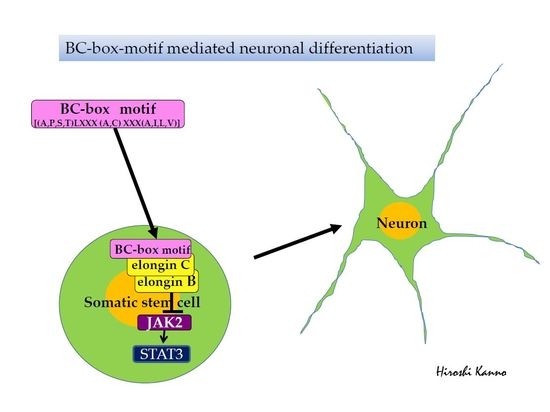
BC-Box Motif-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation of Somatic Stem Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
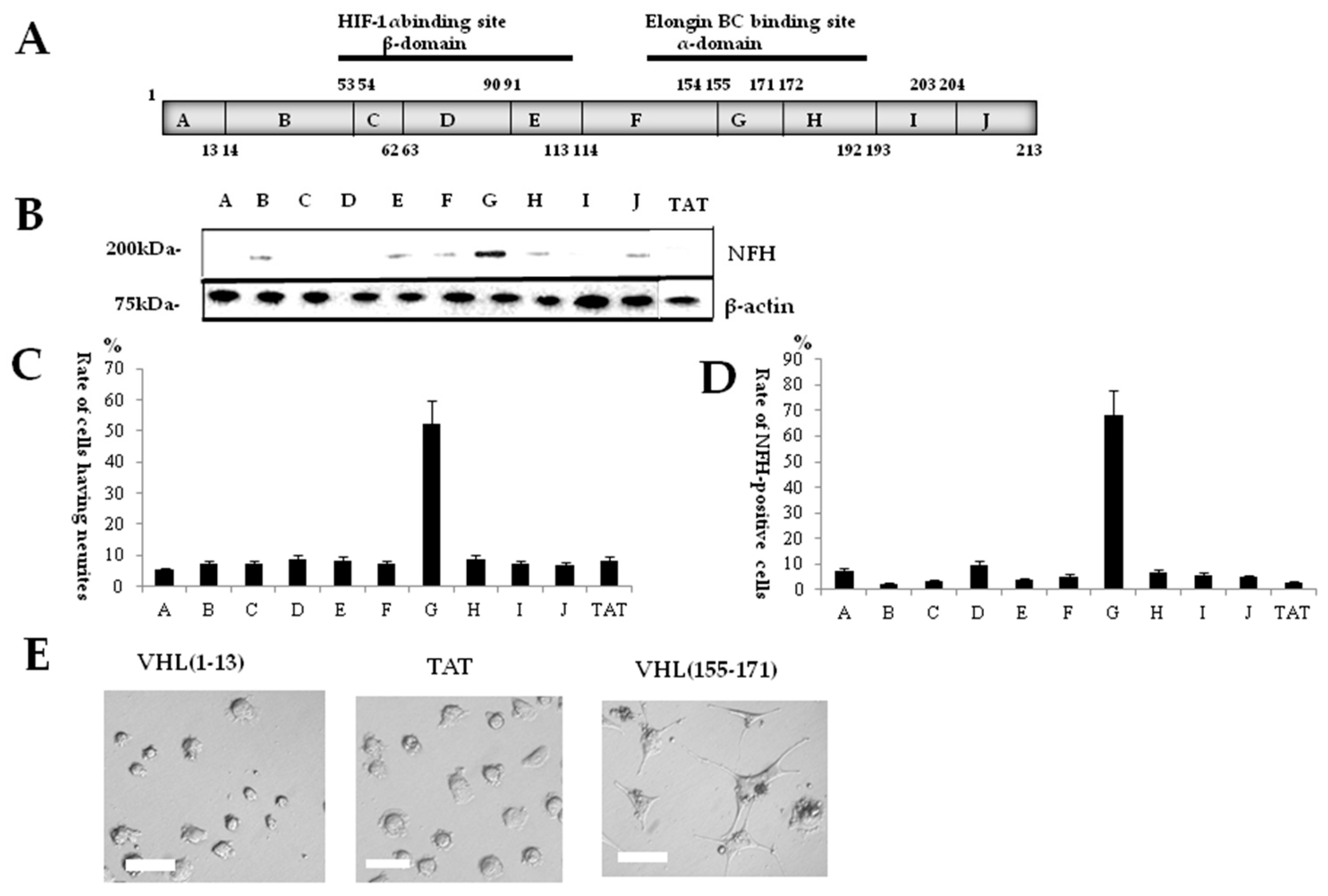
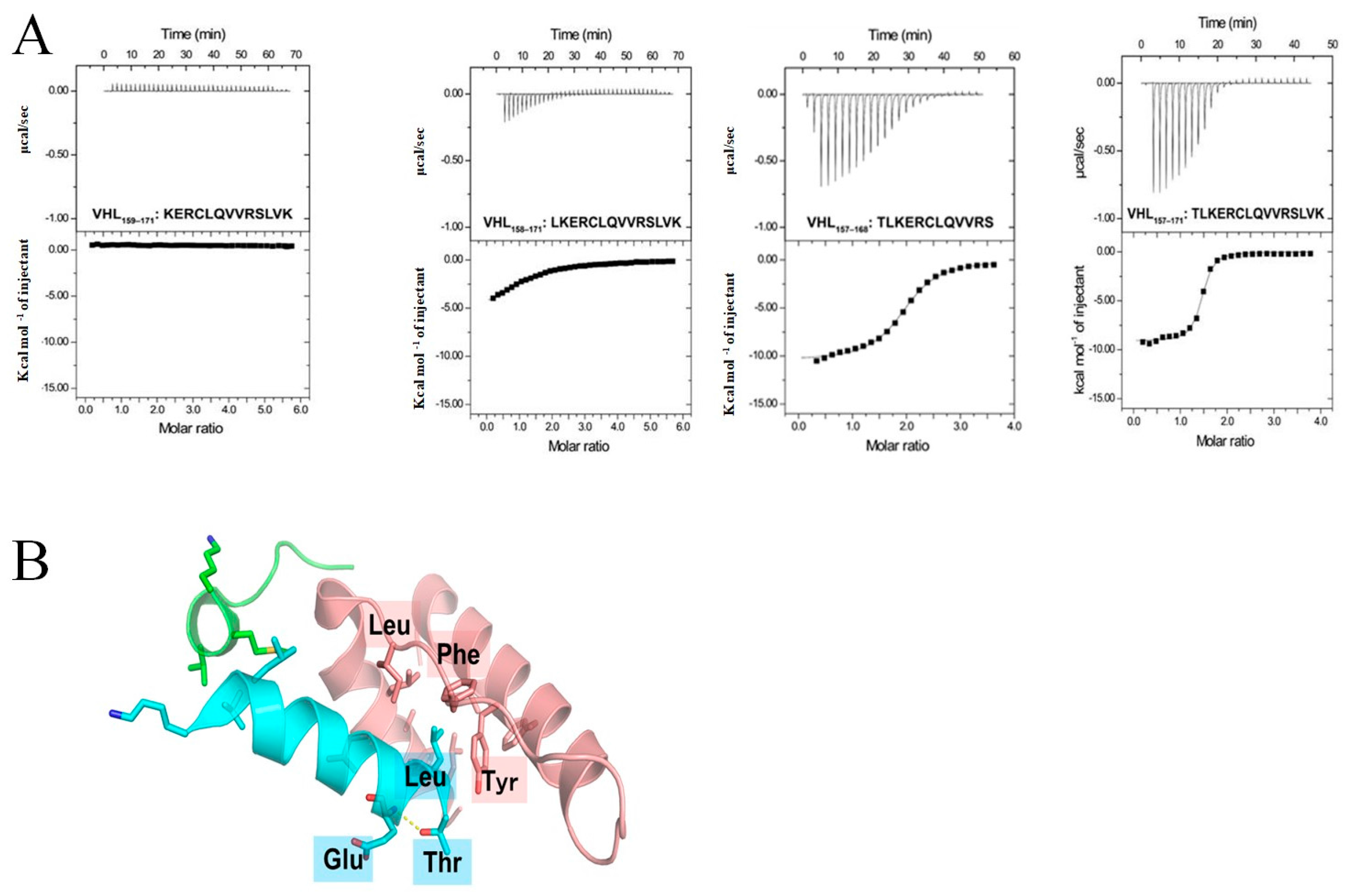
2.1. Identification of a Neuronal Differentiation Domain in pVHL
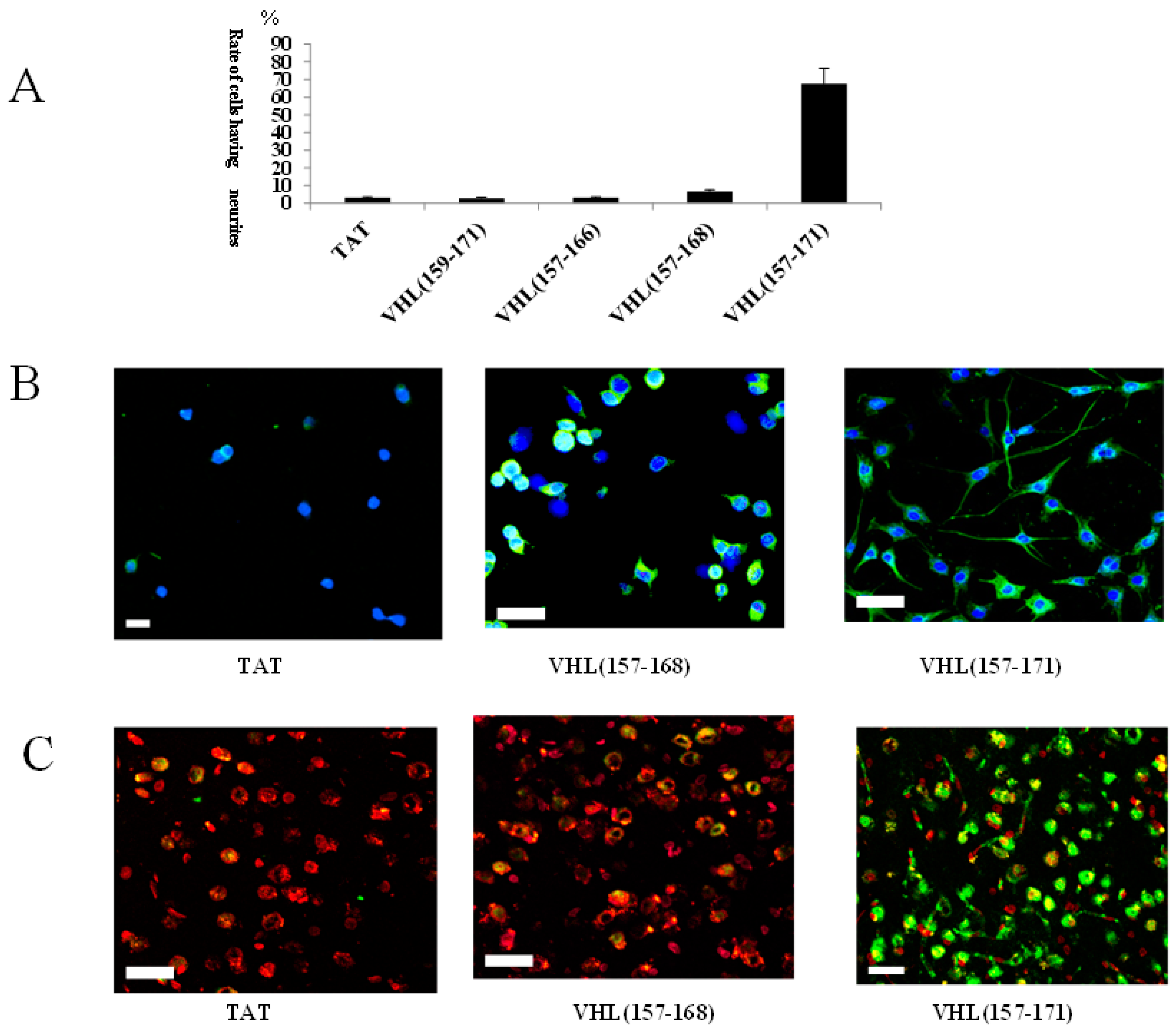
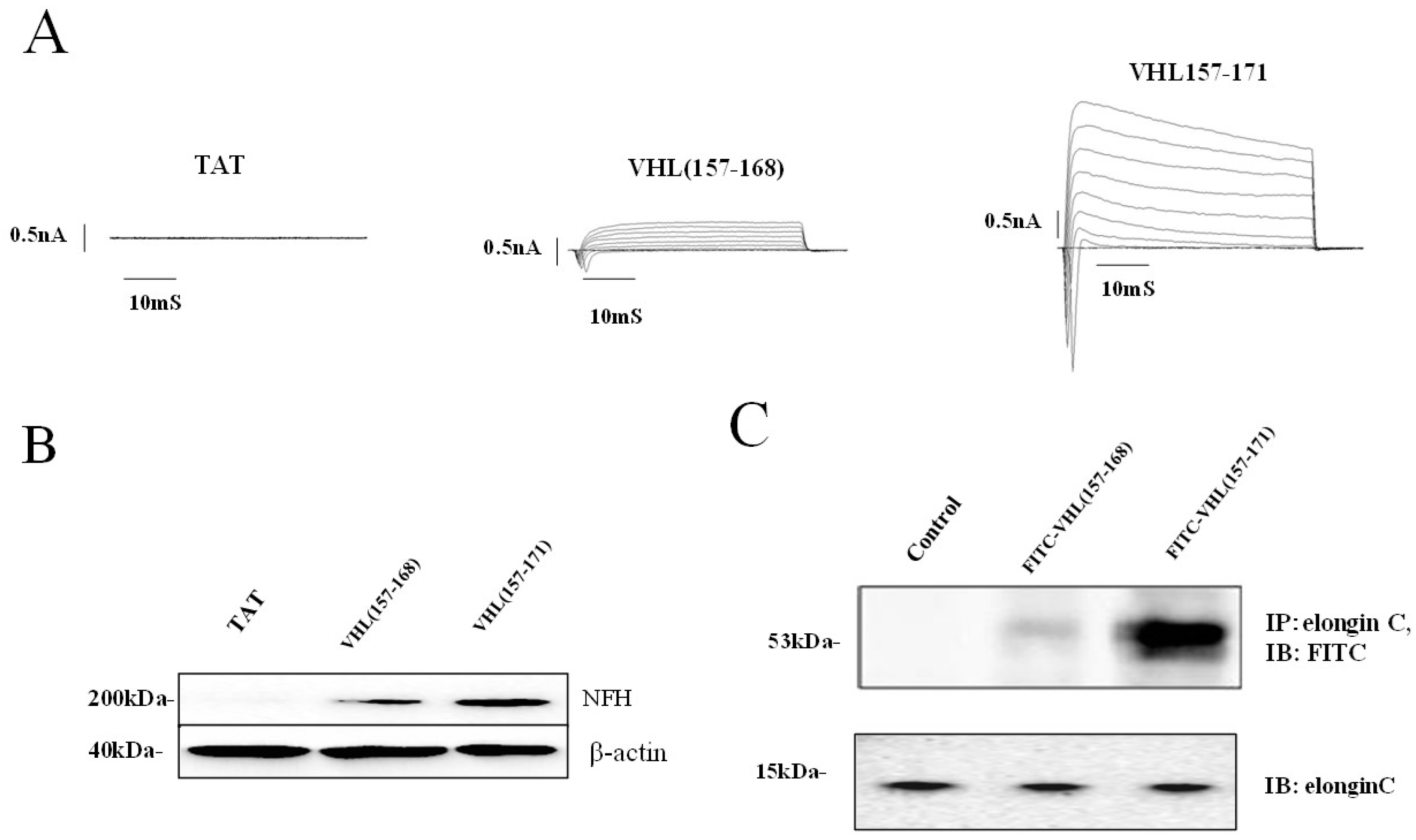
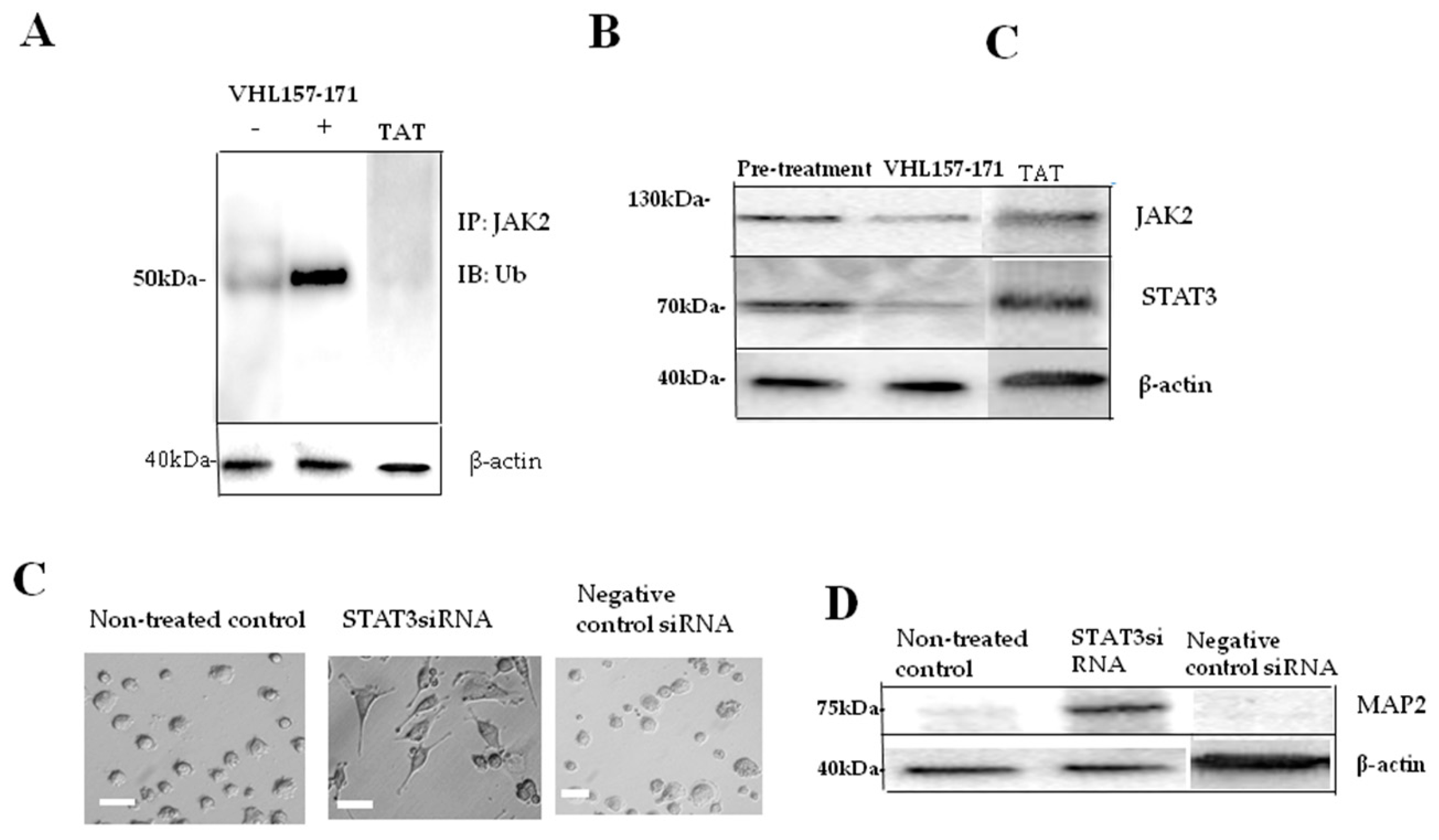
2.2. JAK2 Ubiquitination and Neuronal Differentiation
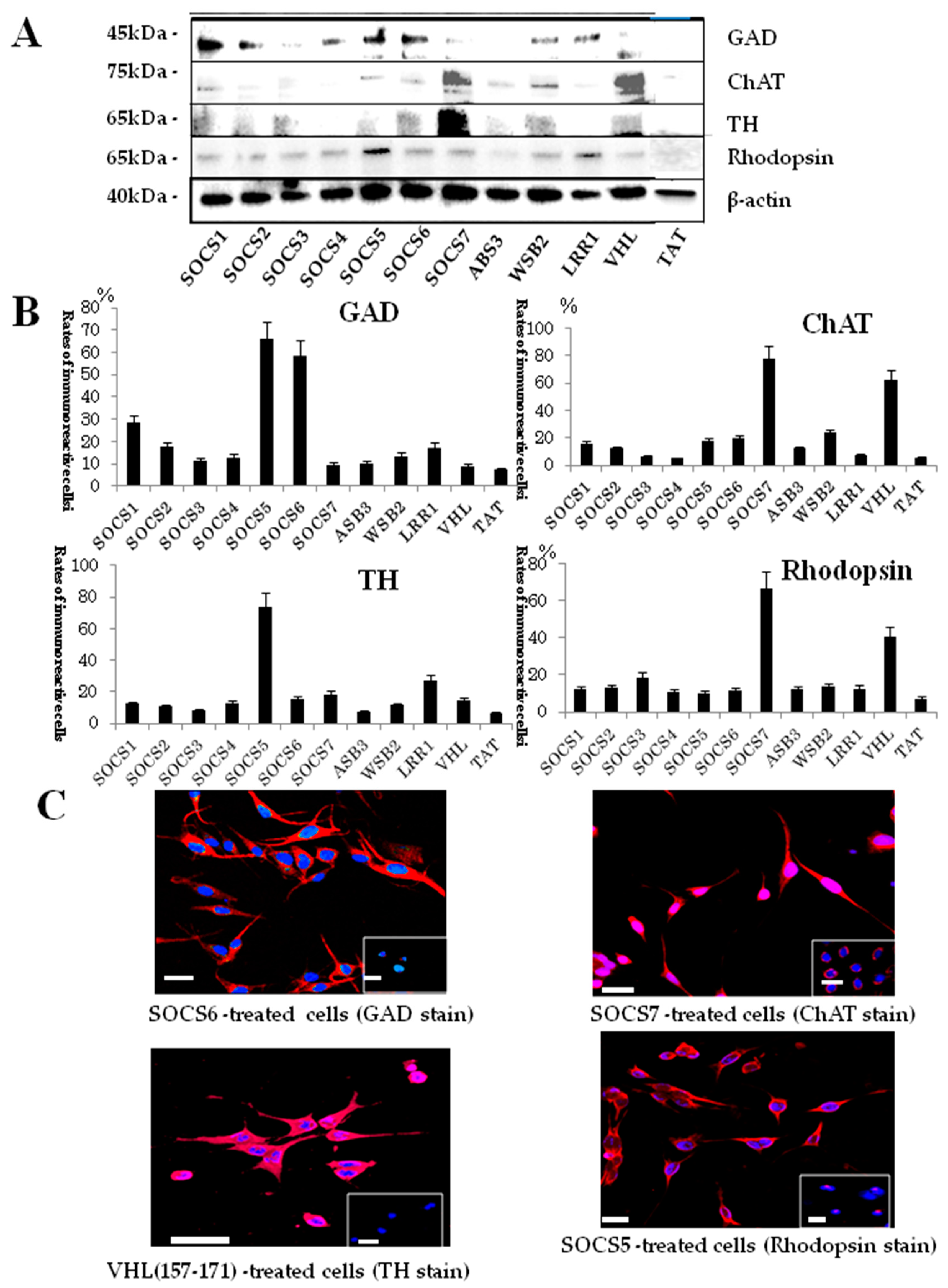
2.3. Neuronal Differentiation Domains in Other BC-Box Proteins
2.4. Protein Expression in BC-Box Protein-Derived Neuronal-Differentiation-Domain-Peptide-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Peptide Design and Synthesis
4.2. Cell Culture and Neuronal Differentiation
4.3. Gene Knockdown
4.4. Morphological Evaluation for Neuronal Differentiation
4.5. Immunocytochemisty
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Immunoprecipitation
4.9. Electrophysiology
4.10. Cloning, Overexpression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins for Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
4.11. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
4.12. Ubiquitination Assay
4.13. Approval of Animal Experiment
