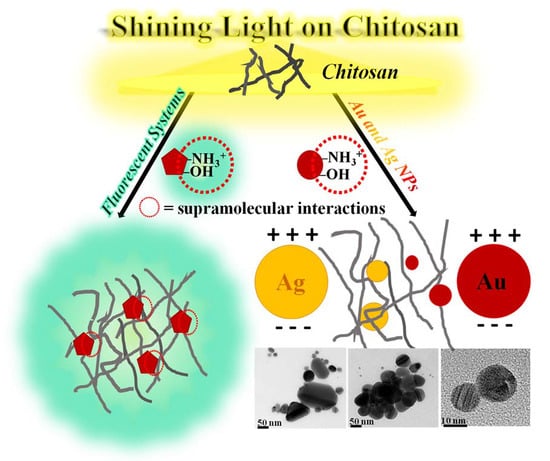
Shining Light on Chitosan: A Review on the Usage of Chitosan for Photonics and Nanomaterials Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Selective Applications of Chitosan
1.1.1. Antibacterial
1.1.2. Antioxidant
1.1.3. Corrosion Protection
1.1.4. Drug Delivery
1.1.5. Food Packaging/Preservation
1.1.6. Heavy Metal Removal/Water Treatment
1.1.7. Tissue Engineering
2. Chitosan Polymer for Photonic Applications
2.1. Luminescent Chitosan Systems
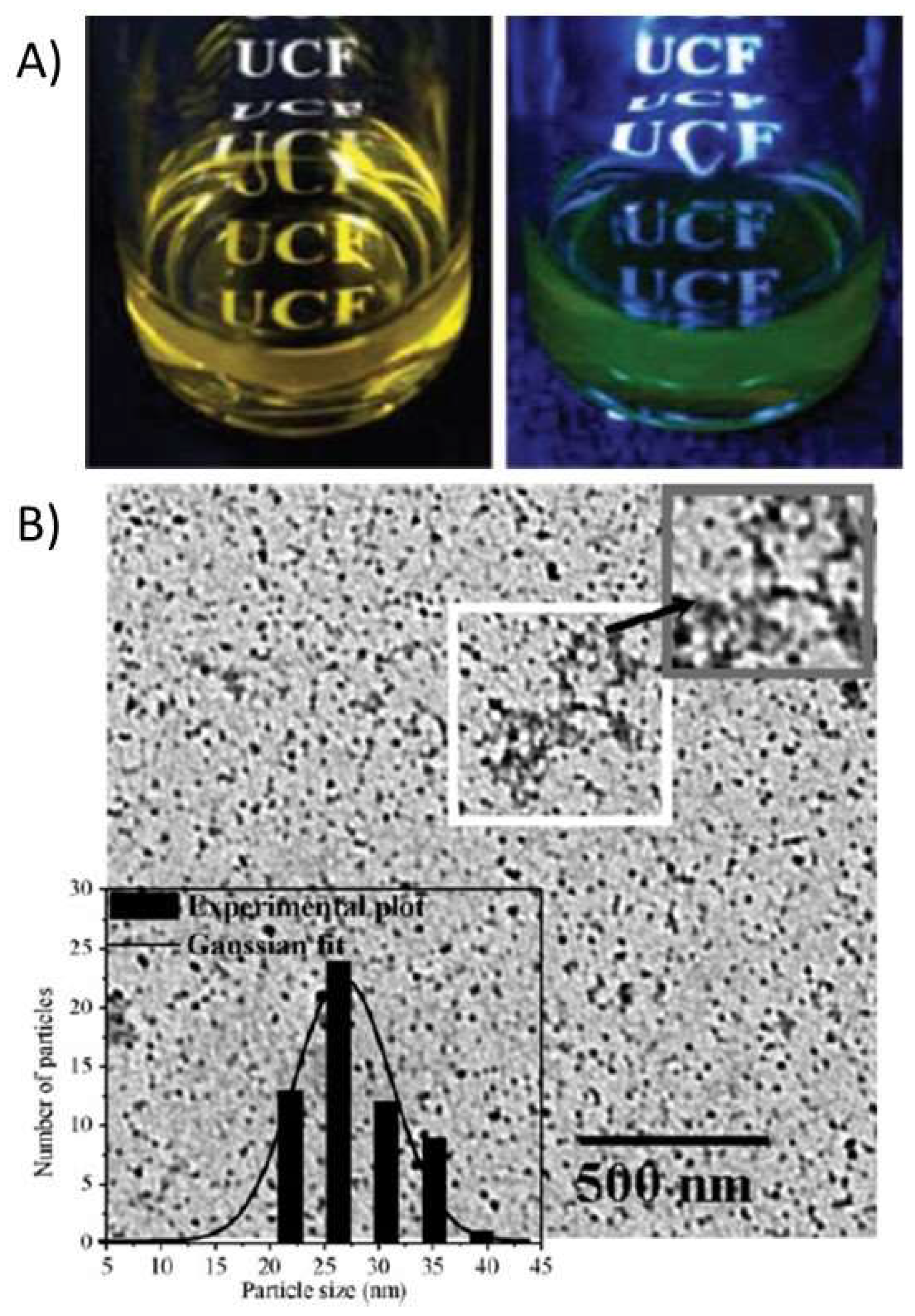
2.1.1. Luminescent Chitosan Nanoparticles
2.1.2. Quantum Dots
2.1.3. Carbon Dots
2.1.4. Aggregation-Induced Emission Nanoparticles
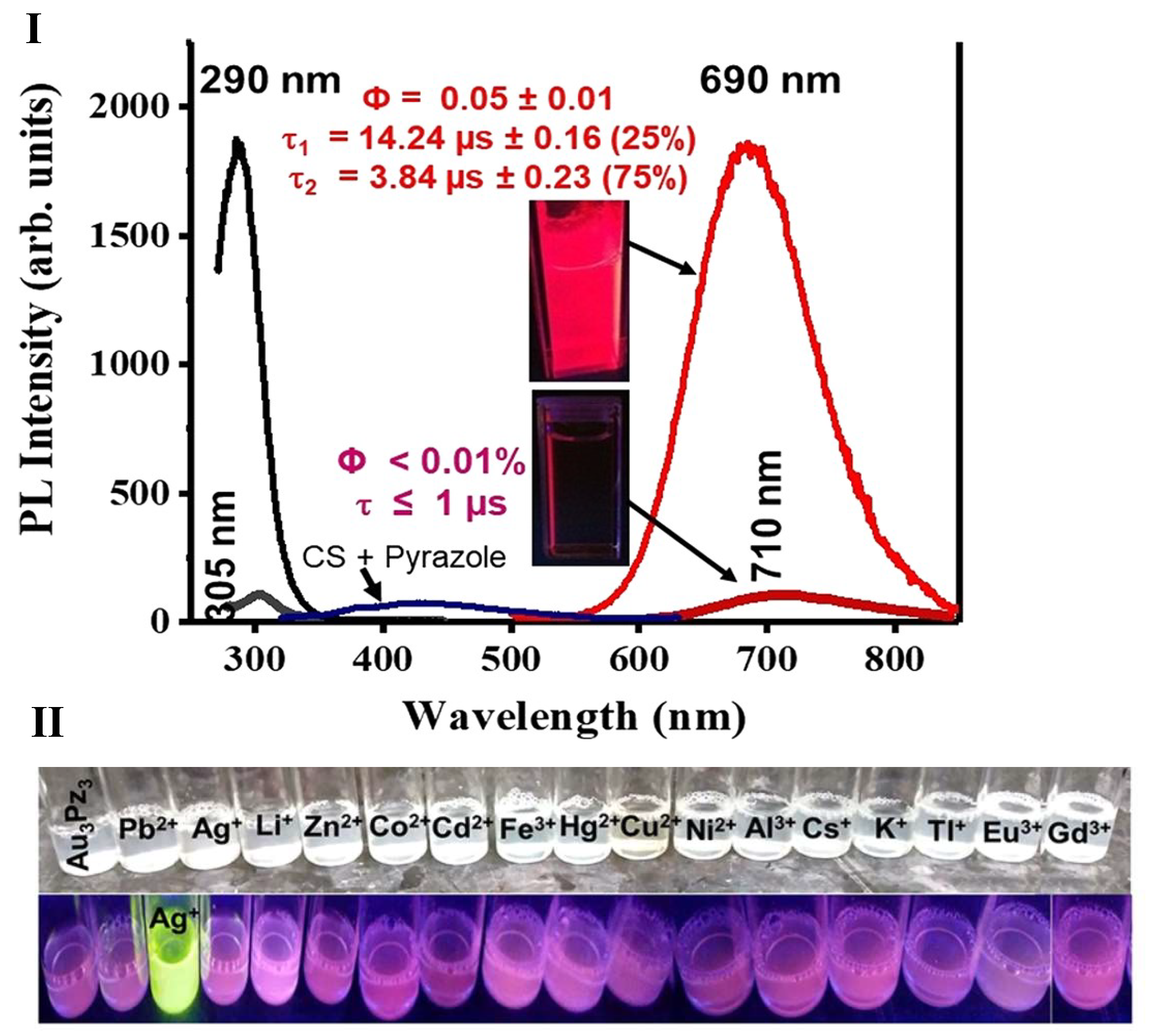
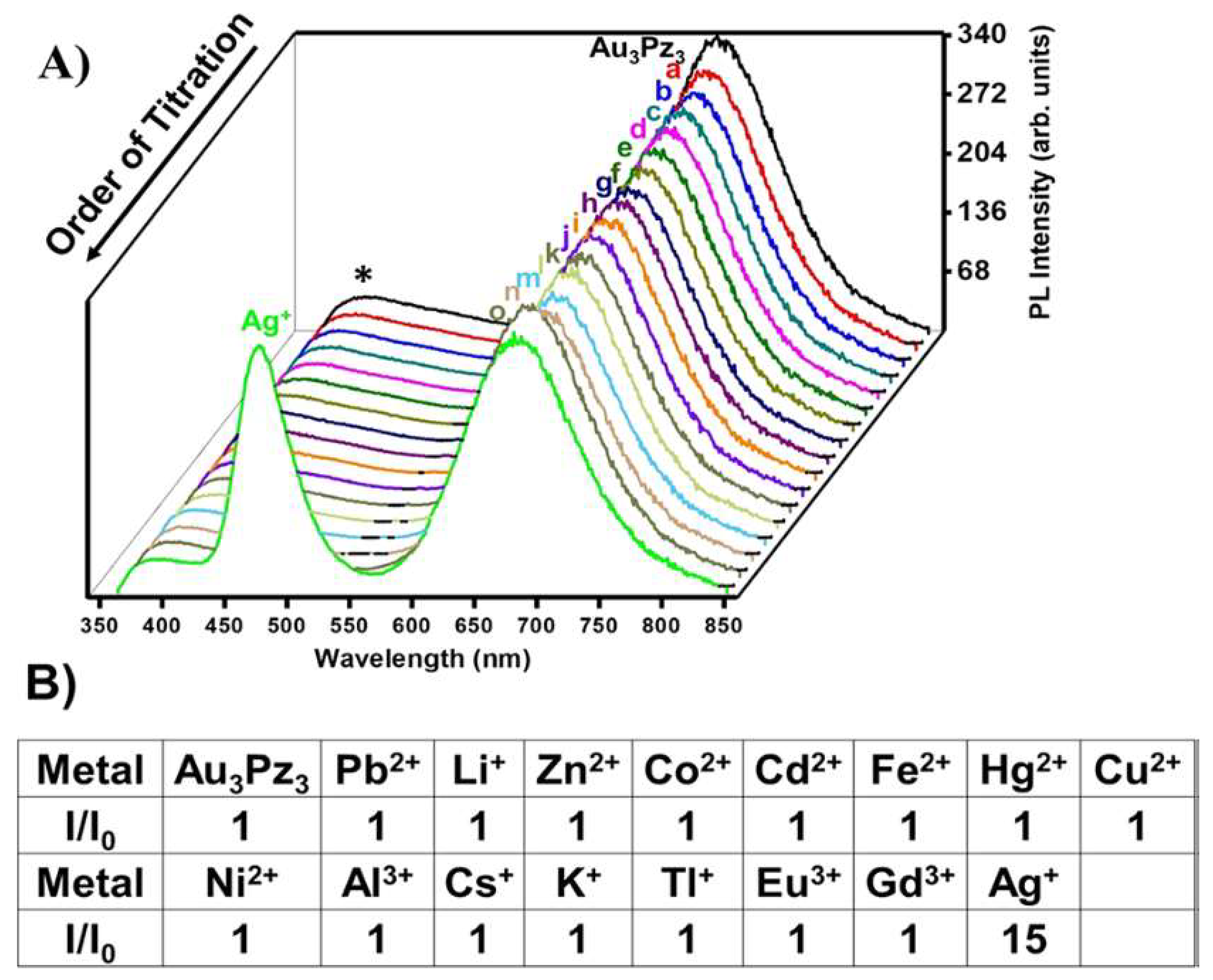
2.1.5. Metal Nanoclusters
2.1.6. Luminescent Organometallic Complexes
2.2. Plasmonic Metal Nanoparticle–Chitosan Systems
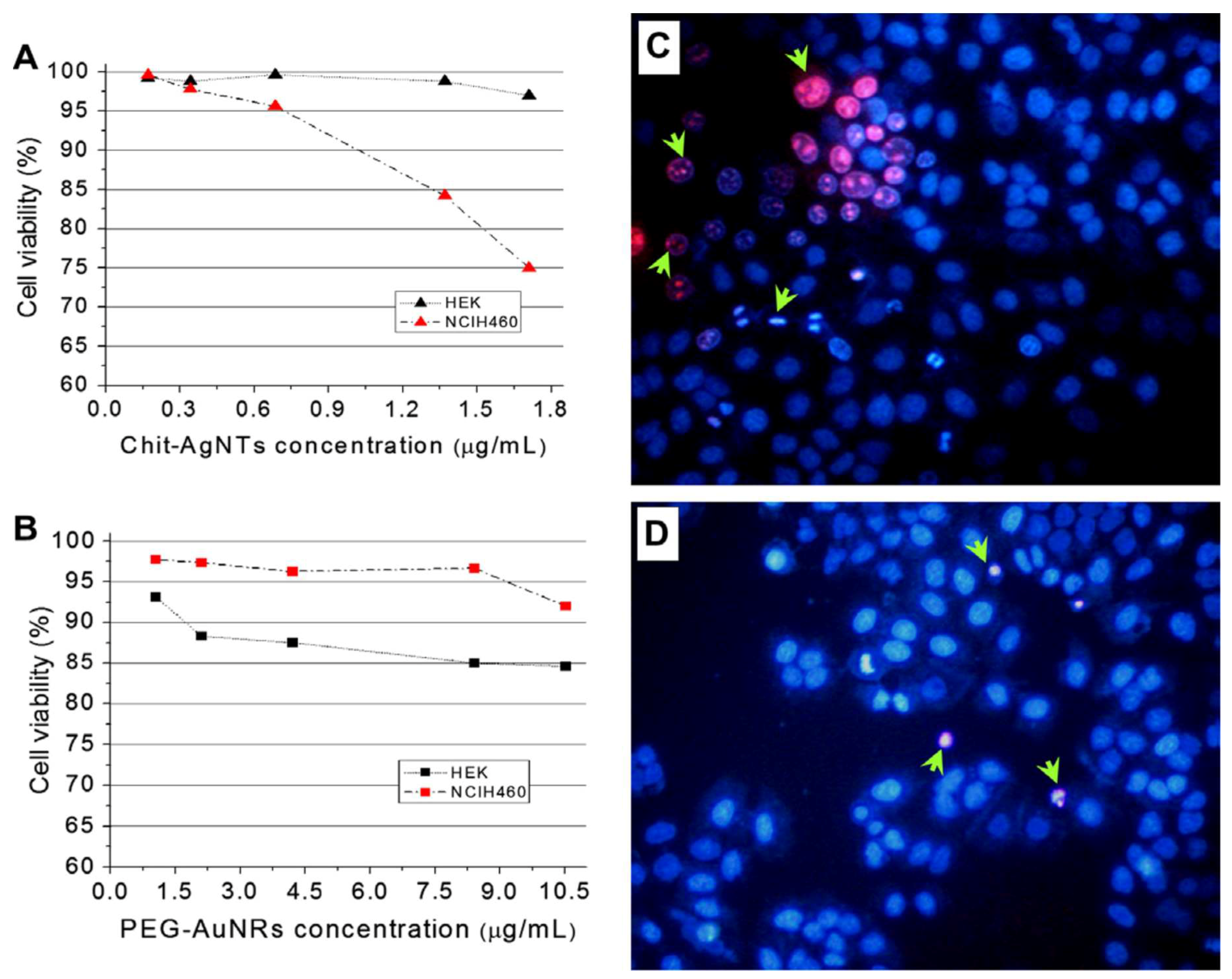
2.2.1. Chitosan Containing Silver Nanoparticles
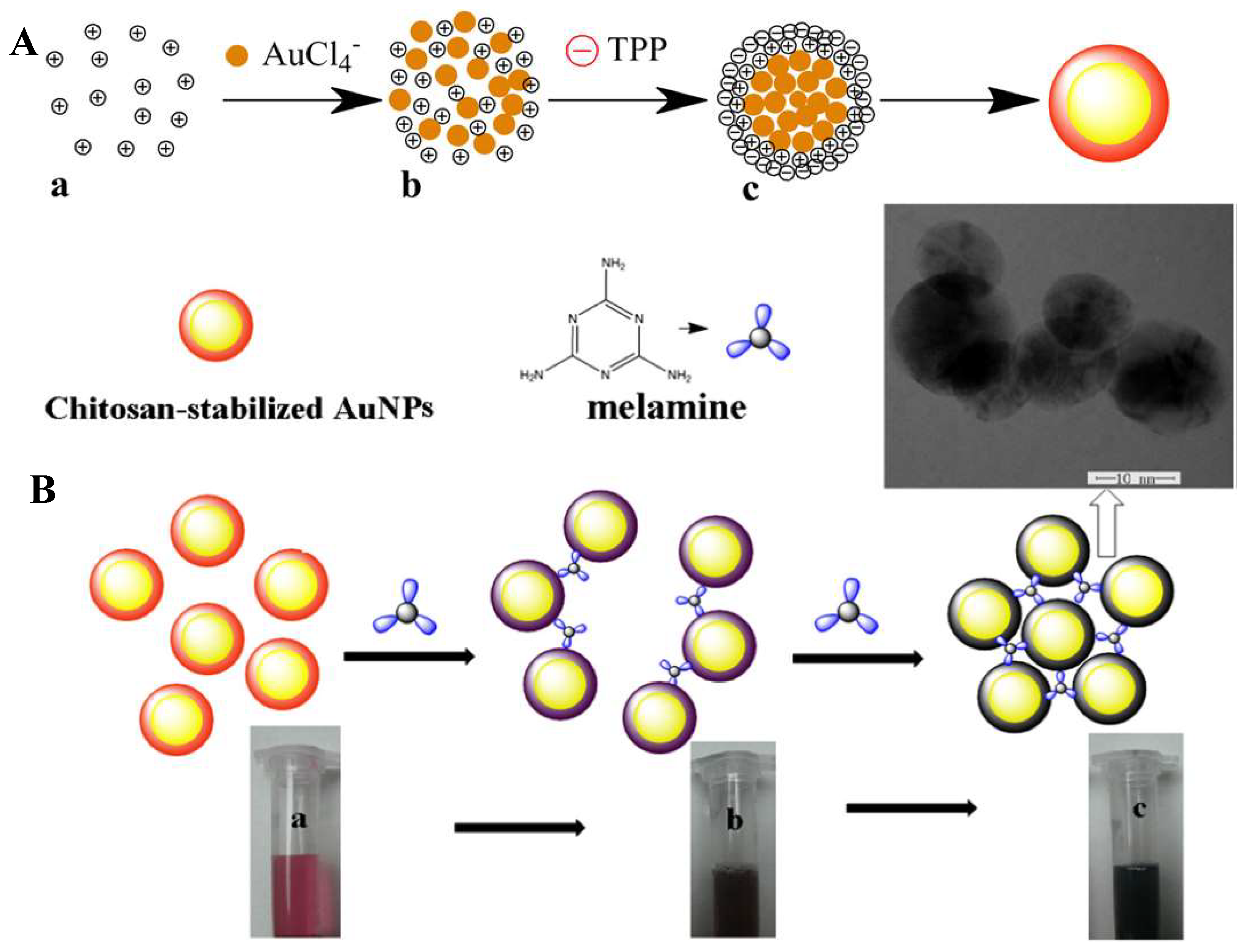
2.2.2. Chitosan Containing Gold Nanoparticles
2.3. Some Selective Applications of Chitosan-Based Photonic Systems
2.3.1. Bioimaging and Cancer Research
2.3.2. Sensing
2.3.3. Gene Therapy
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CS | Chitosan |
| TPP | Tripolyphosphate |
| LBL | Layer by layer |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| ZnONPs | Zinc oxide nanoparticles |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| FCSNPs | Fluorescent chitosan nanoparticles |
| CPT | Camptothecin |
| PEC | Polyelectrolyte complexation |
| CCHNs | Chitosan–carbon dot hybrid nanogels |
| SERS | Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy |
| MEF | Metal-enhanced fluorescence |
| SPA | Surface plasmon resonance |
| PL | Photoluminescence |
| LPNs | Luminescent polymeric nanoparticles |
| NIRF | Near-infrared fluorescent |
| ACQ | Aggregation-caused quenching |
| AIEgens | Aggregated-induced emission luminogens |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| QDs | Quantum dots |
| CDs | Carbon dots |
| AIE | Aggregated-induced emission |
References
- Hudson, S.M.; Jenkins, D.W. Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 569–580. [Google Scholar]
- Ruel-Gariѐpy, E.; Leroux, J. Chitosan: A Natural Polycation with Multiple Applications; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 243–259. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Gulbake, A.; Shilpi, S.; Jain, A.; Hurkat, P.; Jain, S.K. A New Horizon in Modifications of Chitosan: Syntheses and Applications. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2013, 30, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kumar, M.N.V. A Review of Chitin and Chitosan Applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Ling, Y.; Shen, Z.; Han, G.; Sun, R. Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications; Nova Science: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sanford, P.A.; Hutchings, G.P. Industrial Polysaccharides: Genetic Engineering, Structure/Property Relations, and Applications; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 363–376. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, S.M.; Kannadasan, M.; Roy, R.K. Review of Chitosan and its Relevance in Pharmaceutical Sciences. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 425–430. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, P.; Strijkers, G.J.; Nicolay, K. Chitosan-Based Systems for Molecular Imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, P. Characterisation and Cooperative Antimicrobial Properties of Chitosan/Nano-ZnO Composite Nanofibrous Membranes. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, L.X.; Lin, G.Y.; Zhi, Y.D.; Zhi, L.; De, Y.K. Antibacterial Action of Chitosan and Carboxymethylated Chitosan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 79, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Sudarshan, N.R.; Hoover, D.G.; Knorr, D. Antibacterial Action of Chitosan. Food Biotechnol. 1992, 6, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial Properties of Chitosan and Mode of Action: A State of the Art Review. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honary, S.; Ghajar, K.A.; Khazaeli, P.; Shalchian, P. Preparation, Characterization and Antibacterial Properties of Silver-Chitosan Nanocomposites using Different Molecular Weight Grades of Chitosan. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, X. Synthesis of Polysaccharide-Stabilized Gold and Silver Nanoparticles: A Green Method. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Tay, M.; Shameli, K.; Hussein, M.; Lim, J. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver/Chitosan/Polyethylene Glycol Nanocomposites without any Reducing Agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 4872–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, R.; Yu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, P. Antioxidant Activity of Differently Regioselective Chitosan Sulfates in Vitro. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, F.; Guebitz, G.M.; Kokol, V. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Chitosan Enzymatically Functionalized with Flavonoids. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinsova, J.; Vavrikova, E. Chitosan Derivatives with Antimicrobial, Antitumour and Antioxidant Activities—A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3596–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Zhong, Z.; Li, P. Synthesis and Hydroxyl Radicals Scavenging Activity of Quaternized Carboxymethyl Chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemor, M.F. Functional and Smart Coatings for Corrosion Protection: A Review of Recent Advances. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 258, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.; Tedim, J.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Chitosan as a Smart Coating for Corrosion Protection of Aluminum Alloy 2024: A Review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 89, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.; Tedim, J.; Fernandes, S.C.M.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Gandini, A.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Chitosan-Based Self-Healing Protective Coatings Doped with Cerium Nitrate for Corrosion Protection of Aluminum Alloy 2024. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 75, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Urban, M.W. Self-Repairing Oxetane-Substituted Chitosan Polyurethane Networks. Science 2009, 323, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgadir, M.A.; Uddin, M.S.; Ferdosh, S.; Adam, A.; Chowdhury, A.J.K.; Sarker, M.Z.I. Impact of Chitosan Composites and Chitosan Nanoparticle Composites on various Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Patel, A.K.; Kumari, N.; Kumar, A. A Review on Chitosan Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2014, 4, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Key, J.; Park, K. Multicomponent, Tumor-Homing Chitosan Nanoparticles for Cancer Imaging and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.H.; Park, K.; Kim, Y.; Bae, S.M.; Lee, S.; Jo, H.G.; Park, R.; Kim, I.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, K.; et al. Hydrophobically Modified Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles-Encapsulated Camptothecin Enhance the Drug Stability and Tumor Targeting in Cancer Therapy. J. Controll. Release 2008, 127, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.; Kim, Y.; Park, K.; Nam, H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.H.; Park, R.; Kim, I.; et al. Tumor-Homing Multifunctional Nanoparticles for Cancer Theragnosis: Simultaneous Diagnosis, Drug Delivery, and Therapeutic Monitoring. J. Controll. Release 2010, 146, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi Kumar, M.N.V.; Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Muzzarelli, C.; Sashiwa, H.; Domb, A.J. Chitosan Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6017–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, V.G.L.; Fernando, A.L. Nanoparticles in Food Packaging: Biodegradability and Potential Migration to food—A Review. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2016, 8, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.R.V.; Alves, V.D.; Coelhoso, I.M. Polysaccharide-Based Membranes in Food Packaging Applications. Membranes 2016, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- No, H.K.; Meyers, S.P.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Xu, Z. Applications of Chitosan for Improvement of Quality and Shelf Life of Foods: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R87–R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, D.H.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Youn, S.K.; Park, S.M. Effects on Preservation and Quality of Bread with Coating High Molecular Weight Chitosan. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2003, 16, 430–436. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaouth, A.; Arul, J.; Ponnampalam, R.; Boulet, M. Chitosan Coating Effect on Storability and Quality of Fresh Strawberries. J. Food Sci. 2006, 56, 1618–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, Z. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions using Chitosan and Modified Chitosan: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Applications of Chitin- and Chitosan-Derivatives for the Detoxification of Water and Wastewater—A Short Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontoni, L.; Fabbricino, M. Use of Chitosan and Chitosan-Derivatives to Remove Arsenic from Aqueous Solutions—A Mini Review. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 356, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, F.; Samiei, M.; Adibkia, K.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Davaran, S. Biodegradable and Biocompatible Polymers for Tissue Engineering Application: A Review. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Vázquez, M.; Vega-Ruiz, B.; Ramos-Zúñiga, R.; Saldaña-Koppel, D.A.; Quiñones-Olvera, L.F. Chitosan and its Potential use as a Scaffold for Tissue Engineering in Regenerative Medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, S.; Nie, F.; Teng, G.; Gu, N. Fluorescence Modified Chitosan-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for High-Efficient Cellular Imaging. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Ma, Z.; Khor, E.; Lim, L. Uptake of FITC-Chitosan Nanoparticles by A549 Cells. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, V.; Park, D.; Lee, Y. Chitosan Combined with ZnO, TiO2 and Ag Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Wound Healing Applications: A Mini Review of the Research Trends. Polymers 2017, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Tan, W.B.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Monodisperse Chitosan Nanoparticles with Embedded Quantum Dots. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yu, J.; Qi, X.; Wu, X.; Hua, R.; Fan, S. Bio-Conjugation of CaF2:Eu/Chitosan Nanoparticles with BSA and Photoluminescent Properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2009, 20, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J. Chitosan-Based Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle for Enhanced Anticancer Effect in Cervical Cancer: A Physicochemical and Biological Perspective. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marpu, S.; Upadhyay, P.K.; Nguyen, D.T.; Oswald, I.W.H.; Arvapally, R.K.; Petros, R.A.; Hu, Z.; Omary, M.A. Self-Assembly of Linear Polymers into Phosphorescent Nanoparticles: Optimization Toward Non-Cytotoxic Bioimaging and Photonic Devices. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 12551–12561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Dutta, D.; Walter, G.A.; Moudgil, B.M. Fluorescent Nanoparticle Probes for Cancer Imaging. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 4, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucky, S.S.; Soo, K.C.; Zhang, Y. Nanoparticles in Photodynamic Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1990–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Gurny, R. Structure and Interactions in Chitosan Hydrogels Formed by Complexation or Aggregation for Biomedical Applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Hein, S.; Misra, R.D.K. New Generation of Chitosan-Encapsulated ZnO Quantum Dots Loaded with Drug: Synthesis, Characterization and in Vitro Drug Delivery Response. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Duan, R.; Liu, R.; Guan, M.; Chen, W.; Ma, M.; Du, B.; Zhang, Q. Chitosan-Stabilized Self-Assembled Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters for Cell Imaging and Biodistribution in Vivo. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallury, P.; Kar, S.; Bamrungsap, S.; Huang, Y.; Tan, W.; Santra, S. Ultra-Small Water-Dispersible Fluorescent Chitosan Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Specific Targeting. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2347–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, J. Preparation and Characterization of the Fluorescent Chitosan Nanoparticle Probe. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2006, 34, 1555–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, M. One-Pot Synthesis of Chitosan/LaF3 :Eu3+ Nanocrystals for Bio-Applications. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandros, M.G.; Behrendt, M.; Maysinger, D.; Tabrizian, M. InGaP@ZnS-Enriched Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Versatile Fluorescent Probe for Deep-Tissue Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3724–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
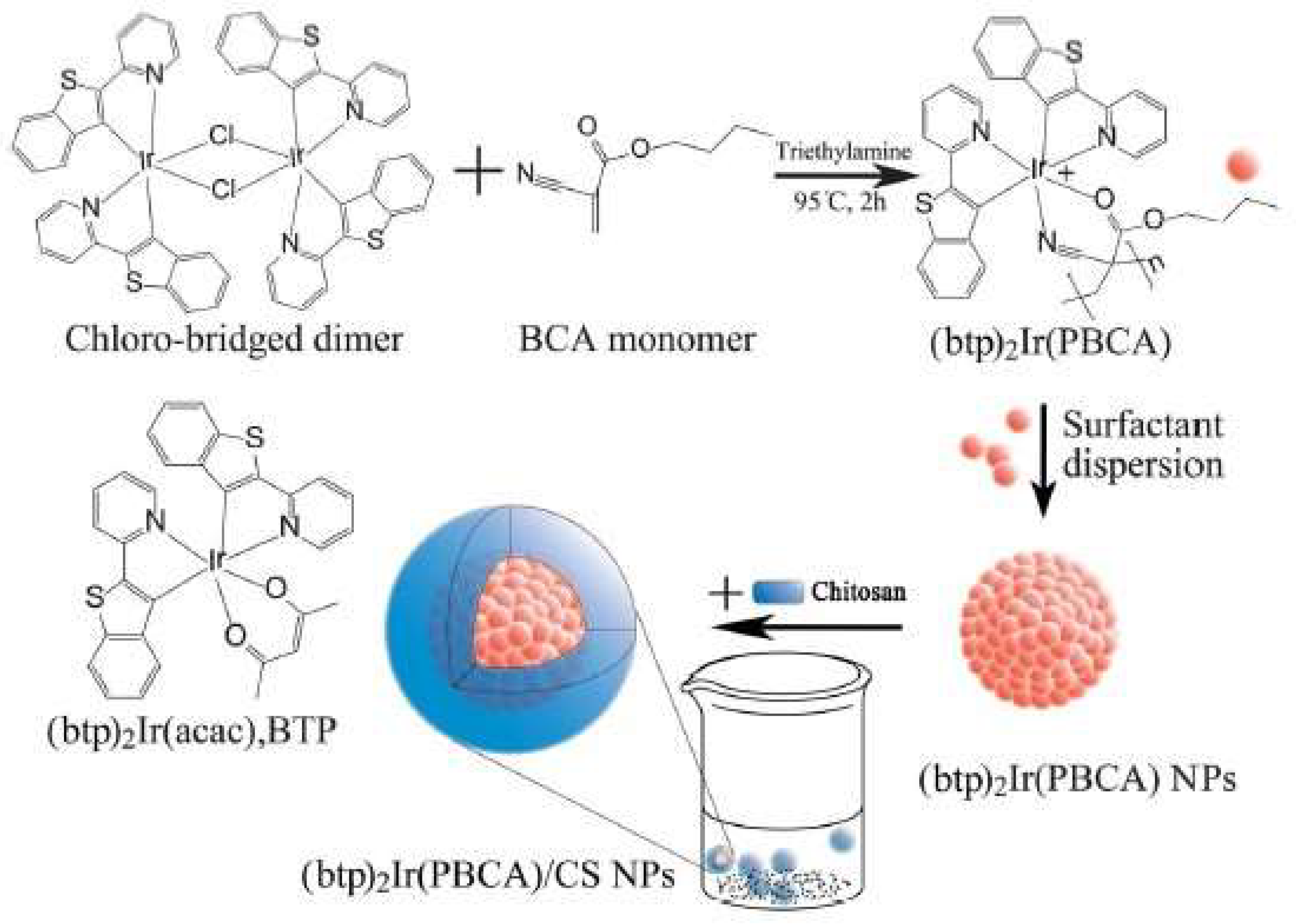
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jia, M.; Liu, Y.; Shang, J.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, D. Hypoxia-Sensitive Bis(2-(2′-Benzothienyl)Pyridinato-N,C3′)Iridium[Poly(N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate]/Chitosan Nanoparticles and their Phosphorescence Tumor Imaging in Vitro and in Vivo. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12633–12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Yin, M. Design and Development of Fluorescent Nanostructures for Bioimaging. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 365–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghormade, V.; Gholap, H.; Kale, S.; Kulkarni, V.M.; Bhat, S.; Paknikar, K.M. Fluorescent Cadmium Telluride Quantum Dots Embedded Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Stable, Biocompatible Preparation for Bio-Imaging. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2015, 26, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, C.L.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Mansur, H.S.; Monteiro, F.J.M. Fluorescent Bionanoprobes Based on Quantum Dot-Chitosan-O-Phospho-L-Serine Conjugates for Labeling Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 49016–49027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfbeis, O.S. An Overview of Nanoparticles Commonly used in Fluorescent Bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4743–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.; Zhou, W.; Lu, J.; Lu, C. Luminescent Films for Chemo- and Biosensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6981–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, B. Bioimaging Based on Fluorescent Carbon Dots. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 27184–27200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, J.; Zheng, M.; Hu, C.; Tan, S.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y. One-Step Synthesis of Amino-Functionalized Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles by Hydrothermal Carbonization of Chitosan. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.; Liu, M.; Xu, D.; Mao, L.; Tian, J.; Huang, H.; Gao, P.; Deng, F.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Fabrication of Aggregation Induced Emission Active Luminescent Chitosan Nanoparticles Via a “one-Pot” Multicomponent Reaction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Hong, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Fabrication of Fluorescent Nanoparticles Based on AIE Luminogens (AIE Dots) and their Applications in Bioimaging. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Wei, Y. Chitosan-Based Cross-Linked Fluorescent Polymer Containing Aggregation-Induced Emission Fluorogen for Cell Imaging. Dyes Pigm. 2017, 143, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Peng, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y. A Novel Picric Acid Film Sensor Via Combination of the Surface Enrichment Effect of Chitosan Films and the Aggregation-Induced Emission Effect of Siloles. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7347–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K. Lanthanide-Based Luminescent Hybrid Materials. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4283–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Y. Facile Preparation of Fluorescent Ag-Clusters-Chitosan-Hybrid Nanocomposites for Bio-Applications. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, P.K.; Marpu, S.B.; Benton, E.N.; Williams, C.L.; Telang, A.; Omary, M.A. A Phosphorescent Trinuclear Gold(I) Pyrazolate Chemosensor for Silver Ion Detection and Remediation in Aqueous Media. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4999–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvirko, M.; Tkaczyk, S.; Kozak, M.; Kalota, B. Luminescent Temperature Sensor Based on Ru(Bpy)3]2+ Incorporated into Chitosan. Funct. Mater. 2013, 20, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, N.; Lelasi, G.; Bedoya, M.; Orellana, G. Optimization of Temperature Sensing with Polymer-Embedded Luminescent Ru(II) Complexes. Polymers 2018, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takato, K.; Gokan, N.; Kaneko, M. Effect of Humidity on Photoluminescence from Ru(Bpy)32+ Incorporated into a Polysaccharide Solid Film and its Application to Optical Humidity Sensor. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2005, 169, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, I.; Jimenez, J.; Mascharak, P.K. CO-Induced Apoptotic Death of Colorectal Cancer Cells by a Luminescent photoCORM Grafted on Biocompatible Carboxymethyl Chitosan. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5519–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Mukherjee, S.; Yi, J.; Banerjee, P.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, S. Biocompatible Chitosan–Carbon Dot Hybrid Nanogels for NIR-Imaging-Guided Synergistic Photothermal–Chemo Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18639–18649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wu, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Tan, M. Ultrasmall Chitosan–Genipin Nanocarriers Fabricated from Reverse Microemulsion Process for Tumor Photothermal Therapy in Mice. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, K. Photofunctional Transition Metal Complexes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 205–245. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, M.; Astruc, D. Gold Nanoparticles: Assembly, Supramolecular Chemistry, Quantum-Size-Related Properties, and Applications toward Biology, Catalysis, and Nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustis, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Why Gold Nanoparticles are More Precious than Pretty Gold: Noble Metal Surface Plasmon Resonance and its Enhancement of the Radiative and Nonradiative Properties of Nanocrystals of Different Shapes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Park, S.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Jon, S. Antibiofouling Polymer-Coated Gold Nanoparticles as a Contrast Agent for in Vivo X-Ray Computed Tomography Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7661–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, R.; Mandal, D.; Mishra, N.; Bahadur, A. Effect of Surfactants on Phosphatase Level of Fresh Water Fish Labeo Rohita. J. Environ. Biol. 2010, 31, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bindu, P.C.; Babu, P. Surfactant-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in a Tropical Euryhaline Teleost Oreochromis Mossambicus (Tilapia) Adapted to Fresh Water. Indian. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 39, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Alkilany, A.; Murphy, C. Toxicity and Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanoparticles: What we have Learned so Far? J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 2313–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, G.; Corain, B. Nanoparticulated Gold: Syntheses, Structures, Electronics, and Reactivities. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2003, 3081–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaymat, T.M.; El Badawy, A.M.; Genaidy, A.; Scheckel, K.G.; Luxton, T.P.; Suidan, M. An Evidence-Based Environmental Perspective of Manufactured Silver Nanoparticle in Syntheses and Applications: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal of Peer-Reviewed Scientific Papers. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveendran, P.; Fu, J.; Wallen, S.L. Completely “Green” Synthesis and Stabilization of Metal Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13940–13941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Ai, K.; Ozaki, Y. Environmentally Friendly Synthesis of Highly Monodisperse Biocompatible Gold Nanoparticles with Urchin-Like Shape. Langmuir 2008, 24, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sur, I.; Cam, D.; Kahraman, M.; Baysal, A.; Culha, M. Interaction of Multi-Functional Silver Nanoparticles with Living Cells. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 175104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Tenhu, H. Recent Advances in Polymer Protected Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Chem. Commun. 2007, 44, 4580–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A Review on Plants Extract Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications: A Green Expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Ikram, S. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles using Plant Extract: An Overview. Nano Res. Appl. 2015, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pasca, R.; Mocanu, A.; Cobzac, S.; Petean, I.; Horovitz, O.; Tomoaia-Cotisel, M. Biogenic Syntheses of Gold Nanoparticles using Plant Extracts. Part. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Jasuja, N.D.; Kumar, M.; Ali, M.I. Biological Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Cell-Free Extract of Spirulina Platensis. J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, Z.; Moadi, T.; Ghahremanzadeh, R. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles using Ferula Latisecta Leaf Extract and their Application as a Catalyst for the Safe and Simple One-Pot Preparation of Spirooxindoles in Water. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3343–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukan, A.; Chetia, B. Green Synthesis, Catalytic and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Olax Acuminata. Asian J. Chem. 2015, 27, 4549–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, F.; Xian, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, L. Glucose Biosensor Based on Au Nanoparticles–conductive Polyaniline Nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1996–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazio, B.; D’Andrea, C.; Foti, A.; Messina, E.; Irrera, A.; Donato, M.G.; Villari, V.; Micali, N.; Marago, O.; Gucciardi, P. SERS Detection of Biomolecules at Physiological pH Via Aggregation of Gold Nanorods Mediated by Optical Forces and Plasmonic Heating. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaohua, H.; Jain, P.K.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Determination of the Minimum Temperature Required for Selective Photothermal Destruction of Cancer Cells with the use of Immunotargeted Gold Nanoparticles. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 82, 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Fierro-Gonzalez, J.C.; Guzman, J.; Gates, B.C. Role of Cationic Gold in Supported CO Oxidation Catalysts. Top. Catal. 2007, 44, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallidi, S.; Kim, S.; Karpiouk, A.; Joshi, P.P.; Sokolov, K.; Emelianov, S. Visualization of Molecular Composition and Functionality of Cancer Cells using Nanoparticle-Augmented Ultrasound-Guided Photoacoustics. Photoacoustics 2015, 3, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.J.; Sau, T.K.; Gole, A.M.; Orendorff, C.J.; Gao, J.; Gou, L.; Hunyadi, S.E.; Li, T. Anisotropic Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Assembly, and Optical Applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13857–13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Li, Q.; Ouyang, J.; Li, X.; Xing, M.M. Nanosilver Particles in Medical Applications: Synthesis, Performance, and Toxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 16, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, K.; Lakowicz, J.R.; Geddes, C.D. Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence using Anisotropic Silver Nanostructures: Critical Progress to Date. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tien, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Ma, C.M. The Production of Graphene Nanosheets Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles for use in Transparent, Conductive Films. Carbon 2011, 49, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloupka, K.; Malam, Y.; Seifalian, A.M. Nanosilver as a New Generation of Nanoproduct in Biomedical Applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomoni, R.; Léo, P.; Montemor, A.F.; Rinaldi, B.G.; Rodrigues, M.F.A. Antibacterial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2017, 10, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, S.Z.; Kiran, U.; Ali, M.I.; Jamal, A.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, N. Combined Efficacy of Biologically Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles and Different Antibiotics Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3187–3195. [Google Scholar]
