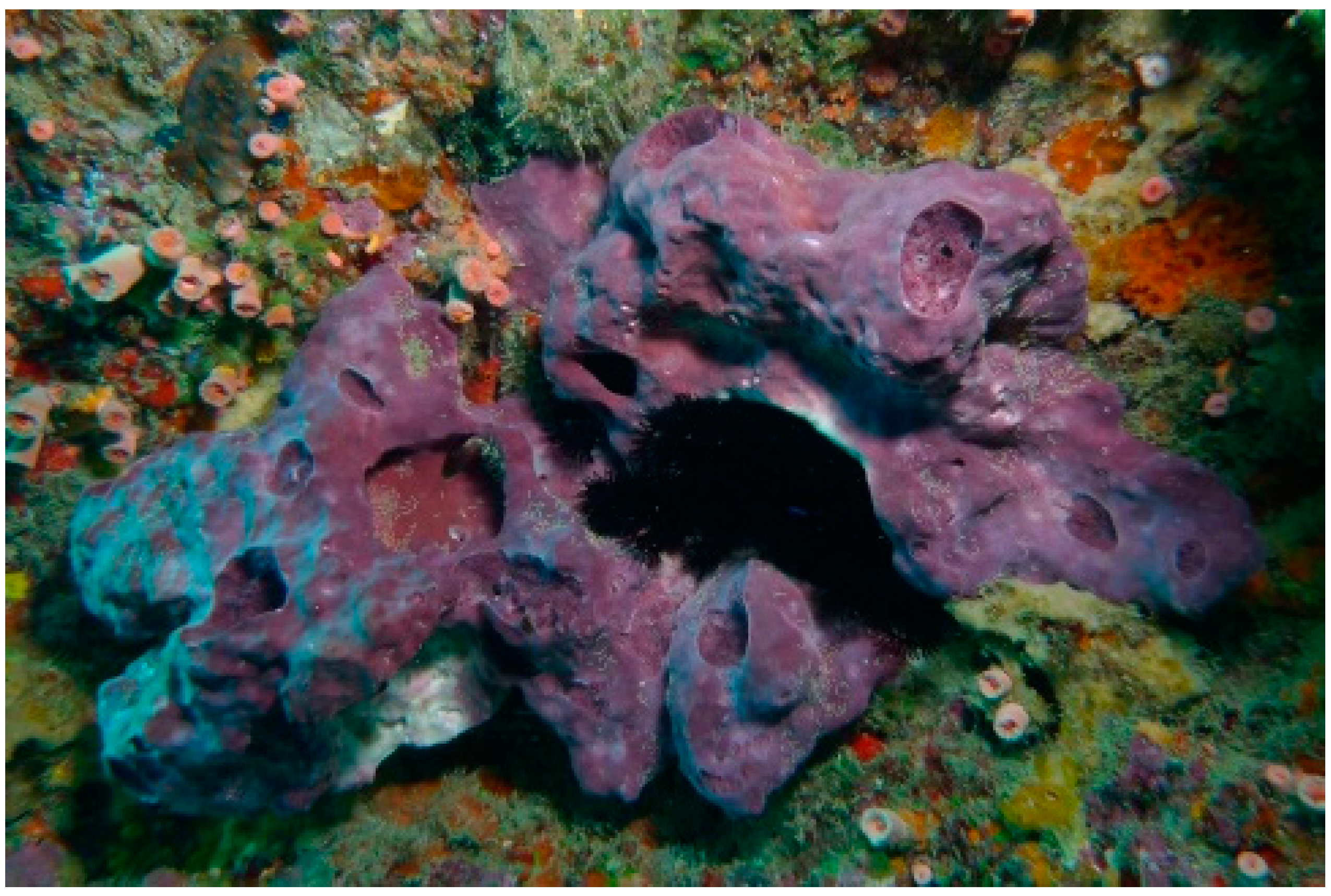
Structure Elucidation and Cytotoxic Evaluation of New Polyacetylenes from a Marine Sponge Petrosia sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction

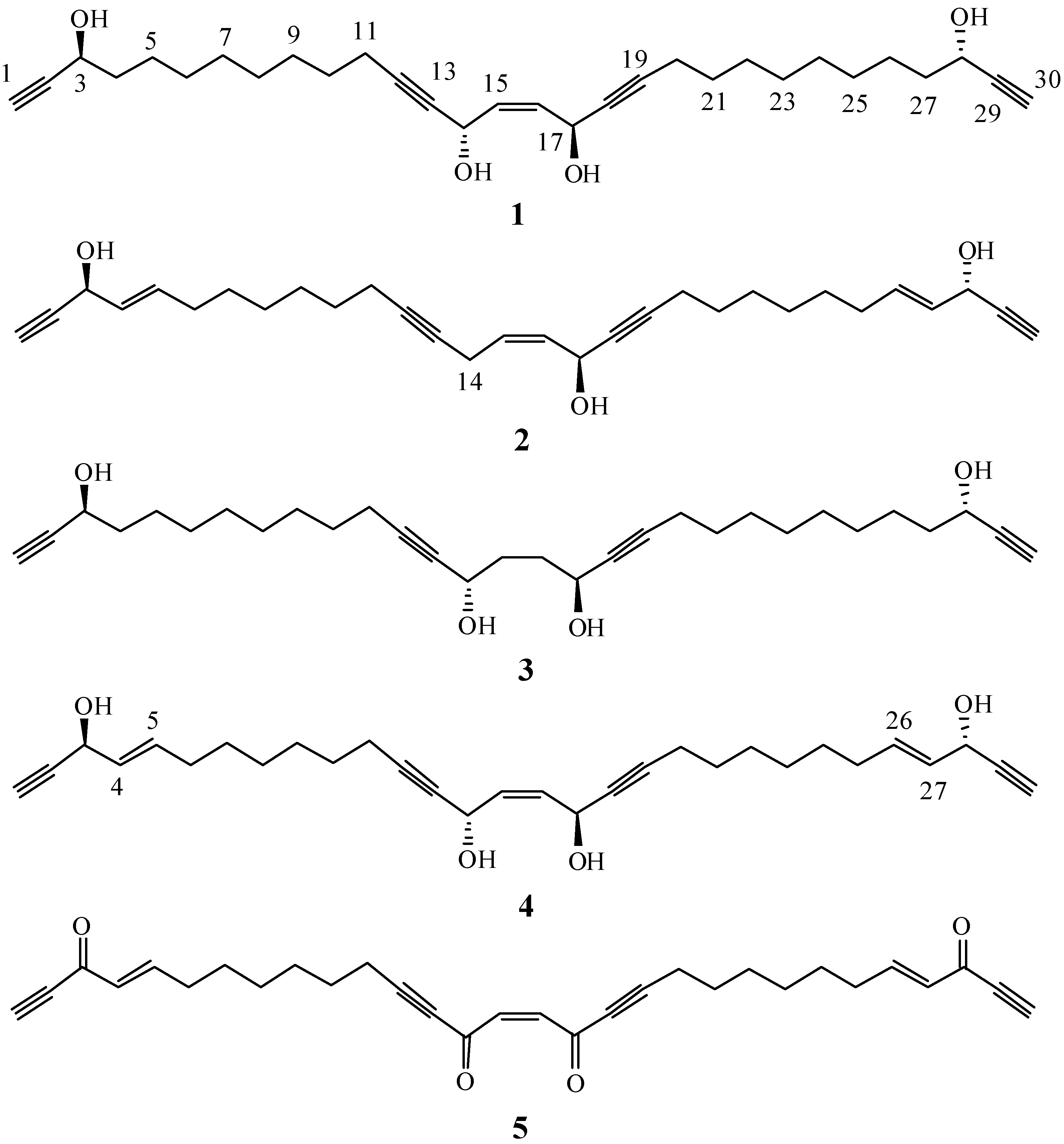
2. Results and Discussion
| Position | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) a | δc (mult.) b | δH (J in Hz) a | δc (mult.) b | |
| 1 | 2.47 d (2.0) | 72.8 (CH) | 2.57 d (2.0) | 74.0 (CH) |
| 2 | 85.0 (C) | 83.3 (C) | ||
| 3 | 4.38 ddd (6.5, 6.5, 2.0) | 62.3 (CH) | 4.84 d (6.0) | 62.8 (CH) |
| 4 | 1.72 m | 37.6 (CH2) | 5.60 m | 128.5 (CH) |
| 5 | 1.45 m | 24.9 (CH2) | 5.91 dt (15.0, 7.0) | 134.3 (CH) |
| 6 | 1.28–1.40, m | 28.7–29.2 (CH2) | 2.08 m | 31.8 (CH2) |
