Thymoquinone Modulates Blood Coagulation in Vitro via Its Effects on Inflammatory and Coagulation Pathways
Abstract
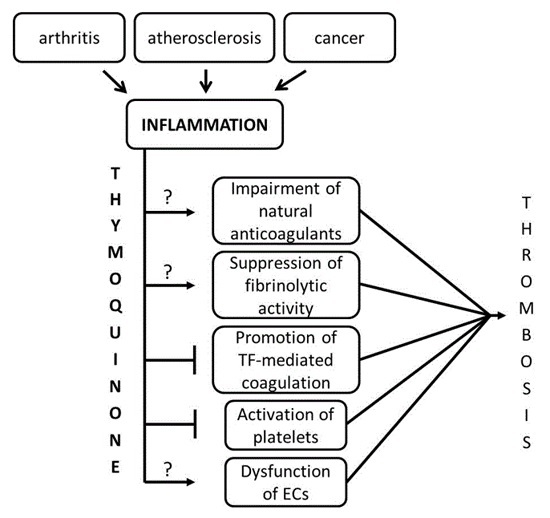
:1. Introduction
2. Results
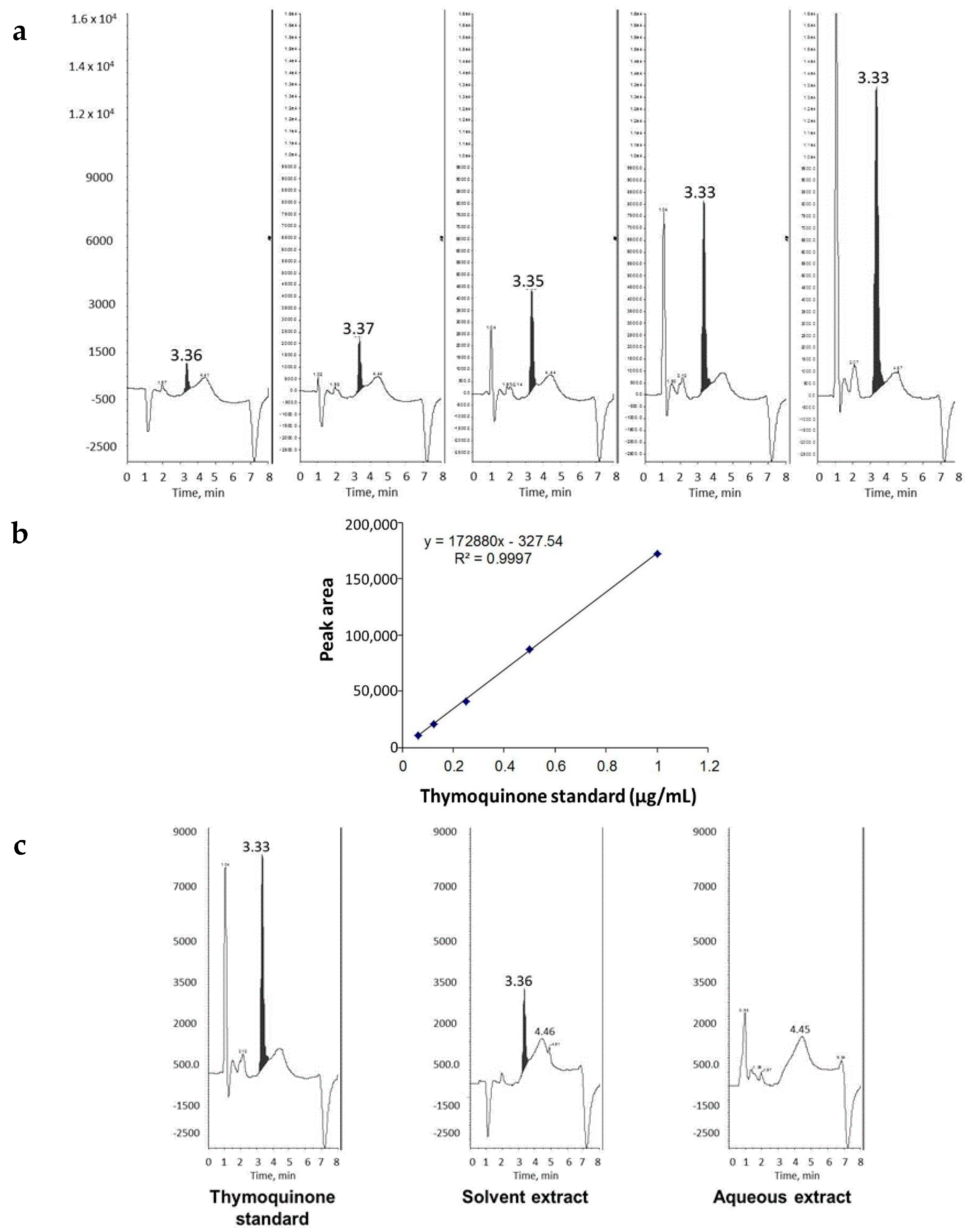
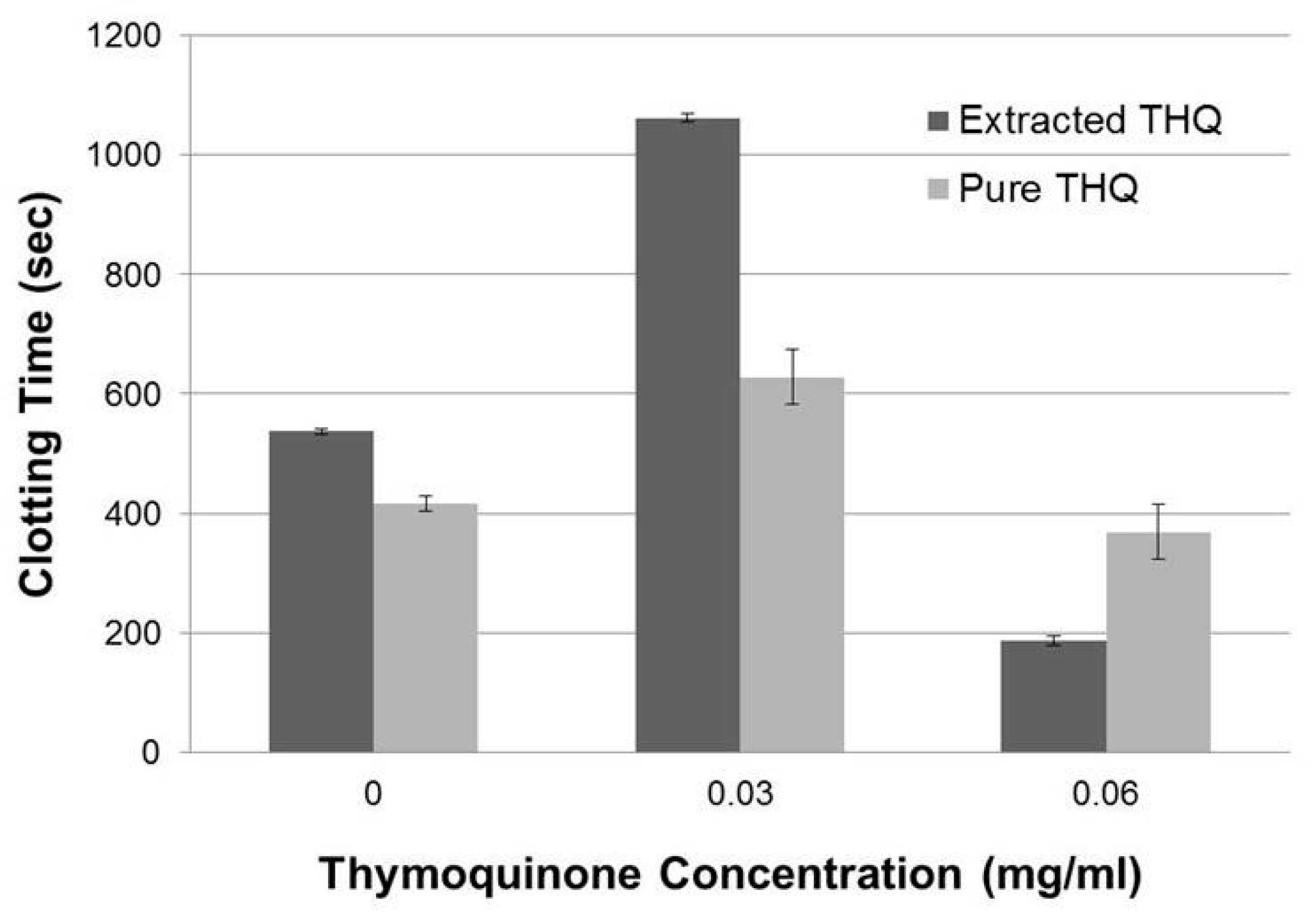
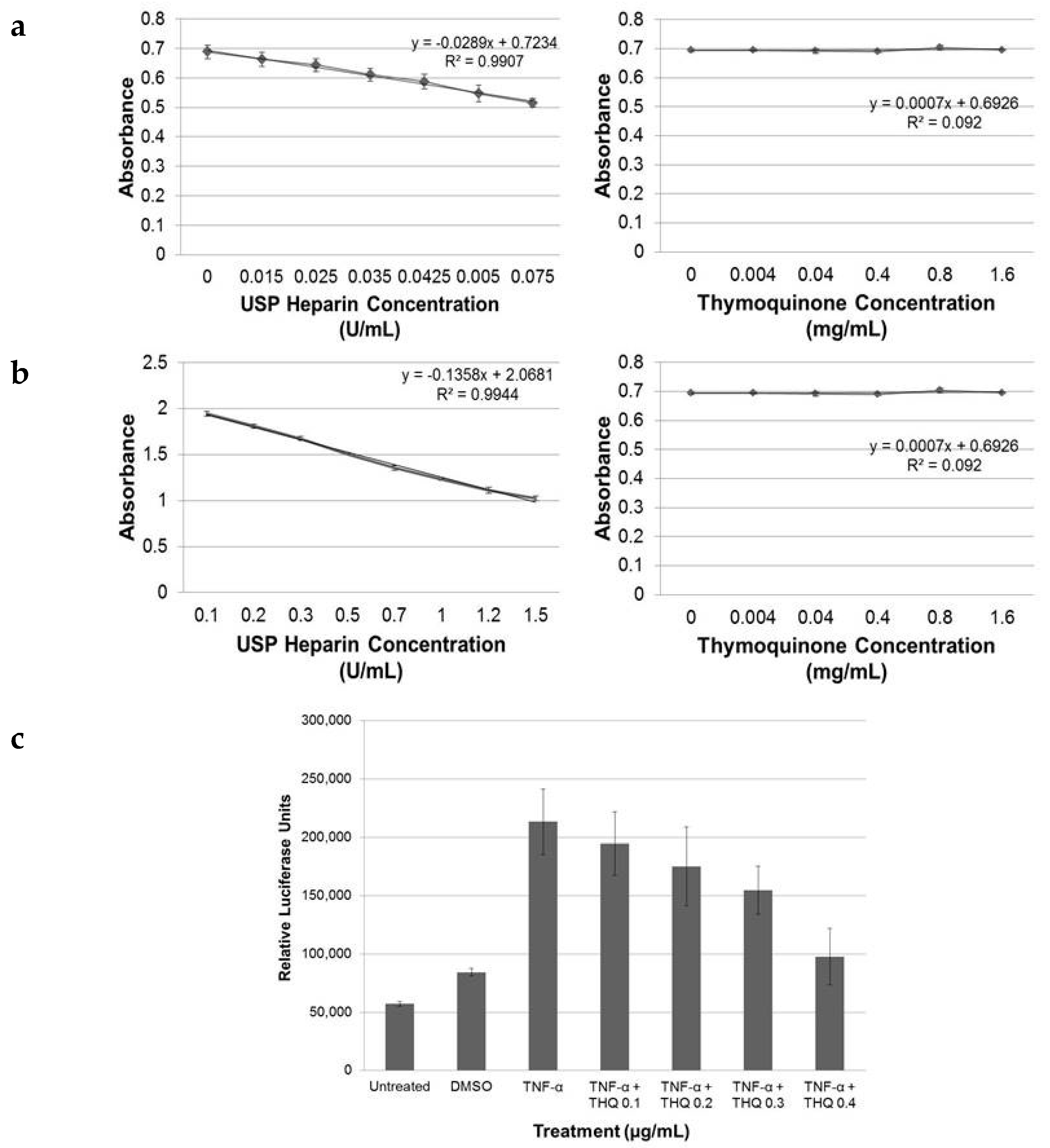
2.1. THQ in Black Seed Oil Extract Exhibits Anticoagulant Activity
2.2. Pure THQ Modulates Coagulation in Normal Blood and Plasma
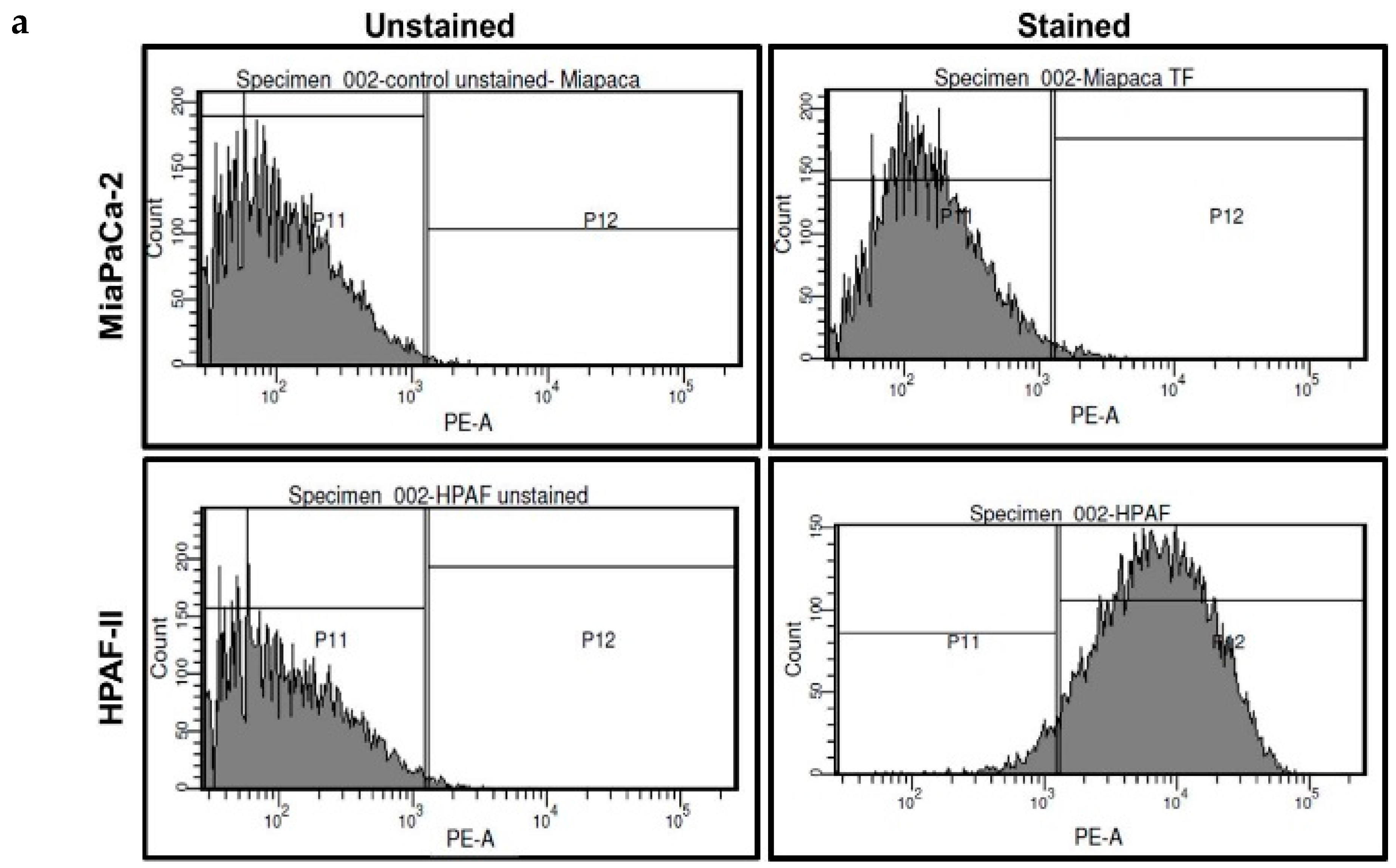
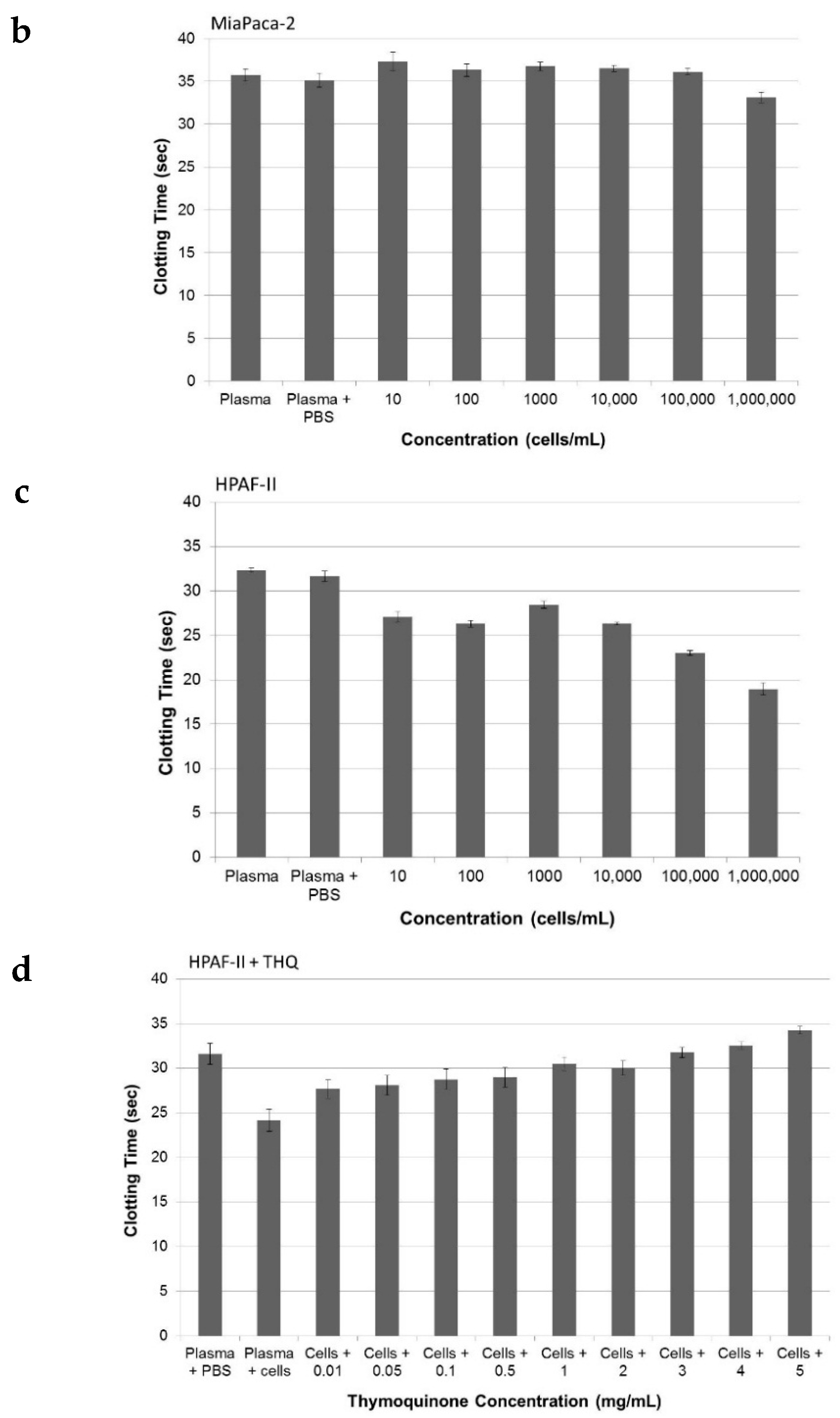
2.3. Pure THQ Can Reverse TF-Mediated Coagulation on Cancer Cells
2.4. Pure THQ Can Reverse Coagulation Mediated by Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
2.5. THQ Moderately Inhibits Factor Xa but Not Factor IIa Activity of Coagulation Cascade
2.6. THQ Down-Regulates TNF-α-Mediated Activation of NF-κB
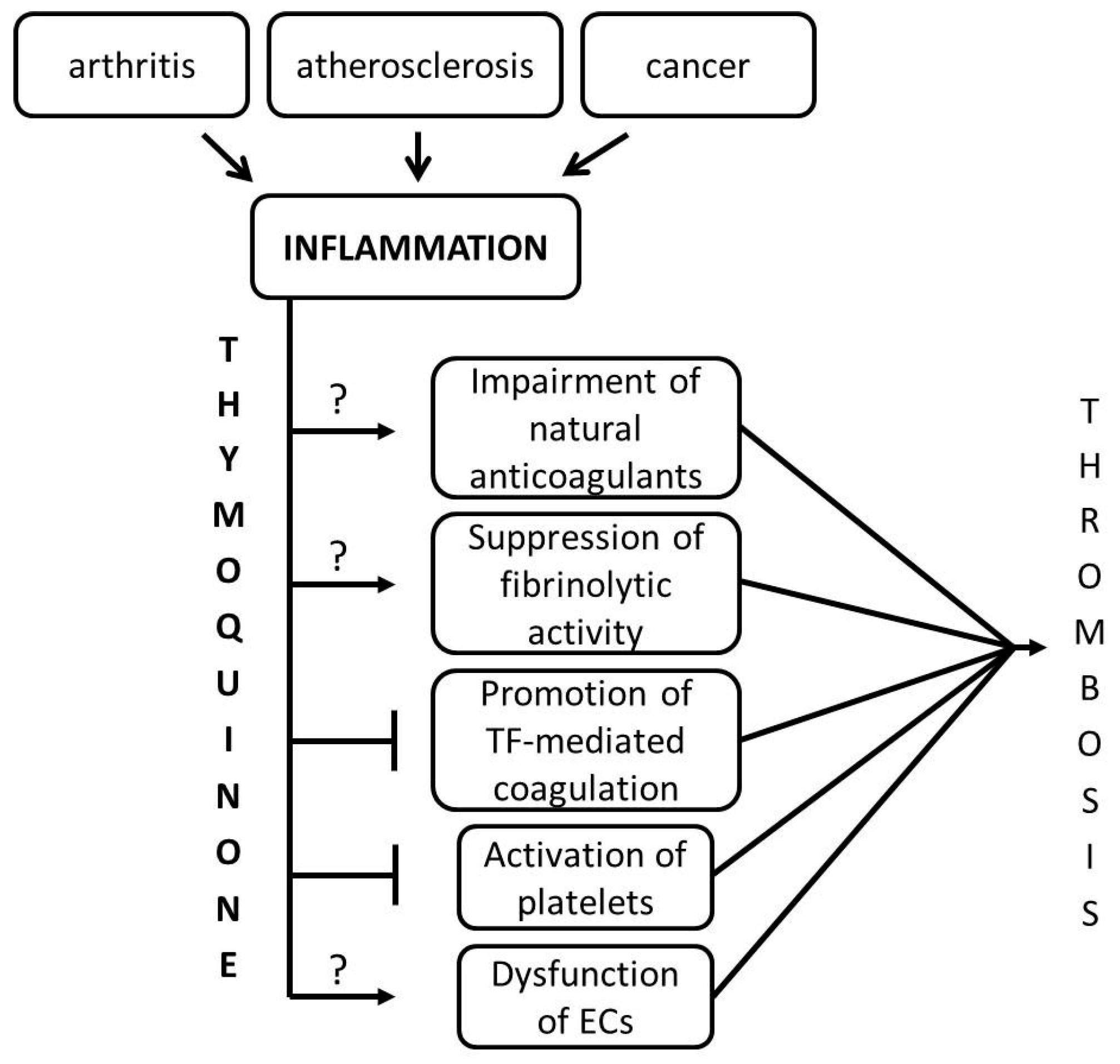
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Blood Sampling
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. Luciferase Assay
4.6. Extraction and Estimation of Amount of THQ in Black Seeds
4.7. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) Assay
4.8. Thrombelastography (TEG) Assay
4.9. Factor IIa/Xa Assays
4.10. Statistics
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aPTT | activated partial thromboplastic time |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| TF | tissue factor |
| TEG | thrombelastography |
| THQ | Thymoquinone |
| VTE | venous thromboembolism |
References
- Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Roessner, A.; Schneider-Stock, R. Thymoquinone: A promising anti-cancer drug from natural sources. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khader, M.; Bresgen, N.; Eckl, P.M. In vitro toxicological properties of thymoquinone. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, C.C.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Tan, K.H. Thymoquinone: Potential cure for inflammatory disorders and cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dakhakhny, M. Studies on the egyptian nigella sativa l. IV. Some pharmacological properties of the seeds’ active principle in comparison to its dihydro compound and its polymer. Arzneimittel.-Forschung 1965, 15, 1227–1229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Dakhakhny, M.; Mady, N.; Lembert, N.; Ammon, H.P. The hypoglycemic effect of Nigella sativa oil is mediated by extrapancreatic actions. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 465–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dakhakhny, M.; Mady, N.I.; Halim, M.A. Nigella sativa L. oil protects against induced hepatotoxicity and improves serum lipid profile in rats. Arzneimittel.-Forschung 2000, 50, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkharfy, K.M.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Al-Attas, O.S.; Alokail, M.S. The protective effect of thymoquinone against sepsis syndrome morbidity and mortality in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perveen, T.; Haider, S.; Zuberi, N.A.; Saleem, S.; Sadaf, S.; Batool, Z. Increased 5-HT levels following repeated administration of Nigella sativa L. (black seed) oil produce antidepressant effects in rats. Sci. Pharm. 