Abstract
Plant cell walls are complex and dynamic structures that play important roles in growth and development, as well as in response to stresses. Pectin is a major polysaccharide of cell walls rich in galacturonic acid (GalA). Homogalacturonan (HG) is considered the most abundant pectic polymer in plant cell walls and is partially methylesterified at the C6 atom of galacturonic acid. Its degree (and pattern) of methylation (DM) has been shown to affect biomechanical properties of the cell wall by making pectin susceptible for enzymatic de-polymerization and enabling gel formation. Pectin methylesterases (PMEs) catalyze the removal of methyl-groups from the HG backbone and their activity is modulated by a family of proteinaceous inhibitors known as pectin methylesterase inhibitors (PMEIs). As such, the interplay between PME and PMEI can be considered as a determinant of cell adhesion, cell wall porosity and elasticity, as well as a source of signaling molecules released upon cell wall stress. This review aims to highlight recent updates in our understanding of the PMEI gene family, their regulation and structure, interaction with PMEs, as well as their function in response to stress and during development.
1. Introduction
Plant cells are surrounded by a wall composed of interacting networks of polysaccharides, highly glycosylated proteins and other polymers. Plant cell walls are complex and highly dynamic structures, responding and adapting to normal processes of growth and development as well as to biotic and abiotic stresses. They have to fulfil several different functions: on one hand, they need to be flexible to allow fast and directional cell elongation (e.g., pollen tubes) and on the other hand they have to be rigid enough to resist the internal turgor pressure, to protect against pathogens and to provide structural and mechanical support for the upright growth of the whole organism.
The major carbohydrates of primary cell walls are cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectins. Cellulose and hemicellulose form a hydrogen-bonded network that is embedded in a gel-like pectic matrix. Pectin is a galacturonan-based polysaccharide containing five distinct subclasses that can be distinguished based on the structure of their backbones and the diversity of their side chains: homogalacturonan (HG), rhamnogalacturonan I and rhamnogalacturonan II (RG-II), xylogalacturonan and apiogalacturonan [1]. In dicots and non-graminaceous plants, pectins constitute about 35% of primary cell walls, whereas in grasses only 2–10% of primary walls are pectic polysaccharides [2]. Pectin has been shown to play roles controlling cell wall porosity [3], cell elongation [4], and cell adhesion [5] and constitutes an important factor in plant development (for reviews see [6,7]).
HG constitutes ~65% of pectin and is the most abundant pectic polysaccharide in primary cell walls [1]. It consists of an α-1,4-linked D-galacturonic acid (GalA) backbone, which is synthesized by HG galacturonosyl-transferases (GAUTs) from the nucleotide sugar uridine diphosphate (UDP)-GalA in the Golgi apparatus. So far, the galacturonosyl-transferase GAUT1 has been biochemically characterized in Arabidopsis [8,9] and a hetero-complex formation of two GAUT1 with one GAUT7 molecule has been shown responsible for retaining GAUT1 in the Golgi apparatus [10]. In addition, GAUT4 from Arabidopsis thaliana, switchgrass and poplar was shown to synthesize HG and downregulate of the gene reduced HG and RG-II in the cell wall [11]. When HG is secreted into the cell wall, it is highly methyl-esterified at the C6 atom of the GalA residue (~80% [2]) and a putative pectin methyltransferase conferring this methyl-esterification has been identified in the Golgi [12,13]. In addition, some GalA residues of HG carry acetyl groups at O2 or O3, which affect the physiochemical properties of HG in vitro [14].
Once incorporated into the cell wall, HG is further selectively modified and the pattern and degree of these modifications affect pectin hydrolysis and properties such as pH, charge and crosslinking. Pectin acetyl esterases catalyze de-acetylation and the release of acetate from the cell wall, causing changes in cell wall mechanics and developmental aberrations [15,16]. Pectin methyl esterases (PMEs) catalyze the specific de-methylesterification of HG, releasing methanol and protons, and creating negatively charged carboxyl groups in the process (Figure 1). The degree and pattern of methylesterification of HG determine the biomechanical properties of the cell wall. When several consecutive GalA residues are de-methylesterified (block-wise de-methylesterification), the negatively charged carboxyl groups can form calcium bonds with other HG molecules, leading to so-called ‘egg-box’ structures that underlie the formation of pectin gels [17]. De-methylesterified, calcium cross-linked HG increased the amount of bound water maintaining wall hydration [18] and the hydration state was shown to affect biomechanical properties of the cell wall, such as its rigidity [19]. In addition, the strength of pectin gels is highly dependent on the amount of free calcium ions in the apoplast, as stiffness of the gel is reduced by disassociation of calcium crosslinks [20]. On the other hand, partially de-methylesterified HG (random or block-wise de-methylesterification) can become a target for pectin-degrading enzymes such as polygalacturonases and pectate/pectin lyases.
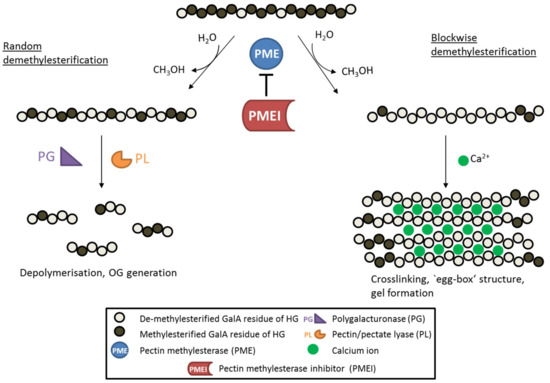
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram showing the de-methylesterification of HG and the effects on its structure. HG is highly methylesterified when deposited into the cell wall. PMEs can de-methylesterify HG in a block-wise fashion, leading to several consecutive GalA residues without methylester groups. These HG backbones are negatively charged and can therefore form crosslinks with cations like calcium ions, leading to so called ‘egg-box‘ structures responsible for gel formation. On the other hand, PMEs can de-methylesterify single GalA residues leading to a random methylesterification pattern. Low-methylesterified HG is depolymerized by pectin-degrading enzymes such as polygalacturonases (PG) and pectin/pectate lyases (PL), which leads to the formation of oligogalacturonides (OG). PME activity is inhibited by its proteinaceous inhibitor PMEI.
The degree of methylesterification (DM) of HG, which is controlled by the activity of large PME families, has vast consequences on the mechanical properties of the cell wall [21], affecting developmental processes such as stomata opening [22,23], cell adhesion [5], organ initiation [24] and anisotropic cell growth [25]. In addition, hydrolysis of partially de-methylesterified HG can lead to the formation of signaling molecules (oligogalacturonides), for instance, during plant-pathogen interactions [26,27]. Consequently, PME activity is tightly regulated at: (a) the transcriptional level [28], (b) by protein processing [1] and degradation [29], (c) by the pH of the cell wall environment [6,30], and (d) by endogenous inhibitor proteins called pectin methylesterase inhibitors (PMEI, Figure 1) [31,32]. The first PMEI was identified in kiwi fruit (Actinidia deliciosa [33]) and to date several PMEIs have been investigated in different plant species. This review therefore aims to give a comprehensive overview on the current knowledge about PMEIs and their various roles in plant development and stress response.
2. PMEI Occurrence and Regulation
PMEIs belong to large multigene families, containing almost as many members as PME genes in several plant species [34]. The PMEI proteins first appeared in mosses (Physcomitrella patens), which coincided with the appearance of pectin in cell walls [34]. In Arabidopsis, 71 putative PMEI genes have been identified in silico (not including proPME genes containing PMEI domains) [34], compared to 100 open reading frames (ORFs) in Brassica campestris [35] and 97 putative PMEI genes in Brassica rapa [36]. Pinzón-Latorre and Deyholos [37] listed 95 PMEI ORFs in flax (Linum usitatissimum), whereas in poplar (Populus trichocarpa), only 54 genes have been annotated [34]. In monocots, the PMEI families generally contain fewer isoforms. For example, in rice (Oryza sativa), 49 ORFs were annotated as putative PMEIs [38] compared to 37 genes in Sorghum bicolor [34] and 38 putative PMEI members in Brachypodium distachyon [1]. The smaller family size in grasses is likely due to differences in the structure of cell wall polysaccharides, with pectins being less abundant and less methylesterified in graminaceous species [2,28]. Gene family synteny and phylogenetic analyses suggest that the expansion of the PMEI families in several angiosperm species is due to whole genome duplication and tandem duplication events during evolution [34,35,37].
PMEIs are crucial factors in regulating the DM of HG, which has tremendous effects on cell wall mechanics and affects many biological processes (Figure 2).
