Flavonoids as Cytokine Modulators: A Possible Therapy for Inflammation-Related Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
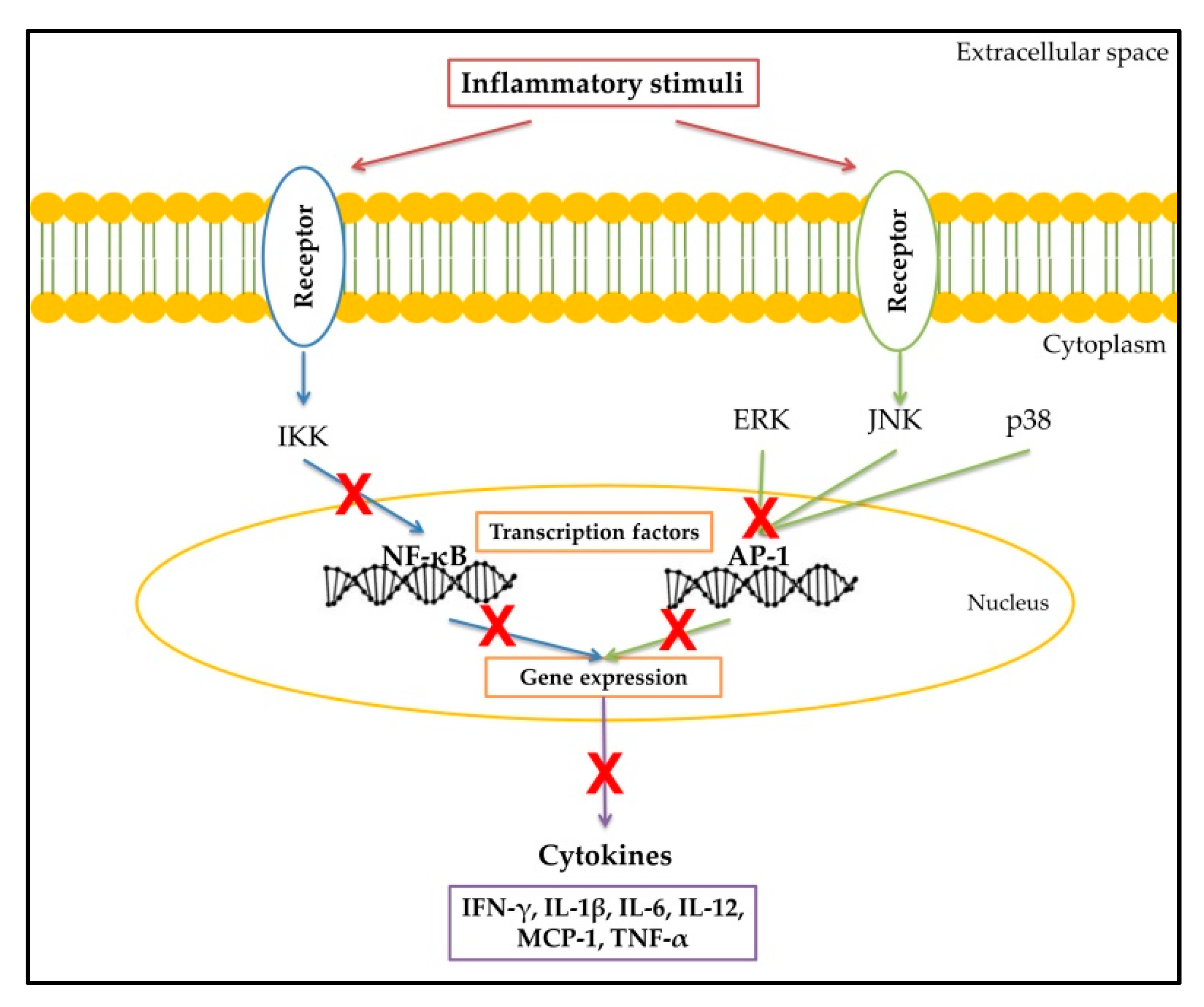
2. Inflammatory Response
3. Cytokines
Cytokines as Biomarkes in Inflammation-Related Diseases
4. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
4.1. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
4.2. Cytokine Receptor Inhibitors
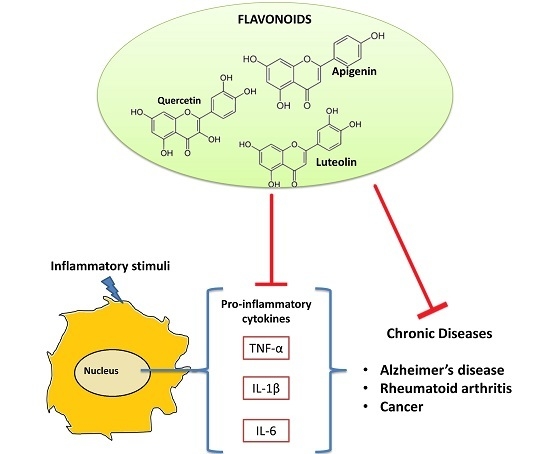
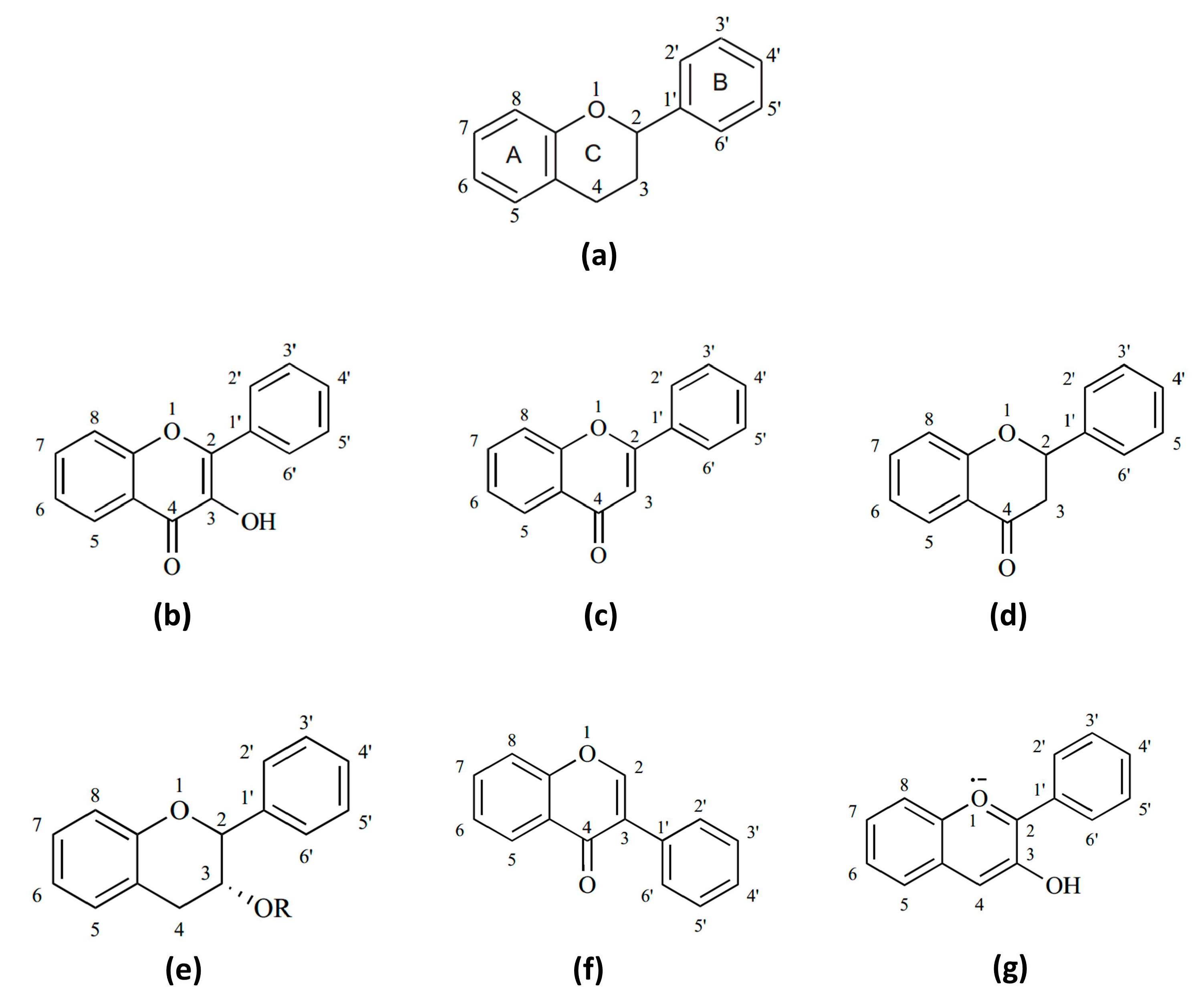
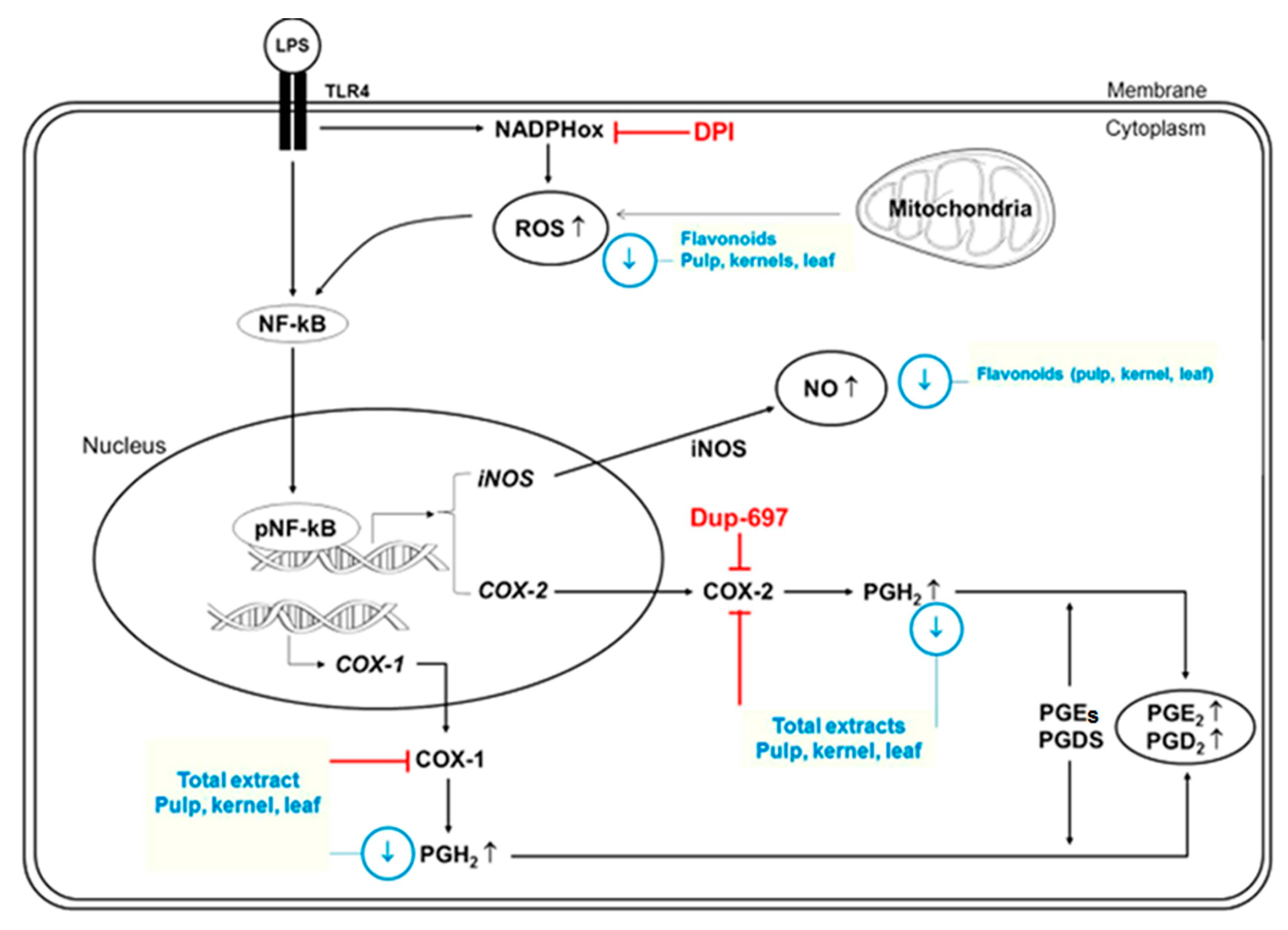
5. Flavonoids and Their Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Flavonoids as Anti-Cytokine Agents
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP-1 | Activating protein-1 |
| bDMARD | Biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs |
| COX | Cyclooxygenase |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases |
| IL | Interleukin |
| iNOS | Nitric oxide synthase inducible |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinases |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| NSAIDs | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Agati, G.; Azzarello, E.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Flavonoids as antioxidants in plants: Location and functional significance. Plant Sci. 2012, 196, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, P.V.A.; Liu, D.; Gilbert, E.R. Recent advances in understanding the anti-diabetic actions of dietary flavonoids. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Wei, H.; He, B. Dietary flavonoids intake and the risk of coronary heart disease: A dose-response meta-analysis of 15 prospective studies. Thromb. Res. 2015, 135, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturelli, S.; Burkard, M.; Biendl, M.; Lauer, U.M.; Frank, J.; Busch, C. Prenylated chalcones and flavonoids for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Nutrition 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunon, M.; Garcia-Mediavilla, M.; Sanchez-Campos, S.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J. Potential of flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents: Modulation of pro-inflammatory gene expression and signal transduction pathways. Curr. Drug Metab. 2009, 10, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, D.; Freitas, M.; Lima, J.L.F.C.; Fernandes, E. Proinflammatory pathways: The modulation by flavonoids. Med. Res. Rev. 2015, 35, 877–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Tuñón, M.J. Fruit polyphenols, immunity and inflammation. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, S15–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, E.; Kandaswami, C.; Theoharides, T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 673–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baecklund, E.; Iliadou, A.; Askling, J.; Ekbom, A.; Backlin, C.; Granath, F.; Catrina, A.I.; Rosenquist, R.; Feltelius, N.; Sundström, C. Association of chronic inflammation, not its treatment, with increased lymphoma risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, S.; Tsoukas, A.; Robertson, J.; McInnes, I. Cytokines as therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 280–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, N.T.; Weil, Z.M.; Nelson, R.J. Inflammation: Mechanisms, costs, and natural variation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Abbas, A.K.; Fausto, N.; Mitchell, R.N. Robbins Basic Pathology; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadephia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, G.; Navabi, S.S.; Al-Shukaili, A.; Seyedzadeh, M.H.; Yazdani, R.; Mirshafiey, A. The role of inflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of alzheimer’s disease. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2015, 15, e305–e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, K.L.; Kono, H. The inflammatory response to cell death. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2008, 3, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.; Hughes, A.L. Molecular evolution of the NF-κB signaling system. Immunogenetics 2002, 53, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Proell, M.; Riedl, S.J.; Fritz, J.H.; Rojas, A.M.; Schwarzenbacher, R. The nod-like receptor (NLR) family: A tale of similarities and differences. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaulian, E.; Karin, M. AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene 2001, 20, p2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzustewicz, E.; Bryl, E. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis—Practical and potential application of cytokines as biomarkers and targets of personalized therapy. Cytokine 2015, 76, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.P.; Singh, N.P.; Murphy, E.A.; Price, R.L.; Fayad, R.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Chemokine and cytokine levels in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Cytokine 2016, 77, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, V.S.; Huang, R.-Y.; Chen, L.-P.; Chen, Z.-S.; Fu, L.; Huang, R.-P. Cytokines in cancer drug resistance: Cues to new therapeutic strategies. BBA—Rev. Cancer 2016, 1865, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Boyle, D.; Manning, A.; Firestein, G. AP-1 and NF-κB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity 1998, 28, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, C.-W.; Downey, G.P. Chapter 1—Inflammation. In Clinical Critical Care Medicine; Albert, R.K., Slutsky, A.S., Ranieri, V.M., Takala, J., Torres, A., Eds.; Mosby: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Feghali, C.A.; Wright, T.M. Cytokines in acute and chronic inflammation. Front. Biosci. 1997, 2, d12–d26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belkhelfa, M.; Rafa, H.; Medjeber, O.; Arroul-Lammali, A.; Behairi, N.; Abada-Bendib, M.; Makrelouf, M.; Belarbi, S.; Masmoudi, A.N.; Tazir, M.; et al. IFN-γ and TNF-α are involved during alzheimer disease progression and correlate with nitric oxide production: A study in algerian patients. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.Y.; Cesari, M.; Anton, S.; Marzetti, E.; Giovannini, S.; Seo, A.Y.; Carter, C.; Yu, B.P.; Leeuwenburgh, C. Molecular inflammation: Underpinnings of aging and age-related diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2009, 8, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Han, S.B.; Nam, S.-Y.; Oh, K.-W.; Hong, J.T. Inflammation and alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 1539–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.; Lue, L.-F. Microglial chemotaxis, activation, and phagocytosis of amyloid β-peptide as linked phenomena in alzheimer‘s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2001, 39, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamarron, B.F.; Chen, W. Dual roles of immune cells and their factors in cancer development and progression. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerkvaleekul, B.; Soponkanaporn, S.; Vilaiyuk, S. The correlations of serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels and serum soluble IL-6 receptor levels with disease activity in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients with and without tocilizumab treatment. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2014, 12, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Huang, J.; Zhong, H.; Shen, N.; Faggioni, R.; Fung, M.; Yao, Y. Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilopoulos, Y.; Sourli, F.; Zafiriou, E.; Klimi, E.; Ioannou, M.; Mamuris, Z.; Simos, G.; Koukoulis, G.; Roussaki-Schulze, A. High serum levels of HIF-1α in psoriatic patients correlate with an over-expression of IL-6. Cytokine 2013, 62, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, J.; Ohnesorge, N.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 trans-signalling in chronic inflammation and cancer. Scand. J. Immunol. 2006, 63, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blay, J.-Y.; Negrier, S.; Combaret, V.; Attali, S.; Goillot, E.; Merrouche, Y.; Mercatello, A.; Ravault, A.; Tourani, J.-M.; Moskovtchenko, J.-F. Serum level of interleukin 6 as a prognosis factor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costes, V.; Liautard, J.; Picot, M.C.; Robert, M.; Lequeux, N.; Brochier, J.; Baldet, P.; Rossi, J.F. Expression of the interleukin 6 receptor in primary renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 1997, 50, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Therapeutic targeting of the interleukin-6 receptor. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atreya, R.; Mudter, J.; Finotto, S.; Müllberg, J.; Jostock, T.; Wirtz, S.; Schütz, M.; Bartsch, B.; Holtmann, M.; Becker, C. Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation: Evidence in crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, H.; Arai, T.; Kondo, H.; Tanno, E.; Haga, C.; Ikeda, K. Cell mediators of inflammation in the alzheimer disease brain. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2000, 14, S47–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpathy, A.; Ravindra, S.; Thakur, S.; Kulkarni, S.; Porwal, A.; Panda, S. Serum interleukin-1β in subjects with abdominal obesity and periodontitis. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N. Anti-TNFα therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: What have we learned? Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazawa, M.; Yamasaki, T.R.; Laferla, F.M. Microglia as a potential bridge between the amyloid β-peptide and Tau. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1035, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandilands, E.A.; Bateman, D.N. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicine 2016, 44, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, T. Epidemiology and pharmacoeconomic implications of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated gastrointestinal toxicity. Rheumatology 2000, 39, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, J.F.; Romero-Sandoval, E.A.; Gaitan, G.; Mazario, J. Antinociception and the new cox inhibitors: Research approaches and clinical perspectives. CNS Drug Rev. 2003, 9, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warden, S.J. Prophylactic use of nsaids by athletes: A risk/benefit assessment. Physician Sports Med. 2010, 38, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.; Rubin, G.; Berenbaum, F.; Scheiman, J. Gastrointestinal and cardiovascular risks of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanas, A.; García-Rodríguez, L.-A.; Arroyo, M.-T.; Gomollón, F.; Feu, F.; González-Pérez, A.; Zapata, E.; Bástida, G.; Rodrigo, L.; Santolaria, S. Risk of upper gastrointestinal ulcer bleeding associated with selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors, traditional non-aspirin non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, aspirin and combinations. Gut 2006, 55, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arend, W.P. The mode of action of cytokine inhibitors. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 65, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- McGeehan, G.M.; Becherer, J.D.; Bast, R.C.; Boyer, C.M.; Champion, B.; Connolly, K.M.; Conway, J.G.; Furdon, P.; Karp, S.; Kidao, S. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor-α processing by a metalloproteinase inhibitor. Nature 1994, 370, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornberry, N.A.; Bull, H.G.; Calaycay, J.R.; Chapman, K.T.; Howard, A.D.; Kostura, M.J.; Miller, D.K.; Molineaux, S.M.; Weidner, J.R.; Aunins, J. A novel heterodimeric cysteine protease is required for interleukin-1βprocessing in monocytes. Nature 1992, 356, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, G.; Walter, M.R. Cytokine-receptor interactions as drug targets. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, P.; Keystone, E.; Tony, H.; Cantagrel, A.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Sanchez, A.; Alecock, E.; Lee, J.; Kremer, J. IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: Results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, I.-R.M.R.A. The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: A mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet 2012, 379, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Sebba, A. Tocilizumab: The first interleukin-6-receptor inhibitor. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2008, 65, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, V.; Dhillon, S.; Plosker, G.L. Tocilizumab: A review of its use in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs 2009, 69, 609–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, S.; Liu, X.; Fang, L.; Chen, X.; Guo, T.; Zhang, J. The cytokine milieu in the interplay of pathogenic Th1/Th17 cells and regulatory T cells in autoimmune disease. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, M.C.; McKay, J.D.; Nasonov, E.L.; Mysler, E.F.; da Silva, N.A.; Alecock, E.; Woodworth, T.; Gomez-Reino, J.J. Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: The tocilizumab in combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2968–2980. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- So, A.; de Smedt, T.; Revaz, S.; Tschopp, J. A pilot study of IL-1 inhibition by anakinra in acute gout. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2007, 9, R28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, K.A.; Langley, R.G.; Lebwohl, M.; Krueger, G.G.; Szapary, P.; Yeilding, N.; Guzzo, C.; Hsu, M.-C.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriasis: 52-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (phoenix 2). Lancet 2008, 371, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, J.; Perry, C.M. Anakinra: A review of its use in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Biodrugs 2004, 19, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, L. Mixed results with modulation of Th-17 cells in human autoimmune diseases. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S.; Lyseng-Williamson, K.A.; Scott, L.J. Etanercept: A review of its use in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs 2007, 67, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stübgen, J.P. Tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists and neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2008, 37, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maini, R.N.; Breedveld, F.C.; Kalden, J.R.; Smolen, J.S.; Furst, D.; Weisman, M.H.; St Clair, E.W.; Keenan, G.F.; van der Heijde, D.; Marsters, P.A. Sustained improvement over two years in physical function, structural damage, and signs and symptoms among patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab and methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R. Humanized anti-CD25 antibody treatment with daclizumab in multiple sclerosis. Neurodegener. Dis. 2008, 5, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrussa, E.; Braidot, E.; Zancani, M.; Peresson, C.; Bertolini, A.; Patui, S.; Vianello, A. Plant flavonoids—Biosynthesis, transport and involvement in stress responses. Inter. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Yonekura-Sakakibara, K.; Nakabayashi, R.; Higashi, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R. The flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in arabidopsis: Structural and genetic diversity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 72, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.K.; Weng, M.S. Flavonoids as Nutraceuticals. In The Science Of Flavonoids; Grotewold, E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Lazaro, M. Distribution and biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroon, J.C.; Bost, J.W.; Maroon, A. Natural anti-inflammatory agents for pain relief. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2010, 1, 80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.; Bang, W.Y.; Schreckinger, E.; Andarwulan, N.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L. Protective role of ternatin anthocyanins and quercetin glycosides from butterfly pea (clitoria ternatea leguminosae) blue flower petals against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in macrophage cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6355–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambriz-Perez, D.L.; Bang, W.Y.; Nair, V.; Angulo-Escalante, M.A.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Heredia, J.B. Protective role of flavonoids and lipophilic compounds from jatropha platyphylla on the suppression of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in macrophage cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-López, N.; Nair, V.; Bang, W.Y.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Heredia, J.B. Protective role of terpenes and polyphenols from three species of oregano (lippia graveolens, lippia palmeri and hedeoma patens) on the suppression of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in raw 264.7 macrophage cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 187, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.; Yang, W.S.; Yang, Y.; Nam, G.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, D.H.; Noh, H.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, T.W.; Sung, G.-H.; et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory effect of rhodomyrtus tomentosa methanol extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.K.; Lee, P.; Park, J.A.; Oh, H.R.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Lee, E.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, K.R.; Kim, S.Y. Apigenin inhibits the production of NO and PGE2 in microglia and inhibits neuronal cell death in a middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced focal ischemia mice model. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince Vijeya Singh, J.; Selvendiran, K.; Mumtaz Banu, S.; Padmavathi, R.; Sakthisekaran, D. Protective role of apigenin on the status of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense against hepatocarcinogenesis in wistar albino rats. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrvová, N.; Škandík, M.; Kuniaková, M.; Račková, L. Modulation of BV-2 microglia functions by novel quercetin pivaloyl ester. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 90, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramyaa, P.; Krishnaswamy, R.; Padma, V.V. Quercetin modulates OTA-induced oxidative stress and redox signalling in HepG2 cells—Up-regulation of Nrf2 expression and down regulation of Nf-κB and COX-2. BBA—Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-W.; Lin, H.-W.; Yang, D.-J.; Chen, S.-Y.; Tseng, J.-K.; Chang, T.-J.; Chang, Y.-Y. Luteolin inhibits viral-induced inflammatory response in RAW 264.7 cells via suppression of STAT1/3 dependent NF-κB and activation of HO-1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, C.; Varì, R.; Scazzocchio, B.; Di Benedetto, R.; Filesi, C.; Masella, R. Polyphenols, intracellular signalling and inflammation. Annali-istituto Super. di Sanita 2007, 43, 394. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Serafini, M.; Peluso, I.; Raguzzini, A. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Lafuente, A.; Guillamón, E.; Villares, A.; Rostagno, M.; Martínez, J. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents: Implications in cancer and cardiovascular disease. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, M.; Hobiger, S.; Jungbauer, A. Anti-inflammatory activity of extracts from fruits, herbs and spices. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.S.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, S.N.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, E.C. Anti-inflammatory effects of apigenin on nicotine- and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human periodontal ligament cells via heme oxygenase-1. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comalada, M.; Ballester, I.; Bailón, E.; Sierra, S.; Xaus, J.; Gálvez, J.; de Medina, F.S.; Zarzuelo, A. Inhibition of pro-inflammatory markers in primary bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by naturally occurring flavonoids: Analysis of the structure–activity relationship. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.-K.; Ou, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Pan, H.-C.; Song, P.-J.; Raung, S.-L.; Lai, C.-Y.; Liao, S.-L.; Lu, H.-C.; Chen, C.-J. Luteolin inhibits cytokine expression in endotoxin/cytokine-stimulated microglia. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, W.; Yun, J.-M. Luteolin inhibits hyperglycemia-induced proinflammatory cytokine production and its epigenetic mechanism in human monocytes. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-L.; Fang, S.-C.; Yen, G.-C. Anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds isolated from the flowers of nymphaea mexicana zucc. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, D.; Freitas, M.; Tomé, S.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Laufer, S.; Lima, J.L.F.C.; Fernandes, E. Flavonoids inhibit COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes and cytokine/chemokine production in human whole blood. Inflammation 2015, 38, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egert, S.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Seiberl, J.; Kürbitz, C.; Settler, U.; Plachta-Danielzik, S.; Wagner, A.E.; Frank, J.; Schrezenmeir, J.; Rimbach, G.; et al. Quercetin reduces systolic blood pressure and plasma oxidised low-density lipoprotein concentrations in overweight subjects with a high-cardiovascular disease risk phenotype: A double-blinded, placebo-controlled cross-over study. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Huang, C.; Hu, G.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Y. Therapeutic effects of quercetin on early inflammation in hypertriglyceridemia-related acute pancreatitis and its mechanism. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Su, J.; Guo, B.