| 7 | 1.28–1.40, m | 28.7–29.2 (CH2) | 1.27–1.42, m | 28.4–29.7 (CH2) |
| 8 | 1.28–1.40, m | 28.7–29.2 (CH2) | 1.27–1.42, m | 28.4–29.7 (CH2) |
| 9 | 1.28–1.40, m | 28.7–29.2 (CH2) | 1.27–1.42, m | 28.4–29.7 (CH2) |
| 10 | 1.51 m | 28.4 (CH2) | 1.48 m | 28.4–29.7 (CH2) |
| 11 | 2.21 ddd (7.0, 7.0, 2.0) | 18.7 (CH2) | 2.14 m | 18.7 (CH2) |
| 12 | 86.7 (C) | 81.0 (C) | ||
| 13 | 79.6 (C) | 77.3 (C) | ||
| 14 | 5.28 dd (5.0, 1.5) | 58.6 (CH) | 3.03 dd (6.5, 5.5) | 17.6 (CH2) |
| 15 | 5.71 dd (5.0, 1.5) | 132.0 (CH) | 5.59 m | 128.0 (CH) |
| 16 | 5.71 dd (5.0, 1.5) | 132.0 (CH) | 5.59 m | 131.0 (CH) |
| 17 | 5.28 dd (5.0, 1.5) | 58.6 (CH) | 5.18 d (7.0) | 58.2 (CH) |
| 18 | 79.6 (C) | 79.8 (C) | ||
| 19 | 86.7 (C) | 86.1 (C) | ||
