The Effect of Agomelatine Treatment on Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Rats: Concomitant Alterations in the Hippocampal Neuron Numbers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
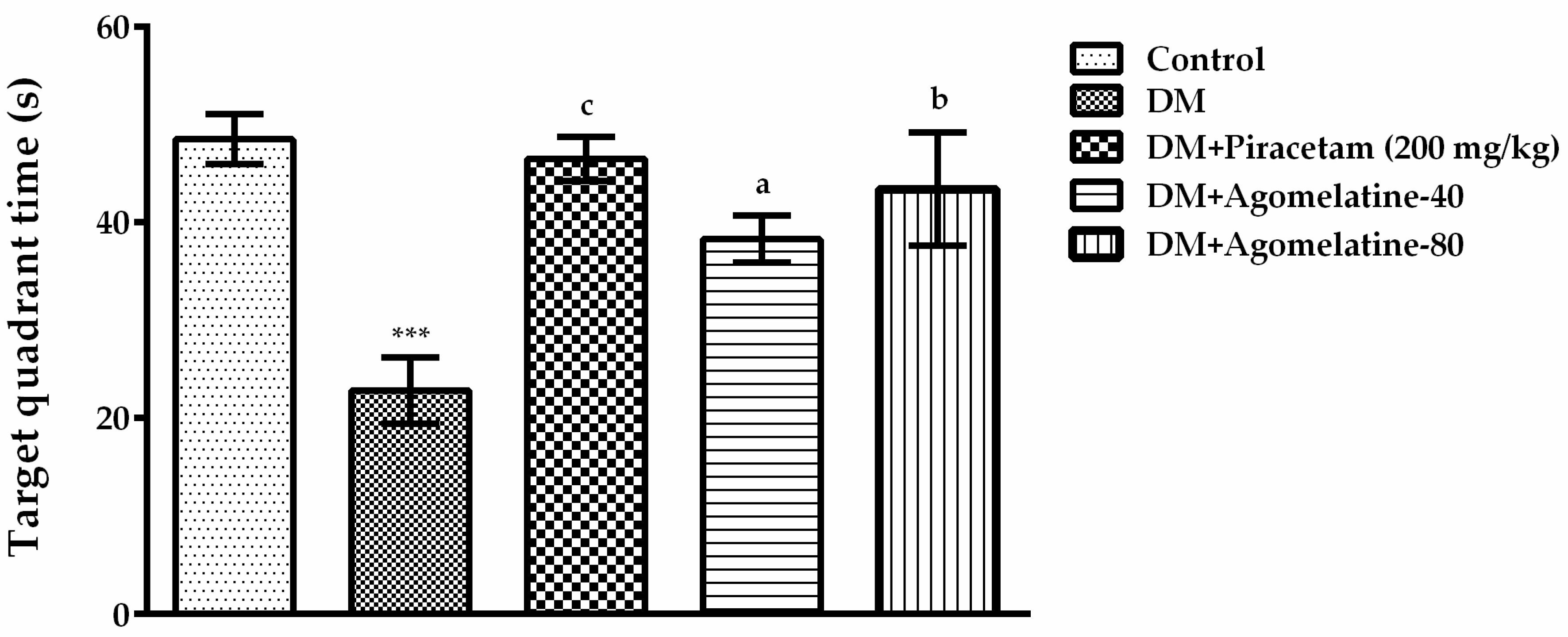
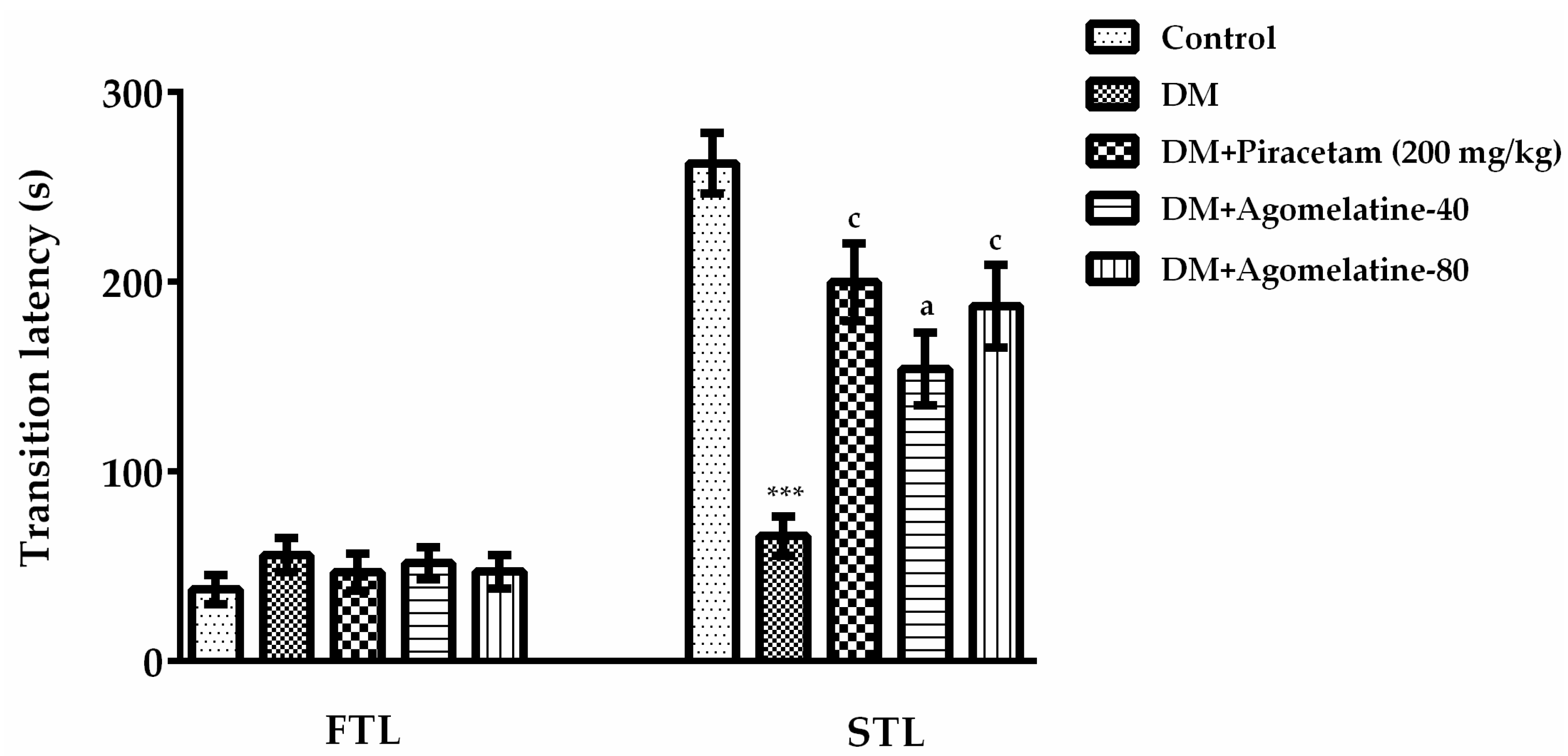
2.1. The Improving Effect of Agomelatine Treatment on Learning and Memory Impairements in Diabetic Rats
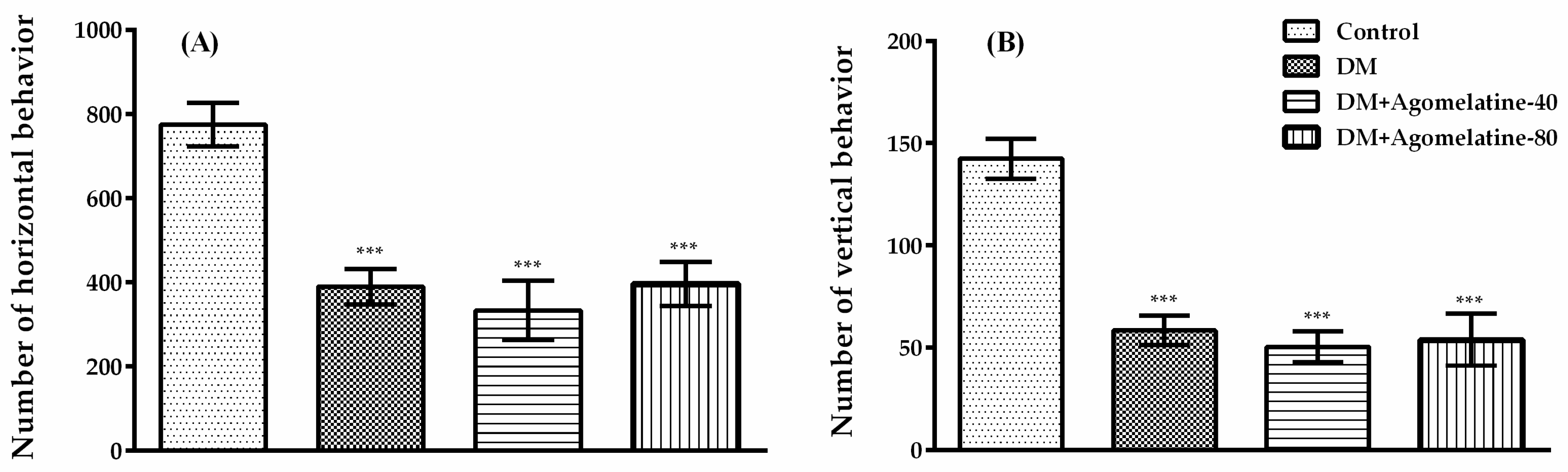
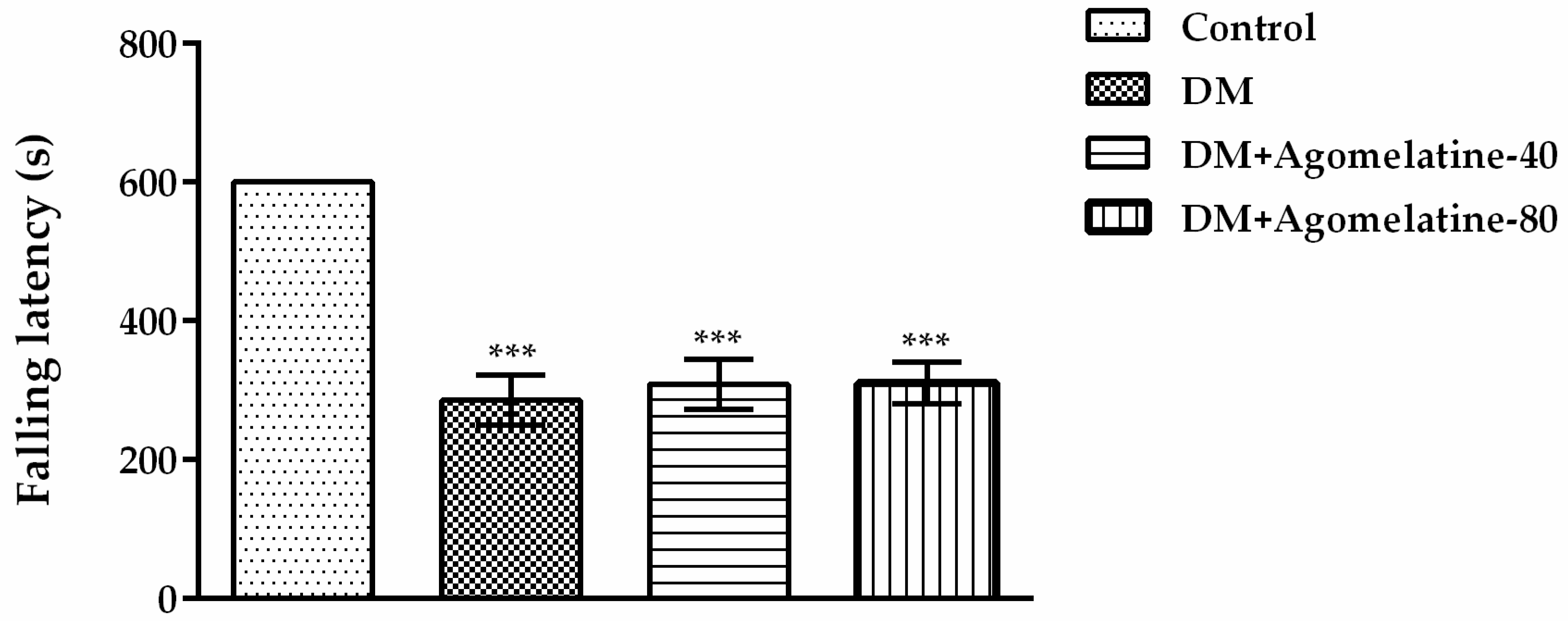
2.2. Unchanged Motor Activity in Diabetic Rats Following Agomelatine Treatment
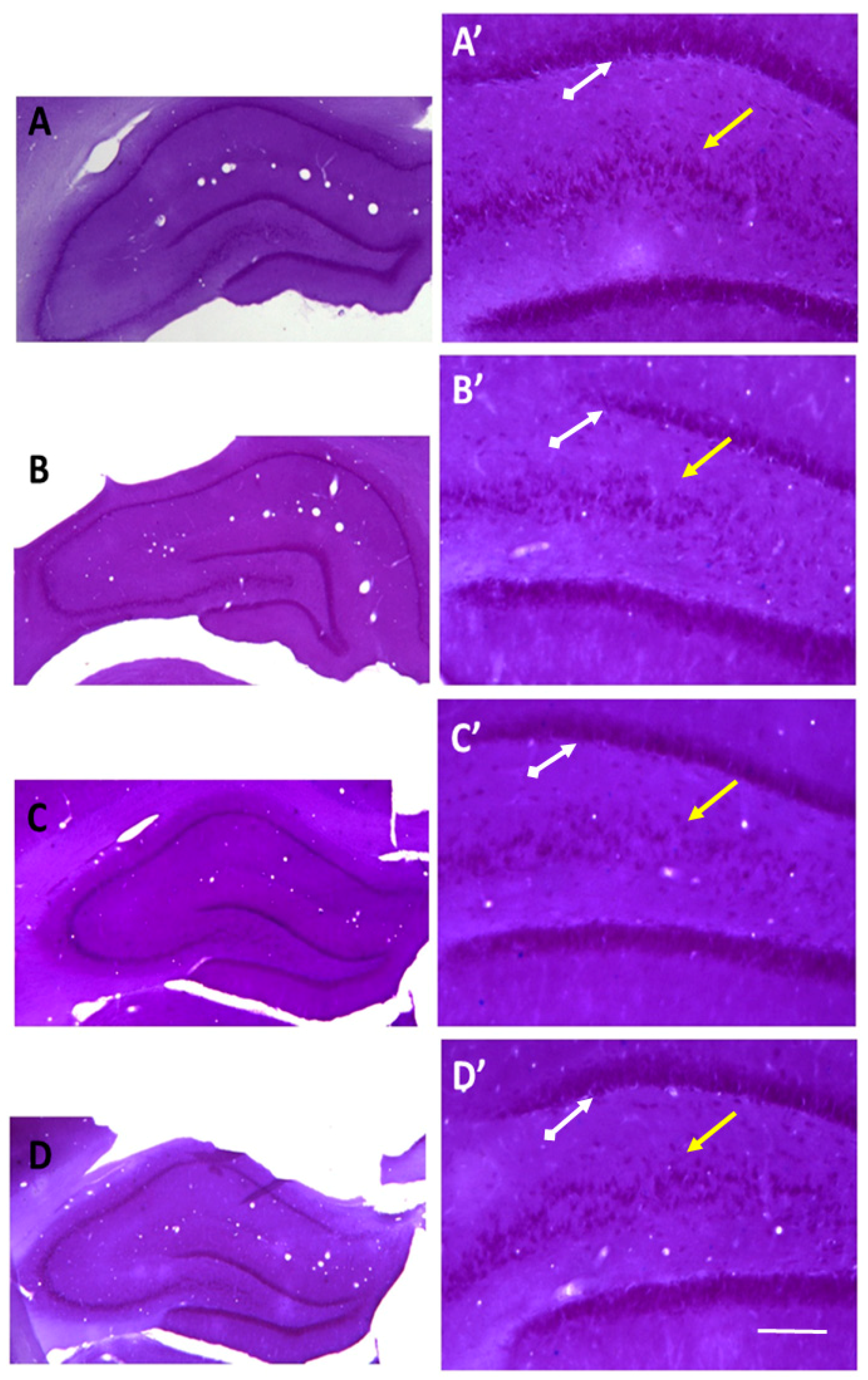
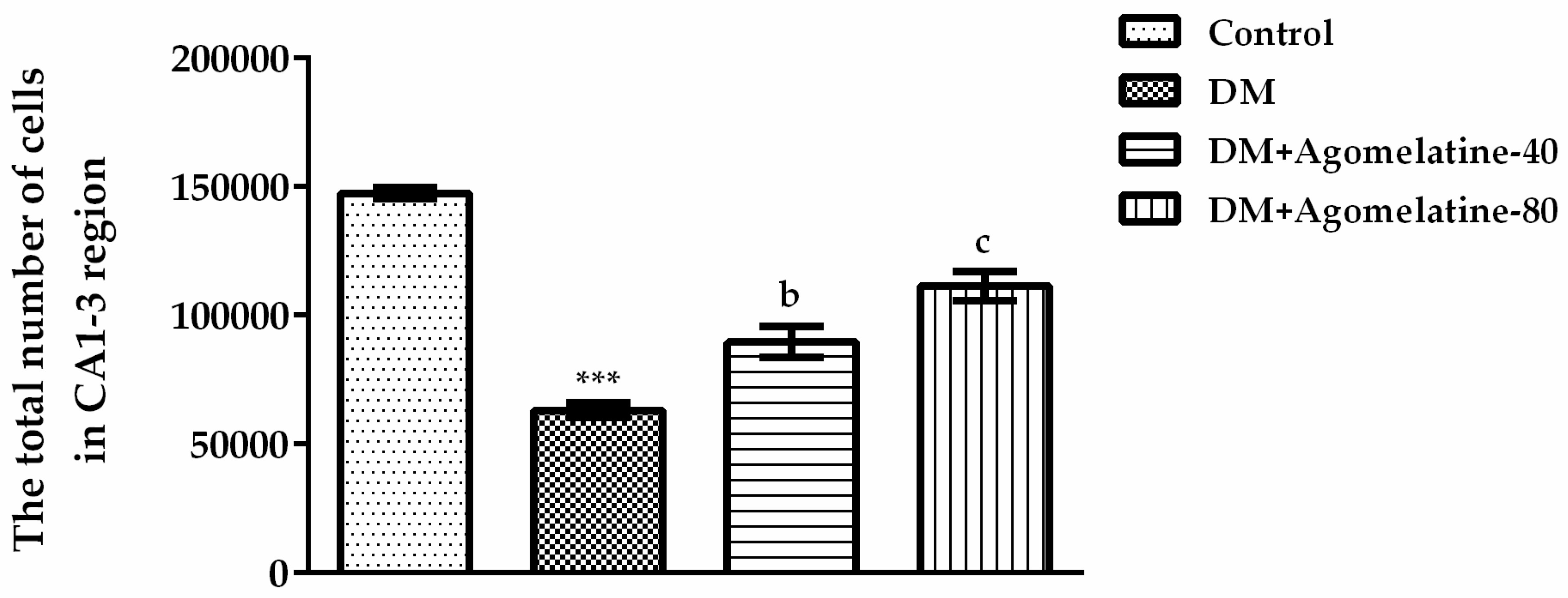
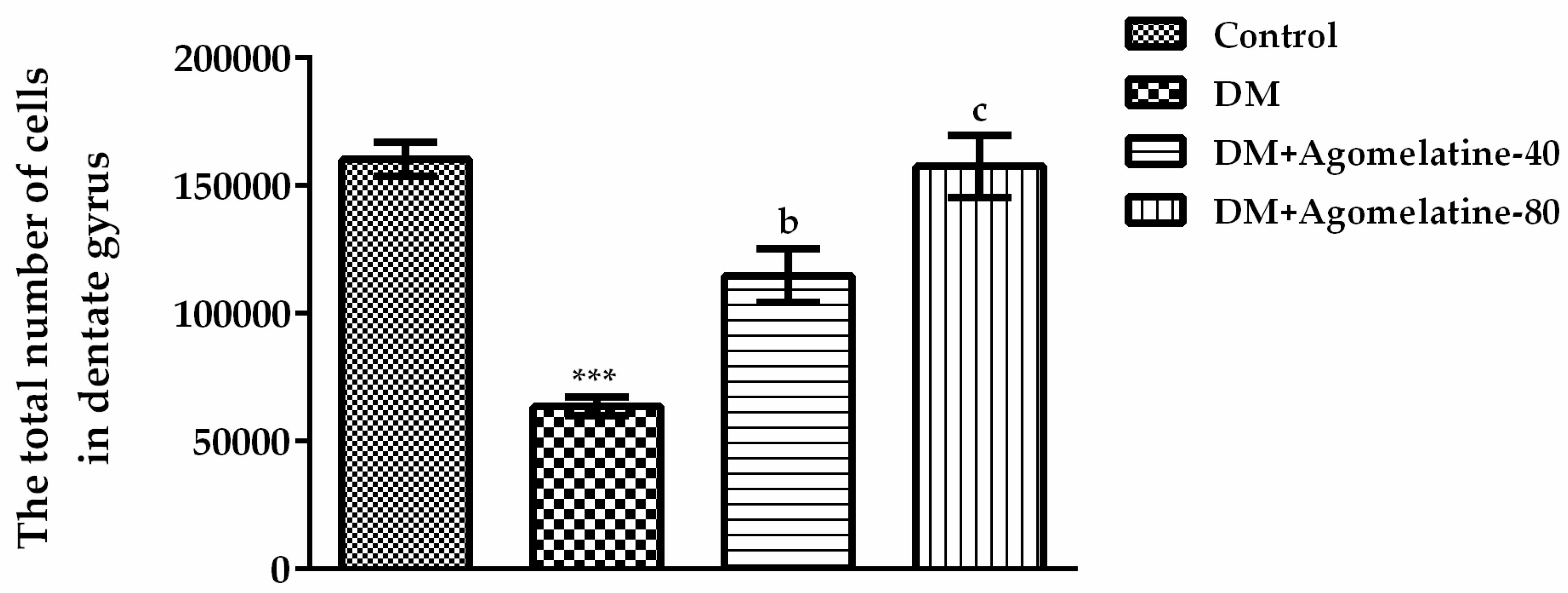
2.3. Recovery of the Hippocampal Neuronal Loss Following Agomelatine Treatment in Diabetic Rats
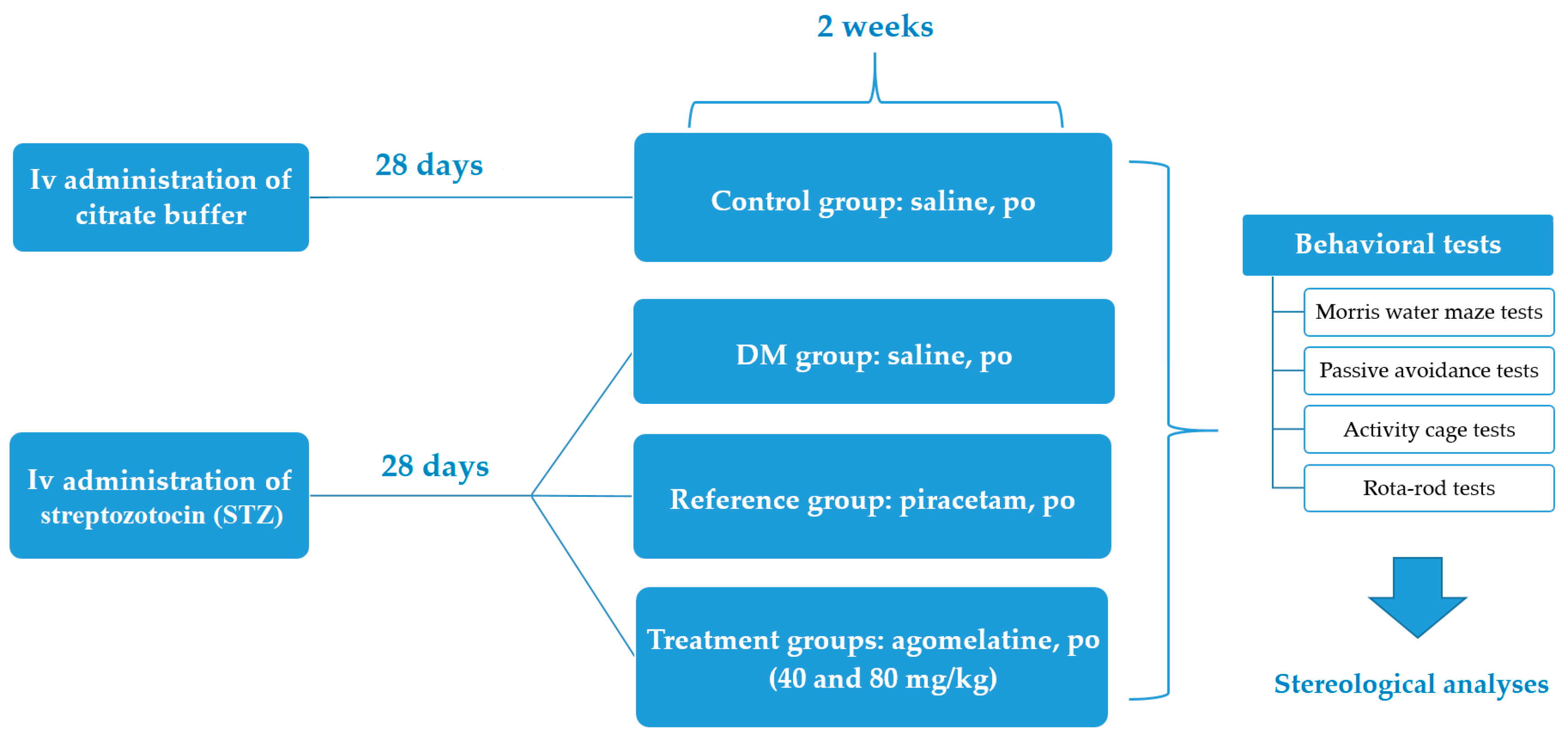
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Animals
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Induction of Experimental Diabetes Model in Rats
3.4. Experimental Groups
3.5. Behavioral Tests
3.5.1. Morris Water Maze (MWM) Test
3.5.2. Passive Avoidance Test
3.5.3. Activity Cage Test
3.5.4. Rota-rod Test
3.6. Morphological Methods
3.6.1. Tissue Processing and Nissl Staining
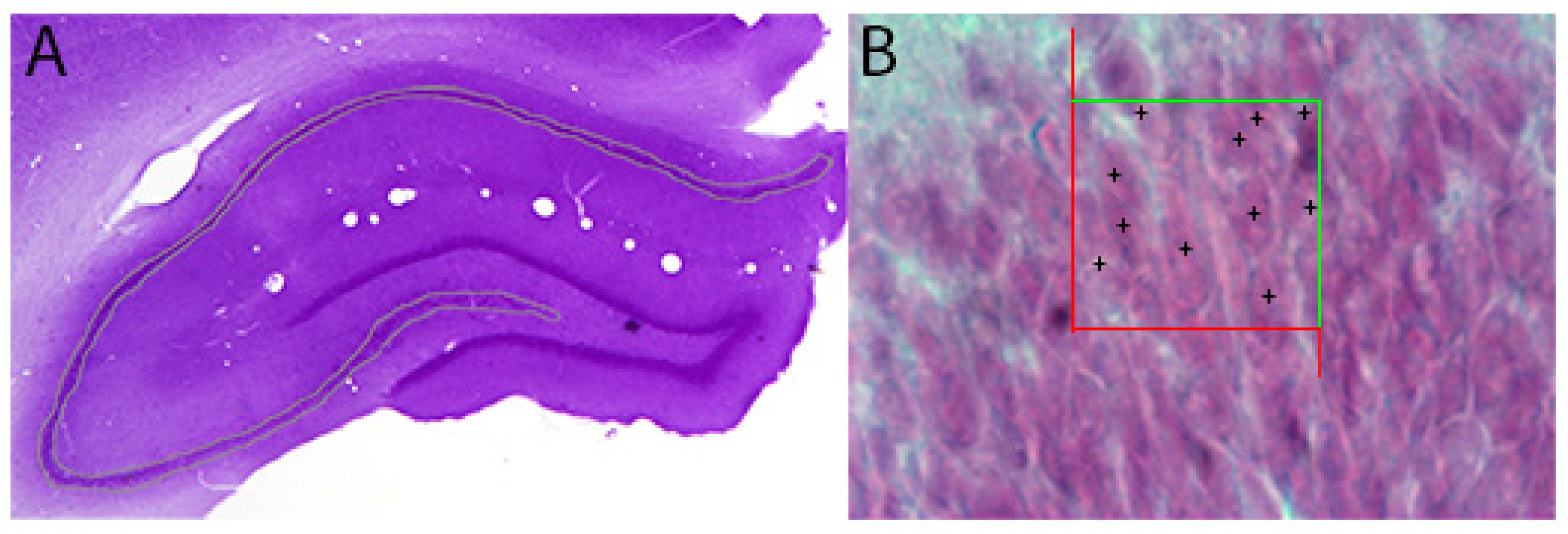
3.6.2. Optical Fractionator Counting Method
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| Arc | Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein |
| Bcl2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BrdU | 5-Bromo-2’-deoxyuridine |
| CA | Cornu Ammonis |
| CD45 | Lymphocyte common antigen |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DCX | Doublecortin |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| FGF-2 | Fibroblast growth factor 2 |
| FTL | First transition latency |
| GABA | γ-aminobutyric acid |
| GDNF | Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| 5-HT2C | Serotonergic receptor subtype |
| Iba1 | Ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 |
| IGF1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| MT1, MT2 | Melatonergic receptor subtypes |
| MWM | Morris Water Maze |
| NCAM | Neural cell adhesion molecule |
| NEUROD1 | Neurogenic differentiation factor 1 |
| PSA-NCAM | Polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule |
| S.E.M. | Standard error of mean |
| STL | Second transition latency |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
References
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of Diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, S64–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, B.K.; Srivastava, A.K. Diabetes mellitus: Complications and therapeutics. Med. Sci. Monit. 2006, 12, 130–147. [Google Scholar]
