RpoN Regulates Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Modulating the PqsR Quorum Sensing Regulator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
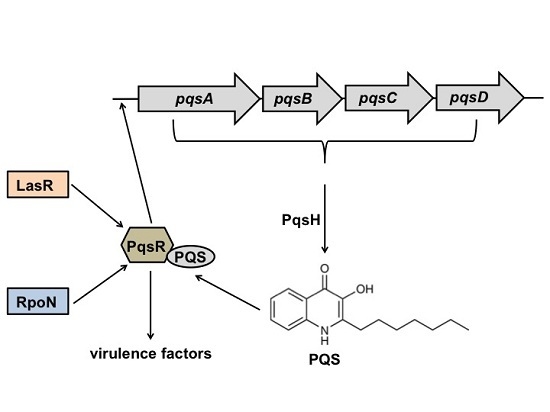
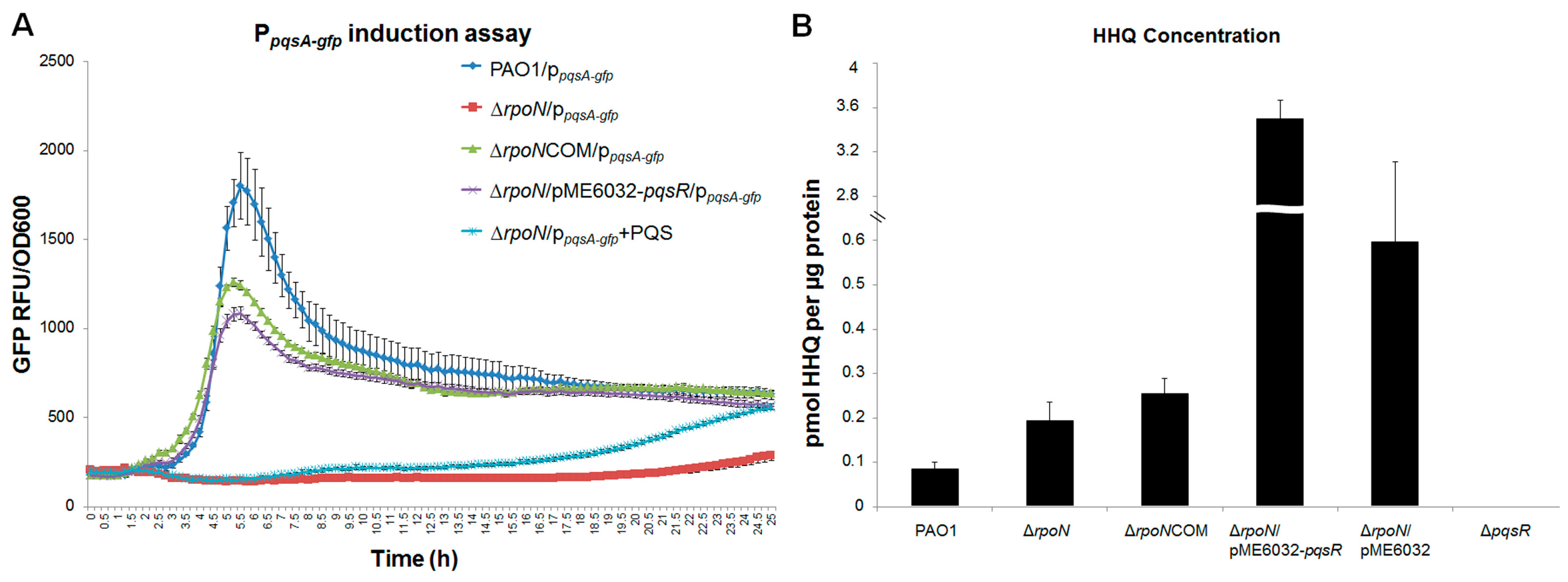
2.1. RpoN Regulates P. aeruginosa pqs Quorum Sensing via PqsR
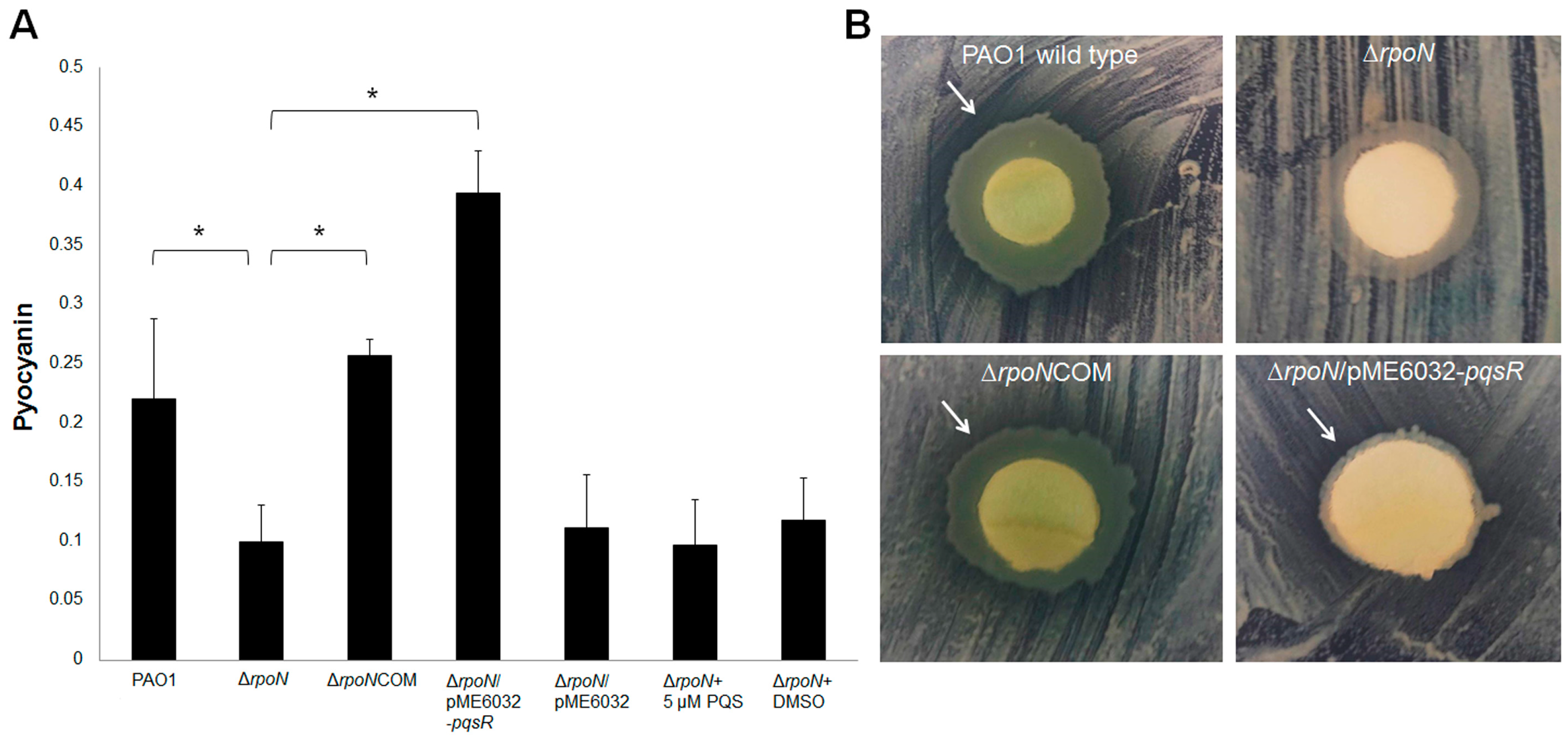
2.2. RpoN Regulates Virulence Factors and Interspecies Competition through pqs Signaling

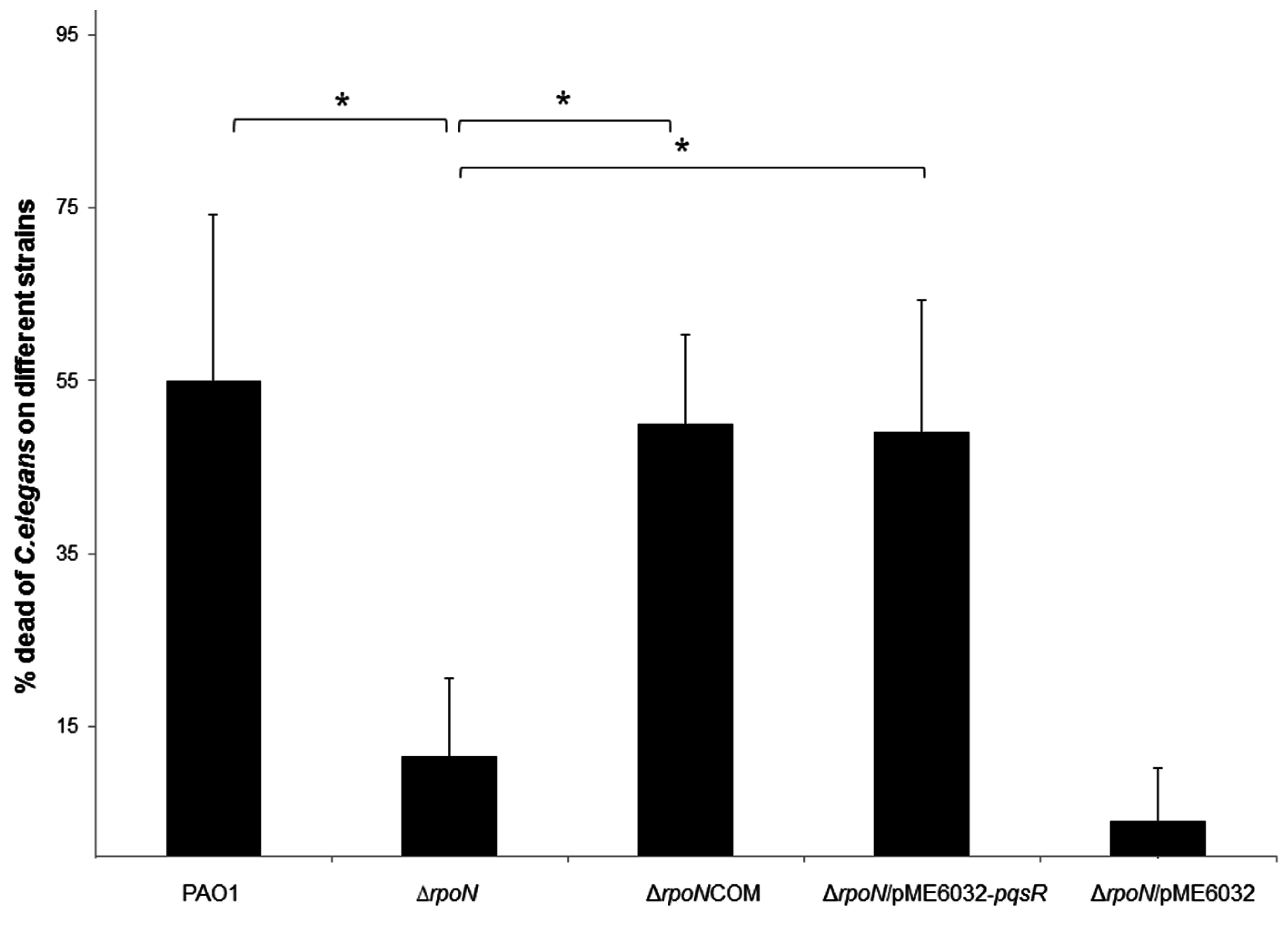
2.3. RpoN Mediates Killing of Caenorhabditis elegans through pqs Quorum Sensing
2.4. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
| Strain(s) or Plasmid | Relevant Characteristic(s) | Source or Reference |
|---|---|---|
| P. aeruginosa strains | ||
| PAO1 | Prototypic wild-type strain | [13] |
| ΔrpoN | Gmr; rpoN derivative of PAO1 constructed by allelic exchange | [13] |
| ΔrpoNCOM | Gmr;Tcr; ΔrpoN carrying the pME6031-rpoN vector | This work |
| ΔrpoN/pME6032-pqsR | Gmr;Tcr; ΔrpoN carrying the pME6032-pqsR vector | This work |
| ΔrpoN/pME6032-pqsR/ppqsA-gfp | Gmr;Tcr; Carbr; ΔrpoN/pME6032-pqsR carrying the ppqsA-gfp vector | This work |
| ΔrpoNCOM/ppqsA-gfp | Gmr;Tcr; Carbr; ΔrpoNCOM carrying the ppqsA-gfp vector | This work |
| ΔrpoN/pME6032 | Gmr;Tcr; ΔrpoN carrying the pME6032 vector | This work |
| ΔpqsR | pqsR derivative of PAO1 constructed by allelic exchange | [15] |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ||
| 15981 | Prototypic wild-type strain | [29] |
| 15981/pSB2019 | Chlr; 15981 carrying the pSB2019 gfp-expressing vector | [29] |
| Plasmids | ||
| pME6031 | Tcr; Broad-host-range cloning vector | [30] |
| pME6031-rpoN | Tcr; pME6031 carrying the rpoN gene | [4] |
| pME6032 | Tcr; broad host range vector | [30] |
| pME6032-pqsR | Tcr; pME6032 carrying the pqsR gene | [15] |
| ppqsA-gfp | Gmr;Carbr; pUCP22 carrying the pqsA-gfp transcriptional fusion | [16] |
3.2. HHQ Quantification by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
3.3. Pyocyanin Quantification
3.4. Mixed-Species Biofilm Assay
3.5. Staphylococcus aureus Inhibitory Assay
3.6. PpqsA-gfp Induction Assay
3.7. Caenorhabditis elegans Killing Assay
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lieberman, T.D.; Flett, K.B.; Yelin, I.; Martin, T.R.; McAdam, A.J.; Priebe, G.P.; Kishony, R. Genetic variation of a bacterial pathogen within individuals with cystic fibrosis provides a record of selective pressures. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feliziani, S.; Marvig, R.L.; Lujan, A.M.; Moyano, A.J.; di Rienzo, J.A.; Krogh Johansen, H.; Molin, S.; Smania, A.M. Coexistence and within-host evolution of diversified lineages of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa in long-term cystic fibrosis infections. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwangi, M.M.; Wu, S.W.; Zhou, Y.; Sieradzki, K.; de Lencastre, H.; Richardson, P.; Bruce, D.; Rubin, E.; Myers, E.; Siggia, E.D.; et al. Tracking the in vivo evolution of multidrug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by whole-genome sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9451–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Jelsbak, L.; Marvig, R.L.; Damkiaer, S.; Workman, C.T.; Rau, M.H.; Hansen, S.K.; Folkesson, A.; Johansen, H.K.; Ciofu, O.; et al. Evolutionary dynamics of bacteria in a human host environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7481–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.E.; Buckley, D.G.; Wu, Z.; Saenphimmachak, C.; Hoffman, L.R.; D’Argenio, D.A.; Miller, S.I.; Ramsey, B.W.; Speert, D.P.; Moskowitz, S.M.; et al. Genetic adaptation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8487–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latifi, A.; Winson, M.K.; Foglino, M.; Bycroft, B.W.; Stewart, G.S.; Lazdunski, A.; Williams, P. Multiple homologues of LuxR and LuxI control expression of virulence determinants and secondary metabolites through quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 17, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, J.P.; Pesci, E.C.; Iglewski, B.H. Roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and rhl quorum-sensing systems in control of elastase and rhamnolipid biosynthesis genes. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5756–5767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.C.; Yu, H.; Mudd, M.H.; Deretic, V. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: Characterization of muc mutations in clinical isolates and analysis of clearance in a mouse model of respiratory infection. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3838–3846. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cabral, D.A.; Loh, B.A.; Speert, D.P. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa resists nonopsonic phagocytosis by human neutrophils and macrophages. Pediatr. Res. 1987, 22, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totten, P.A.; Lara, J.C.; Lory, S. The rpoN gene product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is required for expression of diverse genes, including the flagellin gene. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lovewell, R.R.; Collins, R.M.; Acker, J.L.; O'Toole, G.A.; Wargo, M.J.; Berwin, B. Step-wise loss of bacterial flagellar torsion confers progressive phagocytic evasion. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahenthiralingam, E.; Campbell, M.E.; Speert, D.P. Nonmotility and phagocytic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from chronically colonized patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.S.; Webb, J.S.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. The alternative sigma factor rpon regulates the quorum sensing gene rhli in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 220, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, D.S.; Calfee, M.W.; Rocha, E.R.; Ling, E.A.; Engstrom, E.; Coleman, J.P.; Pesci, E.C. Regulation of pseudomonas quinolone signal synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4372–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilangovan, A.; Fletcher, M.; Rampioni, G.; Pustelny, C.; Rumbaugh, K.; Heeb, S.; Camara, M.; Truman, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Emsley, J.; et al. Structural basis for native agonist and synthetic inhibitor recognition by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing regulator PqsR (MvfR). PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Barken, K.B.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Christensen, A.B.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Effects of iron on DNA release and biofilm development by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1318–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Nilsson, M.; Gjermansen, M.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Pyoverdine and pqs mediated subpopulation interactions involved in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 74, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.B.; Gao, Q.G.; Chen, W.Y.; Qin, H.Y.; Wang, H.Z.; Chen, Y.C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, G. Regulation of pqs quorum sensing via catabolite repression control in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol-Sgm 2013, 159, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashburn, L.M.; Jett, A.M.; Akins, D.R.; Whiteley, M. Staphylococcus aureus serves as an iron source for Pseudomonas aeruginosa during in vivo coculture. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.Q.; Yang, L.; Qu, D.; Molin, S.