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Kanno, H.; Saljooque, F.; Yamamoto, I.; Hattori, S.; Yao, M.; Shuin, T.; Hoi-Sang, U. Role of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein during neuronal differentiation. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2820–2824. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Dezawa, M.; Shimazu, S.; Baba, M.; Sawada, H.; Kuroiwa, Y.; Yamamoto, I.; Kanno, H. Transfer of the von Hippel-Lindau gene to neuronal progenitor cells in treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, H.; Tajima, N.; Nagashima, Y.; Yao, M.; Baba, M.; Goto, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Yamamoto, I.; Okuda, K.; Kanno, H. Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein transforms human neuroblastoma cells into functional neuron-like cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 7004–7011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamura, T.; Maenaka, K.; Kotoshiba, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Kohda, D.; Conaway, R.C.; Conaway, J.W.; Nakayama, K.I. VHL-box and SOCS-box domains determine binding specificity for Cul2-Rbx1 and Cul5-Rbx2 modules of ubiquitin ligases. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 3055–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, H.; Nakano, S.; Kubo, A.; Mimura, T.; Tajima, N.; Sugimoto, N. Neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells by intracellular delivery of synthetic oligopeptide derived from von Hippel-Lindau protein. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Kanno, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kubo, A.; Sato, F.