2014, 82, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.R.; Ahmed, M.; Ahmed, S.; Manogaran, P.; Platanias, L.C.; Alvi, S.N.; Al-Kuraya, K.S.; Uddin, S. Thymoquinone suppresses growth and induces apoptosis via generation of reactive oxygen species in primary effusion lymphoma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragheb, A.; Attia, A.; Eldin, W.S.; Elbarbry, F.; Gazarin, S.; Shoker, A. The protective effect of thymoquinone, an anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, against renal injury: A review. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2009, 20, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajput, S.; Mandal, M. Antitumor promoting potential of selected phytochemicals derived from spices: A review. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 21, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, M.A.; Alghamdi, M.S. Anticancer activity of Nigella sativa (black seed)—A review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, B.; Prasad, S.; Yadav, V.R.; Aggarwal, B.B. Cancer cell signaling pathways targeted by spice-derived nutraceuticals. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 173–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider-Stock, R.; Fakhoury, I.H.; Zaki, A.M.; El-Baba, C.O.; Gali-Muhtasib, H.U. Thymoquinone: Fifty years of success in the battle against cancer models. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, R.L.; Lim, S.N.; Khaw, A.K.; Soon, J.F.; Shenoy, K.; Mohamed Ali, S.; Jayapal, M.; Sethu, S.; Baskar, R.; Hande, M.P. Thymoquinone induces telomere shortening, DNA damage and apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, C.C.; Loo, S.Y.; Gee, V.; Yap, C.W.