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Liang, G. Apigenin protects blood-brain barrier and ameliorates early brain injury by inhibiting tlr4-mediated inflammatory pathway in subarachnoid hemorrhage rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-H.; Lee, S.; Oh, J.-M.; Lee, M.-S.; Yoon, K.-H.; Park, B.H.; Kim, J.W.; Song, H.; Kim, S.-H. Anti-inflammatory activity of fisetin in human mast cells (HMC-1). Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 55, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kwon, T.H.; Song, H.-H.; Oh, S.-R.; Yoon, D.Y. Luteolin 8-C-β-fucopyranoside downregulates IL-6 expression by inhibiting mapks and the NF-κB signaling pathway in human monocytic cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.-J.; Luo, S.-F.; Lai, J.-H. Biological effects of interleukin-6: Clinical applications in autoimmune diseases and cancers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 97, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, M.; Kawamata, H.; Kawai, K.; Oyasu, R. Enhancement of transformation in vitro of a nontumorigenic rat urothelial cell line by interleukin 6. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 4581–4585. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qu, D.; Liu, J.; Lau, C.W.; Huang, Y. Il-6 in diabetes and cardiovascular complications. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3595–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; de Haar, C.; Chen, M.; Deuring, J.; Gerrits, M.M.; Smits, R.; Xia, B.; Kuipers, E.J.; van der Woude, C.J. Disease-related expression of the IL6/STAT3/SOCS3 signalling pathway in ulcerative colitis and ulcerative colitis-related carcinogenesis. Gut 2010, 59, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semerano, L.; Thiolat, A.; Minichiello, E.; Clavel, G.; Bessis, N.; Boissier, M.-C. Targeting IL-6 for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Phase II investigational drugs. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2014, 23, 979–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, S.; Niu, J.; Schmidt, C.; Sclabas, G.M.; Peng, B.; Uwagawa, T.; Li, Z.; Evans, D.B.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Chiao, P.J. NF-κB and AP-1 connection: Mechanism of NF-κB-dependent regulation of AP-1 activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7806–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, A.; Yang, J. The role of NF-κB in modulating antitumor immunity. OncoImmunology 2016, 5, e1005522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; He, H.; Jonsson, P.; Sinha, I.; Zhao, C.; Dahlman-Wright, K. AP-1 is a key regulator of proinflammatory cytokine tnfα-mediated triple-negative breast cancer progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker, S.R.; Sreenivas, P.; Babu, M.S.; Karunagaran, D.; Kartha, C.C. Quercetin attenuates monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene expression in glucose primed aortic endothelial cells through NF-κB and AP-1. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.M.; Lee, Y.S. Luteolin suppresses IL-1β-induced cytokines and MMPs production via p38 MAPK, JNK, NF-κB and AP-1 activation in human synovial sarcoma cell line, SW982. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2607–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Hsu, J.