Improving Cerebral Blood Flow after Arterial Recanalization: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
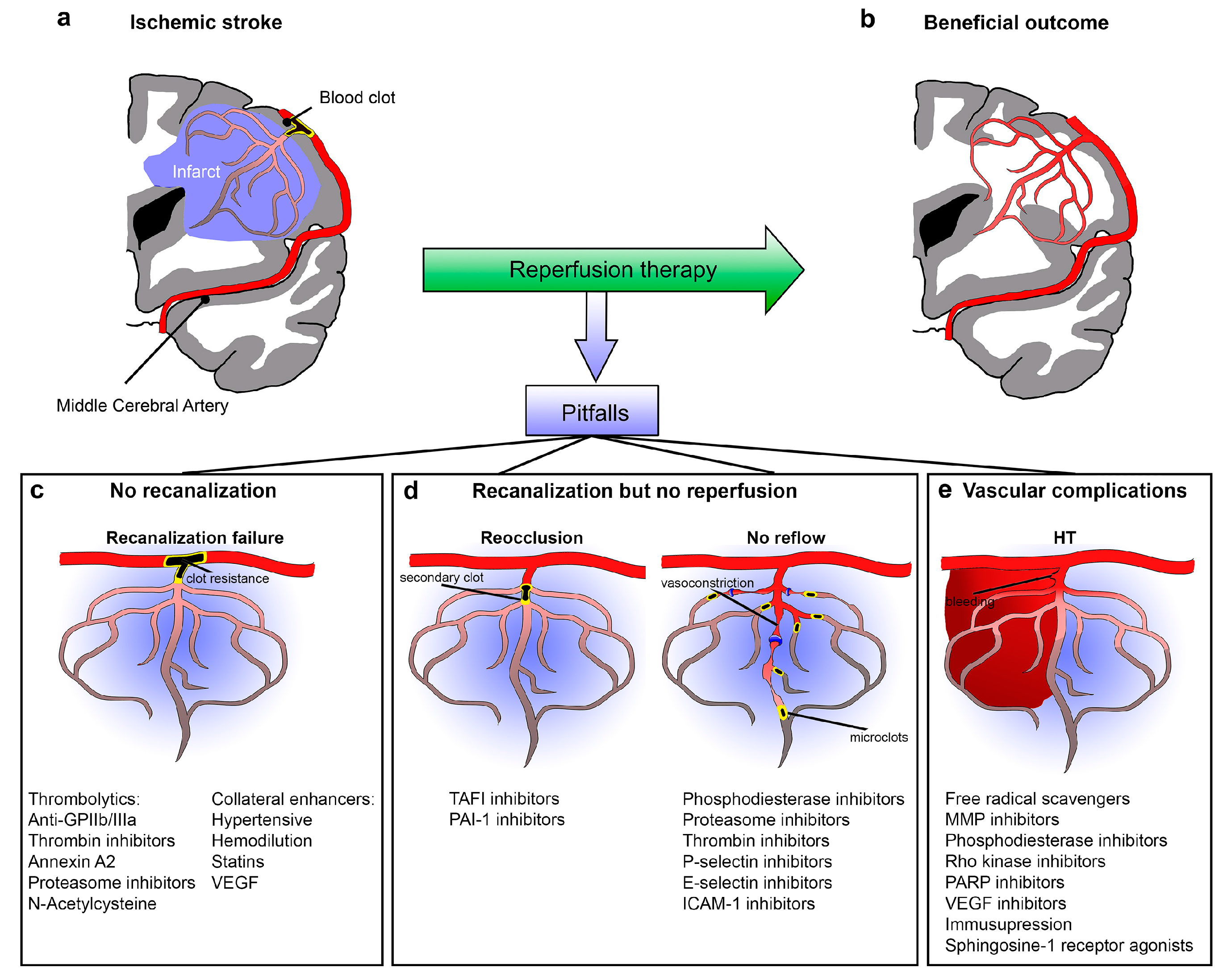
2. Recanalization Failure
2.1. Recanalization Rate
2.2. Therapeutic Strategies for a Better “Clot-Buster”
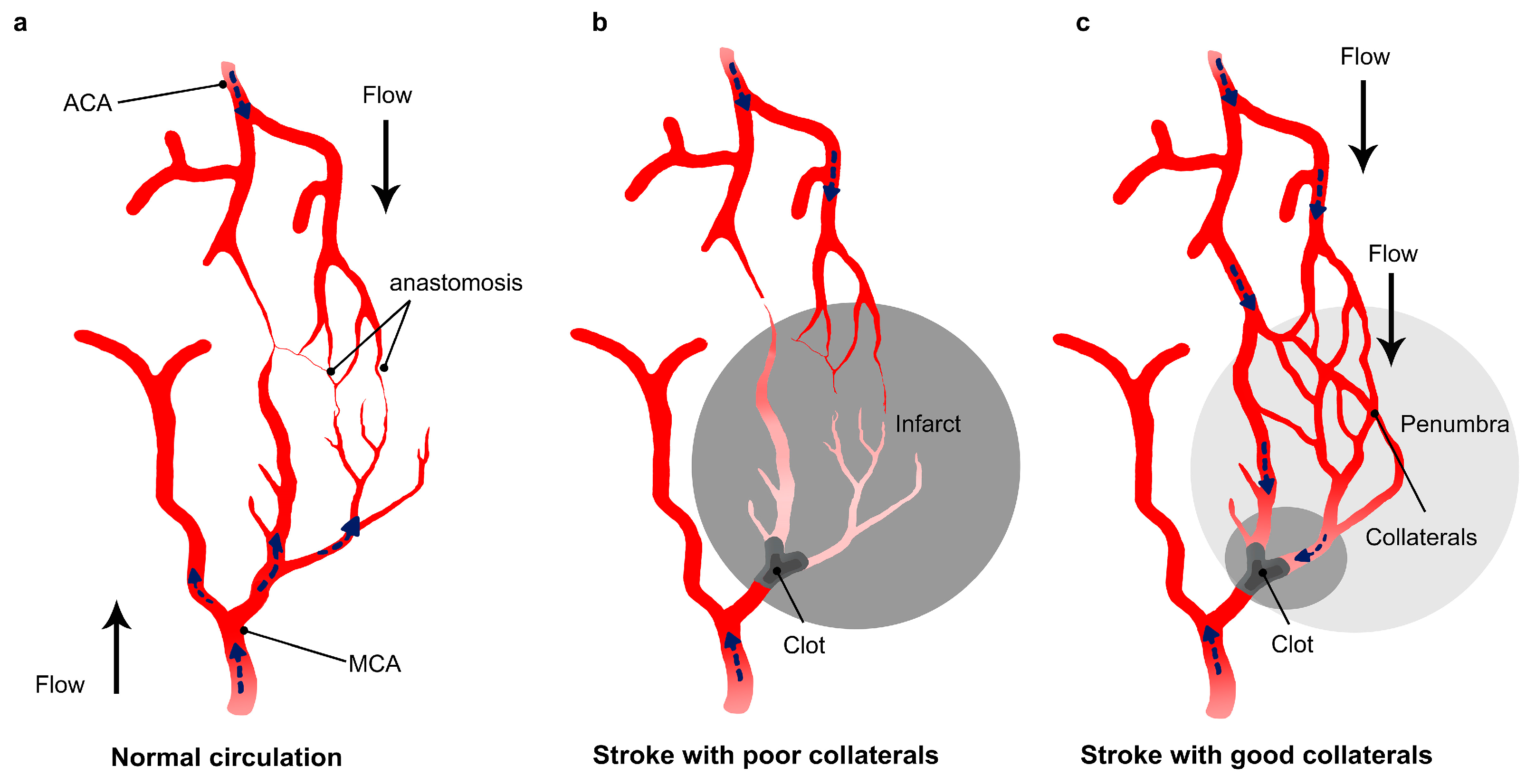
2.3. Collaterals
2.4. Strategies to Enhance Collateral Circulation
3. No Reperfusion Despite Recanalization Successes (Futile Recanalization)
3.1. Arterial Reocclusion
3.2. Therapeutic Targets against Arterial Reocclusion
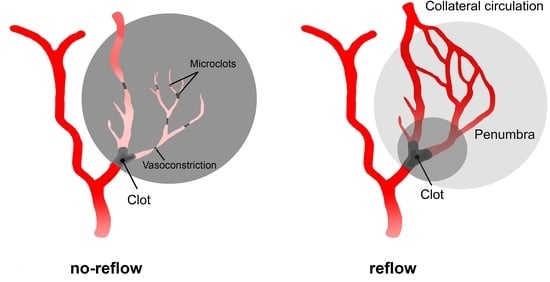
3.3. No-Reflow
3.4. Therapeutic Strategies for Treatment of No-Reflow
4. Reperfusion with Vascular Complications
4.1. Hemorrhagic Transformation
4.2. Strategies against Hemorrhagic Transformation
5. Conclusions and Future Direction
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| rt-PA | Recombinant tissue Plasminogen Activator |
| HT | Hemorrhagic Transformation |
| CBF | Cerebral Blood Flow |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| LRP | Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein |
| ICH | Intracerebral Hemorrhage |
| MCA | Middle Cerebral artery |
| ACA | Anterior Cerebral Artery |
| PCA | Posterior Cerebral Artery |
| ICA | Internal Carotid Artery |
| BBB | Blood Brain Barrier |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
References
- WHO. The World Health Report 2002—Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life. Available online: http://www.who.int/whr/2002/en/ (accessed on 23 July 2012).
