Dissecting the Structure–Activity Relationship of Galectin–Ligand Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Galectins in Cancer and Translational Medicine
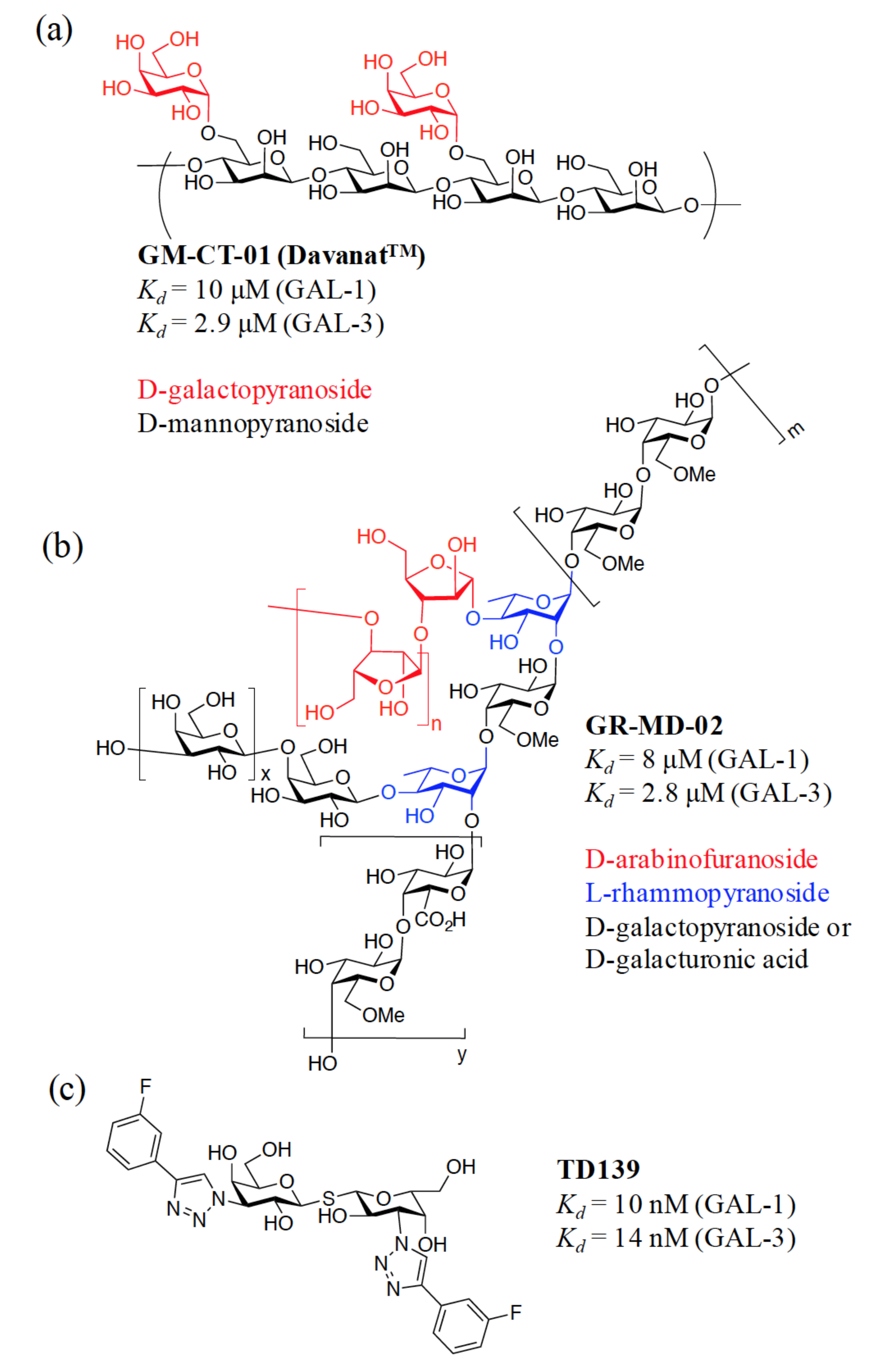
3. Rationale for the Design of Anti-Galectin Agents
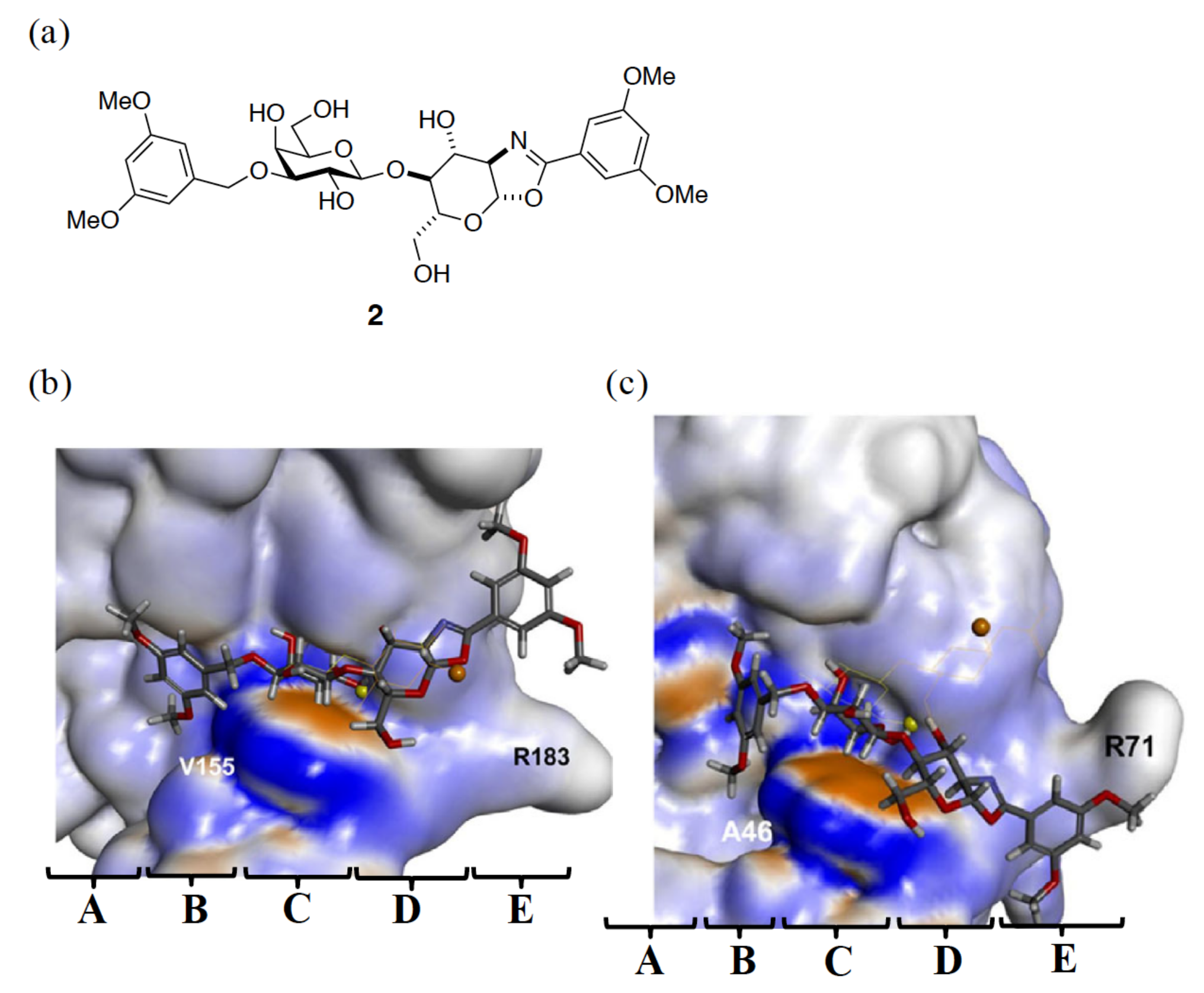
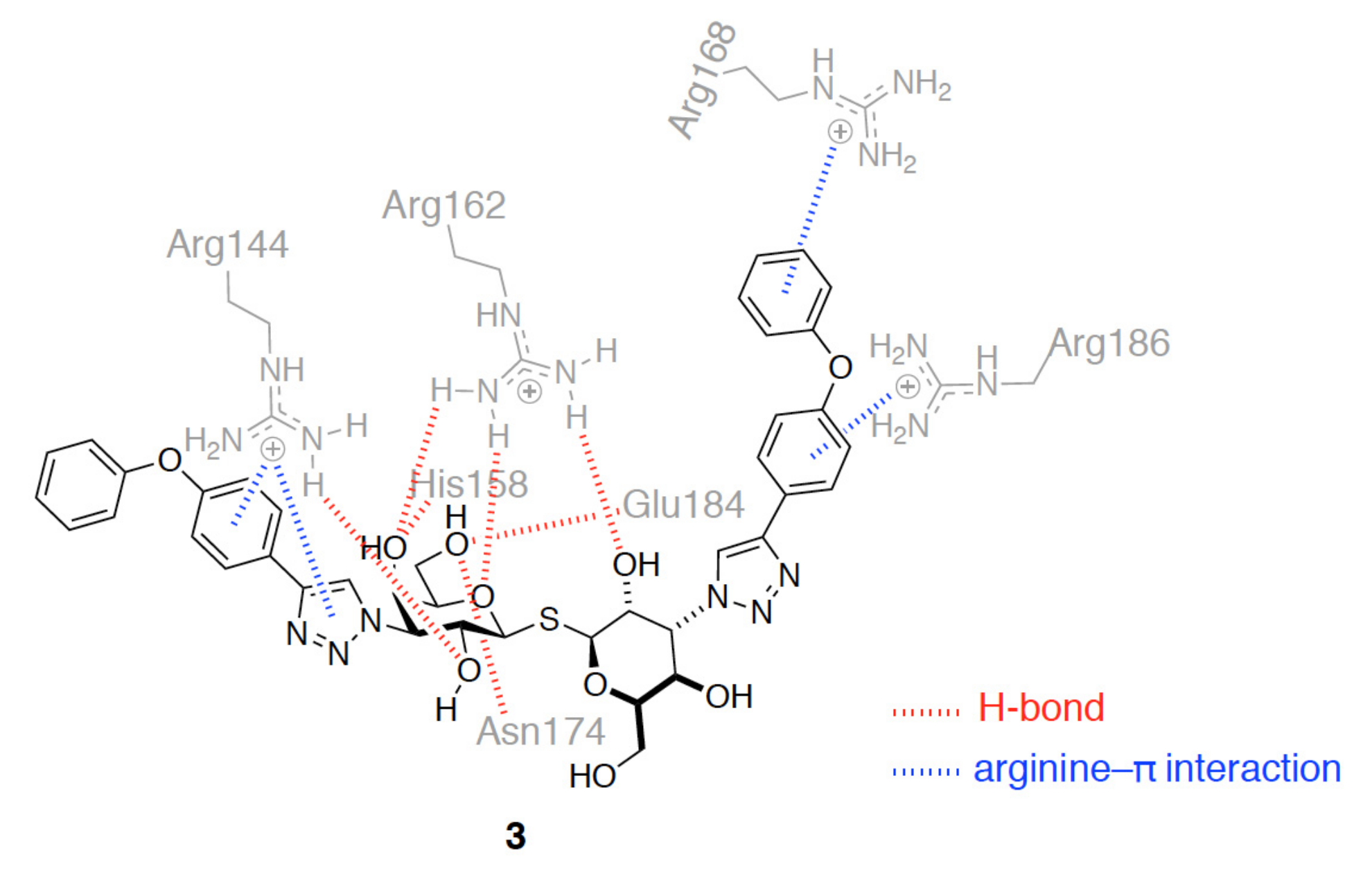
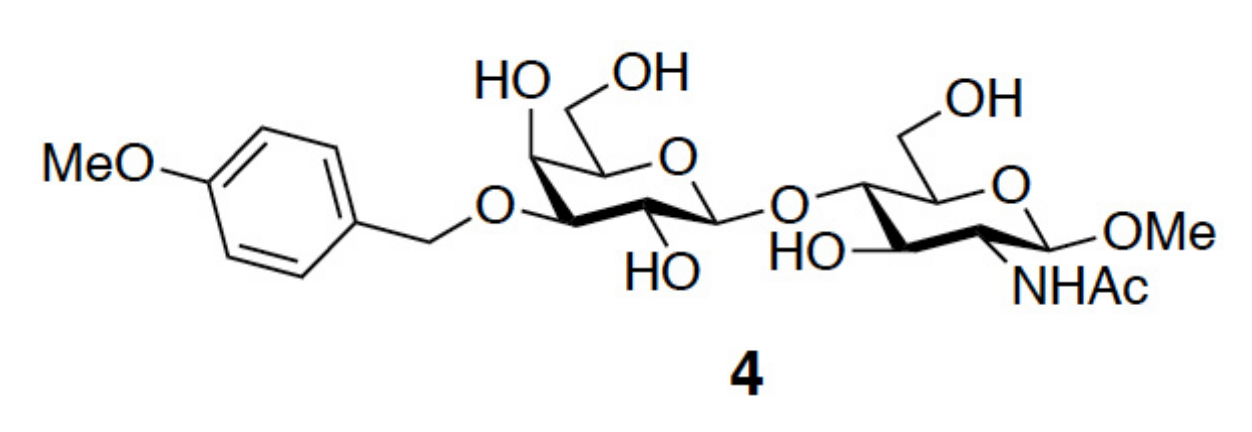
3.1. Enhancement of the Binding Affinity
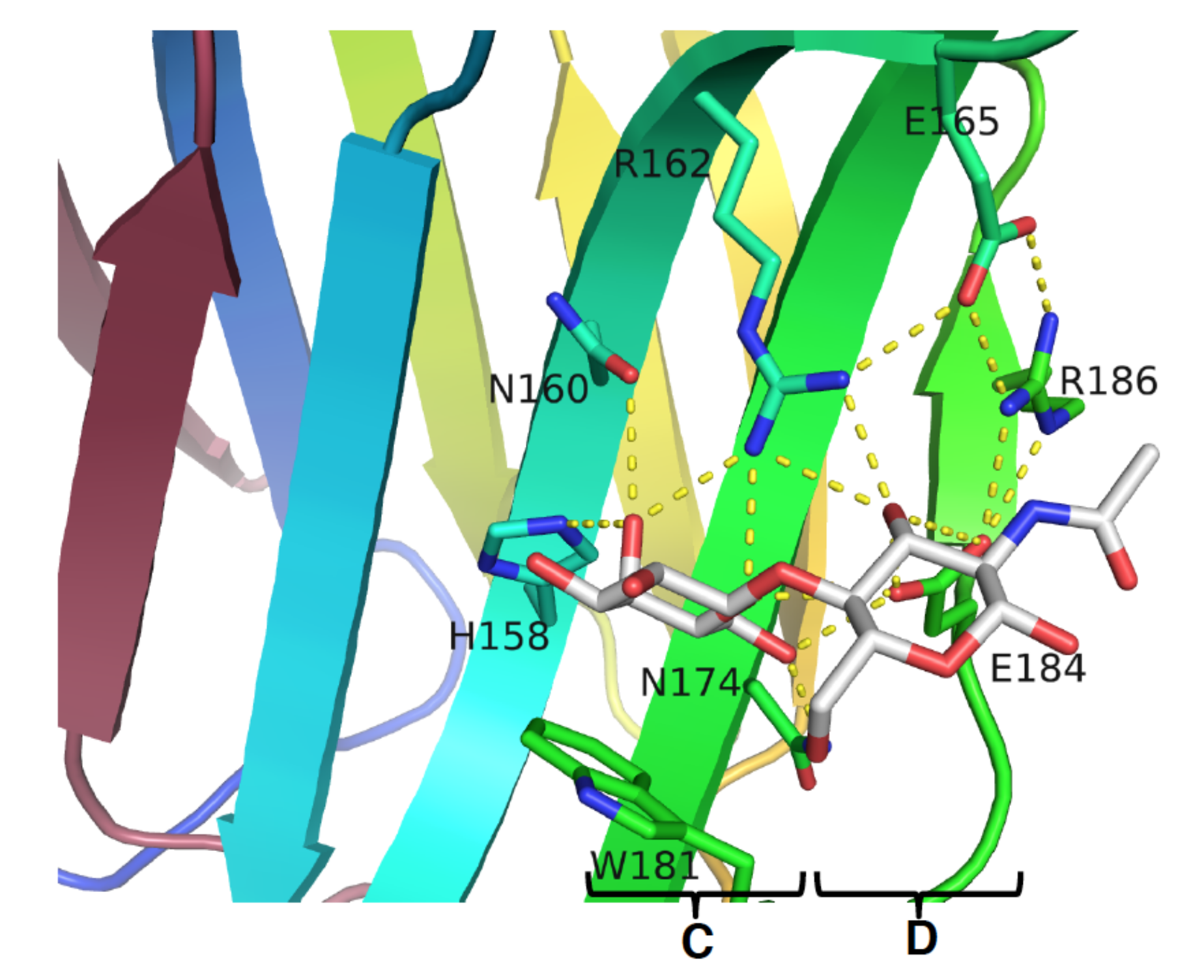
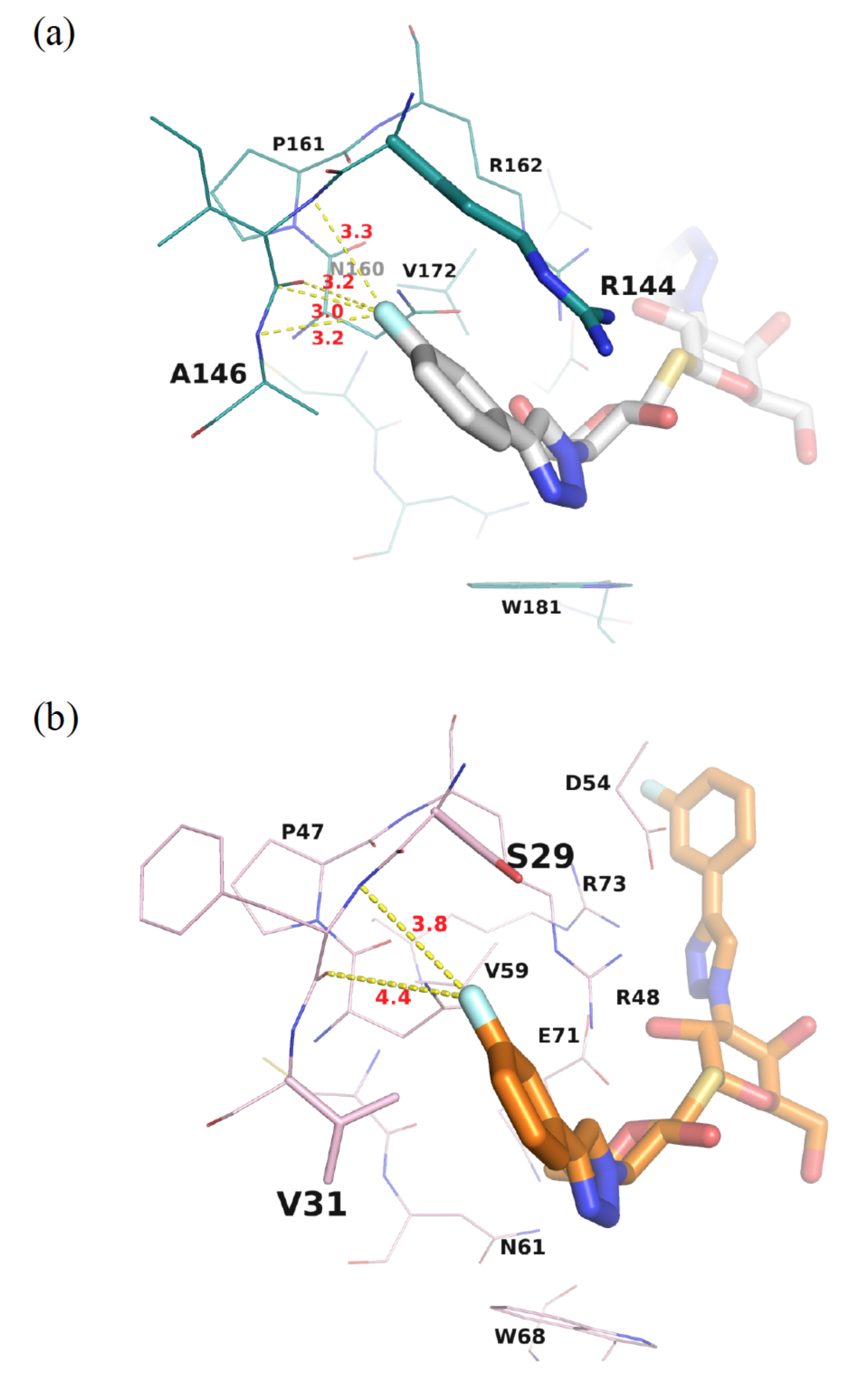
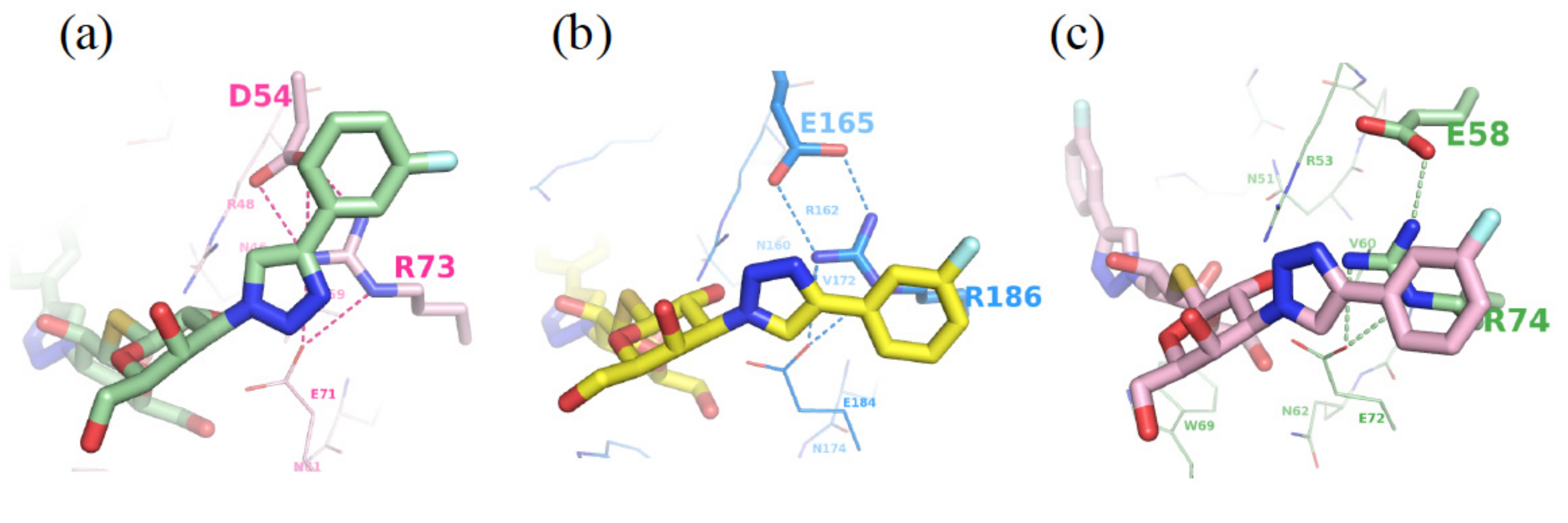
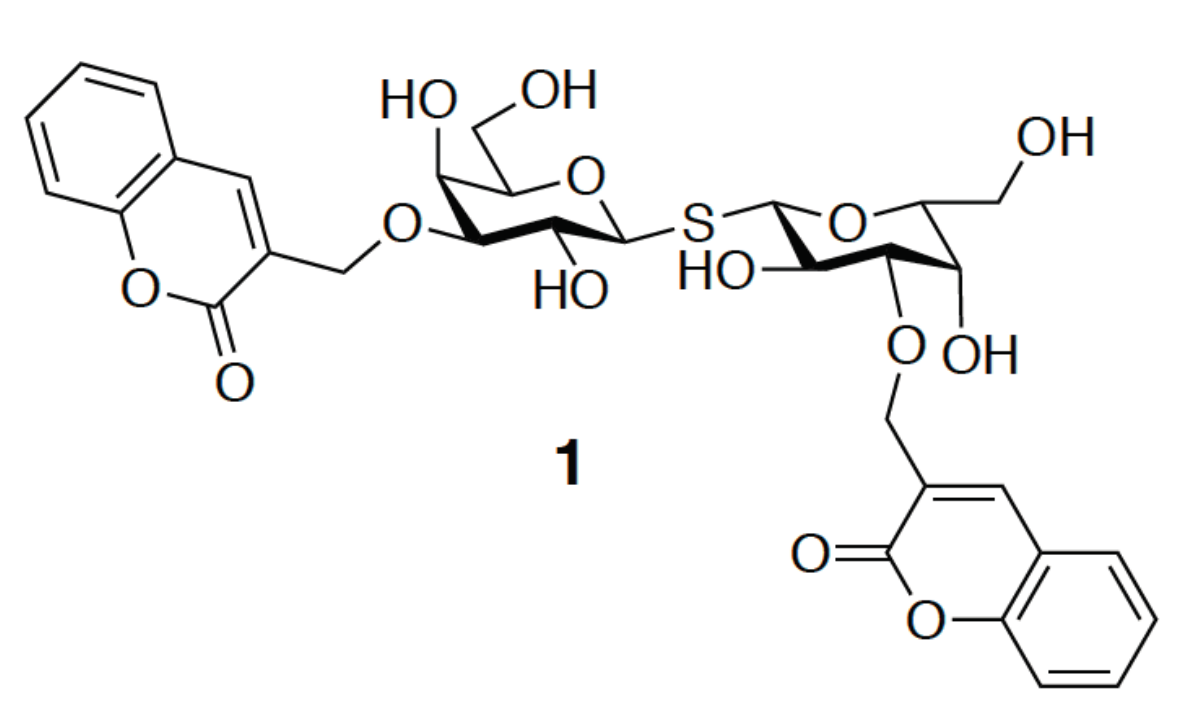
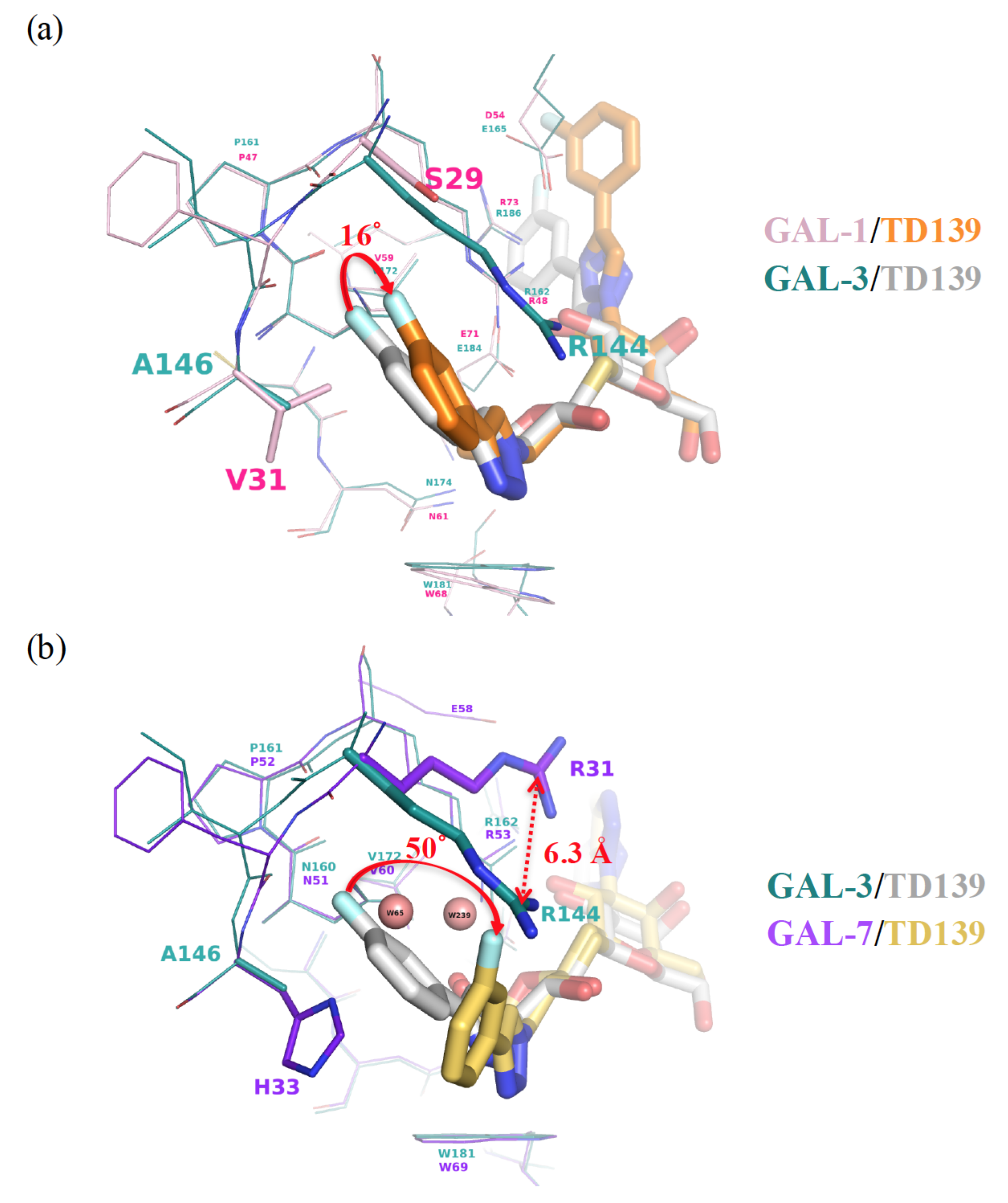
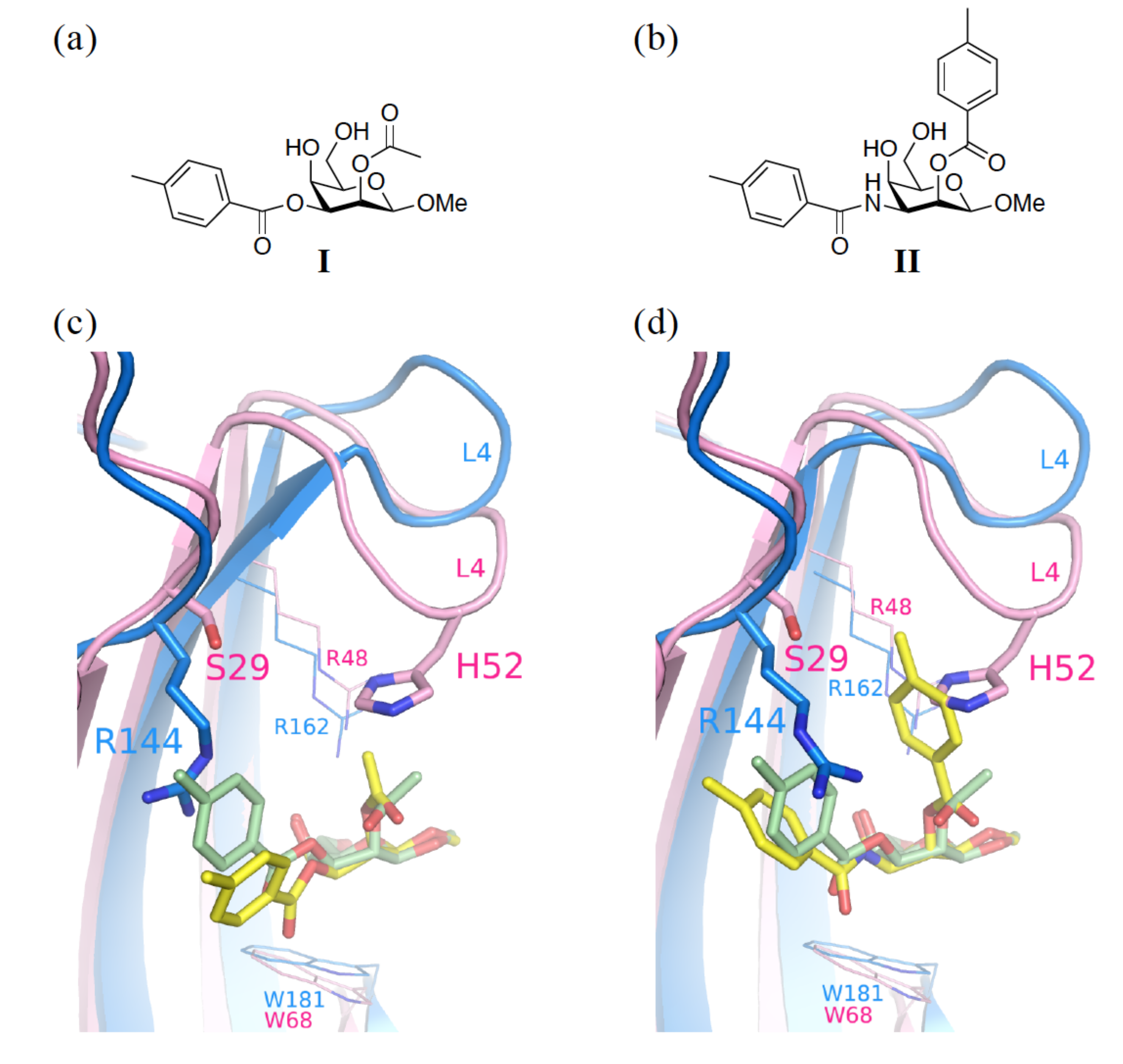
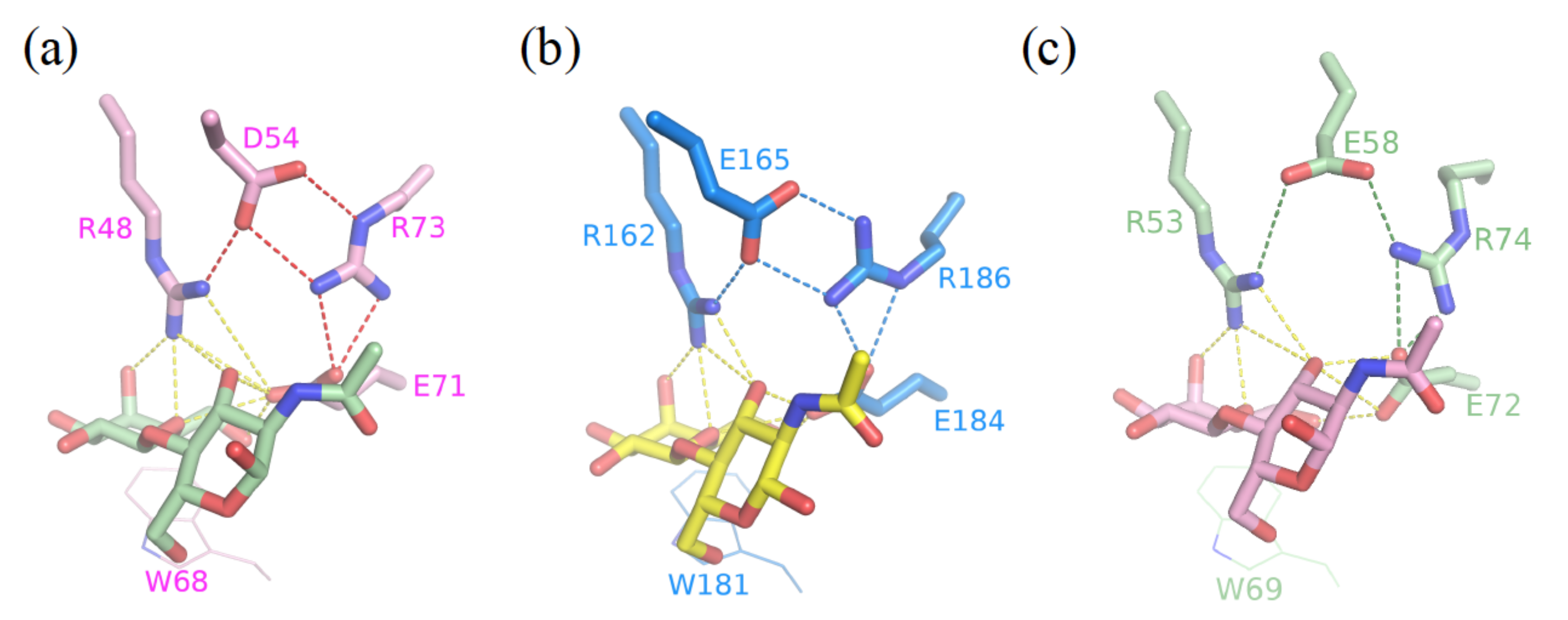
3.2. Enhancement of the Binding Selectivity
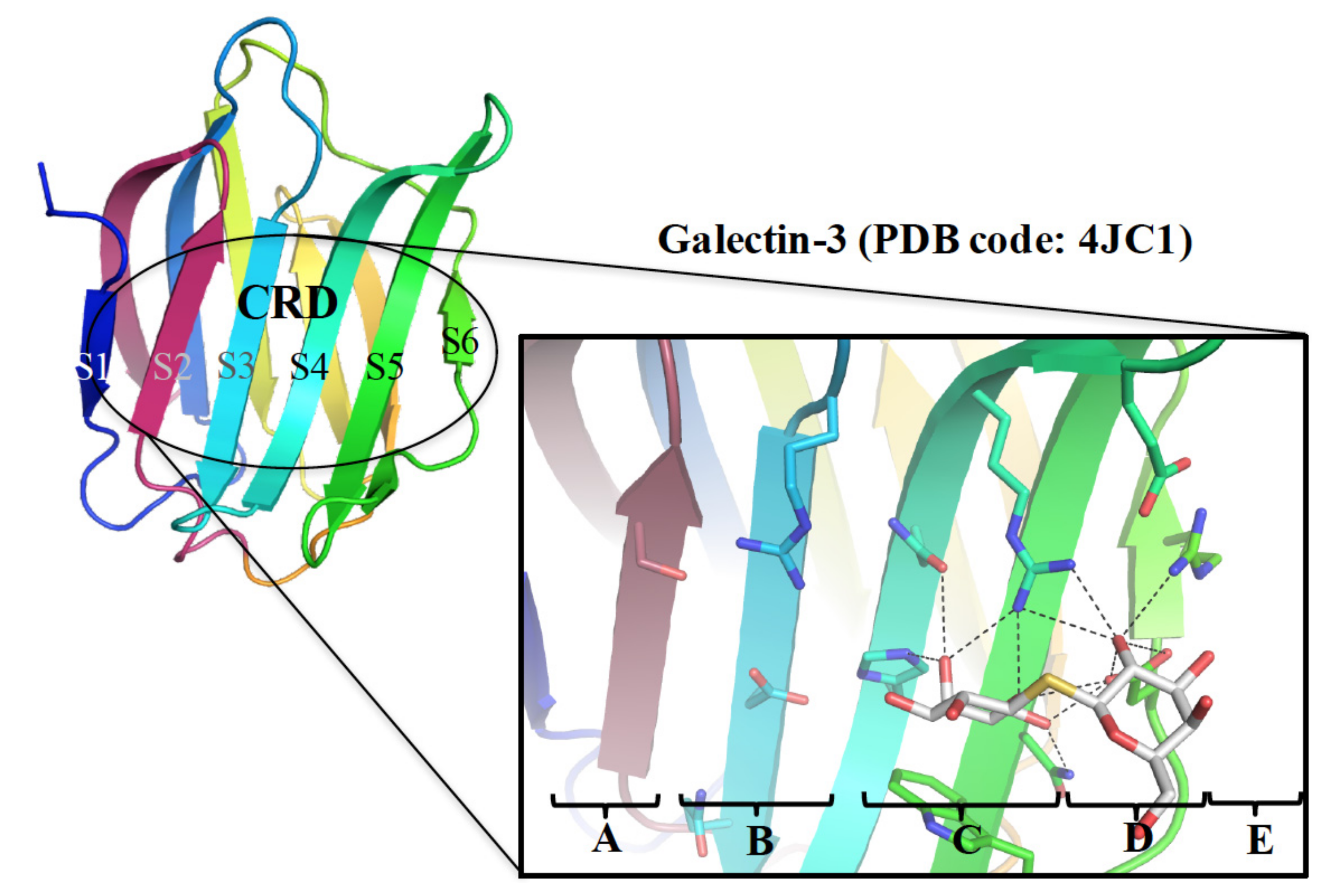
4. Tools to Characterize the Binding Interactions
4.1. Fluorescence Polarization
4.2. Biolayer Interferometry
4.3. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
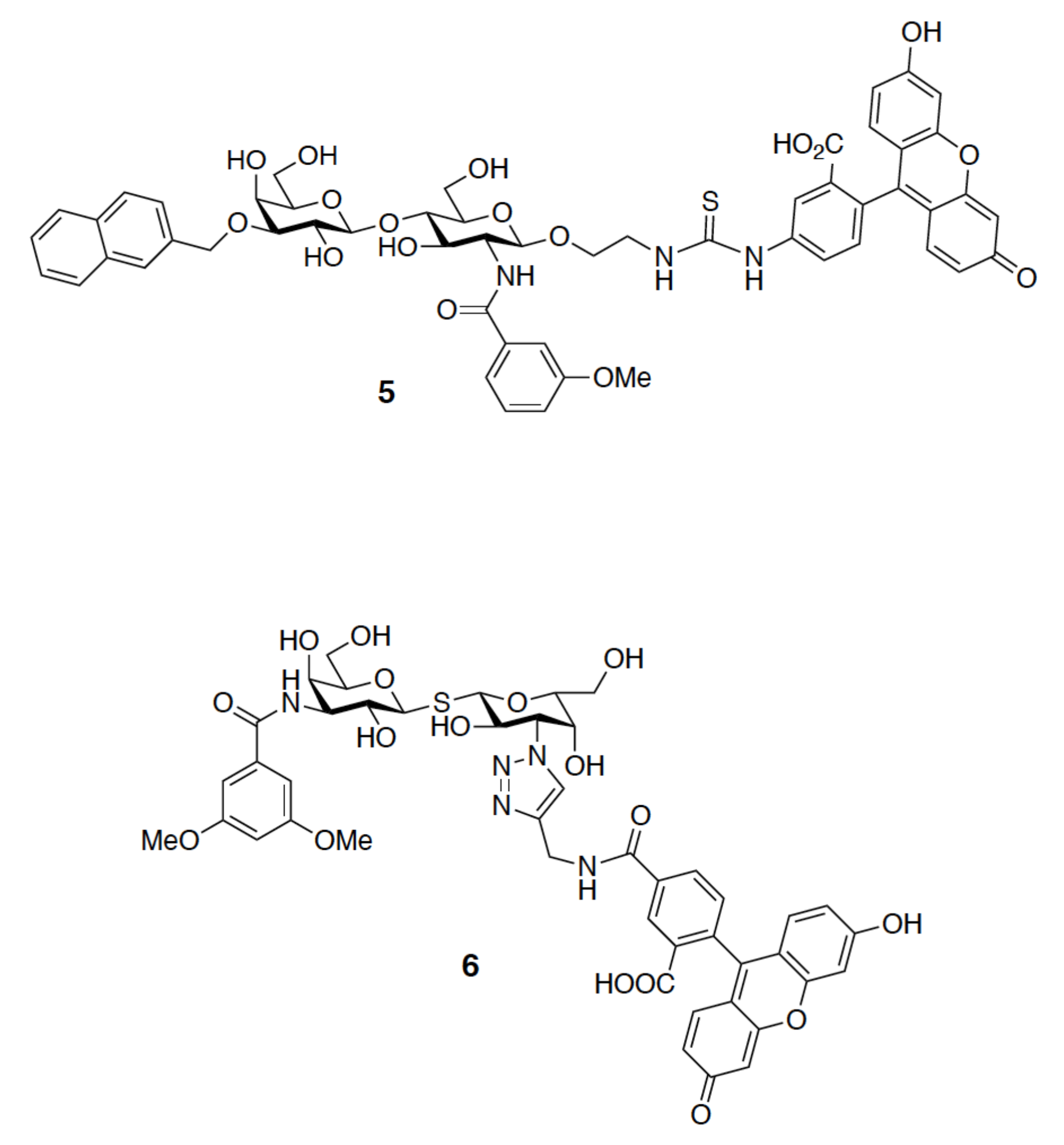
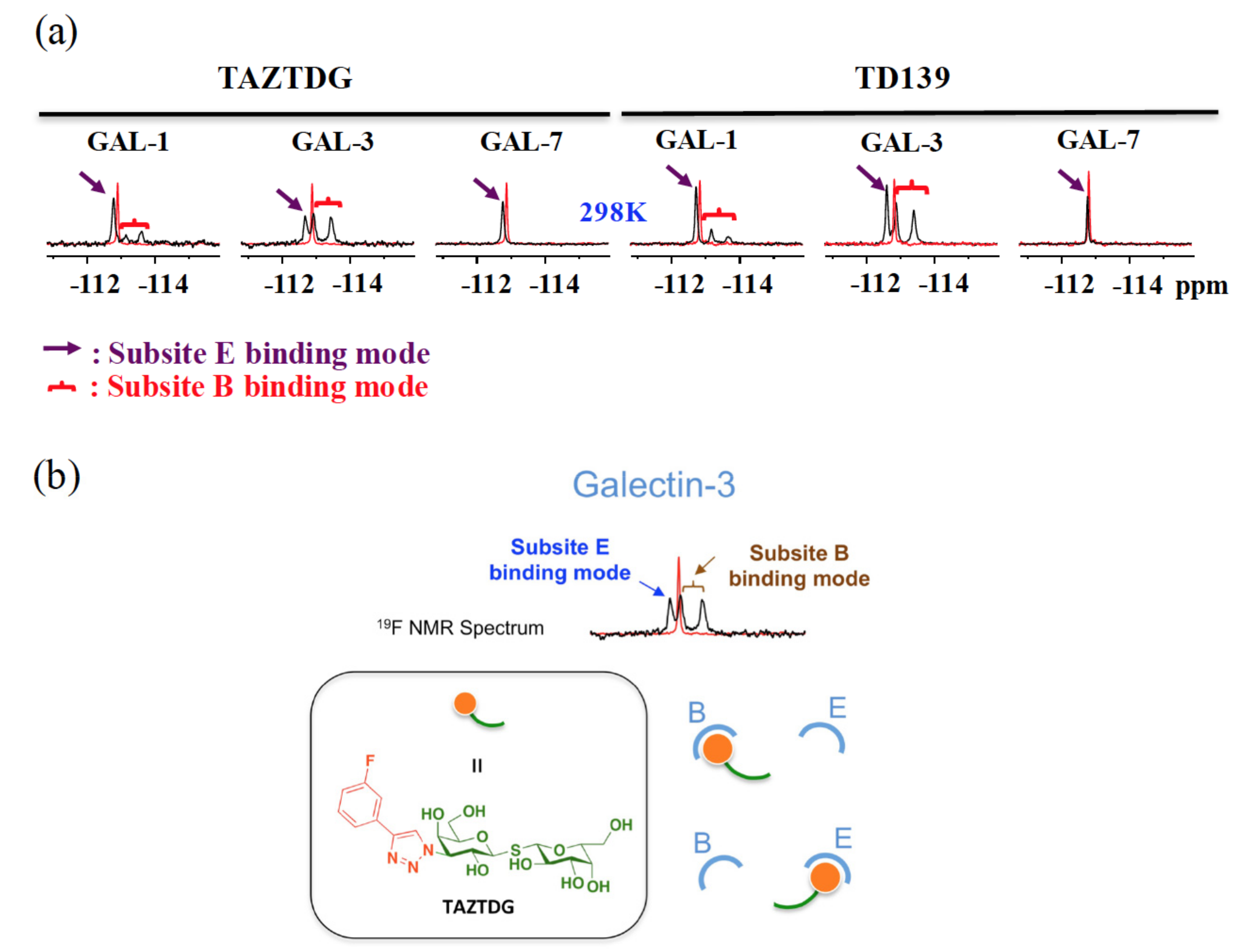
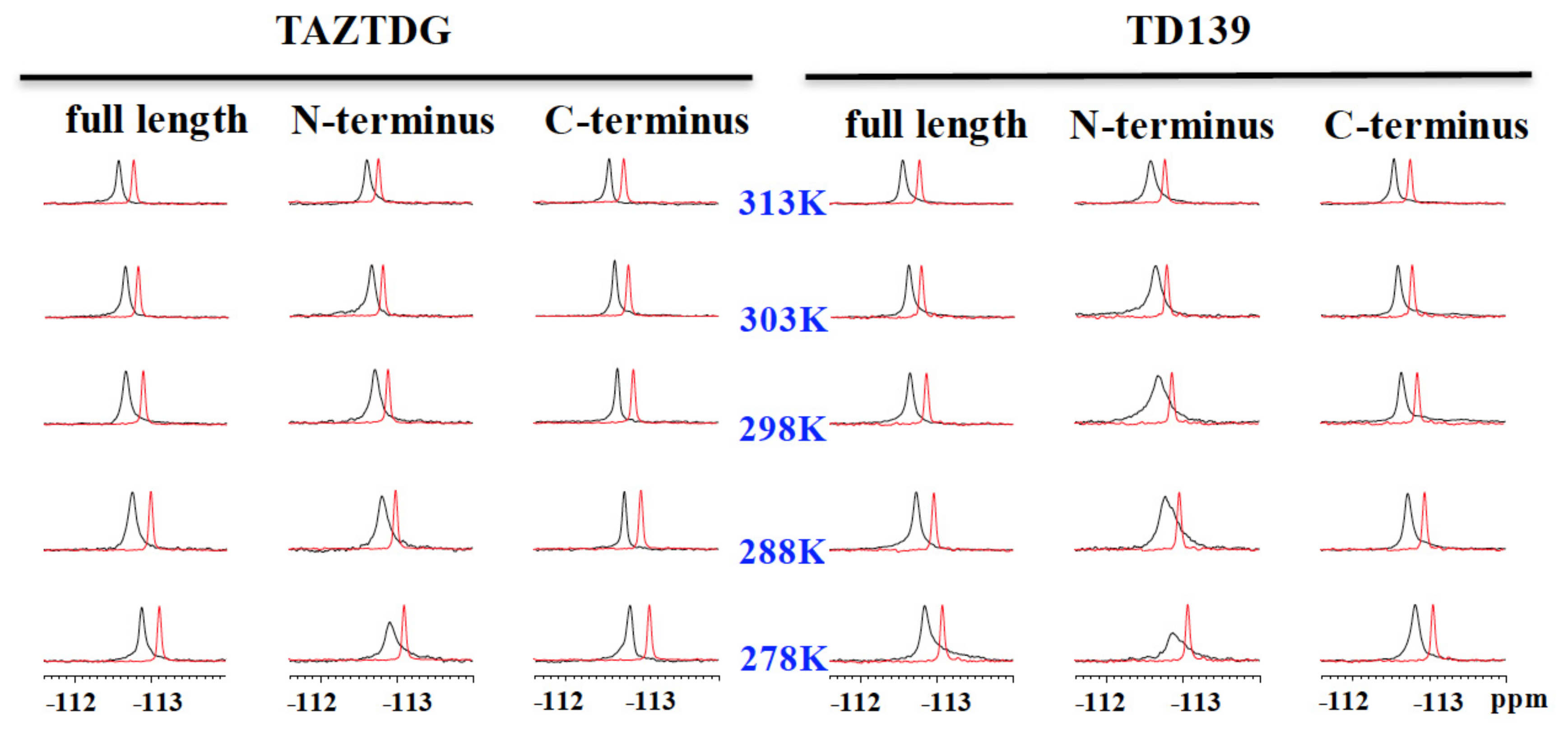
4.4. 19F-NMR Spectroscopy
5. Future Direction
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pieters, R.J. Inhibition and detection of galectins. ChemBioChem 2006, 7, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leffler, H.; Carlsson, S.; Hedlund, M.; Qian, Y.; Poirier, F. Introduction to galectins. Glycoconj. J. 2002, 19, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrassia, L.; Camby, I.; Lefranc, F.; Mathieu, V.; Nshimyumukiza, P.; Darro, F.; Kiss, R. Anti-galectin compounds as potential anti-cancer drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 3513–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuyer, G.; Jabeen, T.; Oberg, C.T.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J.; Acharya, K.R. Inhibition mechanism of human galectin-7 by a novel galactose-benzylphosphate inhibitor. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.-T.; Rabinovich, G.A. Galectins as modulators of tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepur, A.; Salomonsson, E.; Nilsson, U.J.; Leffler, H. Ligand induced galectin-3 protein self-association. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21751–21756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.; AlSadek, D.M.M. Galectin-3 as a Potential target to prevent cancer metastasis. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2015, 9, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendronneau, G.; Sidhu, S.S.; Delacour, D.; Dang, T.; Calonne, C.; Houzelstein, D.; Magnaldo, T.; Poirier, F. Galectin-7 in the control of epidermal homeostasis after injury. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 5541–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovich, G.A.; Toscano, M.A. Turning ‘sweet’ on immunity: Galectin-glycan interactions in immune tolerance and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Weng, I.