Anticarcinogenic Properties of Medium Chain Fatty Acids on Human Colorectal, Skin and Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Medium Chain Fatty Acids Inhibit the Growth of Human Cancer Cell Types
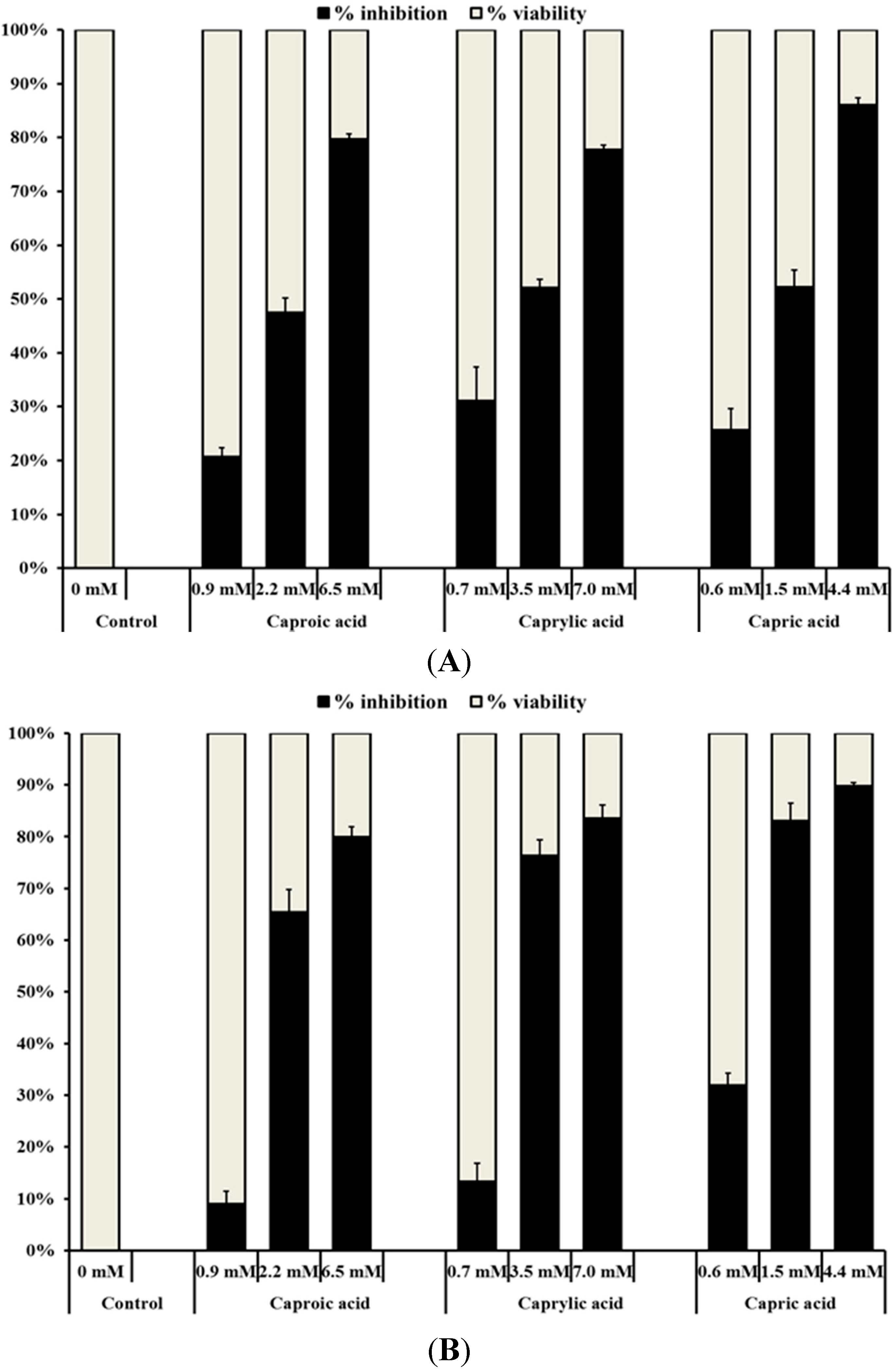
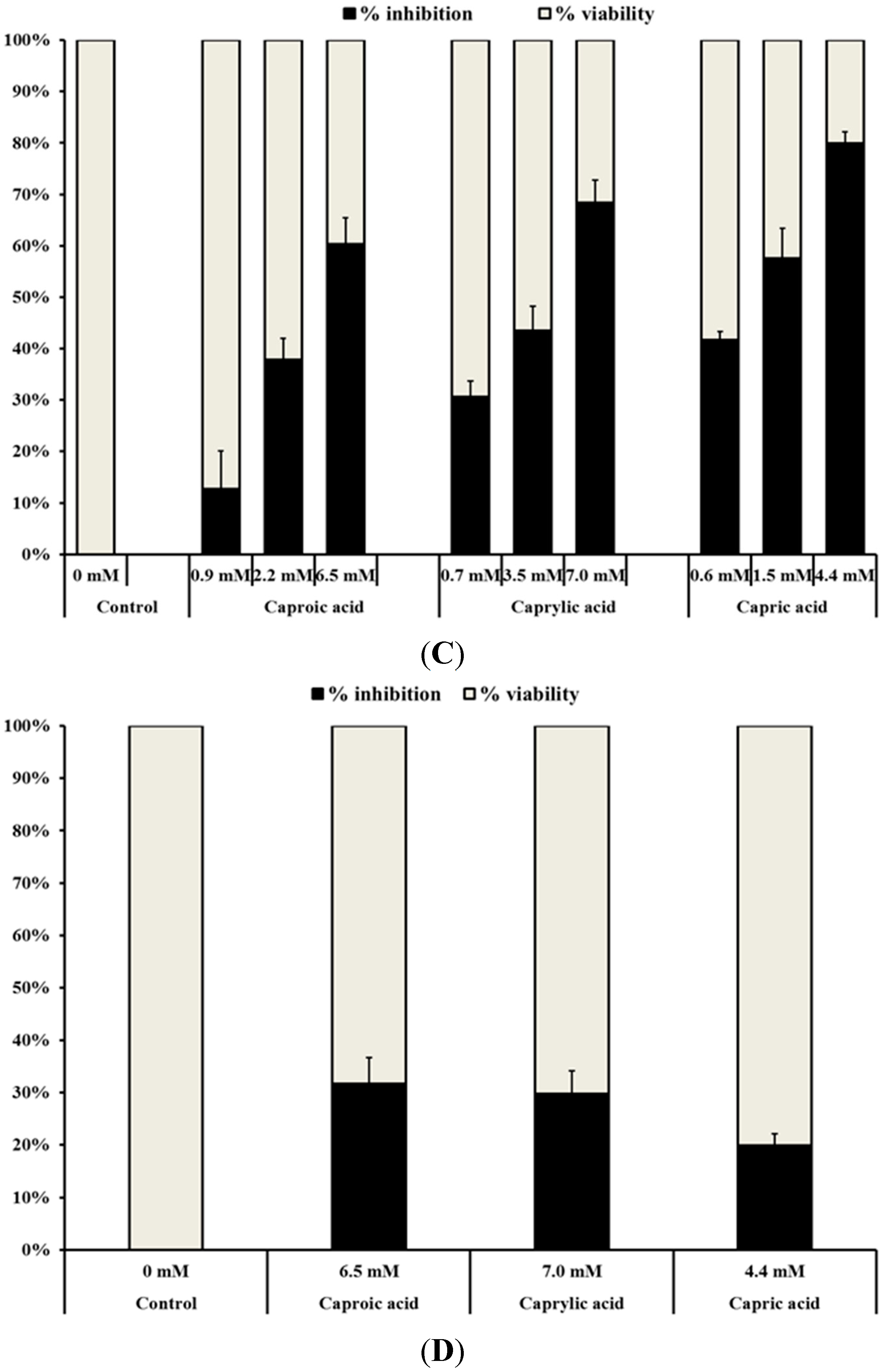
2.1.2. Medium Chain Fatty Acids Modulate Critical Genes Required for Cell Progression and Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cell Types
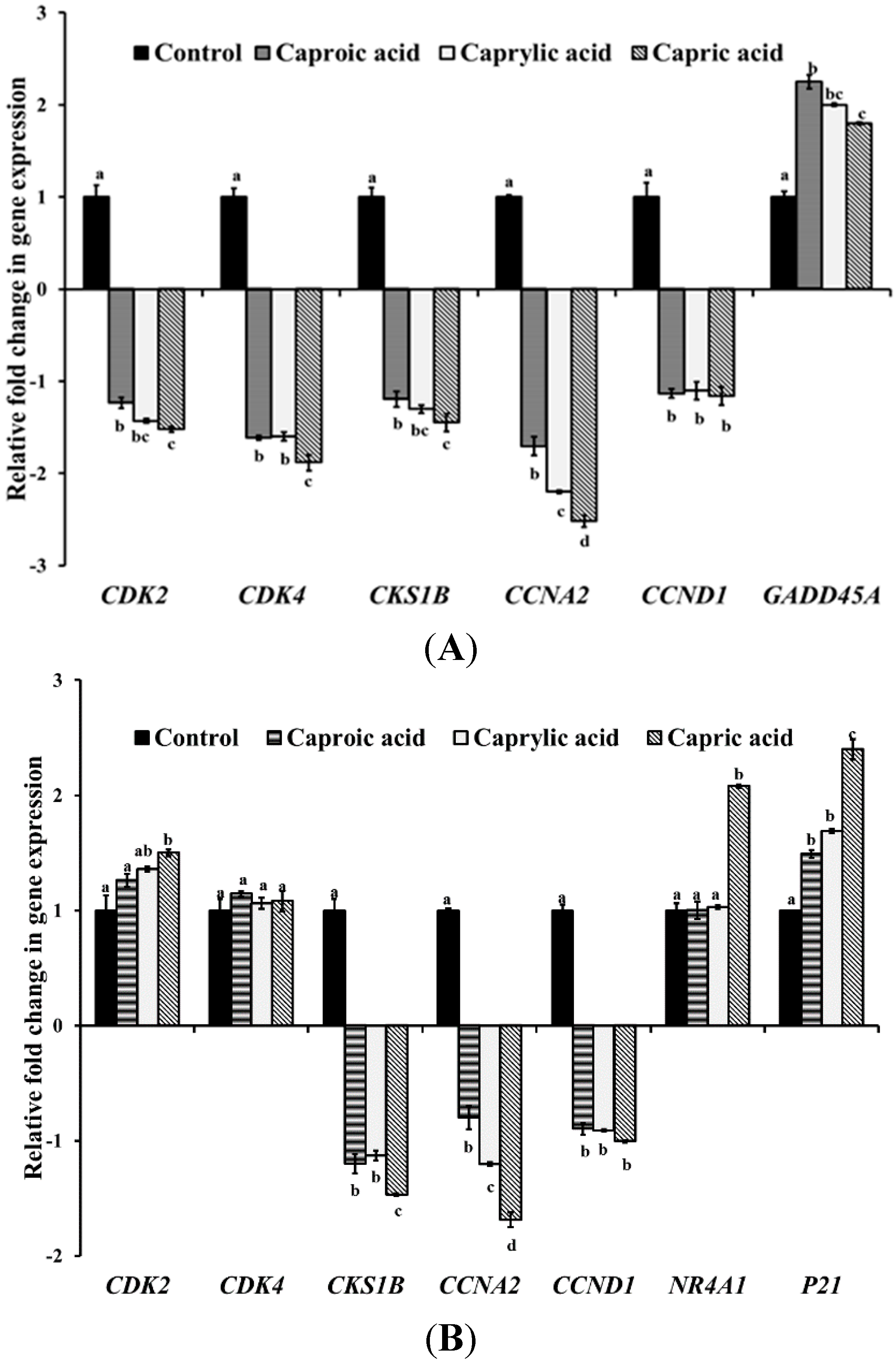
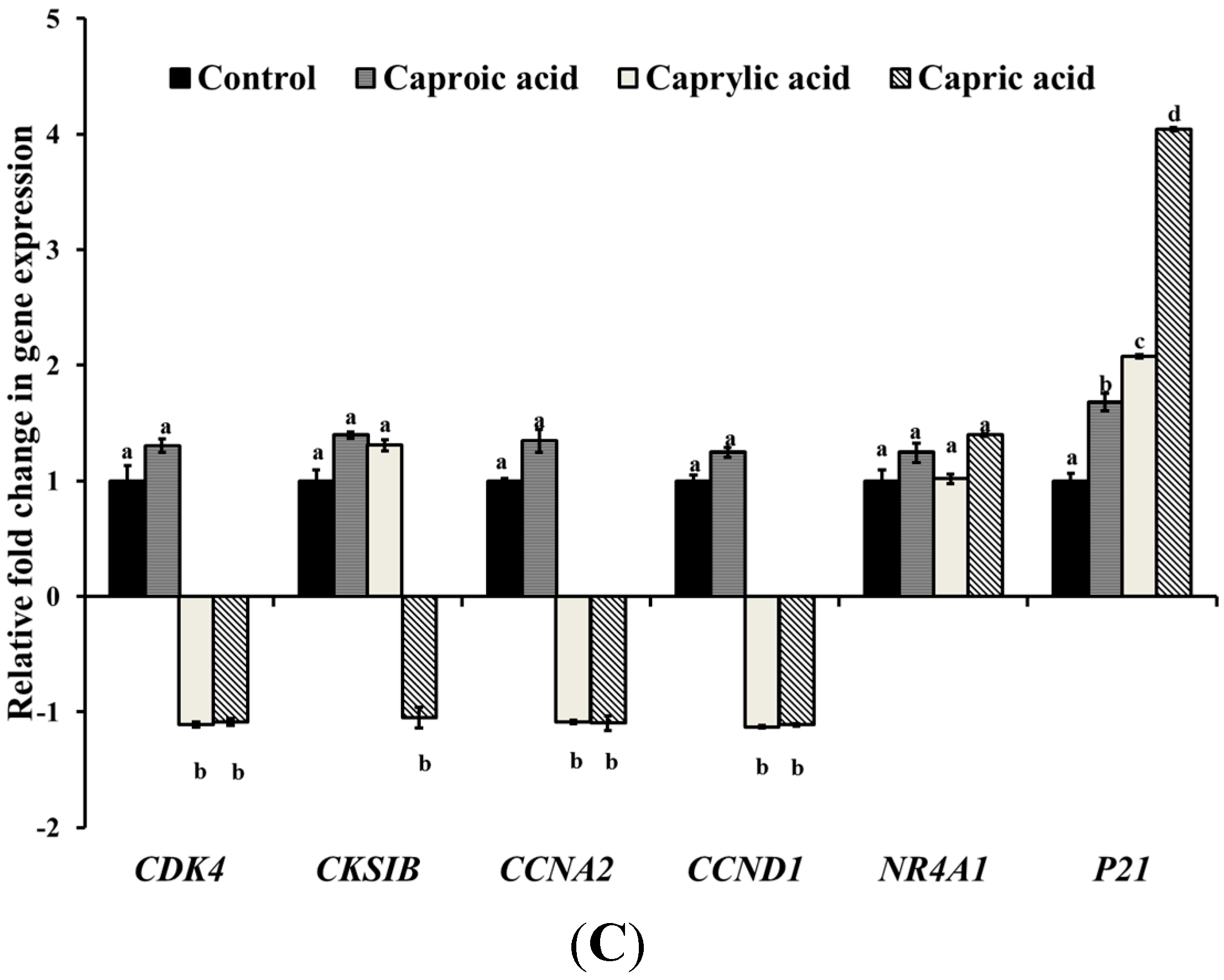
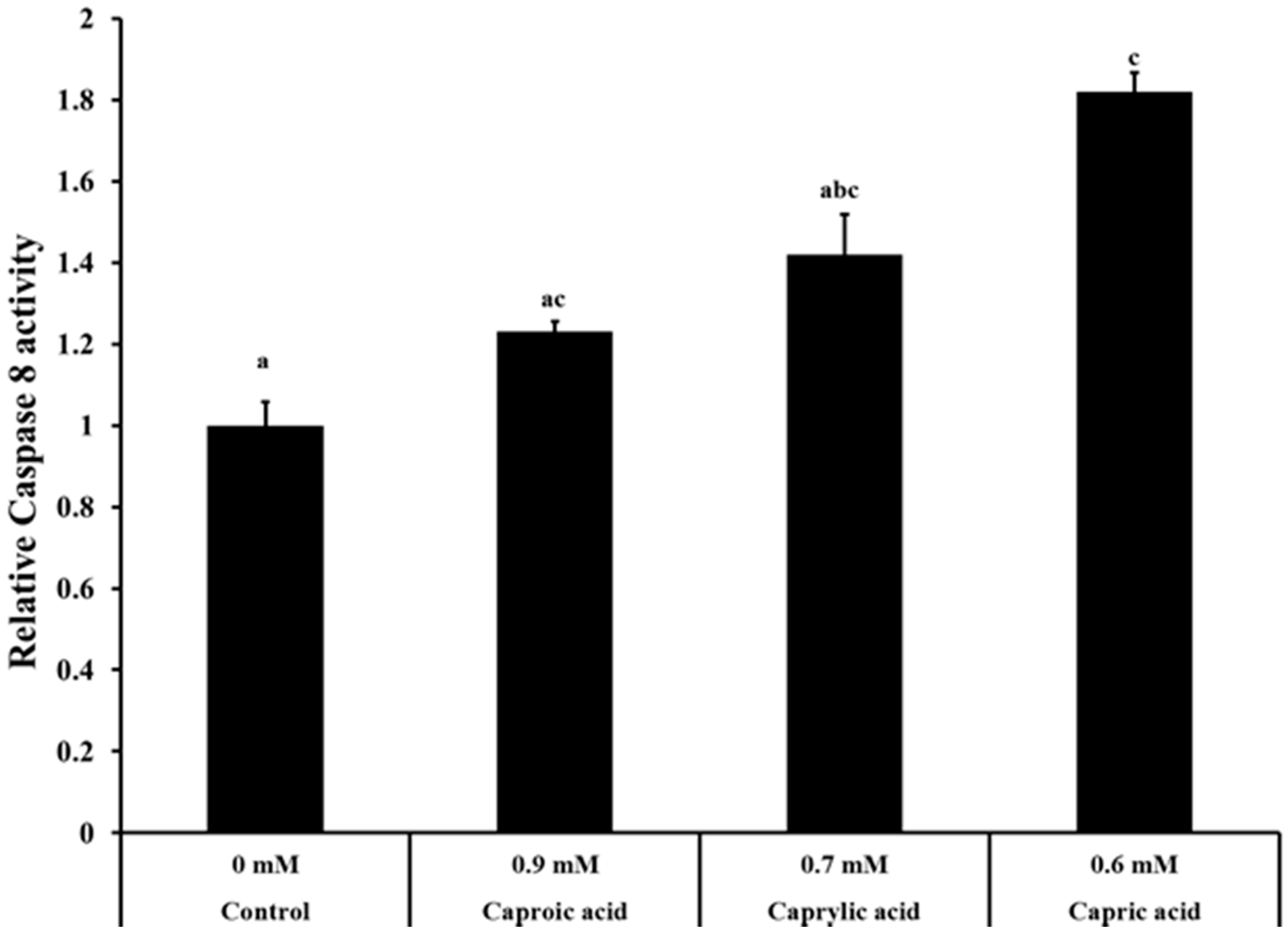
2.1.3. Goat Milk Medium Chain Fatty Acids Induced Activation of Caspase-8 and Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
3.2. Growth Inhibition Assay
