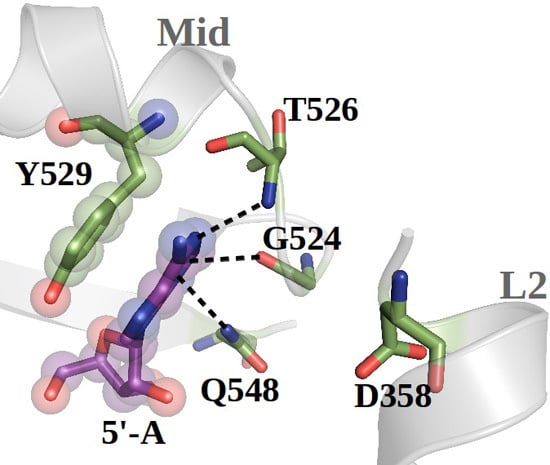
Novel Insights into Guide RNA 5′-Nucleoside/Tide Binding by Human Argonaute 2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
| Chemical System | Force Field | MD Production Run Length |
|---|---|---|
| hAgo2 apo–enzyme | Amber03 ILDN | 100 ns |
| hAgo2_5’-U–guide | AMBER Parmbsc0 | 100 ns |
| hAgo2_5’-A–guide | AMBER Parmbsc0 | 100 ns |
| hAgo2_5’-C–guide | AMBER Parmbsc0 | 100 ns |
| hAgo2_5’-G–guide | AMBER Parmbsc0 | 100 ns |
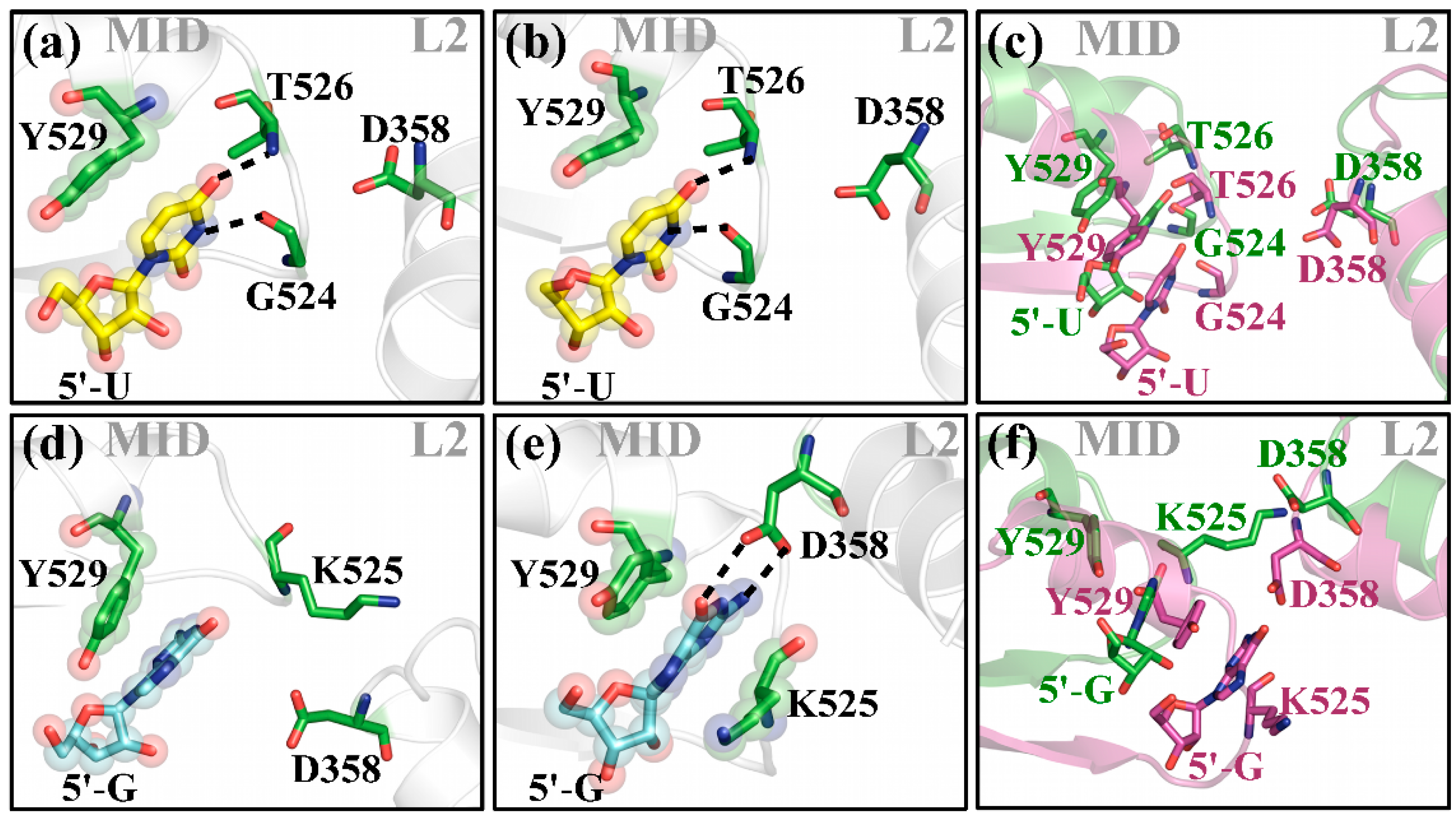
2.1. hAgo2 Is Stabilized by Protein–RNA Interactions
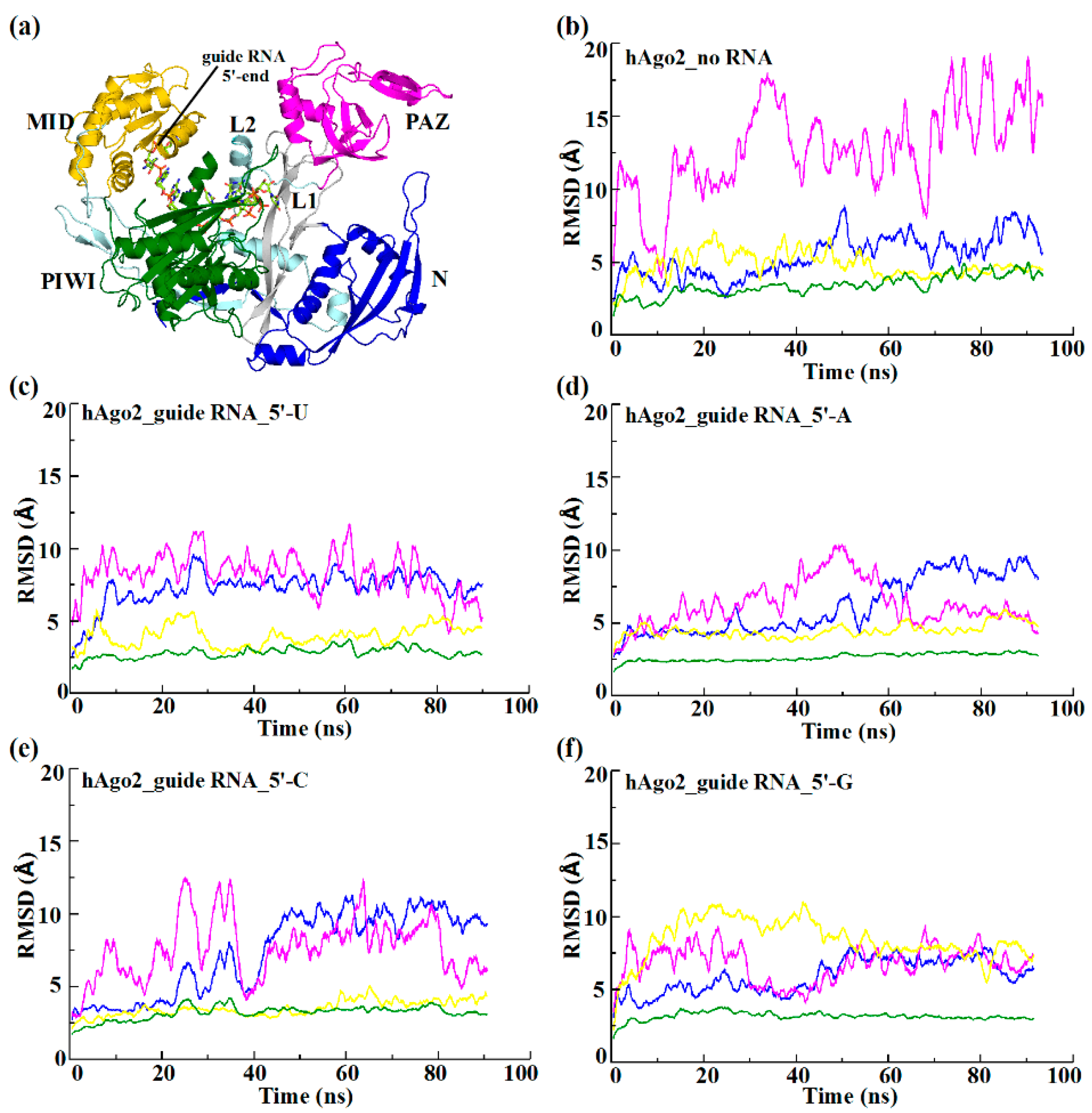