-W.; Gidwani, M.; Hughes, A.D.; King, M.R. Phenotypic switch in blood: Effects of pro-inflammatory cytokines on breast cancer cell aggregation and adhesion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riegsecker, S.; Wiczynski, D.; Kaplan, M.J.; Ahmed, S. Potential benefits of green tea polyphenol EGCG in the prevention and treatment of vascular inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, J.; Toledo-Arruda, A.; Mernak, M.; Barrosa, K.; Martins, M.; Tibério, I.; Prado, C. Structure-activity association of flavonoids in lung diseases. Molecules 2014, 19, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, R.; Jachak, S.M. Recent developments in anti-inflammatory natural products. Med. Res. Rev. 2009, 29, 767–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, V.; Figueirinha, A.; Costa, G.; Liberal, J.; Lopes, M.C.; García-Rodríguez, C.; Geraldes, C.F.G.C.; Cruz, M.T.; Batista, M.T. Chemical characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of luteolin glycosides isolated from lemongrass. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Therapeutic Agent | Mode of Action | Cytokine Targeted | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tocilizumab | Anti-IL-6 receptor | IL-6 | Oldfield, Dhillon and Plosker [59] |
| Ustekinumab | Anti-P40 | IL-12/IL-23 | Papp, et al. [63] |
| Anakinra | IL-1β antagonist | IL-1β | Waugh and Perry [64] |
| Amgen | Anti-IL-17 | TNF-α | Steinman [65] |
| Etanercept | Soluble receptor | TNF-α | [66,67] |
| Infliximab | Anti-TNF-α | TNF-α | [67,68] |
| Dacliqumab | Anti-IL-2 receptor | IL-2 | Martin [69] |
| Flavonoid | Effect | Molecular Mechanism Involved | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apigenin | Reduction of NO and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production. Inhibition of IL-6, IL-1β, IL-12 and TNF-α secretion | Inhibition in the iNOS, COX-2, IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α gene expression. Amelioration of p38-MAPK, JNK and ERK phosphorylation | [79,80,87,88,89,96] |
| Fisetin | Decreased TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 expression and production | Inhibited p38, JNK and ERK phosphorylation. Inhibited nuclear translocation of NF-κB | [97] |
| Luteolin | Reduction of NO, IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-α, IL-1β and IFN-γ production. Stimulation of IL-10 secretion | Reduction of iNOS and COX-2 expression. Inhibition of the JNK and p38 activation. Diminished NF-κB and AP-1 activation | [83,87,89,90,91,93,108] |
| Naringenin | Diminished NO, MCP-1, IL-6 and TNF-α secretion | Inhibited iNOS, COX-2 and ERK expression | [87,92] |
| Quercetin | Inhibition of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and interferon (IFN)-γ production. Increased IL-10 secretion | Suppression in the COX-2, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and NF-κB expression. Inhibition of the NF-κB and AP-1 activity | [81,82,87,89,93,94,95,107] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leyva-López, N.; Gutierrez-Grijalva, E.P.; Ambriz-Perez, D.L.; Heredia, J.B. Flavonoids as Cytokine Modulators: A Possible Therapy for Inflammation-Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060921
Leyva-López N, Gutierrez-Grijalva EP, Ambriz-Perez DL, Heredia JB. Flavonoids as Cytokine Modulators: A Possible Therapy for Inflammation-Related Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(6):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060921
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeyva-López, Nayely, Erick P. Gutierrez-Grijalva, Dulce L. Ambriz-Perez, and J. Basilio Heredia. 2016. "Flavonoids as Cytokine Modulators: A Possible Therapy for Inflammation-Related Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 6: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060921
APA StyleLeyva-López, N., Gutierrez-Grijalva, E. P., Ambriz-Perez, D. L., & Heredia, J. B. (2016). Flavonoids as Cytokine Modulators: A Possible Therapy for Inflammation-Related Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(6), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060921