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa extracellular products inhibit staphylococcal growth, and disrupt established biofilms produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Microbiol-Sgm 2009, 155, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, E.L.; Plotnikova, J.; Mahajan-Miklos, S.; Rahme, L.G.; Ausubel, F.M. Differential roles of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 rpoN gene in pathogenicity in plants, nematodes, insects, and mice. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 7126–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitzer, L. Nitrogen assimilation and global regulation in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, A.J.; Millikan, D.S.; Campbell, J.M.; Visick, K.L. Vibrio fischeri sigma(54) controls motility, biofilm formation, luminescence, and colonization. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2004, 70, 2520–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Rau, M.H.; Yang, L.; Hoiby, N.; Molin, S.; Jelsbak, L. Bacterial adaptation during chronic infection revealed by independent component analysis of transcriptomic data. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lore, N.I.; Cigana, C.; de Fino, I.; Riva, C.; Juhas, M.; Schwager, S.; Eberl, L.; Bragonzi, A. Cystic fibrosis-niche adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa reduces virulence in multiple infection hosts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, S.; Eckweiler, D.; Bielecka, A.; Nicolai, T.; Franke, R.; Dotsch, A.; Hornischer, K.; Bruchmann, S.; Duvel, J.; Haussler, S. Elucidation of sigma factor-associated networks in Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals a modular architecture with limited and function-specific crosstalk. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004744. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sonnleitner, E.; Gonzalez, N.; Sorger-Domenigg, T.; Heeb, S.; Richter, A.S.; Backofen, R.; Williams, P.; Huttenhofer, A.; Haas, D.; Blasi, U. The small RNA PhrS stimulates synthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnleitner, E.; Schuster, M.; Sorger-Domenigg, T.; Greenberg, E.P.; Blasi, U. Hfq-dependent alterations of the transcriptome profile and effects on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 1542–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo-Arana, A.; Merino, N.; Vergara-Irigaray, M.; Debarbouille, M.; Penades, J.R.; Lasa, I. Staphylococcus aureus develops an alternative, ica-independent biofilm in the absence of the arlRS two-component system. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5318–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeb, S.; Itoh, Y.; Nishijyo, T.; Schnider, U.; Keel, C.; Wade, J.; Walsh, U.; O'Gara, F.; Haas, D. Small, stable shuttle vectors based on the minimal pVS1 replicon for use in gram-negative, plant-associated bacteria. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2000, 13, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertani, G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1951, 62, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.J.; Maaløe, O. DNA replication and the division cycle in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1967, 23, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, M.P.; Diggle, S.P.; Camara, M.; Williams, P. Biosensor-based assays for PQS, HHQ and related 2-alkyl-4-quinolone quorum sensing signal molecules. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, S.C.; Kundukad, B.; Seviour, T.; van der Maarel, J.R.; Yang, L.; Rice, S.A.; Doyle, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Dynamic remodeling of microbial biofilms by functionally distinct exopolysaccharides. MBio 2014, 5, e01536–e01514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yam, J.K.H.; Chew, S.C.; Chua, S.L.; Wang, K.; Givskov, M.; Yang, L. RpoN Regulates Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Modulating the PqsR Quorum Sensing Regulator. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28311-28319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226103
Cai Z, Liu Y, Chen Y, Yam JKH, Chew SC, Chua SL, Wang K, Givskov M, Yang L. RpoN Regulates Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Modulating the PqsR Quorum Sensing Regulator. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(12):28311-28319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226103
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Zhao, Yang Liu, Yicai Chen, Joey Kuok Hoong Yam, Su Chuen Chew, Song Lin Chua, Ke Wang, Michael Givskov, and Liang Yang. 2015. "RpoN Regulates Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Modulating the PqsR Quorum Sensing Regulator" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 12: 28311-28319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226103
APA StyleCai, Z., Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Yam, J. K. H., Chew, S. C., Chua, S. L., Wang, K., Givskov, M., & Yang, L. (2015). RpoN Regulates Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Modulating the PqsR Quorum Sensing Regulator. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(12), 28311-28319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226103