Adverse Intrauterine Environment and Cardiac miRNA Expression
Abstract
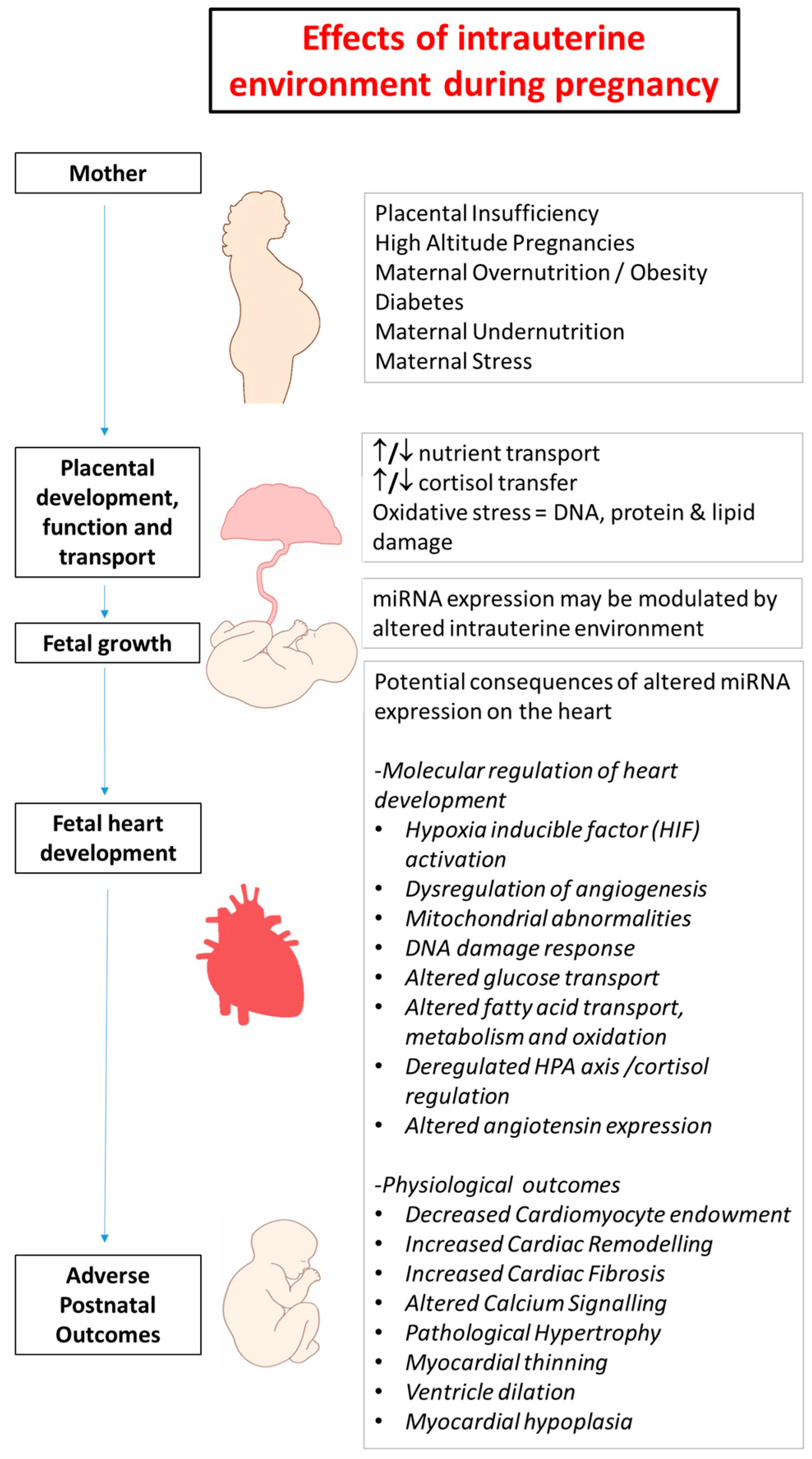
:1. Introduction
2. Developmental Programming in Early Life and Heart Disease
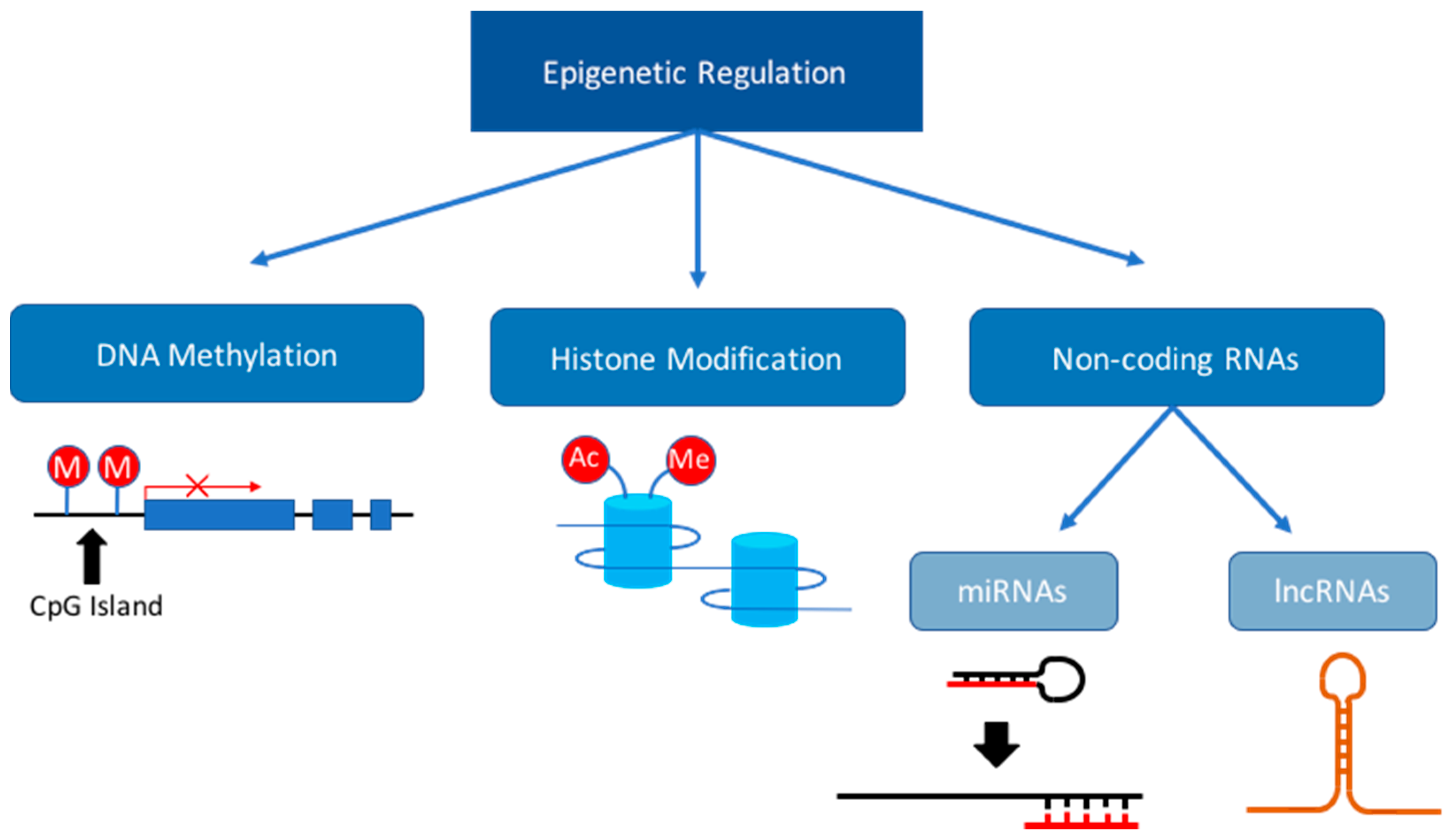
3. Dysregulation of the Epigenome during Fetal Development
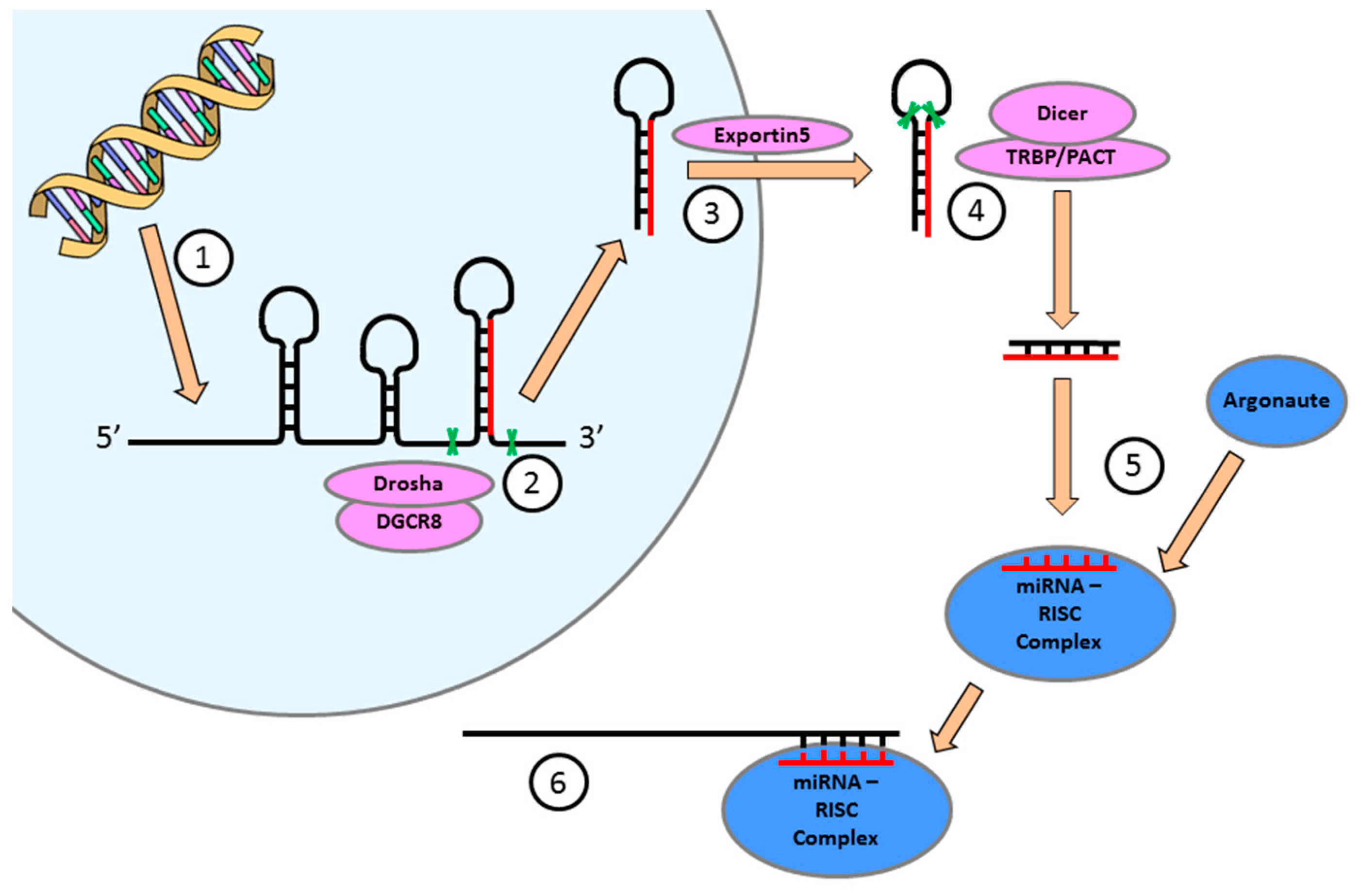
4. miRNA Expression is Essential for the Regulation of Cellular Function in the Heart
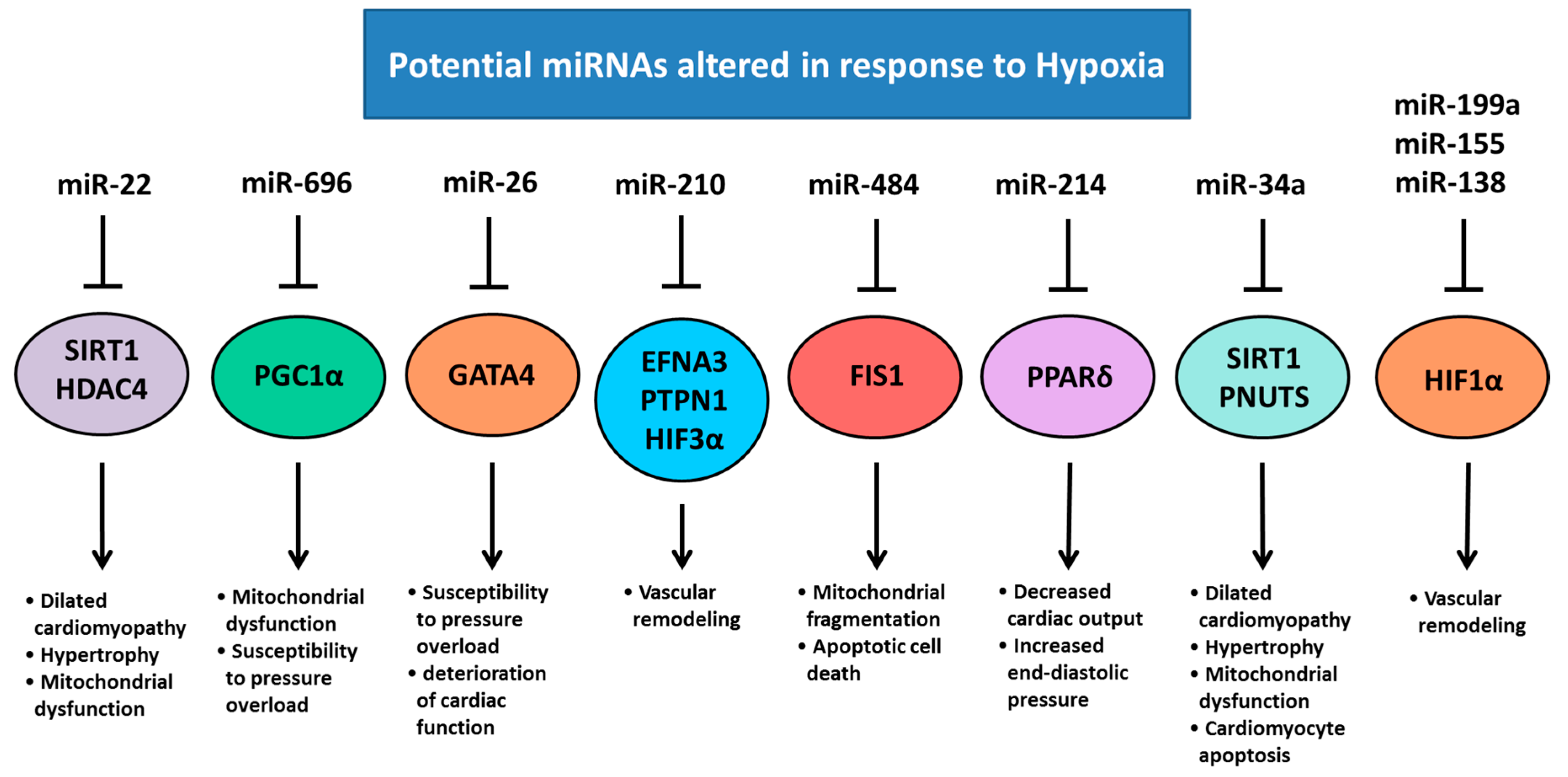
5. Chronic Hypoxemia Alters Heart Development and Changes the Expression of Cardiac miRNAs
