Quercetin Mitigates Inflammatory Responses Induced by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Mouse Retinal Photoreceptor Cells through Suppression of Nuclear Factor Kappa B
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
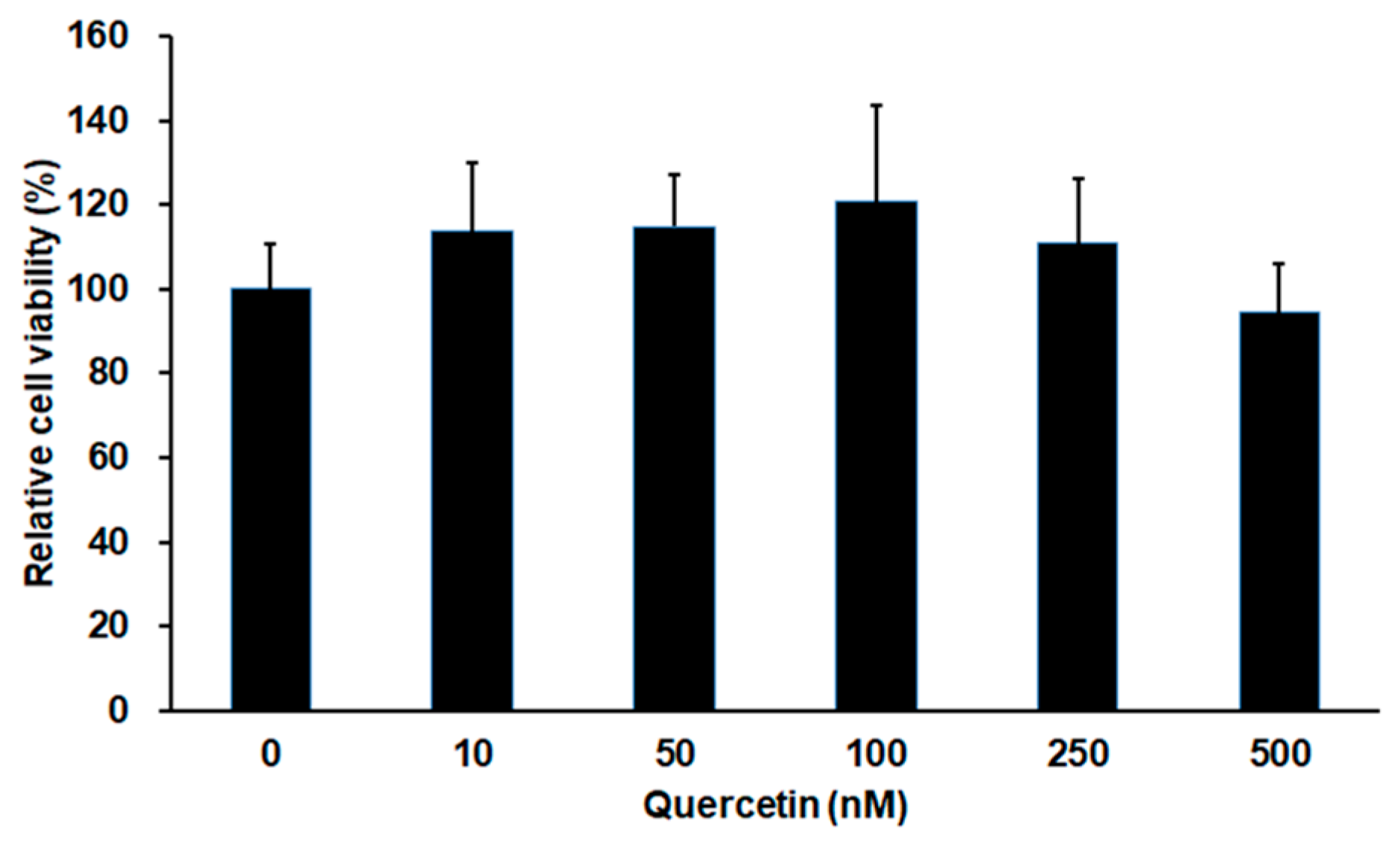
2.1. Effect of Quercetin on Cell Viability in 661W Cells
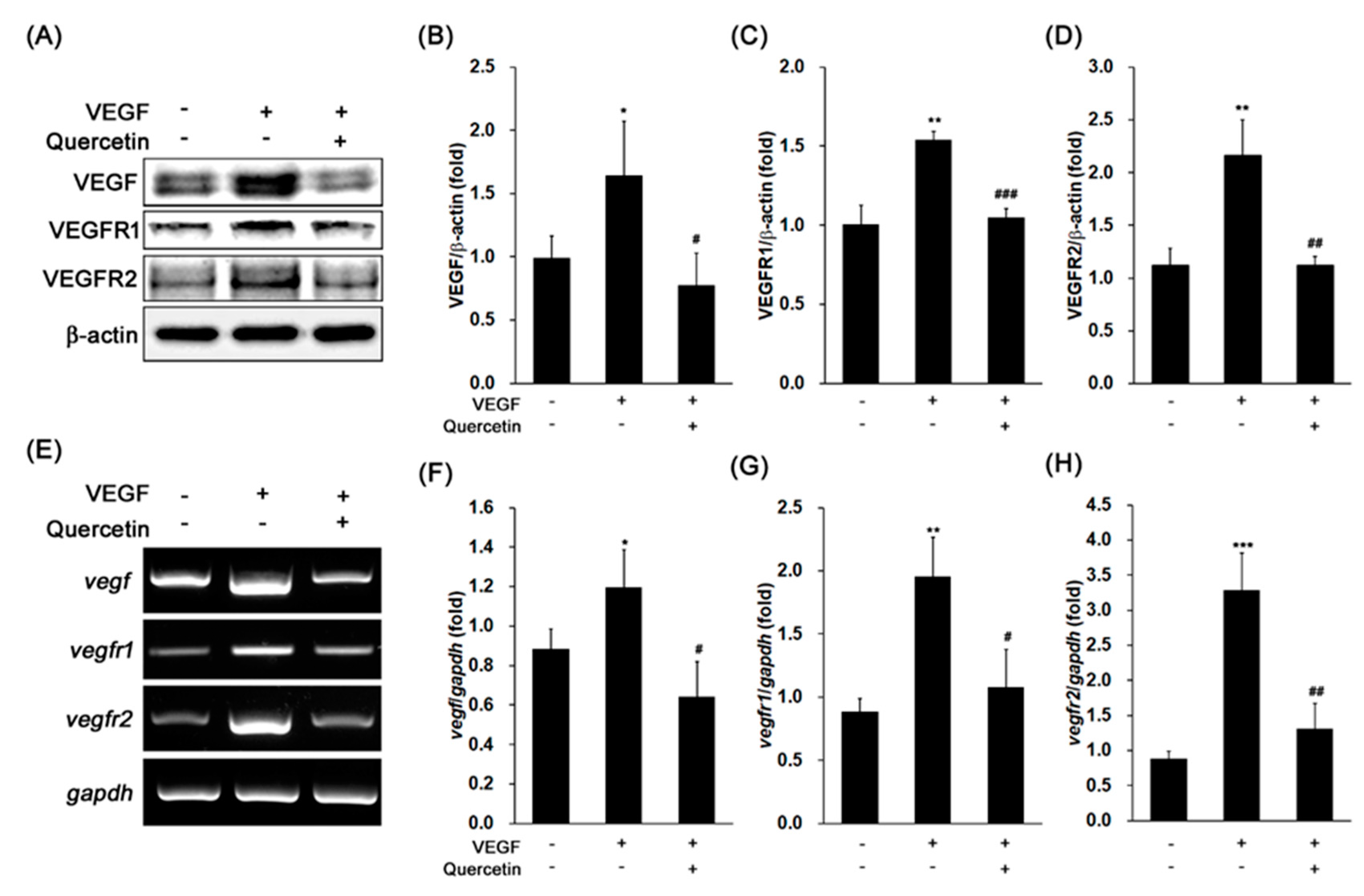
2.2. Effect of Quercetin on the Production of VEGF
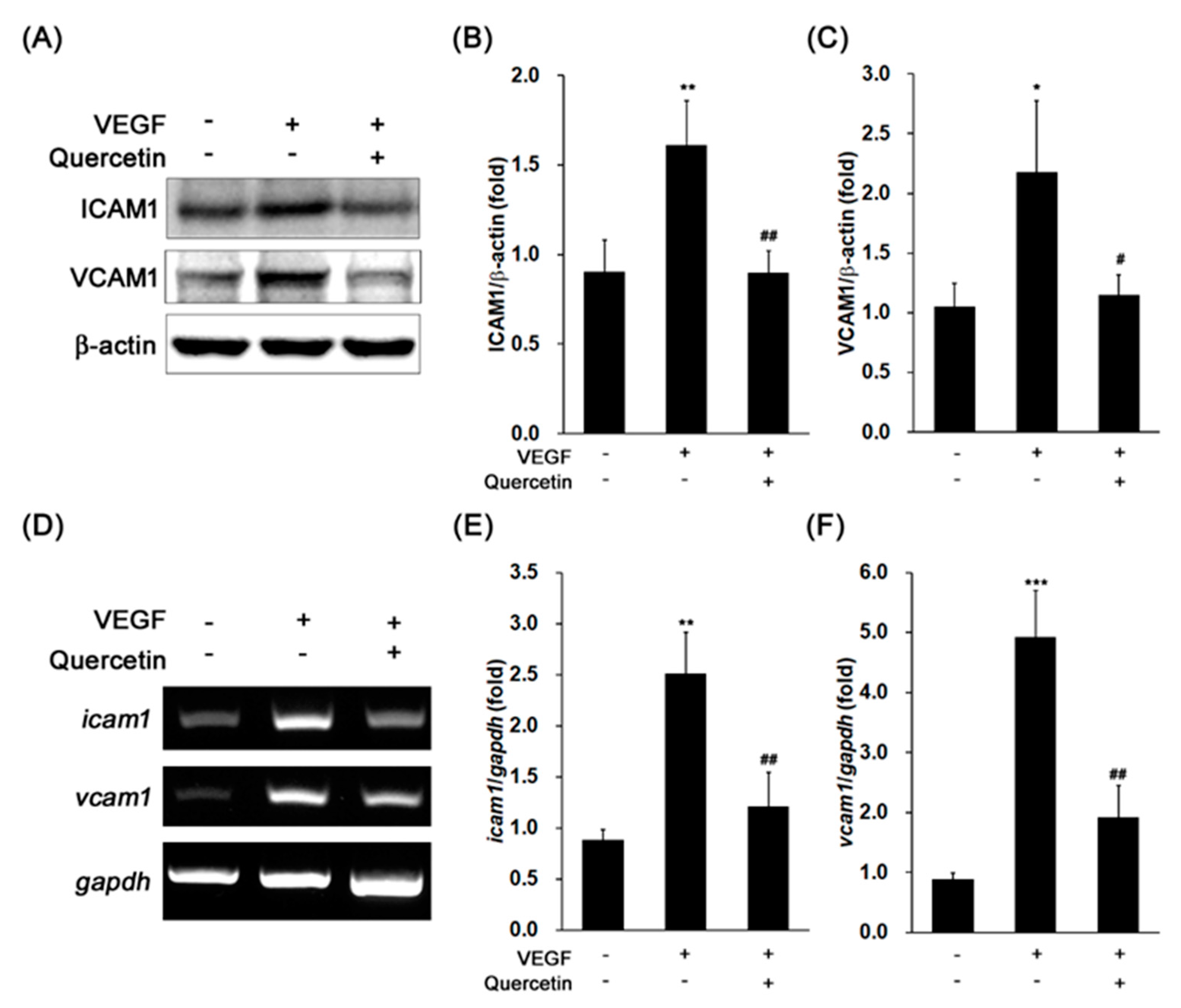
2.3. Effect of Quercetin on the Production of Adhesion Proteins
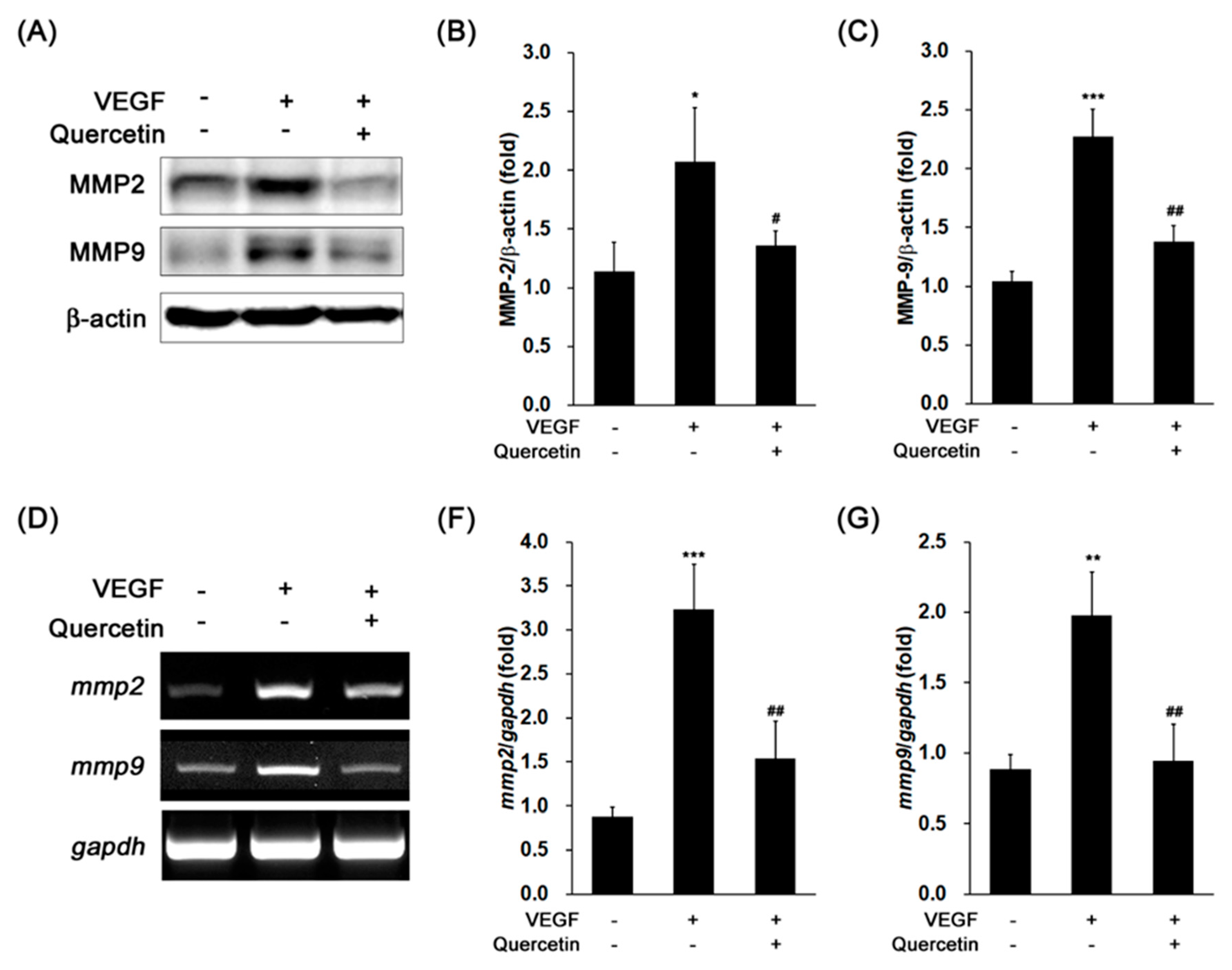
2.4. Effect of Quercetin on the Production of Proteinases
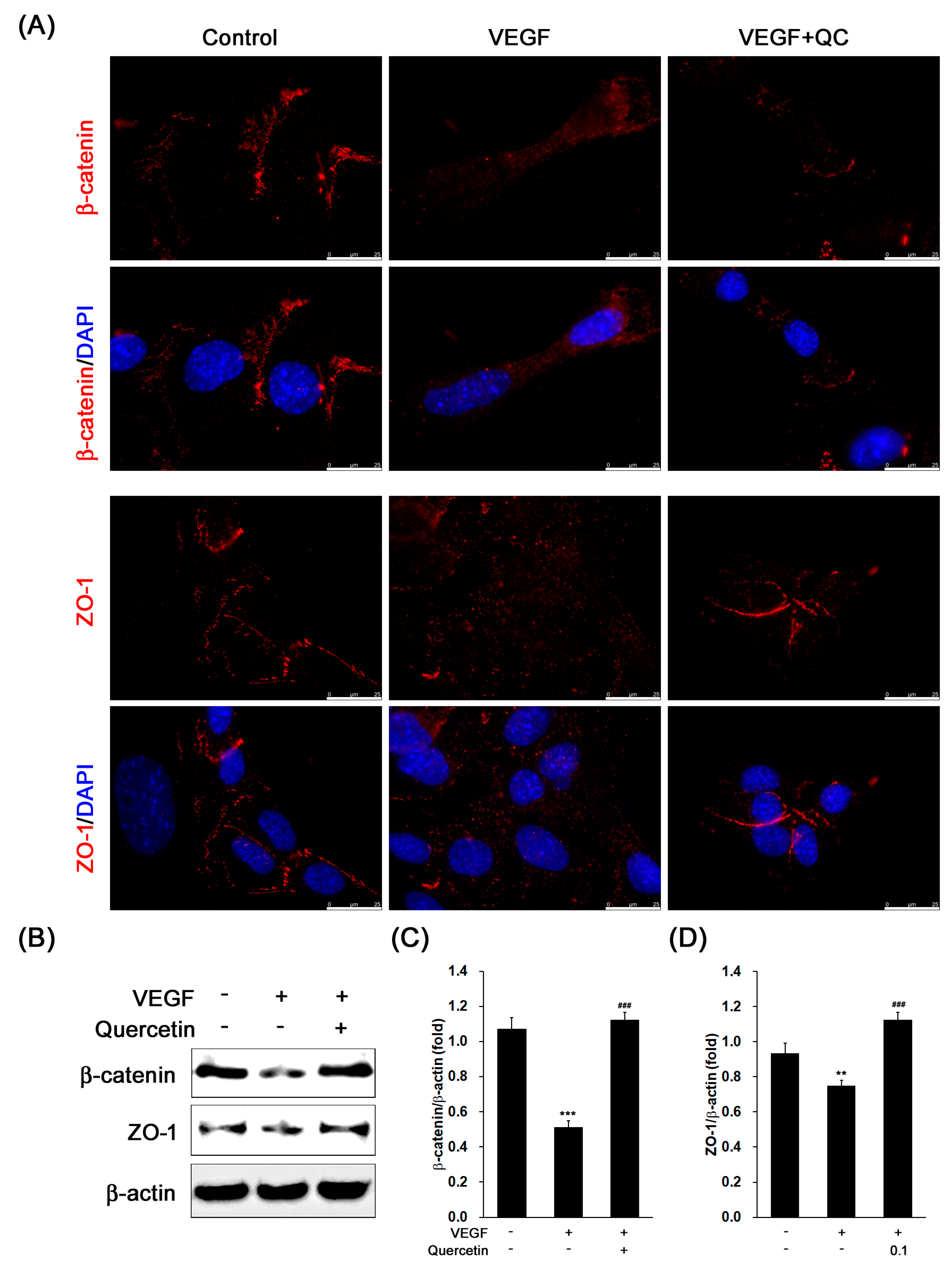
2.5. Effect of Quercetin on the Production of Tight Junction Proteins
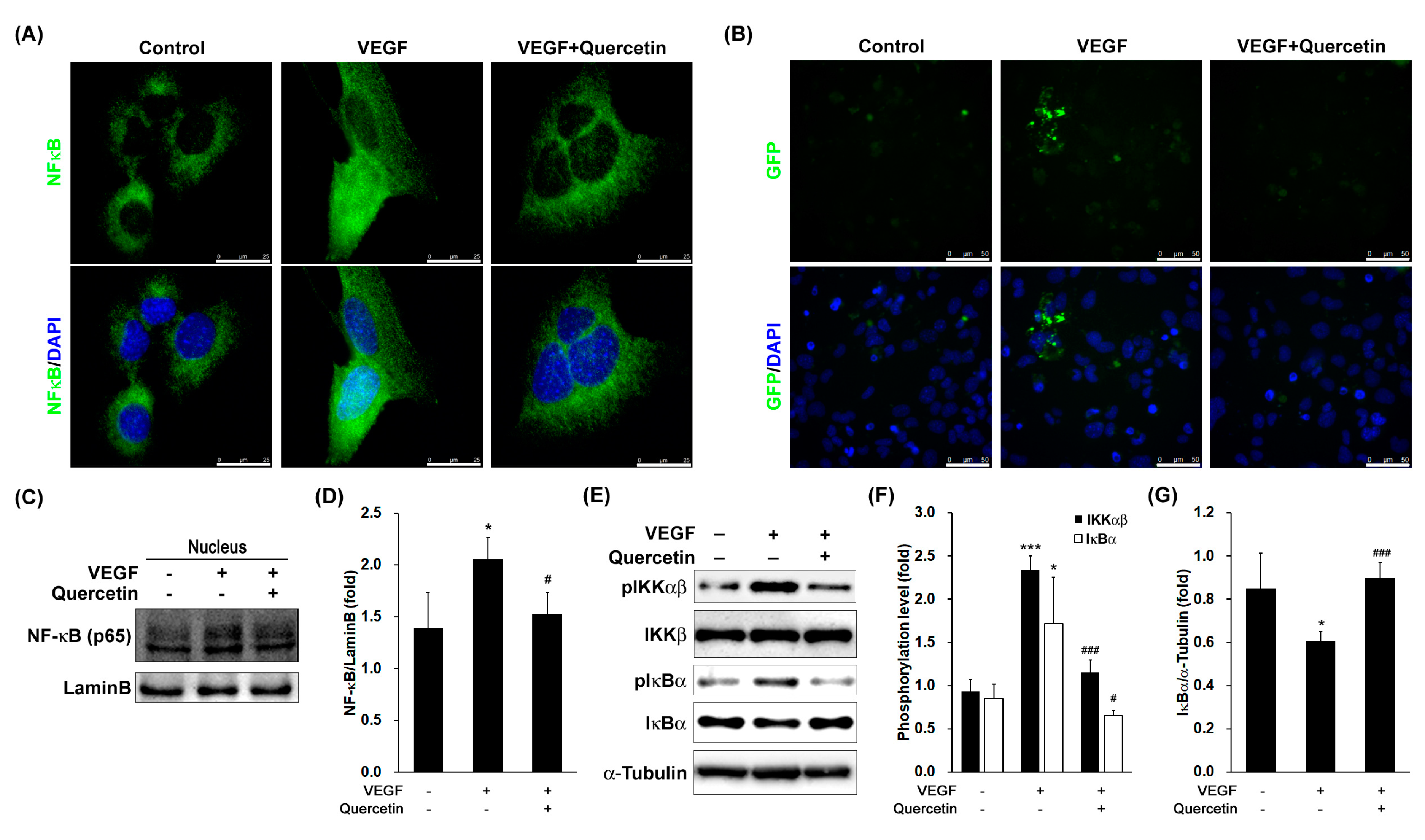
2.6. Effect of Quercetin on the Activation and Translocation of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB)
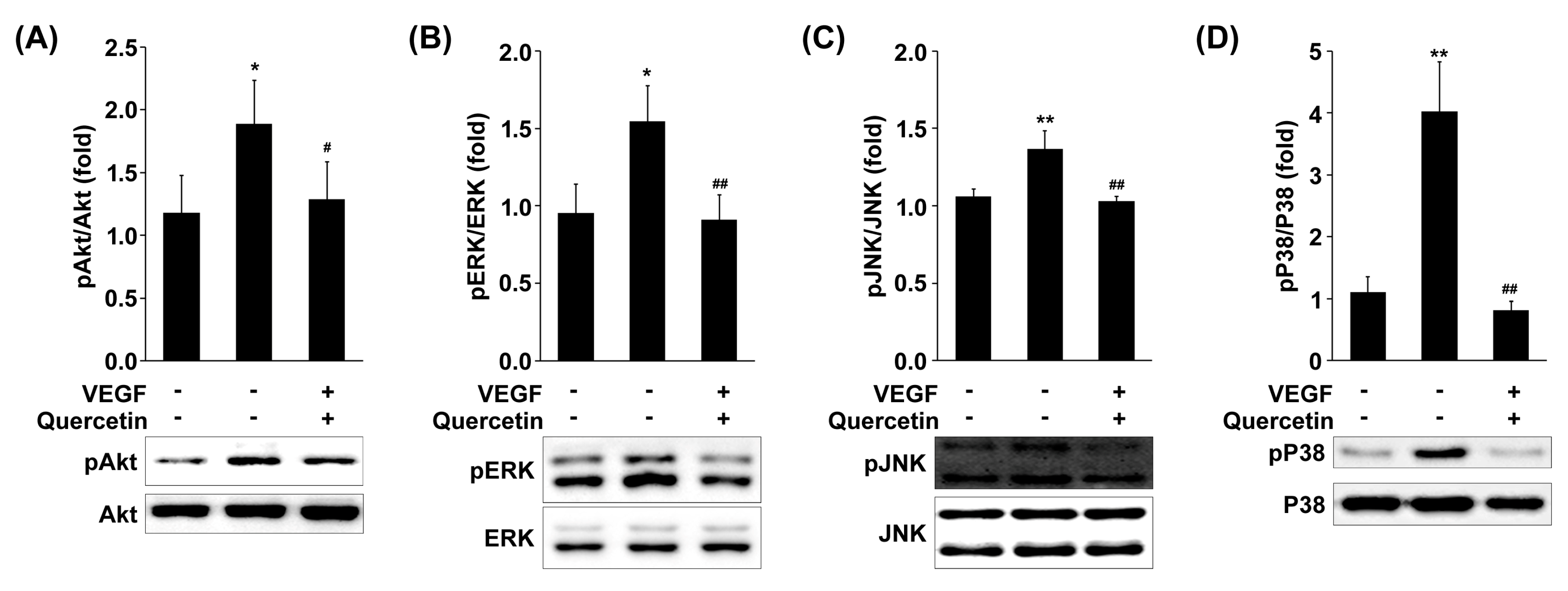
2.7. Effect of Quercetin on the Phosphorylation of MAPKs and Akt
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
4.3. Preparation of Protein Extract and Cell Fractionation
4.4. Western Immunoblot Analysis
4.5. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.6. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.7. Transient Transfection and Reporter Gene Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campochiaro, P.A. Molecular pathogenesis of retinal and choroidal vascular diseases. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 49, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campochiaro, P.A. Ocular neovascularization. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, R.S.; Basavarajappa, H.D.; Corson, T.W. Natural product inhibitors of ocular angiogenesis. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 129, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.X.; Ma, J.X. Ocular neovascularization: Implication of endogenous angiogenic inhibitors and potential therapy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2007, 26, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Sharma, N.K.; Singh, R.; Anand, A. Exploring the role of VEGF in Indian Age related macular degeneration. Ann. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.A.; Murthy, R.; Chibber, R.; Nunn, A.; Molinatti, P.A.; Kohner, E.M.; Gregor, Z.J. Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor are elevated in the vitreous of patients with subretinal neovascularisation. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 80, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Saxena, S.; Khanna, V.K.; Shukla, R.K.; Meyer, C.H. Status of serum VEGF and ICAM-1 and its association with external limiting membrane and inner segment-outer segment junction disruption in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Elliott, M.H.; Zhu, M.; Le, Y.Z. Muller cell-derived VEGF is essential for diabetes-induced retinal inflammation and vascular leakage. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Parlier, R.; Shen, J.K.; Lutty, G.A.; Vinores, S.A. VEGF receptor blockade markedly reduces retinal microglia/macrophage infiltration into laser-induced CNV. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Shen, J.; Vinores, S.A. Blockade of VEGFR1 and 2 suppresses pathological angiogenesis and vascular leakage in the eye. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, T.A.; Alex, A.F.; Engel, D.R.; Kurts, C.; Eter, N. VEGF-production by CCR2-dependent macrophages contributes to laser-induced choroidal neovascularization. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Afridi, R.; Sadiq, M.A.; Soliman, M.K.; Agarwal, A.; Sepah, Y.J.; Do, D.V.; Nguyen, Q.D. The role of Aflibercept in the management of age-related macular degeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, S.; Clearfield, E.; Soliman, M.K.; Sadiq, M.A.; Baldwin, A.J.; Hanout, M.; Agarwal, A.; Sepah, Y.J.; Do, D.V.; Nguyen, Q.D. Aflibercept for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Yau, B.; Lee, S.R.; Zhu, L.; Yam, M.; Gillies, M. Effects of ranibizumab and aflibercept on human müller cells and photoreceptors under stress conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucolo, C.; Leggio, G.M.; Drago, F.; Salomone, S. Eriodictyol prevents early retinal and plasma abnormalities in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucolo, C.; Marrazzo, G.; Platania, C.B.; Drago, F.; Leggio, G.M.; Salomone, S. Fortified extract of red berry, Ginkgo biloba, and white willow bark in experimental early diabetic retinopathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 432695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, T.P.; Mann, S.N.; Mandal, N.A. Botanical compounds: Effects on major eye diseases. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 549174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murota, K.; Terao, J. Antioxidative flavonoid quercetin: Implication of its intestinal absorption and metabolism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 417, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, A.W.; Haenen, G.R.; Bast, A. Health effects of quercetin: From antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 585, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanneken, A.; Lin, F.F.; Johnson, J.; Maher, P. Flavonoids protect human retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative-stress-induced death. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 3164–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kook, D.; Wolf, A.H.; Yu, A.L.; Neubauer, A.S.; Priglinger, S.G.; Kampik, A.; Welge-Lussen, U.C. The protective effect of quercetin against oxidative stress in the human RPE in vitro. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Liu, M.; Tuo, J.; Shen, D.; Chan, C.C. The effects of quercetin in cultured human RPE cells under oxidative stress and in Ccl2/Cx3cr1 double deficient mice. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 91, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.R.; Yu, H.T.; Yang, Y.; Hang, L.; Yang, X.W.; Ding, S.H. Quercetin phospholipid complex significantly protects against oxidative injury in ARPE-19 cells associated with activation of Nrf2 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 770, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.M.; Lee, B.L.; Guo, Y.R.; Choung, S.Y. Preventive effect of Vaccinium uliginosum L. extract and its fractions on age-related macular degeneration and its action mechanisms. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, P.; Shen, Y.; Lin, B.Q.; Zhang, W.Y.; Chiou, G.C. Effect of quercetin on formation of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) in age-related macular degeneration(AMD). Eye Sci. 2011, 26, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.; Ding, X.Q.; Saadi, A.; Agarwal, N.; Naash, M.I.; Al-Ubaidi, M.R. Expression of cone-photoreceptor-specific antigens in a cell line derived from retinal tumors in transgenic mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, S.; Omri, B.; Savoldelli, M.; Jonet, L.; Thillaye-Goldenberg, B.; Thuret, G.; Gain, P.; Jeanny, J.C.; Crisanti, P.; Behar-Cohen, F. The outer limiting membrane (OLM) revisited: Clinical implications. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2010, 4, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pearson, R.A.; Barber, A.C.; West, E.L.; MacLaren, R.E.; Duran, Y.; Bainbridge, J.W.; Sowden, J.C.; Ali, R.R. Targeted disruption of outer limiting membrane junctional proteins (Crb1 and ZO-1) increases integration of transplanted photoreceptor precursors into the adult wild-type and degenerating retina. Cell Transplant. 2010, 19, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foresti, R.; Bucolo, C.; Platania, C.M.; Drago, F.; Dubois-Rande, J.L.; Motterlini, R. Nrf2 activators modulate oxidative stress responses and bioenergetic profiles of human retinal epithelial cells cultured in normal or high glucose conditions. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platania, C.B.M.; Giurdanella, G.; Di Paola, L.; Leggio, G.M.; Drago, F.; Salomone, S.; Bucolo, C. P2X7 receptor antagonism: Implications in diabetic retinopathy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 138, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ved, N.; Hulse, R.P.; Bestall, S.M.; Donaldson, L.F.; Bainbridge, J.W.; Bates, D.O. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A165b ameliorates outer-retinal barrier and vascular dysfunction in the diabetic retina. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1225–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, M.; Huang, L.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. Quercetin inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-induced choroidal and retinal angiogenesis in vitro. Ophthalmic Res. 2015, 53, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Hart, E.; Shchurin, A.; Hoover-Plow, J. Inflammatory macrophage migration requires MMP-9 activation by plasminogen in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3012–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, M.; Okumura, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Shiraishi, I.; Itoi, T.; Hamaoka, K. MMP-2 inhibition reduces renal macrophage infiltration with increased fibrosis in UUO. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caicedo, A.; Espinosa-Heidmann, D.G.; Pina, Y.; Hernandez, E.P.; Cousins, S.W. Blood-derived macrophages infiltrate the retina and activate Muller glial cells under experimental choroidal neovascularization. Exp. Eye Res. 2005, 81, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omri, S.; Behar-Cohen, F.; de Kozak, Y.; Sennlaub, F.; Verissimo, L.M.; Jonet, L.; Savoldelli, M.; Omri, B.; Crisanti, P. Microglia/macrophages migrate through retinal epithelium barrier by a transcellular route in diabetic retinopathy: Role of PKCζ in the Goto Kakizaki rat model. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Khosrof, S.; Bursell, S.E.; Moromizato, Y.; Aiello, L.P.; Ogura, Y.; Adamis, A.P. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced retinal vascular permeability is mediated by intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litts, K.M.; Ach, T.; Hammack, K.M.; Sloan, K.R.; Zhang, Y.; Freund, K.B.; Curcio, C.A. Quantitative analysis of outer retinal tubulation in age-related macular degeneration from spectral-domain optical coherence tomography and histology. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi-Kurashige, Y.; Tsujikawa, A.; Oishi, A.; Ooto, S.; Yamashiro, K.; Tamura, H.; Nakata, I.; Ueda-Arakawa, N.; Yoshimura, N. Relationship between retinal morphological findings and visual function in age-related macular degeneration. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 250, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.C. Association between foveal microstructure and visual outcome in age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2011, 31, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.C. Association between photoreceptor integrity and visual outcome in diabetic macular edema. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 250, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kishi, S. Correlation between visual acuity and foveal microstructural changes in diabetic macular edema. Retina 2010, 30, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.C. Association between integrity of foveal photoreceptor layer and visual outcome in retinal vein occlusion. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011, 89, e35–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Pavert, S.A.; Kantardzhieva, A.; Malysheva, A.; Meuleman, J.; Versteeg, I.; Levelt, C.; Klooster, J.; Geiger, S.; Seeliger, M.W.; Rashbass, P.; et al. Crumbs homologue 1 is required for maintenance of photoreceptor cell polarization and adhesion during light exposure. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 4169–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Moon, S.O.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Koh, Y.S.; Koh, G.Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), and E-selectin through nuclear factor-κB activation in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7614–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Hagler, J.; Palombella, V.J.; Melandri, F.; Scherer, D.; Ballard, D.; Maniatis, T. Signal-induced site-specific phosphorylation targets IκBα to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, N.R.; Zhang, P.; Lee, J.C.; Hogan, E.L. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-α gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Madrid, L.V.; Mayo, M.W.; Reuther, J.Y.; Baldwin, A.S. Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 Subunit of NF-κB through utilization of the IκB kinase and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18934–18940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, M.R.; Schoots, I.G.; Spokes, K.C.; Wu, S.Q.; Mawhinney, C.; Aird, W.C. Vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated induction of manganese superoxide dismutase occurs through redox-dependent regulation of forkhead and IκB/NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44030–44038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ispanovic, E.; Haas, T.L. JNK and PI3K differentially regulate MMP-2 and MT1-MMP mRNA and protein in response to actin cytoskeleton reorganization in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C579–C588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.C.; Thapa, D.