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, K.H. Anticancer activity of thymoquinone in breast cancer cells: Possible involvement of PPAR-γ pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafa, El-S.A.; Zhu, Q.; Shah, Z.I.; Wani, G.; Barakat, B.M.; Racoma, I.; El-Mahdy, M.A.; Wani, A.A. Thymoquinone up-regulates PTEN expression and induces apoptosis in doxorubicin-resistant human breast cancer cells. Mutat. Res. 2011, 706, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mahdy, M.A.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, Q.E.; Wani, G.; Wani, A.A. Thymoquinone induces apoptosis through activation of Caspase-8 and mitochondrial events in p53-null myeloblastic leukemia HL-60 cells. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafri, S.H.; Glass, J.; Shi, R.; Zhang, S.; Prince, M.; Kleiner-Hancock, H. Thymoquinone and cisplatin as a therapeutic combination in lung cancer: In vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roepke, M.; Diestel, A.; Bajbouj, K.; Walluscheck, D.; Schonfeld, P.; Roessner, A.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Gali-Muhtasib, H. Lack of p53 augments thymoquinone-induced apoptosis and caspase activation in human osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, L.R.; Jones, P.; Benghuzzi, H.; Tucci, M. A comparison of the morphological changes associated with conventional and sustained treatment with pigallocatechin3gallate, thymoquinone, and tannic acid on lncap cells. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 2008, 44, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Kaseb, A.O.; Wang, Z.; Kong, D.; Mohammad, M.; Padhye, S.; Sarkar, F.H.; Mohammad, R.M. Antitumor activity of gemcitabine and oxaliplatin is augmented by thymoquinone in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5575–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaseb, A.O.; Chinnakannu, K.; Chen, D.; Sivanandam, A.; Tejwani, S.; Menon, M.; Dou, Q.P.; Reddy, G.P. Androgen