Influence of Bxpel1 Gene Silencing by dsRNA Interference on the Development and Pathogenicity of the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
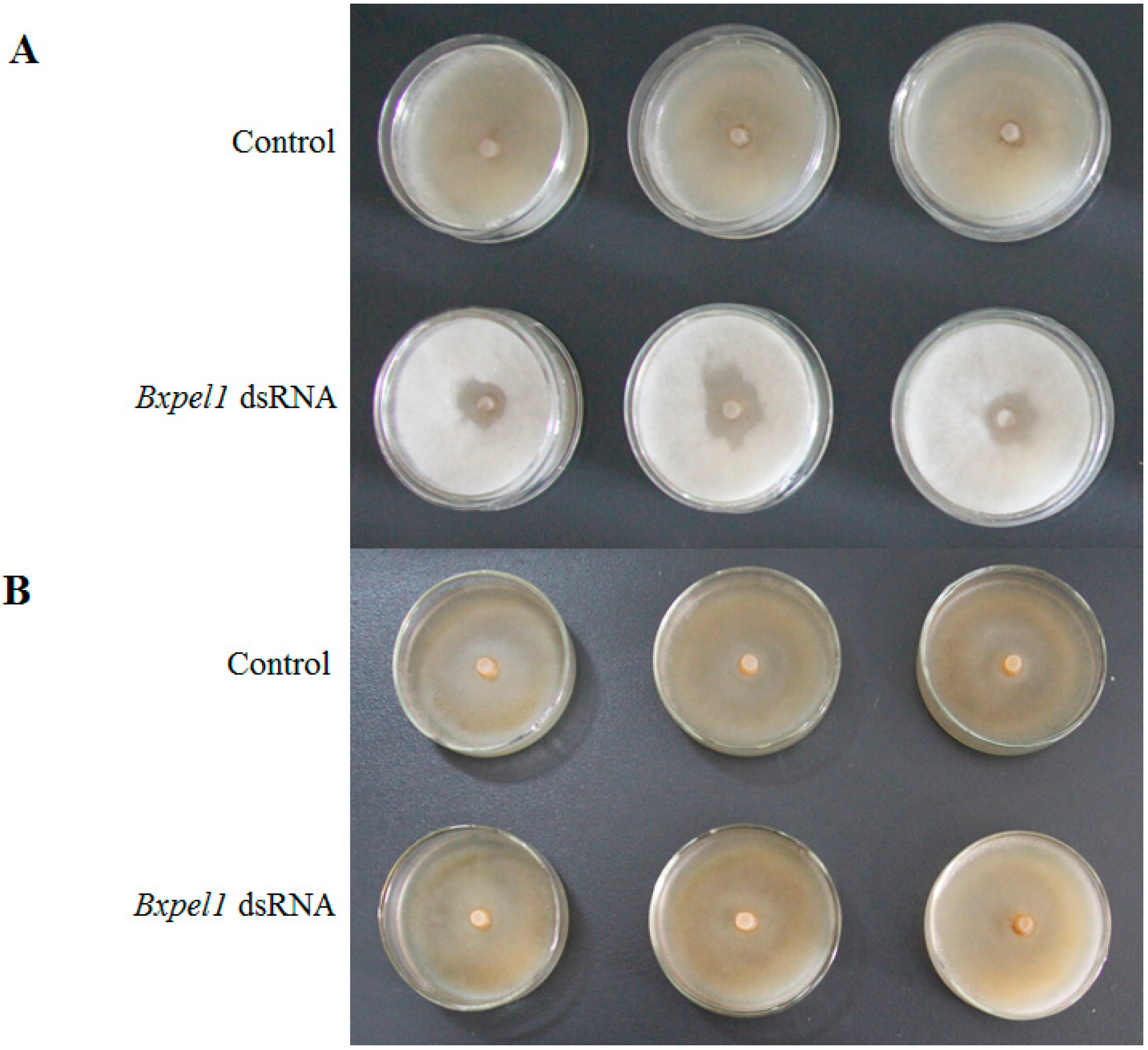
2.1. Morphology of B. xylophilus after Double-Stranded RNA Interference (dsRNAi)
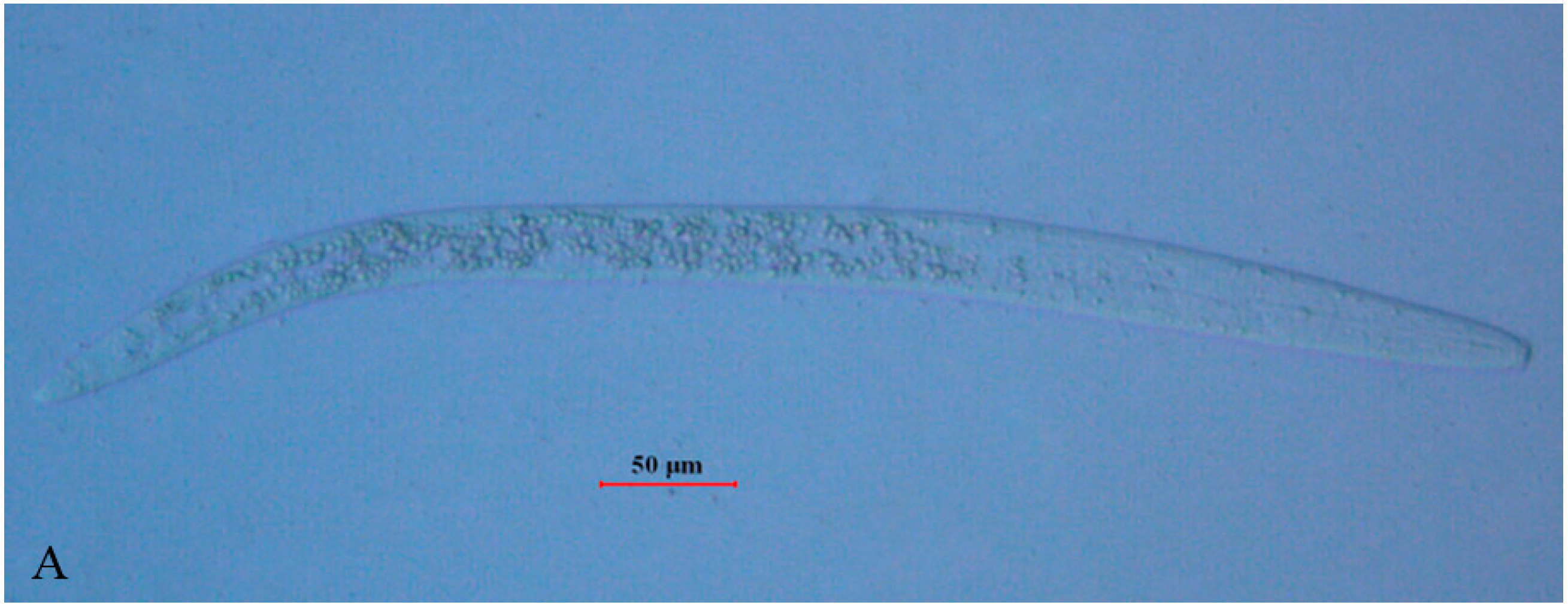
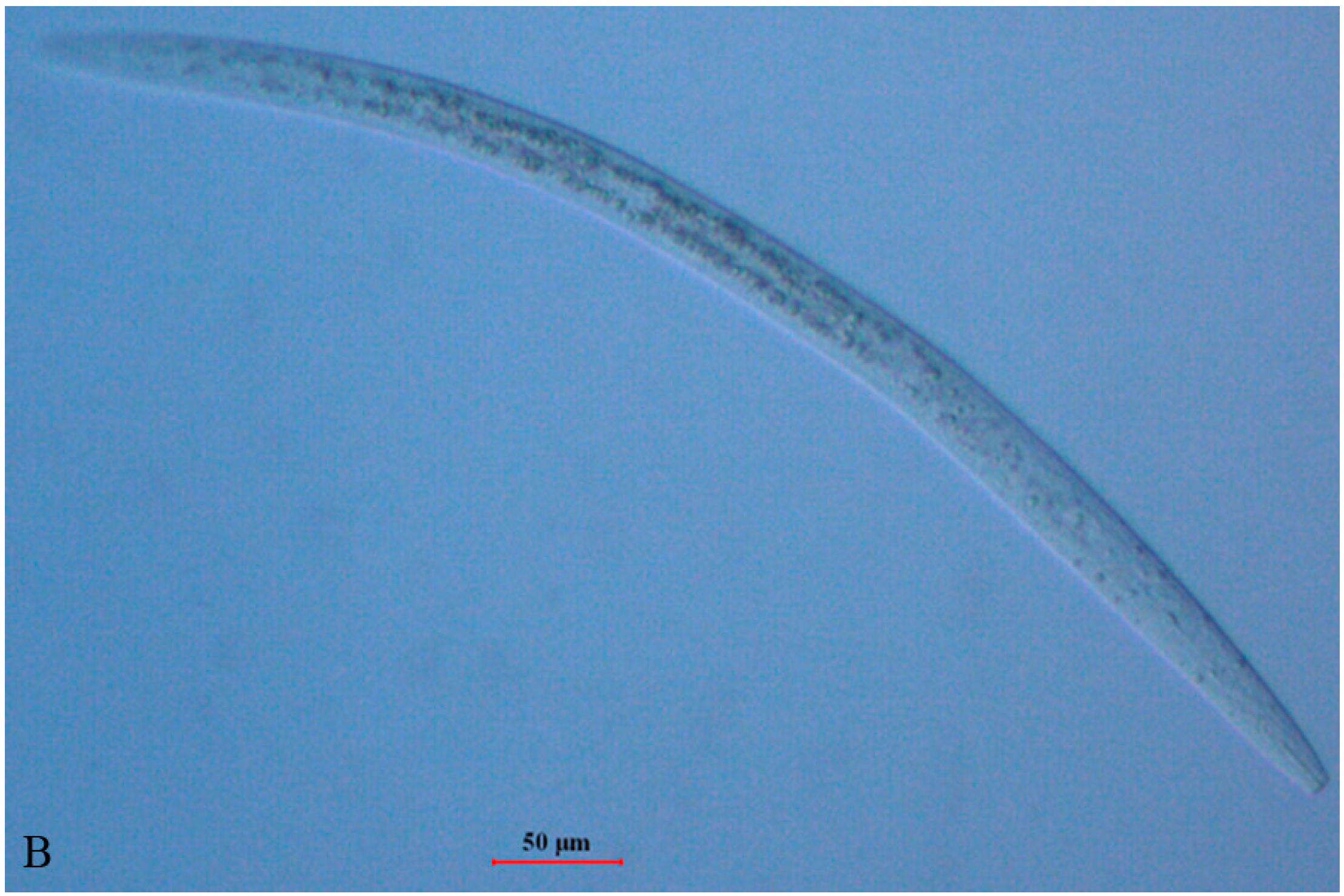

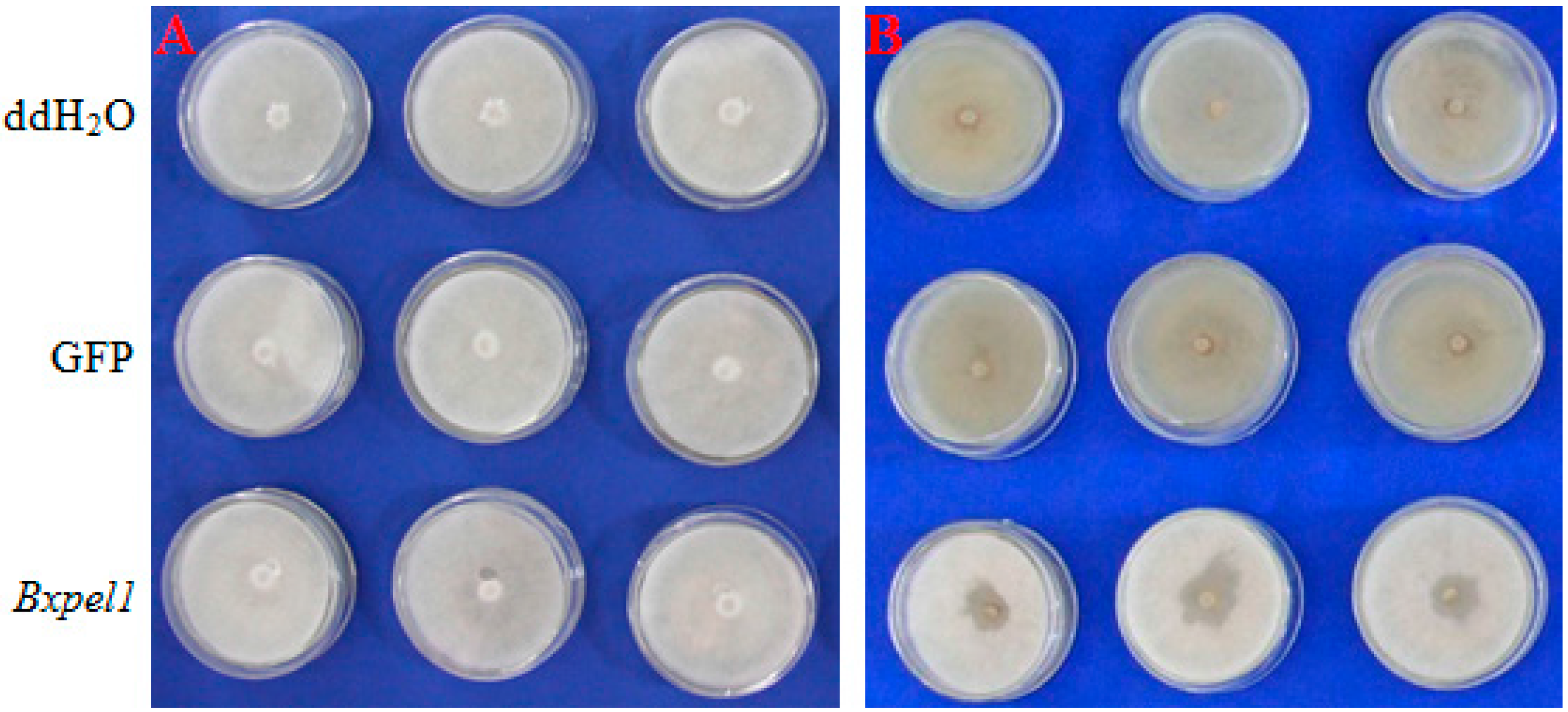
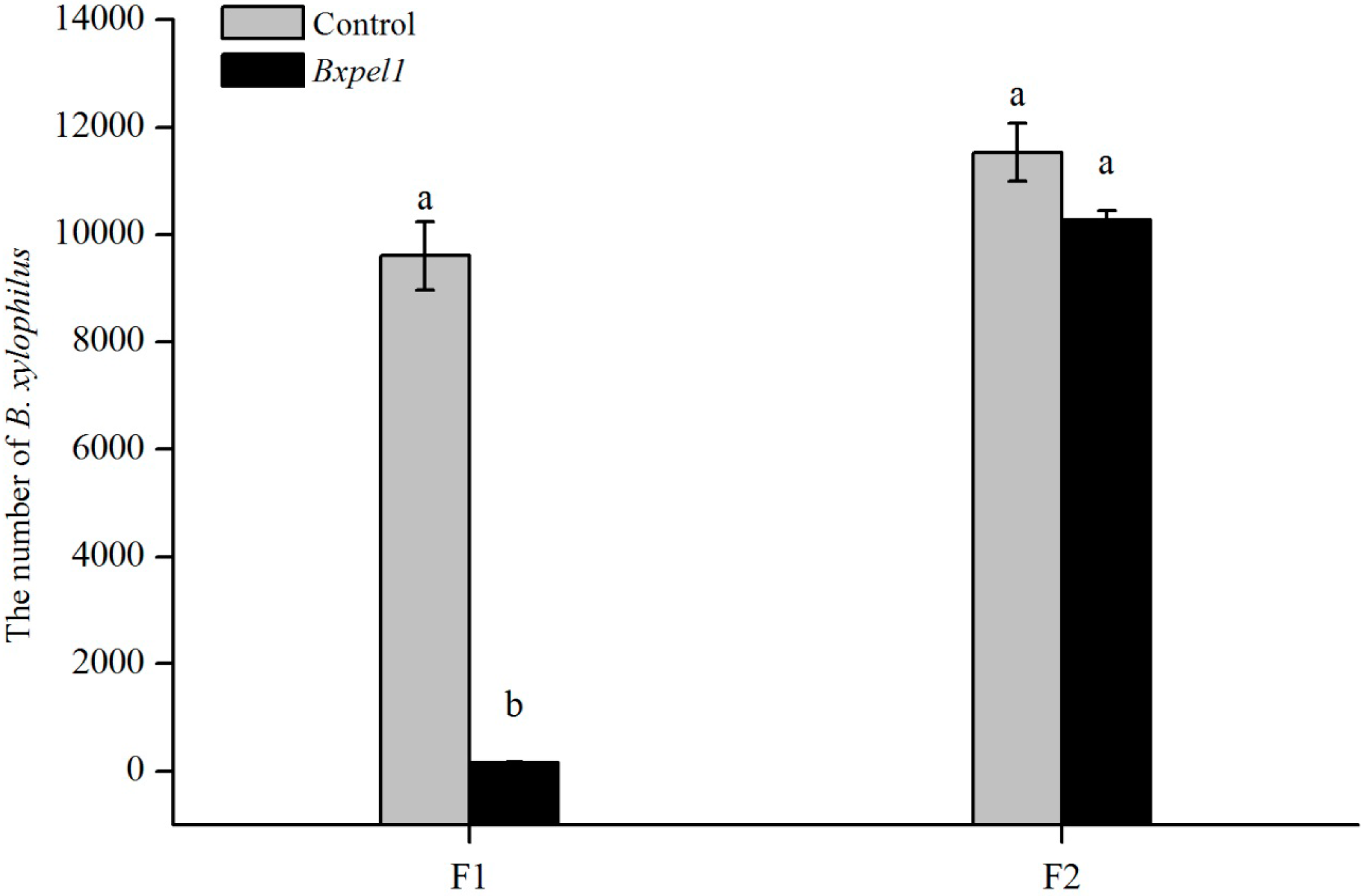
2.2. Propagation of B. xylophilus on Fungal Culture after dsRNAi

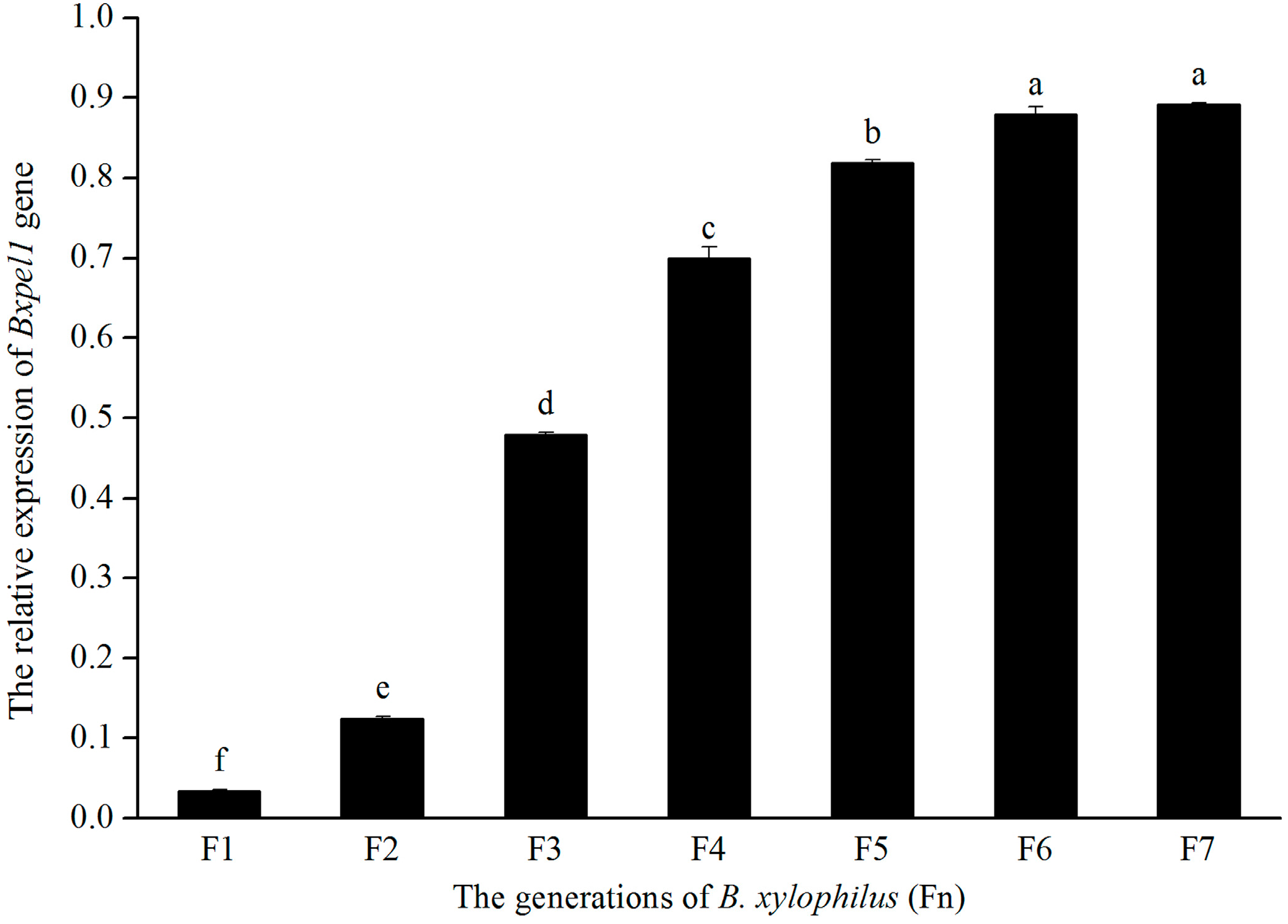
2.3. Efficiency of RNAi in B. xylophilus
2.4. Mortality of Pinus thunbergii after Inoculating B. xylophilus with dsRNAi
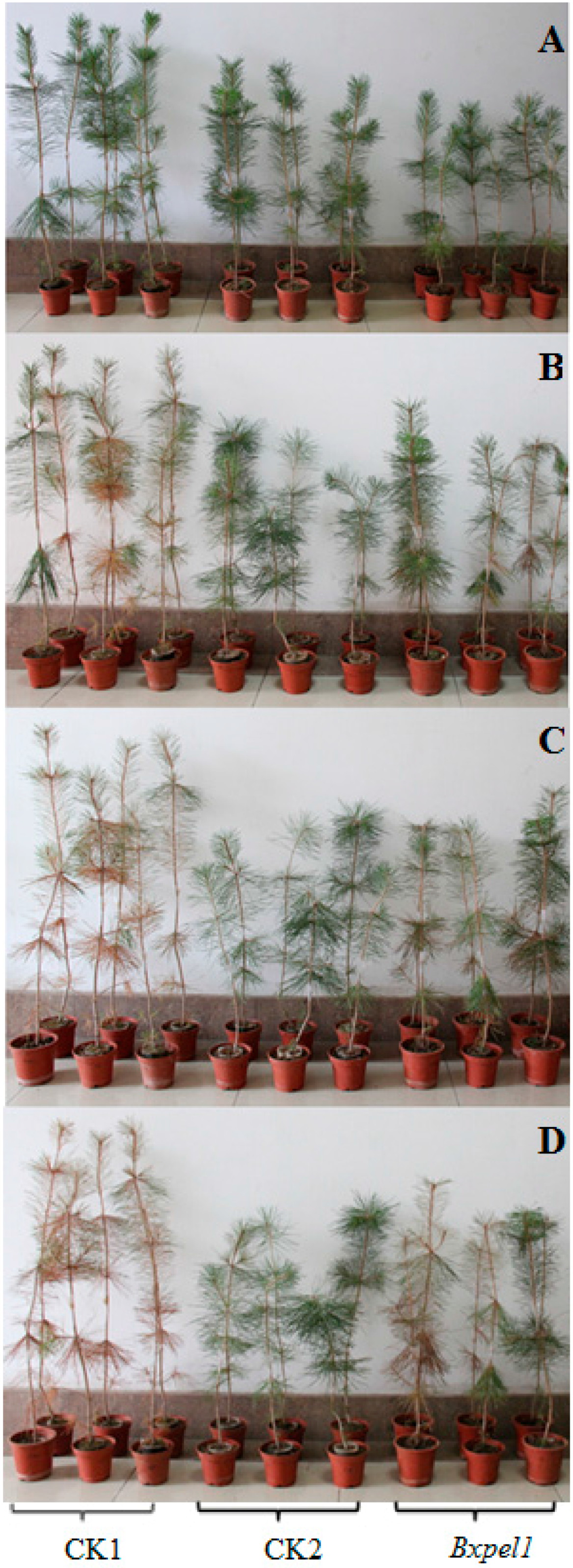

2.5. Migration and Reproduction of B. xylophilus in P. thunbergii after Soaking in dsRNA
| Distance | Treatment | 4 Days | 8 Days | 12 Days | 16 Days | 20 Days | 24 Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-5 cm | Control | 66 ± 11 a A | 222 ± 27 a | 3022 ± 279 a | 6133 ± 321 a | 14,933 ± 789 a | 13,562 ± 280 a |
| Bxpel1 | 39 ± 7 b | 122 ± 9 b | 1288 ± 85 b | 2933 ± 152 b | 3511 ± 189 b | 5362 ± 157 b | |
| Up-10 cm | Control | 0 | 177 ± 7 a | 1466 ± 32 a | 4333 ± 306 a | 15,000 ± 392 a | 15,244 ± 398 a |
| Bxpel1 | 0 | 44 ± 4 b | 822 ± 55 b | 2577 ± 103 b | 6422 ± 270 b | 8412 ± 176 b | |
| Up-15 cm | Control | 0 | 133 ± 27 | 1977 ± 24 a | 2244 ± 205 b | 6866 ± 376 b | 10,228 ± 1461 a |
| Bxpel1 | 0 | 0 | 466 ± 26 b | 3000 ± 160 a | 7700 ± 102 a | 9026 ± 248 a | |
| Up-20 cm | Control | 0 | 67 ± 13 | 3977 ± 207 a | 4866 ± 36 a | 2311 ± 185 b | 1094 ± 123 b |
| Bxpel1 | 0 | 0 | 200 ± 19 b | 2311 ± 139 b | 5022 ± 220 a | 4866 ± 108 a | |
| Down-5 cm | Control | 300 ± 19 a | 424 ± 22 a | 2844 ± 97 a | 6177 ± 213 a | 16,000 ± 475 a | 12,123 ± 522 a |