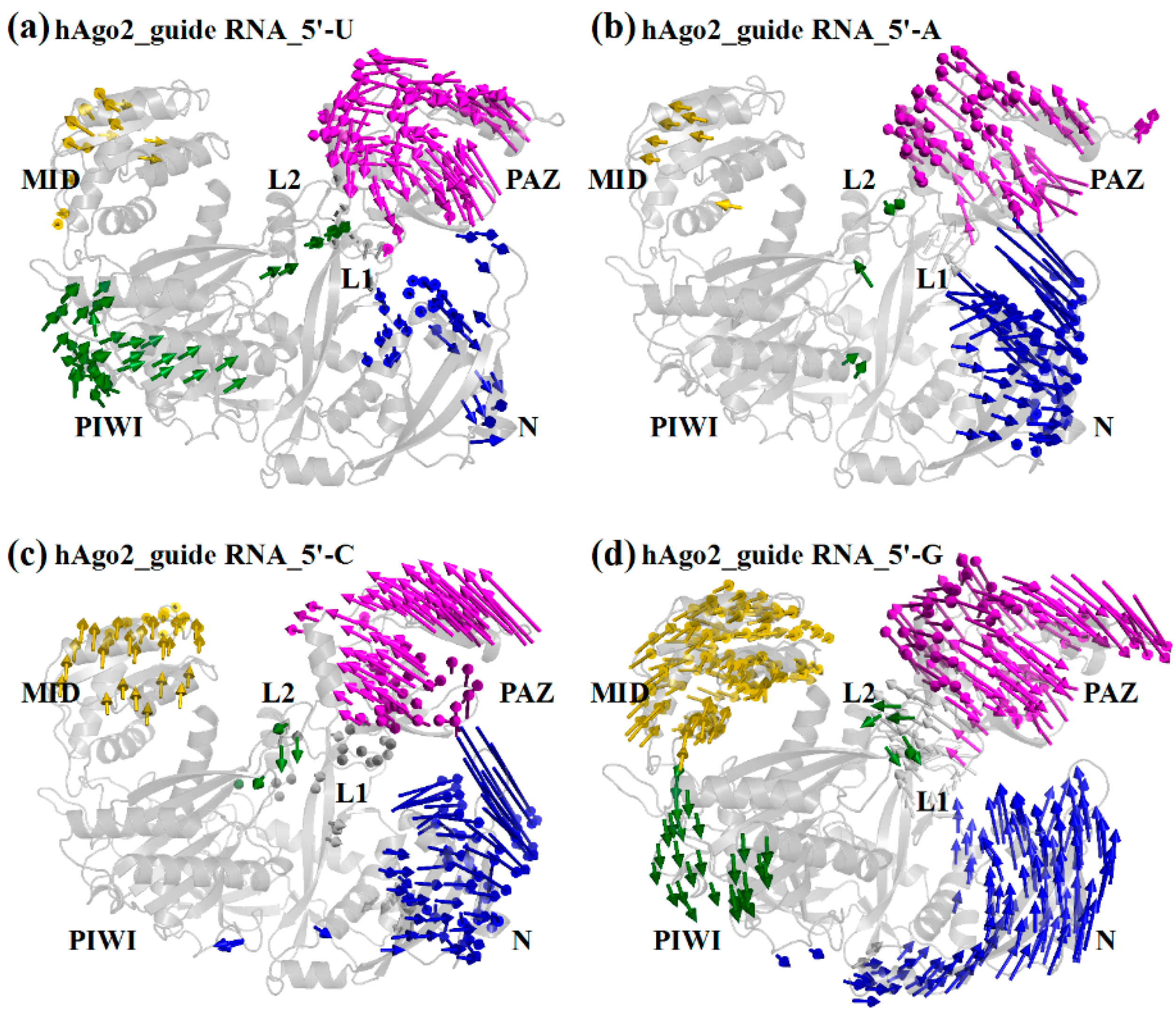
2.2. Different Guide 5′-Bases Induce Different Inter-Domain Motion Patterns in hAgo2
| Simulation System Name | RMSD (Å) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | PAZ | MID | PIWI | |
| hAgo2_guide RNA_5′-U | 0.72 ± 0.13 | 0.74 ± 0.18 | 0.42 ± 0.07 | 0.30 ± 0.03 |
| hAgo2_guide RNA_5′-A | 0.61 ± 0.20 | 0.62 ± 0.17 | 0.45 ± 0.06 | 0.26 ± 0.02 |
| hAgo2_guide RNA_5′-C | 0.73 ± 0.23 | 0.76 ± 0.23 | 0.35 ± 0.06 | 0.32 ± 0.05 |
| hAgo2_guide RNA_5′-G | 0.59 ± 0.12 | 0.67 ± 0.14 | 0.84 ± 0.16 | 0.32 ± 0.03 |

2.3. Steady-State and Pre-Steady-State Binding Experiments of hAgo2 with Different Guide and Target Substrates