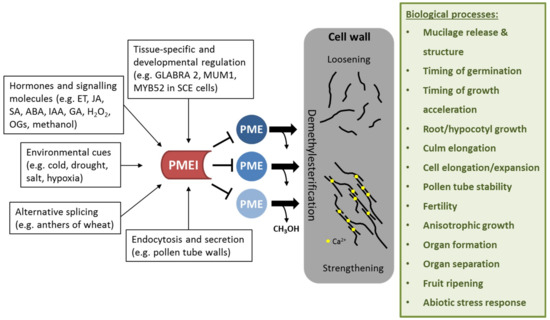
Figure 2.
Effect of PMEI regulation on cell wall properties and biological processes affected by PMEI manipulation. PMEIs are transcriptionally regulated in a tissue-specific and development-dependent manner. Several plant hormones and signaling molecules as well as environmental stresses can activate PMEI gene expression. Alternative splicing and directed endocytosis and secretion regulate the level of active PMEIs in the cell wall. PMEI can inhibit several PME enzymes, thereby regulating de-methylesterification of HG. This in turn modulates cell wall properties such as loosening or strengthening, which is required for several biological processes.
Therefore, it is not surprising that their expression is highly coordinated with other pectin modifying enzymes, such as PMEs [28]. Transcriptional analyses (using microarrays, RNAseq, qRT-PCR) showed that PMEI expression is spatially and developmentally controlled in various species (Brassica rapa [36], Brassica campestris [39], Arabidopsis [40], grapevine [41], wheat [42], rice [38], and flax [37,43]). Cluster analysis for a fraction of PME and PMEI genes already identified expression clusters specific for e.g., seed coat, endosperm, pollen, shoot apex in Arabidopsis [1]. For example, AtPMEI6 and AtPMEI14 are specifically expressed in seed coat epidermal cells and their expression is modulated by the transcriptional regulators GLABRA2 and MUCILAGE-MODIFIED 1 (MUM1), known to be involved in seed coat differentiation and mucilage production [44]. In addition, the R2R3-MYB (myeloblastosis) transcription factor MYB52 has been identified as a negative regulator of pectin de-methylesterification in seed coat mucilage due to its control of AtPMEI6 and AtPMEI14 expression [45].
Hormones are also involved in regulation of PMEI expression in several species [38,46,47,48,49]. For example, transcriptional activation of PMEI was shown to be ethylene-dependent during the ripening process of banana fruits [46], whereas a wheat PMEI was inducible by salicylic and jasmonic acid as well as hydrogen peroxide, indicating a role in defense responses [48]. Moreover, post-transcriptional regulation has also been indicated for PMEIs. Rocchi et al. [42] showed that two PMEI genes from durum wheat undergo intron retention. Mature transcripts were predominantly found in floral organs, indicating a role in flower development and in particular, anther and pollen development.
In pollen tubes, dynamic pectin metabolism is the key to polar growth and concurrently, different PME and PMEI isoforms are highly expressed in this cell type. By immuno-labelling, it was shown that HG with a low DM is found at the flanks of the pollen tube, whereas methylesterified pectin is predominantly present at the growing tip region where wall extensibility is required for cell growth [50,51]. This transition from apical to distal pectin epitopes seems to be correlated with an increase in cell wall rigidity and decrease in visco-elasticity. The maintenance of the distribution of esterified and de-esterified HG is ensured by a dedicated mechanism involving localized secretion of specific PMEI proteins [52]. The pectin methylesterase AtPPME1 is distributed evenly in the cell wall of the pollen tube. In contrast, the pollen-specific AtPMEI2, which interacts with AtPPME1, is exclusively localized at the cell wall of the pollen tube tip. This specific localization was shown to be dependent on endocytic internalization of AtPMEI2 at the flanks of the pollen tube. Therefore, protein secretion and endocytosis seems to be an efficient mechanism for regulating DM of pectin in a temporally and spatially controlled manner in pollen tubes. It remains to be seen if other PMEIs in other plant tissues are also regulated by such a mechanism.
In general, the large number of PMEI family members with distinct expression and regulation patterns could suggest the existence of dedicated interaction pairs required for localized modifications of HG methylesterification during development. Additionally, this could indicate different inhibitory activities of PMEIs depending on the cell wall environment and/or different specificities for target PMEs to guarantee a development- and stress-dependent adjustment of cell wall mechanics.
3. PME Inhibitor Structure and Interaction with Pectin Esterases
PME inhibitors and invertase inhibitors belong to the same protein family (PF04043, http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF04043), although their respective target proteins are part of different metabolite pathways. The overall sequence identity between PMEIs and invertase inhibitors is only moderate (20–30%), but their three-dimensional structure is highly similar [53]. As shown by crystallographic approaches, PMEIs consist of four long α-helices arranged in an up-down-up-down topology, forming a four-helix bundle. They contain an N-terminal signal peptide responsible for extracellular targeting and four highly conserved cysteine residues, which are involved in the formation of two disulfide (S-S) bridges essential for the maintenance of the secondary structure of the protein [54,55]. One S-S bridge connects helices α2 and α3; the second S-S bridge is located in a fifth, N-terminal anchor region consisting of short distorted helices [56].
Interaction studies performed in vitro at different pH values (pH 5.5, 7.5 & 8.5; pH 7.5; pH 5.5 & 7.5; pH 6.5, 7.5 & 8.5) indicated formation of a stoichiometric 1:1 complex of PMEIs with endogenous PMEs but also with enzymes from other species [41,53,56,57]. For example, Jolie et al. [58] showed that purified PMEI from kiwi can bind to PMEs from carrot and broccoli (at pH 6.5), whereas tomato and Arabidopsis PMEIs can interact and inhibit PMEs from orange (at pH 7.5 and pH 7, respectively) [30,59]. On the other hand, plant PMEIs do not seem capable of inhibiting fungal or bacterial PMEs, as was shown for PMEI1 and PMEI2 from Arabidopsis, which did not affect PME activity of Botrytis cinerea [26]. Similarly, Reca et al. [59] showed that purified tomato PMEI only inhibited plant PMEs but was not active against PME from Erwinia chrysantemi. An explanation for this lack of inhibition might be that residues critical for PME-PMEI interaction are not conserved in fungal and bacterial PMEs [56].
The three-dimensional structure of Arabidopsis and kiwi PMEI interacting with purified PME from tomato revealed that the inhibitor covers the putative active site of the enzyme, thus preventing substrate binding [53]. The N-terminal anchor region interacts with the C-terminus of PME, potentially supporting the structural stability. The complex formation of PMEI with PME has been shown to be pH sensitive [60]. A detailed study on kiwi PMEI indicated that PMEI-PME complex formation in vitro was reduced at pH values above 6.0, due to reversible conformation changes in the 3D structure of the PMEI protein. At pH levels above 7.5, irreversible changes in PMEI secondary structure occur, such as cleavage of the S-S bridges, inducing helix instability. Once the PMEI-PME complex is formed, it is rather stable and only dissociates under extreme pH conditions (such as pH 10), indicating that interaction with the endogenous PME enzyme protects the inhibitor from conformational changes. Different PMEIs have been shown to function at different pH values; Nguyen et al. [61] analyzed a PMEI of rice (OsPMEI28), which had a highest inhibitor activity against commercial PME at pH 8.5, whereas complex formation between PME3 and PMEI7 of Arabidopsis was highly sensitive to pH variation between 5 and 7 [62]. The observed sensitivity was the result of changes in the protonation of amino acid residues at the interface of the two proteins, which caused residues to shift between inter- and intra-molecular interactions. These results indicate that the prevalent cell wall environment, i.e., the pH of the cell wall, can affect the activity of PMEIs, thereby fine-tuning the DM of pectic polysaccharides.
It was also shown that one PMEI protein can bind and inhibit several endogenous PME enzymes [39,56], indicating a complex mechanism for regulation of PME activity. For example, key residues involved in the interaction between the inhibitors AtPMEI4 or AtPMEI9 and AtPME3 were identified by computational approaches and indicated that functional diversity between the two PMEIs leads to distinct consequences on pollen tube elongation [63]. However, the existence of strictly specific PMEI-PME pairs cannot be excluded at this time.