| Bxpel1 | 83 ± 14 b | 177 ± 18 b | 1355 ± 66 b | 3088 ± 125 b | 6822 ± 393 b | 10,482 ± 545 b | |
| Down-10 cm | Control | 38 ± 9 a | 211 ± 14 a | 3777 ± 205 a | 8511 ± 506 a | 8866 ± 397 a | 10,486 ± 1443 a |
| Bxpel1 | 28 ± 3 a | 55 ± 9 b | 711 ± 23 b | 3488 ± 25 b | 8855 ± 242 a | 10,424 ± 587 a | |
| Down-15 cm | Control | 11 ± 3 | 188 ± 43 a | 3022 ± 82 a | 15,488 ± 319 a | 16,400 ± 265 a | 15,724 ± 860 a |
| Bxpel1 | 0 | 33 ± 2 b | 777 ± 42 b | 3244 ± 93 b | 7848 ± 454 b | 12,111 ± 246 b | |
| Down-20 cm | Control | 0 | 98 ± 8 | 5177 ± 152 a | 12,177 ± 1223 a | 10,600 ± 1651 a | 11,806 ± 765 a |
| Bxpel1 | 0 | 0 | 2066 ± 284 b | 3478 ± 139 b | 4244 ± 304 b | 8711 ± 126 b |
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Biological Materials
4.2. Total RNA Preparation and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. dsRNA Synthesis and in Vitro RNAi
| Gene Name | Forward Sequence 5′–3′ | Reverse Sequence 5′–3′ |
|---|---|---|
| Bxpel1-T7 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG |
| TTGTTTCGGCTCAGTTTGGA | TTTGGGTTCCTGGTTGTTGT |
4.4. The Expression of Bxpel1 Gene after B. xylophilus Soaking in dsRNA
| Probe Name | Forward Sequence 5′–3′ | Reverse Sequence 5′–3′ |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | GCAACACGGAGTTCGTTGTA | GTATCGTCACCAACTGGGAT |
| Bxpel1 | ACCATCAAGAATTTCCAGGTAG | TTTCCGCAAGAACGATAGAG |
4.5. Effect of RNAi on Reproduction of B. xylophilus
4.6. Effect of RNAi on the Pathogenicity of B. xylophilus
4.7. Effect of RNAi on the Dispersal of B. xylophilus
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mamiya, Y.; Kiyohara, T. Description of Bursaphelenchus lignicolus n. sp. (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from pine wood and histopathology of nematode-infested trees. Nematologica 1972, 18, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, G.; Buhrer, E.M. Aphelenchoides xylophilus, n. sp., a nematode associated with blue-stain and other fungi in timber. J. Agric. Res. 1934, 48, 949–951. [Google Scholar]
