VEGFR-1 Overexpression Identifies a Small Subgroup of Aggressive Prostate Cancers in Patients Treated by Prostatectomy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
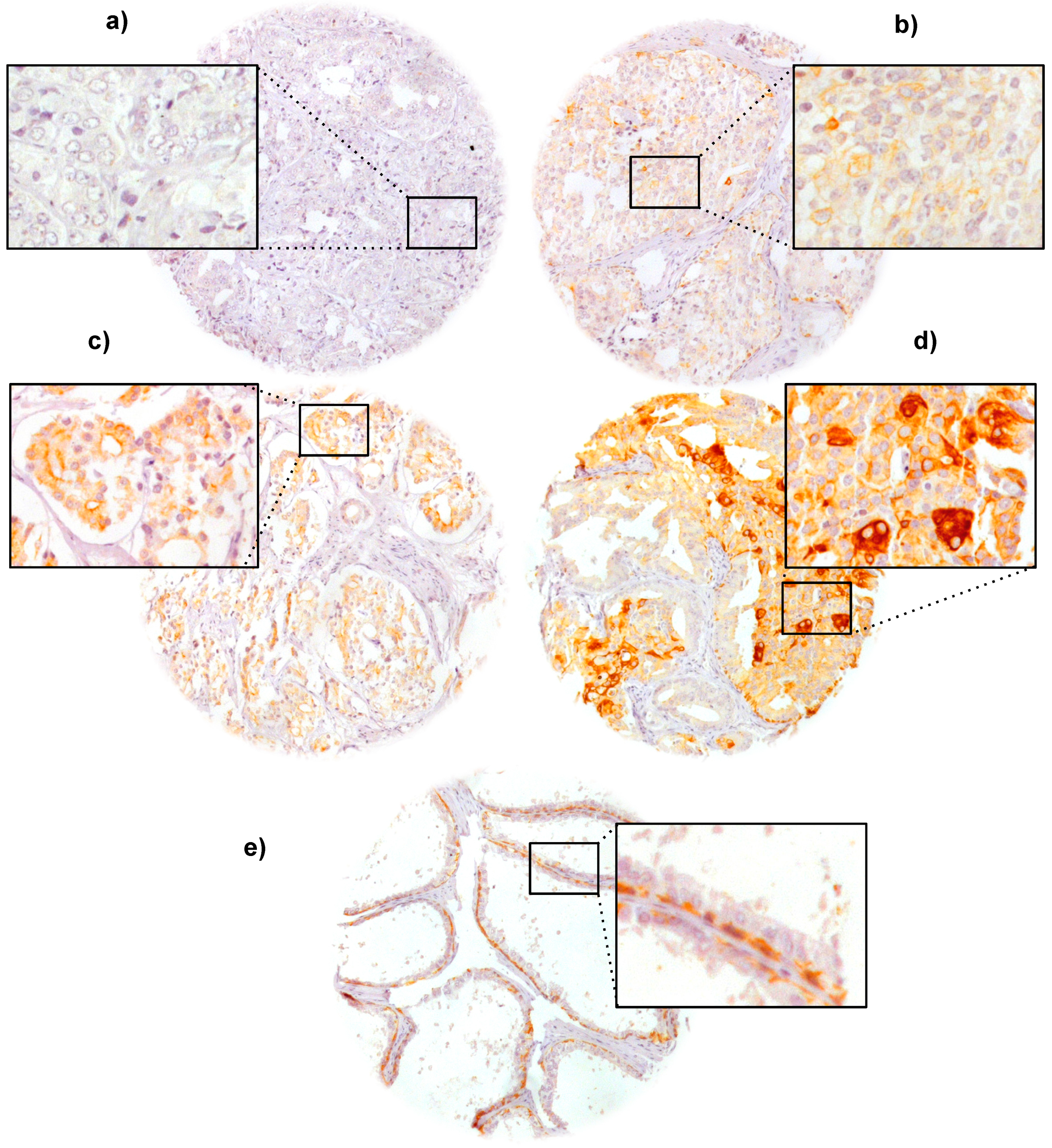
2.1. Technical Issues
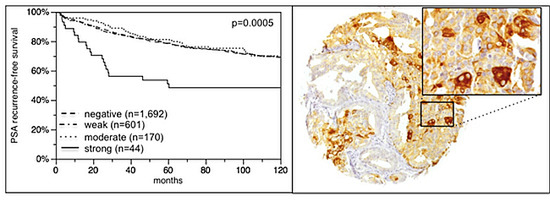
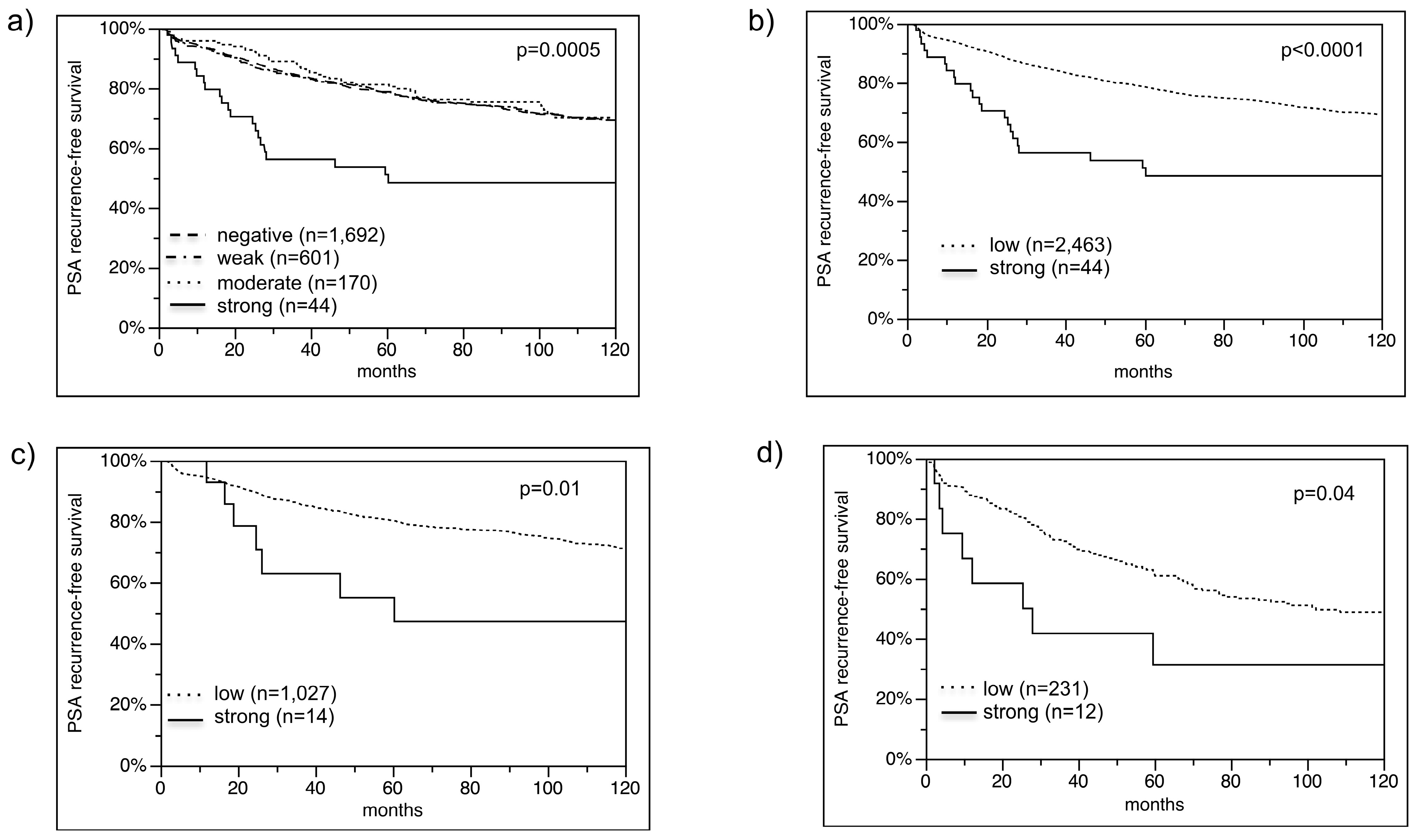
2.2. VEGFR-1 Expression in Prostate Cancer
2.3. Association with TMPRSS2:ERG Fusion Status and ERG Protein Expression
2.4. Association with Tumor Phenotype

| Parameter | Evaluable (N) | Immunostaining (%) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Weak | Moderate | Strong | |||
| All cancers | 2669 | 67 | 24 | 6.7 | 1.7 | |
| Tumor stage | ||||||
| pT2 | 1728 | 69 | 23 | 7.0 | 1.0 | <0.0001 |
| pT3a | 553 | 68 | 23 | 7.0 | 2.0 | |
| pT3b | 326 | 63 | 29 | 4.6 | 3.7 | |
| pT4 | 34 | 50 | 29 | 5.9 | 15 | |
| Gleason grade | ||||||
| ≤3 + 3 | 1156 | 69 | 23 | 7.3 | 1.1 | 0.03 |
| 3 + 4 | 1165 | 66 | 26 | 6.8 | 1.7 | |
| 4 + 3 | 273 | 69 | 23 | 4.8 | 3.7 | |
| ≥4 + 4 | 47 | 68 | 23 | 2.1 | 6.4 | |
| Lymph node metastasis | ||||||
| N0 | 1316 | 67 | 26 | 5.3 | 1.6 | 0.05 |
| N+ | 84 | 57 | 32 | 4.8 | 6.0 | |
| PSA preoperative | ||||||
| <4 | 401 | 63 | 27 | 8.0 | 2.2 | 0.23 |
| 4–10 | 1435 | 67 | 24 | 7.3 | 1.3 | |
| 11–20 | 564 | 69 | 23 | 5.7 | 2.5 | |
| >20 | 204 | 72 | 22 | 4.4 | 1.5 | |
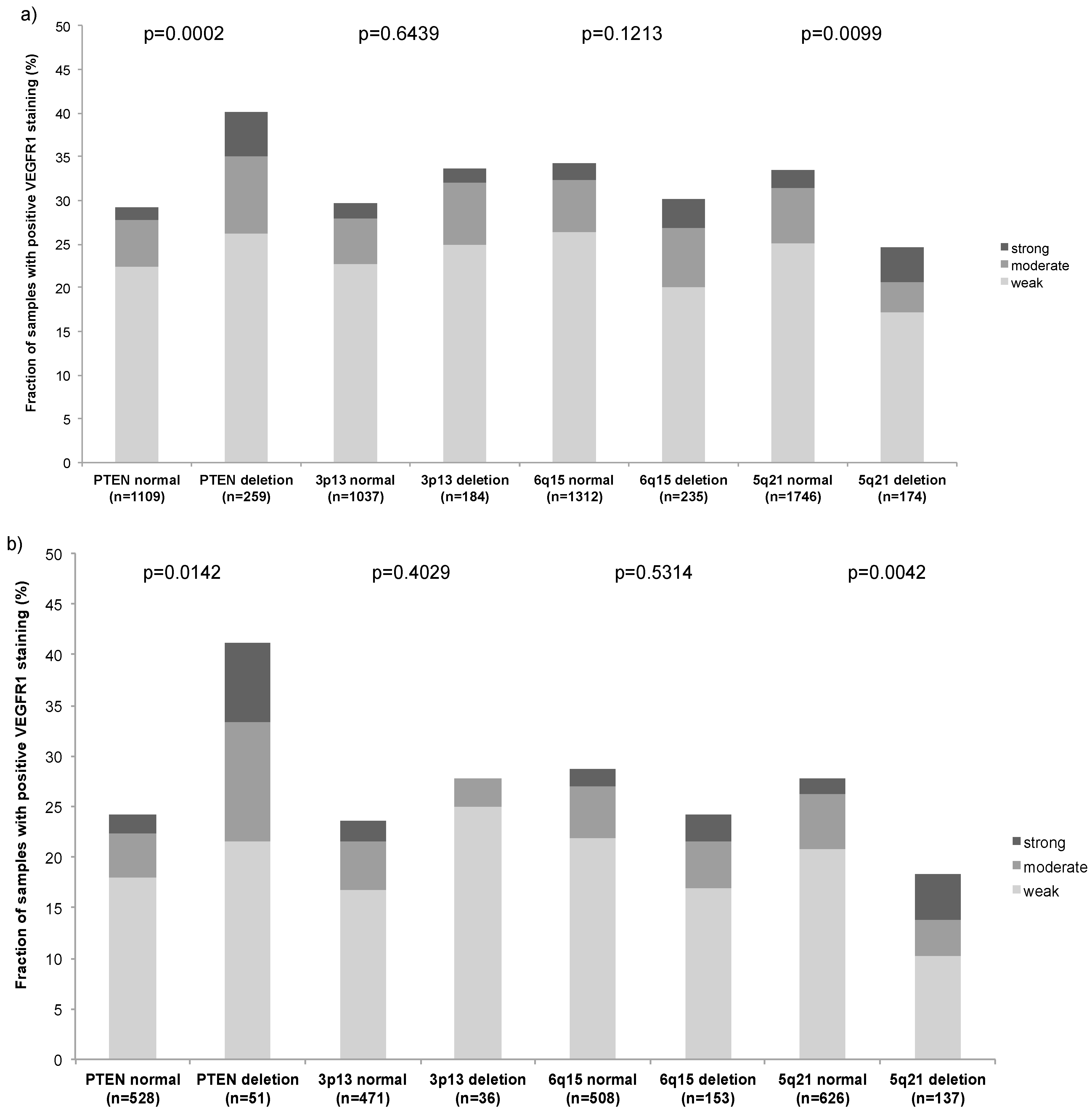
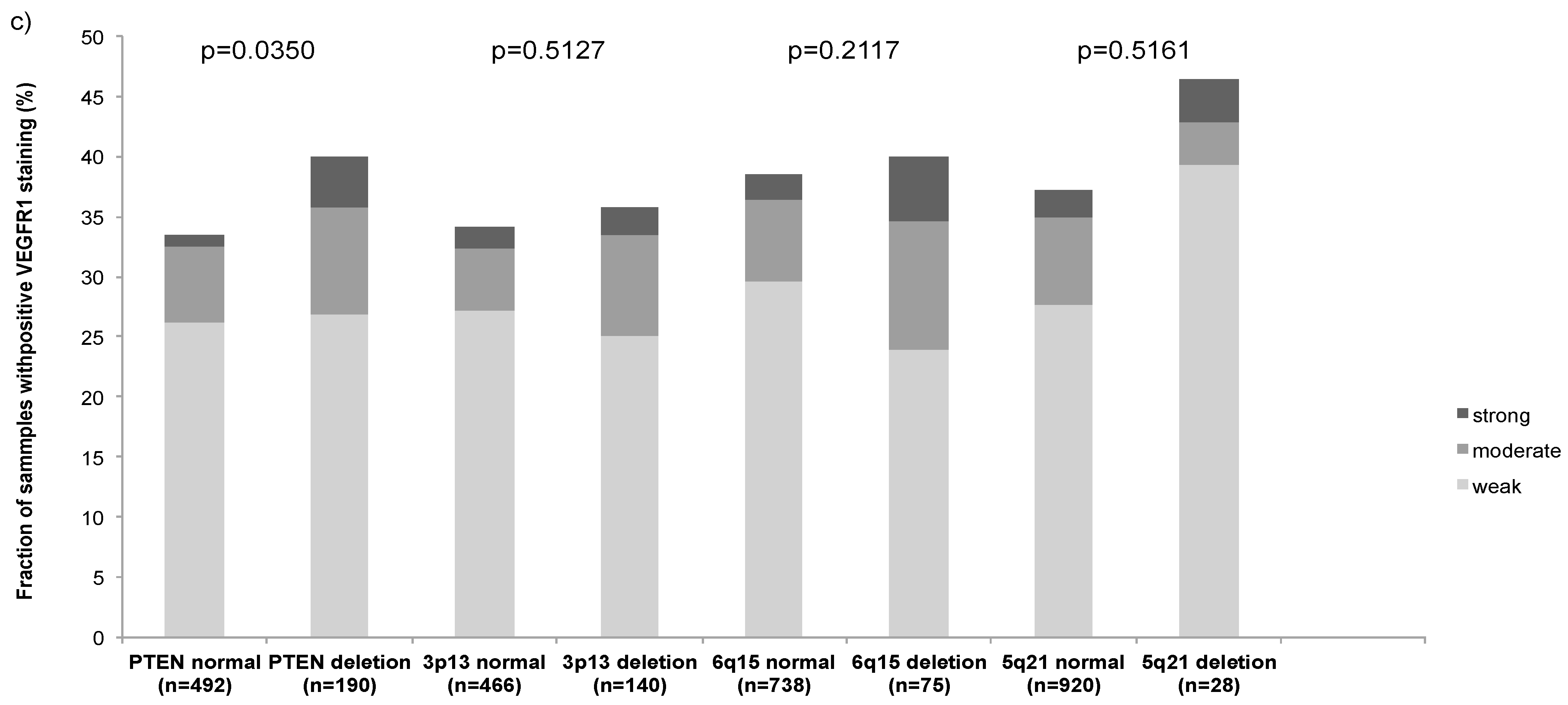
2.5. Association with Other Key Genomic Deletions
2.6. Association with PSA Recurrence
3. Discussion
| Parameter | RR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor stage | |||
| pT3a vs. pT2 | 1.9 | 1.5–2.4 | <0.0001 |
| pT3b vs. pT3a | 1.8 | 1.4–2.2 | |
| pT4 vs. pT3b | 1.4 | 0.9–2.1 | |
| Gleason grade | |||
| 3 + 4 vs. ≤3 + 3 | 2.4 | 1.8–3.3 | <0.0001 |
| 4 + 3 vs. 3 + 4 | 2.3 | 1.8–2.8 | |
| ≥4 + 4 vs. 4 + 3 | 1.4 | 1.0–2.1 | |
| Nodal stage | |||
| pN1 vs. pN0 | 1.9 | 1.5–2.5 | < 0.0001 |
| Resection margin status | |||
| R1 vs. R0 | 1.5 | 1.2–1.8 | <0.0001 |
| Pre-operative PSA (ng/mL) | |||
| 4–10 vs. <4 | 1.1 | 0.8–1.6 | 0.05 |
| 11–20 vs. 4–10 | 1.1 | 0.9–1.4 | |
| >20 vs. 11–20 | 1.2 | 0.9–1.5 | |
| VEGFR-1 | |||
| strong vs. low | 1.9 | 1.1–3.0 | 0.02 |
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Patients
| Parameter | n = 3261 on TMA | n = 2891 with Clinical Follow-up |
|---|---|---|
| Follow-up (months) | ||
| Mean | 72.1 | |