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Saito, T. Transplantation of von Hippel-Lindau peptide delivered neural stem cells promotes recovery in the injured rat spinal cord. Neuroreport 2009, 20, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Kanno, H.; Maeda, K.; Yoshida, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Kubo, A.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Saito, T. Engrafted VHL peptide-delivered bone marrow stromal cells promote spinal cord repair in rats. Neuroreport 2010, 21, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, A.; Yoshida, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Yokoyama, T.; Mimura, T.; Nishiguchi, T.; Higashida, T.; Yamamoto, I.; Kanno, H. Efficient generation of dopamine neuron-like cells from skin-derived precursors with a synthetic peptide derived from von Hippel-Lindau protein. Stem Cells Dev. 2009, 18, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashida, T.; Jitsuk, I.S.; Kubo, A.; Mitsushima, D.; Kamiya, Y.; Kanno, H. Skin-derived precursors differentiate into dopaminergic neuronal cells in the brains of Parkinson’s disease model rats. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørbaek, C.; Bjørbaek, C.; Elmquist, J.K.; El-Haschimi, K.; Kelly, J.; Ahima, R.S.; Hileman, S.; Flier, J.S. Activation of SOCS-3 messenger ribonucleic acid in the hypothalamus by ciliary neurotrophic factor. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldshmit, Y.; Walters, C.E.; Scot, H.J.; Greenhalgh, C.J.; Turnley, A.M. SOCS2 induces neurite outgrowth by regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16349–16355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Mishra, K.; Surolia, A.; Banerjee, K. Suppressor of cytokine signalling-6 promotes neurite outgrowth via JAK2/STAT5-mediated signalling pathway, involving negative feedback inhibition. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasukawa, T.; Bhatt, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Kawauchi, J.; Takahashi, H.; Tsutsui, A.; Muraoka, T.; Inoue, M.; Tsuda, M.; Kitajima, S.; et al. Transcriptional elongation factor elongin A regulated retinoic acid-induced gene expression during neuronal differentiation. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, K.K.; Gupta, S.; Banerjee, K. SOCS3 induces neurite differentiation and promotes neuronal cell survival. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Ma, X.L.; Sun, J.; He, J.Q.; Shen, L.; Li, F.G. Overexpression of suppressors of cytokine signaling 1 regulate the proliferation and differentiation of rat-derived neural stem cells. Acta Histochem. 2017, 117, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohh, M.; Takagi, Y.; Aso, T.; Stebbins, C.E.; Pavletich, N.P.; Zbar, B.; Conaway, R.C.; Conaway, J.W.