Cholesterol Crystal Embolism and Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Etiology
3. Epidemiology
4. Pathogenesis
4.1. Necroinflammation
4.2. Activation of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
4.3. Complement Activation
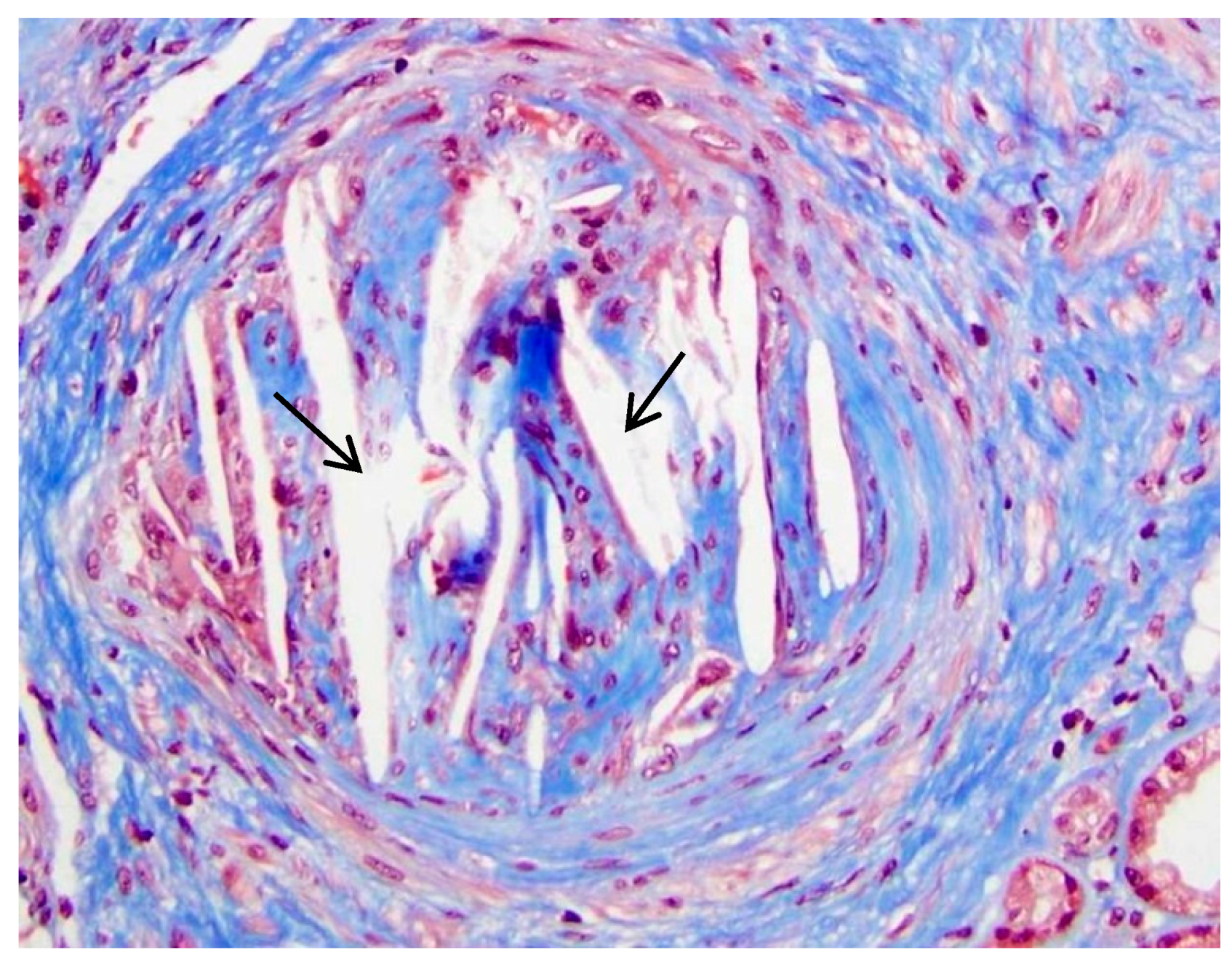
5. Pathology
6. Clinic Presentations
6.1. Renal Complication of Cholesterol Crystal Embolism (CCE)
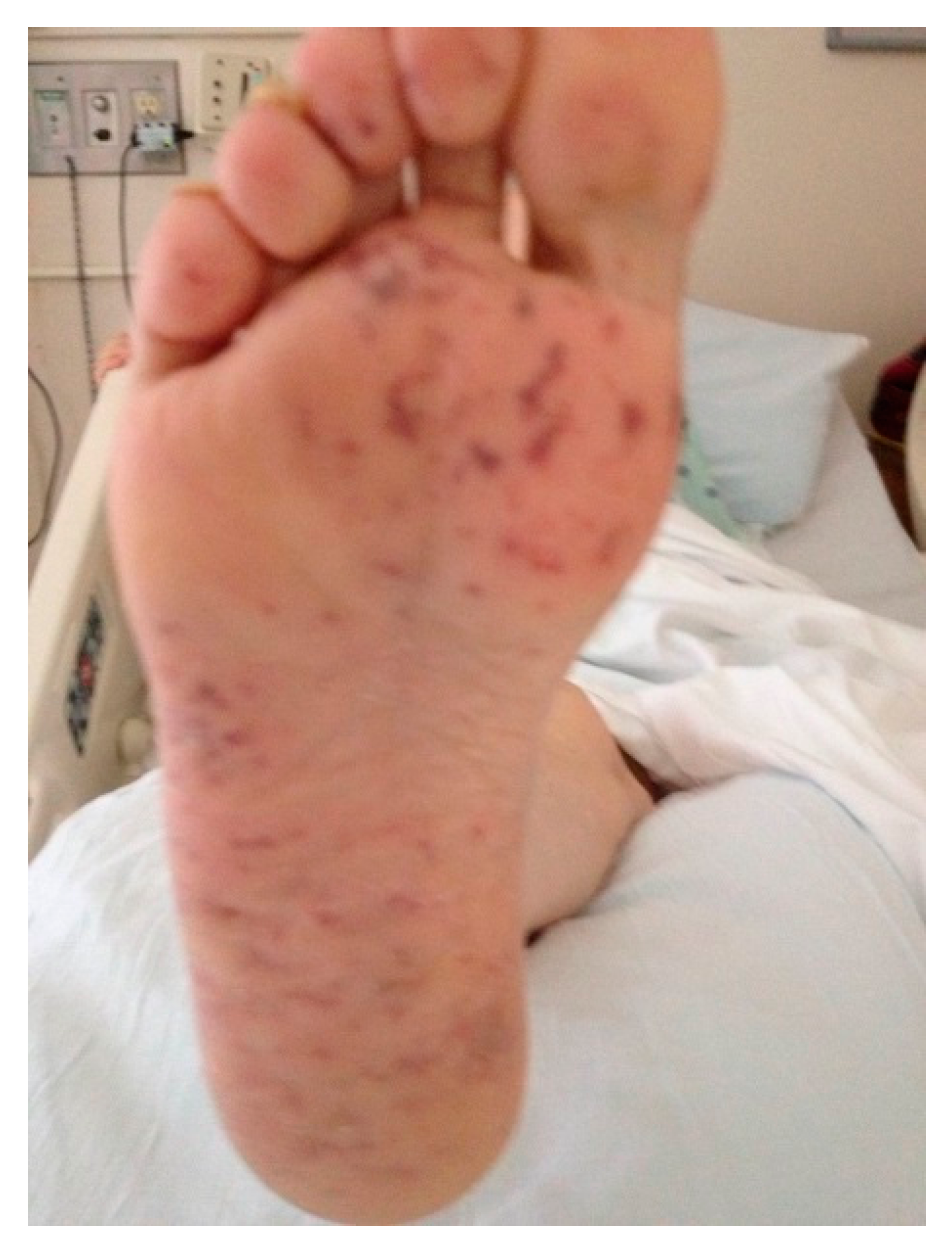
6.2. Extra-Renal Manifestation
7. Treatments
7.1. Corticosteroids
7.2. Lipid-Lowering Therapies
7.3. Dialysis and Other Therapies
8. Outcome
9. Prevention
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mulay, S.R.; Anders, H.J. Crystallopathies. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2465–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolari, F.; Ravani, P. Atheroembolic renal disease. Lancet 2010, 375, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronopoulos, A.; Rosner, M.H.; Cruz, D.N.; Ronco, C. Acute kidney injury in the elderly: A review. Contrib. Nephrol. 2010, 165, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venturelli, C.; Jeannin, G.; Sottini, L.; Dallera, N.; Scolari, F. Cholesterol crystal embolism (atheroembolism). Heart Int. 2006, 2, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saric, M.; Kronzon, I. Cholesterol embolization syndrome. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2011, 26, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rosendael, P.J.; Kamperidis, V.; van der Kley, F.; Katsanos, S.; Al Amri, I.; Regeer, M.V.; Schalij, M.J.; de Weger, A.; Marsan, N.A.; Bax, J.J.; et al. Atherosclerosis burden of the aortic valve and aorta and risk of acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2015, 9, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolari, F.; Ravani, P.; Gaggi, R.; Santostefano, M.; Rollino, C.; Stabellini, N.; Colla, L.; Viola, B.F.; Maiorca, P.; Venturelli, C.; et al. The challenge of diagnosing atheroembolic renal disease: Clinical features and prognostic factors. Circulation 2007, 116, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, S.T.; Negrete, H.; Roy, P.; Julius, C.J.; Sarac, E. A case of dabigatran-associated acute renal failure. WMJ 2013, 112, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carron, P.L.; Florea, A.; Ducloux, D.; Jamali, M.; Chalopin, J.M. Atheroembolic disease associated with the use of low-molecular-weight heparin during haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999, 14, 520–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, A.F.; Sakuma, T.H.; Lima, R.B.; de Figueiredo, W.M.; Valle Hde, A.; Tolstoy, F.A.; Coimbra, D.D.; Lupi, O. Cholesterol crystal embolization caused by anticoagulant therapy. Int. J. Dermatol. 2009, 48, 989–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turina, S.; Mazzola, G.; Venturelli, C.; Valerio, F.; Dallera, N.; Kenou, R.; Sottini, L.; Maffeo, D.; Tardanico, R.; Faggiano, P.; et al. Atheroembolic renal disease. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2009, 26, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mittal, B.V.; Alexander, M.P.; Rennke, H.G.; Singh, A.K. Atheroembolic renal disease: A silent masquerader. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, R.R.; Swartz, R.D. Redefining the incidence of clinically detectable atheroembolism. Am. J. Med. 1996, 100, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, Y.; Tsutsui, H.; Tsuchihashi, M.; Masumoto, A.; Takeshita, A.; Cholesterol Embolism Study(CHEST) Investigators. The incidence and risk factors of cholesterol embolization syndrome, a complication of cardiac catheterization: A prospective study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolenaar, W.; Lamers, C.B. Cholesterol crystal embolization in the Netherlands. Arch. Intern. Med. 1996, 156, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, M.; Spargo, B.H.; Wit, E.J.; Meehan, S.M. Etiologies and outcome of acute renal insufficiency in older adults: A renal biopsy study of 259 cases. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, B.A.; Vales, O. The ultrastructure of the stages of atheroembolic occlusion of renal arteries. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1973, 54, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.B.; Iannaccone, P.M. Atheromatous emboli in renal biopsies. An ultrastructural study. Am. J. Pathol. 1975, 78, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bradamante, M. Cholesterol crystal embolization. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat 2007, 15, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinon, F.; Petrilli, V.; Mayor, A.; Tardivel, A.; Tschopp, J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 2006, 440, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duewell, P.; Kono, H.; Rayner, K.J.; Sirois, C.M.; Vladimer, G.; Bauernfeind, F.G.; Abela, G.S.; Franchi, L.; Nunez, G.; Schnurr, M.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature 2010, 464, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corr, E.M.; Cunningham, C.C.; Dunne, A. Cholesterol crystals activate Syk and PI3 kinase in human macrophages and dendritic cells. Atherosclerosis 2016, 251, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyotake, R.; Oh-Hora, M.; Ishikawa, E.; Miyamoto, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Yamasaki, S. Human Mincle Binds to Cholesterol Crystals and Triggers Innate Immune Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 25322–25332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Matsuo, K.; Shoda, H.; Takami, S.; Naruse, M.; Matsuyama, K. Severe hyperreninemic hypertension associated with spontaneous renal cholesterol crystal embolization. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2004, 8, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calo, L.A.; Schiavo, S.; Davis, P.A.; Pagnin, E.; Mormino, P.; D’Angelo, A.; Pessina, A.C. Angiotensin II signaling via type 2 receptors in a human model of vascular hyporeactivity: Implications for hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samstad, E.O.; Niyonzima, N.; Nymo, S.; Aune, M.H.; Ryan, L.; Bakke, S.S.; Lappegard, K.T.; Brekke, O.L.; Lambris, J.D.; Damas, J.K.; et al. Cholesterol crystals induce complement-dependent inflammasome activation and cytokine release. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 2837–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyonzima, N.; Samstad, E.O.; Aune, M.H.; Ryan, L.; Bakke, S.S.; Rokstad, A.M.; Wright, S.D.; Damas, J.K.; Mollnes, T.E.; Latz, E.; et al. Reconstituted High-Density Lipoprotein Attenuates Cholesterol Crystal-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Reducing Complement Activation. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerschmidt, D.E.; Greenberg, C.S.; Yamada, O.; Craddock, P.R.; Jacob, H.S. Cholesterol and atheroma lipids activate complement and stimulate granulocytes. A possible mechanism for amplification of ischemic injury in atherosclerotic states. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1981, 98, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nymo, S.; Niyonzima, N.; Espevik, T.; Mollnes, T.E. Cholesterol crystal-induced endothelial cell activation is complement-dependent and mediated by TNF. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lye, W.C.; Cheah, J.S.; Sinniah, R. Renal cholesterol embolic disease. Case report and review of the literature. Am. J. Nephrol. 1993, 13, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dummer, C.D.; Veronese, F.J.; Piana, M. Atheroembolic renal disease: A cause of acute renal failure not much explored. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2010, 56, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, K.S.; Rao, V.K. Atheroembolic renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scolari, F.; Tardanico, R.; Zani, R.; Pola, A.; Viola, B.F.; Movilli, E.; Maiorca, R. Cholesterol crystal embolism: A recognizable cause of renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 36, 1089–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polu, K.R.; Wolf, M. Clinical problem-solving. Needle in a haystack. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyrier, A. Cholesterol crystal embolism: Diagnosis and treatment. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, A.; Bastacky, S.I.; Iqbal, A.; Borochovitz, D.; Johnson, J.P. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis associated with nephrotic syndrome in cholesterol atheroembolism: Clinicopathological correlations. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1997, 29, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinones, A.; Saric, M. The cholesterol emboli syndrome in atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2013, 15, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.M.; Salazer, T.L.; Farkouh, M.E. Eosinophiluria in atheroembolic renal disease. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakan, H.; Nakatani, K.; Asai, O.; Matsui, M.; Iwano, M.; Saito, Y. Case of purpura nephritis accompanied by idiopathic cholesterol embolism. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 2012, 54, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.K.; Folkert, V.W. Renal function recovery in chronic dialysis patients. Semin. Dial. 2010, 23, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Quaglia, M.; Quaglino, P.; Burdese, M.; Bermond, F.; Mezza, E.; Jeantet, A.; Segoloni, G.P. Acute digital gangrene in a long-term dialysis patient—A diagnostic challenge. Med. Sci. Monit. 2002, 8, CS83–CS89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.K.; Randhawa, P.S. Cholesterol embolization in renal allografts: A clinicopathologic study of 12 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulay, S.R.; Evan, A.; Anders, H.J. Molecular mechanisms of crystal-related kidney inflammation and injury. Implications for cholesterol embolism, crystalline nephropathies and kidney stone disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, A.P.; Juega, J.; Vazquez, C.; Hernandez-Gallego, A.; Lopez, D.; Canas, L.; Bancu, I.; Bonet, J.; Lauzurica, R. Late Onset of Cholesterol Embolism Leading to Graft Failure After Renal Transplantation: Report of Two Cases. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 2361–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolari, F.; Tardanico, R.; Pola, A.; Mazzucchelli, C.; Maffeis, R.; Bonardelli, S.; Maiorca, P.; Movilli, E.; Sandrini, S. Cholesterol crystal embolic disease in renal allografts. J. Nephrol. 2003, 16, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herzog, A.L.; Wanner, C. Case Report: Atheroembolic renal disease in a 72-year-old patient through coronary intervention after myocardial infarction. Hemodial. Int. 2008, 12, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohue, K.G.; Saap, L.; Falanga, V. Cholesterol crystal embolization: An atherosclerotic disease with frequent and varied cutaneous manifestations. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2003, 17, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolari, F.; Ravani, P.; Pola, A.; Guerini, S.; Zubani, R.; Movilli, E.; Savoldi, S.; Malberti, F.; Maiorca, R. Predictors of renal and patient outcomes in atheroembolic renal disease: A prospective study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, A.; Insalaco, M.; di Pietro, F.; di Rosa, S.; Romano, G.; Scuderi, R. Atheroembolism renal disease: Diagnosis and etiologic factors. Clin. Ter. 2012, 163, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cosio, F.G.; Zager, R.A.; Sharma, H.M. Atheroembolic renal disease causes hypocomplementaemia. Lancet 1985, 2, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Ram, R.; Prayaga, A.; Dakshinamurty, K.V. Cholesterol crystal embolization (CCE): Improvement of renal function with high-dose corticosteroid treatment. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2011, 22, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fabbian, F.; Catalano, C.; Lambertini, D.; Bordin, V.; di Landro, D. A possible role of corticosteroids in cholesterol crystal embolization. Nephron 1999, 83, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabellini, N.; Cerretani, D.; Russo, G.; Rizzioli, E.; Gilli, P. Renal atheroembolic disease: Evaluation of the efficacy of corticosteroid therapy. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2002, 19, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kronzon, I.; Tunick, P.A. Aortic atherosclerotic disease and stroke. Circulation 2006, 114, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S.J.; Sos, T.A. Treatment of atheroembolization with corticosteroids. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Izumaru, K.; Nagata, M.; Ikeda, H.; Nishida, K.; Hasegawa, E.; Ohta, Y.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Urabe, K. The effect of low-dose corticosteroids on short- and long-term renal outcome in patients with cholesterol crystal embolism. Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abela, G.S.; Vedre, A.; Janoudi, A.; Huang, R.; Durga, S.; Tamhane, U. Effect of statins on cholesterol crystallization and atherosclerotic plaque stabilization. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 107, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, K.; Sato, T.; Taguma, Y. Low-Density Lipoprotein Apheresis Ameliorates Renal Prognosis of Cholesterol Crystal Embolism. Ther. Apheresis Dial. 2015; 19, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, A. Hyperlipoproteinaemia(a)—Apheresis and emerging therapies. Clin. Res. Cardiol. Suppl. 2017, 12 (Suppl. S1), 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belenfant, X.; Meyrier, A.; Jacquot, C. Supportive treatment improves survival in multivisceral cholesterol crystal embolism. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1999, 33, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shames, M.L.; Rubin, B.G.; Sanchez, L.A.; Thompson, R.W.; Sicard, G.A. Treatment of embolizing arterial lesions with endoluminally placed stent grafts. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2002, 16, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theriault, J.; Agharazzi, M.; Dumont, M.; Pichette, V.; Ouimet, D.; Leblanc, M. Atheroembolic renal failure requiring dialysis: Potential for renal recovery? A review of 43 cases. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2003, 94, c11–c18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyabalan, G.; Wallace, J.R.; Chaer, R.A.; Leers, S.A.; Marone, L.K.; Makaroun, M.S. Endovascular strategies for treatment of embolizing thoracoabdominal aortic lesions. J. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 59, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, B.; Vidinha, J.; Pego, C.; Garrido, J.; Lemos, S.; Lima, C.; Sorbo, G.; Gomes, E.L.; Carvalho, T.; Loureiro, P.; Sousa, T. Atheroembolic renal disease with rapid progression and fatal outcome. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2011, 15, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlberg, P.J.; Frecentese, D.F.; Cogbill, T.H. Cholesterol embolism: Experience with 22 histologically proven cases. Surgery 1989, 105, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thadhani, R.I.