-C.; Hong, M.-H.; Liu, F.-T. Galectins as bacterial sensors in the host innate response. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovich, G.A.; van Kooyk, Y.; Cobb, B.A. Glycobiology of immune responses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1253, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, F.L.; Gatto, M.; Bassi, N.; Luisetto, R.; Ghirardello, A.; Punzi, L.; Doria, A. Galectin-3 in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscher, C.; Zheng, Y.-Z.; Lakshminarayan, R.; Johannes, L.; Dennis, J.W.; Foster, L.J.; Nabi, I.R. Galectin-3 protein regulates mobility of N-cadherin and GM1 ganglioside at cell-cell junctions of mammary carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 32940–32952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.C. Galectins as modulators of cell adhesion. Biochimie 2001, 83, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuta, C.; Yano, F.; Fujii, A.; Shearer, T.R.; Azuma, M. Galectin-3 enhances epithelial cell adhesion and wound healing in rat cornea. Ophthalmic Res. 2014, 51, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, S.; Le Mercier, M.; Camby, I.; Spiegl-Kreinecker, S.; Berger, W.; Lefranc, F.; Kiss, R. Galectin-1 is implicated in the protein kinase C epsilon/vimentin-controlled trafficking of integrin-beta1 in glioblastoma cells. Brain Pathol. 2010, 20, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjwani, N. Role of galectins in re-epithelialization of wounds. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Hsu, D.-K.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yang, R.-Y.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd; Isseroff, R.R.; Liu, F.-T. Galectin-3 regulates intracellular trafficking of EGFR through Alix and promotes keratinocyte migration. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2828–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Ouellet, M.; St-Pierre, C.; Tremblay, M.J. Glycans, galectins, and HIV-1 infection. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1253, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klyosov, A.A.; Traber, P.G. Galectins in Disease and Potential Therapeutic Approaches. In Galectins and Disease Implications for Targeted Therapeutics. ACS Symp. Ser. 2012, 1115, 3–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hrynchyshyn, N.; Jourdain, P.; Desnos, M.; Diebold, B.; Funck, F. Galectin-3: A new biomarker for the diagnosis, analysis and prognosis of acute and chronic heart failure. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 106, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radosavljevic, G.; Volarevic, V.; Jovanovic, I.; Milovanovic, M.; Pejnovic, N.; Arsenijevic, N.; Hsu, D.-K.; Lukic, M.L. The roles of Galectin-3 in autoimmunity and tumor progression. Immunol. Res. 2012, 52, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reticker-Flynn, N.E.; Malta, D.F.; Winslow, M.M.; Lamar, J.M.; Xu, M.