- Valadas, V.; Laranjo, M.; Barbosa, P.; Espada, M.; Mota, M.; Oliveira, S. The pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, in Portugal: Possible introductions and spread routes of a serious biological invasion revealed by molecular methods. Nematology 2012, 14, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.J.; Wang, Q.L. Distribution of the pinewood nematode in China and susceptibility of some Chinese and exotic pines to the nematode. Can. J. For. Res. 1989, 19, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, T.; Mourits, M.C.M.; van der Werf, W.; Hengeveld, G.M.; Robinet, C.; Lansink, A.G.J.M.O. Framework for modelling economic impacts of invasive species, applied to pine wood nematode in Europe. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, M.; Shoda-Kagaya, E.; Maehara, T.; Zhou, Z.H.; Lian, C.L.; Iwata, R.; Yamane, A.; Hogetsu, T. Genetic structure of pine sawyer Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) populations in northeast Asia: Consequences of the spread of pine wilt disease. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linit, M. Nemtaode-vector relationships in the pine wilt disease system. J. Nematol. 1988, 20, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Togashi, K.; Shigesada, N. Spread of the pinewood nematode vectored by the Japanese pine sawyer: Modeling and analytical approaches. Popul. Ecol. 2006, 48, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Utsuzawa, S.; Sakaue, D. Correlation between acoustic emission, water status and xylem embolism in pine wilt disease. Tree Physiol. 