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.A. Troglitazone inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenic signaling via suppression of reactive oxygen species production and extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation in endothelial cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 111, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radisavljevic, Z.; Avraham, H.; Avraham, S. Vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulates ICAM-1 expression via the phosphatidylinositol 3 OH-kinase/AKT/Nitric oxide pathway and modulates migration of brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 20770–20774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Rice, S.; Sharp, T.; Qi, J.; Mu, D.; Han, B.; Zander, D.S. Akt regulates Raf/MEK/ERK cascade, VEGF and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression, and malignant characteristics of NSCLC cells. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 567. [Google Scholar]
| Antibody | Manufacturer | Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| α-Tubulin | Santacruz (Santa Cruz, CA, USA) | 1:3000 |
| β-actin | Santacruz | 1:3000 |
| β-catenin | Cell signaling (Danvers, MA, USA) | 1:1000 1:200 * |
| Akt | Cell signaling | 1:3000 |
| ERK | Cell signaling | 1:3000 |
| ICAM1 | Bioss Antibodies (Woburn, MA, USA) | 1:1000 |
| IκBα | Cell signaling | 1:1000 |
| IKKβ | Cell signaling | 1:1000 |
| JNK | Cell signaling | 1:3000 |
| LaminB | Santacruz | 1:1000 |
| MMP2 | abcam (Cambridge, UK) | 1:1000 |
| MMP9 | LSBio (Seattle, WA, USA) | 1:1000 |
| NF-κB | Cell signaling | 1:1000 1:200 * |
| P38 | Cell signaling | 1:3000 |
| Phosphor-IKKαβ | Cell signaling | 1:1000 |
| Phosphor-IκBα | Cell signaling | 1:1000 |
| Phosphor-ERK | Cell signaling | 1:1,000 |
| Phosphor-JNK | Cell signaling | 1:1000 |
| Phosphor-P38 | Cell signaling | 1:1000 |
| Phosphor-Akt | Cell signaling | 1:1000 |
| VCAM1 | Bioss Antibodies | 1:1000 |
| VEGF | Santacruz | 1:500 |
| VEGFR1 | Santacruz | 1:500 |
| VEGFR2 | Santacruz | 1:500 |
| ZO-1 | Cell signaling | 1:1000 1:200 * |
| Goat-anti-mouse-HRP | Santacruz | 1:5000 |
| Goat-anti-rabbit-HRP | Santacruz | 1:5000 |
| Donkey anti-mouse IgG-TR | Santacruz | 1:500 * |