-J.; Underhill, G.H.; Hynes, R.O.; Jacks, T.E.; Bhatia, S.N. A combinatorial extracellular matrix platform identifies cell-extracellular matrix interactions that correlate with metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, H.; Rhodes, J.M.; Yu, L.-G. The role of galectins in colorectal cancer progression. International journal of cancer. J. Int. Cancer 2011, 129, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouo, T.; Huang, L.; Pucsek, A.B.; Cao, M.; Solt, S.; Armstrong, T.; Jaffee, E. Galectin-3 shapes antitumor immune responses by suppressing CD8+ T cells via LAG-3 and inhibiting expansion of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieers, G.; Demotte, N.; Godelaine, D.; Van der Bruggen, P. Immune suppression in tumors as a surmountable obstacle to clinical efficacy of cancer vaccines. Cancers 2011, 3, 2904–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.-Y.; Hsu, D.-K.; Liu, F.-T. Expression of galectin-3 modulates T-cell growth and apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6737–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovich, G.A.; Rubinstein, N.; Toscano, M.A. Role of galectins in inflammatory and immunomodulatory processes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1572, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.C.; Pang, M.; Hsu, D.-K.; Liu, F.-T.; de Vos, S.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Said, J.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-3 binds to CD45 on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells to regulate susceptibility to cell death. Blood 2012, 120, 4635–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, N.; Abe, A.; Iwaki, J.; Yoshida, H.; Itoh, A.; Shoji, H.; Kamitori, S.; Hirabayashi, J.; Nakamura, T. Functional and structural bases of a cysteine-less mutant as a long-lasting substitute for galectin-1. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battig, P.; Saudan, P.; Gunde, T.; Bachmann, M.F. Enhanced apoptotic activity of a structurally optimized form of galectin-1. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 41, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Glinsky, V.V.; Landon, L.A.; Matthews, L.; Deutscher, S.L. Peptides specific to the galectin-3 carbohydrate recognition domain inhibit metastasis-associated cancer cell adhesion. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, D.; Raz, A. Modulation of the lung colonization of B16-F1 melanoma cells by citrus pectin. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1992, 84, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pienta, K.J.; Naik, H.; Akhtar, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Replogle, T.S.; Lehr, J.; Donat, T.L.; Tait, L.; Hogan, V.; Raz, A. Inhibition of spontaneous metastasis in a rat prostate cancer model by oral administration of modified citrus pectin. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuliffe, J.; Hindsgaul, O. Carbohydrates in Medicine. In Molecular and Cellular Glycobiology; Fukuda, M., Hindsgaul, O., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 249–285. [Google Scholar]