4. Role of PMEIs in Stress
The cell wall is the first barrier against pathogens and maintenance of cell wall integrity plays an important role in pathogen defense [64]. For many bacteria and fungi, secretion of cell wall degrading enzymes that hydrolyze pectin is an important component for successfully infecting a plant [65,66,67,68]. Conversely, inactivation of pectin degrading enzymes in pathogens can reduce their virulence on host plants [69,70,71,72]. Plant PME activity and the level of pectin methylesterification are highly regulated by pathogens during an infection process and an increase in PME activity is correlated with reduced DM of pectin in Arabidopsis during infection with different pathogens [67,68,73]. In addition, degradation of HG by pathogenic polygalacturonases releases de-esterified pectin fragments or oligogalacturonides (OGs) which in turn act as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPS [74]). Several studies demonstrated that OGs are sensed by specific plant receptors (wall-associated kinase, WAK) and can activate a stress response by the plant [75,76]. It has been shown that the DM of OGs influences the strength of the elicited response [27,77]. Furthermore, PME activity on HG results in release of methanol, a signaling molecule that is involved in priming of (neighboring) plants and able to retard bacterial growth [78].
Constitutive expression of the PMEI genes AtPMEI-1 and AtPMEI-2 in Arabidopsis reduced the PME activity and resulted in an increase in DM of HG [26]. The transgenic mutants were more resistant to the necrotrophic fungus Botrytis cinerea, which was not due to inhibition of fungal PME but rather to an impaired fungal growth on methylesterified pectin. Further PMEI genes, AtPMEI10, AtPMEI11 and AtPMEI12, were identified as upregulated in response to B. cinerea infection [47]. Genetic studies indicated that AtPMEI expression is dependent on jasmonic acid and ethylene signaling but only AtPMEI11 can be induced by OGs [47]. The pmei10, pmei11 and pmei12 mutants showed increased PME activity, decreased DM of pectin and increased lesion formation upon B. cinerea infection. This indicates that plants modulate PME activity by expressing PMEIs in response to pathogen attack.
Similarly, transgenic wheat lines expressing the PMEI from kiwi fruit also showed a reduction of disease symptoms caused by two fungal pathogens, Fusarium gramineum and Bipolaris sorokiniana [79]. This was related to reduced fungal growth on pectin with high DM and the activity of fungal PG to hydrolyze the plant pectin was impaired. In addition, the transgenic wheat plants showed less disease symptoms upon infection with the biotrophic fungal pathogen Claviceps purpurea [80]. This also shows the importance of pectin (and its methylesterification status) in grass species, despite its low abundance [2]. In barley (Hordeum vulgare), a family of putative pectin esterase inhibitors (PEIs) has been associated with a resistance gene (Rrs2 locus), which is involved in defense against Rhynchosporium commune which causes leaf blotch [81]. Overexpression of HvPEI4 led to an improvement of the resistance, but none of the candidate genes alone caused a high increase in resistance level. In a recent study, a PME inhibitor from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) was identified as being involved in the defense response to the fungus Verticilium dahliae [39]. GhPMEI3 expression in Arabidopsis led to reduced disease symptoms upon infection with V. dahlia and silencing of GhPMEI3 in cotton resulted in an increased susceptibility to the fungus.
Based on current evidence, the proposed role of PMEI in the immune response is the dynamic modulation of the PME activity (Figure 3). The degree of methylesterification determines the susceptibility of the plant cell wall to the pectin-degrading enzymes of the pathogen [82]. Plant PME activity generates methanol as an alarm signal of the damaged self that can regulate the transcription of pathogen-related PMEI genes either directly (e.g., AtPMEI11 [47]) or via modulation of DAMP or defense hormone signaling (AtPMEI10, AtPMEI11, AtPMEI12 [47]). OGs are released by partial hydrolysis of HG by fungal/bacterial polygalacturonases. They serve as DAMPs and bind to WAKs at the plasmamembrane, leading to activation of plant immune signaling, which induces classic defense responses. The DM of OGs can influence the intensity of the defense response. PMEIs (e.g., AtPMEI10, AtPMEI11, AtPMEI12 [47]) are transcriptionally upregulated by defense-related signaling pathways including jasmonic acid and ethylene, and inhibit plant PMEs leading to a higher DM of pectin, which makes it less susceptible to being broken down by fungal cell wall degrading enzymes.
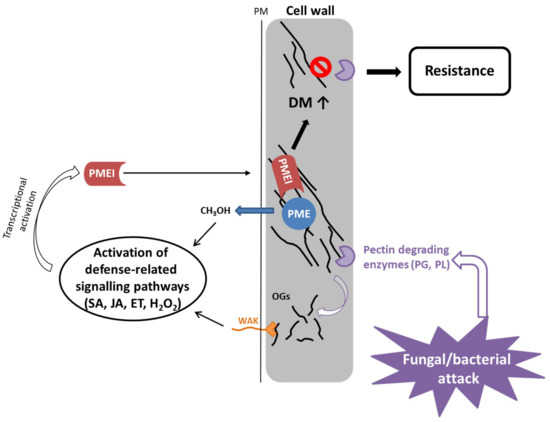
Figure 3.
PMEIs modulate PME activity and DM of pectin in response to fungal and bacterial attack. Bacteria and fungi secrete pectin degrading enzymes, like polygalacturonases and pectate/pectin lyases, upon infection. PME activity leads to release of methanol, which serves as an alarm signal, activating the expression of pathogen-related PMEIs. Similarly, OGs, which are generated by degradation of pectin by fungal/bacterial PGs and PLs, serve as DAMPs, leading also to activation of defense related signaling pathways, which have been shown to activate PMEI gene expression. PMEIs inhibit PME activity leading to a higher degree of methylesterification of pectin, which contributes to resistance to fungal/bacterial enzymes resulting in less disease symptoms.
PMEIs have also been implicated to play a role in defense against bacteria. CaPMEI1 from pepper (Capsicum annuum) was identified in pepper leaves infected with Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria (Xcv) [83]. Xcv secretes plant cell wall degrading enzymes like pectate lyases and polygalacturonases upon infection. CaPMEI1 was transcriptionally upregulated by different biotic stress signals (e.g., salicylic acid, jasmonic acid, ethylene, H2O2) and consequently, silenced pepper plants exhibited an increased susceptibility to Xcv. Conversely, overexpression of CaPMEI1 in Arabidopsis conferred an enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae but not to the biotrophic fungus Hyaloperonospora parasitica.
Little is known about the role of PMEIs in viral infections. In tobacco, plant PMEs have been shown to be involved in tobacco mosaic virus movement between host cells via interaction with the viral movement protein [84]. Accordingly, overexpression of PMEIs in tobacco and Arabidopsis counteracted the action of PMEs, leading to increased resistance to tobacco mosaic virus and turnip vein clearing virus infection respectively [85]. This was characterized by the reduced or delayed movement of the viruses and decreased disease symptoms. It is suggested that PMEI reduces viral spreading via limiting viral-induced PME activity and by hindering the enlargement of plasmodesmata.
Plants respond to abiotic stresses, e.g., water deficit, salt stress, and temperature extremes, with changes in cell wall architecture, although available literature is more focused on transcriptomic data rather than biochemical experiments [86,87]. PMEIs are also involved in the plants’ response to changing environmental conditions, however; only little is known about their molecular role. CaPMEI1 from pepper is transcriptionally induced by cold treatment, drought stress, as well as the plant stress hormone abscisic acid and hydrogen peroxide [83]. Arabidopsis lines overexpressing CaPMEI1 exhibited an increased tolerance to water stress, as shown by improved germination rate and seedling root growth in the presence of high mannitol concentrations as compared to control plants. In addition, a reduced transpiration rate was accompanied by less withering upon drought stress, and improved tolerance to oxidative stress caused by methyl viologen [83].
Several studies using expression analysis have revealed the functional importance of PMEIs in response to abiotic stresses. RT-PCR analysis of the wheat TaPMEI showed the responsiveness of the gene to H2O2 stimulus, salinity, water stress (caused by polyethylene glycol) and abscisic acid treatment [48]. Time course analysis further indicated a specificity of the transcriptional response based on the investigated tissue (leaf, stem and root). In silico meta expression analysis using Affymetrics array data for rice [38] revealed the importance for several PMEI family members in diverse stress responses. Drought stress, salt stress, cold and anaerobic conditions (during germination) were analyzed, and showed specific transcriptional regulations of PMEI genes [38]. Similarly, in Arabidopsis, the effect of hormone and stress treatments on the expression of PMEI family members was analyzed in silico. [35]. The microarray data analysis of the PMEI family showed that several PMEI are differentially expressed in response to abscisic acid, gibberellic acid, auxin and methyl jasmonate treatment, and many are involved in cold, drought, heat, oxidation, salt, and wounding regulation in Arabidopsis [35]. In the same study, a cis-element analysis of promotor regions of the Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis PMEI gene family also indicated an involvement of several PMEI genes in environmental stress responses. For example, of the 100 PMEI genes in Brassica campestris, 38 BcPMEI promotors contained both abscisic acid and auxin (indole-3-acetic acid) related cis-elements, 63 and 35 promotors contained heat stress elements and low-temperature response elements, respectively. Additionally, MYB binding sites involved in drought stress were found in 58 PMEI promotors [35]. However, these in silico results will have to be validated by experimental data.