2007, 27, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Ye, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Zhu, L.; Lin, S. Deep sequencing analyses of pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus microRNAs reveal distinct miRNA expression patterns during the pathological process of pine wilt disease. Gene 2015, 555, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Wu, X.Q.; Zhou, A.D. Bacterial diversity and community structure in the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and B. mucronatus with different virulence by high-throughput sequencing of the 16S rDNA. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espada, M.; Silva, A.C.; Akker, S.E.V.; Cock, P.J.; Mota, M.; Jones, J.T. Identification and characterization of parasitism genes from the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus reveals a multilayered detoxification strategy. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, T.M.; Albershe, P.; Anderson, A.J. Host-Pathogen Interactions IV. Studies on polysaccharide-degrading enzymes secreted by Fusarium Oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1972, 2, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, P.D.; Jurale, J.B.; Albershe, P. Host-Pathogen Interactions II. Parameters affecting polysaccharide-degrading enzyme secretion by Colletotrichum-lindemuthianum grown in culture. Plant Physiol. 1971, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomassini, A.; Sella, L.; Raiola, A.; D’Ovidio, R.; Favaron, F. Characterization and expression of Fusarium graminearum endo-polygalacturonases in vitro and during wheat infection. Plant Pathol. 2009, 58, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoby, N.; Beno-Moualem, D.; Keen, N.T.; Dinoor, A.; Pines, O.; Prusky, D. Colletotrichum gloeosporioides pelB is an important virulence factor in avocado fruit-fungus interaction. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2001, 14, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barras, F.; van Gijsegem, F.; Chatterjee, A.K. Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1994, 32, 201–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravin, A.A.; Naumova, N.M.; Tulin, A.V.; Vagin, V.V.; Rozovsky, Y.M.; Gvozdev, V.A. Double-stranded RNA-mediated silencing of genomic tandem repeats and transposable elements in the D. melanogaster germline. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, A. High-throughput RNAi in Caenorhabditis elegans: Genome-wide screens and functional genomics. Differentiation 2004, 72, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesley, S.V.; Helliwell, C.A.; Smith, N.A.; Wang, M.; Rouse, D.T.; Liu, Q.; Gooding, P.S.; Singh, S.P.; Abbott, D.; Stoutjesdijk, P.A. Construct design for efficient, effective and high-throughput gene silencing in plants. Plant J. 2001, 27, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urwin, P.E.; Lilley, C.J.; Atkinson, H.J. Ingestion of double-stranded RNA by preparasitic juvenile cyst nematodes leads to RNA interference. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, E.; di Vito, M.; Jones, J.T.; de Giorgi, C. Analysis of chitin synthase function in a plant parasitic nematode, Meloidogyne artiellia, using RNAi. Gene 2005, 349, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.Z.; Allen, R.; Davis, E.L.; Baum, T.J.; Hussey, R.S. Engineering broad root-knot resistance in transgenic plants by RNAi silencing of a conserved and essential root-knot nematode parasitism gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14302–14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.B.; Lu, Q.; Liang, J.; Zhang, X.Y. Functional analysis of the cellulose gene of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, using RNA interference. Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.H.; Jian, H.; Xu, J.M.; Chen, C.D.; Guo, Q.X.; Liu, Q.; Guo, Y.D. RNAi silencing of the Meloidogyne incognita Rpn7 gene reduces nematode parasitic success. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 134, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Y.; Dai, S.M.; Xiao, L.; Xie, B.Y. Influence of cellulase gene knockdown by dsRNA interference on the development and reproduction of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Nematology 2010, 12, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.W.; Wu, X.Q.; Huang, L.; Tian, M.Q.; Ye, J.R. Specifically expressed genes of the nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus involved with early interactions with pine trees. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.L.; Hussey, R.S.; Baum, T.J. Getting to the roots of parasitism by nematodes. Trends Parasitol. 2004, 20, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, T.; Shibuya, H.; Aikawa, T.; Jones, J.T. Cloning and characterization of pectate lyases expressed in the esophageal gland of the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosso, M.N.; Jones, J.T.; Abad, P. RNAi and functional genomics in plant parasitic nematodes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 207–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Kemphues, K.J. Par-1, a gene required for establishing polarity in C. elegans embryos, encodes a putative Ser/Thr kinase that is asymmetrically distributed. Cell 1995, 81, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalzell, J.J.; Warnock, N.D.; Stevenson, M.A.; Mousley, A.; Fleming, C.C.; Maule, A.G. Short interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of drosha and pasha in undifferentiated Meloidogyne incognita eggs leads to irregular growth and embryonic lethality. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haegeman, A.; Vanholme, B.; Gheysen, G. Characterization of a putative endoxylanase in the migratory plant-parasitic nematode Radopholus similis. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, W.S.; Jeong, P.Y.; Woo, T.; Kim, C.B.; Paik, Y.K.; Koo, H.S. The efficiency of RNA interference in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Mol. Cells 2008, 26, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.N.; Oh, B.K.; Kawasaki, I.; Oh, W.S.; Lee, Y.; Paik, Y.K.; Shim, Y.H. Identification of cdc25 gene in pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, and its function in reproduction. Mol. Cells 2010, 29, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.T.; Moens, M.; Mota, M.; Li, H.M.; Kikuchi, T. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus: Opportunities in comparative genomics and molecular host-parasite interactions. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.R.; Cheng, X.; Li, Y.D.; Zhang, J.A.; Zhang, Z.F.; Wu, H.R. Cloning arginine kinase gene and its RNAi in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus causing pine wilt disease. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 134, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishok, A.; Tabara, H.; Mello, C.C. Genetic requirements for inheritance of RNAi in C. elegans. Science 2000, 287, 2494–2497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bakhetia, M.; Urwin, P.E.; Atkinson, H.J. qPCR analysis and RNAi define pharyngeal gland cell-expressed genes of Heterodera glycines required for initial interactions with the host. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popeijus, H.; Overmars, H.; Jones, J.; Blok, V.; Goverse, A.; Helder, J.; Schots, A.; Bakker, J.; Smant, G. Enzymology—Degradation of plant cell walls by a nematode. Nature 2000, 406, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaubert, S.; Laffaire, J.B.; Abad, P.; Rosso, M.N. A polygalacturonase of animal origin isolated from the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. FEBS Lett. 2002, 522, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitreva-Dautova, M.; Roze, E.; Overmars, H.; de Graaff, L.; Schots, A.; Helder, J.; Goverse, A.; Bakker, J.; Smant, G. A symbiont-independent endo-1,4-β-xylanase from the plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.L.; Zhang, J.P.; Huang, L.; Tao, J.; Zhao, B.G.S. A method of massively isolating PWN larvae and obtaining sterile larvae. For. Pest Dis. 2011, 30, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, X.-W.; Wu, X.-Q.; Huang, L.; Ye, J.-R. Influence of Bxpel1 Gene Silencing by dsRNA Interference on the Development and Pathogenicity of the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010125
Qiu X-W, Wu X-Q, Huang L, Ye J-R. Influence of Bxpel1 Gene Silencing by dsRNA Interference on the Development and Pathogenicity of the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Xiu-Wen, Xiao-Qin Wu, Lin Huang, and Jian-Ren Ye. 2016. "Influence of Bxpel1 Gene Silencing by dsRNA Interference on the Development and Pathogenicity of the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010125
APA StyleQiu, X.-W., Wu, X.-Q., Huang, L., & Ye, J.-R. (2016). Influence of Bxpel1 Gene Silencing by dsRNA Interference on the Development and Pathogenicity of the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010125