Immunomodulating Activity of Aronia melanocarpa Polyphenols
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fractionation and Chemical Characterization
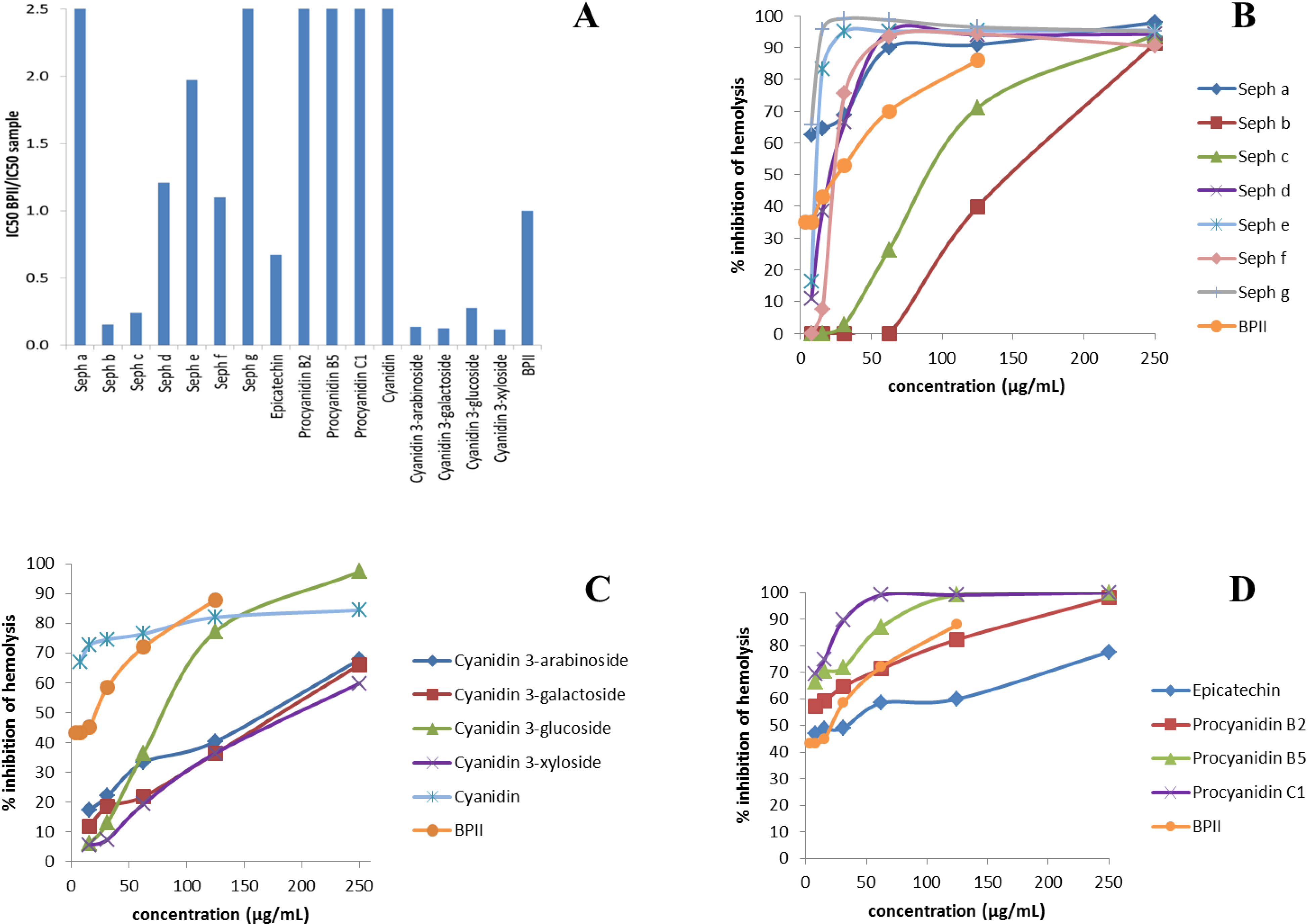
2.2. Complement-Fixing Activity
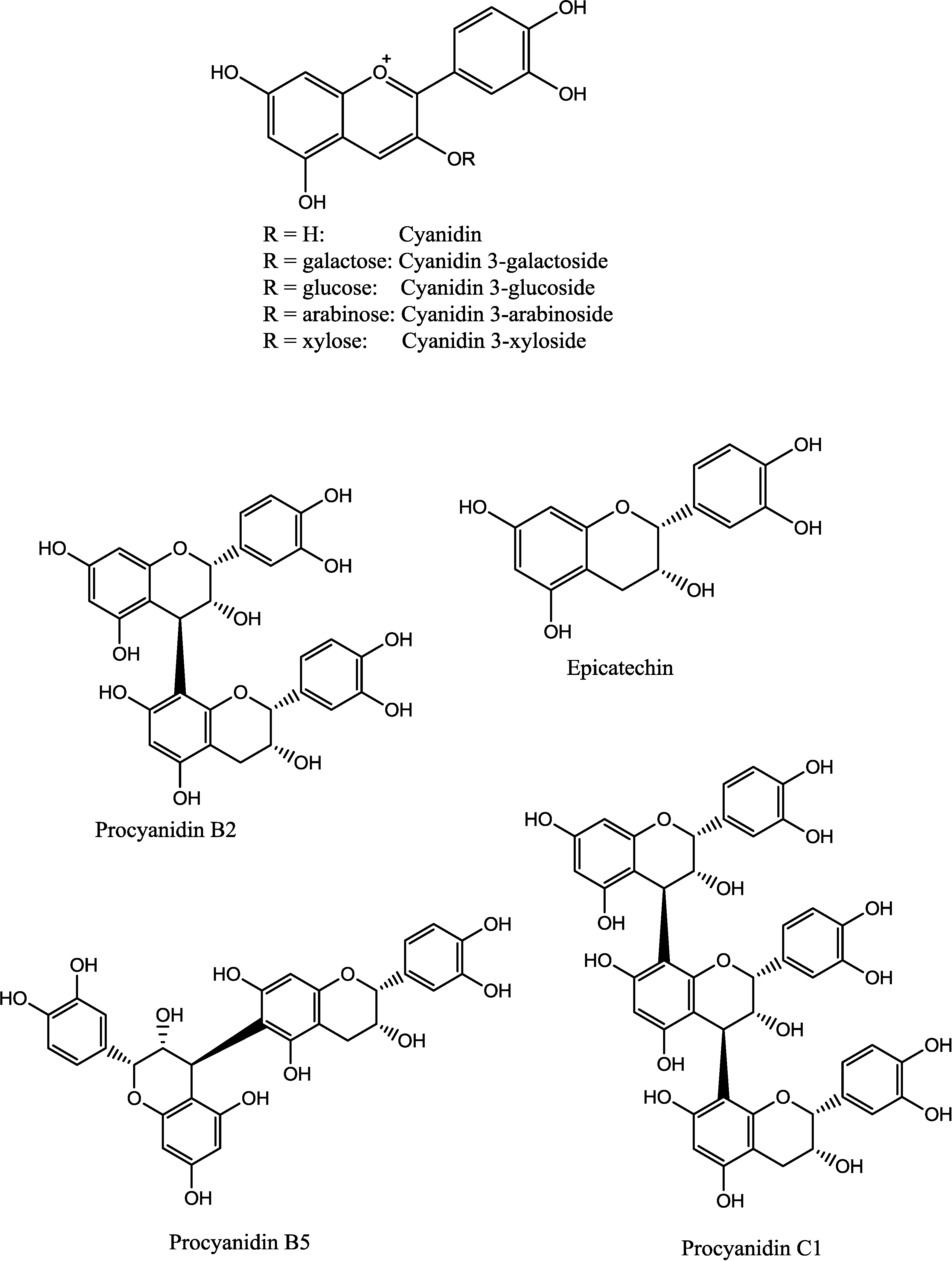
| Fraction | Percent of Crude Extract | Main Constituents (from NMR Spectroscopy) |
|---|---|---|
| Seph a | 33 | Carbohydrates |
| Seph b | 11 | Carbohydrates |
| Seph c | 1.6 | Carbohydrates |
| Seph d | 1.2 | Proanthocyanidins |
| Seph e | 1.1 | Proanthocyanidins |
| Seph f | 2.5 | Proanthocyanidins |
| Seph g | 8.0 | Proanthocyanidins |
| Substance | Content |
|---|---|
| Cyanidin 3-galactoside | 168.4 ± 11.9 |
| Cyanidin 3-glucoside | Trace |
| Cyanidin 3-arabinoside | 83.0 ± 6.6 |
| Cyanidin 3-xyloside | 2.7 ± 0.8 |
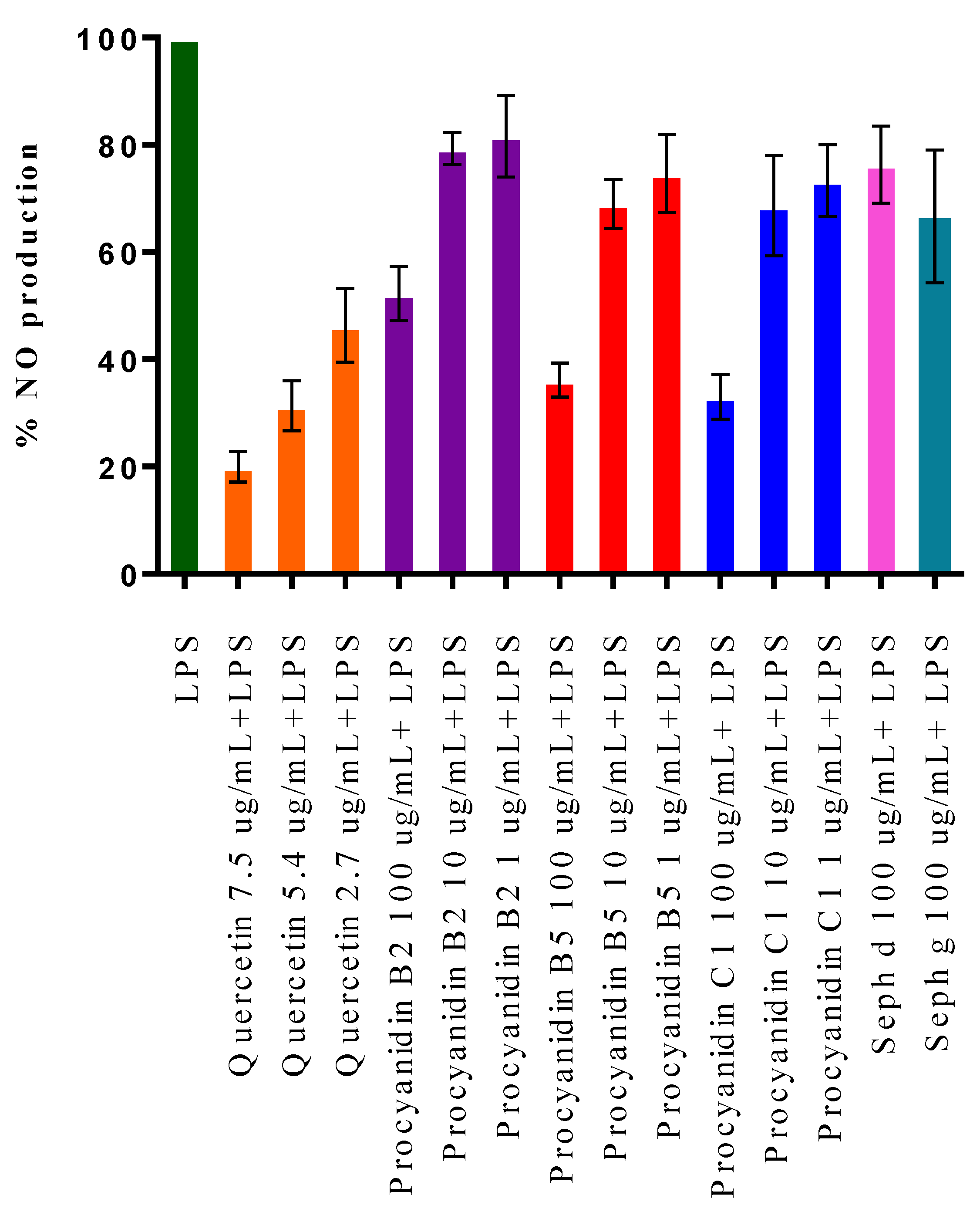
2.3. Cell Viability and Inhibition of NO Production in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells
| Fraction | % Cell Viability |
|---|---|
| Quercetin 7.5 µg/mL | 95 |
| Procyanidin B2 100 µg/mL | 117 |
| Procyanidin B5 100 µg/mL | 112 |
| Procyanidin C1 100 µg/mL | 115 |
| Seph d 100 µg/mL | 90 |
| Seph g 100 µg/mL | 32 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Extracts, Fractions and Compounds
3.3. Complement Fixing Assay
3.4. Inhibition of NO Production in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells
3.5. MTS Assay for Cell Viability