| Median | 68.9 | |
| Range | 1–219 | |
| Age (years) | ||
| <50 | 83 | 78 |
| 50–60 | 998 | 912 |
| 60–70 | 1807 | 1699 |
| >70 | 175 | 169 |
| Pretreatment PSA (ng/mL) | ||
| <4 | 513 | 478 |
| 4–10 | 1673 | 1544 |
| 11–20 | 641 | 608 |
| >20 | 225 | 212 |
| pT category (AJCC 2002) | ||
| pT2 | 2080 | 1907 |
| pT3a | 609 | 579 |
| pT3b | 372 | 361 |
| pT4 | 42 | 42 |
| Gleason grade | ||
| ≤3 + 3 | 1426 | 1307 |
| 3 + 4 | 1311 | 1238 |
| 4 + 3 | 313 | 297 |
| ≤4 + 4 | 55 | 49 |
| pN category | ||
| pN0 | 1544 | 1492 |
| pN+ | 96 | 93 |
| pNx | 1457 | 1298 |
| Surgical margin | ||
| Negative | 2475 | 2295 |
| Positive | 627 | 594 |
4.2. Immunochemistry
4.3. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilt, T.J.; Brawer, M.K.; Jones, K.M.; Barry, M.J.; Aronson, W.J.; Fox, S.; Gingrich, J.R.; Wei, J.T.; Gilhooly, P.; Grob, B.M.; et al. Radical prostatectomy versus observation for localized prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, I.M., Jr.; Tangen, C.M. Prostate cancer—Uncertainty and a way forward. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Hooper, A.T.; Zhong, Z.; Witte, L.; Bohlen, P.; Rafii, S.; Hicklin, D.J. The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (vegfr-1) supports growth and survival of human breast carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor system: Physiological functions in angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases. J. Biochem. 2013, 153, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.Y.; Li, J.F.; Gnatovskiy, L.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Grzesik, D.A.; Qian, H.; Xue, X.N.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophages regulate the angiogenic switch in a mouse model of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11238–11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Zheng, Y.; Hirashima, M.; Suda, T.; Morita, Y.; Ooehara, J.; Ema, H.; Fong, G.H.; Shibuya, M. Vegfr1 tyrosine kinase signaling promotes lymphangiogenesis as well as angiogenesis indirectly via macrophage recruitment. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.S.