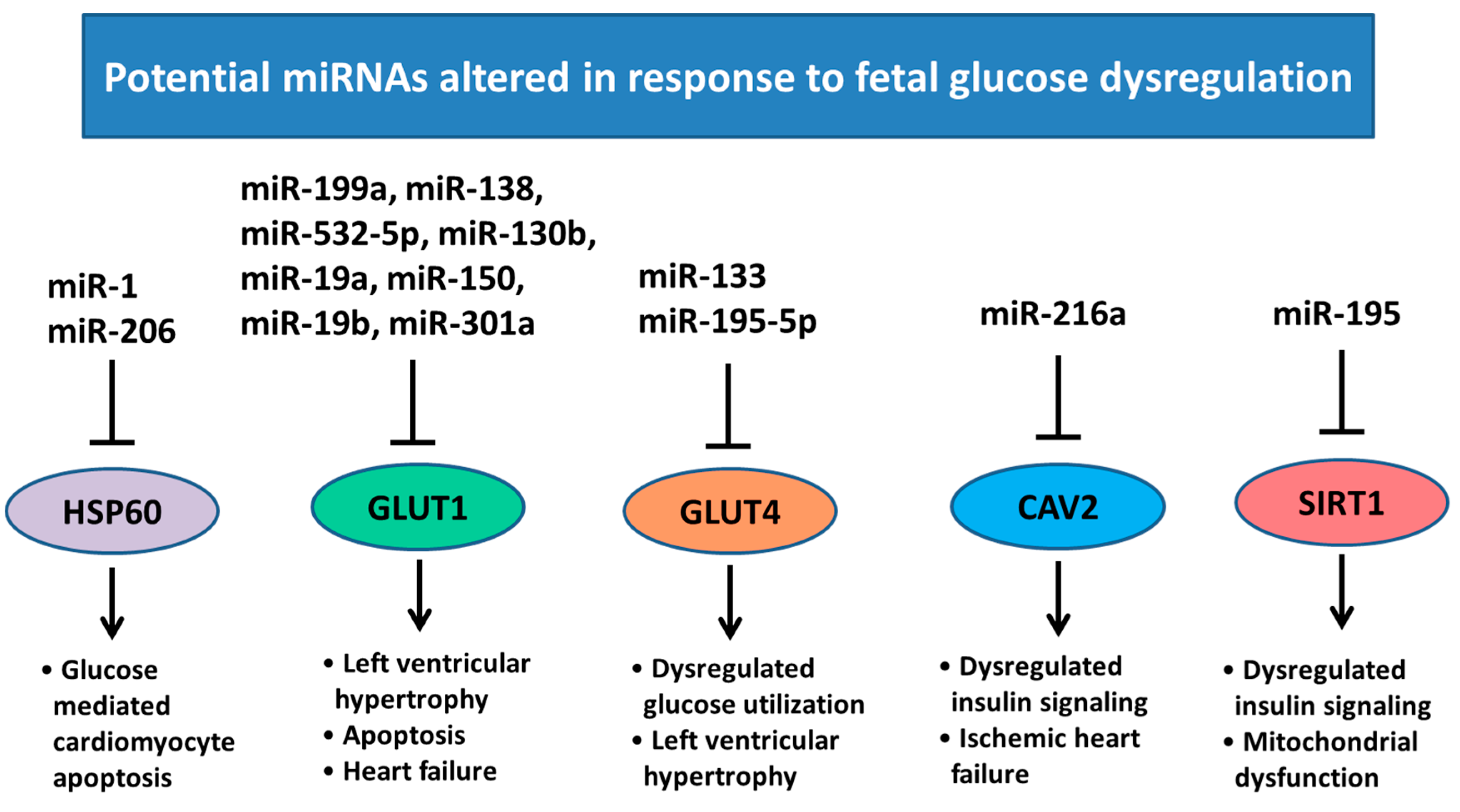
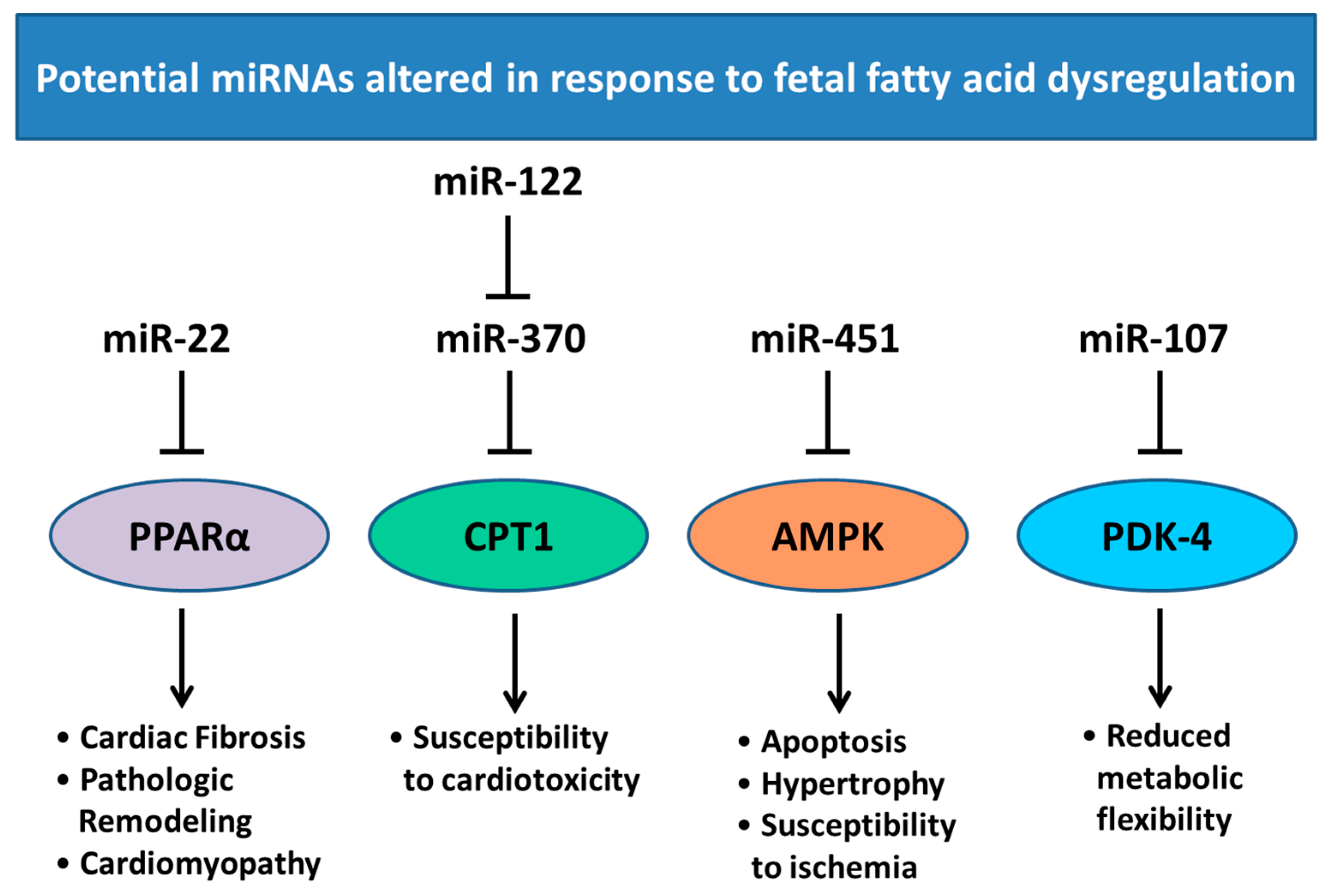
6. Changes in Heart Development and miRNA Expression as a Result of Altered Maternal Nutrition or Diabetes
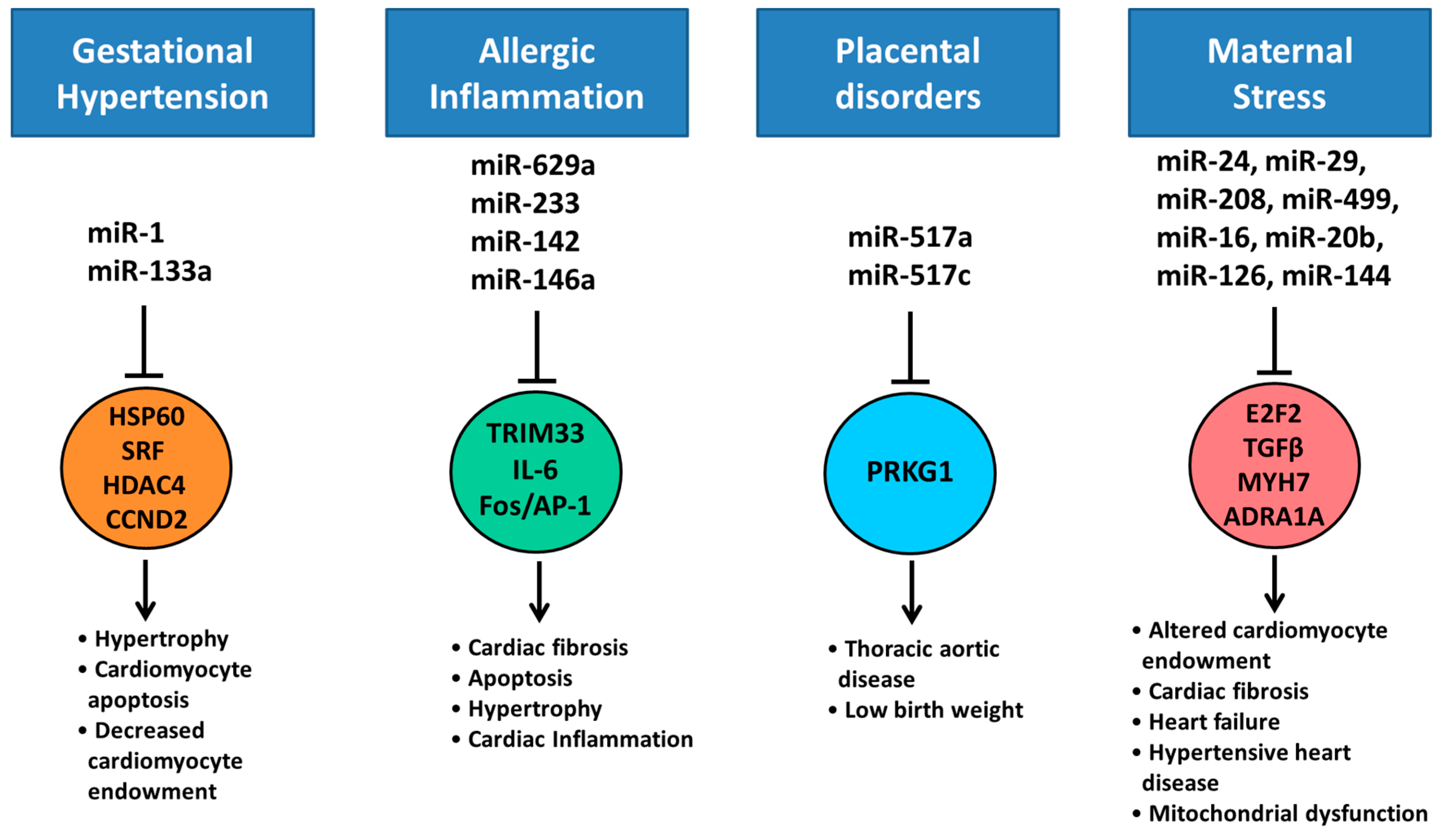
7. Altered Cardiac miRNA Expression in Response to Maternal Disease and Stress
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McMillen, I.C.; Robinson, J.S. Developmental origins of the metabolic syndrome: Prediction, plasticity, and programming. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 571–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J.; Osmond, C.; Golding, J.; Kuh, D.; Wadsworth, M.E. Growth in utero, blood pressure in childhood and adult life, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. BMJ 1989, 298, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master, J.S.; Zimanyi, M.A.; Yin, K.V.; Moritz, K.M.; Gallo, L.A.; Tran, M.; Wlodek, M.E.; Black, M.J. Transgenerational left ventricular hypertrophy and hypertension in offspring after uteroplacental insufficiency in male rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 41, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaCoursiere, D.Y.; Bloebaum, L.; Duncan, J.D.; Varner, M.W. Population-based trends and correlates of maternal overweight and obesity, Utah 1991–2001. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 192, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Australia’s Mothers and Babies 2014—In Brief; Perinatal Statistics Series No. 32; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2016; Volume 32 (PER 72).