- Sriram, M.I.; Kanth, S.B.M.; Kalishwaralal, K.; Gurunathan, S. Antitumor Activity of Silver Nanoparticles in Dalton’s Lymphoma Ascites Tumor Model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, T.; Aljaeid, B. Preparation, Characterization, and Potential Application of Chitosan, Chitosan Derivatives, and Chitosan Metal Nanoparticles in Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, C.; Alcock, E.; Buttimer, F.; Schmidt, M.; Clarke, D.; Pemble, M.; Bardosova, M. Synthesis and Characterisation of Cross-Linked Chitosan Composites Functionalised with Silver and Gold Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinehart, S.J.; Campbell, T.D.; Burke, K.J.; Garcia, B.C.; Mlynarski, A.; Brain, S.J.; Truffa, J.M.; Rago, J.; Chura, W.E.; Keleher, J.J. Synthesis and Characterization of a Chitosan/PVA Antimicrobial Hydrogel Nanocomposite for Responsive Wound Management Materials. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2016, 8, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Sun, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P. Preparation and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles on Silk Fibroin/Carboxymethylchitosan Composite Sponge as Anti-Bacterial Wound Dressing. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2015, 26, S111–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hien, N.; Phu, D.; Duy, N.; Anh Quoc, L.; Kim Lan, N.T.; Hoang, D.; Hong Van, H.T.; Diem, H.N.; Thai Hoa, T. Influence of Chitosan Binder on the Adhesion of Silver Nanoparticles on Cotton Fabric and Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity. Adv. Nanopart. 2015, 4, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marpu, S.; Kolailat, S.S.; Korir, D.; Kamras, B.L.; Chaturvedi, R.; Joseph, A.; Smith, C.M.; Palma, M.C.; Shah, J.; Omary, M.A. Photochemical Formation of Chitosan-Stabilized Near-Infrared-Absorbing Silver Nanoworms: A “Green” Synthetic Strategy and Activity on Gram-Negative Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 507, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potara, M.; Baia, M.; Farcau, C.; Astilean, S. Chitosan-Coated Anisotropic Silver Nanoparticles as a SERS Substrate for Single-Molecule Detection. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boca, S.C.; Potara, M.; Gabudean, A.; Juhem, A.; Baldeck, P.L.; Astilean, S. Chitosan-Coated Triangular Silver Nanoparticles as a Novel Class of Biocompatible, Highly Effective Photothermal Transducers for in Vitro Cancer Cell Therapy. Cancer Lett. 2011, 311, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Yang, X. Synthesis of Chitosan-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles in the Absence/Presence of Tripolyphosphate. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2340–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potara, M.; Maniu, D.; Astilean, S. The Synthesis of Biocompatible and SERS-Active Gold Nanoparticles using Chitosan. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupusoru, R.V.; Simion, L.; Sandu, I.; Pricop, D.A.; Chiriac, A.P.; Poroch, V. Aging Study of Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with Chitosan in Aqueous Solutions. Rev. Chim. 2017, 68, 2385–2388. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.L.; Dinh, Q.K.; Tran, T.H.; Nguyen, H.P.; Hoang, T.L.H.; Nguyen, Q.H. Synthesis of Water Soluble Chitosan Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles and Determination of Uric Acid. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 025014. [Google Scholar]
- Sugunan, A.; Thanachayanont, C.; Dutta, J.; Hilborn, J.G. Heavy-Metal Ion Sensors using Chitosan-Capped Gold Nanoparticles. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2005, 6, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curulli, A.; Di Carlo, G.; Ingo, G.M.; Riccucci, C.; Zane, D.; Bianchini, C. Chitosan Stabilized Gold Nanoparticle-Modified Au Electrodes for the Determination of Polyphenol Index in Wines: A Preliminary Study. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ding, Y.; Li, R.; Jiang, X.; Liu, B. Entering and Lighting Up Nuclei using Hollow Chitosan–Gold Hybrid Nanospheres. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3639–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erathodiyil, N.; Jana, N.R.; Ying, J.Y. Functionalization of Gold Nanospheres and Nanorods by Chitosan Oligosaccharide Derivatives. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2068–2073. [Google Scholar]