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Hicklin, D.J.; Moore, M.A. Targeting autocrine and paracrine vegf receptor pathways inhibits human lymphoma xenografts in vivo. Blood 2004, 104, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragoso, R.; Pereira, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Cabecadas, J.; Dias, S. Vegfr-1 (flt-1) activation modulates acute lymphoblastic leukemia localization and survival within the bone marrow, determining the onset of extramedullary disease. Blood 2006, 107, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, L.; Jin, D.K.; Karajannis, M.A.; Shido, K.; Hooper, A.T.; Rashbaum, W.K.; Pytowski, B.; Wu, Y.; Hicklin, D.J.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Fetal stromal-dependent paracrine and intracrine vascular endothelial growth factor-a/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 signaling promotes proliferation and motility of human primary myeloma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3185–3192. [Google Scholar]
- Lacal, P.M.; Failla, C.M.; Pagani, E.; Odorisio, T.; Schietroma, C.; Falcinelli, S.; Zambruno, G.; D’Atri, S. Human melanoma cells secrete and respond to placenta growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaussin, M.; Sartelet, H.; Robert, C.; Moro, D.; Claraz, C.; Brambilla, C.; Brambilla, E. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (vegf) and its two receptors (vegf-r1-flt1 and vegf-r2-flk1/kdr) in non-small cell lung carcinomas (nsclcs): Correlation with angiogenesis and survival. J. Pathol. 1999, 188, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.; Wey, J.S.; McCarty, M.F.; Belcheva, A.; Liu, W.; Bauer, T.W.; Somcio, R.J.; Wu, Y.; Hooper, A.; Hicklin, D.J.; et al. Expression and function of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 on human colorectal cancer cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar]
- Wey, J.S.; Fan, F.; Gray, M.J.; Bauer, T.W.; McCarty, M.F.; Somcio, R.; Liu, W.; Evans, D.B.; Wu, Y.; Hicklin, D.J.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 promotes migration and invasion in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer 2005, 104, 427–438. [Google Scholar]
- Laird, A.; O’Mahony, F.C.; Nanda, J.; Riddick, A.C.; O'Donnell, M.; Harrison, D.J.; Stewart, G.D. Differential expression of prognostic proteomic markers in primary tumour, venous tumour thrombus and metastatic renal cell cancer tissue and correlation with patient outcome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentheroudakis, G.; Nicolaou, I.; Kotoula, V.; Fountzilas, E.; Markou, K.; Eleftheraki, A.G.; Fragkoulidi, A.; Karasmanis, I.; Tsigka, A.; Angouridakis, N.; et al. Prognostic utility of angiogenesis and hypoxia effectors in patients with operable squamous cell cancer of the larynx. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 709–716. [Google Scholar]
