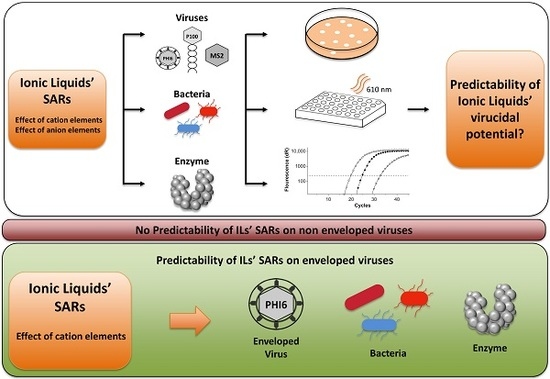
Virucidal or Not Virucidal? That Is the Question—Predictability of Ionic Liquid’s Virucidal Potential in Biological Test Systems
Abstract
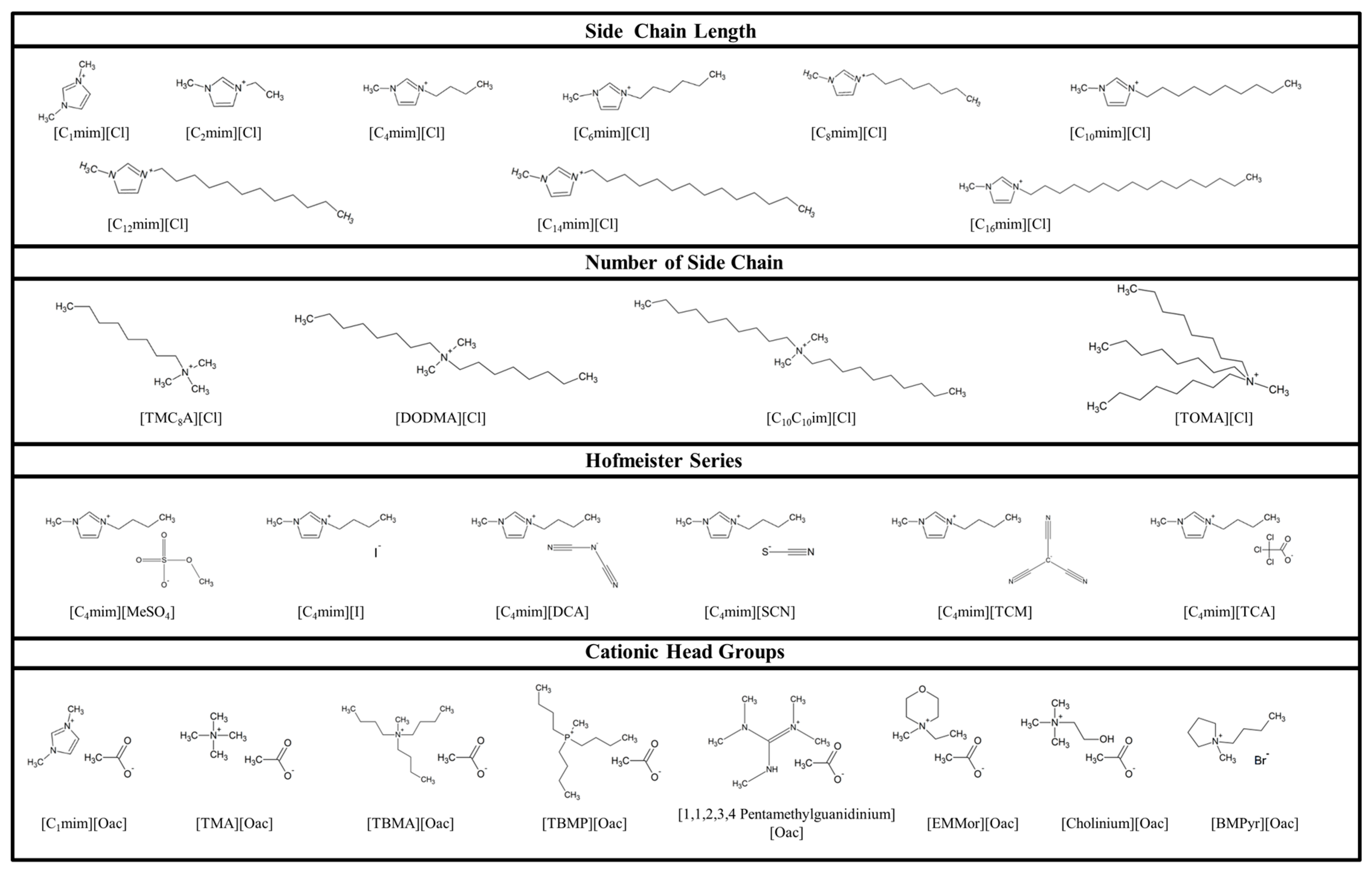
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
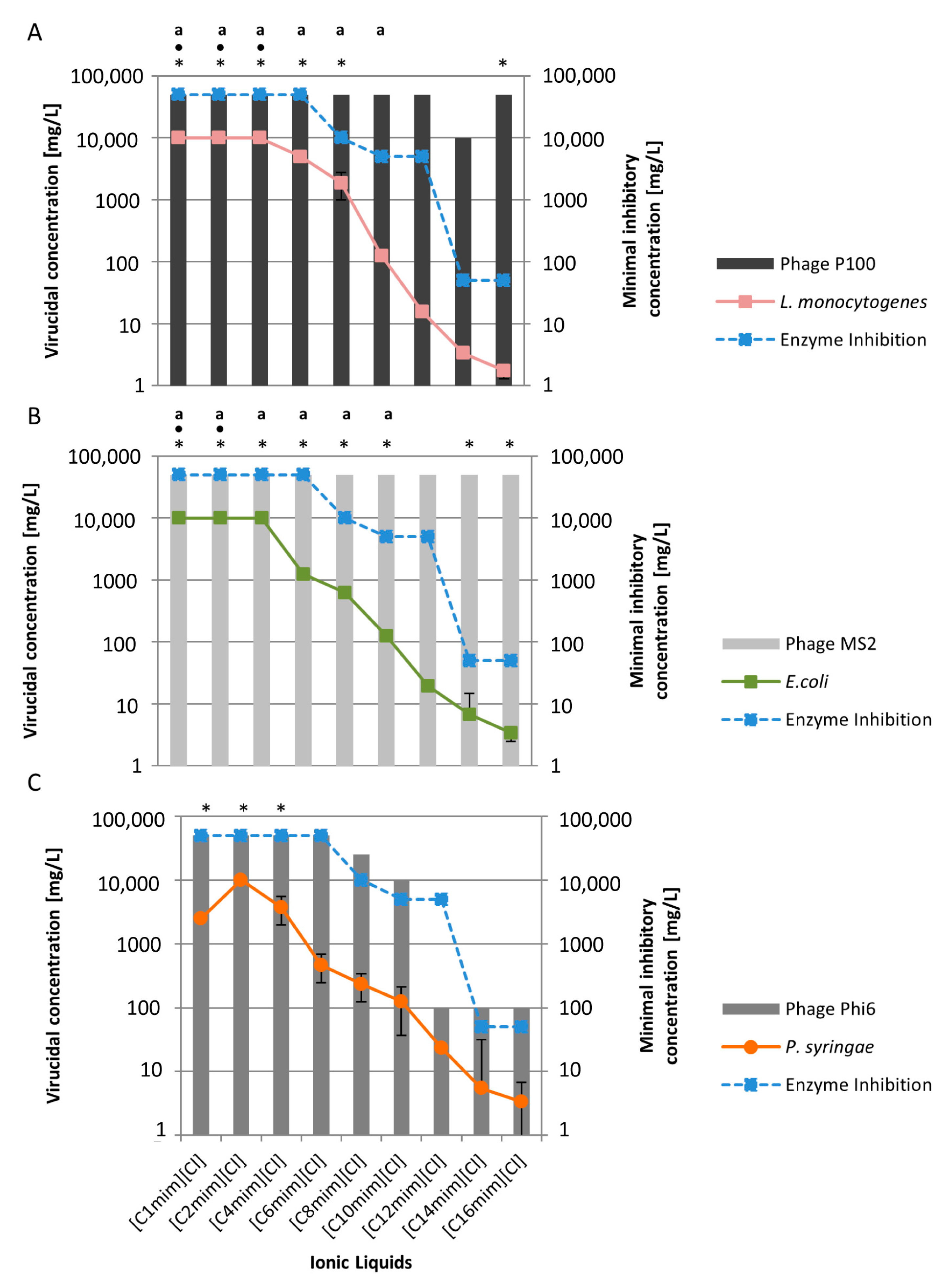
2.1. Behaviour of Viruses to the Cationic Alkyl Side Chain Effect
2.2. Virucidal Activity Correlates with the Number of Cationic Side Chains
2.3. Virus Inactivation Is Independent of Cationic Head Group
2.4. Anion Chaotropicity Does Not Exhibit Virucidal Activity
3. Material & Methods
3.1. Ionic Liquids
3.2. Phages and Host Strains
3.3. Numeration of Plaque Forming Units
3.4. Determination of Virucidal Concentration (VC)
3.5. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assessment
3.6. qPCR Enzyme Inhibition Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bailey, M.M.; Townsend, M.B.; Jernigan, P.L.; Sturdivant, J.; Hough-Troutman, W.L.; Rasco, J.F.; Swatloski, R.P.; Rogers, R.D.; Hood, R.D. Developmental toxicity assessment of the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride in CD-1 mice. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Radošević, K.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Halambek, J.; Gaurina Srček, V. A brief overview of the potential environmental hazards of ionic liquids. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, J.; Consorti, C.S.; Spencer, J. Room temperature molten salts: Neoteric “green” solvents for chemical reactions and processes. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2000, 11, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrey, J.D.; Turner, M.B.; Rogers, R.D. Selection of ionic liquids for green chemical applications. In Ionic Liquids as Green Solvents; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 856, pp. 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Thuy Pham, T.P.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolte, S.; Matzke, M.; Arning, J.; Boschen, A.; Pitner, W.-R.; Welz-Biermann, U.; Jastorff, B.; Ranke, J. Effects of different head groups and functionalised side chains on the aquatic toxicity of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.K.K.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Venugopalan, V.P. Long alkyl-chain imidazolium ionic liquids: Antibiofilm activity against phototrophic biofilms. Colloid Surf. B 2017, 155, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolte, S.; Arning, J.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Matzke, M.; Stock, F.; Thiele, K.; Uerdingen, M.; Welz-Biermann, U.; Jastorff, B.; Ranke, J. Anion effects on the cytotoxicity of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.G.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Alviano, D.S.; Coelho, M.A.Z. Toxicity of ionic liquids toward microorganisms interesting to the food industry. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37157–37163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.; Spulak, M.; Garcia, M.T.; Gathergood, N. Antimicrobial toxicity studies of ionic liquids leading to a ‘hit’ mrsa selective antibacterial imidazolium salt. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyhing-Zerrer, N.; Gundolf, T.; Kalb, R.; Oßmer, R.; Rossmanith, P.; Mester, P. Predictability of ionic liquid toxicity from a SAR study on different systematic levels of pathogenic bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; Marques, C.S.; Rosatella, A.A.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Gonçalves, F.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Toxicity assessment of various ionic liquid families towards vibrio fischeri marine bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 76, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, D.O.; PetkoVC, M.; Silva Pereira, C. Ionic liquids as unforeseen assets to fight life-threatening mycotic diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendleton, J.N.; Gilmore, B.F. The antimicrobial potential of ionic liquids: A source of chemical diversity for infection and biofilm control. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajfarajollah, H.; Mokhtarani, B.; Noghabi, K.A.; Sharifi, A.; Mirzaei, M. Antibacterial and antiadhesive properties of butyl-methylimidazolium ionic liquids toward pathogenic bacteria. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 42751–42757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mester, P.; Wagner, M.; Rossmanith, P. Antimicrobial effects of short chained imidazolium-based ionic liquids—Influence of anion chaotropicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 111, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, T.J. Ionic liquids—Pharmaceutical potential. Sci. Prog. 2012, 95, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, R.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M.; Araujo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; da Ponte, M.N.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z. Development of novel ionic liquids based on ampicillin. Med. Chem. Commun. 2012, 3, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Teixeira, V.; Rodrigues, D.; Fernandes, R.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z.; Branco, L.C. Antibacterial activity of ionic liquids based on ampicillin against resistant bacteria. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4301–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Kelley, S.P.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Chemistry: Develop ionic liquid drugs. Nature 2015, 528, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrewsky, M.; Lovejoy, K.S.; Kern, T.L.; Miller, T.E.; Le, V.; Nagy, A.; Goumas, A.M.; Iyer, R.S.; Del Sesto, R.E.; Koppisch, A.T.; et al. Ionic liquids as a class of materials for transdermal delivery and pathogen neutralization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13313–13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, G.; Macinga, D.; Arbogast, J.; Jaykus, L.A. Efficacy of commonly used disinfectants for inactivation of human noroviruses and their surrogates. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, N.; Rodoni, B.; Constable, F.; Varghese, S.; Davis, J.H. Enhanced stabilization of the tobacco mosaic virus using protic ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 10119–10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampf, G. Efficacy of ethanol against viruses in hand disinfection. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franck, K.T.; Nielsen, R.T.; Holzknecht, B.J.; Ersbøll, A.K.; Fischer, T.K.; Böttiger, B. Norovirus genotypes in hospital settings: Differences between nosocomial and community-acquired infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, J. Surrogate viruses for testing virucidal efficacy of chemical disinfectants. J. Hosp. Infect. 2004, 56, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopmans, M.; Duizer, E. Foodborne viruses: An emerging problem. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 90, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hall, A.J.; Robinson, A.E.; Verhoef, L.; Premkumar, P.; Parashar, U.D.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fister, S.; Mester, P.; Sommer, J.; Witte, A.K.; Kalb, R.; Wagner, M.; Rossmanith, P. Virucidal influence of ionic liquids on phages P100 and MS2. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäälinoja, H.T.; Huiskonen, J.T.; Butcher, S.J. Electron cryomicroscopy comparison of the architectures of the enveloped bacteriophages ϕ6 and ϕ8. Structure 2007, 15, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, L.P.; Hirvonen, J.J.; Laurinmäki, P.; Butcher, S.J.; Bamford, D.H.; Poranen, M.M. Bacteriophage ϕ6 nucleocapsid surface protein 8 interacts with virus-specific membrane vesicles containing major envelope protein 9. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5376–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgeon, N.; Toulouse, M.J.; Martel, B.; Moineau, S.; Duchaine, C. Comparison of five bacteriophages as models for viral aerosol studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4242–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, S.P.; Goncalves, A.M.; Sintra, T.; Pereira, J.L.; Goncalves, F.; Coutinho, J.A. Designing ionic liquids: The chemical structure role in the toxicity. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubalo, M.C.; Radosevic, K.; Redovnikovic, I.R.; Slivac, I.; Srcek, V.G. Toxicity mechanisms of ionic liquids. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolte, S.; Arning, J.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Muller, A.; Pitner, W.-R.; Welz-Biermann, U.; Jastorff, B.; Ranke, J. Effects of different head groups and functionalised side chains on the cytotoxicity of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranke, J.; Mölter, K.; Stock, F.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Poczobutt, J.; Hoffmann, J.; Ondruschka, B.; Filser, J.; Jastorff, B. Biological effects of imidazolium ionic liquids with varying chain lengths in acute vibrio fischeri and wst-1 cell viability assays. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 58, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.P.F.; Azevedo, A.M.O.; Pinto, P.C.A.G.