3.3. Determination of the Anticancer Mechanisms of Goat Milk Medium Chain Fatty Acids
3.3.1. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis and Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR)
| Primer | Sequence (5ꞌ→3ꞌ) | NCBI Reference No. |
|---|---|---|
| P27F P27R | CGGTGGACCACGAAGAGTTAA GGCTCGCCTCTTCCATGTC | NM_004064.3 |
| CDK4F CDK4R | AGGCGACTGGAGGCTTTTG GTGGCACAGACGTCCATCAG | NM_000075.2 |
| CDK2F CDK2R | GACTCGCTGGCGCTTCA CGTGCCCTCTCCGATCTTT | NM_001798.3 |
| CCND1F CCNDIR | CGTGGCCTCTAAGATGAAGGA CGGTGTAGATGCACAGCTTCTC | NM_053056.2 |
| CCNA2F CCNA2R | CAACAGAGGTTGGGAGTGGAA GCATTTCTCGTCTGTTAATTTGCA | NM_001237.3 |
| GADD45AF GADD45AR | GATGTGGCTCTGCAGATCCA ATGTCGTTCTCGCAGCAAAA | NM_001924.2 |
| CKS1BF CKS1BR | CCACTACCCAAGAAACCAAAGAA GCTGTGTAAAGCTTGAGGCTGAA | NM_001826.2 |
| HPRT1F ‡ HPRT1R ‡ | CGTCTTGCTCGAGATGTGATG GCACACAGAGGGCTACAATGTG | NM_000194.2 |
| NR4A1F NR4A1R | AGGGCTGCAAGGGCTTCT GGCAGATGTACTTGGCGTTTTT | NM_002135.3 |
| P21F P21R | TGGAGACTCTCAGGGTCGAAA GCGTTTGGAGTGGTAGAAATCTG | NM_000389.3 |
3.3.2. Caspase-8 Activity Assay for Apoptosis
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngamkitidechakul, C.; Jaijoy, K.; Hansakul, P.; Soonthornchareonnon, N.; Sireeratawong, S. Antitumour effects of Phyllanthus emblica L: Induction of cancer cell apoptosis and inhibition of in vivo tumour promotion and in vitro invasion of human cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2014. Available online : http://www.cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/cancerfactsfigures2014/ (accessed on 24 July 2014).
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Hao, Y.; Xu, J.; Murray, T.; Thun, M.J. Cancer statics, 2008. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2008, 58, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Bommareddy, A.; Chen, W.; Khalifa, S.; Kaushik, R.S.; Fahmy, H.; Dwivedi, C. Sarcophine-diol, a chemopreventive agent of skin cancer, inhibits cell growth and induces apopotosis through extrinsic pathway in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Transl. Oncol. 2009, 2, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einspahr, J.G.; Bowden, G.T.; Alberts, D.S. Skin cancer chemoprevention: Strategies to save our skin. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2003, 163, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Murray, T.; Xu, J.; Smigal, C.; Thun, M.J. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2006, 56, 106–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.L.; Jang, S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, M.J.; Kim, K.J.; Ha, N.J. Anti-proliferative effects of Bifidobacterium adolescentis SPM0212 extract on human colon cancer lines. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, S.; Sun, R.W.; Lin, M.C.M.; Cui, J.T.; Zou, B.; Gu, Q.; Wong, B.C.Y. Gold (III) porphyrin complexes induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and inhibit tumor growth in colon cancer. Cancer 2009, 115, 4459–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, S.; Wang, J.; Lin, P.; Liu, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Wei, Y. Anticancer activity of litchi fruit pericarp extract against human breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 215, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Understanding chemotherapy a guide for patients and families/understanding-chemotherapy-chemo-side-effects. Avaliable online: http://www.cancer.org/Treatment/TreatmentsandSideEffects/TreatmentTypes/Chemotherapy/ (accessed on 27 September 2014).
