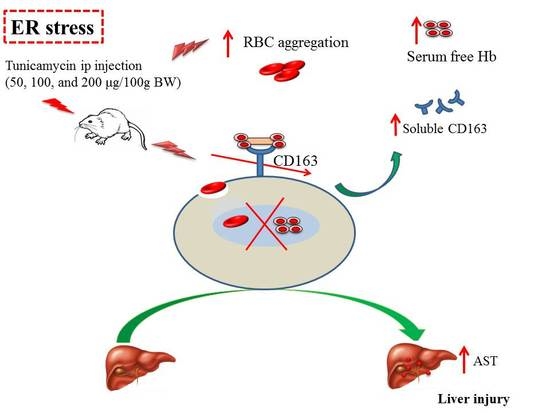
Effect of Endoplasmic Reticular Stress on Free Hemoglobin Metabolism and Liver Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
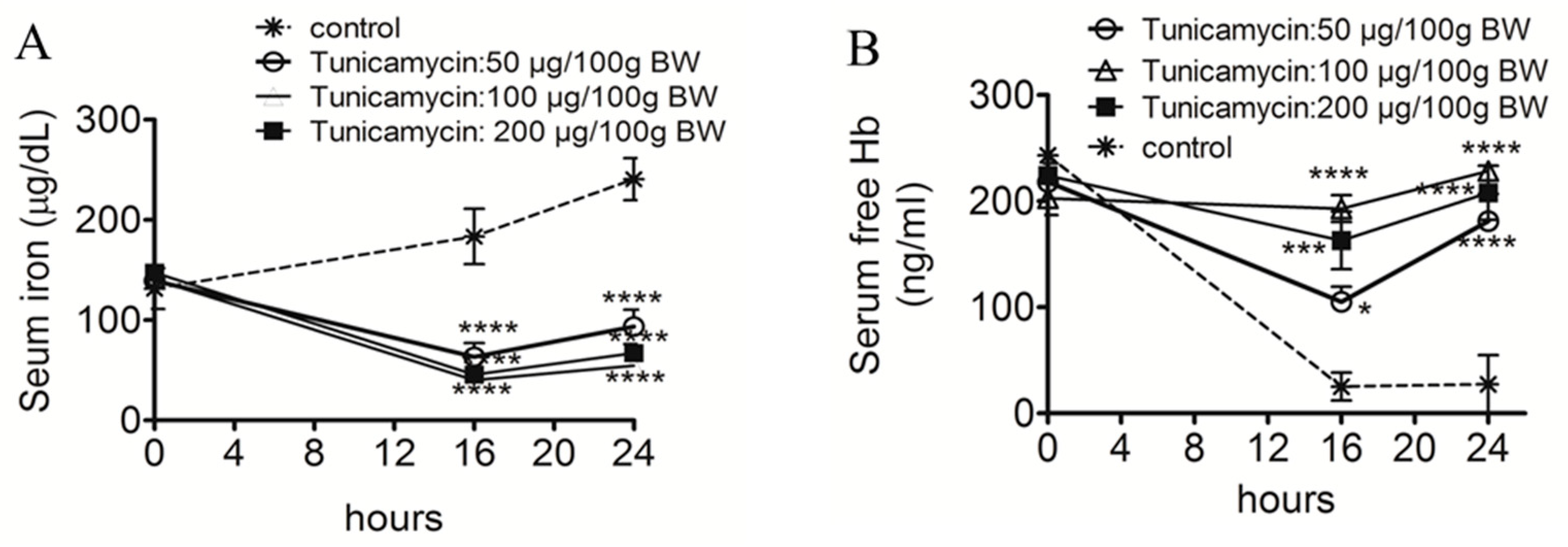
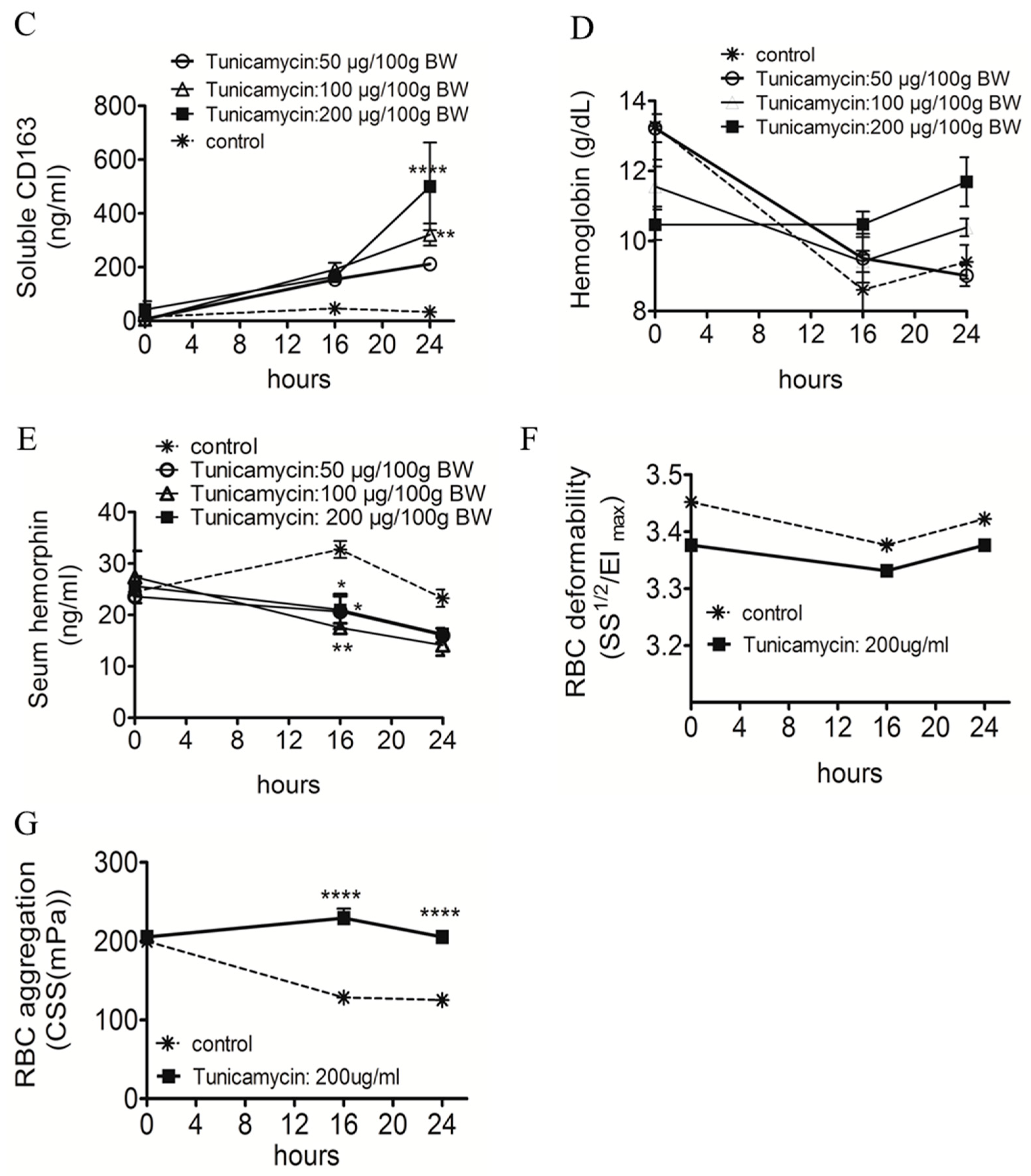
2.1. ER Stress Attenuates RBC Aggregability and Free Hb Uptake
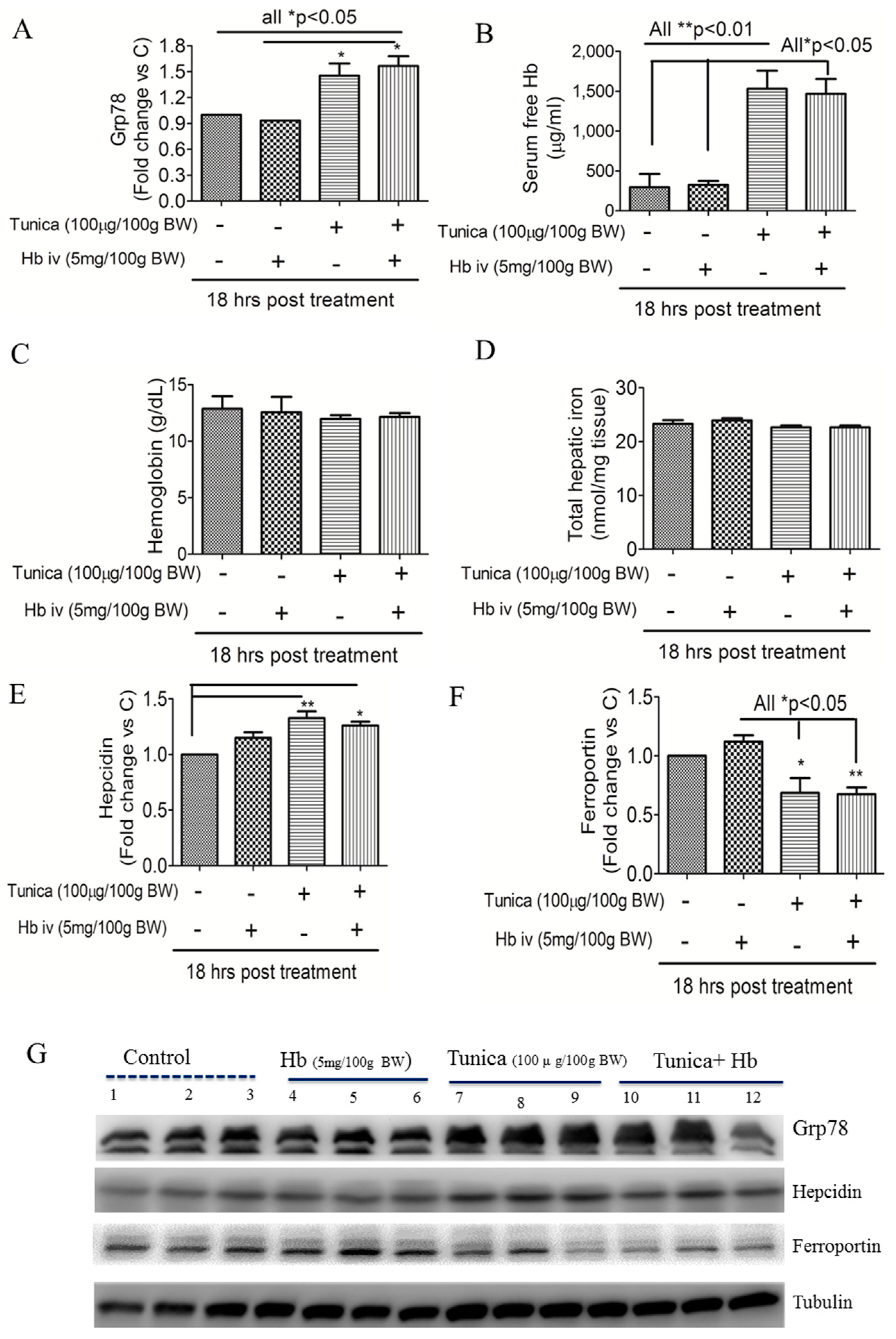
2.2. ER Stress Alters Hepatic Hepcidin-Ferroportin Expression
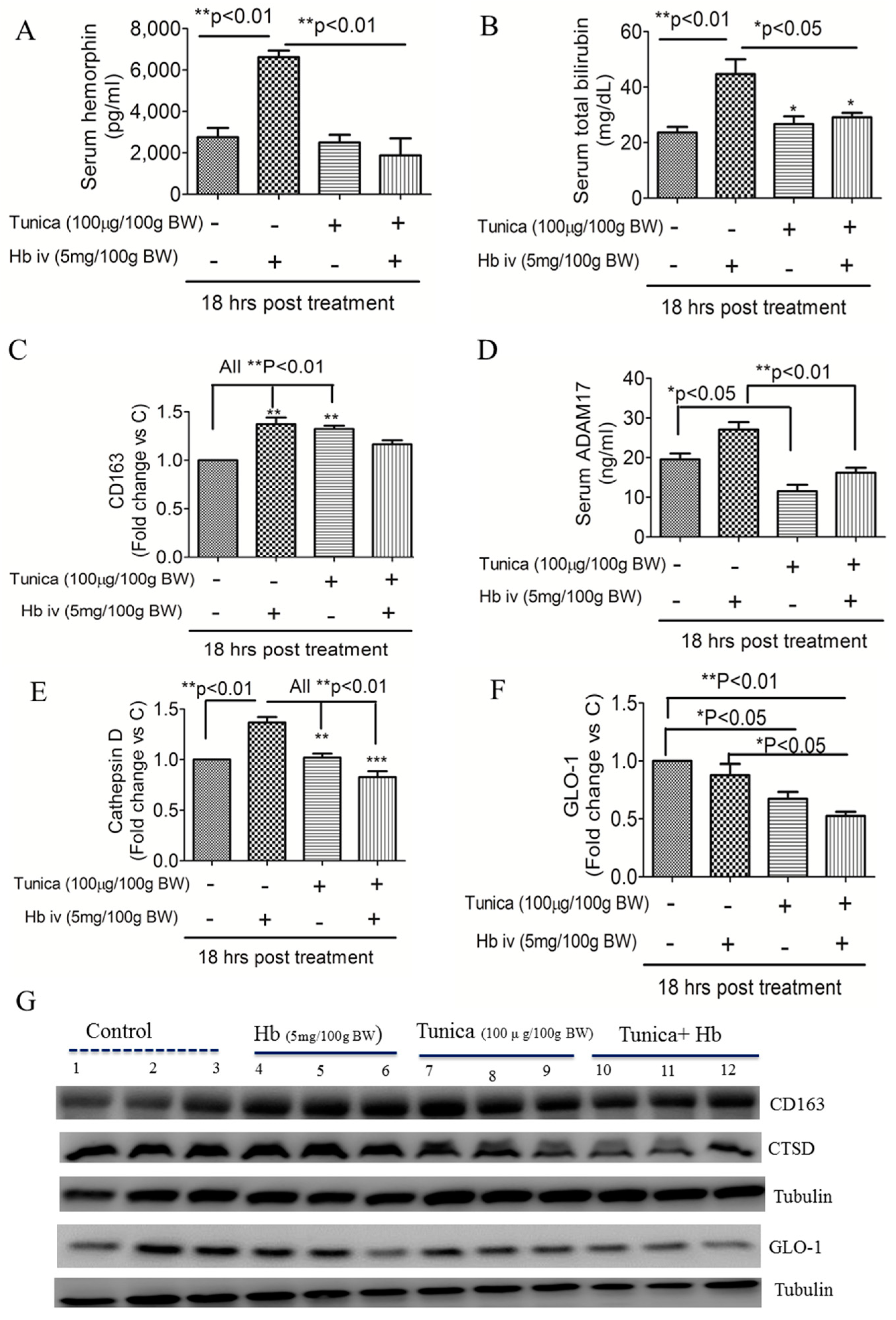
2.3. ER Stress Suppresses Globin Degradation
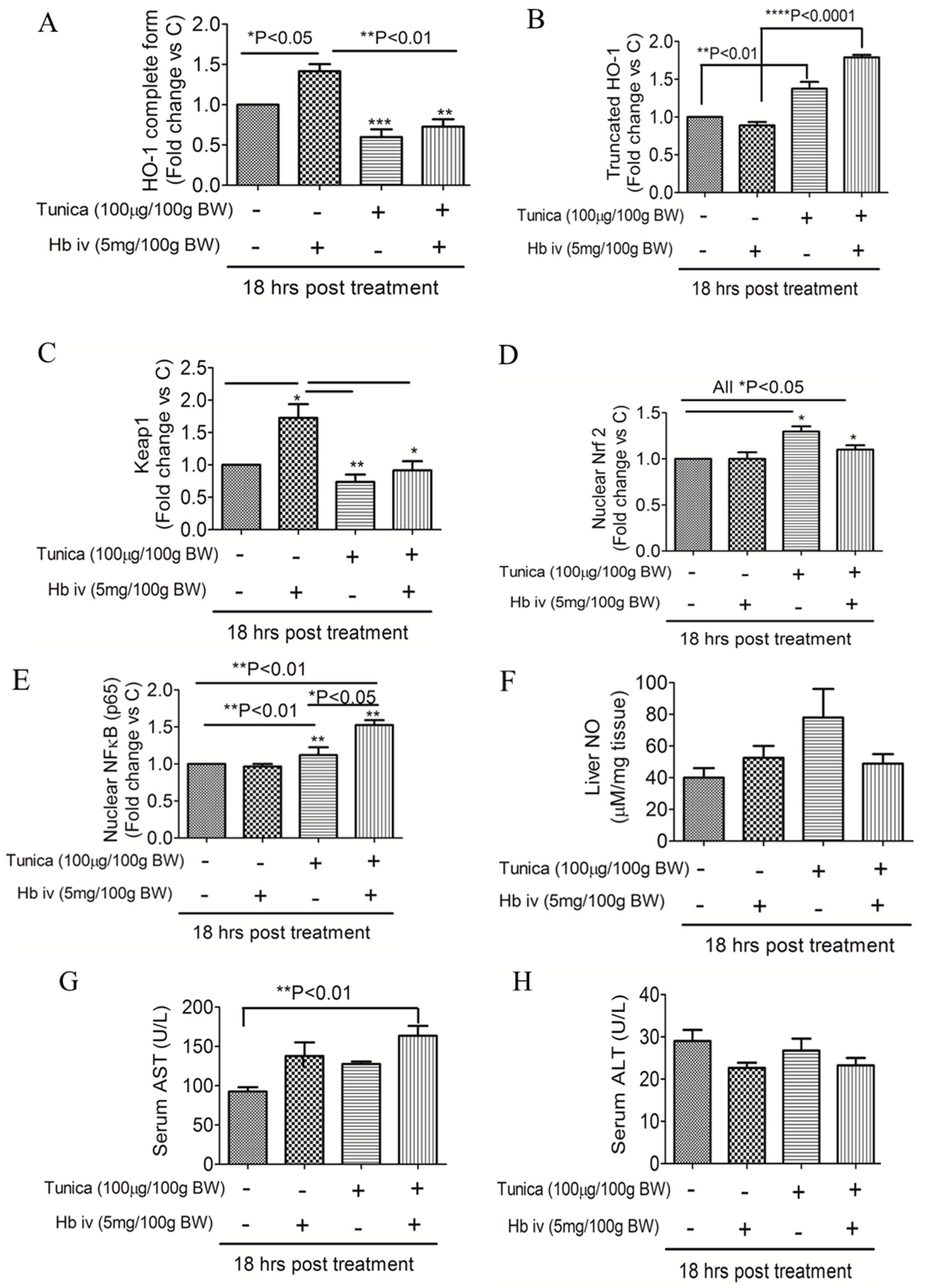
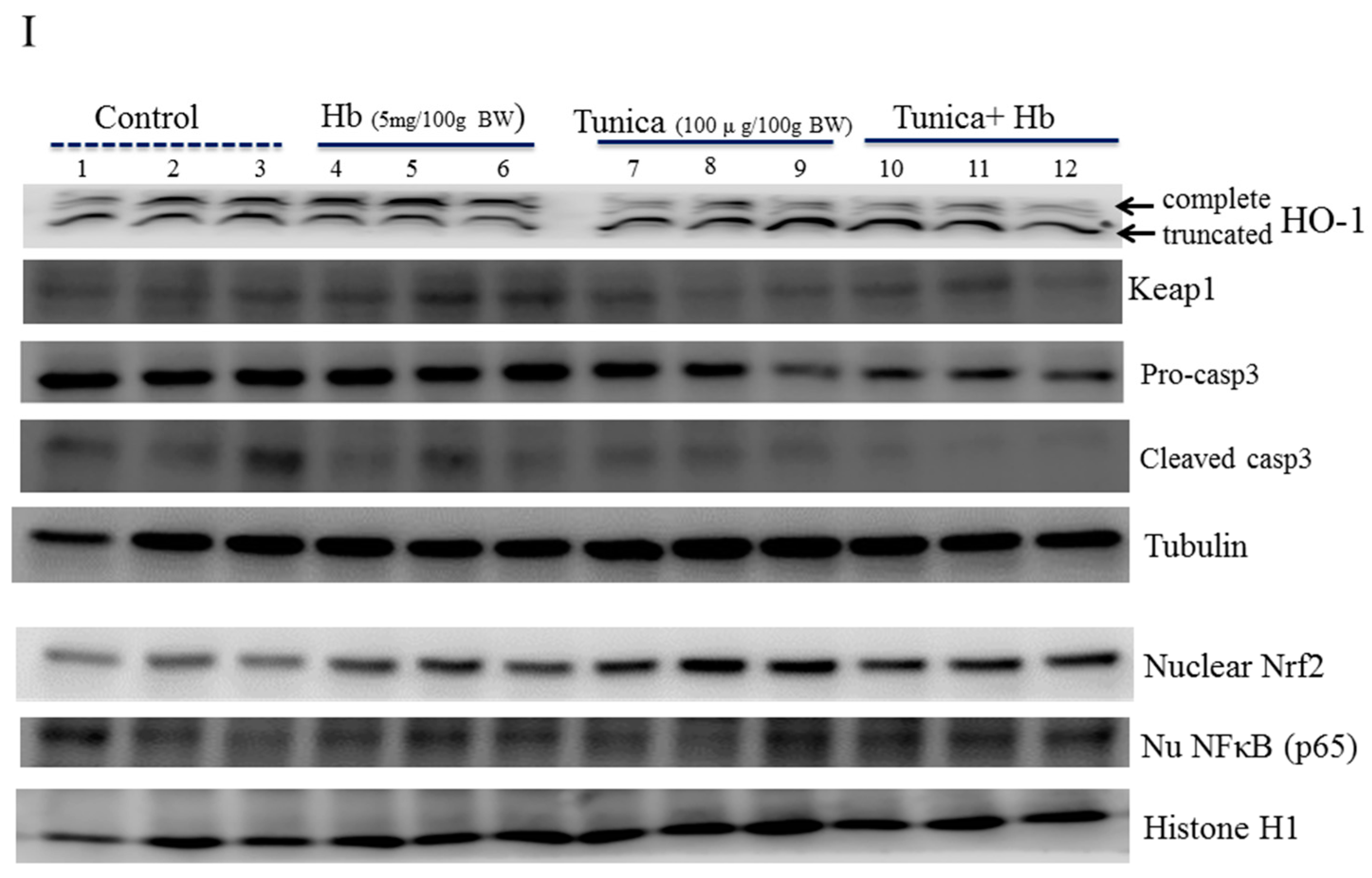
2.4. ER Stress Alters Heme Iron Degradation via Increasing Heme Oxygesnase-1 Trafficking
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rat Experiment
4.2. Blood Biochemistry
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pagliassotti, M.J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 32, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trak-Smayra, V.; Dargere, D.; Noun, R.; Albuquerque, M.; Yaghi, C.; Gannage-Yared, M.H.; Bedossa, P.; Paradis, V. Serum proteomic profiling of obese patients: Correlation with liver pathology and evolution after bariatric surgery. Gut 2009, 58, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Senates, E.; Ayyildiz, T.; Colak, Y.; Tuncer, I.; Ovunc, A.O.; Dolar, E.; Kalayci, C. Characterization of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease unrelated to the metabolic syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Xu, C.; Xu, L.; Yu, J.; Miao, M.; Li, Y. Serum proteomic analysis revealed diagnostic value of hemoglobin for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjeldborg, K.; Christiansen, T.; Bennetzen, M.; H, J.M.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. The macrophage-specific serum marker, soluble cd163, is increased in obesity and reduced after dietary-induced weight loss. Obesity 2013, 21, 2437–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazankov, K.; Barrera, F.; Moller, H.J.; Rosso, C.; Bugianesi, E.; David, E.; Ibrahim Kamal Jouness, R.; Esmaili, S.; Eslam, M.; McLeod, D.; et al. The macrophage activation marker scd163 is associated with morphological disease stages in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazankov, K.; Moller, H.J.; Lange, A.; Birkebaek, N.H.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Solvig, J.; Horlyck, A.; Kristensen, K.; Rittig, S.; Handberg, A.; et al. The macrophage activation marker scd163 is associated with changes in nafld and metabolic profile during lifestyle intervention in obese children. Pediatr. Obes. 2015, 10, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, J.L.; Feeney, E.R.; Zheng, H.; Misdraji, J.; Kruger, A.J.; Alatrakchi, N.; King, L.Y.; Gelrud, L.; Corey, K.E.; Chung, R.T. Circulating soluble cd163 is associated with steatohepatitis and advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazankov, K.; Tordjman, J.; Moller, H.J.; Vilstrup, H.; Poitou, C.; Bedossa, P.; Bouillot, J.L.; Clement, K.; Gronbaek, H. Macrophage activation marker soluble cd163 and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in morbidly obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatology. 2015, 30, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgaard-Hansen, S.; St George, A.; Kazankov, K.; Bauman, A.; George, J.; Gronbaek, H.; Jon Moller, H. Effects of lifestyle intervention on soluble cd163, a macrophage activation marker, in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2017, 77, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, T. Macrophages and systemic iron homeostasis. J. Innate Immun. 2012, 4, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, J.H.; Etzerodt, A.; Svendsen, P.; Moestrup, S.K. The haptoglobin-cd163-heme oxygenase-1 pathway for hemoglobin scavenging. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 523652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaer, C.A.; Schoedon, G.; Imhof, A.; Kurrer, M.O.; Schaer, D.J. Constitutive endocytosis of cd163 mediates hemoglobin-heme uptake and determines the noninflammatory and protective transcriptional response of macrophages to hemoglobin. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, I.; Dale, C.S.; Casten, K.; Geigner, M.A.; Gozzo, F.C.; Ferro, E.S.; Heimann, A.S.; Devi, L.A. Hemoglobin-derived peptides as novel type of bioactive signaling molecules. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruitier, I.; Garreau, I.; Lacroix, A.; Cupo, A.; Piot, J.M. Proteolytic degradation of hemoglobin by endogenous lysosomal proteases gives rise to bioactive peptides: Hemorphins. FEBS Lett. 1999, 447, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.J.; Moestrup, S.K. Receptor targeting of hemoglobin mediated by the haptoglobins: Roles beyond heme scavenging. Blood 2009, 114, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.L.; Chen, P.Y.; Wang, C.M.; Chen, W.Y.; Chen, C.W.; Owaga, E.; Chang, J.S. Dose-related effects of ferric citrate supplementation on endoplasmic reticular stress responses and insulin signalling pathways in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetes. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-M.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chang, J.-S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to ferritin molecules-mediated macrophage migration via P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.M.; Li, S.J.; Wu, C.H.; Hu, C.M.; Cheng, H.W.; Chang, J.S. Transient knock down of grp78 reveals roles in serum ferritin mediated pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion in rat primary activated hepatic stellate cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchi, C.; Montosi, G.; Zhang, K.; Lamberti, I.; Duncan, S.A.; Kaufman, R.J.; Pietrangelo, A. Er stress controls iron metabolism through induction of hepcidin. Science 2009, 325, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzerodt, A.; Maniecki, M.B.; Moller, K.; Moller, H.J.; Moestrup, S.K. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme (tace/adam17) mediates ectodomain shedding of the scavenger receptor cd163. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzerodt, A.; Rasmussen, M.R.; Svendsen, P.; Chalaris, A.; Schwarz, J.; Galea, I.; Moller, H.J.; Moestrup, S.K. Structural basis for inflammation-driven shedding of cd163 ectodomain and tumor necrosis factor-α in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzerodt, A.; Kjolby, M.; Nielsen, M.J.; Maniecki, M.; Svendsen, P.; Moestrup, S.K. Plasma clearance of hemoglobin and haptoglobin in mice and effect of cd163 gene targeting disruption. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, F.; Sanderson, K.; Glamsta, E.L. The hemorphins: A new class of opioid peptides derived from the blood protein hemoglobin. Biopolymers 1997, 43, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruitier-Arnaudin, I.; Cohen, M.; Bordenave, S.; Sannier, F.; Piot, J.M. Comparative effects of angiotensin iv and two hemorphins on angiotensin-converting enzyme activity. Peptides 2002, 23, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Albiston, A.L.; Allen, A.M.; Mendelsohn, F.A.; Ping, S.E.; Barrett, G.L.; Murphy, M.; Morris, M.J.; McDowall, S.G.; Chai, S.Y. Effect of i.C.V. Injection of at4 receptor