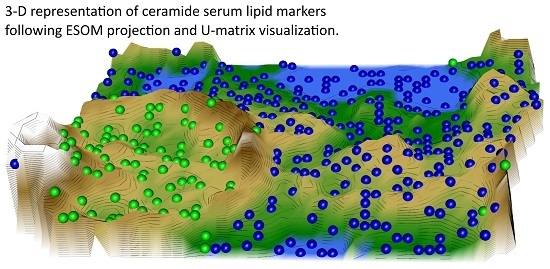
Machine-Learned Data Structures of Lipid Marker Serum Concentrations in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Differ from Those in Healthy Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
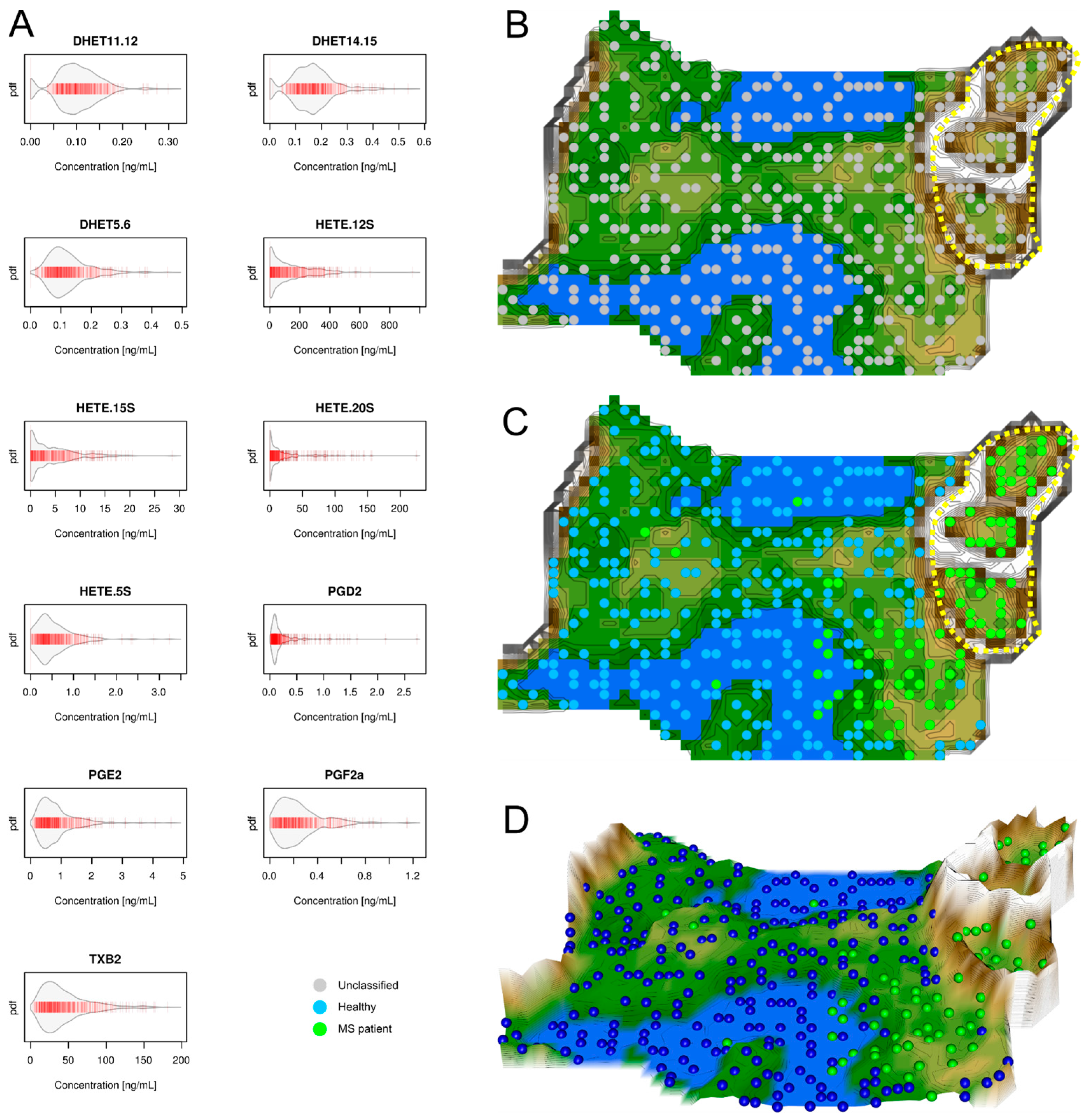
2.1. Data Structures of Eicosanoid Concentrations
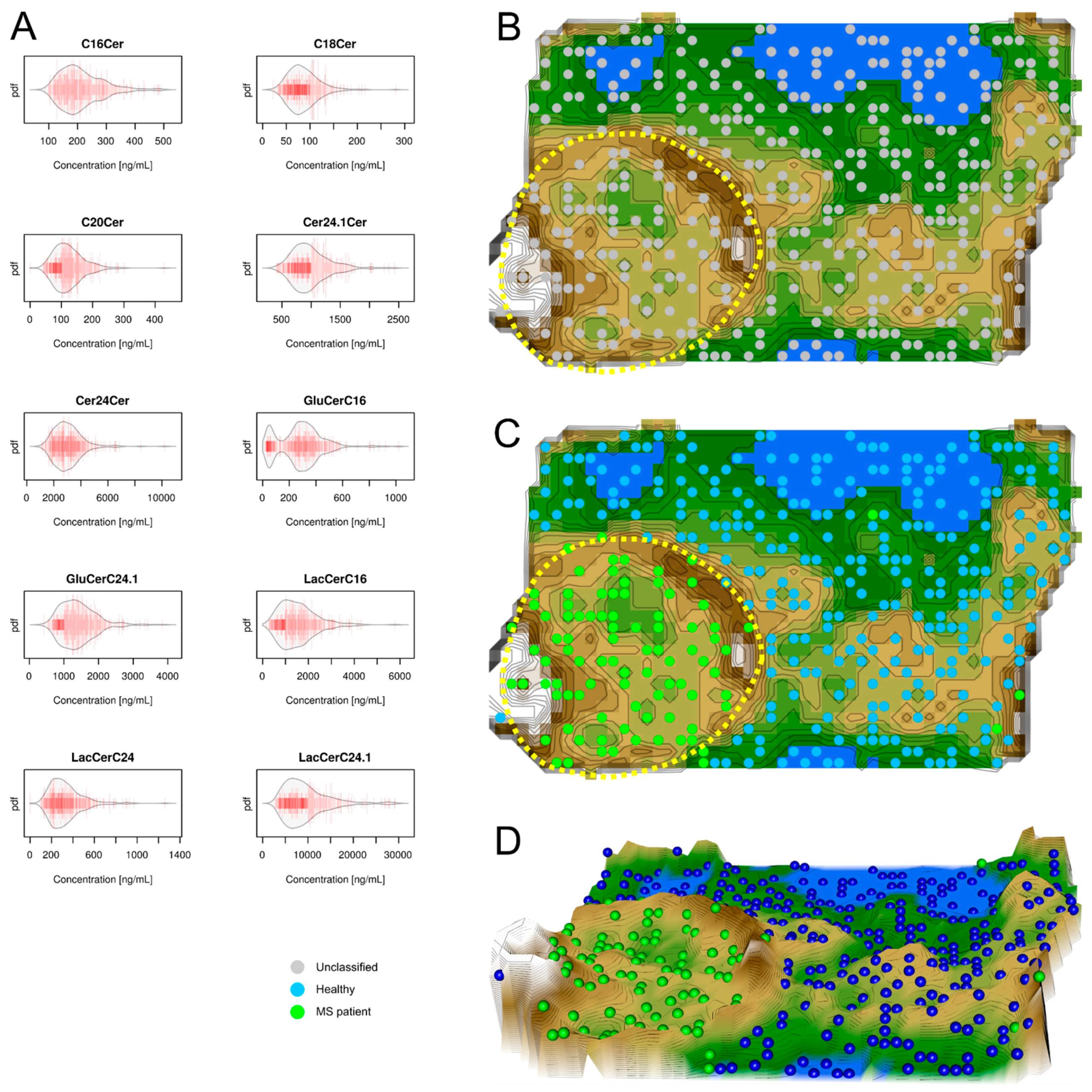
2.2. Data Structures of Ceramide Concentrations
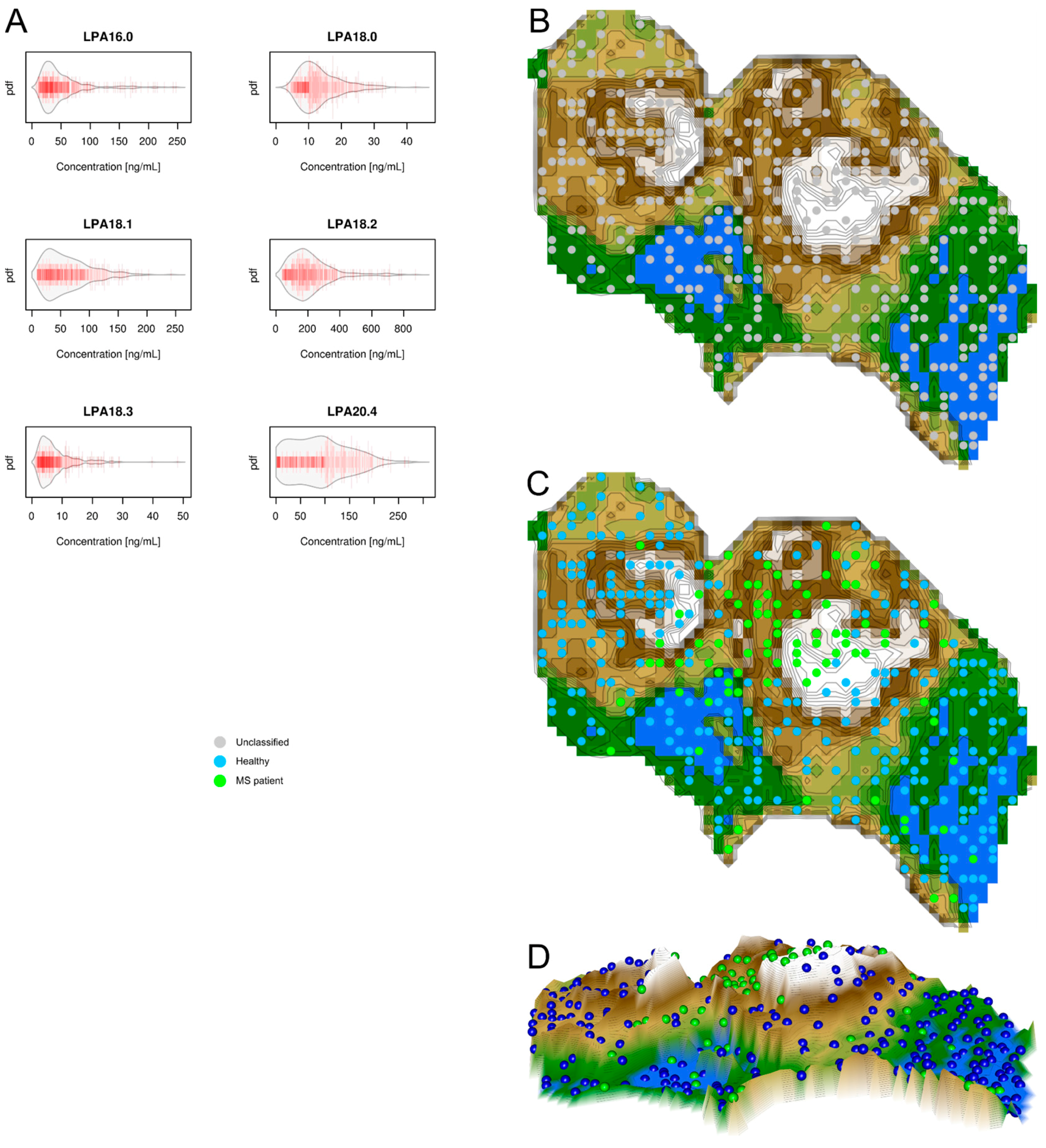
2.3. Data Structures of Lysophosphatidic Acid Concentrations
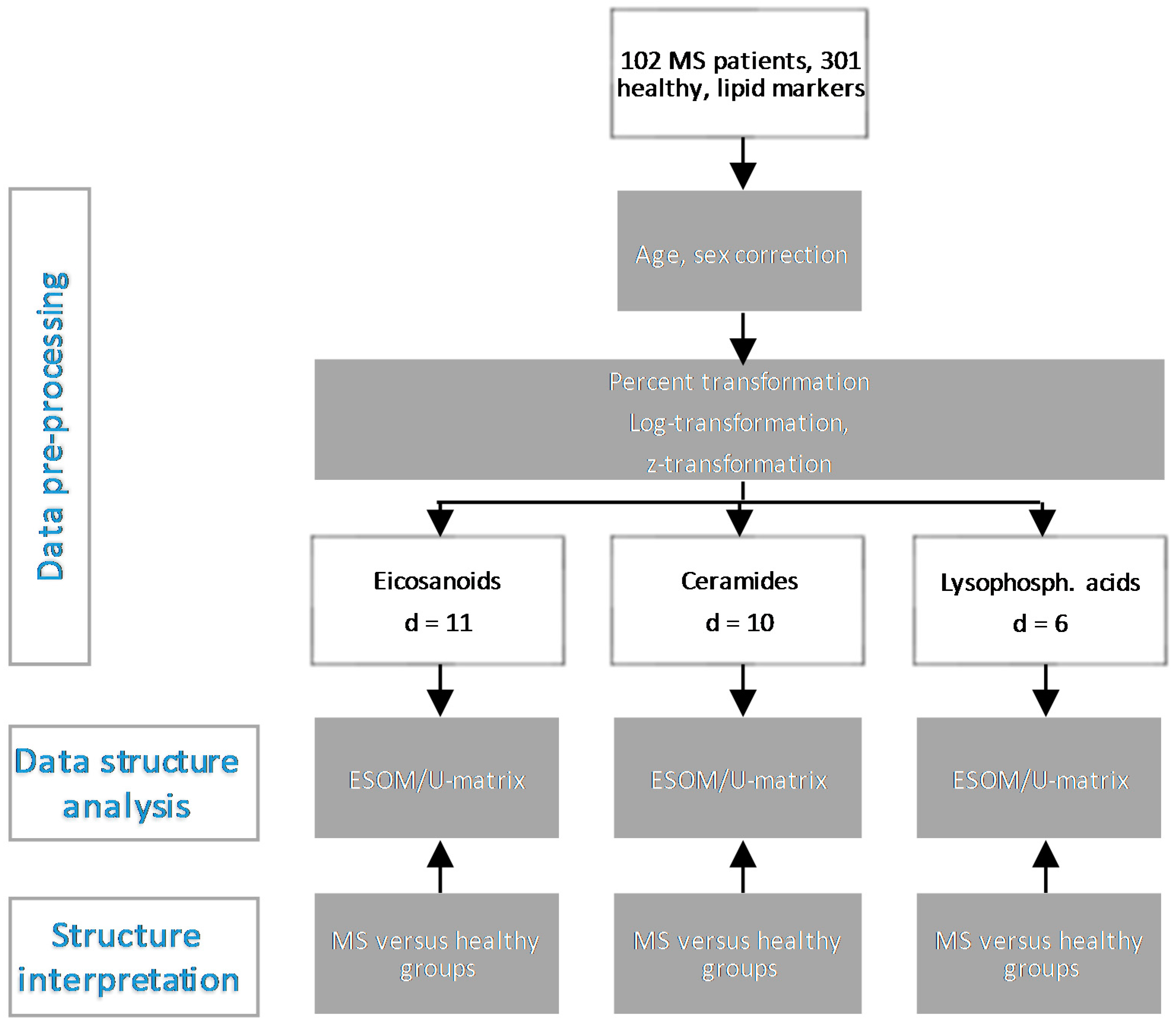
3. Methods
3.1. Data Acquisition and Lipid Serum Concentration Analytics
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lassmann, H.; Bruck, W.; Lucchinetti, C.F. The immunopathology of multiple sclerosis: An overview. Brain Pathol. 2007, 17, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, I.; Woelk, H. Investigations of the lipid metabolism of the white matter in multiple sclerosis: Changes in glycero-phosphatides and lipid-splitting enzymes. Neurochem. Res. 1982, 7, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corthals, A.P. Multiple sclerosis is not a disease of the immune system. Q. Rev. Biol. 2011, 86, 287–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhornitsky, S.; McKay, K.A.; Metz, L.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Rangachari, M. Cholesterol and markers of cholesterol turnover in multiple sclerosis: Relationship with disease outcomes. Mult. Scler. Relat. Dis. 2016, 5, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, S.; Ruck, T.