- Damia, G.; Garattini, S. The pharmacological point of view of resistance to therapy in tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabik, C.A.; Dolan, M.E. Molecular mechanisms of resistance and toxicity associated with platinating agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slambrouck, S.V.; Daniels, A.L.; Hooten, C.J.; Brock, S.L.; Jenkins, A.R.; Ogaswara, M.A.; Baker, J.M.; Adkins, G.; Elias, E.M.; Agustin, V.J.; et al. Effects of crude aqueous medicinal plants extracts on growth and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, M.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Roy, S.; Mandal, C. Natural products: Promising resources for cancer drug discovery. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.; Gyllenhaal, C.; Soejarto, D.D. Biodiversity as a source of anticancer drugs. Curr. Drug Targ. 2006, 7, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.F.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, H.Y. Natural products and drug discovery. Can thousands of years of ancient medical knowledge lead us to new and powerful drug combinations in the fight against cancer and dementia? EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Pratheeshkumar, P.; Sreekala, C.; Zhang, Z.; Budhraja, A.; Ding, S.; Son, Y.O.; Wang, X.; Hitron, A.; Hyun-jung, K.; Wang, L.; et al. Cancer prevention with promising natural products: Mechanisms of action and molecular targets. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1159–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Lev, E. Healing with animals in the Levant from the 10th to the 18th century. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 1996, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kues, W.A.; Niemann, H. The contribution of farm animals to human health. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preuss, J. Biblical and Talmudic Medicine; Rosner, F., Ed.; Sanhedrin Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 435–437. [Google Scholar]
- Belewu, M.A.; Adewole, A.M. Goat milk: A feasible dietary based approach to improve the nutrition of orphan and vulnerable children. Pak. J. Nutr. 2009, 8, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Jirillo, F.; Jirillo, E.; Magron, T. Donkey’s and goat’s milk consumption and benefits to human health with special reference to the inflammatory status. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohiokpehai, O. Processed food products and nutrient composition of goat milk. Pak. J. Nutr. 2003, 2, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, U.K.; Mandal, P.K.; Rao, V.K.; Das, C.D. Quality and utility of goat milk with special reference to India: An overview. Asian J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 5, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullett, N.P.; Ruhul Amin, A.R.; Bayraktar, S.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Shin, D.M.; Khuri, F.R.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Surh, Y.J.; Kucuk, O. Cancer prevention with natural compounds. Semin. Oncol. 2010, 37, 258–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, H.; Ohshima, Y.; Nomoto, H.; Fujita, K.; Matsuda, E.; Iigo, M.; Moore, M.A. Cancer prevention by natural compounds. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 19, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J. Natural products in cancer chemotherapy: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. 2002, 2, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenlein, G.F.W. Goat milk in human nutrition. Small Rumin. Res. 2004, 51, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, R.R. Importance of goat milk. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 7, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, K.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Microarray analysis of butyrate regulated genes in colonic epithelial cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2006, 25, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dronamraju, S.S.; Coxhead, J.M.; Kelly, S.B.; Mathers, J.C. Differential antineoplastic effects of butyrate in cells with and without a functioning DNA mismatch repair. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwell, L.H.; Kastan, M.B. Cell cycle control and cancer. Science 1994, 266, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherr, C.J.; Roberts, J.M. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotto, G.P. P21(WAF1/Cip1): More than a break to the cell cycle? Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1471, M43–M56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hildesheim, J.; Bulavin, D.V.; Anver, M.R.; Alvord, W.G.; Hollander, M.C.; Vardanian, L.