- Pajares, M.J.; Agorreta, J.; Larrayoz, M.; Vesin, A.; Ezponda, T.; Zudaire, I.; Torre, W.; Lozano, M.D.; Brambilla, E.; Brambilla, C.; et al. Expression of tumor-derived vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors is associated with outcome in early squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo de Santa Pau, E.; Arias, F.C.; Caso Pelaez, E.; Munoz Molina, G.M.; Sanchez Hernandez, I.; Muguruza Trueba, I.; Moreno Balsalobre, R.; Sacristan Lopez, S.; Gomez Pinillos, A.; del Val Toledo Lobo, M. Prognostic significance of the expression of vascular endothelial growth factors a, b, c, and d and their receptors r1, r2, and r3 in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 2009, 115, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Kitadai, Y.; Bucana, C.D.; Cleary, K.R.; Ellis, L.M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, kdr, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3964–3968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ieni, A.; Giuffre, G.; Adamo, V.; Tuccari, G. Prognostic impact of cd133 immunoexpression in node-negative invasive breast carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Talagas, M.; Uguen, A.; Garlantezec, R.; Fournier, G.; Doucet, L.; Gobin, E.; Marcorelles, P.; Volant, A.; de Braekeleer, M. Vegfr1 and nrp1 endothelial expressions predict distant relapse after radical prostatectomy in clinically localized prostate cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.; Camparo, P.; Badoual, C.; Peyromaure, M.; Delongchamps, N.B.; Vieillefond, A.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T. The association of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 with the risk of cancer progression following radical prostatectomy. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, F.A.; Miller, L.J.; Lindquist, R.; Kowalczyk, P.; Laudone, V.P.; Albertsen, P.C.; Kreutzer, D.L. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in human prostate cancer. Urology 1999, 54, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woollard, D.J.; Opeskin, K.; Coso, S.; Wu, D.; Baldwin, M.E.; Williams, E.D. Differential expression of vegf ligands and receptors in prostate cancer. Prostate 2013, 73, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Nakayama, M.; Nakai, Y.; Takayama, H.; Nishimura, K.; Ujike, T.; Nishimura, K.; Aozasa, K.; Okuyama, A.; Nonomura, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 expression in pelvic lymph nodes predicts the risk of cancer progression after radical prostatectomy. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minner, S.; Enodien, M.; Sirma, H.; Luebke, A.M.; Krohn, A.; Mayer, P.S.; Simon, R.; Tennstedt, P.; Muller, J.; Scholz, L.; et al. Erg status is unrelated to psa recurrence in radically operated prostate cancer in the absence of antihormonal therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5878–5888. [Google Scholar]
- Kluth, M.; Hesse, J.; Heinl, A.; Krohn, A.; Steurer, S.; Sirma, H.; Simon, R.; Mayer, P.S.; Schumacher, U.; Grupp, K.; et al. Genomic deletion of map3k7 at 6q12–22 is associated with early psa recurrence in prostate cancer and absence of tmprss2:Erg fusions. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 975–983. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, M.F.; Lawrence, M.S.; Demichelis, F.; Drier, Y.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.Y.; Sboner, A.; Esgueva, R.; Pflueger, D.; Sougnez, C.; et al. The genomic complexity of primary human prostate cancer. Nature 2011, 470, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Krohn, A.; Diedler, T.; Burkhardt, L.; Mayer, P.S.; de Silva, C.; Meyer-Kornblum, M.; Kotschau, D.; Tennstedt, P.; Huang, J.; Gerhauser, C.; et al. Genomic deletion of pten is associated with tumor progression and early psa recurrence in erg fusion-positive and fusion-negative prostate cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 401–412. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt, L.; Fuchs, S.; Krohn, A.; Masser, S.; Mader, M.; Kluth, M.; Bachmann, F.; Huland, H.; Steuber, T.; Graefen, M.; et al. Chd1 is a 5q21 tumor suppressor required for erg rearrangement in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2795–2805. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, R.; Mirlacher, M.; Sauter, G. Immunohistochemical analysis of tissue microarrays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 664, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simon, R.; Mirlacher, M.; Sauter, G. Tissue microarrays. Methods Mol. Med. 2005, 114, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schlomm, T.; Iwers, L.; Kirstein, P.; Jessen, B.; Kollermann, J.; Minner, S.; Passow-Drolet, A.; Mirlacher, M.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Graefen, M.; et al. Clinical significance of p53 alterations in surgically treated prostate cancers. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Lesslie, D.P.; Summy, J.M.; Parikh, N.U.; Fan, F.; Trevino, J.G.; Sawyer, T.K.; Metcalf, C.A.; Shakespeare, W.C.; Hicklin, D.J.; Ellis, L.M.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 mediates migration of human colorectal carcinoma cells by activation of src family kinases. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, J.D.; Rowinsky, E.K.; Youssoufian, H.; Pytowski, B.; Wu, Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 in human cancer: Concise review and rationale for development of imc-18f1 (human antibody targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1). Cancer 2010, 116, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, S.M.; Salanga, M.C.; Krieg, P.A. Kruppel-like factor 2 cooperates with the ets family protein erg to activate flk1 expression during vascular development. Development 2009, 136, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Dvorak, H.F.; Mukhopadhyay, D. Vascular permeability factor (vpf)/vascular endothelial growth factor (vegf) peceptor-1 down-modulates vpf/vegf receptor-2-mediated endothelial cell proliferation, but not migration, through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26969–26979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhiyong, C.; Wentong, L.; Xiaoyang, Y.; Ling, P. Pten’s regulation of vegf and vegfr1 expression and its clinical significance in myeloid leukemia. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, J.D.; Chen, Y.N.; Cornell-Kennon, S.A.; Dorsch, M.; Kim, S.; Leszczyniecka, M.; Sellers, W.R.; Lengauer, C. Validating cancer drug targets. Nature 2006, 441, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canil, C.M.; Moore, M.J.; Winquist, E.; Baetz, T.; Pollak, M.; Chi, K.N.; Berry, S.; Ernst, D.S.; Douglas, L.; Brundage, M.; et al. Randomized phase ii study of two doses of gefitinib in hormone-refractory prostate cancer: A trial of the national cancer institute of