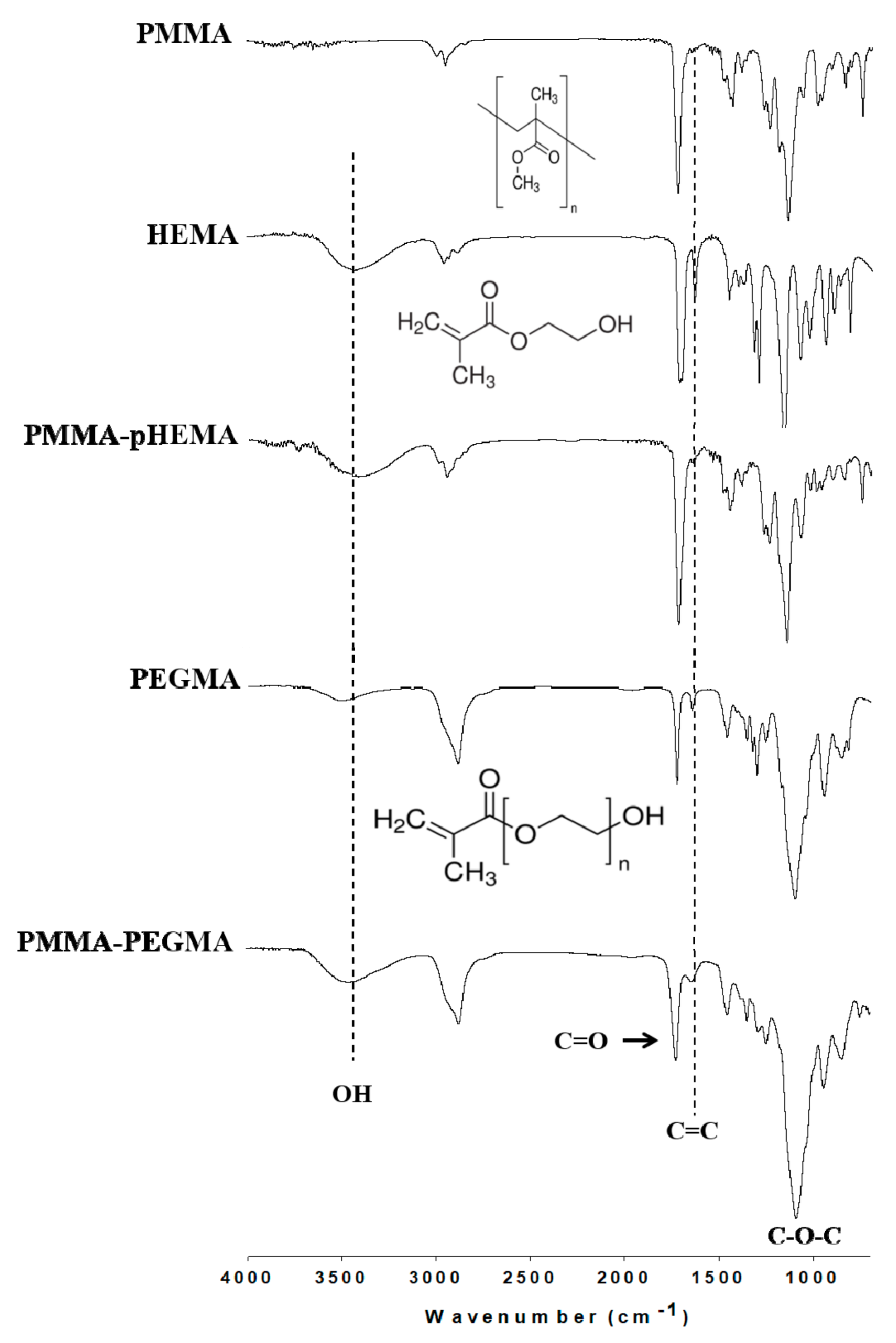
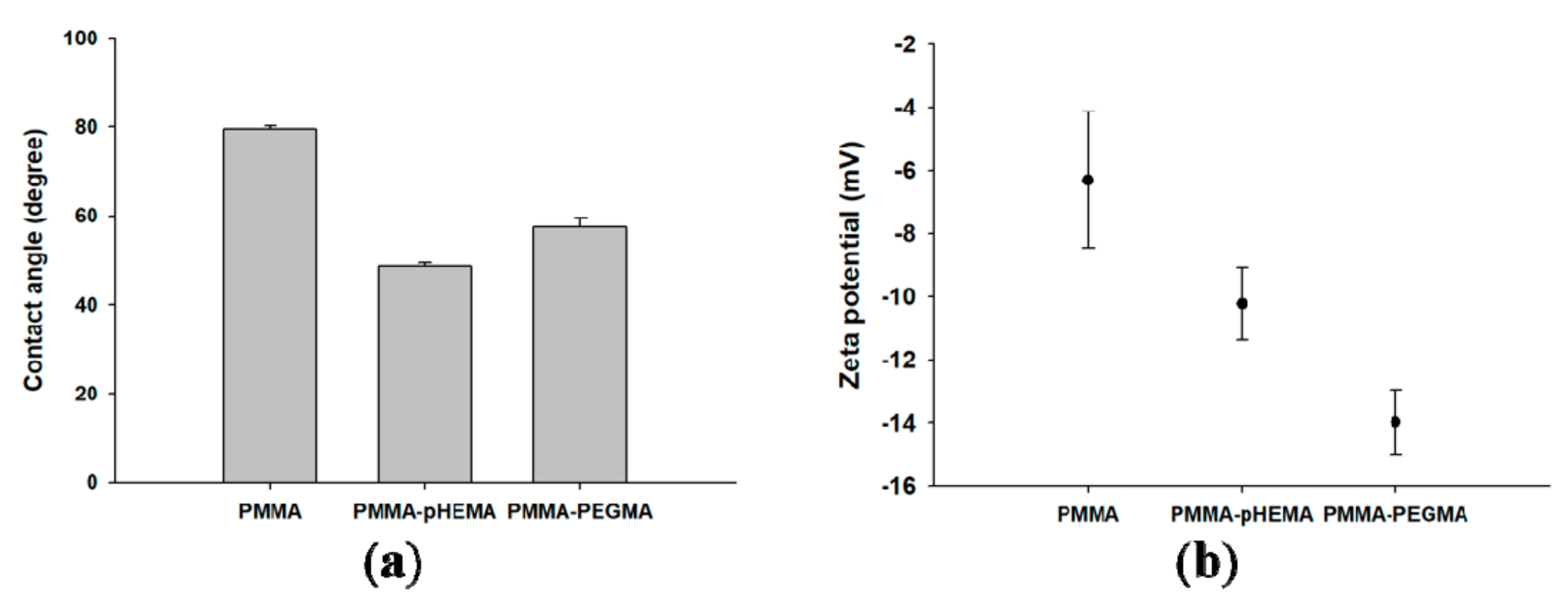
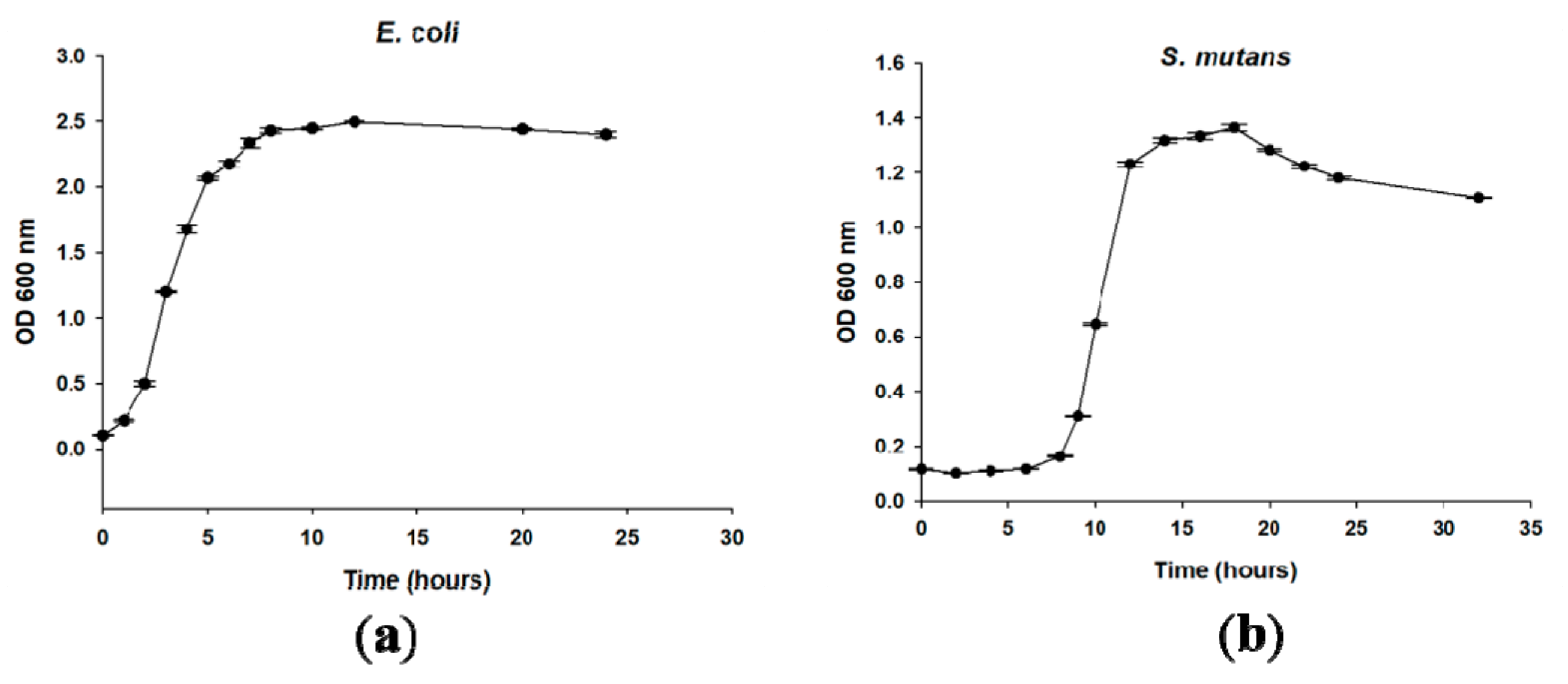
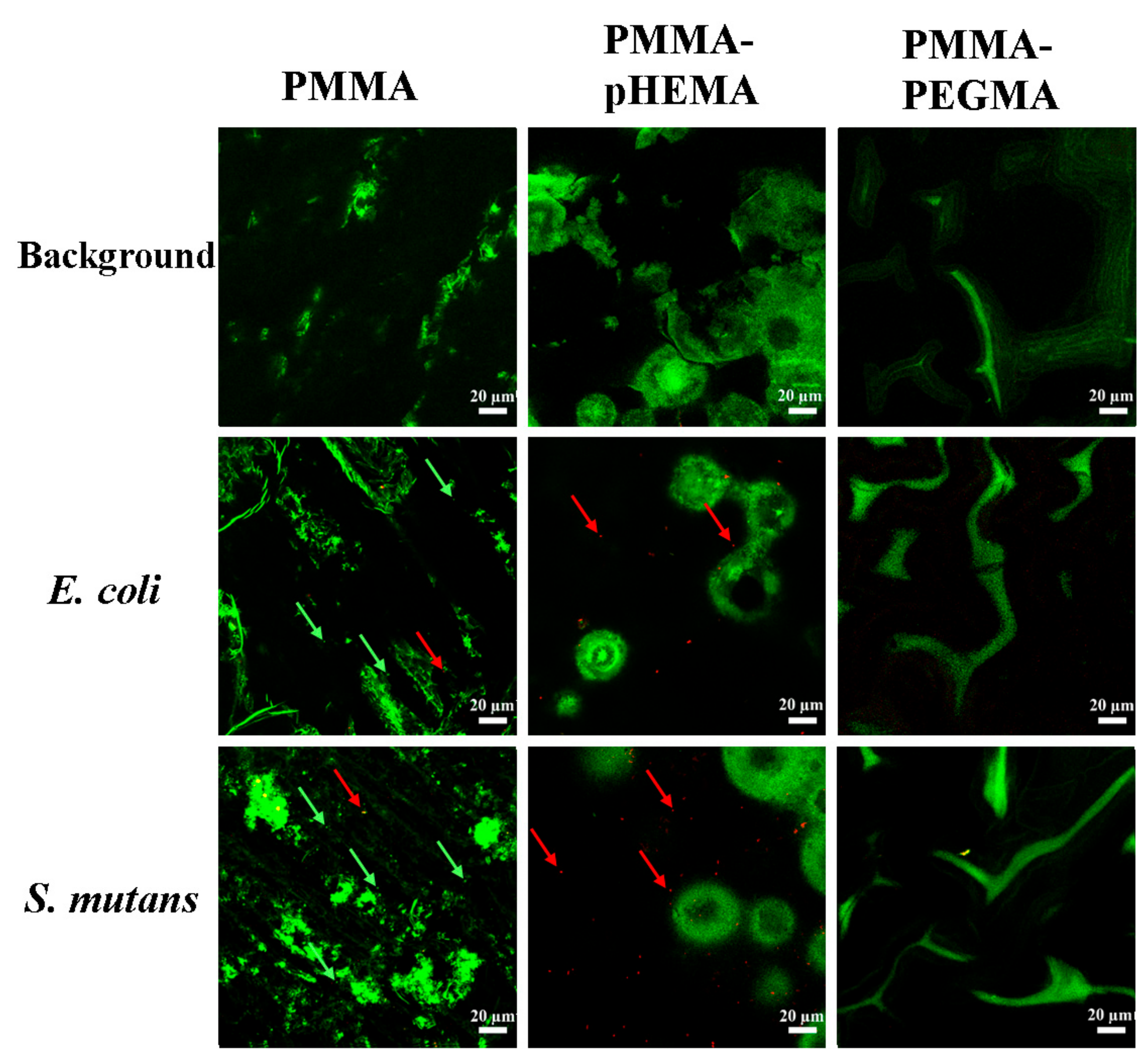
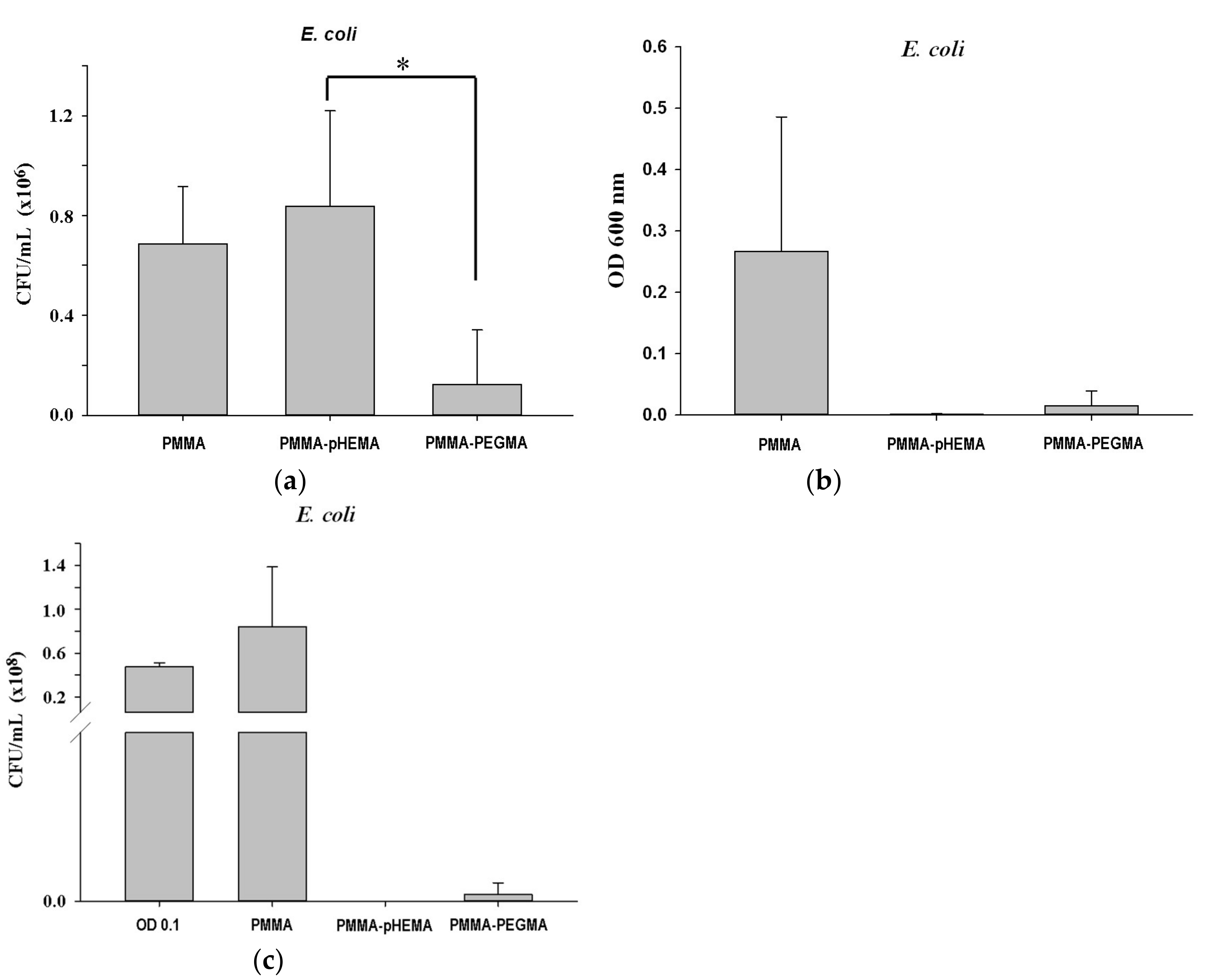
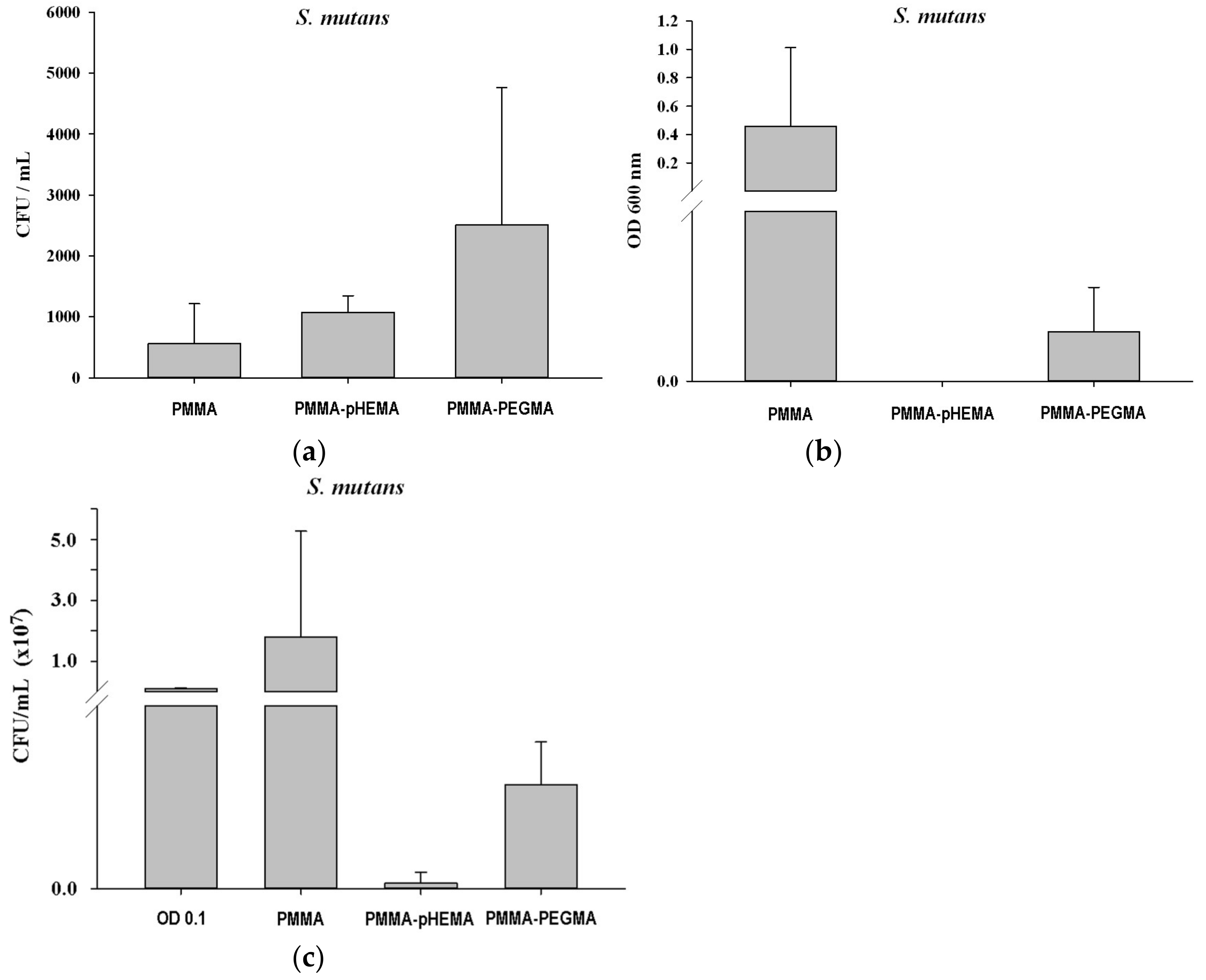
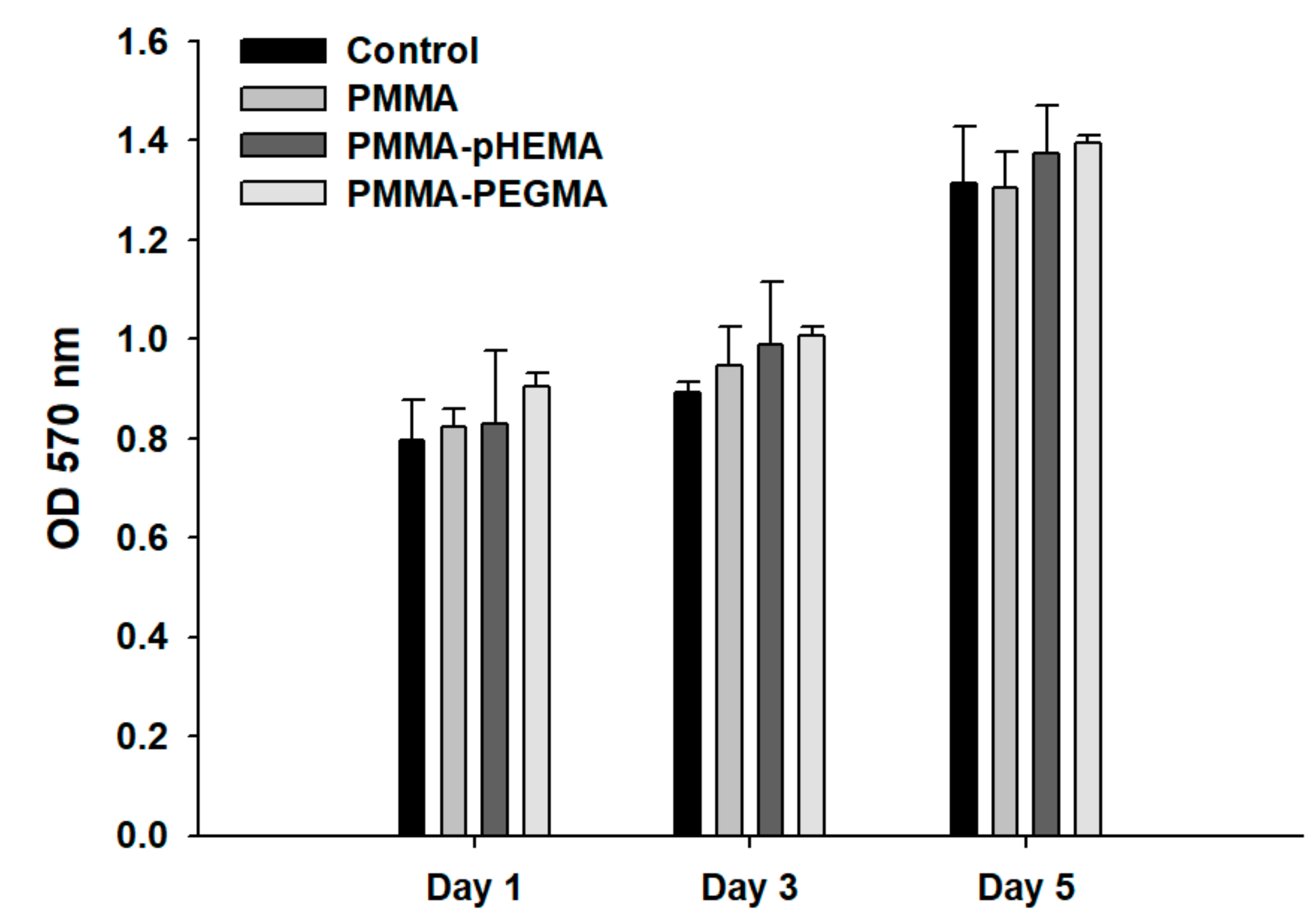
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. pHEMA and PEGMA Grafting on PMMA
4.3. Attenuated Total Reflection (ATR)-FTIR Analysis
4.4. Contact Angle Measurements
4.5. Zeta Potential Analysis
4.6. Bacterial Culture
4.7. Bacterial Growth Curve
4.8. Bacterial Adhesion Study
4.9. Cell Viability Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATR-FTIR | attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared |
| CFU | colony-forming units |
| CLSM | confocal laser scanning microscope |
| EG | ethylene glycol |
| F–M | Fairbrother–Mastin |
| HEMA | 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate |
| HGFs | human gingival fibroblasts |
| MMA | methyl methacrylate |
| MTT assay | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide assay |
| OD | optical density |
| OD600 | OD value at 600 nm |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| PEGMA | polyethylene glycol methacrylate |
| pHEMA | poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) |
| PI | propidium iodide |
| PMMA | polymethyl methacrylate |
| PMMA-PEGMA | PMMA grafted with PEGMA |
| PMMA-pHEMA | PMMA grafted with pHEMA |
| QAMS | quaternary ammonium methacryloxy silicate |
| SP-SDS | single plate-serial dilution spotting |
| TSA | tryptic soy agar |
| TSB | tryptic soy broth |
Appendix A
References
- Balazs, D.J.; Triandafillu, K.; Wood, P.; Chevolot, Y.; van Delben, C.; Harms, H.; Hollenstein, C.; Mathieu, H.J. Inhibition of bacterial adhesion on PVC endotracheal tubes by RF-oxygen glow discharge, sodium hydroxide and silver nitrate treatments. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, D.R.; Gorup, L.F.; Takamiya, A.S.; Ruvollo-Filho, A.C.; Camargo, E.R.; Barbosa, D.B. The growing importance of materials that prevent microbial adhesion: Antimicrobial effect of medical devices containing silver. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, V.B.; Thétiot, F.; Ritz, S.; Pütz, S.; Choritz, L.; Lappas, A.; Förch, R.; Landfester, K.; Jonas, U. Antibacterial surface coatings from zinc oxide nanoparticles embedded in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel surface layers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2376–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Song, J.; Jang, J. Photocatalytic antibacterial capabilities of TiO2-biocidal polymer nanocomposites synthesized by a surface-initiated photopolymerization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5672–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Cu and CuO nanoparticles immobilized by silica thin films as antibacterial materials and photocatalysts. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, H.J.; Rinastiti, M.; Siswomihardjo, W.; van der Mei, H.C. Biofilm formation on dental restorative and implant materials. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannig, C.; Hannig, M. The oral cavity–a key system to understand substratum-dependent bioadhesion on solid surfaces in man. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2009, 13, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anusavice, K.J.; Zhang, N.Z.; Shen, C. Controlled release of chlorhexidine from UDMA–TEGDMA resin. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imazato, S.; Ebi, N.; Tarumi, H.; Russell, R.R.; Kaneko, T.; Ebisu, S. Bactericidal activity and cytotoxicity of antibacterial monomer MDPB. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.Q.; Epasinghe, D.J.; Zhou, B.; Niu, L.N.; Kimmerling, K.A.; Rueggeberg, F.A.; Yiu, C.K.; Mao, J.; Pashley, D.H.; Tay, F.R. Effect of water-aging on the antimicrobial activities of an ORMOSIL-containing orthodontic acrylic resin. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6964–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.Q.; Epasinghe, J.; Rueggeberg, F.A.; Niu, L.N.; Mettenberg, D.; Yiu, C.K.; Blizzard, J.D.; Wu, C.D.; Mao, J.; Drisko, C.L.; et al. An ORMOSIL-containing orthodontic acrylic resin with concomitant improvements in antimicrobial and fracture toughness properties. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. A review of the biomaterials technologies for infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8533–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthley, C.H.; Constantopoulos, K.T.; Ginic-Markovic, M.; Pillar, R.J.; Matisons, J.G.; Clarke, S. Surface modification of commercial cellulose acetate membranes using surface-initiated polymerization of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate to improve membrane surface biofouling resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 385–386, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, L.Y.; Wang, Q.M.; Yu, Q.M.; Zheng, J. Effect of film thickness on the antifouling performance of poly(hydroxy-functional methacrylates) grafted surfaces. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4906–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedjo, C.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.T.; Fang, N.; Chan, V. Bacteria-surface interaction in the presence of proteins and surface attached poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate chains. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 82, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldez, M.J.; Resua, C.G.; Lira, M.; Oliveira, M.E.; Magarinos, B.; Toranzo, A.E.; Yebra-Pimentel, E. Contact lens hydrophobicity and roughness effects on bacterial adhesion. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, E426–E431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruinsma, G.M.; Rustema-Abbing, M.; de Vries, J.; Busscher, H.J.; van der Linden, M.L.; Hooymans, J.M.M.; van der Mei, H.C. Multiple surface properties of worn RGP lenses and adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiroa, M.S.; de Melo, L.S.A.; Farooq, S.; Baptista, A.; Kato, I.T.; Núñez, S.C.; de Araujo, R.E. Photodynamic inactivation assisted by localized surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles: In vitro evaluation on Escherichia coli and Streptococcus mutans. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2018, 22, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.H.; Qiu, J.J.; Su, J.S.; Liu, X.Y. Minocycline hydrochloride loaded on titanium by graphene oxide: An excellent antibacterial platform with the synergistic effect of contact-killing and release-killing. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badihi Hauslich, L.; Sela, M.N.; Steinberg, D.; Rosen, G.; Kohavi, D. The adhesion of oral bacteria to modified titanium surfaces: Role of plasma proteins and electrostatic forces. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24 (Suppl. A100), 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukka, T.; Roger, V.; Söderling, E.; Tenovuo, J. Binding of Streptococcus mutans, serotype c, to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite in the presence and absence of human lactoferrin. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1994, 7, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, V.; Tenovuo, J.; Lenander-Lumikari, M.; Söderling, E.; Vilja, P. Lysozyme and lactoperoxidase inhibit the adherence of Streptococcus mutans NCTC 10449 (serotype c) to saliva-treated hydroxyapatite in vitro. Caries Res. 1994, 28, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, A.; Yang, X.; Lu, L.; Wang, X. Preparation and characterization of mesoporous zirconia made by using a poly(methyl methacrylate) template. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemal, E.; Deb, S. Design and synthesis of three-dimensional hydrogel scaffolds for intervertebral disc repair. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 10725–10735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K. Spectroscopy, 20th ed.; Krishna Prakash Media Ltd.: Uttar Pradesh, India, 2007; p. S302. ISBN 8182830184. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Wu, J.; Tian, H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J. High-strength cellulose/poly(ethylene glycol) gels. ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, A.; Wutscher, E.; Brambilla, E.; Schneider-Feyrer, S.; Giessibl, F.J; Hahnel, S. Influence of surface properties of resin-based composites on in vitro Streptococcus mutans biofilm development. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2012, 120, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirynen, M.; Bollen, C.M.; Papaioannou, W.; van Eldere, J.; van Steenberghe, D. The influence of titanium abutment surface roughness on plaque accumulation and gingivitis: Short-term observations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1996, 11, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.; Santa Maria, J.P.; Walker, S. Wall teichoic acids of Gram-positive bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlander, R.S.; Vlamakis, H.; Kim, P.; Khan, M.; Kolter, R.; Aizenberg, J. Bacterial flagella explore microscale hummocks and hollows to increase adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5624–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerning, J. Exocellular polysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1990, 87, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, J.M.; Loushine, R.J.; Babb, B.R.; Bryan, T.E.; Lockwood, P.E.; Sui, M.; Roberts, S.; Weller, R.N.; Pashley, D.H.; Tay, F.R. Contemporary methacrylate resin-based root canal sealers exhibit different degrees of ex vivo cytotoxicity when cured in their self-cured mode. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, M.; Cai, X.; Huang, X.; Li, L.; Zhu, H.; Shen, J.; Yuan, J. Chemically induced graft copolymerization of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate onto polyurethane surface for improving blood compatibility. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmel, S.; Kern, W.; Luxbacher, T. Zeta potential of photochemically modified polymer surfaces. Characterization of polymer surfaces and thin films. Polym. Sci. 2006, 132, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, P.; Sekhar, A.C.; Upreti, R.; Mujawar, M.M.; Pasha, S.S. Optimization of single plate-serial dilution spotting (SP-SDS) with sample anchoring as an assured method for bacterial and yeast cfu enumeration and single colony isolation from diverse samples. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 8, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghayedi, M.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Ghazvini, K.; Goharshadi, E.K. Neglected antibacterial activity of ethylene glycol as a common solvent. Microb. Pathogenesis 2017, 107, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalawade, T.M.; Bhat, K.; Sogi, S.H.P. Bactericidal activity of propylene glycol, glycerine, polyethylene glycol 400, and polyethylene glycol 1000 against selected microorganisms. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2015, 5, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, D.; Gong, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Z. Modification of titanium surfaces via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization to graft PEG-RGD polymer brushes to inhibit bacterial adhesion and promote osteoblast cell attachment. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2017, 32, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirife, J.; Herszage, L.; Joseph, A.; Bozzini, J.P.; Leardini, N.; Kohn, E.S. In vitro antibacterial activity of concentrated polyethylene glycol 400 solutions. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1983, 24, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.; Joo, H.W.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, S.; Yoon, S.; Kwon, T.H. Biosurfactant as an enhancer of geologic carbon storage: Microbial modification of interfacial tension and contact angle in carbon dioxide/water/quartz systems. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paria, S.; Biswal, N.R.; Chaudhuri, R.G. Surface tension, adsorption, and wetting behaviors of natural surfactants on a PTFE surface. AlChE J. 2015, 61, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Shih, K.S.; Lai, C.H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Chen, Y.W. Surface property alterations and osteoblast attachment to contaminated titanium surfaces after different surface treatments: An in vitro study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okshevsky, M.; Meyer, R.L. The role of extracellular DNA in the establishment, maintenance and perpetuation of bacterial biofilms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Sharma, P.K.; Krom, B.P.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Role of eDNA on the adhesion forces between Streptococcus mutans and substratum surfaces: Influence of ionic strength and substratum hydrophobicity. Langmuir 2011, 27, 10113–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Study on antibacterial property of PMMA denture base materials with negative ion powder. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual International Conference on Material Science and Environmental Engineering (MSEE2017), Xiamen, China, 15–17 December 2017; IOP Conf. Ser. 301. p. 12034. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, A.; Zhou, C.; Michaelis, J.; Brauchle, C.; Zumbusch, A. Intermolecular interactions of polymer molecules determined by single-molecule force spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 9821–9825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, S. Interaction between particles suspended in solutions of macromolecules. J. Polym. Sci. 1958, 33, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, S.; Cao, Z.J.; Mokkapati, V.R.S.S.; Celauro, E.; Yurgens, A.; Lovmar, M.; Westerlund, F.; Sun, J.; Mijakovic, I. Vertically aligned graphene coating is bactericidal and prevents the formation of bacterial biofilms. Adv. Mater. Interf. 2018, 5, 1701331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laloyaux, X.; Fautré, E.; Blin, T.; Purohit, V.; Leprince, J.; Jouenne, T.; Jonas, A.M.; Glinel, K. Temperature-responsive polymer brushes switching from bactericidal to cell-repellent. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5024–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Paired Samples of Analysis | Test Statistics (P) | |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli | S. mutans | |