receptor and E2F-1 targeted thymoquinone therapy for hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7782–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gali-Muhtasib, H.U.; Abou Kheir, W.G.; Kheir, L.A.; Darwiche, N.; Crooks, P.A. Molecular pathway for thymoquinone-induced cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in neoplastic keratinocytes. Anticancer Drugs 2004, 15, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, T.; Cho, S.G.; Yi, Z.; Pang, X.; Rodriguez, M.; Wang, Y.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Liu, M. Thymoquinone inhibits tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth through suppressing AKT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.; Khorana, A.A. Risk assessment for thrombosis in cancer. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2014, 40, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A. Venous thromboembolism prevention in cancer outpatients. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2013, 11, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, H.T.; Mellemkjaer, L.; Olsen, J.H.; Baron, J.A. Prognosis of cancers associated with venous thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A. Cancer and coagulation. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, S82–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggerstaff, J.P.; Seth, N.; Amirkhosravi, A.; Amaya, M.; Fogarty, S.; Meyer, T.V.; Siddiqui, F.; Francis, J.L. Soluble fibrin augments platelet/tumor cell adherence in vitro and in vivo, and enhances experimental metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1999, 17, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.L.; Biggerstaff, J.; Amirkhosravi, A. Hemostasis and malignancy. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1998, 24, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwicker, J.I.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. Cancer-associated thrombosis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2007, 62, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bick, R.L. Cancer-associated thrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.A.; Chen, J. Pathophysiology of venous thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2009, 123, S30–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Cohan, N. Cancer-associated thrombosis. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2010, 4, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwicker, J.I.; Liebman, H.A.; Neuberg, D.; Lacroix, R.; Bauer, K.A.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. Tumor-derived tissue factor-bearing microparticles are associated with venous thromboembolic events in malignancy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6830–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila, M.; Amirkhosravi, A.; Coll, E.; Desai, H.; Robles, L.; Colon, J.; Baker, C.H.; Francis, J.L. Tissue factor-bearing microparticles derived from tumor cells: Impact on coagulation activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; van der Poll, T. Two-way interactions between inflammation and coagulation. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2005, 15, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M. The coagulant response in sepsis and inflammation. Hamostaseologie 2010, 30, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whayne, T.F. A review of the role of anticoagulation in the treatment of peripheral arterial disease. Int. J. Angiol. 2012, 21, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margetic, S. Inflammation and haemostasis. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Poll, T.; Levi, M. Crosstalk between inflammation and coagulation: The lessons of sepsis. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 10, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Guo, B.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B. Tissue factor in tumor microenvironment: A systematic review. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesselaar, M.E.T.; Romijn, F.P.H.T.M.; Van Der Linden, I.K.; Prins, F.A.; Bertina, R.M.; Osanto, S. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity: A link between cancer and thrombosis? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, S.A.; Khurana, S.; Forsythe, M.S. Comparative in vitro efficacy of different platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists on platelet-mediated clot strength induced by tissue factor with use of thromboelastography: Differentiation among glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, T.; Mammen, E.F. LMW heparin (anti-Xa) assays for clinical monitoring and pharmacokinetic studies on the automated coagulation laboratory (ACL). Thromb. Res. 1992, 66, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Final Concentration (mg/mL) | Heparin avg. Coagulation T (Sec) | Standard Deviation | THQ avg. Coagulation T (Sec) | Standard Deviation | T-test p values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000 | 36.567 | 0.513 | 38.200 | 0.000 | |