- Strong, K.; Mathers, C.; Bonita, R. Preventing stroke: Saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Murray, V.; Berge, E.; del Zoppo, G.J. Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, CD000213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Menon, B.K.; van Zwam, W.H.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Mitchell, P.J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Dávalos, A.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; van der Lugt, A.; de Miquel, M.A.; et al. HERMES collaborators Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016, 387, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rha, J.-H.; Saver, J.L. The impact of recanalization on ischemic stroke outcome: A meta-analysis. Stroke 2007, 38, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Wahlgren, N.; Grond, M.; Hennerici, M.; Lees, K.R.; Mikulik, R.; Parsons, M.; Roine, R.O.; Toni, D.; Ringleb, P. SITS investigators Implementation and outcome of thrombolysis with alteplase 3–4.5 h after an acute stroke: An updated analysis from SITS-ISTR. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; Hill, M.D. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, M.T.; Pisapia, J.M.; Tilwa, S.; Messé, S.R.; Stein, S.C. Systematic review of outcome after ischemic stroke due to anterior circulation occlusion treated with intravenous, intra-arterial, or combined intravenous+intra-arterial thrombolysis. Stroke 2012, 43, 2350–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauch, E.C.; Saver, J.L.; Adams, H.P.; Bruno, A.; Connors, J.J.B.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Khatri, P.; McMullan, P.W.; Qureshi, A.I.; Rosenfield, K.; et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013, 44, 870–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meschia, J.F.; Barrett, K.M.; Brott, T.G. Reperfusion therapy for acute ischemic stroke: How should we react to the Third Interventional Management of Stroke (IMS III) trial? Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechsler, L.R. Imaging evaluation of acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, S12–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, R.; Hill, M.D.; Shobha, N.; Menon, B.; Bal, S.; Kochar, P.; Watson, T.; Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M. Low rates of acute recanalization with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in ischemic stroke: Real-world experience and a call for action. Stroke 2010, 41, 2254–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubiera, M.; Alvarez-Sabín, J.; Ribo, M.; Montaner, J.; Santamarina, E.; Arenillas, J.F.; Huertas, R.; Delgado, P.; Purroy, F.; Molina, C.A. Predictors of early arterial reocclusion after tissue plasminogen activator-induced recanalization in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2005, 36, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobin, Y.P.; Starkman, S.; Duckwiler, G.R.; Grobelny, T.; Kidwell, C.S.; Jahan, R.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Segal, A.; Vinuela, F.; Saver, J.L. MERCI 1: A phase 1 study of Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia. Stroke 2004, 35, 2848–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.S.; Sung, G.; Saver, J.; Budzik, R.; Duckwiler, G.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Lutsep, H.L.; Rymer, M.M.; Higashida, R.T.; Starkman, S.; et al. Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: Final results of the Multi MERCI trial. Stroke 2008, 39, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.S. Safety of mechanical thrombectomy and intravenous tissue plasminogen activator in acute ischemic stroke. Results of the multi Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia (MERCI) trial, part I. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Penumbra Pivotal Stroke Trial Investigators. The penumbra pivotal stroke trial: Safety and effectiveness of a new generation of mechanical devices for clot removal in intracranial large vessel occlusive disease. Stroke 2009, 40, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saver, J.L.; Jahan, R.; Levy, E.I.; Jovin, T.G.; Baxter, B.; Nogueira, R.G.; Clark, W.; Budzik, R.; Zaidat, O.O. Solitaire flow restoration device versus the Merci Retriever in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (SWIFT): A randomised, parallel-group, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Lutsep, H.L.; Gupta, R.; Jovin, T.G.; Albers, G.W.; Walker, G.A.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Smith, W.S. TREVO 2 Trialists Trevo versus Merci retrievers for thrombectomy revascularisation of large vessel occlusions in acute ischaemic stroke (TREVO 2): A randomised trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rueda, M.E.; Parrilla, G.; Manzano-Fernández, S.; García-Villalba, B.; Zamarro, J.; Hernández-Fernández, F.; Sánchez-Vizcaino, C.; Carreón, E.; Morales, A.; Moreno, A. Combined Multimodal Computed Tomography Score Correlates with Futile Recanalization after Thrombectomy in Patients with Acute Stroke. Stroke 2015, 46, 2517–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorado, L.; Millán, M.; Dávalos, A. Reperfusion Therapies for Acute Ischemic Stroke: An Update. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2014, 10, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, B.P.; Tong, E.; Hom, J.; Cheng, S.-C.; Bredno, J.; Boussel, L.; Smith, W.S.; Wintermark, M. Reperfusion is a more accurate predictor of follow-up infarct volume than recanalization: A proof of concept using CT in acute ischemic stroke patients. Stroke 2010, 41, e34–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomsick, T.; Broderick, J.; Carrozella, J.; Khatri, P.; Hill, M.; Palesch, Y.; Khoury, J. Interventional Management of Stroke II Investigators Revascularization results in the Interventional Management of Stroke II trial. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, B.P.; Chien, J.D.; Wintermark, M. MR and CT monitoring of recanalization, reperfusion, and penumbra salvage: Everything that recanalizes does not necessarily reperfuse! Stroke 2009, 40, S24–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemisci, M.; Gursoy-Ozdemir, Y.; Vural, A.; Can, A.; Topalkara, K.; Dalkara, T. Pericyte contraction induced by oxidative-nitrative stress impairs capillary reflow despite successful opening of an occluded cerebral artery. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, I.; Alexandrov, A.V.; Burgin, W.S.; Wojner, A.W.; Felberg, R.A.; Malkoff, M.; Grotta, J.C. Timing of recanalization after tissue plasminogen activator therapy determined by transcranial doppler correlates with clinical recovery from ischemic stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 1812–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, A.V.; Grotta, J.C. Arterial reocclusion in stroke patients treated with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Neurology 2002, 59, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqqur, M.; Molina, C.A.; Salam, A.; Siddiqui, M.; Ribo, M.; Uchino, K.; Calleja, S.; Garami, Z.; Khan, K.; Akhtar, N.; et al. CLOTBUST Investigators Clinical deterioration after intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator treatment: A multicenter transcranial Doppler study. Stroke 2007, 38, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Mitchell, P.J.; Kleinig, T.J.; Dewey, H.M.; Churilov, L.; Yassi, N.; Yan, B.; Dowling, R.J.; Parsons, M.W.; Oxley, T.J.; et al. EXTEND-IA Investigators Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.S.; Sung, G.; Starkman, S.; Saver, J.L.; Kidwell, C.S.; Gobin, Y.P.; Lutsep, H.L.; Nesbit, G.M.; Grobelny, T.; Rymer, M.M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of mechanical embolectomy in acute ischemic stroke: Results of the MERCI trial. Stroke 2005, 36, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhemer, O.A.; Fransen, P.S.S.; Beumer, D.; van den Berg, L.A.; Lingsma, H.F.; Yoo, A.J.; Schonewille, W.J.; Vos, J.A.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Wermer, M.J.H.; et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanacker, P.; Heldner, M.R.; Amiguet, M.; Faouzi, M.; Cras, P.; Ntaios, G.; Arnold, M.; Mattle, H.P.; Gralla, J.; Fischer, U.; et al. Prediction of Large Vessel Occlusions in Acute Stroke: National Institute of Health Stroke Scale Is Hard to Beat. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, e336–e343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.S.; Lev, M.H.; English, J.D.; Camargo, E.C.; Chou, M.; Johnston, S.C.; Gonzalez, G.; Schaefer, P.W.; Dillon, W.P.; Koroshetz, W.J.; et al. Significance of Large Vessel Intracranial Occlusion Causing Acute Ischemic Stroke and TIA. Stroke 2009, 40, 3834–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, A.J.; Andersson, T. Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke: Challenges to Procedural Success. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, C.H.; Zimmermann, P.; Jensen-Kondering, U.; Stingele, R.; Deuschl, G.; Jansen, O. The importance of size: Successful recanalization by intravenous thrombolysis in acute anterior stroke depends on thrombus length. Stroke 2011, 42, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, A.D. Intravenous thrombolytics for ischemic stroke. Neurotherapeutics 2011, 8, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlinn, K.; Becker, U.; Puetz, V.; Dzialowski, I.; Kunz, A.; Kepplinger, J.; von Kummer, R.; Gahn, G. Combined treatment with intravenous abciximab and intraarterial tPA yields high recanalization rate in patients with acute basilar artery occlusion. J. Neuroimaging 2012, 22, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, R.J.; Meisel, S.; Moll, M.; Wittsack, H.-J.; Junghans, U.; Siebler, M. The effect of combined thrombolysis with rtPA and tirofiban on ischemic brain lesions. Neurology 2004, 62, 2110–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancioli, A.M.; Broderick, J.; Brott, T.; Tomsick, T.; Khoury, J.; Bean, J.; del Zoppo, G.; Kleindorfer, D.; Woo, D.; Khatri, P.; et al. The combined approach to lysis utilizing eptifibatide and rt-PA in acute ischemic stroke: The CLEAR stroke trial. Stroke 2008, 39, 3268–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, I.K.; Gold, H.K.; Leinbach, R.C.; Fallon, J.T.; Collen, D. In vivo thrombin inhibition enhances and sustains arterial recanalization with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. Circ. Res. 1990, 67, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, A.D.; Alexandrov, A.V.; Lyden, P.; Lee, J.; Martin-Schild, S.; Shen, L.; Wu, T.-C.; Sisson, A.; Pandurengan, R.; Chen, Z.; et al. The argatroban and tissue-type plasminogen activator stroke study: Final results of a pilot safety study. Stroke 2012, 43, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinkstok, S.M.; Roos, Y.B. ARTIS investigators early administration of aspirin in patients treated with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diedler, J.; Ahmed, N.; Sykora, M.; Uyttenboogaart, M.; Overgaard, K.; Luijckx, G.-J.; Soinne, L.; Ford, G.A.; Lees, K.R.; Wahlgren, N.; et al. Safety of intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in patients receiving antiplatelet therapy at stroke onset. Stroke 2010, 41, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broeg-Morvay, A.; Mordasini, P.; Slezak, A.; Liesirova, K.; Meisterernst, J.; Schroth, G.; Arnold, M.; Jung, S.; Mattle, H.P.; Gralla, J.; et al. Does Antiplatelet Therapy during Bridging Thrombolysis Increase Rates of Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Stroke Patients? PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Fan, X.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, C.; Wang, X.-S.; Lo, E.H.; Sun, X.; Wang, X. Low dose tPA plus annexin A2 combination attenuates tPA delayed treatment-associated hemorrhage and improves recovery in rat embolic focal stroke. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 602, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Yu, Z.; Liao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Mandeville, E.; Guo, S.; Lo, E.H.; Wang, X. Effects of tissue plasminogen activator and annexin A2 combination therapy on long-term neurological outcomes of rat focal embolic stroke. Stroke 2014, 45, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.G.; Liu, X.; Hozeska, A.; Stagliano, N.; Riordan, W.; Lu, M.; Chopp, M. Treatment of embolic stroke in rats with bortezomib and recombinant human tissue plasminogen activator. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 95, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.G.; Buller, B.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Morris, D.; Chopp, M. Combination treatment with VELCADE and low-dose tissue plasminogen activator provides potent neuroprotection in aged rats after embolic focal ischemia. Stroke 2010, 41, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lizarrondo, S.M.; Gakuba, C.; Herbig, B.A.; Repessé, Y.; Ali, C.; Denis, C.V.; Lenting, P.J.; Touzé, E.; Diamond, S.L.; Vivien, D.; et al. Potent Thrombolytic Effect of N-Acetylcysteine on Arterial Thrombi. Circulation 2017, 136, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuaib, A.; Butcher, K.; Mohammad, A.A.; Saqqur, M.; Liebeskind, D.S. Collateral blood vessels in acute ischaemic stroke: A potential therapeutic target. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, H.; Bivard, A.; Lin, L.; Spratt, N.J.; Miteff, F.; Parsons, M.W.; Levi, C.R. Relationship between Collateral Status, Contrast Transit, and Contrast Density in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, L.C.S.; Yoo, A.J.; Chaudhry, Z.A.; Payabvash, S.; Kemmling, A.; Schaefer, P.W.; Hirsch, J.A.; Furie, K.L.; González, R.G.; Nogueira, R.G.; et al. Malignant CTA collateral profile is highly specific for large admission DWI infarct core and poor outcome in acute stroke. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, M.B.; Lev, M.H.; Ay, H.; Singhal, A.B.; Greer, D.M.; Smith, W.S.; Harris, G.J.; Halpern, E.; Kemmling, A.; Koroshetz, W.J.; et al. Collateral vessels on CT angiography predict outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 3001–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frölich, A.M.J.; Wolff, S.L.; Psychogios, M.N.; Klotz, E.; Schramm, R.; Wasser, K.; Knauth, M.; Schramm, P. Time-resolved assessment of collateral flow using 4D CT angiography in large-vessel occlusion stroke. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, O.Y.; Saver, J.L.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, G.-M.; Chung, C.-S.; Ovbiagele, B.; Lee, K.H.; Liebeskind, D.S. Collateral flow predicts response to endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.P.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, J.-W.; Cha, J.; Kim, G.-M.; Chung, C.-S.; Lee, K.H.; Bang, O.Y. Impact of Slow Blood Filling via Collaterals on Infarct Growth: Comparison of Mismatch and Collateral Status. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, M.D. The cerebral collateral circulation: Relevance to pathophysiology and treatment of stroke. Neuropharmacology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, O.Y.; Saver, J.L.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, G.-M.; Chung, C.-S.; Ovbiagele, B.; Lee, K.H.; Liebeskind, D.S. UCLA-Samsung Stroke Collaborators Collateral flow averts hemorrhagic transformation after endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 2235–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoforidis, G.A.; Karakasis, C.; Mohammad, Y.; Caragine, L.P.; Yang, M.; Slivka, A.P. Predictors of hemorrhage following intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: The role of pial collateral formation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Lai, Y.; Han, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, M.; Parsons, M.W.; Wang, S.; Lou, M. The velocity of collateral filling predicts recanalization in acute ischemic stroke after intravenous thrombolysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomares, S.M.; Cipolla, M.J. Vascular Protection Following Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion. J. Neurol. Neurophysiol. 2011, 2011, S1-004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolla, M.J.; Bullinger, L.V. Reactivity of brain parenchymal arterioles after ischemia and reperfusion. Microcirculation 2008, 15, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolla, M.J.; McCall, A.L.; Lessov, N.; Porter, J.M. Reperfusion decreases myogenic reactivity and alters middle cerebral artery function after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 1997, 28, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebeskind, D.S. Collateral lessons from recent acute ischemic stroke trials. Neurol. Res. 2014, 36, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuccione, E.; Padovano, G.; Versace, A.; Ferrarese, C.; Beretta, S. Cerebral collateral circulation in experimental ischemic stroke. Exp. Transl. Stroke Med. 2016, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Akamatsu, Y.; Lee, C.C.; Stetler, R.A.; Lawton, M.T.; Yang, G.-Y. Vascular remodeling after ischemic stroke: Mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 115, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.K.; Nishimura, M.; Jones, P.B.; Ay, H.; Boas, D.A.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Ayata, C. Mild induced hypertension improves blood flow and oxygen metabolism in transient focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2008, 39, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smrcka, M.; Ogilvy, C.S.; Crow, R.J.; Maynard, K.I.; Kawamata, T.; Ames, A. Induced hypertension improves regional blood flow and protects against infarction during focal ischemia: Time course of changes in blood flow measured by laser Doppler imaging. Neurosurgery 1998, 42, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geeganage, C.; Tracy, M.; England, T.; Sare, G.; Moulin, T.; Woimant, F.; Christensen, H.; De Deyn, P.P.; Leys, D.; O’Neill, D.; et al. Relationship between baseline blood pressure parameters (including mean pressure, pulse pressure, and variability) and early outcome after stroke: Data from the Tinzaparin in Acute Ischaemic Stroke Trial (TAIST). Stroke 2011, 42, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, M.; Liebeskind, D.S. Blood Pressure in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 12, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFazio, R.A.; Zhao, W.; Deng, X.; Obenaus, A.; Ginsberg, M.D. Albumin therapy enhances collateral perfusion after laser-induced middle cerebral artery branch occlusion: A laser speckle contrast flow study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.H.; Yeatts, S.D.; Hill, M.D.; Moy, C.S.; Ginsberg, M.D.; Palesch, Y.Y. ALIAS (Albumin in Acute Ischemic Stroke) Trials: Analysis of the Combined Data From Parts 1 and 2. Stroke 2016, 47, 2355–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrigan, M.R.; Ennis, S.R.; Sullivan, S.E.; Keep, R.F. Effects of intraventricular infusion of vascular endothelial growth factor on cerebral blood flow, edema, and infarct volume. Acta Neurochir. (Wien.) 2003, 145, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovbiagele, B.; Saver, J.L.; Starkman, S.; Kim, D.; Ali, L.K.; Jahan, R.; Duckwiler, G.R.; Viñuela, F.; Pineda, S.; Liebeskind, D.S. Statin enhancement of collateralization in acute stroke. Neurology 2007, 68, 2129–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaner, J.; Bustamante, A.; García-Matas, S.; Martínez-Zabaleta, M.; Jiménez, C.; de la Torre, J.; Rubio, F.R.; Segura, T.; Masjuán, J.; Cánovas, D.; et al. Combination of Thrombolysis and Statins in Acute Stroke Is Safe: Results of the STARS Randomized Trial (Stroke Treatment with Acute Reperfusion and Simvastatin). Stroke 2016, 47, 2870–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotta, J.C.; Welch, K.M.; Fagan, S.C.; Lu, M.; Frankel, M.R.; Brott, T.; Levine, S.R.; Lyden, P.D. Clinical deterioration following improvement in the NINDS rt-PA Stroke Trial. Stroke 2001, 32, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.J.; Monsein, L.H.; Ulatowski, J.; Mirski, M.; Williams, M.; Hanley, D.F. Intraarterial thrombolysis in vertebrobasilar occlusion. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1996, 17, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, R. Dynamics of coronary thrombolysis and reocclusion. Clin. Cardiol. 1997, 20, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Siddiqui, A.M.; Kim, S.H.; Hanel, R.A.; Xavier, A.R.; Kirmani, J.F.; Suri, M.F.K.; Boulos, A.S.; Hopkins, L.N. Reocclusion of recanalized arteries during intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ames, A.; Wright, R.L.; Kowada, M.; Thurston, J.M.; Majno, G. Cerebral ischemia. II. The no-reflow phenomenon. Am. J. Pathol. 1968, 52, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khatri, P.; Neff, J.; Broderick, J.P.; Khoury, J.C.; Carrozzella, J.; Tomsick, T. Revascularization end points in stroke interventional trials: Recanalization versus reperfusion in IMS-I. Stroke 2005, 36, 2400–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nour, M.; Scalzo, F.; Liebeskind, D.S. Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Stroke. Interv. Neurol. 2013, 1, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalkara, T.; Arsava, E.M. Can restoring incomplete microcirculatory reperfusion improve stroke outcome after thrombolysis? J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, E.; Yoneda, Y.; Tabuchi, M.; Yoshida, T.; Ohkawa, S.; Ohsumi, Y.; Kitano, K.; Tsutsumi, A.; Yamadori, A. Intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in acute carotid artery territory stroke. Neurology 1992, 42, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Amki, M.; Lerouet, D.; Coqueran, B.; Curis, E.; Orset, C.; Vivien, D.; Plotkine, M.; Marchand-Leroux, C.; Margaill, I. Experimental modeling of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator effects after ischemic stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, M.J.; Lawrence, C.B. The blood–brain barrier after stroke: Structural studies and the role of transcytotic vesicles. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, U.; Hakamata, Y.; Kawakami, E.; Oyanagi, K. Temporary focal cerebral ischemia results in swollen astrocytic end-feet that compress microvessels and lead to focal cortical infarction. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M.; Goussev, A.; Lu, D.; Morris, D.; Tsang, W.; Powers, C.; Ho, K.L. Cerebral microvascular obstruction by fibrin is associated with upregulation of PAI-1 acutely after onset of focal embolic ischemia in rats. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10898–10907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janjua, N.; Alkawi, A.; Suri, M.F.K.; Qureshi, A.I. Impact of arterial reocclusion and distal fragmentation during thrombolysis among patients with acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heye, N.; Cervos-Navarro, J. Microthromboemboli in acute infarcts: Analysis of 40 autopsy cases. Stroke 1996, 27, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvinsson, L.I.H.; Povlsen, G.K. Vascular plasticity in cerebrovascular disorders. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 1554–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, W.I. Selective impairment of response to acetylcholine after ischemia/reperfusion in mice. Stroke 1997, 28, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, W.I. A review of vasomotor responses of arterioles on the surface of the mouse brain: The necessary prelude to studies using genetically manipulated mice. Microcirculation 1998, 5, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, W.I.; Wormley, B. Selective depression of endothelium-dependent dilations during cerebral ischemia. Stroke 1995, 26, 1877–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayhan, W.G.; Amundsen, S.M.; Faraci, F.M.; Heistad, D.D. Responses of cerebral arteries after ischemia and reperfusion in cats. Am. J. Physiol. 1988, 255, H879–H884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salinas, P.; Jimenez-Valero, S.; Moreno, R.; Sanchez-Recalde, A.; Galeote, G.; Calvo, L.; Ruiz-Garcia, J.; Carrizo, S.; Trucco, G.; Lopez-Sendon, J. Update in Pharmacological Management of Coronary No-Reflow Phenomenon. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 10, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Choudhri, T.F.; Winfree, C.J.; McTaggart, R.A.; Kiss, S.; Mocco, J.; Kim, L.J.; Protopsaltis, T.S.; Zhang, Y.; Pinsky, D.J.; et al. Postischemic cerebrovascular E-selectin expression mediates tissue injury in murine stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 3047–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudin, A.; Yemisci, M.; Eroglu, H.; Lepetre-Mouelhi, S.; Turkoglu, O.F.; Dönmez-Demir, B.; Caban, S.; Sargon, M.F.; Garcia-Argote, S.; Pieters, G.; et al. Squalenoyl adenosine nanoparticles provide neuroprotection after stroke and spinal cord injury. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, E.S.; Winfree, C.J.; Prestigiacomo, C.J.; Kim, S.C.; Choudhri, T.F.; Hoh, B.L.; Naka, Y.; Solomon, R.A.; Pinsky, D.J. Exacerbation of cerebral injury in mice that express the P-selectin gene: Identification of P-selectin blockade as a new target for the treatment of stroke. Circ. Res. 1997, 81, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, E.S.; Winfree, C.J.; Springer, T.A.; Naka, Y.; Liao, H.; Yan, S.D.; Stern, D.M.; Solomon, R.A.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; Pinsky, D.J. Cerebral protection in homozygous null ICAM-1 mice after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Role of neutrophil adhesion in the pathogenesis of stroke. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hase, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Kitamura, A.; Nakabayashi, H.; Ito, H.; Maki, T.; Washida, K.; Takahashi, R.; Ihara, M. Cilostazol, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, prevents no-reflow and hemorrhage in mice with focal cerebral ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collino, M.; Patel, N.S.A.; Thiemermann, C. Review: PPARs as new therapeutic targets for the treatment of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 2, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, C.; Zuo, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.H.; Ruan, H.; Feng, H. Hemoglobin induced NO/cGMP suppression Deteriorate Microcirculation via Pericyte Phenotype Transformation after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.; Rom, S.; Ramirez, S.H.; Persidsky, Y. Emerging roles of pericytes in the regulation of the neurovascular unit in health and disease. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Minematsu, K.; Miyashita, T.; Sawada, T.; Sadoshima, S.; Fujishima, M.; Omae, T. Hemorrhagic transformation in cerebral embolism. Stroke 1989, 20, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.A.; Willey, J.Z.; Keyrouz, S.; Butera, J.; McTaggart, R.A.; Cutting, S.; Silver, B.; Thompson, B.; Furie, K.L.; Yaghi, S. Therapies for Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2017, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacke, W.; Donnan, G.; Fieschi, C.; Kaste, M.; von Kummer, R.; Broderick, J.P.; Brott, T.; Frankel, M.; Grotta, J.C.; Haley, E.C., Jr.; et al. Association of outcome with early stroke treatment: Pooled analysis of ATLANTIS, ECASS, and NINDS rt-PA stroke trials. Lancet 2004, 363, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, D.M.; Hinchey, J.; Price, L.L.; Levine, S.R.; Selker, H.P. In acute ischemic stroke, are asymptomatic intracranial hemorrhages clinically innocuous? Stroke 2004, 35, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Kummer, R. Brain hemorrhage after thrombolysis: Good or bad? Stroke 2002, 33, 1446–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Fieschi, C.; Toni, D.; Lesaffre, E.; von Kummer, R.; Boysen, G.; Bluhmki, E.; Höxter, G.; Mahagne, M.H. Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 1995, 274, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Fieschi, C.; von Kummer, R.; Davalos, A.; Meier, D.; Larrue, V.; Bluhmki, E.; Davis, S.; Donnan, G.; et al. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet 1998, 352, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Liao, X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, T.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y. TIMS-CHINA investigators Thrombolytic-Related Asymptomatic Hemorrhagic Transformation Does Not Deteriorate Clinical Outcome: Data from TIMS in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kablau, M.; Kreisel, S.H.; Sauer, T.; Binder, J.; Szabo, K.; Hennerici, M.G.; Kern, R. Predictors and early outcome of hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 32, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontos, C.D.; Wei, E.P.; Williams, J.I.; Kontos, H.A.; Povlishock, J.T. Cytochemical detection of superoxide in cerebral inflammation and ischemia in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263, H1234–H1242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gourdin, M.J.; Bree, B.; De Kock, M. The impact of ischaemia-reperfusion on the blood vessel. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2009, 26, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontos, H.A. Oxygen Radicals in Cerebral Ischemia: The 2001 Willis Lecture. Stroke 2001, 32, 2712–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jickling, G.C.; Liu, D.; Stamova, B.; Ander, B.P.; Zhan, X.; Lu, A.; Sharp, F.R. Hemorrhagic transformation after ischemic stroke in animals and humans. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merali, Z.; Huang, K.; Mikulis, D.; Silver, F.; Kassner, A. Evolution of blood-brain-barrier permeability after acute ischemic stroke. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nagai, N.; Umemura, K. A Review of the Mechanisms of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability by Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator Treatment for Cerebral Ischemia. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J. Hemorrhagic Transformation after Tissue Plasminogen Activator Reperfusion Therapy for Ischemic Stroke: Mechanisms, Models, and Biomarkers. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.A.; Shuaib, A.; Todd, K.G. Matrix metalloproteinase activation and blood-brain barrier breakdown following thrombolysis. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 200, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nagai, N.; Umemura, K. Novel situations of endothelial injury in stroke--mechanisms of stroke and strategy of drug development: Intracranial bleeding associated with the treatment of ischemic stroke: Thrombolytic treatment of ischemia-affected endothelial cells with tissue-type plasminogen activator. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 116, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lee, S.-R.; Arai, K.; Lee, S.-R.; Tsuji, K.; Rebeck, G.W.; Lo, E.H. Lipoprotein receptor-mediated induction of matrix metalloproteinase by tissue plasminogen activator. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, M.; Furie, K.L.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Lee, H.; Barron, M.; Lederer, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Sorensen, A.G.; Lo, E.H.; et al. Association between tPA therapy and raised early matrix metalloproteinase-9 in acute stroke. Neurology 2006, 66, 1550–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaner, J.; Molina, C.A.; Monasterio, J.; Abilleira, S.; Arenillas, J.F.; Ribó, M.; Quintana, M.; Alvarez-Sabín, J. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 pretreatment level predicts intracranial hemorrhagic complications after thrombolysis in human stroke. Circulation 2003, 107, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadrado, E.; Ortega, L.; Hernández-Guillamon, M.; Penalba, A.; Fernández-Cadenas, I.; Rosell, A.; Montaner, J. Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) promotes neutrophil degranulation and MMP-9 release. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yepes, M.; Sandkvist, M.; Moore, E.G.; Bugge, T.H.; Strickland, D.K.; Lawrence, D.A. Tissue-type plasminogen activator induces opening of the blood-brain barrier via the LDL receptor-related protein. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polavarapu, R.; Gongora, M.C.; Yi, H.; Ranganthan, S.; Lawrence, D.A.; Strickland, D.; Yepes, M. Tissue-type plasminogen activator-mediated shedding of astrocytic low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein increases the permeability of the neurovascular unit. Blood 2007, 109, 3270–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanos, E.; Planas, A.M.; Amaro, S.; Chamorro, A. Uric acid reduces brain damage and improves the benefits of rt-PA in a rat model of thromboembolic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuaib, A.; Lees, K.R.; Lyden, P.; Grotta, J.; Davalos, A.; Davis, S.M.; Diener, H.