| (a) | ||
| PMMA vs. PMMA-pHEMA | 0.5252 | 0.1952 |
| PMMA-pHEMA vs. PMMA-PEGMA | 0.0174 * | 0.4737 |
| PMMA vs. PMMA-PEGMA | 0.0118 * | 0.2773 |
| (b) | ||
| PMMA vs. PMMA-pHEMA | 0.0268 * | 0.0404 # |
| PMMA-pHEMA vs. PMMA-PEGMA | 0.2481 | 0.1340 |
| PMMA vs. PMMA-PEGMA | 0.0340 * | 0.0409 # |
| (c) | ||
| PMMA vs. PMMA-pHEMA | 0.0219 * | 0.0588 |
| PMMA-pHEMA vs. PMMA-PEGMA | 0.3160 | 0.1311 |
| PMMA vs. PMMA-PEGMA | 0.0221 * | 0.0691 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, B.-S.; Chen, Y.-J.; Wei, T.-C.; Ma, T.-L.; Chang, C.-C. Comparison of Antibacterial Adhesion When Salivary Pellicle Is Coated on Both Poly(2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate)- and Polyethylene-glycol-methacrylate-grafted Poly(methyl methacrylate). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092764
Lee B-S, Chen Y-J, Wei T-C, Ma T-L, Chang C-C. Comparison of Antibacterial Adhesion When Salivary Pellicle Is Coated on Both Poly(2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate)- and Polyethylene-glycol-methacrylate-grafted Poly(methyl methacrylate). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092764
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Bor-Shiunn, Yu-Jia Chen, Ta-Chin Wei, Tien-Li Ma, and Che-Chen Chang. 2018. "Comparison of Antibacterial Adhesion When Salivary Pellicle Is Coated on Both Poly(2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate)- and Polyethylene-glycol-methacrylate-grafted Poly(methyl methacrylate)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092764
APA StyleLee, B.-S., Chen, Y.-J., Wei, T.-C., Ma, T.-L., & Chang, C.-C. (2018). Comparison of Antibacterial Adhesion When Salivary Pellicle Is Coated on Both Poly(2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate)- and Polyethylene-glycol-methacrylate-grafted Poly(methyl methacrylate). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092764