- Ofir, Y.; Samanta, B.; Rotello, V.M. Polymer and Biopolymer Mediated Self-Assembly of Gold Nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1814–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, N. Polymer-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles as Versatile Sensing Materials. Anal. Sci. 2010, 26, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, S.; Yallapu, M.; Bajpai, M.; Tankhiwale, R.; Thomas, V. Synthesis of Polymer Stabilized Silver and Gold Nanostructures. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 2994–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Shuford, K.L.; Park, S. Optical Property of a Colloidal Solution of Platinum and Palladium Nanorods: Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 19049–19053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Deng, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J. Multifunctional PS@CS@Au-Fe3O4-FA Nanocomposites for CT, MR and Fluorescence Imaging Guided Targeted-Photothermal Therapy of Cancer Cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4221–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yan, D.; Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zalewski, O.; Yan, B.; Lu, W. Combinatorial Photothermal and Immuno Cancer Therapy using Chitosan-Coated Hollow Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5670–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfbeis, O. Optical Fiber Sensors; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1997; pp. 53–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, T.; Nagano, T. Fluorescent Probes for Sensing and Imaging. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranwal, A.; Kumar, A.; Priyadharshini, A.; Oggu, G.S.; Bhatnagar, I.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P. Chitosan: An Undisputed Bio-Fabrication Material for Tissue Engineering and Bio-Sensing Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, I.; Mahato, K.; Ealla, K.K.R.; Asthana, A.; Chandra, P. Chitosan Stabilized Gold Nanoparticle Mediated Self-Assembled gliP Nanobiosensor for Diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, Z.; Lai, Z.; Chen, Z. Chitosan/Prussian Blue-Based Biosensors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; He, G.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Fang, Y. Preparation and Fluorescent Sensing Applications of Novel CdSe–chitosan Hybrid Films. Appl. Surface Sci. 2010, 256, 7270–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, M.; Yoon, Y.; Park, W. Fluorescent Property of Chitosan Oligomer and its Application as a Metal Ion Sensor. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Yu, J.; Chi, D. Label-Free Colorimetric Sensing of Melamine Based on Chitosan-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles Probes. Food Control 2013, 32, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanulla, B.; Palanisamy, S.; Chen, S.; Chiu, T.; Velusamy, V.; Hall, J.; Chen, T.; Ramaraj, S. Selective Colorimetric Detection of Nitrite in Water using Chitosan Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, J. Chitosan-Capped Gold Nanoparticles for Selective and Colorimetric Sensing of Heparin. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, W.; Tang, R.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X. Gene Regulation with Carbon-Based siRNA Conjugates for Cancer Therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Nam, J.; Nah, J. Application of Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives as Biomaterials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fluorescent CS Systems | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon dots | Bioimaging Photothermal therapy Gene therapy | [75,76] |
| Quantum dots | Bioimaging in vitro drug delivery Deep tissue imaging Bioconjugation to biomolecules | [44,50,55] |
| AIE nanoparticles | Sensing Bioimaging | [67] |
| Fluorescent CS nanoparticles | Specific targeting Cellular imaging Probes Cell uptake and imaging Bioconjugation Chemotherapy Gene therapy | [40,41,44,52,53] |
| Au/Ag fluorescent nanoclusters | Bioimaging Chemo and biosensing Luminescent films for sensing | [51,61,68,69] |
| Luminescent organometallic complexes | Temperature sensing Hypoxia sensing Silver metal sensing Sensing small molecules Eradication of carcinoma cells Humidity sensors Determination of heavy metals (Hg2+, Ag+, Cu2+, etc.) | [46,56,70,71,72,77] |
| Selective Applications of AuNPs & AgNPs | Comments | References |
|---|---|---|
| Calorimetric detection by AuNPs | Nanoplasmonic molecular ruler by AuNPs decorated with DNA | [71,72] |
| Sensing biomolecules by AuNPs | Polyaniline stabilized AuNPs | [72,96] |
| Detection by SERS (surface-enhanced Raman scattering) of AuNPs | Probing different biomolecules of DNA or nucleic acids or differentiating tumor cells | [97] |
| Detection by FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer) of AuNPs | Detect analyte concentration by quenching | [72] |
| Sensing by SPR of AuNPs | Presence of analyte by a change in color | [79] |
| Hyperthermia or plasmonic photothermal therapy using AuNPs | Kill cancer cells The opening of polymeric capsules Melting of DNA or protein bonds Photoacoustic tomography Photothermal imaging | [97,98] |