An Arabidopsis mutant with reduced expression of a PMEI gene (At1g62760) exhibited reduced sensitivity to salt stress [88]. Enhanced root growth, higher fresh weight and less chlorosis and necrosis upon NaCl treatment were accompanied with reduced salt stress signaling in the mutant, suggesting this PMEI as a negative regulator of salinity tolerance. In contrast, overexpression of AtPMEI13 (At5g62360) in Arabidopsis also led to increased salt tolerance, as transgenic lines showed higher rates of germination, root growth, and survival under salinity conditions as compared to wild type plants [89]. This phenotype was also observed in plants overexpressing the closest homolog CbPMEI1 from Chorispora bungeana, an alpine plant highly tolerant to chilling and freezing stress. Both genes were repressed by salt stress and abscisic acid but were induced by cold, suggesting distinct roles of the genes in freezing and salinity tolerance. The transgenic overexpression plants showed decreased freezing tolerance; however, they exhibited increased root growth under cold conditions. Plants increase pectin levels in the cell wall under low temperatures [90] probably to reduce cell wall porosity and increase cell adhesion. It was previously reported that DM of pectin increases during cold acclimation in pea [91]. In contrast, loss of AtPME41 in Arabidopsis by a transfer DNA insertion caused an increase in freezing sensitivity [92]. Since pectins are important under low temperature conditions, PMEI activity could play a role in balancing the trade-off between freezing tolerance and growth by modifying the mechanical properties of cell walls.
5. Role of PMEIs in Development
PME-mediated changes in methyl-esterification of HG have been shown to affect various vegetative and reproductive stages of plant development (for reviews, see [6,7]). Therefore, we aim to give an overview of the latest results of molecular studies on PMEIs in plant development.
5.1. PMEI Function in Seeds
Upon hydration, mature Arabidopsis seeds rapidly extrude a gelatinous substance from seed coat epidermal (SCE) cells called mucilage, which is mainly composed of cell wall polysaccharides [93]. This layer has adhesive properties and possibly serves as a water-reservoir, which might facilitate seed germination, although it has been shown that mucilage production is not necessary for germination or plant fitness in the laboratory [94,95]. The mucilage is mainly composed of pectin, RG-I and small amounts of HG, but hemicellulose and cellulose have also been identified as minor components, as well as arabinogalactan proteins [96]. Several studies provided evidence that the DM of HG determines mucilage properties. For example, seven PME genes are specifically expressed in Arabidopsis seeds and the pme58 mutant caused an altered pectin distribution in the mucilage [97]. Additionally, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, FLYING SAUCER1, was proposed to regulate the DM and a mutation lead to reduced mucilage extrusion and increased mucilage adherence [29]. Finally, the subtilase atsbt1.7 mutant didn’t show significant sugar compositional changes in its mucilage but a decrease in mucilage methylation, which was correlated with an increased PME activity [98].
More direct evidence was obtained by investigating the role of PMEI6, which was shown to be essential for proper mucilage release [44]. In three pmei6 mutants, the outer primary cell wall of the SCE cells did not rupture into fragments but remained attached, which caused a delay in mucilage extrusion. This was accompanied by a lack of methylesterified HG (detected by antibodies) and reduced methanol release in the mucilage, as well as increased PME activity in seeds. The reduction in methylesterification in the outer primary cell wall of the three pmei6 mutants could possibly lead to more abundant Ca2+ cross-linking of HG, which causes stronger attachment between adjoining cell walls and therefore impairs release of the mucilage. Further evidence indicates that PMEI14 is also involved in regulating pectin methyl-esterification in seed coat mucilage and that PMEI14 together with PMEI6 and ATSBT1.7 are likely transcriptionally controlled by MYB52 [45]. Knock out mutants of PMEI14 had an increased PME activity in seed mucilage but not in demucilated seeds. A reduced level of methylesterification of the mucilage was accompanied by an increased amount of calcium cross-linked HG detected by immuno-labelling. These studies show that PMEI6 function affects both seed coat mucilage and the primary SCE cell wall, and is necessary for proper mucilage release. In contrast, PMEI14 function is confined to inhibiting PME activity, specifically in the seed coat mucilage, potentially influencing pectin structure.
PME activity has also been shown to be tightly controlled during germination in Arabidopsis and garden cress (Lepidium sativum) [99,100], probably leading to cell wall weakening to allow radicle emergence. A small number of PME and PMEIs are strongly up-regulated upon germination, also in the presence of abscisic acid, which delays endosperm weakening and rupture [100]. Furthermore, overexpression of the PME inhibitor PMEI5 resulted in a higher DM of seeds and reduced PME activity, which was accompanied by an earlier and faster germination process compared to wildtype [99]. This suggests that PMEI activity is essential for proper timing of seed germination but the precise molecular events are only beginning to be understood, based on modern techniques such as Chip-Seq [45] and potentially based on novel probes to dynamically monitor cell walls [101].
5.2. PMEI Function in Growth Processes
Plant cell growth is regulated by the interplay between the intracellular turgor pressure and the flexibility of the cell wall. Recent reviews have highlighted the importance of pectin, and especially HG, for mediating changes in the mechanical properties for control of growth processes [4,6,102]. In addition, studies using atomic force microscopy provided evidence that increased pectin de-methylesterification correlates with a decrease in cell wall stiffness [21,25].
A PMEI from Arabidopsis, AtPMEI4, has been shown to be involved in regulating hypocotyl growth. Growth acceleration of dark-grown hypocotyls requires significant cell wall remodeling, which is associated with transcriptional upregulation of pectin-modifying genes [103]. AtPMEI4 was upregulated during this developmental transition and its expression was shown to be specific for rapidly elongating epidermis cells in hypocotyls and roots. In an overexpression line, the onset of hypocotyl growth acceleration was delayed, suggesting that the PME inhibitor controls pectin de-methylesterification essential for the timing of the growth acceleration, but not the growth process itself [103]. On the other hand, OsPMEI28 overexpression in rice had an effect on the growth process, namely inhibition of culm elongation and decreased cell wall thickness of culms, which resulted in a dwarfed phenotype [61]. Conversely, a pmei4 mutant with elevated PME activity in Arabidopsis root cell walls showed an increase in root length [62], suggesting a correlation between increased de-methylesterification and elevated growth.
Controversial results have been reported for purified kiwi PMEI applied on Arabidopsis root tips, where an increase of root growth rate was stated upon inhibition of PME activity [104]. Similarly, Arabidopsis plants overexpressing AtPMEI2 show enhanced growth and increased biomass due to enhanced cell expansion [105] as well as increased root length due to stronger cell elongation [26]. Increased root length and area was also observed in Arabidopsis plants expressing a PMEI from cotton [39]. Therefore, higher levels of DM of pectin seem also to be able to promote growth and cell expansion.
This correlation was also observed in pollen tube growth. Pollen tubes undergo a fast and unidirectional growth at the apex dependent on ion (e.g., calcium) dynamics and PMEs have been shown to play a role in this process [106,107]. A pollen-specific PME inhibitor, AtPMEI2, was shown to inhibit PME activity in Arabidopsis [52]. Although the pollen-specific pectin methylesterase AtPPME1 was expressed along the whole pollen tube, the localization of AtPMEI2 was exclusively restricted to the apex, the site of elongation. This supports the model that elongation requires higher DM of the cell wall, which is caused by inhibition of PME activity, specifically at the tip. Conversely, along the pollen tube, PME activity is less inhibited, resulting in de-methylesterification, which in turn would lead to formation of calcium cross-links due to the availability of free calcium ions, causing increased cell wall stiffness. Corroborative, expression of AtPME1 in tobacco pollen tubes inhibited elongation, whereas AtPMEI2 expression led to an increase in elongation rate [52]. Antisense expression of a pollen-specific PMEI from broccoli (Brassica oleracea) in Arabidopsis triggered silencing of the orthologous Arabidopsis gene At1g10770 and resulted in male sterility. This suggests that disturbance of PME activity imbalances the pectin distribution and affects cell wall dynamics in the pollen cell wall with detrimental effect on fertility [108]. In addition, wheat Tdpmei2.1 and Tdpmei2.2 transcripts have been shown to undergo complete mRNA processing, specifically in anthers [42]. The occurrence of this mechanism suggests a role of the PME inhibitors during pollen development and reproductive processes, but requires further investigations.
The present data indicate a complex relationship between changes of DM of pectin (based on PMEI activity) and growth processes. Further studies are necessary to elucidate in a tissue-specific manner how the interplay of PMEs and PMEIs regulate pectin methylesterification and affect mechanical properties of cell wall necessary for cell elongation.