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Herrmann, A.M.; Maati, H.M.O.; Bobak, N.; Gobel, K.; Langhauser, F.; Stegner, D.; Ehling, P.; et al. Endothelial TWIK-related potassium channel-1 (TREK1) regulates immune-cell trafficking into the CNS. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, N.; Yaong, M.; Rosengren, L.; Blennow, K.; Mansson, J.E.; Andersen, O.; Zetterberg, H.; Haghighi, S.; Zho, I.; Pratico, D. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid levels of prostaglandin E2 and 15-(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid in multiple sclerosis. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelmes, J.; de Bazo, A.M.; Pewzner-Jung, Y.; Schmitz, K.; Mayer, C.A.; Foerch, C.; Eberle, M.; Tafferner, N.; Ferreiros, N.; Henke, M.; et al. Lack of ceramide synthase 2 suppresses the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by impairing the migratory capacity of neutrophils. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 46, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberle, M.; Ebel, P.; Mayer, C.A.; Barthelmes, J.; Tafferner, N.; Ferreiros, N.; Ulshofer, T.; Henke, M.; Foerch, C.; de Bazo, A.M.; et al. Exacerbation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in ceramide synthase 6 knockout mice is associated with enhanced activation/migration of neutrophils. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orešič, M. Bioinformatics and computational approaches applicable to lipidomics. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2009, 111, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X. Bioinformatics in Lipidomics. In Lipidomics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 121–150. [Google Scholar]