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S. Environmental impact of ionic liquids: Recent advances in (Eco)toxicology and (Bio)degradability. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2321–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docherty, K.M.; Kulpa, J.C.F. Toxicity and antimicrobial activity of imidazolium and pyridinium ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.A.; Papaiconomou, N.; Lee, J.M.; Salminen, J.; Clark, D.S.; Prausnitz, J.M. In vitro cytotoxicities of ionic liquids: Effect of cation rings, functional groups, and anions. Environ. Toxicol. 2009, 24, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Tong, Z.-H.; Li, L.-L.; Yu, H.-Q. Toxic effects of imidazolium-based ionic liquids on caenorhabditis elegans: The role of reactive oxygen species. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2399–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterno, A.; D’Anna, F.; Musumarra, G.; Noto, R.; Scire, S. A multivariate insight into ionic liquids toxicities. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 23985–24000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arning, J.; Stolte, S.; Boschen, A.; Stock, F.; Pitner, W.-R.; Welz-Biermann, U.; Jastorff, B.; Ranke, J. Qualitative and quantitative structure activity relationships for the inhibitory effects of cationic head groups, functionalised side chains and anions of ionic liquids on acetylcholinesterase. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.M.O.; Pereira, S.A.P.; Passos, M.L.C.; Costa, S.P.F.; Pinto, P.C.A.G.; Araujo, A.R.T.S.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S. Assessment of ionic liquids’ toxicity through the inhibition of acylase I activity on a microflow system. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, A.; Syguda, A.; Wyrwas, B.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Heipieper, H.J. Toxicity evaluation of selected ammonium-based ionic liquid forms with MCPP and dicamba moieties on pseudomonas putida. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Galla, H.-J.; Drücker, P. Membrane interactions of ionic liquids and imidazolium salts. Biophys. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, M.J.; Li, F.; Morrall, S.W.; Versteeg, D.J. The relationship between the interfacial properties of surfactants and their toxicity to aquatic organisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranke, J.; Müller, A.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Stock, F.; Stolte, S.; Arning, J.; Störmann, R.; Jastorff, B. Lipophilicity parameters for ionic liquid cations and their correlation to in vitro cytotoxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 67, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, G.; Russell, A.D. Antiseptics and disinfectants: Activity, action, and resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H. Methods for stabilizing and activating enzymes in ionic liquids—A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.I.; Goncalves, A.M.M.; Pereira, J.L.; Figueiredo, B.F.H.T.; e Silva, F.A.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Goncalves, F. Environmental safety of cholinium-based ionic liquids: Assessing structure-ecotoxicity relationships. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4657–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Sobaszkiewicz, K.; Mirska, I. Anti-microbial activities of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, M.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Silva Pereira, C. Ionic liquids: A pathway to environmental acceptability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1383–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, D.; Weingartner, H.; Herrmann, C. Protein denaturation by ionic liquids and the hofmeister series: A case study of aqueous solutions of ribonuclease A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8887–8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurinavicius, S.; Kakela, R.; Bamford, D.H.; Somerharju, P. The origin of phospholipids of the enveloped bacteriophage phi6. Virology 2004, 326, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silhavy, T.J.; Kahne, D.; Walker, S. The bacterial cell envelope. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Boil. 2010, 2, a000414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brion, G.M.; Silverstein, J. Iodine disinfection of a model bacteriophage, MS2, demonstrating apparent rebound. Water Res. 1999, 33, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, O.B.; Shah, S.N.; Lévêque, J.-M.; Mutalib, M.I.A.; El-Harbawi, M.; Khan, A.S.; Alnarabiji, M.S.; Al-Absi, H.R.H.; Ullah, Z. Study of the antimicrobial activity of cyclic cation-based ionic liquids via experimental and group contribution qsar model. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatain-Ly, M.H.; Moussaoui, S.; Rigobello, V.; Demarigny, Y.; Vera, A. Antiviral effect of cationic compounds on bacteriophages. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalb, R.; Wesner, W.; Hermann, R.; Kotschan, M.; Schelch, M.; Staber, W. Method for Producing Ionic Liquids, Ionic Solids or Mixtures Thereof. U.S. Patent Application No. PCT/EP2004/009296, 10 March 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kalb, R.S.; Stepurko, E.N.; Emel’yanenko, V.N.; Verevkin, S.P. Carbonate based ionic liquid synthesis (cbils[registered sign]): Thermodynamic analysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 31904–31913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fister, S.; Fuchs, S.; Mester, P.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Wagner, M.; Rossmanith, P. The use of ionic liquids for cracking viruses for isolation of nucleic acids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 155, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, D.H.; Su, X. Efficacy of chemical treatments against murine norovirus, feline calicivirus, and MS2 bacteriophage. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocco, A.; Waddell, T.; Lingohr, E.; Johnson, R. Enumeration of bacteriophages using the small drop plaque assay system. In Bacteriophages; Clokie, M.J., Kropinski, A., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 501, pp. 