ligands, nle1-angiotensin iv and lvv-hemorphin 7, on spatial learning in rats. Neuroscience 2004, 124, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruiter, A., II; Cohen, M.M.; Nervi, S.S.; Bordenave, S.S.; Sannier, F.F.; Piot, J.M. Reduced level of opioid peptides, hemorphin-7 peptides, in serum of diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraninchi, M.; Feron, D.; Fruitier-Arnaudin, I.; Begu-Le Corroller, A.; Nogueira, J.P.; Mancini, J.; Valero, R.; Piot, J.M.; Vialettes, B. Serum hemorphin-7 levels are decreased in obesity. Obesity 2013, 21, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, Y.; Truman, M.; Cohen, L.A.; Leichtmann-Bardoogo, Y.; Meyron-Holtz, E.G. Endoplasmic reticulum anchored heme-oxygenase 1 faces the cytosol. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Weis, S.; Yang, G.; Weng, Y.H.; Helston, R.; Rish, K.; Smith, A.; Bordner, J.; Polte, T.; Gaunitz, F.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 protein localizes to the nucleus and activates transcription factors important in oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20621–20633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, C.; Shah, N.; Muthu, M.; La, P.; Fernando, A.P.; Sengupta, S.; Yang, G.; Dennery, P.A. Nuclear heme oxygenase-1 (ho-1) modulates subcellular distribution and activation of nrf2, impacting metabolic and anti-oxidant defenses. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 26882–26894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oslowski, C.M.; Urano, F. Measuring er stress and the unfolded protein response using mammalian tissue culture system. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 490, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Enns, C.A. N-linked glycosylation is required for transferrin-induced stabilization of transferrin receptor 2, but not for transferrin binding or trafficking to the cell surface. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 3310–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, L.; Brewster, V.L.; Correa, E.; Goodacre, R. Detection of glycosylation and iron-binding protein modifications using raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2017, 142, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyadomari, S.; Mori, M. Roles of chop/gadd153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iurlaro, R.; Munoz-Pinedo, C. Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2640–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Jian, J.; Katz, S.; Abramson, S.B.; Huang, X. 17beta-estradiol inhibits iron hormone hepcidin through an estrogen responsive element half-site. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3170–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Nam, J.H.; Hou, J.X.; Suh, J.S. A transient, microfluidic approach to the investigation of erythrocyte aggregation: The threshold shear-stress for erythrocyte disaggregation. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2009, 42, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alexy, T.; Baskurt, O.K.; Nemeth, N.; Uyuklu, M.; Wenby, R.B.; Meiselman, H.J. Effect of lanthanides on red blood cell deformability and response to mechanical stress: Role of lanthanide ionic radius. Biorheology 2011, 48, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseng, S.-H.; Chang, T.-Y.; Shih, C.-K.; Hsieh, R.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, M.-H.; Chang, J.-S. Effect of Endoplasmic Reticular Stress on Free Hemoglobin Metabolism and Liver Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071977
Tseng S-H, Chang T-Y, Shih C-K, Hsieh R-H, Chen C-W, Chen Y-C, Lin M-H, Chang J-S. Effect of Endoplasmic Reticular Stress on Free Hemoglobin Metabolism and Liver Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071977
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Sung-Hui, Ting-Yun Chang, Chun-Kuang Shih, Rong-Hong Hsieh, Chia-Wen Chen, Yi-Chun Chen, Mei-Hsiang Lin, and Jung-Su Chang. 2018. "Effect of Endoplasmic Reticular Stress on Free Hemoglobin Metabolism and Liver Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071977
APA StyleTseng, S.-H., Chang, T.-Y., Shih, C.-K., Hsieh, R.-H., Chen, C.-W., Chen, Y.-C., Lin, M.-H., & Chang, J.-S. (2018). Effect of Endoplasmic Reticular Stress on Free Hemoglobin Metabolism and Liver Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071977