- Fahy, E.; Cotter, D.; Byrnes, R.; Sud, M.; Maer, A.; Li, J.; Nadeau, D.; Zhau, Y.; Subramaniam, S. Bioinformatics for lipidomics. Methods Enzymol. 2007, 432, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ultsch, A.; Lötsch, J. Machine-learned cluster identification in high-dimensional data. J. Biomed. Inform. 2017, 66, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampstra, P. Beanplot: A boxplot alternative for visual comparison of distributions. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kohonen, T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biol. Cybernet. 1982, 43, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultsch, A. Maps for Visualization of High-Dimensional Data Spaces; WSOM: Kyushu, Japan, 2003; pp. 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Saher, G.; Quintes, S.; Nave, K.A. Cholesterol: A novel regulatory role in myelin formation. Neuroscientist 2011, 17, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruss, H.; Rosche, B.; Sullivan, A.B.; Brommer, B.; Wengert, O.; Gronert, K.; Schwab, J.M. Proresolution lipid mediators in multiple sclerosis-differential, disease severity-dependent synthesis-A clinical pilot trial. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Zivadinov, R.; Mahfooz, N.; Carl, E.; Drake, A.; Schneider, J.; Teter, B.; Hussein, S.; Mehta, B.; Weiskopf, M.; et al. Serum lipid profiles are associated with disability and MRI outcomes in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.; Bandaru, V.V.; Calabresi, P.A.; Nath, A.; Haughey, N.J. A defect of sphingolipid metabolism modifies the properties of normal appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2008, 131, 3092–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, E.M.; Grosser, T.