Can Co-Activation of Nrf2 and Neurotrophic Signaling Pathway Slow Alzheimer’s Disease?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. AD-Causing Factors
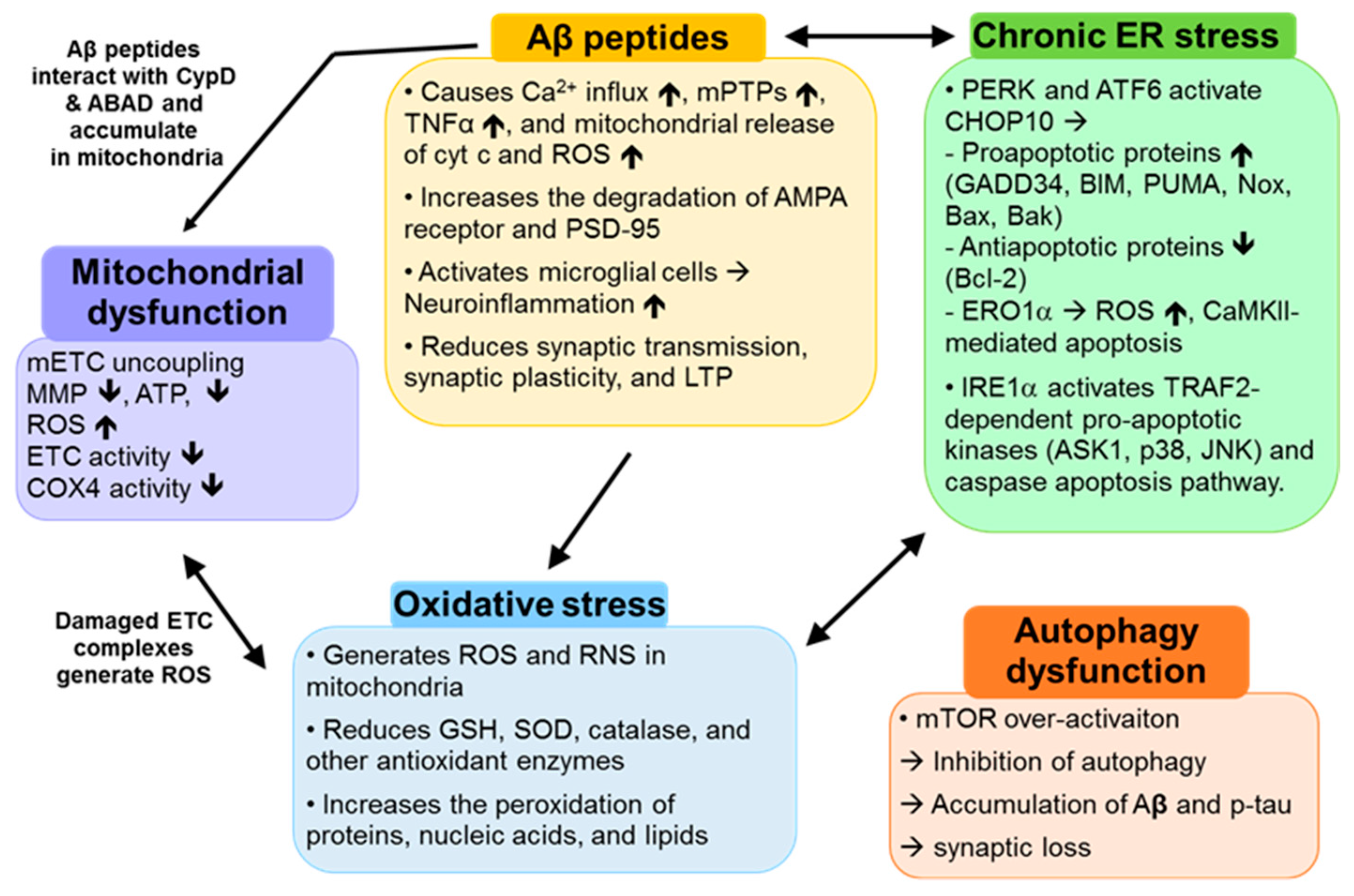
2.1. Aβ Peptides
2.2. Mitochondrial Dysfunction
2.3. Oxidative Stress
2.4. Chronic ER Stress
2.5. Autophagy Dysfunction
3. Key Neuronal Defense Systems
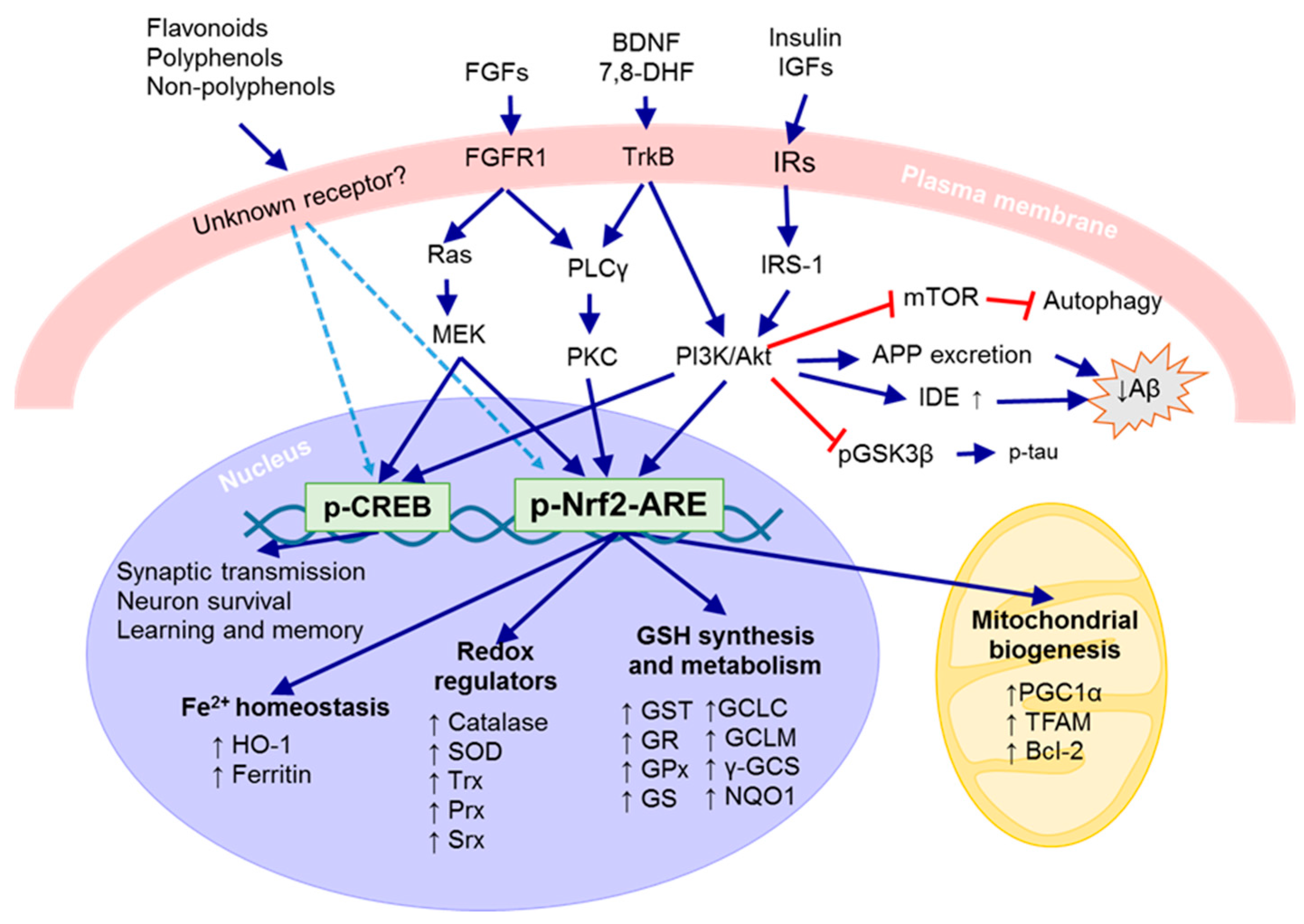
3.1. Antioxidant Defense System
3.2. Neurotrophic Defense System
3.2.1. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)
3.2.2. Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF)
3.2.3. Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGFs)
4. Natural Compounds That Can Activate Nrf2 and/or Neurotrophic Signaling Pathway
4.1. Flavonoids
4.2. Non-Flavonoid Polyphenols
4.3. Non-Polyphenol Compounds
5. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABAD | Aβ-binding alcohol dehydrogenase |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AMPA | α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| APP | Amyloid precursor protein |
| ARE | Antioxidant response element |
| ASK1 | Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 |
| ATF6 | Activating transcription factor 6 |
| ATG | Autophagy-related protein |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BACE1 | β-Secretase 1 |
| BBB | Blood brain barrier |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BIM | Bcl-2 interacting mediator of cell death |
| BVRs | Biliverdin reductases |
| CaMKII | Calmodulin-dependent kinase II |
| CHOP10 | C/EBP homologous protein-10 |
| COX | Cytochrome c oxidase |
| CREB | cAMP response element binding protein |
| CypD | Cyclophilin D |
| cyt c | Cytochrome c |
| 7,8-DHF | 7,8-dihydroxyflavone |
| eIF2α | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| ERO1α | ER oxidase 1α |
| F2-IsoPs | F2-isoprostanes |
| FAK | focal adhesion kinase |
| FGF | fibroblast growth factor |
| FGL | flbroblast growth loop |
| FIP200 | FAK-family interacting protein 200 |
| GADD34 | Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 34 |
| GAP-43 | Growth-associated protein 43 |
| GCI | Global cerebral ischemia |
| GCLM | Glutathione cysteine ligase modulatory subunit |
| GCLC | Glutathione cysteine ligase regulatory subunit |
| γ-GCS | γ-Glutamyl cysteine sythetase |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GR | Glutathione reductase |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| Grx | Glutaredoxin |
| GS | Glutathione synthetase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| 4HNE | 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase 1 |
| Hsp70 | 70-kDa Heat shock protein |
| IDE | Insulin-degrading enzyme |
| IGF | Insulin-like growth factor |
| IR | Insulin receptor |
| IRE1α | Inositol-requiring kinase 1α |
| IRS | Insulin receptor substrate |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LTD | Long-term depression |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MEK | MAPK/ERK kinase |
| mETC | Mitochondrial electron transport chain |
| MMP | Mitochondrial membrane potential |
| mPTP | Mitochondrial permeability transition pore |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| mTORC | mTOR complex |
| NADP | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NCAM1 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| NFTs | Neurofibrillary tangles |
| NMDA | N-Methyl-d-aspartate |
| NQO1 | Quinone recycling (NAD(P)H:quinoneoxidoreductase 1 |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2 [NF-E2]-related factor 2, |
| 6-OHDA | 6-Hydroxydopamine |
| 8-OHdG | 8-Hydroxy-2-deoxyguanine |
| PDI | Protein disulfide isomerase |
| PERK | Protein kinase RNA like ER kinase |
| PGC1α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1-α |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3 phosphate kinase |
| PKR | Protein kinase double-stranded RNA-dependent |
| PLC-γ | Phospholipase-γ |
| Prx | Peroxiredoxin |
| PS1 | Presenilin 1 |
| PSD-95 | Postsynaptic density protein 95 |
| PUMA | p53 Upregulated modulator of apoptosis |
| RAGE | Receptor for advanced glycation end-products |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| Srx | Sulfiredoxin |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances |
| TFAM | Transcriptional factor A of mitochondria |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| TOM | Translocase of the outer membrane |
| TRAF2 | Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 |
| TrkB | Tropomyosin-related kinase B |
| Trx | Thioredoxin, Txnrd; thioredoxin reductase |
| ULK1 | Unc-51 like kinase 1 |
| XBP-1 | X-Box binding protein 1 |
References
- Barthet, G.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Robakis, N.K. Cellular mechanisms of γ-secretase substrate selection, processing and toxicity. Prog. Neurobiol. 2012, 98, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, F.G.; Velasco, P.T.; Lambert, M.P.; Viola, K.; Fernandez, S.J.; Ferreira, S.T.; Klein, W.L. Aβ oligomers induce neuronal oxidative stress through an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-dependent mechanism that is blocked by the Alzheimer drug memantine. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11590–11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, D.G. Mitochondrial function and dysfunction in the cell: Its relevance to aging and aging-related disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.L.; Yang, F.; Rosario, E.R.; Ubeda, O.J.; Beech, W.; Gant, D.J.; Chen, P.P.; Hudspeth, B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. β-amyloid oligomers induce phosphorylation of tau and inactivation of insulin receptor substrate via c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling: Suppression by omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9078–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Beja-Glasser, V.F.; Nfonoyim, B.M.; Frouin, A.; Li, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Merry, K.M.; Shi, Q.; Rosenthal, A.; Barres, B.A.; et al. Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models. Science 2016, 352, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayed, R.; Lasagna-Reeves, C.A. Molecular mechanisms of amyloid oligomers toxicity. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 33 (Suppl. S1), S67–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, H.; Boehm, J.; Sato, C.; Iwatsubo, T.; Tomita, T.; Sisodia, S.; Malinow, R. AMPAR removal underlies Aβ-induced synaptic depression and dendritic spine loss. Neuron 2006, 52, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselli, F.; Tirard, M.; Lu, J.; Hutzler, P.; Lamberti, P.; Livrea, P.; Morabito, M.; Almeida, O.F. Soluble β-amyloid1-40 induces NMDA-dependent degradation of postsynaptic density-95 at glutamatergic synapses. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 11061–11070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science 2002, 298, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hong, S.; Shepardson, N.E.; Walsh, D.M.; Shankar, G.M.; Selkoe, D. Soluble oligomers of amyloid β protein facilitate hippocampal long-term depression by disrupting neuronal glutamate uptake. Neuron 2009, 62, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, G.M.; Li, S.; Mehta, T.H.; Garcia-Munoz, A.; Shepardson, N.E.; Smith, I.; Brett, F.M.; Farrell, M.A.; Rowan, M.J.; Lemere, C.A.; et al. Amyloid-β protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer’s brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, P.I.; Cardoso, S.M.; Santos, M.S.; Oliveira, C.R. The key role of mitochondria in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2006, 9, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptmann, S.; Scherping, I.; Drose, S.; Brandt, U.; Schulz, K.L.; Jendrach, M.; Leuner, K.; Eckert, A.; Muller, W.E. Mitochondrial dysfunction: An early event in Alzheimer pathology accumulates with age in AD transgenic mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, M.F.; Ikuta, I.; Zhu, X.; Casadesus, G.; Jordan, J. Mitochondrial biology in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, M.; Coppede, F.; Murri, L.; Siciliano, G. Mitochondrial cascade hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Myth or reality? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1631–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, D.C.; Hauptmann, S.; Scherping, I.; Schuessel, K.; Keil, U.; Rizzu, P.; Ravid, R.; Drose, S.; Brandt, U.; Muller, W.E.; et al. Proteomic and functional analyses reveal a mitochondrial dysfunction in P301L tau transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 23802–23814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hao, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, G.; Su, C.; Miao, J.; Li, Z. Soluble Aβ levels correlate with cognitive deficits in the 12-month-old APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 222, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delic, V.; Brownlow, M.; Joly-Amado, A.; Zivkovic, S.; Noble, K.; Phan, T.A.; Ta, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bell, S.D.; Kurien, C.; et al. Calorie restriction does not restore brain mitochondrial function in P301L tau mice, but it does decrease mitochondrial F0F1-ATPase activity. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 67, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson Petersen, C.A.; Alikhani, N.; Behbahani, H.; Wiehager, B.; Pavlov, P.F.; Alafuzoff, I.; Leinonen, V.; Ito, A.; Winblad, B.; Glaser, E.; et al. The amyloid β-peptide is imported into mitochondria via the TOM import machinery and localized to mitochondrial cristae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13145–13150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takuma, K.; Fang, F.; Zhang, W.; Yan, S.; Fukuzaki, E.; Du, H.; Sosunov, A.; McKhann, G.; Funatsu, Y.; Nakamichi, N.; et al. RAGE-mediated signaling contributes to intraneuronal transport of amyloid-β and neuronal dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20021–20026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, K.A.; Grater, F.; Dougan, L.; Badilla, C.L.; Berne, B.J.; Fernandez, J.M. Signatures of hydrophobic collapse in extended proteins captured with force spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7916–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yan, S.S. Mitochondrial permeability transition pore in Alzheimer’s disease: Cyclophilin D and amyloid β. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustbader, J.W.; Cirilli, M.; Lin, C.; Xu, H.W.; Takuma, K.; Wang, N.; Caspersen, C.; Chen, X.; Pollak, S.; Chaney, M.; et al. ABAD directly links Aβ to mitochondrial toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2004, 304, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, M.Y.; Han, S.H.; Son, S.M.; Hong, H.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Byun, J.; Mook-Jung, I. Mitochondria-specific accumulation of amyloid β induces mitochondrial dysfunction leading to apoptotic cell death. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casley, C.S.; Canevari, L.; Land, J.M.; Clark, J.B.; Sharpe, M.A. β-Amyloid inhibits integrated mitochondrial respiration and key enzyme activities. J. Neurochem. 2002, 80, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manczak, M.; Anekonda, T.S.; Henson, E.; Park, B.S.; Quinn, J.; Reddy, P.H. Mitochondria are a direct site of A β accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease neurons: Implications for free radical generation and oxidative damage in disease progression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspersen, C.; Wang, N.; Yao, J.; Sosunov, A.; Chen, X.; Lustbader, J.W.; Xu, H.W.; Stern, D.; McKhann, G.; Yan, S.D. Mitochondrial Aβ: A potential focal point for neuronal metabolic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 2040–2041. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.S.; Pae, C.U.; Yoon, S.J.; Jang, W.Y.; Lee, N.J.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, C.; Paik, I.H.; Lee, C.U. Decreased plasma antioxidants in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 21, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; LeVault, K.R.; Barnett, A.J.; Brewer, G.J. A reversible early oxidized redox state that precedes macromolecular ROS damage in aging nontransgenic and 3xTg-AD mouse neurons. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 5821–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, T.A.; Navarro, B.C.; Pérez, J.A. Endogenous Antioxidants: A Review of their Role in Oxidative Stress. In A Master Regulator of Oxidative Stress—The Transcription Factor Nrf2; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, R.F.; Martins, D.B.; Borba, M.A. Oxidative Stress and Disease. In A Master Regulator of Oxidative Stress—The Transcription Factor Nrf2; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 185–199. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, B. Role of free radicals in the neurodegenerative diseases: Therapeutic implications for antioxidant treatment. Drugs Aging 2001, 18, 685–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, D.A.; Germain, M.; Kelly, M.A.; Slack, R.S. Reactive oxygen species: Stuck in the middle of neurodegeneration. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 20 (Suppl. S2), S357–S367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, J.C., Jr.; Augusto, O. Connecting the chemical and biological properties of nitric oxide. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Chen, B.; Chicoine, L.G.; Nelin, L.D. Overexpression of cationic amino acid transporter-1 increases nitric oxide production in hypoxic human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011, 38, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adibhatla, R.M.; Hatcher, J.F. Lipid oxidation and peroxidation in CNS health and disease: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 125–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, K.; Maidt, M.L.; Yu, Z.; Sang, H.; Markesbery, W.R.; Floyd, R.A. Electrochemical analysis of protein nitrotyrosine and dityrosine in the Alzheimer brain indicates region-specific accumulation. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 8126–8132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Sayre, L.M.; Anderson, V.E.; Harris, P.L.; Beal, M.F.; Kowall, N.; Perry, G. Cytochemical demonstration of oxidative damage in Alzheimer disease by immunochemical enhancement of the carbonyl reaction with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1998, 46, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunomura, A.; Perry, G.; Pappolla, M.A.; Wade, R.; Hirai, K.; Chiba, S.; Smith, M.A. RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of vulnerable neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hensley, K.; Hall, N.; Subramaniam, R.; Cole, P.; Harris, M.; Aksenov, M.; Aksenova, M.; Gabbita, S.P.; Wu, J.F.; Carney, J.M.; et al. Brain regional correspondence between Alzheimer’s disease histopathology and biomarkers of protein oxidation. J. Neurochem. 1995, 65, 2146–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyras, L.; Cairns, N.J.; Jenner, A.; Jenner, P.; Halliwell, B. An assessment of oxidative damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA in brain from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1997, 68, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Richey Harris, P.L.; Sayre, L.M.; Beckman, J.S.; Perry, G. Widespread peroxynitrite-mediated damage in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 2653–2657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marcus, D.L.; Thomas, C.; Rodriguez, C.; Simberkoff, K.; Tsai, J.S.; Strafaci, J.A.; Freedman, M.L. Increased peroxidation and reduced antioxidant enzyme activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 150, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.A.; Scheff, S.W. Oxidative stress in the progression of Alzheimer disease in the frontal cortex. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucassen, P.J.; Chung, W.C.; Kamphorst, W.; Swaab, D.F. DNA damage distribution in the human brain as shown by in situ end labeling; area-specific differences in aging and Alzheimer disease in the absence of apoptotic morphology. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 56, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Poon, H.F.; St Clair, D.; Keller, J.N.; Pierce, W.M.; Klein, J.B.; Markesbery, W.R. Redox proteomics identification of oxidatively modified hippocampal proteins in mild cognitive impairment: Insights into the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 22, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.I.; Lynn, B.C.; Markesbery, W.R.; Lovell, M.A. Increased levels of 4-hydroxynonenal and acrolein, neurotoxic markers of lipid peroxidation, in the brain in Mild Cognitive Impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 1094–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhukareva, V.; Sung, S.; Clark, C.M.; Rokach, J.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Pratico, D. Enhanced brain levels of 8,12-iso-iPF2α-VI differentiate AD from frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 2003, 61, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Zhu, H.; Morishima, N.; Li, E.; Xu, J.; Yankner, B.A.; Yuan, J. Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-β. Nature 2000, 403, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, M.; Kaufman, R.J. ER stress and the unfolded protein response. Mutat. Res. 2005, 569, 29–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, H.P.; Zhang, Y.; Ron, D. Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature 1999, 397, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Novoa, I.; Zeng, H.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Feedback inhibition of the unfolded protein response by GADD34-mediated dephosphorylation of eIF2α. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameri, K.; Harris, A.L. Activating transcription factor 4. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Matsui, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Okada, T.; Mori, K. XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 2001, 107, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfon, M.; Zeng, H.; Urano, F.; Till, J.H.; Hubbard, S.R.; Harding, H.P.; Clark, S.G.; Ron, D. IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 2002, 415, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollien, J.; Lin, J.H.; Li, H.; Stevens, N.; Walter, P.; Weissman, J.S. Regulated Ire1-dependent decay of messenger RNAs in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Rawson, R.B.; Komuro, R.; Chen, X.; Dave, U.P.; Prywes, R.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. ER stress induces cleavage of membrane-bound ATF6 by the same proteases that process SREBPs. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Yoshida, H.; Akazawa, R.; Negishi, M.; Mori, K. Distinct roles of activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) and double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) in transcription during the mammalian unfolded protein response. Biochem. J. 2002, 366 Pt 2, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Haze, K.; Yanagi, H.; Yura, T.; Mori, K. Identification of the cis-acting endoplasmic reticulum stress response element responsible for transcriptional induction of mammalian glucose-regulated proteins. Involvement of basic leucine zipper transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33741–33749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Back, S.H.; Hur, J.; Lin, Y.H.; Gildersleeve, R.; Shan, J.; Yuan, C.L.; Krokowski, D.; Wang, S.; Hatzoglou, M.; et al. ER-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szegezdi, E.; Logue, S.E.; Gorman, A.M.; Samali, A. Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shore, G.C.; Papa, F.R.; Oakes, S.A. Signaling cell death from the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urra, H.; Dufey, E.; Lisbona, F.; Rojas-Rivera, D.; Hetz, C. When ER stress reaches a dead end. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3507–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er, E.; Oliver, L.; Cartron, P.F.; Juin, P.; Manon, S.; Vallette, F.M. Mitochondria as the target of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1757, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.J.; Singh, P.; Lee, K.; Foss, K.; Lee, S.; Park, M.; Lee, S.; Aluvila, S.; Park, M.; Singh, P.; et al. Conformational changes in BAK, a pore-forming proapoptotic Bcl-2 family member, upon membrane insertion and direct evidence for the existence of BH3–BH3 contact interface in BAK homo-oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28924–28937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Armstrong, J.S. Bax and the mitochondrial permeability transition cooperate in the release of cytochrome c during endoplasmic reticulum-stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brush, M.H.; Weiser, D.C.; Shenolikar, S. Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 targets protein phosphatase 1 α to the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes dephosphorylation of the α subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, E.; Takeuchi, A.; Haneda, M.; Yagi, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamaki, K.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S.; Shimokata, K.; Isobe, K. The function of GADD34 is a recovery from a shutoff of protein synthesis induced by ER stress: Elucidation by GADD34-deficient mice. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1573–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, K.D.; Martindale, J.L.; Klotz, L.O.; Aw, T.Y.; Holbrook, N.J. Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the cellular redox state. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Mongillo, M.; Chin, K.T.; Harding, H.; Ron, D.; Marks, A.R.; Tabas, I. Role of ERO1-α-mediated stimulation of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor activity in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmins, J.M.; Ozcan, L.; Seimon, T.A.; Li, G.; Malagelada, C.; Backs, J.; Backs, T.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N.; Anderson, M.E.; Tabas, I. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II links ER stress with Fas and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2925–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabas, I.; Ron, D. Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urano, F.; Wang, X.; Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, P.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 2000, 287, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, T.; Imaizumi, K.; Oono, K.; Yui, D.; Gomi, F.; Katayama, T.; Tohyama, M. Activation of caspase-12, an endoplastic reticulum (ER) resident caspase, through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2-dependent mechanism in response to the ER stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 13935–13940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishitoh, H.; Matsuzawa, A.; Tobiume, K.; Saegusa, K.; Takeda, K.; Inoue, K.; Hori, S.; Kakizuka, A.; Ichijo, H. ASK1 is essential for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal cell death triggered by expanded polyglutamine repeats. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoozemans, J.J.; van Haastert, E.S.; Nijholt, D.A.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Eikelenboom, P.; Scheper, W. The unfolded protein response is activated in pretangle neurons in Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, B.D.; Kruppa, A.J.; Miranda, E.; Crowther, D.C.; Lomas, D.A.; Marciniak, S.J. Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in neurological disease. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoozemans, J.J.; Veerhuis, R.; Van Haastert, E.S.; Rozemuller, J.M.; Baas, F.; Eikelenboom, P.; Scheper, W. The unfolded protein response is activated in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2005, 110, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honjo, Y.; Ito, H.; Horibe, T.; Takahashi, R.; Kawakami, K. Protein disulfide isomerase-immunopositive inclusions in patients with Alzheimer disease. Brain Res. 2010, 1349, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Mattioli, M.; Gobert, D.; Stern, E.; Gamache, K.; Colina, R.; Cuello, C.; Sossin, W.; Kaufman, R.; Pelletier, J.; Rosenblum, K.; et al. eIF2α Phosphorylation bidirectionally regulates the switch from short- to long-term synaptic plasticity and memory. Cell 2007, 129, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, E.; Chinnakkaruppan, A.; David, O.; Sonenberg, N.; Rosenblum, K. Blocking the eIF2α kinase (PKR) enhances positive and negative forms of cortex-dependent taste memory. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Prisco, G.V.; Huang, W.; Buffington, S.A.; Hsu, C.C.; Bonnen, P.E.; Placzek, A.N.; Sidrauski, C.; Krnjevic, K.; Kaufman, R.J.; Walter, P.; et al. Translational control of mGluR-dependent long-term depression and object-place learning by eIF2α. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Belforte, J.E.; Lu, Y.; Yabe, Y.; Pickel, J.; Smith, C.B.; Je, H.S.; Lu, B.; Nakazawa, K. eIF2α Phosphorylation-dependent translation in CA1 pyramidal cells impairs hippocampal memory consolidation without affecting general translation. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 2582–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, T.; Sadleir, K.R.; Maus, E.; Velliquette, R.A.; Zhao, J.; Cole, S.L.; Eimer, W.A.; Hitt, B.; Bembinster, L.A.; Lammich, S.; et al. Phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF2α increases BACE1 levels and promotes amyloidogenesis. Neuron 2008, 60, 988–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakagami, Y.; Kudo, T.; Tanimukai, H.; Kanayama, D.; Omi, T.; Horiguchi, K.; Okochi, M.; Imaizumi, K.; Takeda, M. Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in tauopathy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, M.; Hino, S.; Saito, A.; Morikawa, K.; Kondo, S.; Kanemoto, S.; Murakami, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Tanii, I.; Yoshinaga, K.; et al. Autophagy is activated for cell survival after endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 9220–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulamek-Koziol, M.; Furmaga-Jablonska, W.; Januszewski, S.; Brzozowska, J.; Scislewska, M.; Jablonski, M.; Pluta, R. Neuronal autophagy: Self-eating or self-cannibalism in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimobayashi, M.; Hall, M.N. Making new contacts: The mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N. The role of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in autophagy regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiese, K.; Chong, Z.Z.; Wang, S.; Shang, Y.C. Oxidant stress and signal transduction in the nervous system with the PI 3-K, Akt, and mTOR cascade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13830–13866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kundu, M.; Viollet, B.; Guan, K.L. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi-Nishino, M.; Fujita, N.; Noda, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Yoshimori, T.; Yamamoto, A. A subdomain of the endoplasmic reticulum forms a cradle for autophagosome formation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Noda, T.; Ohsumi, Y. Apg16p is required for the function of the Apg12p–Apg5p conjugate in the yeast autophagy pathway. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 3888–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Ni, T.; Hong, B.; Wang, H.Y.; Jiang, F.J.; Zou, S.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.L.; Klionsky, D.J.; Liang, Y.; et al. Dual roles of Atg8-PE deconjugation by Atg4 in autophagy. Autophagy 2012, 8, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidberg, H.; Shvets, E.; Shpilka, T.; Shimron, F.; Shinder, V.; Elazar, Z. LC3 and GATE-16/GABARAP subfamilies are both essential yet act differently in autophagosome biogenesis. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, Y.; Kumanomidou, T.; Sou, Y.S.; Mizushima, T.; Ezaki, J.; Ueno, T.; Kominami, E.; Yamane, T.; Tanaka, K.; Komatsu, M. Structural basis for sorting mechanism of p62 in selective autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 22847–22857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C, O.N. PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling: Impaired on/off switches in aging, cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Caccamo, A.; Majumder, S.; Richardson, A.; Strong, R.; Oddo, S. Molecular interplay between mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), amyloid-β, and Tau: Effects on cognitive impairments. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13107–13120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spilman, P.; Podlutskaya, N.; Hart, M.J.; Debnath, J.; Gorostiza, O.; Bredesen, D.; Richardson, A.; Strong, R.; Galvan, V. Inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin abolishes cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid-β levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Yan, J.; Jiang, W.; Yao, X.G.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Hu, L.; Jiang, H.; Shen, X. Arctigenin effectively ameliorates memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease model mice targeting both β-amyloid production and clearance. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 13138–13149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamano, T.; Gendron, T.F.; Causevic, E.; Yen, S.H.; Lin, W.L.; Isidoro, C.; Deture, M.; Ko, L.W. Autophagic-lysosomal perturbation enhances tau aggregation in transfectants with induced wild-type tau expression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caccamo, A.; De Pinto, V.; Messina, A.; Branca, C.; Oddo, S. Genetic reduction of mammalian target of rapamycin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-like cognitive and pathological deficits by restoring hippocampal gene expression signature. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 7988–7998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; An, C.; Gao, Y.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F. Emerging roles of Nrf2 and phase II antioxidant enzymes in neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 100, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Gerfo, A.; Petrozzi, L.; Chico, L.; Siciliano, G. Nrf2 Signaling: An Adaptive Response Pathway for Neurodegenerative Disorders. In A Master Regulator of Oxidative Stress—The Transcription Factor Nrf2; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 145–166. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2—A therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88 Pt B, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, A.; Kang, M.I.; Okawa, H.; Ohtsuji, M.; Zenke, Y.; Chiba, T.; Igarashi, K.; Yamamoto, M. Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scapagnini, G.; Vasto, S.; Abraham, N.G.; Caruso, C.; Zella, D.; Fabio, G. Modulation of Nrf2/ARE pathway by food polyphenols: A nutritional neuroprotective strategy for cognitive and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calkins, M.J.; Johnson, D.A.; Townsend, J.A.; Vargas, M.R.; Dowell, J.A.; Williamson, T.P.; Kraft, A.D.; Lee, J.M.; Li, J.; Johnson, J.A. The Nrf2/ARE pathway as a potential therapeutic target in neurodegenerative disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, H.E.; Witte, M.; Hondius, D.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Drukarch, B.; Hoozemans, J.; van Horssen, J. Nrf2-induced antioxidant protection: A promising target to counteract ROS-mediated damage in neurodegenerative disease? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenki, P.; Khodagholi, F.; Shaerzadeh, F. Inhibition of phosphorylation of JNK suppresses Aβ-induced ER stress and upregulates prosurvival mitochondrial proteins in rat hippocampus. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 49, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, N.; Izumi, H.; Miyamoto, R.; Kondo, H.; Tawara, A.; Sasaguri, Y.; Kohno, K. Quercetin induces the expression of peroxiredoxins 3 and 5 via the Nrf2/NRF1 transcription pathway. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maines, M.D.; Trakshel, G.M.; Kutty, R.K. Characterization of two constitutive forms of rat liver microsomal heme oxygenase. Only one molecular species of the enzyme is inducible. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schipper, H.M. Heme oxygenase-1: Role in brain aging and neurodegeneration. Exp. Gerontol. 2000, 35, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, E.; Di Domenico, F.; Sultana, R.; Coccia, R.; Mancuso, C.; Perluigi, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Heme oxygenase-1 posttranslational modifications in the brain of subjects with Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 2292–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, H.; Zhao, X.; Lin, X.; Tan, C.; Cao, G.; Wang, Z. Neuroprotective effects of salidroside against β-amyloid-induced oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maines, M.D. The heme oxygenase system: A regulator of second messenger gases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1997, 37, 517–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapitulnik, J.; Maines, M.D. Pleiotropic functions of biliverdin reductase: Cellular signaling and generation of cytoprotective and cytotoxic bilirubin. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, S.; Snyder, S.H. Neuroprotective action of bilirubin against oxidative stress in primary hippocampal cultures. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 890, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, A.; Itoyama, Y.; Kimpara, T.; Zhu, X.; Avila, J.; Dwyer, B.E.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A. Heme catabolism and heme oxygenase in neurodegenerative disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2004, 6, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, E.; Di Domenico, F.; Mancuso, C.; Butterfield, D.A. The Janus face of the heme oxygenase/biliverdin reductase system in Alzheimer disease: It’s time for reconciliation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 62, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okado-Matsumoto, A.; Fridovich, I. Subcellular distribution of superoxide dismutases (SOD) in rat liver: Cu,Zn-SOD in mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38388–38393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Hoeffer, C.A.; Wong, H.; Massaad, C.A.; Zhou, P.; Iadecola, C.; Murphy, M.P.; Pautler, R.G.; Klann, E. Amyloid β-induced impairments in hippocampal synaptic plasticity are rescued by decreasing mitochondrial superoxide. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5589–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.P. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, L.; Raber, J.; Kekonius, L.; Yan, F.; Yu, G.Q.; Bien-Ly, N.; Puolivali, J.; Scearce-Levie, K.; Masliah, E.; Mucke, L. Reduction in mitochondrial superoxide dismutase modulates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and accelerates the onset of behavioral changes in human amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5167–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Calingasan, N.Y.; Yu, F.; Mauck, W.M.; Toidze, M.; Almeida, C.G.; Takahashi, R.H.; Carlson, G.A.; Flint Beal, M.; Lin, M.T.; et al. Increased plaque burden in brains of APP mutant MnSOD heterozygous knockout mice. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, M.; Wille, E.; Stack, C.; Calingasan, N.Y.; Beal, M.F.; Lin, M.T. Reduction of oxidative stress, amyloid deposition, and memory deficit by manganese superoxide dismutase overexpression in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaad, C.A.; Washington, T.M.; Pautler, R.G.; Klann, E. Overexpression of SOD-2 reduces hippocampal superoxide and prevents memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13576–13581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 2006, 443, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-Sueta, G.; Radi, R. Chemical biology of peroxynitrite: Kinetics, diffusion, and radicals. ACS Chem. Biol. 2009, 4, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, A.; Lu, J. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase: Current research with special reference to human disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillig, C.H.; Berndt, C.; Holmgren, A. Glutaredoxin systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 1304–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strange, R.C.; Spiteri, M.A.; Ramachandran, S.; Fryer, A.A. Glutathione-S-transferase family of enzymes. Mutat. Res. 2001, 482, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, C.P.; Glass, C.A.; Montgomery, M.B.; Lindl, K.A.; Ritson, G.P.; Chia, L.A.; Hamilton, R.L.; Chu, C.T.; Jordan-Sciutto, K.L. Expression of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 66, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, G.; Johnson, J.A. The Nrf2-ARE pathway: A valuable therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, G.; Gan, K.A.; Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, J.A. Increased Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in the APP/PS1DeltaE9 mouse model lacking Nrf2 through modulation of autophagy. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanninen, K.; Malm, T.M.; Jyrkkanen, H.K.; Goldsteins, G.; Keksa-Goldsteine, V.; Tanila, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Yla-Herttuala, S.; Levonen, A.L.; Koistinaho, J. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 protects against β amyloid. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 39, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; LeVault, K.R.; Brewer, G.J. Dual-energy precursor and nuclear erythroid-related factor 2 activator treatment additively improve redox glutathione levels and neuron survival in aging and Alzheimer mouse neurons upstream of reactive oxygen species. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, M.; Wille, E.; Calingasan, N.Y.; Tampellini, D.; Williams, C.; Gouras, G.K.; Liby, K.; Sporn, M.; Nathan, C.; Flint Beal, M.; et al. Triterpenoid CDDO-methylamide improves memory and decreases amyloid plaques in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Vargas, M.R.; Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, J.A. Astrocyte-specific overexpression of Nrf2 delays motor pathology and synuclein aggregation throughout the CNS in the α-synuclein mutant (A53T) mouse model. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 17775–17787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, J.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Woo, J.M.; Junn, E.; Mouradian, M.M. DJ-1 induces thioredoxin 1 expression through the Nrf2 pathway. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 3013–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Fu, K.; Wang, D.; Mu, C.; Wang, G. Oxidized DJ-1 interacts with the mitochondrial protein BCL-XL. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35308–35317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhu, M.; Wilson, M.A.; Petsko, G.A.; Fink, A.L. The oxidation state of DJ-1 regulates its chaperone activity toward α-synuclein. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 356, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, E.; Barco, A. CREB’s control of intrinsic and synaptic plasticity: Implications for CREB-dependent memory models. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barco, A.; Marie, H. Genetic approaches to investigate the role of CREB in neuronal plasticity and memory. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, C.H.; Simon, D.K.; Aminova, L.R.; Andreyev, A.Y.; Kushnareva, Y.E.; Murphy, A.N.; Lonze, B.E.; Kim, K.S.; Ginty, D.D.; et al. Mitochondrial cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) mediates mitochondrial gene expression and neuronal survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40398–40401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Takeuchi, A.; Pages, G.; Pouyssegur, J.; Kazama, T. Deletion of ERK1 and ERK2 in the CNS causes cortical abnormalities and neonatal lethality: Erk1 deficiency enhances the impairment of neurogenesis in Erk2-deficient mice. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, M.S.; Jaumotte, J.D.; Wyrostek, S.L.; Zigmond, M.J.; Cavanaugh, J.E. Role of ERK1, 2, and 5 in dopamine neuron survival during aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetman, M.; Gozdz, A. Role of extracellular signal regulated kinases 1 and 2 in neuronal survival. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowansage, K.K.; LeDoux, J.E.; Monfils, M.H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A dynamic gatekeeper of neural plasticity. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 3, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minichiello, L. TrkB signalling pathways in LTP and learning. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Tian, F.; Mearow, K.; Okagaki, P.; Lipsky, R.H.; Marini, A.M. The excitoprotective effect of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors is mediated by a brain-derived neurotrophic factor autocrine loop in cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, D.R.; Miller, F.D. Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2000, 10, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patapoutian, A.; Reichardt, L.F. Trk receptors: Mediators of neurotrophin action. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.; Lindholm, D.; Castren, E.; Wree, A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects against ischemic cell damage in rat hippocampus. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1994, 14, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schabitz, W.R.; Sommer, C.; Zoder, W.; Kiessling, M.; Schwaninger, M.; Schwab, S. Intravenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces infarct size and counterregulates Bax and Bcl-2 expression after temporary focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2000, 31, 2212–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, R.D.; Manadas, B.J.; Melo, C.V.; Gomes, J.R.; Mendes, C.S.; Graos, M.M.; Carvalho, R.F.; Carvalho, A.P.; Duarte, C.B. Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 1329–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murer, M.G.; Yan, Q.; Raisman-Vozari, R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the control human brain, and in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 63, 71–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, B.; Fahnestock, M. Pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor is decreased in parietal cortex in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 111, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wuu, J.; Mufson, E.J.; Fahnestock, M. Precursor form of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor are decreased in the pre-clinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, R.; Marcussen, A.B.; Wortwein, G.; Knudsen, G.M.; Aznar, S. Aβ(1–42) injection causes memory impairment, lowered cortical and serum BDNF levels, and decreased hippocampal 5-HT(2A) levels. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Garzon, D.J.; Marchese, M.; Klein, W.; Ginsberg, S.D.; Francis, B.M.; Mount, H.T.; Mufson, E.J.; Salehi, A.; Fahnestock, M. Decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor depends on amyloid aggregation state in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9321–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccato, C.; Cattaneo, E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 5, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockhorst, U.; de Fries, D.; Steingrueber, H.J.; Scherbaum, W.A. Insulin and the CNS: Effects on food intake, memory, and endocrine parameters and the role of intranasal insulin administration in humans. Physiol. Behav. 2004, 83, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, S. Glucose metabolism and insulin receptor signal transduction in Alzheimer disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 490, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, C.; Hallschmid, M.; Hatke, A.; Schultes, B.; Fehm, H.L.; Born, J.; Kern, W. Intranasal insulin improves memory in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2004, 29, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Moore, E.; Meiri, N.; Quon, M.J.; Alkon, D.L. Brain insulin receptors and spatial memory. Correlated changes in gene expression, tyrosine phosphorylation, and signaling molecules in the hippocampus of water maze trained rats. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 34893–34902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freude, S.; Schilbach, K.; Schubert, M. The role of IGF-1 receptor and insulin receptor signaling for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: From model organisms to human disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2009, 6, 213–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Monte, S.M.; Wands, J.R. Review of insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression, signaling, and malfunction in the central nervous system: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2005, 7, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plum, L.; Schubert, M.; Bruning, J.C. The role of insulin receptor signaling in the brain. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 16, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, G.M.; Bloodgood, B.L.; Townsend, M.; Walsh, D.M.; Selkoe, D.J.; Sabatini, B.L. Natural oligomers of the Alzheimer amyloid-β protein induce reversible synapse loss by modulating an NMDA-type glutamate receptor-dependent signaling pathway. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwood, J.M.; Dufour, F.; Laroche, S.; Davis, S. Signalling mechanisms mediated by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt cascade in synaptic plasticity and memory in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 3375–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condorelli, F.; Salomoni, P.; Cotteret, S.; Cesi, V.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Calabretta, B. Caspase cleavage enhances the apoptosis-inducing effects of BAD. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 3025–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halestrap, A.P.; Doran, E.; Gillespie, J.P.; O’Toole, A. Mitochondria and cell death. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2000, 28, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Teter, B.; Morihara, T.; Lim, G.P.; Ambegaokar, S.S.; Ubeda, O.J.; Frautschy, S.A.; Cole, G.M. Insulin-degrading enzyme as a downstream target of insulin receptor signaling cascade: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease intervention. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 11120–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, W.; Mansourian, S.; Chang, Y.; Lindsley, L.; Eckman, E.A.; Frosch, M.P.; Eckman, C.B.; Tanzi, R.E.; Selkoe, D.J.; Guenette, S. Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid β-protein, and the β-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4162–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, G.S.; Peskind, E.R.; Asthana, S.; Purganan, K.; Wait, C.; Chapman, D.; Schwartz, M.W.; Plymate, S.; Craft, S. Insulin increases CSF Aβ42 levels in normal older adults. Neurology 2003, 60, 1899–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, H.; Datta, S.R.; Franke, T.F.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Yao, R.; Cooper, G.M.; Segal, R.A.; Kaplan, D.R.; Greenberg, M.E. Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt. Science 1997, 275, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A.; Dohgu, S.; Lynch, J.L.; Fleegal-DeMotta, M.A.; Erickson, M.A.; Nakaoke, R.; Vo, T.Q. Nitric oxide isoenzymes regulate lipopolysaccharide-enhanced insulin transport across the blood-brain barrier. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reger, M.A.; Watson, G.S.; Frey, W.H., 2nd; Baker, L.D.; Cholerton, B.; Keeling, M.L.; Belongia, D.A.; Fishel, M.A.; Plymate, S.R.; Schellenberg, G.D.; et al. Effects of intranasal insulin on cognition in memory-impaired older adults: Modulation by APOE genotype. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamoon, M.S.; Noble, J.M.; Craft, S. Intranasal insulin improves cognition and modulates β-amyloid in early AD. Neurology 2009, 72, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltier, J.; O’Neill, A.; Schaffer, D.V. PI3K/Akt and CREB regulate adult neural hippocampal progenitor proliferation and differentiation. Dev. Neurobiol. 2007, 67, 1348–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, I.; Rosenthal, J.J.; Blagburn, J.M.; Blanco, R.E. Fibroblast growth factor 2 applied to the optic nerve after axotomy up-regulates BDNF and TrkB in ganglion cells by activating the ERK and PKA signaling pathways. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraud, P.; He, X.; Zhao, C.; Caldwell, M.A.; Franklin, R.J. FGF but not EGF induces phosphorylation of the cAMP response element binding protein in olfactory mucosa-derived cell cultures. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, M.R.; Pehar, M.; Cassina, P.; Martinez-Palma, L.; Thompson, J.A.; Beckman, J.S.; Barbeito, L. Fibroblast growth factor-1 induces heme oxygenase-1 via nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in spinal cord astrocytes: Consequences for motor neuron survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 25571–25579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Y.; Chuang, J.I. Fibroblast growth factor 9 upregulates heme oxygenase-1 and γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase expression to protect neurons from 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium toxicity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, J.I.; Huang, J.Y.; Tsai, S.J.; Sun, H.S.; Yang, S.H.; Chuang, P.C.; Huang, B.M.; Ching, C.H. FGF9-induced changes in cellular redox status and HO-1 upregulation are FGFR-dependent and proceed through both ERK and AKT to induce CREB and Nrf2 activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeldich, E.; Chen, C.D.; Colvin, T.A.; Bove-Fenderson, E.A.; Liang, J.; Tucker Zhou, T.B.; Harris, D.A.; Abraham, C.R. The neuroprotective effect of Klotho is mediated via regulation of members of the redox system. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24700–24715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.A.; Kendal, C.E.; Garcia-Maya, M.; Kenny, A.V.; Morris-Triggs, S.A.; Wu, T.; Reynolds, R.; Hohenester, E.; Saffell, J.L. A peptide from the first fibronectin domain of NCAM acts as an inverse agonist and stimulates FGF receptor activation, neurite outgrowth and survival. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavi, F.; Hosseini, R.; Saso, L.; Firuzi, O. Modulation of neurotrophic signaling pathways by polyphenols. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Miao, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Pinocembrin protects SH-SY5Y cells against MPP+-induced neurotoxicity through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 53, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Liu, R.; Zhu, S.Y.; Du, G.H. Acute neurovascular unit protective action of pinocembrin against permanent cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 10, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wu, C.X.; Zhou, D.; Yang, F.; Tian, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.T.; Du, G.H. Pinocembrin protects against β-amyloid-induced toxicity in neurons through inhibiting receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE)-independent signaling pathways and regulating mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.L.; Chen, B.N.; Gao, M.; Zhang, H.A.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Du, G.H. The characteristics of therapeutic effect of pinocembrin in transient global brain ischemia/reperfusion rats. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Liu, R.; Gao, M.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Xuan, Z.; Sun, J.; Yang, F.; Wu, C.; Du, G. Pinocembrin attenuates blood-brain barrier injury induced by global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Brain Res. 2011, 1391, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Liu, Q.; Jia, L.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Pinocembrin attenuates 6-OHDA-induced neuronal cell death through Nrf2/ARE pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, H.J.; Kim, D.O.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, B.G.; Shin, D.H. Effect of antioxidant flavanone, naringenin, from Citrus junoson neuroprotection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1520–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbarsky, V.; Datla, K.P.; Parkar, S.; Rai, D.K.; Aruoma, O.I.; Dexter, D.T. Neuroprotective properties of the natural phenolic antioxidants curcumin and naringenin but not quercetin and fisetin in a 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Jing, X.; Wei, X.; Shi, H.; Ren, D.; Zhang, X. Naringenin protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity via activation of the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology 2014, 79, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linford, N.J.; Dorsa, D.M. 17β-Estradiol and the phytoestrogen genistein attenuate neuronal apoptosis induced by the endoplasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin. Steroids 2002, 67, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreihofer, D.A.; Redmond, L. Soy phytoestrogens are neuroprotective against stroke-like injury in vitro. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Tu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, W.; Cheng, C.; Brann, D.W.; Yang, F. Genistein attenuates ischemic oxidative damage and behavioral deficits via eNOS/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Hippocampus 2013, 23, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, X. Orientin alleviates cognitive deficits and oxidative stress in Aβ1–42-induced mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2015, 121, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Shi, H.; Zhu, X.; Wei, X.; Ren, M.; Han, M.; Ren, D.; Lou, H. Eriodictyol Attenuates β-Amyloid 25–35 Peptide-Induced Oxidative Cell Death in Primary Cultured Neurons by Activation of Nrf2. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, Y.K.; Kim, G.S.; Han, B.H. Neuroprotective effects of flavones on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y neuroblostoma cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 2261–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Hsieh, M.T.; Tsai, F.S.; Wu, C.R.; Chiu, C.S.; Lee, M.M.; Xu, H.X.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Peng, W.H. Neuroprotective effect of luteolin on amyloid β protein (25–35)-induced toxicity in cultured rat cortical neurons. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24 (Suppl. S1), S102–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Wu, M.J.; Liu, I.Y.; Su, J.D.; Yen, J.H. Neurotrophic and cytoprotective action of luteolin in PC12 cells through ERK-dependent induction of Nrf2-driven HO-1 expression. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4477–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.Y.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, C.S.; Yoo, S.K.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, H.C.; Hong, J.T.; Oh, K.W. Protection of apigenin against kainate-induced excitotoxicity by anti-oxidative effects. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, R.; Li, X.X.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, L. Neuroprotective, anti-amyloidogenic and neurotrophic effects of apigenin in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Molecules 2013, 18, 9949–9965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Lu, P.; Sun, Y.; Gao, L.; Fu, D.; et al. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone induces synapse expression of AMPA GluA1 and ameliorates cognitive and spine abnormalities in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. Neuropharmacology 2015, 89, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Tian, M.; Zhao, H.Y.; Xu, Q.Q.; Huang, Y.M.; Si, Q.C.; Tian, Q.; Wu, Q.M.; Hu, X.M.; Sun, L.B.; McClintock, S.M.; Zeng, Y. TrkB activation by 7, 8-dihydroxyflavone increases synapse AMPA subunits and ameliorates spatial memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.W.; Liu, X.; Yepes, M.; Shepherd, K.R.; Miller, G.W.; Liu, Y.; Wilson, W.D.; Xiao, G.; Blanchi, B.; Sun, Y.E.; et al. A selective TrkB agonist with potent neurotrophic activities by 7,8-dihydroxyflavone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2687–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, L.C. Potential protection of curcumin against intracellular amyloid β-induced toxicity in cultured rat prefrontal cortical neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 480, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, A.N.; Jones, M.R.; Lim, G.P.; Morihara, T.; Kim, P.; Heath, D.D.; Rock, C.L.; Pruitt, M.A.; Yang, F.; Hudspeth, B.; et al. Curcumin structure-function, bioavailability, and efficacy in models of neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lian, Y.; Xie, N.; Wu, T.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z. Curcumin improves amyloid β-peptide (1–42) induced spatial memory deficits through BDNF-ERK signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkaew, D.; Changtam, C.; Tocharus, C.; Thummayot, S.