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. Synthetic peptides define critical contacts between elongin C, elongin B, and the von Hippel-Lindau protein. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 11, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamizono, S.; Hanada, T.; Yasukawa, H.; Minoguchi, S.; Kato, R.; Minoguchi, M.; Kato, R.; Minoguchi, M.; Hattori, K.; Hatakeyama, S.; et al. The SOCS box of SOCS-1 accelerates ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of TEL-JAK2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 12530–12538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Nouhi, Z.; Chughtai, N.; Ali, S. SHP-2 regulates SOCS-1-medated Janus kinase-2 ubiquitination/degradation downstream of the prolactin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52021–52031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russel, R.C.; Sufan, R.I.; Zhou, B.; Heir, P.; Bunda, S.; Sybingco, S.S.; Greer, S.N.; Roche, O.; Heathcote, S.A.; Chow, V.W.; et al. Loss of JAK2 regulation via a heterodimeric VHL-SOCS1 E3 ubiquitin ligase underlines Chuvash polycythemia. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungureanu, D.; Saharinen, P.; Junttila, I.; Hilton, D.J.; Silvennoinen, O. Regulation of JAK2 through the ubiquitin-proteosome pathway involves phosphorylation of JAK2 on Y1007 and interaction with SOCS-1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 3316–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.; Schwarze, S.R.; Mermelstein, S.J.; Waksman, G.; Dowdy, S.F. Synthetic