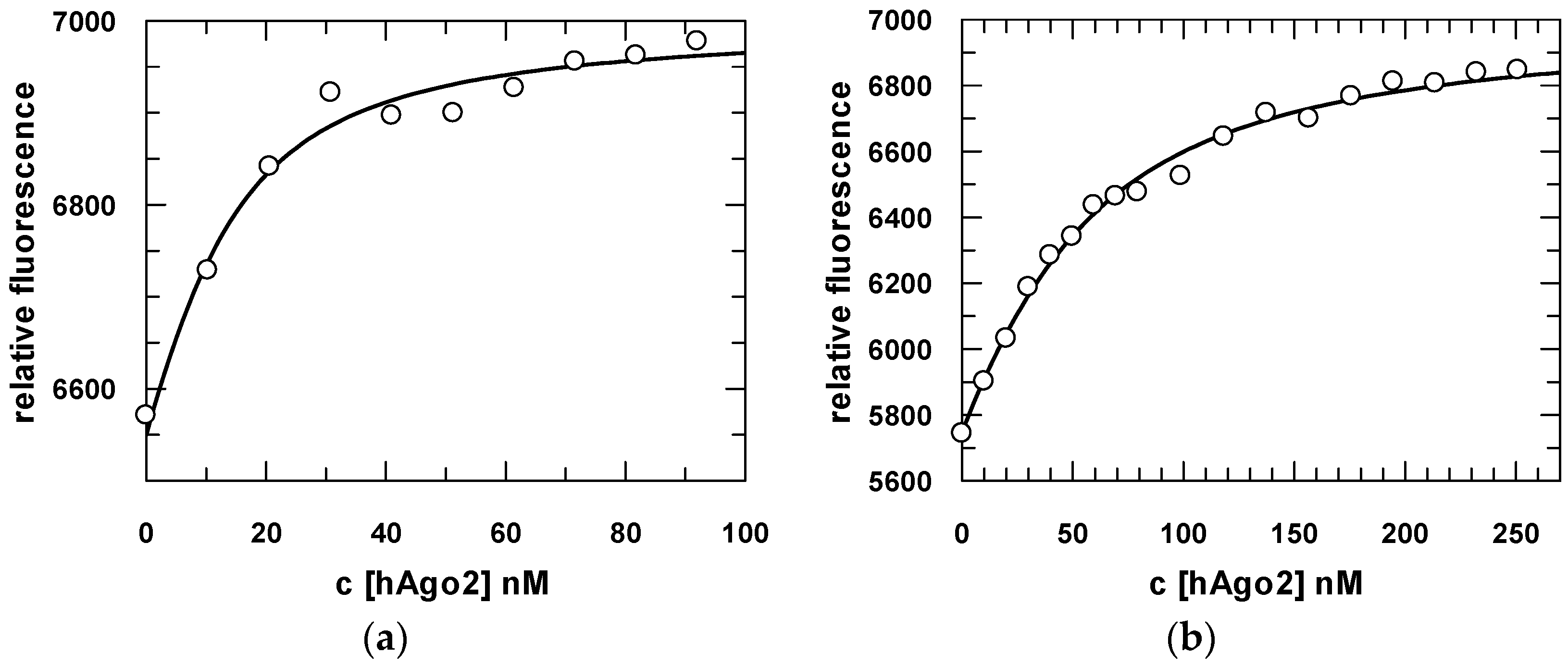
| Substrate | Kd_meas (nM) | Kd_cal (nM) | k1 (M−1·s−1) | k−1 (s−1) | k2 (s−1) | k−2 (s−1) | k3 (s−1) | k−3 (s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U–guide * | 7 ± 0.9 | 36 | 0.6 (±0.001) × 108 | 6.2 ± 0.6 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.012 ± 5 × 10−4 | 0.007 ± 1 × 10−4 |
| G–guide | 35 ± 0.4 | 59 | 0.16 (±0.006) × 108 | 2 ± 0.6 | 0.2 ± 0.06 | 0.54 ± 0.07 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.0023 ± 4 × 10−4 |
| OH-G–guide | 7 ± 0.5 | 21 | 0.27 (±0.005) × 108 | 2.1 ± 0.08 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.02 | 0.013 ± 0.002 | 0.002 ± 7 × 10−4 |