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, J. Di-O-demethylcurcumin protects SK-N-SH cells against mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum-mediated apoptotic cell death induced by Aβ25–35. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 80, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Shuaib, A.; Li, Q.; Siddiqui, M.M. Neuroprotection by delayed administration of topiramate in a rat model of middle cerebral artery embolization. Brain Res. 1998, 804, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebauer, M.; Gruenthal, M. Topiramate reduces neuronal injury after experimental status epilepticus. Brain Res. 1999, 837, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.Y.; Cao, Y.G.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, H.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Sun, H.L. Topiramate protects against glutamate excitotoxicity via activating BDNF/TrkB-dependent ERK pathway in rodent hippocampal neurons. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 60, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, Y.C. Cognitive-enhancing and antioxidant activities of iridoid glycosides from Scrophularia buergeriana in scopolamine-treated mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 588, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ding, X.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, W.; Sun, X.; Xia, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, E.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y. Harpagoside ameliorates the amyloid-β-induced cognitive impairment in rats via up-regulating BDNF expression and MAPK/PI3K pathways. Neuroscience 2015, 303, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, R.; Wu, H.; Jin, Y.; Wei, J.; Buddhala, C.; Prentice, H.; Wu, J.Y. Protective function of taurine in glutamate-induced apoptosis in cultured neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, N.; Sun, Q.; Su, Q.; Dang, S.; Chen, G. Taurine promotes cognitive function in prenatally stressed juvenile rats via activating the Akt-CREB-PGC1α pathway. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.J.; Jin, Y.J.; Li, M.E.; Zhou, R.; Yang, M.Z. PGC-1α may associated with the anti-obesity effect of taurine on rats induced by arcuate nucleus lesion. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, K.; Fukuno, S.; Oda, A.; Konishi, H. Protective effects of taurine on doxorubicin-induced acute hepatotoxicity through suppression of oxidative stress and apoptotic responses. Anticancer Drugs 2016, 27, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpulla, R.C. Metabolic control of mitochondrial biogenesis through the PGC-1 family regulatory network. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. α-Lipoic acid: A metabolic antioxidant and potential redox modulator of transcription. Adv. Pharmacol. 1997, 38, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koriyama, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Matsugo, S.; Kato, S. Protective effect of lipoic acid against oxidative stress is mediated by Keap1/Nrf2-dependent heme oxygenase-1 induction in the RGC-5 cellline. Brain Res. 2013, 1499, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.H.; Li, C.Y.; Xiang, Z.G.; Zhong, F.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lu, J.M. Allicin can reduce neuronal death and ameliorate the spatial memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease models. Neurosciences 2010, 15, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Li, X.H.; Yuan, Z.P.; Li, C.Y.; Tian, R.B.; Jia, W.; Xiao, Z.P. Allicin improves endoplasmic reticulum stress-related cognitive deficits via PERK/Nrf2 antioxidative signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 762, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.C.; Thomas, R.G.; Grundman, M.; Bennett, D.; Doody, R.; Ferris, S.; Galasko, D.; Jin, S.; Kaye, J.; Levey, A.; et al. Vitamin E and donepezil for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2379–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Physiological Condition | Nrf2 Action | Reference |
| Resting condition |
| [104,105,106,107] |
| Oxidative stress |
| [108,109,110,111,112] |
| Alzheimer’s disease (human brain) |
| [134,135] |
| Experimental Condition | Outcome | Reference |
| Nrf2 knockout (APP/PS1 mice) | ↑ Oxidative damage | [136] |
| Nrf2 overexpression (APP/PS1 mice) | ↑ Neuroprotection against Aβ toxicity ↑ Spatial learning and memory | [137] |
| Nrf2 activation via 18 α-glycyrrhetinic acid (3xTg-AD neurons) | ↑ Neuron survival against Aβ stress ↑ GCL and GSH | [138] |
| Nrf2 activation via triterpenoids (Tg19959 AD mice) | ↓ Oxidative stress, inflammation, memory deficit | [139] |
| Activator | Target | Outcome | Research Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | ||||
| Pinocembrin | Nrf2-ARE | ↑ Nuclear Nrf2, HO-1 and λ-GCS activation ↑ Protection from 6-OHDA-induced oxidative stress | SH-SY5Y cells | [196] |
| Naringenin | Nrf2-ARE | ↑ Nuclear Nrf2 and HO-1, GCLC, GCLM, GSH | SH-SY5Y cells, C57BL/6 mouse | [199] |
| Genistein | Nrf2-ARE | ↑ HO-1, learning and memory, ↓ 8-OHdG, 4HNE ↑ eNOS-mediated S-nitrosylation of Keap1 ↑ Nuclear Nrf2 | GCI rat hippocampal CA1 neurons | [202] |
| Orientin | Nrf2-ARE | ↑ HO-1 ↓ ROS, 3-NT, 4HNE, and 8-OHdG, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, cognitive defects | AD mice | [203] |
| Eriodictyol | Nrf2-ARE | ↑ HO-1, GCLC, GCLM ↓ ROS and apoptosis | Aβ peptide- exposed cortical neurons | [204] |
| Luteolin * | Nrf2-ARE and neurotrophic | ↑ Neurite outgrowth, GAP-43, HO-1, ARE-binding of Nrf2 | PC12 cells | [207] |
| Apigenin * | Antioxidant and PI3K-Akt-ERK/CREB | ↓ Excitotoxicity, ROS, ↑GSH ↑ SOD and GPx, learning and memory ↓ Aβ peptide production and deposition | kainic acid-treated neurons and mice APP/PS1 AD mice | [208,209] |
| 7,8-DHF * | Antioxidant and PI3K-Akt-ERK/CREB | ↑ TrkB dimerization and phosphorylation, neuron survival | hippocampal, motor, ganglionic neurons | [190,212] |
| Non-Flavonoid Polyphenols | ||||
| Curcumin | PI3K-Akt/CREB-ERK/insulin | ↑ BDNF, pERK, improved cognitive behavior ↓ Active JNK, inhibitory IRS-1 phosphorylation, memory deficit | Aβ-injected rats (hippocampus) 3xTg-AD mice on HFD | [4,215] |
| O-Demethylcurcumin | Neurotrophic/ER stress response | ↓ Aβ-induced caspase-dependent apoptosis ↓ ER stress protein expression (p-PERK, p-eIF2α, p-IRE1α, XBP-1, ATF6, and CHOP) | SK-N-SH cells | [216] |
| Topiramate | Neurotrophic | ↓ Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity ↑ BDNF, p-TrkB, p-ERK, p-CREB | hippocampal neurons | [219] |
| Harpagoside * | Antioxidant and PI3K-Akt-ERK | ↑ GR, SOD, GSH ↓ Lipid peroxidation, memory deficit ↑ BDNF, ↓ memory defect ↓ Neurite atrophy and apoptosis | cortex and hippocampus in scopolamine- treated mice Aβ peptide- treated rats, Aβ peptide- treated cortical neurons | [220,221] |
| Non-Polyphenol Compounds | ||||
| Taurine * | Akt-CREB-PGC1α | ↓ Glutamate cytotoxicity, maintain MMP, ↓ cytosolic ROS ↓ Mitochondrial ROS ↑ MMP, COX, ATP, SOD2 ↑ Hippocampal PGC1α expression, learning and memory | SH-SY5Y cells prenatally-stressed rats that showed defects in learning and memory | [222,223] |
| R-α-Lipoic acid * | Akt/PI3K and Nrf2-ARE | ↑ HO-1 expression, Nrf2 translocation ↓ ROS, 4HNE, cell death | retinal neuronal RGC-5 cells | [228] |
| Allicin * | Nrf2-ARE and neurotrophic | ↓ Aβ-induced memory deficit ↑ Nrf2, antioxidant enzymes, ↓ PERK, p-tau, ROS, lipid peroxidation, protein carbonylation, cognitive defect | AD mouse model rat brains | [229,230] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murphy, K.E.; Park, J.J. Can Co-Activation of Nrf2 and Neurotrophic Signaling Pathway Slow Alzheimer’s Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061168
Murphy KE, Park JJ. Can Co-Activation of Nrf2 and Neurotrophic Signaling Pathway Slow Alzheimer’s Disease? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061168
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurphy, Kelsey E., and Joshua J. Park. 2017. "Can Co-Activation of Nrf2 and Neurotrophic Signaling Pathway Slow Alzheimer’s Disease?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061168
APA StyleMurphy, K. E., & Park, J. J. (2017). Can Co-Activation of Nrf2 and Neurotrophic Signaling Pathway Slow Alzheimer’s Disease? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061168