canada-clinical trials group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Pezaro, C.; Rosenthal, M.A.; Gurney, H.; Davis, I.D.; Underhill, C.; Boyer, M.J.; Kotasek, D.; Solomon, B.; Toner, G.C. An open-label, single-arm phase two trial of gefitinib in patients with advanced or metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 32, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, W.M.; Cao, D.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Ryan, C.W.; Hoving, K.; Wright, R.; Karrison, T.; Vokes, E.E. A randomized phase II trial of the antiangiogenic agent su5416 in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3365–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, P.N., Jr.; Chee, K.G.; Longmate, J.; Ruel, C.; Meyers, F.J.; Gray, C.R.; Edwards, R.G.; Gumerlock, P.H.; Twardowski, P.; Doroshow, J.H.; et al. Trastuzumab plus docetaxel in her-2/neu-positive prostate carcinoma: Final results from the california cancer consortium screening and phase ii trial. Cancer 2004, 100, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.J.; Reuter, V.E.; Kelly, W.K.; Slovin, S.F.; Kenneson, K.; Verbel, D.; Osman, I.; Scher, H.I. Her-2 profiling and targeting in prostate carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 94, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziada, A.; Barqawi, A.; Glode, L.M.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Crighton, F.; Majeski, S.; Rosenblum, M.; Kane, M.; Chen, L.; Crawford, E.D. The use of trastuzumab in the treatment of hormone refractory prostate cancer; phase ii trial. Prostate 2004, 60, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, P.M.; Krishnamurthi, S.; Youssoufian, H.; Hall, N.; Fox, F.; Dontabhaktuni, A.; Grebennik, D.; Remick, S. Icrucumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody against the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1, in the treatment of patients with advanced solid malignancies: A phase 1 study. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 32, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononen, J.; Bubendorf, L.; Kallioniemi, A.; Barlund, M.; Schraml, P.; Leighton, S.; Torhorst, J.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Sauter, G.; Kallioniemi, O.P. Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krohn, A.; Seidel, A.; Burkhardt, L.; Bachmann, F.; Mader, M.; Grupp, K.; Eichenauer, T.; Becker, A.; Adam, M.; Graefen, M.; et al. Recurrent deletion of 3p13 targets multiple tumour suppressor genes and defines a distinct subgroup of aggressive erg fusion-positive prostate cancers. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 130–141. [Google Scholar]