| AuNPs as contrast agents | Using antibody labeled AuNPs (binding to anti-epidermal growth factor (EFGR)) Detecting cancer cells using a different optical imaging technique | [80,89] |
| Immunostaining by AuNPs | Visualization of cellular organelles using simple optical microscopy | [98] |
| Delivery by AuNPs | Genes DNA Nucleotides or biomolecules either by specific or nonspecific uptake (site specific receptors) | [72,96] |
| Catalysis by AuNPs | Prepared by physical deposition techniques | [99] |
| Differentiating tumor cells vs. normal cells by molecular imaging using AuNPs | Darkfield optical imaging of cancer cells Detection of bioconjugated cancer cells using enhanced Raman signals Detection of tumors in deep tissue using two-Photon enhanced luminescence | [100] |
| Delivery agents (AuNPs) | Multifunctional nanorods for gene delivery Release of plasmids DNA (by laser irradiation) | [101] |
| Diagnostic applications of silver nanoparticles | Biosensors for tagging and quantitative detection | [102] |
| Antibacterial applications of AgNPs | Garments Apparels Paints Wound-dressing gels Skin creams Industrial appliances for antibacterial properties | [102] |
| Conductive applications of AgNPs | Formation of conductive inks Enhances the thermal and electrical conductivity of electrical and optical materials | [103,104] |
| Optical applications of AgNPs | Detection and sensing using metal-enhanced fluorescence Detection and sensing using surface-enhanced Raman scattering | [103,104] |
| Chitosan Stabilized AuNPs and AgNPs | Property and/or Applications | References |
|---|---|---|
| CS-stabilized AuNPs | Demonstrating formation of AuNPs in absence of a reducing agent | [117] |
| Stabilization of Au and AgNPs within CS | Adopting/demonstrating “green” synthesis method for making AuNPs and AgNPs | [14] |
| Synthesis of positively charged AuNPs and negatively charged AgNPs | Adopting/demonstrating “green” synthesis method for making AuNPs and AgNPs | [14] |
| CS-coated AuNPs | Evaluating stability of different size AuNPs with respect to CS molecular weight and concentration | [119] |
| CS-stabilized AuNPs in presence of TPP | Effect of TPP and CS concentration on size and shape of AuNPs demonstrates AuNPs formation without any additional reducing agents | [117] |
| CS-capped AuNPs | Sensing heavy metal ions based on SPR changes | [121] |
| Gold–CS nanocomposites | Selective electrochemical sensors for the determination of antioxidants. Determination of polyphenol index in wines | [122] |
| CS-embedded AuNPs | As a substrate for SERS | [118] |
| CS–PAA–Au hybrid nanospheres via the one-pot route in aqueous media | Contrast agents and delivery agents | [123] |
| Surface functionalization of AuNRs with CS oligosaccharides | Provides multiple binding sites for robust coating and protection against aggregation and as delivery agents | [124] |
| CS-stabilized plasmonic nanoparticle | Penetration and uptake of therapeutic agents such as insulin across the mucosal membrane | [109] |
| CS-stabilized AgNPs | Enhance antibacterial activity and overcome concerns about human and environmental safety related to usage of these metal nanoparticles | [109] |
| CS-stabilized silver nanoparticles in presence of cotton fabric | Antibacterial activity of cotton fabrics | [113] |
| Silk fibroin/carboxymethyl, CS-stabilized AgNPs | Wound healing/wound dressing application | [111,112] |
| CS-stabilized NIR absorbing, anisotropic AgNPs | Demonstration of a photochemical method for stabilizing NIR AgNPs and their antipathogenic properties | [114] |
| CS-stabilized, anisotropic AgNPs | Substrate for SERS and single molecule detection | [115] |
| CS-stabilized nanotriangles | Novel biocompatible and highly effective photothermal transducers for in vitro cancer cell therapy | [116] |
| CS–Siloxane cross-linked silver nanocomposites | Enhanced antibacterial properties | [110] |
| CS-stabilized AgNPs—understanding effect of molecular weight of CS on the size of AgNPs | Antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus | [13] |
| Synthesis of silver/CS/polyethylene glycol nanocomposites | “Green” synthesis methodology, understanding the effect of temperature on the size of AgNPs | [15] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marpu, S.B.; Benton, E.N. Shining Light on Chitosan: A Review on the Usage of Chitosan for Photonics and Nanomaterials Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061795
Marpu SB, Benton EN. Shining Light on Chitosan: A Review on the Usage of Chitosan for Photonics and Nanomaterials Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(6):1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061795
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarpu, Sreekar B., and Erin N. Benton. 2018. "Shining Light on Chitosan: A Review on the Usage of Chitosan for Photonics and Nanomaterials Research" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 6: 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061795
APA StyleMarpu, S. B., & Benton, E. N. (2018). Shining Light on Chitosan: A Review on the Usage of Chitosan for Photonics and Nanomaterials Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(6), 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061795