- Reske-Nielsen, E.; Lundbaek, K.; Rafeisen, Q.J. Pathological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system of young long-term diabetics I. Diabetic encephalopathy. Diabetologia 1966, 1, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sima, A.A.F.; Kamiya, H.; Li, Z.G. Insulin, C-peptide, hyperglycemia, and central nervous system complications in diabetes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 490, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampling, H.; Mittag, O.; Herpertz, S.; Baumeister, H.; Kulzer, B.; Petrak, F. Can trajectories of glycemic control be predicted by depression, anxiety, or diabetes-related distress in a prospective cohort of adults with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes? Results of a five-year follow-up from the German multicenter diabetes cohort study (GMDC-Study). Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 141, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, C.D.; Hopkins, C.W.P.; Ismail, K.; Stahl, D. Repositioning of diabetes treatments for depressive symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 94, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, M.; Goldston, D.; Obrosky, D.S.; Bonar, L.K. Psychiatric disorders in youths with IDDM: Rates and risk factors. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.M.; Lindgren, S.; Mengeling, M.A.; Tsalikian, E.; Engvall, J.C. Effects of diabetes on learning in children. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shao, Y.H.; Gong, Y.P.; Lu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.L. Diabetes mellitus and dementia—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 1778–1789. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pasquier, F.; Boulogne, A.; Leys, D.; Fontaine, P. Diabetes mellitus and dementia. Diabetes Metab. 2006, 32, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, T. Diabetes mellitus and dementia. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buoli, M.; Grassi, S.; Serati, M.; Altamura, A.C. Agomelatine for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.W.; Rusak, B.; Delagrange, P.; Mocaer, E.; Renard, P.; Guardiola-Lemaitre, B. Melatonin analogues as agonists and antagonists in the circadian system and other brain areas. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 296, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, M.J.; Marin, P.; Kamal, M.; Jockers, R.; Chanrion, B.; Labasque, M.; Bockaert, J.; Mannoury la Cour, C. The melatonergic agonist and clinically active antidepressant, agomelatine, is a neutral antagonist at 5-HT(2C) receptors. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 14, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conboy, L.; Tanrikut, C.; Zoladz, P.R.; Campbell, A.M.; Park, C.R.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaer, E.; Sandi, C.; Diamond, D.M. The antidepressant agomelatine blocks the adverse effects of stress on memory and enables spatial learning to rapidly increase neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) expression in the hippocampus of rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 12, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumuslu, E.; Mutlu, O.; Sunnetci, D.; Ulak, G.; Celikyurt, I.K.; Cine, N.; Akar, F.; Savlı, H.; Erden, F. The antidepressant agomelatine improves memory deterioration and upregulates CREB and BDNF gene expression levels in unpredictable chronic mild stress (ucms)-exposed mice. Drug Target Insights 2014, 8, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, P.; Sharma, B.M.; Sharma, B. Neuroprotective effects of agomelatine and vinpocetine against chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced vascular dementia. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2015, 12, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir Özkay, Ü.; Söztutar, E.; Can, Ö.D.; Üçel, U.İ.; Öztürk, Y.; Ulupinar, E. Effects of long-term agomelatine treatment on the cognitive performance and hippocampal plasticity of adult rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2015, 26, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Païzanis, E.; Renoir, T.; Lelievre, V.; Saurini, F.; Melfort, M.; Gabriel, C.; Barden, N.; Mocaër, E.; Hamon, M.; Lanfumey, L. Behavioural and neuroplastic effects of the new-generation antidepressant agomelatine compared to fluoxetine in glucocorticoid receptor-impaired mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley-Fletcher, S.; Mairesse, J.; Soumier, A.; Banasr, M.; Fagioli, F.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaer, E.; Daszuta, A.; McEwen, B.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Chronic agomelatine treatment corrects behavioral, cellular, and biochemical abnormalities induced by prenatal stress in rats. Psychopharmacology 2011, 217, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainer, Q.; Xia, L.; Guilloux, J.P.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaër, E.; Hen, R.; Enhamre, E.; Gardier, A.M.; David, D.J. Beneficial behavioural and neurogenic effects of agomelatine in a model of depression/anxiety. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 15, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junod, A.; Lambert, A.E.; Stauffacher, W.; Renold, A.E. Diabetogenic action of streptozotocin: Relationship of dose to metabolic response. J. Clin. Investig. 