- Alwan, A.D.; Galea, G.; Stuckler, D. Development at risk: Addressing noncommunicable diseases at the United Nations high-level meeting. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 546–546A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease—Australian Facts: Risk Factors; Cardiovascular, Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease Series No. 4; Australian Institute of Health and Welfare: Canberra, Australian, 2015.
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stampfer, M.J.; Hu, F.B.; Manson, J.E.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C. Primary prevention of coronary heart disease in women through diet and lifestyle. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, V.L.; Go, A.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Borden, W.B.; Bravata, D.M.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S.; et al. Executive summary: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2012 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2012, 125, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J. The developmental origins of adult disease. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, S588–S595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A. Programming by early nutrition in man. Ciba Found. Symp. 1991, 156, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaenisch, R.; Bird, A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, F.; Herbstman, J. Prenatal environmental exposures, epigenetics, and disease. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenland, S.; Senn, S.; Rothman, K.; Carlin, J.; Poole, C.; Goodman, S.; Altman, D. Statistical tests, P values, confidence intervals, and power: A guide to misinterpretations. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirtle, R.L.; Skinner, M.K. Environmental epigenomics and disease susceptibility. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reamon-Buettner, S.M.; Borlak, J. A new paradigm in toxicology and teratology: Altering gene activity in the absence of DNA sequence variation. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, F.; Tsuchiya, S.; Meltzer, S.J.; Shimizu, K. MicroRNAs and epigenetics. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flecknoe, S.; Wallace, M.; Cock, M.; Harding, R.; Hooper, S. Changes in alveolar epithelial cell proportions during fetal and postnatal development in sheep. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L664–L670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rooij, E. The art of microRNA research. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, V.N.; Han, J.; Siomi, M.C. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 10, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porrello, E.R. microRNAs in cardiac development and regeneration. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2013, 125, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, E.; Kim, S.Y.; Carmell, M.A.; Murchison, E.P.; Alcorn, H.; Li, M.Z.; Mills, A.A.; Elledge, S.J.; Anderson, K.V.; Hannon, G.J. Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienholds, E.; Koudijs, M.J.; van Eeden, F.J.; Cuppen, E.; Plasterk, R.H. The microRNA-producing enzyme Dicer1 is essential for zebrafish development. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Tabin, C.J. miRNA-processing enzyme Dicer is necessary for cardiac outflow tract alignment and chamber septation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ransom, J.F.; Li, A.; Vedantham, V.; von Drehle, M.; Muth, A.N.; Tsuchihashi, T.; McManus, M.T.; Schwartz, R.J.; Srivastava, D. Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell 2007, 129, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.F.; Murchison, E.P.; Tang, R.; Callis, T.E.; Tatsuguchi, M.; Deng, Z.; Rojas, M.; Hammond, S.M.; Schneider, M.D.; Selzman, C.H.; et al. Targeted deletion of Dicer in the heart leads to dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2111–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa Martins, P.A.; Bourajjaj, M.; Gladka, M.; Kortland, M.; van Oort, R.J.; Pinto, Y.M.; Molkentin, J.D.; De Windt, L.J. Conditional dicer gene deletion in the postnatal myocardium provokes spontaneous cardiac remodeling. Circulation 2008, 118, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; An, X.; Niu, L. Role of microRNAs in cardiac development and disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latronico, M.V.; Catalucci, D.; Condorelli, G. MicroRNA and cardiac pathologies. Physiol. Genom. 2008, 34, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.E., Jr.; Kibiryeva, N.; Zhou, X.G.; Marshall, J.A.; Lofland, G.K.; Artman, M.; Chen, J.; Bittel, D.C. Noncoding RNA expression in myocardium from infants with tetralogy of Fallot. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2012, 5, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.B.; Han, S.P.; Bai, Y.F.; Zhu, C.; Pan, Y.; Guo, X.R. microRNA expression profiling in fetal single ventricle malformation identified by deep sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, A.; Zhang, L. Hypoxia and Fetal Heart Development. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.G.; Niermeyer, S.; Zamudio, S. Human adaptation to high altitude: Regional and life-cycle perspectives. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1998, 107 (Suppl. S27), 25–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio, S. The placenta at high altitude. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2003, 4, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kametas, N.A.; McAuliffe, F.; Krampl, E.; Chambers, J.; Nicolaides, K.H. Maternal cardiac function during pregnancy at high altitude. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2004, 111, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, G.M.; Moore, L.G. The effect of high altitude and other risk factors on birthweight: Independent or interactive effects? Am. J. Public Health 1997, 87, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.G. Fetal growth restriction and maternal oxygen transport during high altitude pregnancy. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2003, 4, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delisle, H. Programming of Chronic Disease by Impaired Fetal Nutrition: Evidence and Implications for Policy and Intervention Strategies; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; pp. 1–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ream, M.; Ray, A.M.; Chandra, R.; Chikaraishi, D.M. Early fetal hypoxia leads to growth restriction and myocardial thinning. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R583–R595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Lucitti, J.L.; Nordman, C.; Tinney, J.P.; Tobita, K.; Keller, B.B. Impact of hypoxia on early chick embryo growth and cardiovascular function. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 59, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.; Yu, A.Y.; Jiang, B.H.; Davis, L.; Kimberly, D.; Hohimer, A.R.; Semenza, G.L. Cardiac hypertrophy in chronically anemic fetal sheep: Increased vascularization is associated with increased myocardial expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 178, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Xiao, Y.; Li, G.; Casiano, C.A.; Zhang, L. Effect of maternal chronic hypoxic exposure during gestation on apoptosis in fetal rat heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 285, H983–H990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubb, K.J.; Cock, M.L.; Black, M.J.; Dodic, M.; Boon, W.M.; Parkington, H.C.; Harding, R.; Tare, M. Intrauterine growth restriction delays cardiomyocyte maturation and alters coronary artery function in the fetal sheep. J. Physiol. 2007, 578 Pt 3, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louey, S.; Jonker, S.S.; Giraud, G.D.; Thornburg, K.L. Placental insufficiency decreases cell cycle activity and terminal maturation in fetal sheep cardiomyocytes. J. Physiol. 2007, 580 Pt 2, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.L.; Botting, K.J.; Dyer, J.L.; Williams, S.J.; Thornburg, K.L.; McMillen, I.C. Restriction of placental function alters heart development in the sheep fetus. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R306–R313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botting, K.J.; McMillen, I.C.; Forbes, H.