protein transduction domains: Enhanced transduction potential in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.C.; Yang, H.; Fribrourgh, J.L.; Wolfe, L.S.; Xiong, Y. Insights into Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase recruitment: Structure of the VHL-EloBC-Cul2 complex. Structure 2014, 23, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Peptide Name | Amino Acid Sequence |
|---|---|
| TAT | YARAAARQARA |
| VHL(1–13) | YARAAARQARAMPRRAENWDEAEV |
| VHL(14–53) | YARAAARQARAGAEEAGVEEYGPEEDGGEESGAEESGPEESGPEELGAEEE |
| VHL(54–62) | YARAAARQARAMEAGRPRPV |
| VHL(63–90) | YARAAARQARALRSVNSRE PSQVIFCNRS PRVVLPVWLN |
| VHL(91–113) | YARAAARQARAFDGEPQPYPTLPPGTGRRIHSYR |
| VHL(114–154) | YARAAARQARAGHLWLFRDAGTHDGLV NQTELFVPSLNVDG |
| VHL(155–171) | YARAAARQARAVYTLKERCLQVVRSLVK |
| VHL(172–192) | YARAAARQARAPENYRRLDIVRSLYEDLEDHP |
| VHL(193–203) | YARAAARQARANVQKDLERLTD |
| VHL(204–213) | YARAAARQARAERIAHQRMGD |
| VHL(159–171) | YARAAARQARAKERCLQVVRS |
| VHL(157–166) | YARAAARQARA TLKERCLQVV |
| VHL(157–168) | YARAAARQARATLKERCLQVVRS |
| VHL(157–171) | YARAAARQARATLKERCLQVVRSLVK |
| FITC-VHL(157–168) | YARAAARQARATLKERCLQVVRS |
| FITC-VHL(157–171) | YARAAARQARATLKERCLQVVRSLVK |
| SOCS1-A | YARAAARQARA PLQELCRQRI |
| SOCS1-B | YARAAARQARAPLQELCRQRIVAAVG |
| SOCS2-A | YARAAARQARATLQHFCRLAI |
| SOCS2-B | YARAAARQARATLQHFCRLAINKCT G |
| SOCS3-A | YARAAARQARATLQHLCRKTV |