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. Gadd45a protects against UV irradiation-induced skin tumors, and promotes apoptosis and stress signaling via MAPK and p53. Cancer Res. 2002, 2, 7305–7315. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.Y.; Hail, N., Jr.; Lotan, R. Apoptosis as a novel target for cancer chemoprevention. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, G.Y.; Faden, A.I. Caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways in CNS injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2001, 24, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.M. Caspases: The executioners of apoptosis. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, M.; Soda, S.; Sakakibara, Y.; Suiko, M.; Nishiyama, K. The importance of 1,2-dithiolane structure in α-lipoic acid for the down-regulation of cell surface β1-integrin expression of human bladder cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1939–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.J.; Robinson, D.P.; Frank, R.D.; Anderson, K.E.; Bamlet, W.R.; Oberg, A.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Olson, J.E.; Sinha, R.; Petersen, G.M.; et al. Fatty acids found in dairy, protein and unsaturated fatty acids are associated with risk of pancreatic cancer in a case-control study. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar]
- El-Najjar, N.; Dakdouki, S.; Darwiche, N.; El-Sabban, M.; Saliba, N.A.; Gali-Muhtasib, H. Anti-colon cancer effects of Salograviolide A isolated from Centaurea ainetensis. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.; Rahumatullah, A.; Yogarajah, T.; Ahmad, M.; Yin, K.B. Potential effects of chrysin on MDA-MB-231 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Agarwal, C.; Singh, R.P.; Guan, X.; Dwivedi, C.; Agarwal, R. Skin cancer chemopreventive agent, a-santalol, induces apoptotic death of human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells via caspase activation together with dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential and cytochrome c release. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, J.L.; Hill, R.; Lee, P.W.; Giacomantonio, C.A.; Hoskin, D.W. Curcumin induces apoptosis in HCT-116 human colon cancer cells in a p21-independent manner. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2010, 84, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Vareed, S.K.; Nair, M.G. Human tumor cell growth inhibition by nontoxic anthocyanidins, the pigments in fruits and vegetables. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobral, R.G.; Jones, A.E.; Des Etages, S.G.; Dougherty, T.J.; Peitzsch, R.M.; Gaasterland, T.; Ludovice, A.M.; de Lencastre, H.; Tomasz, A. Extensive and genome-wide changes in the transcription profile of Staphylococcus aureus induced by modulating the transcription of the cell wall synthesis gene murF. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 2376–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kot, J.B.; Roelofs, R.W.; Giesendorf, B.A.; Pennings, J.L.; Waas, E.T.; Feuth, T.; Swinkels, D.W.; Span, P.N. Normalization of gene expression measurements in tumor tissues: Comparison of 13 endogenous control genes. Lab. Investig. 2005, 85, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Narayanan, A.; Baskaran, S.A.; Amalaradjou, M.A.R.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Anticarcinogenic Properties of Medium Chain Fatty Acids on Human Colorectal, Skin and Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5014-5027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16035014
Narayanan A, Baskaran SA, Amalaradjou MAR, Venkitanarayanan K. Anticarcinogenic Properties of Medium Chain Fatty Acids on Human Colorectal, Skin and Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(3):5014-5027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16035014
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarayanan, Amoolya, Sangeetha Ananda Baskaran, Mary Anne Roshni Amalaradjou, and Kumar Venkitanarayanan. 2015. "Anticarcinogenic Properties of Medium Chain Fatty Acids on Human Colorectal, Skin and Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 3: 5014-5027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16035014
APA StyleNarayanan, A., Baskaran, S. A., Amalaradjou, M. A. R., & Venkitanarayanan, K. (2015). Anticarcinogenic Properties of Medium Chain Fatty Acids on Human Colorectal, Skin and Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(3), 5014-5027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16035014