5.3. PMEI Function in Organ Formation
The mechanical properties of cell walls have been proposed to play a key role in plant morphogenesis and the control of organ outgrowth [7,109,110]. Organ morphogenesis requires a transition from isotropic growth of undifferentiated cells to anisotropic growth pattern, which is dependent on local cell wall loosening and stiffening by e.g., modification of cell wall components.
AtPMEI3, which is expressed in the apical meristem, was inducible expressed in Arabidopsis, which led to hyper-methylesterification of HG throughout the meristem dome upon induction [24]. As a result, the formation of both floral and flower organ primordia was inhibited. Using atomic force microscopy, it was shown that the reduced de-methylesterification of HG was accompanied by increased stiffness of cell walls in the shoot apical meristem in the AtPMEI3 overexpressing lines [25]. This further resulted in shorter cells and loss of growth asymmetry, showing that anisotropic growth requires an asymmetric loosening of longitudinal walls, which is caused by fine-tuned de-methylesterification of pectin.
Constitutive overexpression of AtPMEI5 in Arabidopsis also caused strong morphological phenotypes [111,112]. The stems of the transgenic plants showed an aberrant, twisted growth pattern, especially at branching points and branching organs (e.g., leaf or inflorescence), which failed to separate properly from the main stem [111]. Additionally, root growth was disturbed in the mutant and curled leaves and misshapen siliques were observed, which was proposed to be a result of activated BR signaling [112]. This indicates that PMEIs are involved in the fine-tuning of cell wall biomechanical properties via HG methylesterification that is required for proper organ formation and separation.
PMEIs might also play a role in organ senescence as changes in pectin methylesterification have been described, e.g., for petal senescence [113,114]. However, so far, only transcriptional changes of putative invertase/pectin methylesterase inhibitor genes in petals during senescence have been reported and further, more detailed studies will be necessary to investigate their putative function.
5.4. PMEIs in Fruit Development
Fruit ripening is a highly controlled developmental event during which the fruit undergoes various changes, e.g., in sugar contents, color, flavor, aroma, texture. Softening is a very (economically) important physiological change and several cell wall-modifying enzymes are involved in this process [115]. The first inhibitor of PME was identified in ripe kiwi fruit by Balisteri et al. [33] and was found active only in the mature stage, whereas it was undetectable in unripe fruits [116]. Furthermore, the expression levels of the PMEI genes in kiwi fruit increased with the progression of fruit maturation [117]. In banana (Musa acuminata), a PME inhibitor, MaPMEI1, was shown to be specifically expressed in the fruit and up-regulated during the ethylene-dependent ripening process [46]. Similarly, a PMEI has been identified in the tomato fruit [59]. SolyPMEI was strongly expressed in red fruits and, in lower levels, also in flowers and pollen, but not in green fruits. Interaction with the tomato PME-1 enzyme in the fruit and increased SolyPMEI expression levels with progression of ripening stages implicates the inhibitor in modulating PME activity and degree of methyl-esterification during fruit ripening in tomato. In grape (Vitis vinifera), VvPMEI1 was found to be expressed only during the early phases of berry development, characterized by a rapid berry growth both through cell division and expansion [41]. VvPMEI1 could be involved in regulating PME activity required for rapid cell growth and to maintain firmness, or it could prevent early softening of grape berries related to pectin degradation. This indicates a role for PMEIs in modulating PME activity and pectin methylesterification in different stages of fruit development.
6. Potential of PMEIs for Applications
Lignocellulosic biomass constitutes a sustainable renewable source of chemicals and fuels, but a major bottleneck for an industrial utilization is the natural recalcitrance of the cell wall due to its complex and heterogeneous structure. Modification of cell wall polysaccharides can improve the degradation into soluble sugars, which can be used by microorganisms for fermentation, a process called saccharification [118]. Improved saccharification can make an industrial process more efficient and reduce cost for pre-treatments of the biomass. Lionetti et al. [105] showed that overexpression of AtPMEI2 in Arabidopsis leads to a higher enzymatic saccharification efficiency, indicating a reduced cell wall recalcitrance likely due to the higher degree of HG methylesterification. The same was observed for wheat plants expressing the kiwi PMEI, suggesting that both cellulose and hemicellulose are better digestible during enzymatic hydrolysis in the transgenic plants. As a side effect, transgenic Arabidopsis plants had a higher biomass yield due to enhanced cell expansion. Further, a negative correlation between the level of de-methylesterified HG and cellulose degradability was found for 24 Arabidopsis accessions [119]. The reduction of egg-box structures or other crosslinks of methylesterified HG might be responsible for the accessibility of cellulose fibers for enzymatic digestion, which in turn results in increased saccharification efficiency. This indicates the potential of PMEI as a HG modifying enzyme to improve plant tissues for saccharification by targeted mutation or in wide-scale selection and breeding of plants for further utilization (e.g., as biofuels or for production of chemicals).
PMEIs have been shown to play a role in ripening processes (see above). Therefore, a potential application of this inhibitor would be in food (fruit and vegetable) processing. For food technology, endogenous PME activity is highly relevant because it determines the physiochemical and functional properties of pectin, thereby affecting the quality of plant-derived food products. PME activity in fruit juice causes undesired phase separation because de-methylesterified HG forms calcium crosslinks, and the resulting calcium pectate is insoluble and precipitates [120]. Addition of PMEI to orange juice was shown to control PME activity even over long storage, thereby avoiding phase separation. Application of PMEI would reduce required thermal treatments during juice processing and should result in better flavor and product quality [120]. For development or optimization of food-processing steps, it would be beneficial to determine PME activity in plant tissues. A PMEI-based molecular probe was shown to successfully label plant PMEs in various plant tissues and moreover, to differentiate between active and inactivated PME molecules [121]. This application of PMEIs would give important information about presence and localization of active PMEs after different food processing steps (e.g., thermal or high pressure treatment, microwaving). PMEIs have also been proposed for application in wine and marc production [41]. Pectin de-methylesterification releases high levels of methanol during different stages of grape processing, greatly affecting the composition of the final product [122,123]. Here, PMEIs could be used to reduce methanol formation in grape must and marc, as well as in products derived by fermentation and distillation [124]. Apart from applications in food industry, manipulation of PMEIs in planta could also be of interest. Overexpression of PMEIs, in banana fruits for example, would not only control over-softening but also likely extend banana shelf-life [46]. In conclusion, PMEIs could be good tools to control endogenous PME activity during food production processes, thereby positively influencing product quality.
As mentioned above, PMEIs play an important role in the response to biotic and environmental stresses. Therefore, the inhibitors could be potential targets for genetic engineering, aimed to improve plant fitness. In cold as well as salt stress conditions, PMEIs might be beneficial for balancing growth maintenance with stress tolerance and overexpression of PMEIs would be a promising way to improve salt tolerance of crops [89]. In addition, PMEI activity has been shown to be essential for resistance against fungal and bacterial pathogens [26,79,83]. Therefore, it could be useful as a potential molecular marker in plant breeding programs targeted to the selection of crop varieties with durable resistance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.W.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, A.W.; Writing-Review & Editing, A.W. & B.U.; Visualization, A.W.; Funding Acquisition, B.U. & A.W.