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostanoids in health and disease. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S423–S428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Bielekova, B.; Hohlfeld, R.; Utz, U. Biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. Dis. Markers 2006, 22, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, F.J.; Yeste, A.; Weiner, H.L.; Covacu, R. Lipids and lipid-reactive antibodies as biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 248, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markianos, M.; Evangelopoulos, M.-E.; Koutsis, G.; Davaki, P.; Sfagos, C. Body Mass Index in Multiple Sclerosis: Associations with CSF Neurotransmitter Metabolite Levels. ISRN Neurol. 2013, 2013, 981070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschiebsch, K.; Fischer, C.; Pickert, G.; Haeussler, A.; Radeke, H.; Grosch, S.; Ferreiros, N.; Geisslinger, G.; Werner, E.R.; Tegeder, I. Tetrahydrobiopterin attenuates DSS-evoked colitis in mice by rebalancing redox and lipid signaling. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisignano, M.; Angioni, C.; Ferreiros, N.; Schuh, C.D.; Suo, J.; Schreiber, Y.; Dawes, J.M.; Antunes-Martins, A.; Bennett, D.L.; McMahon, S.B.; et al. Synthesis of lipid mediators during UVB-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia in rats and mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubbs, F.E. Sample Criteria for Testing Outlying Observations. Ann. Math. Stat. 1950, 21, 27–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, G.W.; Cooper, M.C. A study of standardization of variables in cluster analysis. J. Classif. 