The Analysis of A Frequent TMPRSS3 Allele Containing P.V116M and P.V291L in A Cis Configuration among Deaf Koreans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Phenotype
2.2. Variant Detection by Targeted Resequencing Data Analysis
2.3. In Silico Prediction of Pathogenic Potential
2.4. Assessment of Minor Allele Frequency
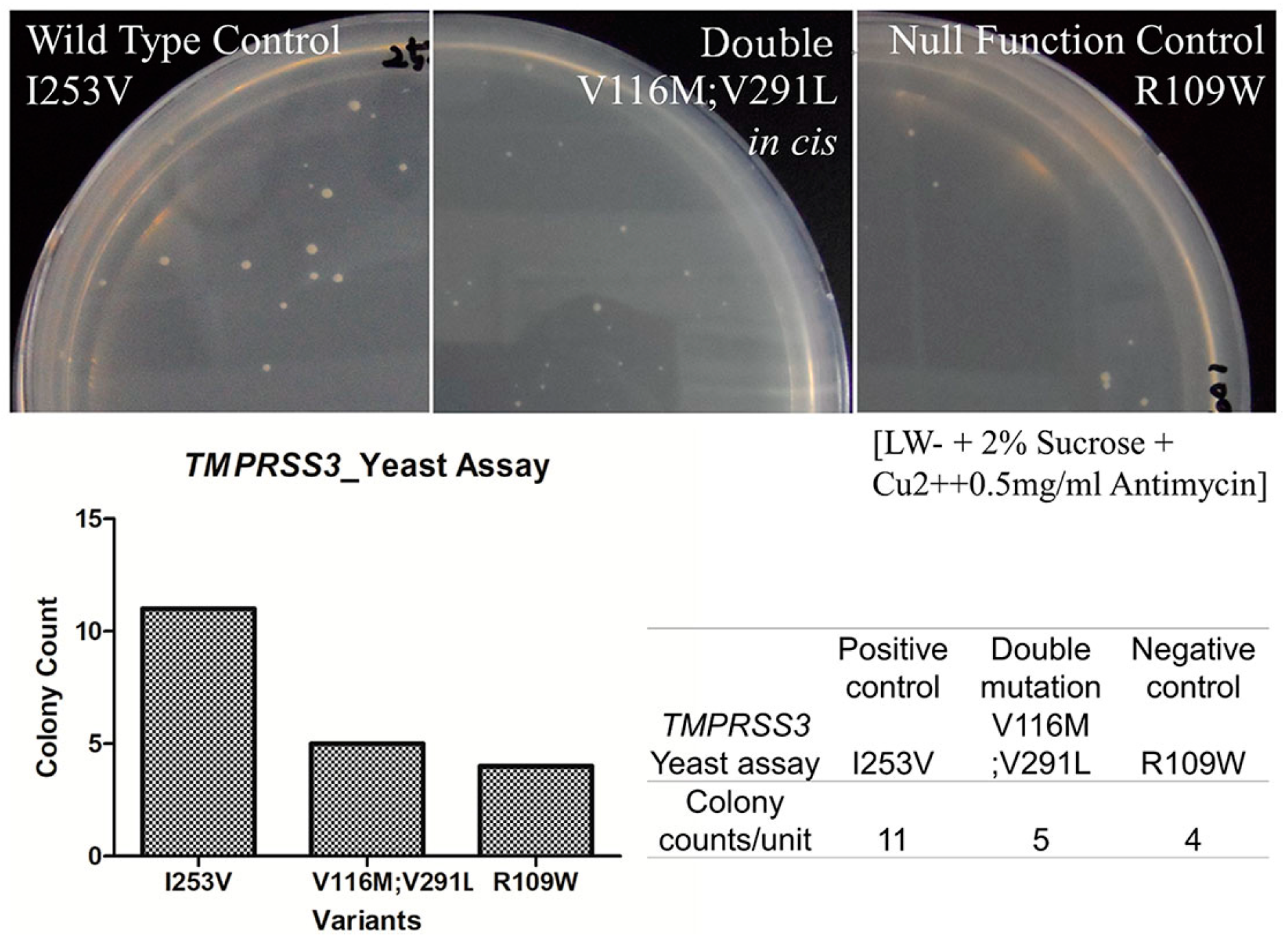
2.5. In Vitro Yeast Based Protease Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects and Clinical Findings
4.2. Molecular Genetic Test
4.3. Prediction of Pathogenic Potential Based on the Minor Allele Frequency of the Candidate Allele of TMPRSS3
4.4. Yeast Based Protease Assay
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramsebner, R.; Volker, R.; Lucas, T.; Hamader, G.; Weipoltshammer, K.; Baumgartner, W.D.; Wachtler, F.J.; Kirschhofer, K.; Frei, K. High incidence of gjb2 mutations during screening of newborns for hearing loss in austria. Ear Hear. 2007, 28, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgert, N.; Smith, R.J.; Van Camp, G. Forty-six genes causing nonsyndromic hearing impairment: Which ones should be analyzed in DNA diagnostics? Mutat. Res. 2009, 681, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masmoudi, S.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Schwede, T.; Ghorbel, A.M.; Gratri, M.; Pappasavas, M.P.; Drira, M.; Elgaied-Boulila, A.; Wattenhofer, M.; Rossier, C.; et al. Novel missense mutations of tmprss3 in two consanguineous tunisian families with non-syndromic autosomal recessive deafness. Hum. Mutat. 2001, 18, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guipponi, M.; Vuagniaux, G.; Wattenhofer, M.; Shibuya, K.; Vazquez, M.; Dougherty, L.; Scamuffa, N.; Guida, E.; Okui, M.; Rossier, C.; et al. The transmembrane serine protease (tmprss3) mutated in deafness dfnb8/10 activates the epithelial sodium channel (enac) in vitro. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 2829–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattenhofer, M.; Di Iorio, M.V.; Rabionet, R.; Dougherty, L.; Pampanos, A.; Schwede, T.; Montserrat-Sentis, B.; Arbones, M.L.; Iliades, T.; Pasquadibisceglie, A.; et al. Mutations in the tmprss3 gene are a rare cause of childhood nonsyndromic deafness in caucasian patients. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 80, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guipponi, M.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Scott, H.S. Tmprss3, a type ii transmembrane serine protease mutated in non-syndromic autosomal recessive deafness. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weegerink, N.J.; Schraders, M.; Oostrik, J.; Huygen, P.L.; Strom, T.M.; Granneman, S.; Pennings, R.J.; Venselaar, H.; Hoefsloot, L.H.; Elting, M.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation in dfnb8/10 families with tmprss3 mutations. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2011, 12, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Park, S.M.; Chang, S.O.; Chung, T.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, A.R.; Park, J.H.; Kim, V.; Park, W.Y.; Oh, S.H.; et al. A novel mutation of tmprss3 related to milder auditory phenotype in korean postlingual deafness: A possible future implication for a personalized auditory rehabilitation. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.K.; Chang, Q.; Park, H.J.; Jeon, C.J.; Lin, X.; Bok, J.; Kim, U.K. Functional evaluation of gjb2 variants in nonsyndromic hearing loss. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Kannan-Sundhari, A.; Vishwanath, S.; Qing, J.; Mittal, R.; Kameswaran, M.; Liu, X.Z. The genetic basis of nonsyndromic hearing loss in indian and pakistani populations. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2015, 19, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathy, A.; Pandey, N.; Srisailapathy, C.R.; Jalvi, R.; Malhotra, V.; Venkatappa, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Sharma, M.; Santhanam, R.; Chadha, S.; et al. Non-syndromic hearing impairment in india: High allelic heterogeneity among mutations in tmprss3, tmc1, ushic, cdh23 and tmie. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Baek, J.I.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, U.K.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.Y. Genetic analysis of tmprss3 gene in the korean population with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. Gene 2013, 532, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasquelle, L.; Scott, H.S.; Lenoir, M.; Wang, J.; Rebillard, G.; Gaboyard, S.; Venteo, S.; Francois, F.; Mausset-Bonnefont, A.L.; Antonarakis, S.E.; et al. Tmprss3, a transmembrane serine protease deficient in human dfnb8/10 deafness, is critical for cochlear hair cell survival at the onset of hearing. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17383–17397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagawa, M.; Nishio, S.Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Hattori, M.; Tsukada, K.; Moteki, H.; Kojima, H.; Usami, S. The patients associated with tmprss3 mutations are good candidates for electric acoustic stimulation. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2015, 124, 193S–204S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Huang, S.S.; Yuan, Y.Y.; Xu, J.C.; Gu, P.; Bai, D.; Kang, D.Y.; Han, M.Y.; Wang, G.J.; Zhang, M.G.; et al. Identification of TMPRSS3 as a Significant Contributor to Autosomal Recessive Hearing Loss in the Chinese Population. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Park, D.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, W.J. Pathogenic mutations but not polymorphisms in congenital and childhood onset autosomal recessive deafness disrupt the proteolytic activity of tmprss3. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.R.; Chang, M.Y.; Koo, J.W.; Oh, S.H.; Choi, B.Y. Novel tecta mutations identified in stable sensorineural hearing loss and their clinical implications. Audiol. Neurootol. 2015, 20, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Kim, A.R.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, B.Y. Identification of a novel truncation mutation of eya4 in moderate degree hearing loss by targeted exome sequencing. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, D.; Oh, M.; Sellamuthu, S.; Park, W.J. Detection of site-specific proteolysis in secretory pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 296, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
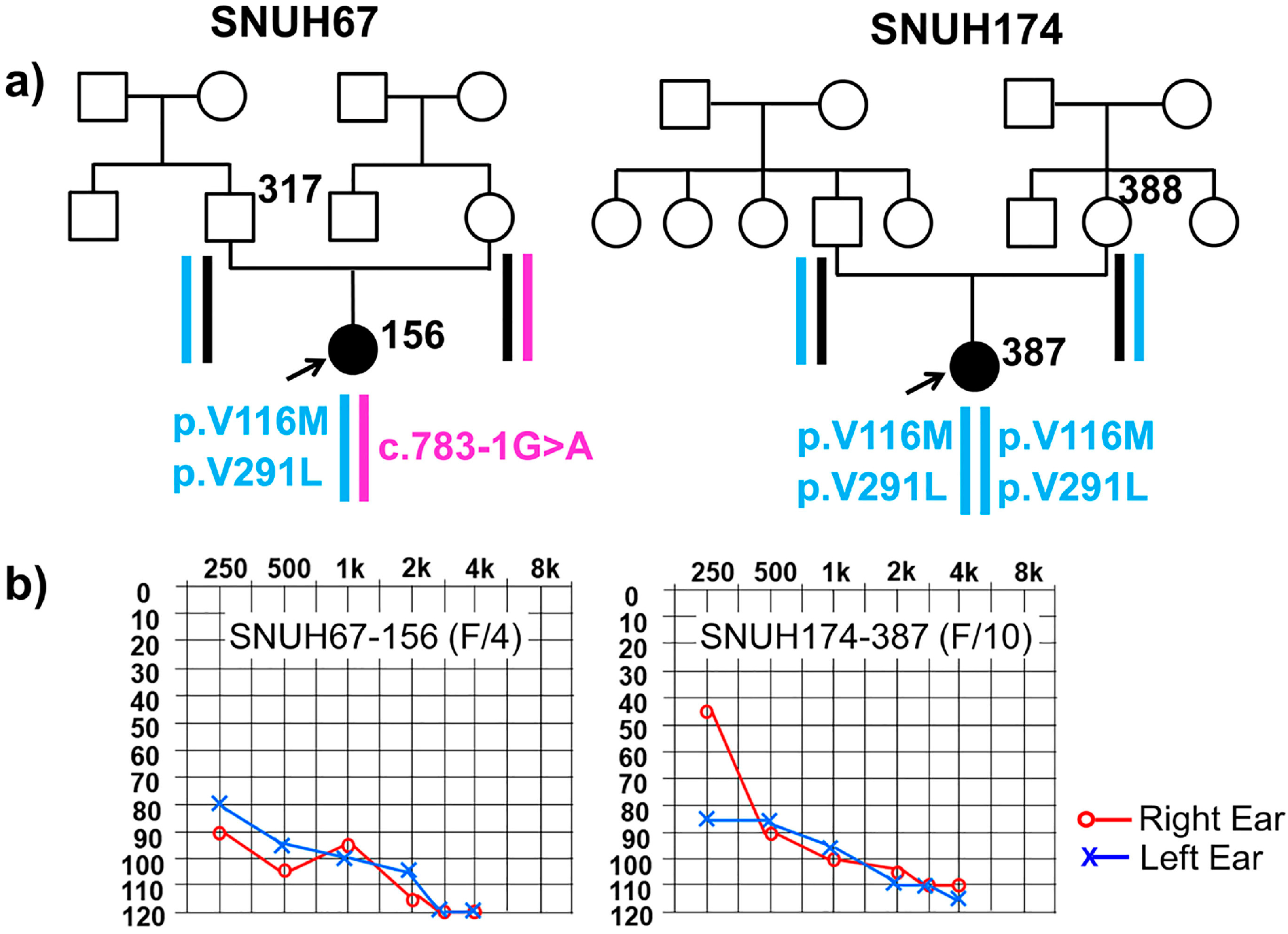
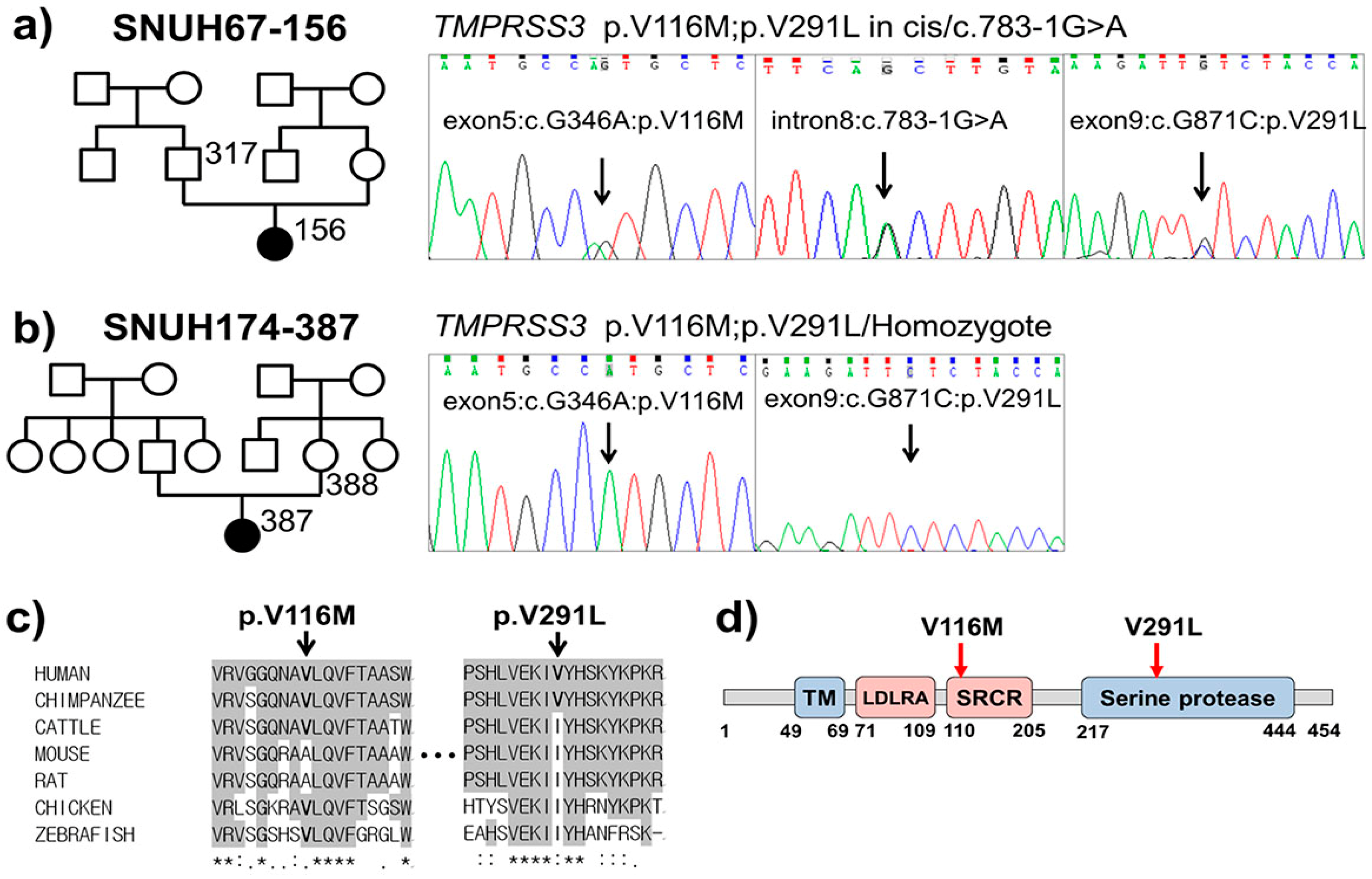
| Gene | Exon | Nucleotide Change | Amino Acid Change | Pathogenicity Prediction | Zygosity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIFT | ||||||
| SNUH67-156 | HSPG2 | exon85 | c.G11602A | p.V3868M | Tolerated | Hetero |
| KCNQ4 | exon1 | c.T140C | p.L47P | Tolerated | Hetero | |
| TMIE | exon4 | c.391_393delAAG | p.K131del | NA | Hetero | |
| GPR98 | exon9 | c.A1567G | p.M523V | Tolerated | Hetero | |
| LAMA2 | exon33 | c.A4772G | p.Q1591R | Tolerated | Hetero | |
| HOXA1 | exon1 | c.215_223delATCACCACC | p.H72_H74del | NA | Hetero | |
| TNC | exon3 | c.G1823A | p.R608H | Tolerated | Hetero | |
| POU4F1 | exon2 | c.486_487insGGC | p.P163delinsGP | NA | Hetero | |
| TMPRSS3* | exon9 | c.G871C | p.V291L | NA | Hetero | |
| TMPRSS3* | intron9 | c.783-1G>A | NA | NA | Hetero | |
| TMPRSS3* | exon5 | c.G346A | p.V116M | NA | Hetero | |
| TRIOBP | exon7 | c.1613_1615delTGT | p.L538_S539delinsP | NA | Hetero | |
| SNUH174-387 | COL9A2 | exon30 | c.G1741A | p.V581I | Tolerated | Hetero |
| FGFR3 | exon3 | c.G193A | p.G65R | Tolerated | Hetero | |
| COL11A2 | exon5 | c.G688T | p.G230W | Damaging | Hetero | |
| TPRN | exon1 | c.C761T | p.S254L | Tolerated | Hetero | |