-C.; Ashwood, T.; Wasiewski, W.W.; Emeribe, U. NXY-059 for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Kamiya, T.; Deguchi, K.; Inaba, T.; Zhang, H.; Shang, J.; Miyazaki, K.; Ohtsuka, A.; Katayama, Y.; Abe, K. Dissociation and protection of the neurovascular unit after thrombolysis and reperfusion in ischemic rat brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapchak, P.A. A critical assessment of edaravone acute ischemic stroke efficacy trials: Is edaravone an effective neuroprotective therapy? Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapchak, P.A.; Chapman, D.F.; Zivin, J.A. Metalloproteinase inhibition reduces thrombolytic (tissue plasminogen activator)-induced hemorrhage after thromboembolic stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 3034–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, Y.; Rosell, A.; Scannevin, R.H.; Rhodes, K.J.; Wang, X.; Lo, E.H. Extension of the thrombolytic time window with minocycline in experimental stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 3372–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, M.; Kawasaki, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Ishizuka, F.; Mishiro, K.; Egashira, Y.; Ikegaki, I.; Tsuruma, K.; Shimazawa, M.; Yoshimura, S.; et al. A Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitor, fasudil, prevents matrix metalloproteinase-9-related hemorrhagic transformation in mice treated with tissue plasminogen activator. Neuroscience 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, F.; Qin, T.; Castillo, J.; Seo, J.H.; Arai, K.; Lo, E.H.; Waeber, C. Fingolimod Reduces Hemorrhagic Transformation Associated With Delayed Tissue Plasminogen Activator Treatment in a Mouse Thromboembolic Model. Stroke 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, M.; Beray-Berthat, V.; Coqueran, B.; Plotkine, M.; Marchand-Leroux, C.; Margaill, I. Combined therapy with PJ34, a poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase inhibitor, reduces tissue plasminogen activator-induced hemorrhagic transformations in cerebral ischemia in mice. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, F.; Beray-Berthat, V.; Coqueran, B.; Lesbats, C.; Kuntz, M.; Palmier, B.; Garraud, M.; Bedfert, C.; Slane, N.; Bérézowski, V.; et al. Prevention of rt-PA induced blood-brain barrier component degradation by the poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase inhibitor PJ34 after ischemic stroke in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 248, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, M.; Furuichi, Y.; Noto, T.; Matsuoka, N.; Mutoh, S.; Yoneda, Y. Tacrolimus (FK506) suppresses rt-PA-induced hemorrhagic transformation in a rat thrombotic ischemia stroke model. Brain Res. 2009, 1254, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, M.; Igarashi, H.; Kawamura, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kakita, A.; Takahashi, H.; Nakada, T.; Nishizawa, M.; Shimohata, T. Inhibition of VEGF signaling pathway attenuates hemorrhage after tPA treatment. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, M.; Takahashi, T.; Nishizawa, M.; Shimohata, T. Therapeutic Strategies to Attenuate Hemorrhagic Transformation after Tissue Plasminogen Activator Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Awano, H.; Matsuda, H.; Tanahashi, N. Edaravone with and without. 6 Mg/Kg Alteplase within 4.5 Hours after Ischemic Stroke: A Prospective Cohort Study (PROTECT4.5). J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimohata, T.; Kanazawa, M.; Kawamura, K.; Takahashi, T.; Nishizawa, M. Therapeutic strategies to attenuate hemorrhagic transformation after tissue plasminogen activator treatment for acute ischemic stroke. Neurol. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 1, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.; Nardai, S. Cerebral ischemia/repefusion injury: From bench space to bedside. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 134, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhu, P.; Fujino, M.; Zhuang, J.; Guo, H.; Sheikh, I.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.-K. Oxidative Stress in Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.D.; Al-Khoury, L.; Zivin, J.A. Neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: Two decades of success and failure. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saver, J.L.; Albers, G.W.; Dunn, B.; Johnston, K.C.; Fisher, M. Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable (STAIR) recommendations for extended window acute stroke therapy trials. Stroke 2009, 40, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M.; Feuerstein, G.; Howells, D.W.; Hurn, P.D.; Kent, T.A.; Savitz, S.I.; Lo, E.H. Update of the Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable Preclinical Recommendations. Stroke 2009, 40, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Therapy | Recanalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Successful | Failed | ||||
| References | Complete | Partial (2b) | Partial | No Recanalization | |
| Thrombolysis | Christou et al., [27] | 30% | 40% | 30% | |
| Alexandrov et al., [28] | 30% | 48% | 22% | ||
| Rubiera et al., [14] | 22% | 37% | 41% | ||
| Saqqur et al., [29] | 27% | 23% | 37% | ||
| Endovascular Thrombectomy | MERCI [31] | 24% | 42% | 33% | |
| Penumbra [18] | 18% | 54% | 28% | ||
| TREVO [20] | 14% | 78% | 8% | ||
| MR CLEAN [32] | 24% | 35% | 27% | 14% | |
| EXTEND-IA [30] | 48% | 38% | 10% | 3% | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Amki, M.; Wegener, S. Improving Cerebral Blood Flow after Arterial Recanalization: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122669
El Amki M, Wegener S. Improving Cerebral Blood Flow after Arterial Recanalization: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122669
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Amki, Mohamad, and Susanne Wegener. 2017. "Improving Cerebral Blood Flow after Arterial Recanalization: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Stroke" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122669
APA StyleEl Amki, M., & Wegener, S. (2017). Improving Cerebral Blood Flow after Arterial Recanalization: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122669