2.4. Cleavage Assay with a 5’-G Guide RNA
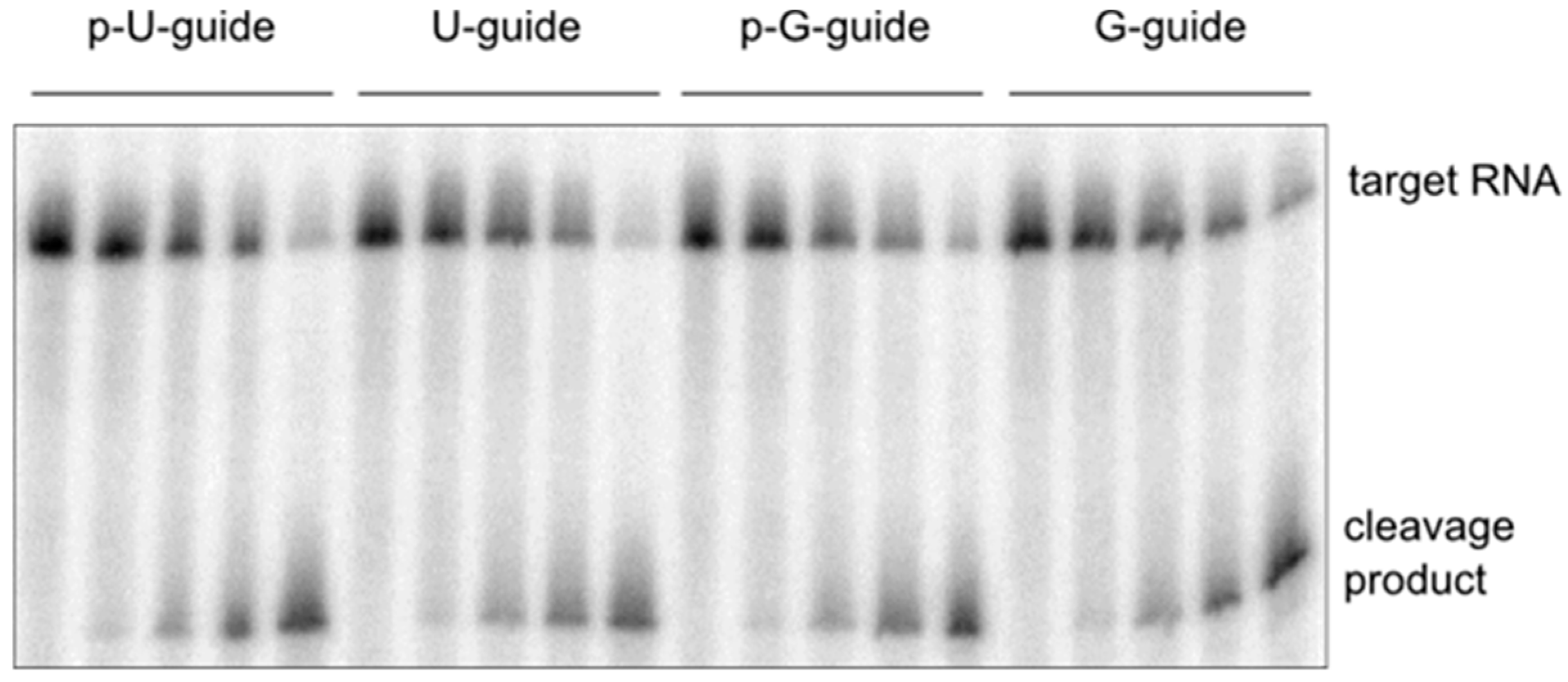
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. MD System Preparation
4.2. Protein Expression and Purification
4.3. Oligonucleotides
4.4. Equilibrium Fluorescence Titrations
4.5. Pre-Steady-State Stopped-Flow Measurements
4.6. RNA Cleavage Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennecke, J.; Hipfner, D.R.; Stark, A.; Russell, R.B.; Cohen, S.M. Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 2003, 113, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, D.; Mecklenbrauker, I.; Das, P.P.; Santana, A.; Koenig, U.; Enright, A.J.; Miska, E.A.; Tarakhovsky, A. A Slicer-independent role for Argonaute 2 in hematopoiesis and the microRNA pathway. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1999–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.; Busslinger, M. Life beyond cleavage: The case of Ago2 and hematopoiesis. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, G.; Slack, F.J. Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat.Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- miRBase. Available online: http://www.mirbase.org/index.shtml (accessed on 3 November 2015).