| SOCS3-B | YARAAARQARATLQHLCRKTVNGHLD |
| SOCS4-A | YARAAARQARASLQHICRTVI |
| SOCS4-B | YARAAARQARASLQHICRTVICNCTT |
| SOCS5-A | YARAAARQARA SLQYICRAVI |
| SOCS5-B | YARAAARQARASLQYICRAVICRCTT |
| SOCS6-A | YARAAARQARASLQYLCRFVI |
| SOCS6-B | YARAAARQARASLQYLCRFVIRQYTR |
| SOCS7-A | YARAAARQARASLQHLCRFRI |
| SOCS7-B | YARAAARQARASLQHLCRFRIRQLVR |
| ASB3-A | YARAAARQARASLTHLCRLEI |
| ASB3-B | YARAAARQARASLTHLCRLEIRSSIK |
| WSB2-A | YARAAARQARA SLKHLCRKAL |
| WSB2-B | YARAAARQARASLKHLCRKALRSFLT |
| LRR1-A | YARAAARQARATLLESSARTI |
| LRR1-B | YARAAARQARATLLESSARTILHNRI |
| Name | Sequence | KD (μM) | ΔH (kcal/mol) | ΔS (cal/mol/deg) | N (Sites) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VHL157–171 | TLKERCLQVVRSLVK | 0.54 ± 0.27 | −7.99 ± 1.60 | 2.01 ± 4.30 | 1.64 ± 0.32 |
| VHL158–171 | LKERCLQVVRSLVK | 18.7 ± 8.8 | −7.82 ± 1.52 | −4.38 ± 4.15 | 1.12 ± 0.01 |
| VHL159-171 | KERCLQVVRSLVK | - | - | - | - |
| VHL157–168 | TLKERCLQVVRS | 2.06 ± 0.09 | −10.3 ± 0.2 | −8.54 ± 0.74 | 1.89 ± 0.07 |
| Derivation | Sequence | Neurite Outgrowth Activity | Sequence | Neurite Outgrowth Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOCS-box family | ||||
| SOCS1 | PLQELCRQRI | - | PLQELCRQRIVAAVG | ++ |
| SOCS2 | TLQHFCRLAI | - | TLQHFCRLAINKCTG | + |
| SOCS3 | TLQHLCRKTV | - | TLQHLCRKTVNGHLD | ++ |
| SOCS4 | SLQHICRTVI | - | SLQHICRTVICNCTT | ++ |
| SOCS5 | SLQYICRAVI | + | SLQYICRAVICRCTT | +++ |
| SOCS6 | SLQYLCRFVI | - | SLQYLCRFVIRQYTR | ++ |