- Cotter, F.; Smith, D.A.; Boyd, T.E.; Richards, D.A.; Alemany, C.; Loesch, D.; Salogub, G.; Tidmarsh, G.F.; Gammon, G.M.; Gribben, J. Single-agent activity of GCS-100, a first-in-class galectin-3 antagonist, in elderly patients with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 7006. [Google Scholar]
- Traber, P.G.; Zomer, E. Therapy of experimental NASH and fibrosis with galectin inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, P.G.; Chou, H.; Zomer, E.; Hong, F.; Klyosov, A.; Fiel, M.I.; Friedman, S.L. Regression of fibrosis and reversal of cirrhosis in rats by galectin inhibitors in thioacetamide-induced liver disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klyosov, A.; Zomer, E.; Platt, D. Studies. In Glycobiology and Drug Design; American Chemical Society: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1102, pp. 89–130. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.C.; Klyosov, A.; Mayo, K.H. The alpha-galactomannan Davanat binds galectin-1 at a site different from the conventional galectin carbohydrate binding domain. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.C.; Ribeiro, J.P.; Roldos, V.; Martin-Santamaria, S.; Canada, F.J.; Nesmelova, I.A.; Andre, S.; Pang, M.; Klyosov, A.A.; Baum, L.G.; et al. Structural aspects of binding of alpha-linked digalactosides to human galectin-1. Glycobiology 2011, 21, 1627–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, H.; Yu, X.; Collins, P.M.; Bum-Erdene, K. Galectin-3 inhibitors: A patent review (2008-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2014, 24, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackinnon, A.C.; Gibbons, M.A.; Farnworth, S.L.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J.; Delaine, T.; Simpson, A.J.; Forbes, S.J.; Hirani, N.; Gauldie, J.; et al. Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta1-driven lung fibrosis by galectin-3. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, K. Galecto Biotech. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaine, T.; Collins, P.; MacKinnon, A.; Sharma, G.; Stegmayr, J.; Rajput, V.K.; Mandal, S.; Cumpstey, I.; Larumbe, A.; Salameh, B.A.; et al. Galectin-3-binding glycomimetics that strongly reduce bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis and modulate intracellular glycan recognition. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorme, P.; Kahl-Knutsson, B.; Huflejt, M.; Nilsson, U.J.; Leffler, H. Fluorescence polarization as an analytical tool to evaluate galectin-ligand interactions. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 334, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorme, P.; Arnoux, P.; Kahl-Knutsson, B.; Leffler, H.; Rini, J.M.; Nilsson, U.J. Structural and thermodynamic studies on cation-Pi interactions in lectin-ligand complexes: High-affinity galectin-3 inhibitors through fine-tuning of an arginine-arene interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpstey, I.; Sundin, A.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J. C2-symmetrical thiodigalactoside bis-benzamido derivatives as high-affinity inhibitors of galectin-3: Efficient lectin inhibition through double arginine-arene interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5110–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, V.K.; MacKinnon, A.; Mandal, S.; Collins, P.; Blanchard, H.; Leffler, H.; Sethi, T.; Schambye, H.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Nilsson, U.J. A selective galactose-coumarin-derived galectin-3 inhibitor demonstrates involvement of galectin-3-glycan interactions in a pulmonary fibrosis model. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 8141–8147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackinnon, A.; Chen, W.-S.; Leffler, H.; Panjwani, N.; Schambye, H.; Sethi, T.; Nilsson, U.J. Design, Synthesis, and Applications of Galectin Modulators in Human Health. In Carbohydrates as Drugs; Seeberger, P.H., Rademacher, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 95–121. [Google Scholar]
- Oberg, C.T.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J. Inhibition of galectins with small molecules. Chimia 2011, 65, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.-J.; Lin, H.-Y.; Tu, Z.; Lin, T.-C.; Wu, S.-C.; Tseng, Y.-Y.; Liu, F.-T.; Hsu, S.-T.D.; Lin, C.-H. Dual thio-digalactoside-binding modes of human galectins as the structural basis for the design of potent and selective inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 29457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leffler, H.; Barondes, S.H. Specificity of binding of three soluble rat lung lectins to substituted and unsubstituted mammalian β-Galactoside. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 10119–10126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lobsanov, Y.D.; Gitt, M.A.; Leffler, H.; Barondes, S.H.; Rini, J.M. X-ray crystal structure of the human dimeric S-Lac lectin, L-14-II, in complex with lactose at 2.9 Å resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 27034–27038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.-J.; Lin, H.-Y.; Tu, Z.; Huang, B.-S.; Wu, S.-C.; Lin, C.-H. Structural Basis Underlying the binding preference of human galectins-1, -3 and -7 for Galβ1-3/4GlcNAc. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorme, P.; Qian, Y.; Nyholm, Per-G.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J. Low micromolar inhibitors of galectin-3 based on 3′-derivatization of N-acetyllactosamine. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpstey, I.; Salomonsson, E.; Sundin, A.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J. Double affinity amplification of galectin-ligand interactions through arginine-arene interactions: Synthetic, thermodynamic, and computational studies with aromatic diamido thiodigalactosides. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 4233–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulini, R.; Muller, K.; Diederich, F. Orthogonal multipolar interactions in structural chemistry and biology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 1788–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, J.; Borkin, D.; Lund, G.; Purohit, T.; Dyguda-Kazimierowicz, E.; Grembecka, J.; Cierpicki, T. Rational design of orthogonal multipolar interactions with fluorine in protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7465–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpstey, I.; Salomonsson, E.; Sundin, A.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J. Studies of arginine-arene interactions through synthesis and evaluation of a series of galectin-binding aromatic lactose esters. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dion, J.; Advedissian, T.; Storozhylova, N.; Dahbi, S.; Lambert, A.; Deshayes, F.; Viguier, M.; Tellier, C.; Poirier, F.; Teletchea, S.; et al. Development of a sensitive microarray platform for the ranking of galectin inhibitors: Identification of a selective galectin-3 inhibitor. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hattum, H.; Branderhorst, H.M.; Moret, E.E.; Nilsson, U.J.; Leffler, H.; Pieters, R.J. Tuning the preference of thiodigalactoside- and lactosamine-based ligands to galectin-3 over galectin-1. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.M.; Oberg, C.T.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J.; Blanchard, H. Taloside inhibitors of galectin-1 and galectin-3. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 79, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorme, P.; Kahl-Knutson, B.; Wellmar, U.; Nilsson, U.J.; Leffler, H. Fluorescence polarization to study galectin-ligand interactions. Methods Enzymol. 2003, 362, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lea, W.A.; Simeonov, A. Fluorescence polarization assays in small molecule screening. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2011, 6, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorme, P.; Kahl-Knutsson, B.; Wellmar, U.; Magnusson, B.G.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J. Design and synthesis of galectin inhibitors. Methods Enzymol. 2003, 363, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dion, J.; Deshayes, F.; Storozhylova, N.; Advedissian, T.; Lambert, A.; Viguier, M.; Tellier, C.; Dussouy, C.; Poirier, F.; Grandjean, C. Lactosamine-based derivatives as tools to delineate the biological functions of galectins: Application to skin tissue repair. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R. Strategies Using Bio-Layer Interferometry biosensor technology for vaccine research and development. Biosensors 2017, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yan, J.; Sun, C.; Zhou, Y.; Tai, G. Multiple approaches to assess pectin binding to galectin-3. Intl. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.-H.; Ho, M.-R.; Lin, C.-H.; Hsu, S.-T.D. Lactose binding induces opposing dynamics changes in human galectins revealed by NMR-based hydrogen-deuterium exchange. Molecules 2017, 22, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Tonge, P.J. Drug-target residence time: Critical information for lead optimization. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez, S.; Venhorst, J.; Kruse, C.G. Target–drug interactions: First principles and their application to drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauquelin, G. Effects of target binding kinetics on in vivo drug efficacy: Koff, kon and rebinding. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2319–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbett, N.C.; Chaires, J.B. Thermodynamic studies for drug design and screening. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Freire, E. Isothermal titration calorimetry to determine association constants for high-affinity ligands. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, E. Do enthalpy and entropy distinguish first in class from best in class? Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachhawat-Sikder, K.; Thomas, C.J.; Surolia, A. Thermodynamic analysis of the binding of galactose and poly-N-acetyllactosamine derivatives to human galectin-3. FEBS Lett. 2001, 500, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebe, G. Applying thermodynamic profiling in lead finding and optimization. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geschwindner, S.; Ulander, J.; Johansson, P. Ligand binding thermodynamics in drug discovery: Still a hot tip? J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6321–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, K.L. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry: Recent therapeutic applications of fluorinated small molecules. J. Fluorine Chem. 2006, 127, 1013–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Gu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, W.; Acena, J.L.; Soloshonok, V.A.; Izawa, K.; Liu, H. Next generation of fluorine-containing pharmaceuticals, compounds currently in phase II–III clinical trials of major pharmaceutical companies: New structural trends and therapeutic areas. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 422–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, H.J.; Banner, D.; Bendels, S.; Kansy, M.; Kuhn, B.; Muller, K.; Obst-Sander, U.; Stahl, M. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Westwell, A.D. The role of fluorine in medicinal chemistry. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2007, 22, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalvit, C.; Vulpetti, A. Fluorine–protein interactions and 19F-NMR isotropic chemical shifts: An empirical correlation with implications for drug design. ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulpetti, A.; Dalvit, C. Fluorine local environment: From screening to drug design. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, J.; Hashidate, T.; Arata, Y.; Nishi, N.; Nakamura, T.; Hirashima, M.; Urashima, T.; Oka, T.; Futai, M.; Muller, W.E.; Yagi, F.; Kasai, K. Oligosaccharide specificity of galectins: A search by frontal affinity chromatography. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1572, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ideo, H.; Seko, A.; Ishizuka, I.; Yamashita, K. The N-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain of galectin-8 recognizes specific glycosphingolipids with high affinity. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ideo, H.; Matsuzaka, T.; Nonaka, T.; Seko, A.; Yamashita, K. Galectin-8-N-domain recognition mechanism for sialylated and sulfated glycans. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 11346–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Than, N.G.; Romero, R.; Balogh, A.; Karpati, E.; Mastrolia, S.A.; Staretz-Chacham, O.; Hahn, S.; Erez, O.; Papp, Z.; Kim, C.J. Galectins: Double-edged swords in the cross-roads of pregnancy complications and female reproductive tract inflammation and neoplasia. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2015, 49, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, T.L.; Wandel, M.P.; Von Muhlinen, N.; Foeglein, A.; Randow, F. Galectin 8 targets damaged vesicles for autophagy to defend cells against bacterial invasion. Nature 2012, 482, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Tu, Z.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Hsu, S.-T.D.; Lin, C.-H. Dissecting the Structure–Activity Relationship of Galectin–Ligand Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020392
Chan Y-C, Lin H-Y, Tu Z, Kuo Y-H, Hsu S-TD, Lin C-H. Dissecting the Structure–Activity Relationship of Galectin–Ligand Interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020392
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Yi-Chen, Hsien-Ya Lin, Zhijay Tu, Yen-Hsi Kuo, Shang-Te Danny Hsu, and Chun-Hung Lin. 2018. "Dissecting the Structure–Activity Relationship of Galectin–Ligand Interactions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020392
APA StyleChan, Y.-C., Lin, H.-Y., Tu, Z., Kuo, Y.-H., Hsu, S.-T. D., & Lin, C.-H. (2018). Dissecting the Structure–Activity Relationship of Galectin–Ligand Interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020392