1969, 48, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, B.L. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic models in mice and rats. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2015, 70, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilakivi-Clarke, L.A.; Wozniak, K.M.; Durcan, M.J.; Linnoila, M. Behavior of streptozotocin-diabetic mice in tests of exploration, locomotion, anxiety, depression and aggression. Physiol. Behav. 1990, 48, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, A.L. The impact of diabetes on the CNS. Diabetes 1992, 41, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biessels, G.J.; Kappelle, A.C.; Bravenboer, B.; Erkelens, D.W.; Gispen, W.H. Cerebral function in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1994, 37, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magariños, A.M.; McEwen, B.S. Experimental diabetes in rats causes hippocampal dendritic and synaptic reorganization and increased glucocorticoid reactivity to stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11056–11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, S.; Miyata, S.; Onodera, K.; Kamei, J. Effects of histamine H (1) receptor antagonists on depressive-like behavior in diabetic mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 83, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnicka, K.; Tomasiak, M.; Bielawska, A. Piracetam—An old drug with novel properties? Acta Pol. Pharm. 2005, 62, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alikatte, K.L.; Akondi, B.R.; Yerragunta, V.G.; Veerareddy, P.R.; Palle, S. Antiamnesic activity of Syzygium cumini against scopolamine induced spatial memory impairments in rats. Brain Dev. 2012, 34, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winblad, B. Piracetam: A review of pharmacological properties and clinical uses. CNS Drug Rev. 2005, 11, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Garabadu, D. Piracetam facilitates the anti-amnesic but not anti-diabetic activity of metformin in experimentally induced Type-2 diabetic encephalopathic rats. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assad, T.; Khan, R.A.; Rajput, M.A. Effect of Trigonella foenum-graecum Linn. seeds methanol extract on learning and memory. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quillfeldt, J.A. Behavioral methods to study learning and memory in rats. In Rodent Model as Tools in Ethical Biomedical Research, 1st ed.; Andersen, M., Tufik, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 271–311. ISBN 978-3-319-11577-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, A.; Biessels, G.J.; Duis, S.E.; Gispen, W.H. Learning and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: Interaction of diabetes and ageing. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Ding, X.; Qin, L.; Mao, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; Ying, C. Zeaxanthin improves diabetes-induced cognitive deficit in rats through activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 132, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.C.; Xie, H.; Chen, F.; Hu, M.; Long, Y.; Sun, H.B.; Kong, L.Y.; Hong, H.; Tang, S.S. Simvastatin ameliorates memory impairment and neurotoxicity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Neuroscience 2017, 355, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahshin-Majd, S.; Zamani, S.; Kiamari, T.; Kiasalari, Z.; Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Roghani, M. Carnosine ameliorates cognitive deficits in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Possible involved mechanisms. Peptides 2016, 86, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Kiasalari, Z.; Afshin-Majd, S.; Ghasemi, Z.; Roghani, M. S-allyl cysteine ameliorates cognitive deficits in streptozotocin-diabetic rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation, and acetylcholinesterase. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 794, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, R.M. Measuring motor coordination in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 75, e2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badescu, S.V.; Tataru, C.P.; Kobylinska, L.; Georgescu, E.L.; Zahiu, D.M.; Zagrean, A.M.; Zagrean, L. Effects of caffeine on locomotor activity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Med. Life 2016, 9, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fox, A.; Eastwood, C.; Gentry, C.; Manning, D.; Urban, L. Critical evaluation of the streptozotocin model of painful diabetic neuropathy in the rat. Pain 1999, 81, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Z.Z.; Li, C.Y.; Hu, J.C.; Yin, J.B.; Zhang, D.L.; Liao, Y.H.; Wu, Z.Y.; Ding, T.; Qu, J.; Li, H.; et al. Alterations in the neural circuits from peripheral afferents to the spinal cord: Possible implications for diabetic polyneuropathy in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic rats. Front. Neural. Circuits 2014, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson-Guilford, J.; Leander, J.D.; Nisenbaum, L.K. The effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on cell proliferation in the rat dentate gyrus. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 293, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Zhang, W.; Grunberger, G.; Sima, A.A.F. Hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in type 1 diabetes. Brain Res. 2002, 946, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranahan, A.M.; Arumugam, T.V.; Cutler, R.G.; Lee, K.; Egan, J.M.; Mattson, M.P. Diabetes impairs hippocampal function through glucocorticoid-mediated effects on new and mature neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baydas, G.; Nedzvetskii, V.S.; Tuzcu, M.; Yasar, A.; Kirichenko, S.V. Increase of glial fibrillary acidic protein and S-100B in hippocampus and cortex of diabetic rats: Effects of vitamin E. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 462, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriach, M.; Flores-Bellver, M.; Romero, F.J.; Barcia, J.M. Diabetes and the brain: Oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baydas, G.; Nedzvetskii, V.S.; Kirichenko, S.V.; Nerush, P.A. Astrogliosis in the hippocampus and cortex and cognitive deficits in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes: Effects of melatonin. Neurophysiology 2008, 40, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, F.; Molteni, R.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaer, E.; Racagni, G.; Riva, M.A. Modulation of neuroplastic molecules in selected brain regions after chronic administration of the novel antidepressant agomelatine. Psychopharmacology 2011, 215, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumier, A.; Banasr, M.; Lortet, S.; Masmejean, F.; Bernard, N.; Kerkerian-Le-Goff, L.; Gabriel, C.; Millan, M.J.; Mocaer, E.; Daszuta, A. Mechanisms contributing to the phase-dependent regulation of neurogenesis by the novel antidepressant, agomelatine, in the adult rat hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2390–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banasr, M.; Soumier, A.; Hery, M.; Mocaër, E.; Daszuta, A. Agomelatine, a new antidepressant, induces regional changes in hippocampal neurogenesis. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Rodríguez, G.; Klempin, F.; Babu, H.; Benítez-King, G.; Kempermann, G. Melatonin modulates cell survival of new neurons in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2180–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilar-Cuéllar, F.; Vidal, R.; Díaz, A.; Castro, E.; dos Anjos, S.; Pascual-Brazo, J.; Linge, R.; Vargas, V.; Blanco, H.; Martínez-Villayandre, B.; et al. Neural plasticity and proliferation in the generation of antidepressant effects: Hippocampal implication. Neural Plast. 2013, 2013, 537265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, F.; Gagnon, S.; Massicotte, G. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity and glutamate receptor regulation: Influences of diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 490, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gispen, W.H.; Biessels, G.J. Cognition and synaptic plasticity in Diabetes mellitus. Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.; Allaïli, N.; Euvrard, M.; Marday, T.; Riffaud, A.; Franc, B.; Mocaër, E.; Gabriel, C.; Fossati, P.; Lehericy, S.; et al. Effect of agomelatine on memory deficits and hippocampal gene expression induced by chronic social defeat stress in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 8, 45907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulle, F.; Massart, R.; Stragier, E.; Païzanis, E.; Zaidan, L.; Marday, S.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaer, E.; Mongeau, R.; Lanfumey, L. Hippocampal and behavioral dysfunctions in a mouse model of environmental stress: Normalization by agomelatine. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagytė, G.; Trentani, A.; Postema, F.; Luiten, P.G.; Den Boer, J.A.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaër, E.; Meerlo, P.; Van der Zee, E.A. The novel antidepressant agomelatine normalizes hippocampal neuronal activity and promotes neurogenesis in chronically stressed rats. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2010, 16, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagytė, G.; Crescente, I.; Postema, F.; Seguin, L.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaër, E.; Boer, J.A.; Koolhaas, J.M. Agomelatine reverses the decrease in hippocampal cell survival induced by chronic mild stress. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 218, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompili, M.; Serafini, G.; Innamorati, M.; Venturini, P.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Sher, L.; Amore, M.; Girardi, P. Agomelatine, a novel intriguing antidepressant option enhancing neuroplasticity: A critical review. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 14, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molteni, R.; Calabrese, F.; Pisoni, S.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaer, E.; Racagni, G.; Riva, M.A. Synergistic mechanisms cortex following acute agomelatine administration. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 11, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydın, T.H.; Can, Ö.D.; Demir Özkay, Ü.; Turan, N. Effect of subacute agomelatine treatment on painful diabetic neuropathy: Involvement of catecholaminergic mechanisms. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 30, 549–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourin, M.; Mocaer, E.; Porsolt, R. Antidepressant-like activity of S-20098 (agomelatine) in the forced swimming test in rodents: Involvement of melatonin and serotonin receptors. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004, 29, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Can, Ö.D.; Ulupinar, E.; Özkay, Ü.D.; Yeğin, B.; Öztürk, Y. The effect of simvastatin treatment on behavioral parameters, cognitive performance, and hippocampal morphology in rats fed a standard or a high-fat diet. Behav. Pharmacol. 2012, 23, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacar, N.; Mutlu, O.; Utkan, T.; Komşuoğlu Çelikyurt, I.; Göçmez, S.S.; Ulak, G. Beneficial effects of resveratrol on scopolamine but not mecamylamine induced memory impairment in the passive avoidance and Morris water maze tests in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 99, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spolidório, P.C.; Echeverry, M.B.; Iyomasa, M.; Guimarães, F.S.; Del Bel, E.A. Anxiolytic effects induced by inhibition of the nitric oxide-cGMP pathway in the rat dorsal hippocampus. Psychopharmacology 2007, 195, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, M.J.; Slomianka, L.; Gundersen, H.J. Unbiased stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in the subdivisions of the rat hippocampus using the optical fractionator. Anat. Rec. 1991, 231, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, C.; Hof, P.R. Recommendations for straightforward and rigorous methods of counting neurons based on a computer simulation approach. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2000, 20, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Can, Ö.D.; Üçel, U.İ.; Demir Özkay, Ü.; Ulupınar, E. The Effect of Agomelatine Treatment on Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Rats: Concomitant Alterations in the Hippocampal Neuron Numbers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082461
Can ÖD, Üçel Uİ, Demir Özkay Ü, Ulupınar E. The Effect of Agomelatine Treatment on Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Rats: Concomitant Alterations in the Hippocampal Neuron Numbers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082461
Chicago/Turabian StyleCan, Özgür Devrim, Umut İrfan Üçel, Ümide Demir Özkay, and Emel Ulupınar. 2018. "The Effect of Agomelatine Treatment on Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Rats: Concomitant Alterations in the Hippocampal Neuron Numbers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082461
APA StyleCan, Ö. D., Üçel, U. İ., Demir Özkay, Ü., & Ulupınar, E. (2018). The Effect of Agomelatine Treatment on Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Rats: Concomitant Alterations in the Hippocampal Neuron Numbers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082461