| 20 | 2.21 ddd (7.0, 7.0, 2.0) | 18.7 (CH2) | 2.21 | 18.7 (CH2) |
| 21 | 1.51 m | 28.4 (CH2) | 1.51 m | 28.4–29.7 (CH2) |
| 22 | 1.28–1.40, m | 28.7–29.2 (CH2) | 1.27–1.42, m | 28.4–29.7 (CH2) |
| 23 | 1.28–1.40, m | 28.7–29.2 (CH2) | 1.27–1.42, m | 28.4–29.7 (CH2) |
| 24 | 1.28–1.40, m | 28.7–29.2 (CH2) | 1.27–1.42, m | 28.4–29.7 (CH2) |
| 25 | 1.28–1.40, m | 28.7–29.2 (CH2) | 2.08 m | 31.8 (CH2) |
| 26 | 1.45 m | 24.9 (CH2) | 5.91 dt (15.0, 7.0) | 134.4 (CH) |
| 27 | 1.72 m | 37.6 (CH2) | 5.60 m | 128.5 (CH) |
| 28 | 4.38 ddd (6.5, 6.5, 2.0) | 62.3 (CH) | 4.84 d (6.0) | 62.8 (CH) |
| 29 | 85.0 (C) | 83.3 (C) | ||
| 30 | 2.47 d (2.0) | 72.8 (CH) | 2.57 d (2.0) | 74.0 (CH) |
 ) correlations of 1 and 2.