| Donkey anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor® 555 | Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA) | 1:500 * |
| Gene Gene ID | Primer | Annealing Temp. | Cycle | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP2 NM_008610.3 | GCTGCGCTTTTCTCGAATCC | 60 °C | 30 | 375 |
| GTAAACAAGGCTTCATGGGGG | ||||
| MMP9 NM_013599.4 | CGCTCATGTACCCGCTGTAT | 65 °C | 30 | 345 |
| TGTCTGCCGGACTCAAAGAC | ||||
| VEGF NM_001025250.3 | CTCCGTAGTAGCCGTGGTCT | 65 °C | 30 | 496 |
| GCTTCGCTGGTAGACATCCA | ||||
| VEGFR1 NM_010228.3 | TCTAGAAGACTCGGGCACCT | 65 °C | 30 | 403 |
| CGTGATCAGCTCCAGGTTTG | ||||
| VEGFR2 X70842.1 | AACACGTGGACTCTGTCCTCC | 65 °C | 30 | 323 |
| GAAGAGCACGCAAACCTTCC | ||||
| ICAM1 NM_010493.3 | CCTGTTTCCTGCCTCTGAAG | 60 °C | 30 | 528 |
| GTCTGCTGAGACCCCTCTTG | ||||
| VCAM1 NM_011693.3 | TCTAGAAGACTCGGGCACCT | 60 °C | 30 | 403 |
| CGTGATCAGCTCCAGGTTTG | ||||
| GAPDH NM_001289726.1 | GTGCCGTTGAATTTGCCGTGA | 60 °C | 30 | 325 |
| ATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTGAAC |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.; Yun, S.; Lee, H.; Yang, J. Quercetin Mitigates Inflammatory Responses Induced by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Mouse Retinal Photoreceptor Cells through Suppression of Nuclear Factor Kappa B. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112497
Lee M, Yun S, Lee H, Yang J. Quercetin Mitigates Inflammatory Responses Induced by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Mouse Retinal Photoreceptor Cells through Suppression of Nuclear Factor Kappa B. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112497
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Minsup, Seohyeon Yun, Hyesook Lee, and Jaewook Yang. 2017. "Quercetin Mitigates Inflammatory Responses Induced by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Mouse Retinal Photoreceptor Cells through Suppression of Nuclear Factor Kappa B" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112497
APA StyleLee, M., Yun, S., Lee, H., & Yang, J. (2017). Quercetin Mitigates Inflammatory Responses Induced by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Mouse Retinal Photoreceptor Cells through Suppression of Nuclear Factor Kappa B. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112497