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Morrison, J.L. Chronic hypoxemia in late gestation decreases cardiomyocyte number but does not change expression of hypoxia-responsive genes. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, M.J.; Siebel, A.L.; Gezmish, O.; Moritz, K.M.; Wlodek, M.E. Normal lactational environment restores cardiomyocyte number after uteroplacental insufficiency: Implications for the preterm neonate. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 302, R1101–R1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Bae, S.; Zhang, L. Effect of prenatal hypoxia on heat stress-mediated cardioprotection in adult rat heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 286, H1712–H1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Xiao, Y.; Estrella, J.L.; Ducsay, C.A.; Gilbert, R.D.; Zhang, L. Effect of fetal hypoxia on heart susceptibility to ischemia and reperfusion injury in the adult rat. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2003, 10, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.J.; Chen, M.; Xue, Q.; Xiao, D.L.; Zhang, L. Chronic prenatal hypoxia induces epigenetic programming of PKC{epsilon} gene repression in rat hearts. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Zhang, L. Prenatal hypoxia causes a sex-dependent increase in heart susceptibility to ischemia and reperfusion injury in adult male offspring: Role of protein kinase C epsilon. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1: Mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2000, 88, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Bruning, U.; Cerone, L.; Neufeld, Z.; Fitzpatrick, S.F.; Cheong, A.; Scholz, C.C.; Simpson, D.A.; Leonard, M.O.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Cummins, E.P.; et al. MicroRNA-155 Promotes Resolution of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α Activity during Prolonged Hypoxia. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 4087–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallamshetty, S.; Chan, S.Y.; Loscalzo, J. Hypoxia: A Master Regulator of MicroRNA Biogenesis and Activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 64, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Liu, P.; Jian, Z.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Xiao, Y. miR-138 protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced apoptosis via MLK3/JNK/c-jun pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Yang, Z.; Sayed, D.; He, M.; Gao, S.; Lin, L.; Yoon, S.; Abdellatif, M. GATA4 expression is primarily regulated via a miR-26b-dependent post-transcriptional mechanism during cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 93, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurha, P.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Wang, T.; Ramirez, M.O.; Drumond, A.L.; van Dongen, S.; Chen, Y.; Bartonicek, N.; Enright, A.J.; Lee, B.; et al. Targeted deletion of microRNA-22 promotes stress-induced cardiac dilation and contractile dysfunction. Circulation 2012, 125, 2751–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabuchi, T.; Satoh, M.; Itoh, T.; Nakamura, M. MicroRNA-34a regulates the longevity-associated protein SIRT1 in coronary artery disease: Effect of statins on SIRT1 and microRNA-34a expression. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2012, 123, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, R.A.; Iekushi, K.; Lechner, S.; Seeger, T.; Fischer, A.; Heydt, S.; Kaluza, D.; Treguer, K.; Carmona, G.; Bonauer, A.; et al. MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac ageing and function. Nature 2013, 495, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, B.C.; Gao, X.M.; Winbanks, C.E.; Boey, E.J.; Tham, Y.K.; Kiriazis, H.; Gregorevic, P.; Obad, S.; Kauppinen, S.; Du, X.J.; et al. Therapeutic inhibition of the miR-34 family attenuates pathological cardiac remodeling and improves heart function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17615–17620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Azzouzi, H.; Leptidis, S.; Dirkx, E.; Hoeks, J.; van Bree, B.; Brand, K.; McClellan, E.A.; Poels, E.; Sluimer, J.C.; van den Hoogenhof, M.M.; et al. The hypoxia-inducible microRNA cluster miR-199a approximately 214 targets myocardial PPARdelta and impairs mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Cell. Metab. 2013, 18, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, S.; He, M.; Sayed, D.; Vashistha, H.; Malhotra, A.; Sadoshima, J.; Vatner, D.E.; Vatner, S.F.; Abdellatif, M. Downregulation of miR-199a derepresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and Sirtuin 1 and recapitulates hypoxia preconditioning in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenz, T. Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and PGC-1alpha under cellular stress. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Ferlito, M.; Kent, O.A.; Fox-Talbot, K.; Wang, R.; Liu, D.; Raghavachari, N.; Yang, Y.; Wheelan, S.J.; Murphy, E.; et al. Nuclear miRNA regulates the mitochondrial genome in the heart. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Long, B.; Jiao, J.Q.; Wang, J.X.; Liu, J.P.; Li, Q.; Li, P.F. miR-484 regulates mitochondrial network through targeting Fis1. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Z.; Lv, Q.; Ye, W.; Wong, C.K.A.; Cai, G.; Gu, D.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.B.; et al. MiRNA-Directed Regulation of VEGF and Other Angiogenic Factors under Hypoxia. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donker, R.B.; Mouillet, J.F.; Chu, T.; Hubel, C.A.; Stolz, D.B.; Morelli, A.E.; Sadovsky, Y. The expression profile of C19MC microRNAs in primary human trophoblast cells and exosomes. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 18, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Y.; Mouillet, J.-F.; Coyne, C.B.; Sadovsky, Y. Placenta-specific microRNAs in exosomes—Good things come in nano-packages. Placenta 2014, 35, S69–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, G.; Mouillet, J.F.; Mishima, T.; Chu, T.; Sadovsky, E.; Coyne, C.B.; Parks, W.T.; Surti, U.; Sadovsky, Y. Expression and trafficking of placental microRNAs at the feto-maternal interface. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2760–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cindrova-Davies, T.; Herrera, E.A.; Niu, Y.; Kingdom, J.; Giussani, D.A.; Burton, G.J. Reduced Cystathionine γ-Lyase and Increased miR-21 Expression Are Associated with Increased Vascular Resistance in Growth-Restricted Pregnancies: Hydrogen Sulfide as a Placental Vasodilator. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccani, M.A.; Padbury, J.F.; Marsit, C.J. miR-16 and miR-21 Expression in the Placenta Is Associated with Fetal Growth. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Kappil, M.A.; Li, A.; Dassanayake, P.S.; Darrah, T.H.; Friedman, A.E.; Friedman, M.; Lambertini, L.; Landrigan, P.; Stodgell, C.J.; et al. Exploring the associations between microRNA expression profiles and environmental pollutants in human placenta from the National Children’s Study (NCS). Epigenetics 2015, 10, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Cardiovascular Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2014, 76, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planavila, A.; Dominguez, E.; Navarro, M.; Vinciguerra, M.; Iglesias, R.; Giralt, M.; Lope-Piedrafita, S.; Ruberte, J.; Villarroya, F. Dilated cardiomyopathy and mitochondrial dysfunction in Sirt1-deficient mice: A role for Sirt1-Mef2 in adult heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorn, G.W.; Vega, R.B.; Kelly, D.P. Mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics in the developing and diseased heart. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, T.; Maillet, M.; Watt, A.J.; Schwartz, R.J.; Aronow, B.J.; Duncan, S.A.; Molkentin, J.D. Cardiac-specific deletion of Gata4 reveals its requirement for hypertrophy, compensation, and myocyte viability. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasanaro, P.; D’Alessandra, Y.; Di Stefano, V.; Melchionna, R.; Romani, S.; Pompilio, G.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Martelli, F. MicroRNA-210 modulates endothelial cell response to hypoxia and inhibits the receptor tyrosine kinase ligand Ephrin-A3. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15878–15883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.-B.; Hausenloy, D.J. Mitochondrial morphology and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 88, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barish, G.D.; Narkar, V.A.; Evans, R.M. PPARδ: A dagger in the heart of the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, T.E.; Wilks, R.J.; Bennett, F.I.; Simeon, D.; Osmond, C.; Allen, M.; Chung, A.P.; Scott, P. Fetal growth and cardiovascular risk factors in Jamaican schoolchildren. BMJ 1996, 312, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J. Mothers, Babies, and Disease in Later Life; British Medical Journal Group, Wiley Inc.: London, UK, 1994; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, C.E.; Fall, C.H.; Kumaran, K.; Osmond, C.; Cox, V.; Barker, D.J. Fetal growth and coronary heart disease in south India. Lancet 1996, 348, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.I. External influences on the fetus and their long-term consequences. Lupus 2006, 15, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Jaswal, J.S. Energy metabolic phenotype of the cardiomyocyte during development, differentiation, and postnatal maturation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 56, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Li, H.; Zeng, X.; Yang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Liang, S. Roles of microRNA on cancer cell metabolism. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, W.W., Jr. Placental transport of nutrients to the fetus. Horm. Res. 1994, 42, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macheda, M.L.; Rogers, S.; Best, J.D. Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins in cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 202, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauersachs, J.; Thum, T. Biogenesis and regulation of cardiovascular microRNAs. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.Y.; Song, Y.H.; Geng, Y.J.; Lin, Q.X.; Shan, Z.X.; Lin, S.G.; Li, Y. Glucose induces apoptosis of cardiomyocytes via microRNA-1 and IGF-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 376, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathaway, Q.A.; Pinti, M.V.; Durr, A.J.; Waris, S.; Shepherd, D.L.; Hollander, J.M. Regulating MicroRNA Expression: At the Heart of Diabetes Mellitus and the Mitochondrion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, S.; Fasanaro, P.; Castelvecchio, S.; D’Alessandra, Y.; Arcelli, D.; Di Donato, M.; Malavazos, A.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Menicanti, L.; Martelli, F. MicroRNA dysregulation in diabetic ischemic heart failure patients. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Li, B.; Wei, Y.Z.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Gan, X.D.; Wang, Z.H.; Xiong, S.X. MicroRNA-34a regulates high glucose-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Tian, R. Glucose Transporters in Cardiac Metabolism and Hypertrophy. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 6, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, R.; Jain, M.; Cui, L.; D’Agostino, J.; Aiello, F.; Luptak, I.; Ngoy, S.; Mortensen, R.M.; Tian, R. Cardiac-specific overexpression of GLUT1 prevents the development of heart failure attributable to pressure overload in mice. Circulation 2002, 106, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarczyk, S.J.; Andrikopoulos, S.; Favaloro, J.; Domenighetti, A.A.; Dunn, A.; Ernst, M.; Grail, D.; Fodero-Tavoletti, M.; Huggins, C.E.; Delbridge, L.M.; et al. Threshold effects of glucose transporter-4 (GLUT4) deficiency on cardiac glucose uptake and development of hypertrophy. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 31, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Z.X.; Lin, Q.X.; Deng, C.Y.; Zhu, J.N.; Mai, L.P.; Liu, J.L.; Fu, Y.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; et al. miR-1/miR-206 regulate Hsp60 expression contributing to glucose-mediated apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3592–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineiro, R.; Iglesias, M.J.; Gallego, R.; Raghay, K.; Eiras, S.; Rubio, J.; Dieguez, C.; Gualillo, O.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; Lago, F. Adiponectin is synthesized and secreted by human and murine cardiomyocytes. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5163–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Gammon, S.R.; Knippers, J.D.; Paulsen, S.R.; Rubink, D.S.; Winder, W.W. Phosphorylation-activity relationships of AMPK and acetyl-CoA carboxylase in muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2002, 92, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Raalte, D.H.; Li, M.; Pritchard, P.H.; Wasan, K.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-alpha: A pharmacological target with a promising future. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarry, J.D. The mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase system: Its broadening role in fuel homoeostasis and new insights into its molecular features. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1995, 23, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Sato, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jaskiewicz, J.; Popov, K.M.; Harris, R.A. Starvation and diabetes increase the amount of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoenzyme 4 in rat heart. Biochem. J. 1998, 329 Pt 1, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugden, M.C.; Holness, M.J. Mechanisms underlying regulation of the expression and activities of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 112, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Drosatos, K.; Hiyama, Y.; Goldberg, I.J.; Zannis, V.I. MicroRNA-370 controls the expression of microRNA-122 and Cpt1alpha and affects lipid metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, K.I.; Ogawa, D.; Rooj, A.K.; Lawler, S.E.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Johnson, M.D.; Chiocca, E.A.; Bronisz, A.; Godlewski, J. Glucose-based regulation of miR-451/AMPK signaling depends on the OCT1 transcription factor. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurha, P.; Wang, T.; Larimore, A.H.; Sassi, Y.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Ramirez, M.O.; Reddy, A.K.; Engelhardt, S.; Taffet, G.E.; Wehrens, X.H.; et al. microRNA-22 promotes heart failure through coordinate suppression of PPAR/ERR-nuclear hormone receptor transcription. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdar, A.; Abadi, A.; Akhtar, M.; Hettinga, B.P.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. miRNA in the Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Adaptation to Acute Endurance Exercise in C57Bl/6J Male Mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finck, B.N. The PPAR regulatory system in cardiac physiology and disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed-Ahmed, M.M.; Aldelemy, M.L.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Hafez, M.M.; Al-Hosaini, K.A.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Al-Sharary, S.D.; Al-Harbi, M.M. Inhibition of gene expression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I and heart fatty acid binding protein in cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide-induced acute cardiotoxic rat models. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2014, 14, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, J.R.B.; Lopaschuk, G.D. AMPK alterations in cardiac physiology and pathology: Enemy or ally? J. Physiol. 2006, 574 Pt 1, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hulver, M.W.; McMillan, R.P.; Cline, M.A.; Gilbert, E.R. The pivotal role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases in metabolic flexibility. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2014, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromadnikova, I.; Kotlabova, K.; Hympanova, L.; Krofta, L. Gestational hypertension, preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction induce dysregulation of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease associated microRNAs in maternal whole peripheral blood. Thromb. Res. 2016, 137, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Chu, D.; Jiang, X.; Hou, D.