1988, 5, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.F.; Keene, O.N.; Pritchard, J.F.; Bye, A. Common noncompartmental pharmacokinetic variables: Are they normally or log-normally distributed? J. Biopharm. Stat. 1997, 7, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.P. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; p. 1096. [Google Scholar]
- Ultsch, A.; Sieman, H.P. In Kohonen’s self organizing feature maps for exploratory data analysis. In Proceedings of the International Neural Network Conference, INNC’90, Paris, France, 9–13 July 1990; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- Lötsch, J.; Ultsch, A. Exploiting the structures of the U-matrix. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Villmann, T., Schleif, F.-M., Kaden, M., Lange, M., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 295, pp. 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Thrun, M.C.; Lerch, F.; Lötsch, J.; Ultsch, A. Visualization and 3D Printing of Multivariate Data of Biomarkers. In International Conference in Central Europe on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer Vision (WSCG); Skala, V., Ed.; Union Agency, Brno, Czech Republic: Plzen, Czech Republic, 2016; Volume 24, pp. 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Diagnostic tests. 1: Sensitivity and specificity. Br. Med. J. 1994, 308, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodersen, K.H.; Ong, C.S.; Stephan, K.E.; Buhmann, J.M. The Balanced Accuracy and Its Posterior Distribution. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 20th International Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 Auguest 2010; pp. 3121–3124. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lötsch, J.; Thrun, M.; Lerch, F.; Brunkhorst, R.; Schiffmann, S.; Thomas, D.; Tegder, I.; Geisslinger, G.; Ultsch, A. Machine-Learned Data Structures of Lipid Marker Serum Concentrations in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Differ from Those in Healthy Subjects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061217
Lötsch J, Thrun M, Lerch F, Brunkhorst R, Schiffmann S, Thomas D, Tegder I, Geisslinger G, Ultsch A. Machine-Learned Data Structures of Lipid Marker Serum Concentrations in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Differ from Those in Healthy Subjects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061217
Chicago/Turabian StyleLötsch, Jörn, Michael Thrun, Florian Lerch, Robert Brunkhorst, Susanne Schiffmann, Dominique Thomas, Irmgard Tegder, Gerd Geisslinger, and Alfred Ultsch. 2017. "Machine-Learned Data Structures of Lipid Marker Serum Concentrations in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Differ from Those in Healthy Subjects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061217
APA StyleLötsch, J., Thrun, M., Lerch, F., Brunkhorst, R., Schiffmann, S., Thomas, D., Tegder, I., Geisslinger, G., & Ultsch, A. (2017). Machine-Learned Data Structures of Lipid Marker Serum Concentrations in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Differ from Those in Healthy Subjects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061217