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Lu, J.; Kulbokas, E.J.; Golub, T.R.; Mootha, V.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Lander, E.S.; Kellis, M. Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 3' UTRs by comparison of several mammals. Nature 2005, 434, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—MicroRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R.J.; van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: MicroRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, M.; Miao, J.; Guo, Y.; Gao, W.; Cui, Q. An analysis of human microRNA and disease associations. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.C.; Doudna, J.A. Molecular mechanisms of RNA interference. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameres, S.L.; Zamore, P.D. Diversifying microRNA sequence and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khvorova, A.; Reynolds, A.; Jayasena, S.D. Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell 2003, 115, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.S.; Hutvagner, G.; Du, T.; Xu, Z.; Aronin, N.; Zamore, P.D. Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex. Cell 2003, 115, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.D.; Carmell, M.A.; Rivas, F.V.; Marsden, C.G.; Thomson, J.M.; Song, J.J.; Hammond, S.M.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Hannon, G.J. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science 2004, 305, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.J.; Smith, S.K.; Hannon, G.J.; Joshua-Tor, L. Crystal structure of Argonaute and its implications for RISC slicer activity. Science 2004, 305, 1434–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, G.; Juranek, S.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Structure of the guide-strand-containing argonaute silencing complex. Nature 2008, 456, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Juranek, S.; Li, H.; Sheng, G.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Structure of an argonaute silencing complex with a seed-containing guide DNA and target RNA duplex. Nature 2008, 456, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Juranek, S.; Li, H.; Sheng, G.; Wardle, G.S.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Nucleation, propagation and cleavage of target RNAs in Ago silencing complexes. Nature 2009, 461, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, G.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Rao, Y.; Tian, W.; Swarts, D.C.; van der Oost, J.; Patel, D.J.; Wang, Y. Structure-based cleavage mechanism of thermus thermophilus Argonaute DNA guide strand-mediated DNA target cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirle, N.T.; MacRae, I.J. The crystal structure of human Argonaute2. Science 2012, 336, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Weinberg, D.E.; Bartel, D.P.; Patel, D.J. Structure of yeast Argonaute with guide RNA. Nature 2012, 486, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkayam, E.; Kuhn, C.D.; Tocilj, A.; Haase, A.D.; Greene, E.M.; Hannon, G.J.; Joshua-Tor, L. The structure of human argonaute-2 in complex with miR-20a. Cell 2012, 150, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faehnle, C.R.; Elkayam, E.; Haase, A.D.; Hannon, G.J.; Joshua-Tor, L. The making of a slicer: Activation of human Argonaute-1. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Ascano, M.; Gogakos, T.; Ishibe-Murakami, S.; Serganov, A.A.; Briskin, D.; Morozov, P.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Eukaryote-specific insertion elements control human ARGONAUTE slicer activity. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirle, N.T.; Sheu-Gruttadauria, J.; MacRae, I.J. Structural basis for microRNA targeting. Science 2014, 346, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, C.D.; Joshua-Tor, L. Eukaryotic Argonautes come into focus. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boland, A.; Huntzinger, E.; Schmidt, S.; Izaurralde, E.; Weichenrieder, O. Crystal structure of the MID-PIWI lobe of a eukaryotic Argonaute protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2011, 108, 10466–10471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, F.; Sonenberg, N.; Nagar, B. Structural basis for 5′-nucleotide base-specific recognition of guide RNA by human AGO2. Nature 2010, 465, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, N.C.; Lim, L.P.; Weinstein, E.G.; Bartel, D.P. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 2001, 294, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghildiyal, M.; Seitz, H.; Horwich, M.D.; Li, C.; Du, T.; Lee, S.; Xu, J.; Kittler, E.L.; Zapp, M.L.; Weng, Z.; Zamore, P.D. Endogenous siRNAs derived from transposons and mRNAs in Drosophila somatic cells. Science 2008, 320, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.Y.; Yan, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hu, H.; Menzel, C.; Zhou, Y.H.; Chen, W.; Khaitovich, P. Sequence features associated with microRNA strand selection in humans and flies. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghildiyal, M.; Xu, J.; Seitz, H.; Weng, Z.; Zamore, P.D. Sorting of Drosophila small silencing RNAs partitions microRNA* strands into the RNA interference pathway. RNA 2010, 16, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, S.J.; Cai, T.; Hu, Y.G.; Chen, Y.; Hodges, E.; Ni, F.R.; Wu, L.; Li, S.; Zhou, H.; Long, C.Z.; et al. Sorting of small RNAs into Arabidopsis argonaute complexes is directed by the 5 ' terminal nucleotide. Cell 2008, 133, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirle, N.T.; Sheu-Gruttadauria, J.; Chandradoss, S.D.; Joo, C.; MacRae, I.J. Water-mediated recognition of t1-adenosine anchors Argonaute2 to microRNA targets. eLife 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deerberg, A.; Willkomm, S.; Restle, T. Minimal mechanistic model of siRNA-dependent target RNA slicing by recombinant human Argonaute 2 protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17850–17855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudel, S.; Wang, Y.; Lenobel, R.; Korner, R.; Hsiao, H.H.; Urlaub, H.; Patel, D.; Meister, G. Phosphorylation of human Argonaute proteins affects small RNA binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 2330–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Huynh, T.; Ren, P.; Zhou, R. Large domain motions in Ago protein controlled by the guide DNA-strand seed region determine the Ago-DNA-mRNA complex recognition process. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, U.J.; Paterok, D.; Koglin, A.; Gohlke, H.; Piehler, J.; Chen, J.C.H. Structure of Aquifex aeolicus Argonaute highlights conformational flexibility of the PAZ domain as a potential regulator of RNA-induced silencing complex function. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13824–13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswar, N.; Webb, B.; Marti-Renom, M.A.; Madhusudhan, M.; Eramian, D.; Shen, M.Y.; Pieper, U.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling using Modeller. Curr. Prot. Bioinform. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, A.; Marchan, I.; Svozil, D.; Sponer, J.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd; Laughton, C.A.; Orozco, M. Refinement of the AMBER force field for nucleic acids: Improving the description of alpha/gamma conformers. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 3817–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willkomm, S.; Restle, T. Conformational Dynamics of Ago-Mediated Silencing Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 14769–14785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.R.; Kim, E.; Hwang, W.; Shin, S.; Song, J.J.; Hohng, S. Dynamic anchoring of the 3′-end of the guide strand controls the target dissociation of Argonaute-guide complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16865–16871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, A.; Holzmeister, P.; Klose, D.; Tinnefeld, P.; Grohmann, D. Single-molecule FRET supports the two-state model of Argonaute action. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalia, M.; Willkomm, S.; Claussen, J.C.; Restle, T.; Bonvin, A.M.J.J. Novel Insights into Guide RNA 5′-Nucleoside/Tide Binding by Human Argonaute 2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010022
Kalia M, Willkomm S, Claussen JC, Restle T, Bonvin AMJJ. Novel Insights into Guide RNA 5′-Nucleoside/Tide Binding by Human Argonaute 2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalia, Munishikha, Sarah Willkomm, Jens Christian Claussen, Tobias Restle, and Alexandre M. J. J. Bonvin. 2016. "Novel Insights into Guide RNA 5′-Nucleoside/Tide Binding by Human Argonaute 2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010022
APA StyleKalia, M., Willkomm, S., Claussen, J. C., Restle, T., & Bonvin, A. M. J. J. (2016). Novel Insights into Guide RNA 5′-Nucleoside/Tide Binding by Human Argonaute 2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010022