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski, A.; Mazzocco, A.; Waddell, T.; Lingohr, E.; Johnson, R. Enumeration of bacteriophages by double agar overlay plaque assay. In Bacteriophages; Clokie, M.J., Kropinski, A., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 501, pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey, S.; Pegot, B.; Coleman, D.; Garcia, M.T.; Ferguson, D.; Quilty, B.; Gathergood, N. Biodegradable, non-bactericidal oxygen-functionalised imidazolium esters: A step towards ‘greener’ ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmanith, P.; Krassnig, M.; Wagner, M.; Hein, I. Detection of listeria monocytogenes in food using a combined enrichment/real-time PCR method targeting the prfA gene. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Effect of Number of Side Chain | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virucidal Concentration mg/L | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration mg/L | ||||||
| Ionic Liquid | P100 | MS2 | Phi6 | L. monocytogenes | E. coli | P. syringae | Enzyme |
| ≥4 Log10 Units | ≥4 Log10 Units | ≥4 Log10 Units | |||||
| [TMC8A][Cl] | 10,000 | 50,000 | 10,000 | 729.17 | 1458.33 | 1041.67 | 50,000 |
| (10,000; 10,000) | (50,000; 50,000) | (10,000; 10,000) | (321.5; 1250) | (1250; 2500) | (625; 1250) | (50,000; 50,000) | |
| [DODMA][Cl] | 10,000 a | >50,000 a | 1000 | 31.25 | 62.50 | 62.50 | 5000 |
| (10,000; 10,000) | (>50,000; >50,000) | (1000; 1000) | (31.25; 31.25) | (625; 625) | (62.5; 62.5) | (5000; 5000) | |
| [C10C10im][Cl] | 10,000 | >50,000 | 100 | 1.43 | 3.39 | 3.65 | 50 |
| (10,000; 10,000) | (>50,000; >50,000) | (100; 100) | (0.8; <4) | (0.8; <4) | (1.6; 7.8) | (50; 50) | |
| [TOMA][Cl] | >50,000 a | >50,000 a | 1000 | 2.34 | 8.98 | 9.38 | 2750 |
| (>50,000; >50,000) | (>50,000; 50,000) | (1000; 1000) | (<0.78; <4) | (6.3; 7.8) | (<0.78; 15.6) | (5000; 500) | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sommer, J.; Fister, S.; Gundolf, T.; Bromberger, B.; Mester, P.-J.; Witte, A.K.; Kalb, R.; Rossmanith, P. Virucidal or Not Virucidal? That Is the Question—Predictability of Ionic Liquid’s Virucidal Potential in Biological Test Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030790
Sommer J, Fister S, Gundolf T, Bromberger B, Mester P-J, Witte AK, Kalb R, Rossmanith P. Virucidal or Not Virucidal? That Is the Question—Predictability of Ionic Liquid’s Virucidal Potential in Biological Test Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030790
Chicago/Turabian StyleSommer, Julia, Susanne Fister, Tobias Gundolf, Birgit Bromberger, Patrick-Julian Mester, Anna Kristina Witte, Roland Kalb, and Peter Rossmanith. 2018. "Virucidal or Not Virucidal? That Is the Question—Predictability of Ionic Liquid’s Virucidal Potential in Biological Test Systems" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030790
APA StyleSommer, J., Fister, S., Gundolf, T., Bromberger, B., Mester, P.-J., Witte, A. K., Kalb, R., & Rossmanith, P. (2018). Virucidal or Not Virucidal? That Is the Question—Predictability of Ionic Liquid’s Virucidal Potential in Biological Test Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030790