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.-Y. Small non-coding RNAs transfer through mammalian placenta and directly regulate fetal gene expression. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staedel, C.; Darfeuille, F. MicroRNAs and bacterial infection. Cell. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.P.; Lewis, A.P.; Jopling, C.L. The role of microRNAs in viral infection. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2011, 102, 101–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouillet, J.F.; Ouyang, Y.; Bayer, A.; Coyne, C.B.; Sadovsky, Y. The role of trophoblastic microRNAs in placental viral infection. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 58, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, T.; Cobos, F.A.; Schleich, F.; Sorbello, V.; Henket, M.; De Preter, K.; Bracke, K.R.; Conickx, G.; Mesnil, C.; Vandesompele, J.; et al. Asthma inflammatory phenotypes show differential microRNA expression in sputum. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, M.M.; Adcock, I.M.; Chung, K.F. Role of microRNAs in allergic asthma: Present and future. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 15, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Miura, K.; Higashijima, A.; Abe, S.; Miura, S.; Yoshiura, K.; Masuzaki, H. Increased Levels of Cell-Free miR-517a and Decreased Levels of Cell-Free miR-518b in Maternal Plasma Samples From Placenta Previa Pregnancies at 32 Weeks of Gestation. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 22, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsella, M.T.; Monk, C. Impact of Maternal Stress, Depression & Anxiety on Fetal Neurobehavioral Development. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 52, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiPietro, J.A. Maternal stress in pregnancy: Considerations for fetal development. J. Adolesc. Health 2012, 51, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucchi, F.C.; Yao, Y.; Ward, I.D.; Ilnytskyy, Y.; Olson, D.M.; Benzies, K.; Kovalchuk, I.; Kovalchuk, O.; Metz, G.A. Maternal stress induces epigenetic signatures of psychiatric and neurological diseases in the offspring. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolic, A.; Feng, X.; Wood, C.E.; Richards, E.M.; Keller-Wood, M. Increased maternal nighttime cortisol concentrations in late gestation alter glucose and insulin in the neonatal lamb. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.P.; Sandman, C.A. The Timing of Prenatal Exposure to Maternal Cortisol and Psychosocial Stress is Associated with Human Infant Cognitive Development. Child Dev. 2010, 81, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, S.; MacKenzie, S.M.; Alvarez-Madrazo, S.; Diver, L.A.; Lin, J.; Stewart, P.M.; Fraser, R.; Connell, J.M.; Davies, E. MicroRNA-24 Is a Novel Regulator of Aldosterone and Cortisol Production in the Human Adrenal Cortex. Hypertension 2013, 62, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, M.; Kuwano, Y.; Katsuura-Kamano, S.; Kamezaki, Y.; Fujita, K.; Akaike, Y.; Kano, S.; Nishida, K.; Masuda, K.; Rokutan, K. Chronic Academic Stress Increases a Group of microRNAs in Peripheral Blood. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Shen, W.-J.; Cortez, Y.; Tang, X.; Liu, L.-F.; Kraemer, F.B.; Azhar, S. Hormonal Regulation of MicroRNA Expression in Steroid Producing Cells of the Ovary, Testis and Adrenal Gland. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Lee, I.; Hammamieh, R.; Wang, K.; Baxter, D.; Scherler, K.; Etheridge, A.; Kulchenko, A.; Gautam, A.; Muhie, S.; et al. Molecular evidence of stress-induced acute heart injury in a mouse model simulating posttraumatic stress disorder. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3188–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumbers, E.R.; Boyce, A.C.; Joulianos, G.; Kumarasamy, V.; Barner, E.; Segar, J.L.; Burrell, J.H. Effects of cortisol on cardiac myocytes and on expression of cardiac genes in fetal sheep. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 288, R567–R574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q. microRNA-133: Expression, function and therapeutic potential in muscle diseases and cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jingushi, K.; Ueda, Y.; Kitae, K.; Hase, H.; Egawa, H.; Ohshio, I.; Kawakami, R.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Tsukada, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. miR-629 Targets TRIM33 to Promote TGFbeta/Smad Signaling and Metastatic Phenotypes in ccRCC. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Varambally, S.; Maher, C.A.; Cao, Q.; Chockley, P.; Toubai, T.; Malter, C.; Nieves, E.; Tawara, I.; Wang, Y.; et al. Targeting of microRNA-142-3p in dendritic cells regulates endotoxin-induced mortality. Blood 2011, 117, 6172–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomer, X.; Capdevila-Busquets, E.; Botteri, G.; Davidson, M.M.; Rodriguez, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, J.; Vidal, F.; Barroso, E.; Chan, T.O.; Feldman, A.M.; et al. miR-146a targets Fos expression in human cardiac cells. Dis. Model Mech. 2015, 8, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Diaz, M.; Blanco-Verea, A.; Teixido, G.; Huguet, F.; Gut, M.; Laurie, S.; Gut, I.; Carracedo, A.; Evangelista, A.; Brion, M. PRKG1 and genetic diagnosis of early-onset thoracic aortic disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 46, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Quattrocchi, A. The Role of miRNAs as Biomarkers for Pregnancy Outcomes: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 8067972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, A.; Navarro, F.; Maher, C.; Maliszewski, L.E.; Yan, N.; O’Day, E.; Chowdhury, D.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Tsai, P.; Hofman, O.; et al. miR-24 inhibits cell proliferation by suppressing expression of E2F2, MYC and other cell cycle regulatory genes by binding to “seedless” 3′UTR microRNA recognition elements. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 610–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rooij, E.; Sutherland, L.B.; Thatcher, J.E.; DiMaio, J.M.; Naseem, R.H.; Marshall, W.S.; Hill, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13027–13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.L.; Hullinger, T.G.; Semus, H.M.; Dickinson, B.A.; Seto, A.G.; Lynch, J.M.; Stack, C.; Latimer, P.A.; Olson, E.N.; van Rooij, E. Therapeutic Inhibition of miR-208a Improves Cardiac Function and Survival During Heart Failure. Circulation 2011, 124, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, J.T.; Huang, Y.; Gilmore, J.; Srivastava, D. Elevated miR-499 levels blunt the cardiac stress response. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Huang, C. MiR-19b and miR-16 cooperatively signaling target the regulator ADRA1A in Hypertensive heart disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Pu, W.T.; Jegga, A.G.; Fan, G.-C. Synergistic Effects of the GATA-4-Mediated miR-144/451 Cluster in Protection against Simulated Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Cardiomyocyte Death. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 49, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Hu, X.; Yu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Han, S.; Zhu, C. Effect of miR-20b on Apoptosis, Differentiation, the BMP Signaling Pathway and Mitochondrial Function in the P19 Cell Model of Cardiac Differentiation In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lock, M.C.; Botting, K.J.; Tellam, R.L.; Brooks, D.; Morrison, J.L. Adverse Intrauterine Environment and Cardiac miRNA Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122628
Lock MC, Botting KJ, Tellam RL, Brooks D, Morrison JL. Adverse Intrauterine Environment and Cardiac miRNA Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122628
Chicago/Turabian StyleLock, Mitchell C., Kimberley J. Botting, Ross L. Tellam, Doug Brooks, and Janna L. Morrison. 2017. "Adverse Intrauterine Environment and Cardiac miRNA Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122628
APA StyleLock, M. C., Botting, K. J., Tellam, R. L., Brooks, D., & Morrison, J. L. (2017). Adverse Intrauterine Environment and Cardiac miRNA Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122628