| 0.010 | 53.967 | 0.751 | 38.400 | 0.361 | |
| 0.015 | 64.500 | 0.693 | |||
| 0.020 | 81.667 | 0.404 | |||
| 0.025 | 109.333 | 0.577 | |||
| 0.030 | 123.000 | 10.536 | |||
| 0.035 | 148.667 | 1.528 | |||
| 0.040 | 184.333 | 2.517 | |||
| 0.045 | 219.000 | 2.000 | |||
| 0.050 | 38.567 | 0.603 | |||
| 0.100 | 39.800 | 1.153 | |||
| 0.200 | 42.800 | 0.854 | 0.004 | ||
| 0.300 | 43.833 | 1.041 | 0.004 | ||
| 0.400 | 44.067 | 0.902 | 0.002 | ||
| 0.500 | 47.667 | 1.258 | 0.002 | ||
| 1.000 | 50.233 | 3.044 | 0.009 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muralidharan-Chari, V.; Kim, J.; Abuawad, A.; Naeem, M.; Cui, H.; Mousa, S.A. Thymoquinone Modulates Blood Coagulation in Vitro via Its Effects on Inflammatory and Coagulation Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040474
Muralidharan-Chari V, Kim J, Abuawad A, Naeem M, Cui H, Mousa SA. Thymoquinone Modulates Blood Coagulation in Vitro via Its Effects on Inflammatory and Coagulation Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(4):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040474
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuralidharan-Chari, Vandhana, Jaehan Kim, Ahlam Abuawad, Mubeena Naeem, Huadong Cui, and Shaker A. Mousa. 2016. "Thymoquinone Modulates Blood Coagulation in Vitro via Its Effects on Inflammatory and Coagulation Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040474
APA StyleMuralidharan-Chari, V., Kim, J., Abuawad, A., Naeem, M., Cui, H., & Mousa, S. A. (2016). Thymoquinone Modulates Blood Coagulation in Vitro via Its Effects on Inflammatory and Coagulation Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040474