- Tsourlakis, M.C.; Walter, E.; Quaas, A.; Graefen, M.; Huland, H.; Simon, R.; Sauter, G.; Steurer, S.; Schlomm, T.; Minner, S. High nr-cam expression is associated with favorable phenotype and late psa recurrence in prostate cancer treated by prostatectomy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013, 16, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsourlakis, M.C.; Khosrawi, P.; Weigand, P.; Kluth, M.; Hube-Magg, C.; Minner, S.; Koop, C.; Graefen, M.; Heinzer, H.; Wittmer, C.; et al. VEGFR-1 Overexpression Identifies a Small Subgroup of Aggressive Prostate Cancers in Patients Treated by Prostatectomy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 8591-8606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16048591
Tsourlakis MC, Khosrawi P, Weigand P, Kluth M, Hube-Magg C, Minner S, Koop C, Graefen M, Heinzer H, Wittmer C, et al. VEGFR-1 Overexpression Identifies a Small Subgroup of Aggressive Prostate Cancers in Patients Treated by Prostatectomy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(4):8591-8606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16048591
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsourlakis, Maria Christina, Puya Khosrawi, Philipp Weigand, Martina Kluth, Claudia Hube-Magg, Sarah Minner, Christina Koop, Markus Graefen, Hans Heinzer, Corinna Wittmer, and et al. 2015. "VEGFR-1 Overexpression Identifies a Small Subgroup of Aggressive Prostate Cancers in Patients Treated by Prostatectomy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 4: 8591-8606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16048591
APA StyleTsourlakis, M. C., Khosrawi, P., Weigand, P., Kluth, M., Hube-Magg, C., Minner, S., Koop, C., Graefen, M., Heinzer, H., Wittmer, C., Sauter, G., Krech, T., Wilczak, W., Huland, H., Simon, R., Schlomm, T., & Steurer, S. (2015). VEGFR-1 Overexpression Identifies a Small Subgroup of Aggressive Prostate Cancers in Patients Treated by Prostatectomy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(4), 8591-8606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16048591