) correlations of 1 and 2.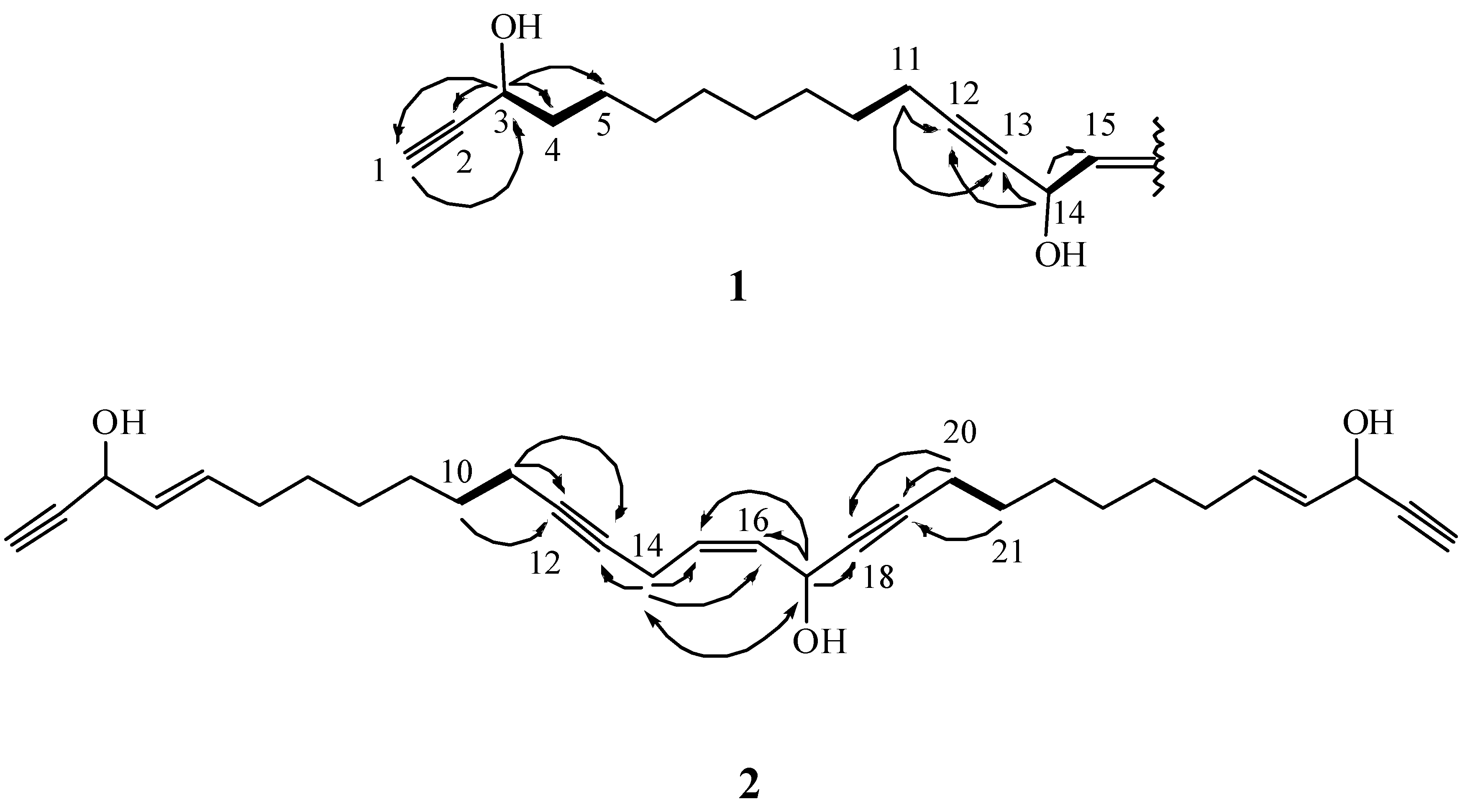
| Compound | Cell Lines | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCRF-CEM | MOLT-4 | K-562 | DLD-1 | LNCaP | T-47D | |
| 1 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | <0.1 | 3.3 ± 1.2 | NA b | 3.2 ± 1.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| 2 | 6.3 ± 2.5 | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 7.8 ± 3.2 | NA | NA | NA |
| 3 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 3.4 ± 1.1 | <0.1 | 3.2 ± 1.4 | NA |
| 4 | 2.5 ± 1.8 | 3.0 ± 1.6 | 4.0 ± 2.3 | 7.4 ± 3.1 | NA | 4.4 ± 1.1 |
| 5 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 3.4 ± 0.4 | 3.7 ± 1.8 | 5.9 ± 2.2 | 7.3 ± 2.2 |
| Doxorubicin a | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 5.8 ± 2.1 | 1.9 ± 1.1 | <0.1 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Separation
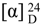 = +82 (c 0.2, CHCl3); IR (neat) νmax 3425, 3280, 2923, 2225, 1651, 1458 and 1270 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 491 [100, (M + Na)+]; HRESIMS m/z 491.3135 (calcd. for C30H44O4Na, 491.3137).