| SOCS7 | SLQHLCRFRI | + | SLQHLCRFRIRQLVR | +++ |
| ASB3 | SLTHLCRLEI | - | SLTHLCRLEIRSSIK | ++ |
| WSB2 | SLKHLCRKAL | - | SLKHLCRKALRSFLT | ++ |
| VHL-box family | ||||
| hLRR-1 | TLLESSARTI | - | TLLESSARTILHNRI | ++ |
| VHL | TLKERCLQVV | - | TLKERCLQVVRSLVK | +++ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanno, H.; Xu, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Kubo, A.; Higashida, T.; Kobayashi, N.B.; Yoshida, T.; Tanokura, M. BC-Box Motif-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation of Somatic Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020466
Kanno H, Xu Y, Miyakawa T, Kubo A, Higashida T, Kobayashi NB, Yoshida T, Tanokura M. BC-Box Motif-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation of Somatic Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020466
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanno, Hiroshi, Yuqun Xu, Taykua Miyakawa, Atsuhiko Kubo, Tetsuhiro Higashida, Nahoko Baily Kobayashi, Tetsuhiko Yoshida, and Masaru Tanokura. 2018. "BC-Box Motif-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation of Somatic Stem Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020466
APA StyleKanno, H., Xu, Y., Miyakawa, T., Kubo, A., Higashida, T., Kobayashi, N. B., Yoshida, T., & Tanokura, M. (2018). BC-Box Motif-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation of Somatic Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020466