Funding
This research was supported by DFG (grant number: US98/13-1), the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (grant number: 031B0193B) as well as the Ministry of Innovation, Science and Research of North-Rhine Westphalia within the framework of the North-Rhine Westphalia Strategieprojekt BioEconomy Science Center (grant number 313/323-400-00213).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Abbreviations
| PMEI | Pectin methylesterase inhibitor |
| PME | Pectin methyl esterase |
| DM | Degree of methylation |
| HG | Homogalacturonan |
| GalA | D-galacturonic acid |
| GAUT | Galacturonosyltransferases |
| OGs | Oligogalacturonides |
| DAMP | Damage associated molecular pattern |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| SCE | Seed coat epidermis |
| MUM1 | Mucilage-modified mutant 1 |
References
- Wolf, S.; Mouille, G.; Pelloux, J. Homogalacturonan methyl-esterification and plant development. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohnen, D. Pectin structure and biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braybrook, S.A.; Hofte, H.; Peaucelle, A. Probing the mechanical contributions of the pectin matrix. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palin, R.; Geitmann, A. The role of pectin in plant morphogenesis. Biosystems 2012, 109, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, F.B.; Braybrook, S.A. How to let go: Pectin and plant cell adhesion. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque-Tremblay, G.; Pelloux, J.; Braybrook, S.A.; Müller, K. Tuning of pectin methylesterification: Consequences for cell wall biomechanics and development. Planta 2015, 242, 791–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffer, A.M. Expanding roles for pectins in plant development. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, J.D.; Quigley, H.F.; Orellana, A.; Mohnen, D. The catalytic site of the pectin biosynthetic enzyme alpha-1,4-galacturonosyltransferase is located in the lumen of the Golgi. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 360–371. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, J.D.; Atmodjo, M.A.; Inwood, S.E.; Kumar Kolli, V.S.; Quigley, H.F.; Hahn, M.G.; Mohnen, D. Functional identification of an Arabidopsis pectin biosynthetic homogalacturonan galacturonosyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5236–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmodjo, M.A.; Sakuragi, Y.; Zhu, X.; Burrell, A.J.; Mohanty, S.S.; Atwood, J.A.; Orlando, R.; Scheller, H.V.; Mohnen, D. Galacturonosyltransferase (GAUT)1 and GAUT7 are the core of a plant cell wall pectin biosynthetic homogalacturonan:galacturonosyltransferase complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20225–20230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, A.K.; Atmodjo, M.A.; Li, M.; Baxter, H.L.; Yoo, C.G.; Pu, Y.; Lee, Y.-C.; Mazarei, M.; Black, I.M.; Zhang, J.-Y.; et al. Sugar release and growth of biofuel crops are improved by downregulation of pectin biosynthesis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouille, G.; Ralet, M.-C.; Cavelier, C.; Eland, C.; Effroy, D.; Hématy, K.; McCartney, L.; Truong, H.N.; Gaudon, V.; Thibault, J.-F.; et al. Homogalacturonan synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana requires a Golgi-localized protein with a putative methyltransferase domain. Plant J. 2007, 50, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupková, E.; Immerzeel, P.; Pauly, M.; Schmülling, T. The TUMOROUS SHOOT DEVELOPMENT2 gene of Arabidopsis encoding a putative methyltransferase is required for cell adhesion and co-ordinated plant development. Plant J. 2007, 50, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralet, M.-C.; Crépeau, M.-J.; Buchholt, H.-C.; Thibault, J.-F. Polyelectrolyte behaviour and calcium binding properties of sugar beet pectins differing in their degrees of methylation and acetylation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 16, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, A.J.; Pauly, M. Comparative genomics of pectinacetylesterases: Insight on function and biology. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e1055434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.-Y.; Miller, L.M.; Hou, G.; Yu, X.-H.; Chen, X.-Y.; Liu, C.-J. Acetylesterase-mediated deacetylation of pectin impairs cell elongation, pollen germination, and plant reproduction. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braccini, I.; Pérez, S. Molecular basis of Ca2+-induced gelation in alginates and pectins: The egg-box model revisited. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.B.; Wang, T.; Park, Y.B.; Cosgrove, D.J.; Hong, M. Water–polysaccharide interactions in the primary cell wall of Arabidopsis thaliana from polarization transfer solid-state NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10399–10409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.-A.; Apperley, D.C.; Jarvis, M.C. Molecular rigidity in dry and hydrated onion cell walls. Plant Physiol. 1997, 115, 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Tibbits, C.W.; MacDougall, A.J.; Ring, S.G. Calcium binding and swelling behaviour of a high methoxyl pectin gel. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 310, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peaucelle, A.; Braybrook, S.A.; Le Guillou, L.; Bron, E.; Kuhlemeier, C.; Höfte, H. Pectin-induced changes in cell wall mechanics underlie organ initiation in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsbury, S.; Hunt, L.; Elhaddad, N.; Baillie, A.; Lundgren, M.; Verhertbruggen, Y.; Scheller, H.V.; Knox, J.P.; Fleming, A.J.; Gray, J.E. Stomatal function requires pectin de-methyl-esterification of the guard cell wall. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2899–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.; Woolfenden, H.; Baillie, A.; Amsbury, S.; Carroll, S.; Healicon, E.; Sovatzoglou, S.; Braybrook, S.; Gray, J.E.; Hobbs, J.; et al. Stomatal opening involves polar, not radial, stiffening of guard cells. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2974.e2–2983.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peaucelle, A.; Louvet, R.; Johansen, J.N.; Höfte, H.; Laufs, P.; Pelloux, J.; Mouille, G. Arabidopsis phyllotaxis is controlled by the methyl-esterification status of cell-wall pectins. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peaucelle, A.; Wightman, R.; Höfte, H. The control of growth symmetry breaking in the Arabidopsis hypocotyl. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, V.; Raiola, A.; Camardella, L.; Giovane, A.; Obel, N.; Pauly, M.; Favaron, F.; Cervone, F.; Bellincampi, D. Overexpression of pectin methylesterase inhibitors in Arabidopsis restricts fungal infection by Botrytis cinerea. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, S.; Castillejo, C.; Quesada, M.A.; Medina-Escobar, N.; Brownsey, G.J.; Suau, R.; Heredia, A.; Botella, M.A.; Valpuesta, V. Partial demethylation of oligogalacturonides by pectin methyl esterase 1 is required for eliciting defence responses in wild strawberry (Fragaria vesca). Plant J. 2008, 54, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sénéchal, F.; Wattier, C.; Rustérucci, C.; Pelloux, J. Homogalacturonan-modifying enzymes: Structure, expression, and roles in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5125–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiniciuc, C.; Dean, G.H.; Griffiths, J.S.; Kirchsteiger, K.; Hwang, Y.T.; Gillett, A.; Dow, G.; Western, T.L.; Estelle, M.; Haughn, G.W. FLYING SAUCER1 Is a transmembrane RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that regulates the degree of pectin methylesterification in Arabidopsis seed mucilage. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 944–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sénéchal, F.; L’Enfant, M.; Domon, J.-M.; Rosiau, E.; Crépeau, M.-J.; Surcouf, O.; Esquivel-Rodriguez, J.; Marcelo, P.; Mareck, A.; Guérineau, F.; et al. Tuning of pectin methylesterification. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 23320–23335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge, N. Plant protein inhibitors of cell wall degrading enzymes. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelloux, J.; Rustérucci, C.; Mellerowicz, E.J. New insights into pectin methylesterase structure and function. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrieri, C.; Castaldo, D.; Giovane, A.; Quagliuolo, L.; Servillo, L. A glycoprotein inhibitor of pectin methylesterase in kiwi fruit (Actinidia chinensis). Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 193, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yuan, D.; Gao, W.; Li, Y.; Tan, J.; Zhang, X. A comparative genome analysis of PME and PMEI families reveals the evolution of pectin metabolism in plant cell walls. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yu, H.; Xiong, X.; Yue, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, L.; Cao, J. Genome-wide identification, molecular evolution, and expression profiling analysis of pectin methylesterase inhibitor genes in Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Liu, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, C.; Ren, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, W.; Peng, S.; Feng, H. Pectin methylesterase inhibitor (PMEI) family can be related to male sterility in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2018, 293, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzón-Latorre, D.; Deyholos, M.K. Characterization and transcript profiling of the pectin methylesterase (PME) and pectin methylesterase inhibitor (PMEI) gene families in flax (Linum usitatissimum). BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Jeong, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, C. Molecular and biochemical characterization of rice pectin methylesterase inhibitors (OsPMEIs). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 101, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Sun, Y.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Hou, Y. A pectin methylesterase inhibitor enhances resistance to Verticillium wilt. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 2202–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.; Vinegar, B.; Nahal, H.; Ammar, R.; Wilson, G.V.; Provart, N.J. An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, V.; Raiola, A.; Mattei, B.; Bellincampi, D. The grapevine VvPMEI1 gene encodes a novel functional pectin methylesterase inhibitor associated to grape berry development. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, V.; Janni, M.; Bellincampi, D.; Giardina, T.; D’Ovidio, R. Intron retention regulates the expression of pectin methyl esterase inhibitor (PMEI) genes during wheat growth and development. Plant Biol. 2012, 14, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzon-Latorre, D.; Deyholos, M.K. Pectinmethylesterases (PME) and pectinmethylesterase inhibitors (PMEI) enriched during phloem fiber development in flax (Linum usitatissimum). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Aguayo, S.; Ralet, M.-C.; Berger, A.; Botran, L.; Ropartz, D.; Marion-Poll, A.; North, H.M. PECTIN METHYLESTERASE INHIBITOR6 promotes Arabidopsis mucilage release by limiting methylesterification of homogalacturonan in seed coat epidermal cells. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Ren, A.; Tang, X.; Qi, G.; Xu, Z.; Chai, G.; Hu, R.; Zhou, G.; Kong, Y. MYB52 negatively regulates pectin demethylesterification in seed coat mucilage. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 2737–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Gupta, S.M.; Sane, A.P.; Nath, P. Isolation and characterization of ripening related pectin methylesterase inhibitor gene from banana fruit. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2012, 18, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, V.; Fabri, E.; De Caroli, M.; Hansen, A.R.; Willats, W.G.T.; Piro, G.; Bellincampi, D. Three pectin methylesterase inhibitors protect cell wall integrity for Arabidopsis immunity to Botrytis. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1844–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, T.G.; Jeon, W.B.; Seo, Y.W. Functional characterization of pectin methylesterase inhibitor (PMEI) in wheat. Genes Genet. Syst. 2010, 85, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- An, S.H.; Choi, H.W.; Hong, J.K.; Hwang, B.K. Regulation and function of the pepper pectin methylesterase inhibitor (CaPMEI1) gene promoter in defense and ethylene and methyl jasmonate signaling in plants. Planta 2009, 230, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Hepler, P.K. Pectin methylesterases and pectin dynamics in pollen tubes. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 3219–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parre, E.; Geitmann, A. Pectin and the role of the physical properties of the cell wall in pollen tube growth of Solanum chacoense. Planta 2005, 220, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röckel, N.; Wolf, S.; Kost, B.; Rausch, T.; Greiner, S. Elaborate spatial patterning of cell-wall PME and PMEI at the pollen tube tip involves PMEI endocytosis, and reflects the distribution of esterified and de-esterified pectins. Plant J. 2008, 53, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, M.; Wolf, S.; Aloy, P.; Greiner, S.; Scheffzek, K. Structural insights into the target specificity of plant invertase and pectin methylesterase inhibitory proteins. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3437–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovane, A.; Servillo, L.; Balestrieri, C.; Raiola, A.; D’Avino, R.; Tamburrini, M.; Ciardiello, M.A.; Camardella, L. Pectin methylesterase inhibitor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1696, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camardella, L.; Carratore, V.; Ciardiello, M.A.; Servillo, L.; Balestrieri, C.; Giovane, A. Kiwi protein inhibitor of pectin methylesterase amino-acid sequence and structural importance of two disulfide bridges. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 4561–4565. [Google Scholar]
- Di Matteo, A.; Giovane, A.; Raiola, A.; Camardella, L.; Bonivento, D.; De Lorenzo, G.; Cervone, F.; Bellincampi, D.; Tsernoglou, D. Structural basis for the interaction between pectin methylesterase and a specific inhibitor protein. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiola, A.; Camardella, L.; Giovane, A.; Mattei, B.; De Lorenzo, G.; Cervone, F.; Bellincampi, D. Two Arabidopsis thaliana genes encode functional pectin methylesterase inhibitors. FEBS Lett. 2004, 557, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Jolie, R.P.; Duvetter, T.; Van Loey, A.M.; Hendrickx, M.E. Pectin methylesterase and its proteinaceous inhibitor: A review. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2583–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reca, I.B.; Lionetti, V.; Camardella, L.; D’Avino, R.; Giardina, T.; Cervone, F.; Bellincampi, D. A functional pectin methylesterase inhibitor protein (SolyPMEI) is expressed during tomato fruit ripening and interacts with PME-1. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 79, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavita, A.; Carratore, V.; Ciardiello, M.A.; Giovane, A.; Servillo, L.; D’Avino, R. Influence of pH on the structure and function of kiwi pectin methylesterase inhibitor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5866–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Jeong, H.Y.; Jeon, S.H.; Kim, D.; Lee, C. Rice pectin methylesterase inhibitor28 (OsPMEI28) encodes a functional PMEI and its overexpression results in a dwarf phenotype through increased pectin methylesterification levels. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 208, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sénéchal, F.; Mareck, A.; Marcelo, P.; Lerouge, P.; Pelloux, J. Arabidopsis PME17 activity can be controlled by pectin methylesterase inhibitor 4. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e983351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocq, L.; Sénéchal, F.; Lefebvre, V.; Lehner, A.; Domon, J.-M.; Mollet, J.-C.; Dehors, J.; Pageau, K.; Marcelo, P.; Guérineau, F.; et al. Combined experimental and computational approaches reveal distinct pH dependence of pectin methylesterase inhibitors. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1075–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, T. The plant cell wall integrity maintenance mechanism—A case study of a cell wall plasma membrane signaling network. Phytochemistry 2015, 112, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, J.J.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, G.; Brito, N.; Shah, P.; Orlando, R.; González, C. The Botrytis cinerea early secretome. Proteomics 2010, 10, 3020–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ovidio, R.; Mattei, B.; Roberti, S.; Bellincampi, D. Polygalacturonases, polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins and pectic oligomers in plant–pathogen interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1696, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, V. PECTOPLATE: The simultaneous phenotyping of pectin methylesterases, pectinases, and oligogalacturonides in plants during biotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiola, A.; Lionetti, V.; Elmaghraby, I.; Immerzeel, P.; Mellerowicz, E.J.; Salvi, G.; Cervone, F.; Bellincampi, D. Pectin methylesterase is induced in Arabidopsis upon infection and is necessary for a successful colonization by necrotrophic pathogens. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Pei, Y.; Li, F.; Hou, Y. Molecular evidence for the involvement of a polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein, GhPGIP1, in enhanced resistance to Verticillium and Fusarium wilts in cotton. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Q.; Hu, K.-D.; Li, T.-T.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.-H.; Liu, H.-P.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhang, H. Polygalacturonase gene pgxB in Aspergillus niger is a virulence factor in apple fruit. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo Ruiz, G.; Di Pietro, A.; Roncero, M.I.G. Combined action of the major secreted exo- and endopolygalacturonases is required for full virulence of Fusarium oxysporum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Jang, M.; Srivastava, A.; Jang, J.-H.; Soung, N.-K.; Ko, S.-K.; Kang, D.-O.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, B.Y. A pectate lyase-coding gene abundantly expressed during early stages of infection is required for full virulence in Alternaria brassicicola. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethke, G.; Grundman, R.E.; Sreekanta, S.; Truman, W.; Katagiri, F.; Glazebrook, J. Arabidopsis PECTIN METHYLESTERASEs contribute to immunity against Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Savatin, D.V.; Sicilia, F.; Gramegna, G.; Cervone, F.; De Lorenzo, G. Oligogalacturonides: Plant damage-associated molecular patterns and regulators of growth and development. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohorn, B.D.; Kohorn, S.L.; Saba, N.J.; Martinez, V.M. Requirement for pectin methyl esterase and preference for fragmented over native pectins for wall-associated kinase-activated, EDS1/PAD4-dependent stress response in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18978–18986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutus, A.; Sicilia, F.; Macone, A.; Cervone, F.; De Lorenzo, G. A domain swap approach reveals a role of the plant wall-associated kinase 1 (WAK1) as a receptor of oligogalacturonides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9452–9457. [Google Scholar]