= +82 (c 0.2, CHCl3); IR (neat) νmax 3425, 3280, 2923, 2225, 1651, 1458 and 1270 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 491 [100, (M + Na)+]; HRESIMS m/z 491.3135 (calcd. for C30H44O4Na, 491.3137).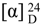 = +37 (c 0.2, CHCl3); IR (neat) νmax 3414, 3284, 2926, 2854, 2209, 2096, 1647 and 1237 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 471 [100, (M + Na)+]; HRESIMS m/z 471.2873 (calcd. for C30H44O3Na, 471.2875).
= +37 (c 0.2, CHCl3); IR (neat) νmax 3414, 3284, 2926, 2854, 2209, 2096, 1647 and 1237 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 471 [100, (M + Na)+]; HRESIMS m/z 471.2873 (calcd. for C30H44O3Na, 471.2875).3.4. Supplementary Files
3.5. Cytotoxicity Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, T.R.A.; Kavlekar, D.P.; LokaBharathi, P.A. Marine drugs from sponge-microbe association—A review. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1417–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Andavan, G.S.B.; Lemmens-Gruber, R. Cyclodepsipeptides from marine sponges: Natural agents for drug research. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 810–834. [Google Scholar]
- Ebada, S.S.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Bioactive sesterterpenes and triterpenes from marine sponges: Occurrence and pharmacological significance. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 313–346. [Google Scholar]
- Essack, M.; Bajic, V.B.; Archer, J.A.C. Recently confirmed apoptosis-inducing lead compounds isolated from marine sponge of potential relevance in cancer treatment. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1580–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Lim, Y.J.; Im, K.S.; Jung, J.H.; Shim, C.J.; Lee, C.O.; Hong, J.; Lee, H. Cytotoxic polyacetylenes from the marine sponge Petrosia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 554–559. [Google Scholar]
- Minto, R.E.; Blacklock, B.J. Biosynthesis and function of polyacetylenes and allied natural products. Prog. Lipid Res. 2008, 47, 233–306. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Yoo, S.J.; Kang, J.S.; Yun, J.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.S. Cytotoxic petrosiacetylenes from the marine sponge Petrosia sp. Lipids 2013, 48, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Im, K.S.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, Y.L.; Kim, J.; Shin, C.J.; Lee, C.O. New bioactive polyacetylenes from the marine sponge Petrosia sp. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 3151–3158. [Google Scholar]
- Mejia, E.J.; Magranet, L.B.; de Voogd, N.J.; TenDyke, K.; Qiu, D.; Shen, Y.Y.; Zhou, Z.; Crews, P. Structures and cytotoxic evaluation of new and known acyclic ene-ynes from an American Samoa Petrosia sp. Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 425–432. [Google Scholar]
- Fusetani, N.; Shiragaki, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Hashimoto, K. Bioactive marine metabolites XX. Petrosynol and petrosynone, antimicrobial C30 polyacetylenes from the marine sponge Petrosia sp.: Determination of the absolute configuration. Tetrahedron Lett. 1987, 28, 4313–4314. [Google Scholar]
- Fusetani, N.; Li, H.Y.; Tamura, K.; Matsunaga, S. Antifungal brominated C18 acetylenic acids from the marine sponge, Petrosia Volcano Hoshino. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N. Corticatic acids A–C, antifungal acetylenic acids from the marine sponge, Petrosia corticata. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs, S.; Kashman, Y.; Loya, S.; Hizi, A.; Loya, Y. Petrosynol and petrosolic acid, two novel natural inhibitors of the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus from petrosia sp. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 10435–10438. [Google Scholar]