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Xavier, R.J.; Fang, L.S.; Bazari, H. Atheroembolic renal failure after invasive procedures. Natural history based on 52 histologically proven cases. Medicine 1995, 74, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, R.D. Cholesterol embolism syndrome: A rare, but severe complication in patients with atherosclerosis. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2012, 137, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Machino-Ohtsuka, T.; Seo, Y.; Ishizu, T.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Sato, A.; Tada, H.; Watanabe, S.; Aonuma, K. Combined assessment of carotid vulnerable plaque, renal insufficiency, eosinophilia, and hs-CRP for predicting risky aortic plaque of cholesterol crystal embolism. Circ. J. 2010, 74, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccala, A.; Zucchelli, P. A renal disease frequently found at postmortem, but rarely diagnosed in vivo. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1997, 12, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasri, H.; Mubarak, M. Contrast induced nephropathy has to be differentiated from kidney injury due to atheroembolic disease. J. Renal. Inj. Prev. 2013, 2, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Organ | Clinical Presentations |
|---|---|
| Kidney | Acute or subacute kidney injury |
| Renal infarction | |
| Chronic kidney disease | |
| Renal allograft failure | |
| Severe hard-to-control hypertension | |
| Extra-renal organs | |
| Skin | Livedo reticularis |
| Blue toe syndrome | |
| Ulceration and gangrene | |
| Purpura | |
| Small nail bed infarcts | |
| Leg, foot, or toe pain | |
| Gastrointestinal System | Abdominal, flank, or back pain |
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | |
| Diarrhea | |
| Bowel ischemia, infarction, and obstruction | |
| Pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and abnormal liver tests | |
| Splenic infarcts | |
| Eyes | Amaurosis fugax |
| Sudden blindness | |
| Retinal plaques (Hollenhorst plaques) | |
| Central Nervous System | Headache |
| Amaurosis fugax | |
| Stroke | |
| Transient ischaemic attacks | |
| Altered mental status | |
| Paraparesis | |
| Mononeuropathy | |
| Cerebral infarction | |
| Spinal cord infarction | |
| Muscle | Muscle pain |
| Arthralgias | |
| Rhabdomyolysis | |
| Systemic signs | |
| Fever | |
| Anorexia | |
| Fatigue | |
| Weight loss | |
| Malaise | |
| Myalgia |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Bayliss, G.; Zhuang, S. Cholesterol Crystal Embolism and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061120
Li X, Bayliss G, Zhuang S. Cholesterol Crystal Embolism and Chronic Kidney Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuezhu, George Bayliss, and Shougang Zhuang. 2017. "Cholesterol Crystal Embolism and Chronic Kidney Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061120
APA StyleLi, X., Bayliss, G., & Zhuang, S. (2017). Cholesterol Crystal Embolism and Chronic Kidney Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061120