- Osorio, S.; Bombarely, A.; Giavalisco, P.; Usadel, B.; Stephens, C.; Aragüez, I.; Medina-Escobar, N.; Botella, M.A.; Fernie, A.R.; Valpuesta, V. Demethylation of oligogalacturonides by FaPE1 in the fruits of the wild strawberry Fragaria vesca triggers metabolic and transcriptional changes associated with defence and development of the fruit. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2855–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, T.V.; Sheshukova, E.V.; Dorokhov, Y.L. Cell wall methanol as a signal in plant immunity. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, C.; Janni, M.; Lionetti, V.; Bellincampi, D.; Favaron, F.; D’Ovidio, R. The ectopic expression of a pectin methyl esterase inhibitor increases pectin methyl esterification and limits fungal diseases in wheat. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tundo, S.; Kalunke, R.; Janni, M.; Volpi, C.; Lionetti, V.; Bellincampi, D.; Favaron, F.; D’Ovidio, R. Pyramiding PvPGIP2 and TAXI-III but not PvPGIP2 and PMEI enhances resistance against Fusarium graminearum. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2016, 29, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzin, S.; Hanemann, A.; Sharma, S.; Hensel, G.; Kumlehn, J.; Schweizer, G.; Röder, M.S. Are PECTIN ESTERASE INHIBITOR genes involved in mediating resistance to Rhynchosporium commune in barley? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, V.; Cervone, F.; Bellincampi, D. Methyl esterification of pectin plays a role during plant–pathogen interactions and affects plant resistance to diseases. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.H.; Sohn, K.H.; Choi, H.W.; Hwang, I.S.; Lee, S.C.; Hwang, B.K. Pepper pectin methylesterase inhibitor protein CaPMEI1 is required for antifungal activity, basal disease resistance and abiotic stress tolerance. Planta 2008, 228, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-H.; Citovsky, V. Systemic movement of a tobamovirus requires host cell pectin methylesterase. Plant J. 2003, 35, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Lionetti, V.; Raiola, A.; Cervone, F.; Bellincampi, D. Transgenic expression of pectin methylesterase inhibitors limits tobamovirus spread in tobacco and Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, H.; Philippe, F.; Domon, J.-M.; Gillet, F.; Pelloux, J.; Rayon, C. Cell wall metabolism in response to abiotic stress. Plants 2015, 4, 112–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenhaken, R. Cell wall remodeling under abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jithesh, M.N.; Wally, O.S.D.; Manfield, I.; Critchley, A.T.; Hiltz, D.; Prithiviraj, B. Analysis of seaweed extract-induced transcriptome leads to identification of a negative regulator of salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. HortScience 2012, 47, 704–709. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, X.; An, L.; Feng, H.; Zhao, Z. A cold-induced pectin methyl-esterase inhibitor gene contributes negatively to freezing tolerance but positively to salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 222, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solecka, D.; Zebrowski, J.; Kacperska, A. Are pectins involved in cold acclimation and de-acclimation of winter oil-seed rape plants? Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, L.; Domon, J.-M.; Klimek, J.F.; Fournet, F.; Sellier, H.; Gillet, F.; Pelloux, J.; Lejeune-Hénaut, I.; Carpita, N.C.; Rayon, C. Structural alteration of cell wall pectins accompanies pea development in response to cold. Phytochemistry 2014, 104, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Liu, R.; Wang, W.; An, L.; Chen, T.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Z. Brassinosteroids regulate pectin methylesterase activity and AtPME41 expression in Arabidopsis under chilling stress. Cryobiology 2011, 63, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, H.M.; Berger, A.; Saez-Aguayo, S.; Ralet, M.-C. Understanding polysaccharide production and properties using seed coat mutants: Future perspectives for the exploitation of natural variants. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, T.L.; Skinner, D.J.; Haughn, G.W. Differentiation of mucilage secretory cells of the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 345–356. [Google Scholar]
- Francoz, E.; Ranocha, P.; Burlat, V.; Dunand, C. Arabidopsis seed mucilage secretory cells: Regulation and dynamics. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiniciuc, C.; Yang, B.; Schmidt, M.H.-W.; Günl, M.; Usadel, B. Starting to gel: How Arabidopsis seed coat epidermal cells produce specialized secondary cell walls. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3452–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turbant, A.; Fournet, F.; Lequart, M.; Zabijak, L.; Pageau, K.; Bouton, S.; Van Wuytswinkel, O. PME58 plays a role in pectin distribution during seed coat mucilage extrusion through homogalacturonan modification. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 2177–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautengarten, C.; Usadel, B.; Neumetzler, L.; Hartmann, J.; Büssis, D.; Altmann, T. A subtilisin-like serine protease essential for mucilage release from Arabidopsis seed coats. Plant J. 2008, 54, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Levesque-Tremblay, G.; Bartels, S.; Weitbrecht, K.; Wormit, A.; Usadel, B.; Haughn, G.; Kermode, A.R. Demethylesterification of cell wall pectins in Arabidopsis plays a role in seed germination. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheler, C.; Weitbrecht, K.; Pearce, S.P.; Hampstead, A.; Büttner-Mainik, A.; Lee, K.J.D.; Voegele, A.; Oracz, K.; Dekkers, B.J.W.; Wang, X.; et al. Promotion of testa rupture during garden cress germination involves seed compartment-specific expression and activity of pectin methylesterases. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiniciuc, C.; Pauly, M.; Usadel, B. Monitoring polysaccharide dynamics in the plant cell wall. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 2590–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Greiner, S. Growth control by cell wall pectins. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, S.; van Orden, J.; Wolf, S.; Vissenberg, K.; Ndong, Y.A.; Pelloux, J.; Bischoff, V.; Urbain, A.; Lemonnier, G.; Renou, J.; et al. A role for pectin de-methylesterification in a developmentally regulated growth acceleration in dark-grown Arabidopsis hypocotyls. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paynel, F.; Leroux, C.; Surcouf, O.; Schaumann, A.; Pelloux, J.; Driouich, A.; Mollet, J.C.; Lerouge, P.; Lehner, A.; Mareck, A. Kiwi fruit PMEI inhibits PME activity, modulates root elongation and induces pollen tube burst in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 74, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, V.; Francocci, F.; Ferrari, S.; Volpi, C.; Bellincampi, D.; Galletti, R.; D’Ovidio, R.; De Lorenzo, G.; Cervone, F. Engineering the cell wall by reducing de-methyl-esterified homogalacturonan improves saccharification of plant tissues for bioconversion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yang, S.-L.; Xie, L.-F.; Puah, C.S.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Yang, W.-C.; Sundaresan, V.; Ye, D. VANGUARD1 encodes a pectin methylesterase that enhances pollen tube growth in the Arabidopsis style and transmitting tract. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.-W.; Chen, M.-H.; Zaltsman, A.; Citovsky, V. Pollen-specific pectin methylesterase involved in pollen tube growth. Dev. Biol. 2006, 294, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Feng, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.W. BoPMEI1, a pollen-specific pectin methylesterase inhibitor, has an essential role in pollen tube growth. Planta 2010, 231, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebli, Y.; Geitmann, A. Cellular growth in plants requires regulation of cell wall biochemistry. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2017, 44, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Chen, W.; Traas, J. Mechanical signaling in plant morphogenesis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 51, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Levesque-Tremblay, G.; Fernandes, A.; Wormit, A.; Bartels, S.; Usadel, B.; Kermode, A. Overexpression of a pectin methylesterase inhibitor in Arabidopsis thaliana leads to altered growth morphology of the stem and defective organ separation. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e26464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Mravec, J.; Greiner, S.; Mouille, G.; Höfte, H. Plant cell wall homeostasis is mediated by brassinosteroid feedback signaling. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeberichts, F.; van Doorn, W.G.; Vorst, O.; Hall, R.D.; van Wordragen, M.F. Sucrose prevents up-regulation of senescence-associated genes in carnation petals. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Stier, G.; Lin, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, Y.; Reid, M.; Jiang, C. Transcriptome Changes Associated with Delayed Flower Senescence on Transgenic Petunia by Inducing Expression of etr1-1, a Mutant Ethylene Receptor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, C.; Posé, S.; Morris, V.J.; Kirby, A.R.; Quesada, M.A.; Mercado, J.A. Fruit softening and pectin disassembly: An overview of nanostructural pectin modifications assessed by atomic force microscopy. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovane, A.; Balestrieri, C.; Quagliuolo, L.; Castaldo, D.; Servillo, L. A glycoprotein inhibitor of pectin methylesterase in kiwi fruit. Purification by affinity chromatography and evidence of a ripening-related precursor. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 233, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irifune, K.; Nishida, T.; Egawa, H.; Nagatani, A. Pectin methylesterase inhibitor cDNA from kiwi fruit. Plant Cell Rep. 2004, 23, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, T.; Commandeur, U.; Fischer, R.; Usadel, B.; Klose, H. Improving the utilization of lignocellulosic biomass by polysaccharide modification. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francocci, F.; Bastianelli, E.; Lionetti, V.; Ferrari, S.; De Lorenzo, G.; Bellincampi, D.; Cervone, F. Analysis of pectin mutants and natural accessions of Arabidopsis highlights the impact of de-methyl-esterified homogalacturonan on tissue saccharification. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, D.; Lovoi, A.; Quagliuolo, L.; Servillo, L.; Balestrieri, C.; Giovane, A. Orange juices and concentrates stabilization by a proteic inhibitor of pectin methylesterase. J. Food Sci. 1991, 56, 1632–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolie, R.P.; Duvetter, T.; Vandevenne, E.; Van Buggenhout, S.; Van Loey, A.M.; Hendrickx, M.E. A pectin-methylesterase-inhibitor-based molecular probe for in Situ detection of plant pectin methylesterase activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5449–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocca, F.; Lomolino, G.; Curioni, A.; Spettoli, P.; Lante, A. Detection of pectinmethylesterase activity in presence of methanol during grape pomace storage. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocca, F.; Lomolino, G.; Spettoli, P.; Lante, A. A Study on the relationship between the volatile composition of moscato and prosecco grappa and enzymatic activities involved in its production. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lante, A.; Zocca, F.; Spettoli, P.; Lomolino, G.; Raiola, A.; Bellincampi, D.; Lionetti, V.; Giovane, A.; Camardella, L. Use of a Protein Inhibitor of Pectin Methylesterase for Reducing Methanol Formation in Grape Must and Marc, and Process Therefor. It. Patent WO2008104555A1, 4 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).