- Hitora, Y.; Takada, K.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Miyakosynes A–F, cytotoxic methyl branched acetylenes from a marine sponge Petrosia sp. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 4530–4534. [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa, K.; Yagyu, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Kanamoto, A.; Okamoto, T.; Ojika, M. Petrosiols A–E, neurotrophic diyne tetraols isolated from the Okinawan sponge Petrosia strongylata. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ochi, M.; Ariki, S.; Tatsukawa, A.; Kotsuki, H.; Fukuyama, Y.; Shibata, K. Bioactive polyacetylenes from the marine sponge Petrosia sp. Chem. Lett. 1994, 1, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M.; Mahmud, T.; Tajima, H.; Wang, W.; Aoki, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Mayumi, T.; Kitagawa, I. Marine natural products. XXXVI. Biologically active polyacetylenes, adociacetylenes A, B, C, and D, from an Okinawan Marine sponge of Adocia sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 44, 720–724. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, J.N.A.; van Soest, R.W.M. Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges; Kluwer Academic/Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 906. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Juan, Y.S.; Lu, M.C.; Chiang, M.Y.N.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Sung, P.J. Pregnane-type steroids from the formosan soft coral Scleronephthya flexilis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 10136–10149. [Google Scholar]
- Hitora, Y.; Takada, K.; Okada, S.; Ise, Y.; Matsunaga, S. Duryne and its homologues, cytotoxic acetylenes from a marine sponge Petrosia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Ueoka, R.; Ise, Y.; Matsunaga, S. Cytotoxic polyacetylenes related to petroformyne-1 from the marine sponge Petrosia sp. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 5204–5208. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Tsuda, Y.; Hamada, M.; Omori, M.I.; Mori, G.; Iguchi, K.; Naoki, H.; Fujita, T.; van Soest, R.W.M. Acetylenic strongylodiols from a Petrosia (Strongylophora) Okinawan marine sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, S.; Matsunaga, S.; Shibazaki, M.; Suzuki, K.; Harada, N.; Naoki, H.; Fusetani, N. Corticatic acids D and E, polyacetylenic geranylgeranyltransferase type I inhibitors, from the marine sponge Petrosia corticata. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.J.; Lee, C.O.; Hong, J.; Kim, D.K.; Im, K.S.; Jung, J.H. Cytotoxic polyacetylenic alcohols from the marine sponge Petrosia species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.; Cho, K.W.; Rho, J.-R.; Shin, J.; Sim, C.J. Petrocortynes and petrosiacetylenes, novel polyacetylenes from a sponge of the genus Petrosia. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 447–462. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Juan, Y.-S.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsao, C.-W.; Lu, M.-C.; El-Shazly, M.; Shih, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wu, Y.-C.; Su, J.-H. Structure Elucidation and Cytotoxic Evaluation of New Polyacetylenes from a Marine Sponge Petrosia sp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 16511-16521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150916511
Juan Y-S, Lee C-C, Tsao C-W, Lu M-C, El-Shazly M, Shih H-C, Chen Y-C, Wu Y-C, Su J-H. Structure Elucidation and Cytotoxic Evaluation of New Polyacetylenes from a Marine Sponge Petrosia sp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(9):16511-16521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150916511
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuan, Yung-Shun, Chien-Chih Lee, Chia-Wei Tsao, Mei-Chin Lu, Mohamed El-Shazly, Huei-Chuan Shih, Yu-Cheng Chen, Yang-Chang Wu, and Jui-Hsin Su. 2014. "Structure Elucidation and Cytotoxic Evaluation of New Polyacetylenes from a Marine Sponge Petrosia sp." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 9: 16511-16521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150916511
APA StyleJuan, Y.-S., Lee, C.-C., Tsao, C.-W., Lu, M.-C., El-Shazly, M., Shih, H.-C., Chen, Y.-C., Wu, Y.-C., & Su, J.-H. (2014). Structure Elucidation and Cytotoxic Evaluation of New Polyacetylenes from a Marine Sponge Petrosia sp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(9), 16511-16521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150916511