| CDH23 | exon40 | c.G5411A | p.R1804Q | Tolerated | Hetero | |
| KCNQ1 | exon16 | c.G1927A | p.G643S | Tolerated | Hetero | |
| MYO1C | exon28 | c.G2785A | p.D929N | Tolerated | Hetero | |
| TMPRSS3* | exon9 | c.G871C | p.V291L | NA | Homo | |
| TMPRSS3* | exon5 | c.G346A | p.V116M | NA | Homo |
| Exon/Intron | Nucleotide Change | Amino Acid Change | Domain | Minor Allele Frequency | Phenotype | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCSC | 1000G | KRGDB | SGI | ||||||
| Exon5 | c.G346A | p.V116M | SRCR | 0.0015 | 0 | 0 | 0 | † Profound | [10,11] |
| Intron8 | c.783-1G>A | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Likely pathogenic | This Study |
| Exon9 | c.G871C | p.V291L | Serine Protease | 0.00005 | 0.0006 | 0.0008 | 0 | Uncertain | [12] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, A.R.; Chung, J.; Kim, N.K.D.; Lee, C.; Park, W.-Y.; Oh, D.-Y.; Choi, B.Y. The Analysis of A Frequent TMPRSS3 Allele Containing P.V116M and P.V291L in A Cis Configuration among Deaf Koreans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112246
Kim AR, Chung J, Kim NKD, Lee C, Park W-Y, Oh D-Y, Choi BY. The Analysis of A Frequent TMPRSS3 Allele Containing P.V116M and P.V291L in A Cis Configuration among Deaf Koreans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112246
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ah Reum, Juyong Chung, Nayoung K. D. Kim, Chung Lee, Woong-Yang Park, Doo-Yi Oh, and Byung Yoon Choi. 2017. "The Analysis of A Frequent TMPRSS3 Allele Containing P.V116M and P.V291L in A Cis Configuration among Deaf Koreans" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112246
APA StyleKim, A. R., Chung, J., Kim, N. K. D., Lee, C., Park, W.-Y., Oh, D.-Y., & Choi, B. Y. (2017). The Analysis of A Frequent TMPRSS3 Allele Containing P.V116M and P.V291L in A Cis Configuration among Deaf Koreans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112246