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tzianabos, A.O. Polysaccharide immunomodulators as therapeutic agents: Structural aspects and biologic function. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, H.; Kiderlen, A.F. Antileishmanial activity and immune modulatory effects of tannins and related compounds on Leishmania parasitised RAW 264.7 cells. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2056–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelsen, T.E.; Gilje, A.; Samuelsen, A.B.; Hagasen, K.; Paulsen, B.S. Interaction between human complement and a pectin type polysaccharide fraction, PMII, from the leaves of Plantago major L. Scand. J. Immunol. 2000, 52, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cos, P.; Hermans, N.; Calomme, M.; Maes, L.; de Bruyne, T.; Pieters, L.; Vlietinck, A.J.; Berghe, D.V. Comparative study of eight well-known polyphenolic antioxidants. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Park, W. Anti-inflammatory effect of myristicin on RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Molecules 2011, 16, 7132–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, X.; Valls, J.; Vitrac, X.; Mérrillon, J.M.; Arola, L.; Ardèvol, A.; Bladé, C.; Fernández-Larrea, J.; Pujadas, G.; Salvadó, J.; et al. Grape-seed procyanidins act as antiinflammatory agents in endotoxin-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages by inhibiting NFκB signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4357–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.B.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, S.K.; Kim, H.C.; Bae, H.; Kim, H.M.; Ko, S.G.; Choi, H.Y.; Oh, M.S.; Park, W. Anti-inflammatory effects of Scutellaria baicalensis water extract on LPS-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 125, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokotkiewicz, A.; Jaremicz, Z.; Luczkiewicz, M. Aronia plants: A review of traditional use, biological activities, and perspectives for modern medicine. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulling, S.E.; Rawel, H.M. Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa)—A review on the characteristic components and potential health effects. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.E.; Park, K.H.; Han, B.H.; Jeong, M.S.; Seo, S.J.; Lee, D.I.; Joo, S.S.; Lee, M.W. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by phenolic compounds from roots of Rhododendron mucronulatum. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Edirisinghe, I.; Banaszewski, K.; Cappozzo, J.; McCarthy, D.; Burton-Freeman, B.M. Effect of black currant anthocyanins on the activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in vitro in human endothelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8616–8624. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, C.; Kim, S. Methanol extract of Codonopsis pilosula inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and protein oxidation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated raw cells. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Liu, X.; Feng, H.; Zhao, S.; Gao, H. Grape seed proanthocyanidin extracts enhance endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression through 5'AMP activated protein kinase/surtuin 1-krüpple like factor 2 pathway and modulate blood pressure in quabain induced hypertensive rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 2192–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgami, K.; Ilieva, I.; Shiratori, K.; Koyama, Y.; Jin, X.; Yashida, K.; Kase, S.; Kitaichi, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Aronia extract on rat endotoxin-induced uiveitis. IOVS 2005, 46, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Auger, C.; Kurita, I.; Anselm, E.; Rivoarilala, L.O.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.W.; Schini-Kerth, V.B. Aronia melanocarpa juice, a rich source of polyphenols, induces endothelium-dependent relaxations in porcine coronary arteries via the redox-sensitive activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nitric Oxide 2013, 35, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräunlich, M.; Christensen, H.; Johannesen, S.; Slimestad, R.; Wangensteen, H.; Malterud, K.E.; Barsett, H. In vitro inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4 by Aronia melanocarpa constituents. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Bräunlich, M.; Slimestad, R.; Wangensteen, H.; Brede, C.; Malterud, K.E.; Barsett, H. Extracts, anthocyanins and procyanidins from Aronia melanocarpa as radical scavengers and enzyme inhibitors. Nutrients 2013, 5, 663–678. [Google Scholar]
- Slimestad, R.; Torskangerpoll, K.; Nateland, H.S.; Johannesen, T.; Giske, N.H. Flavonoids from black chokeberries, Aronia melanocarpa. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2005, 18, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Inngjerdingen, K.T.; Debes, S.C.; Inngjerdingen, M.; Hokputsa, S.; Harding, S.E.; Rolstad, B.; Michaelsen, T.E.; Diallo, D.; Paulsen, B.S. Bioactive pectic polysaccharides from Glinus oppositifolius (L.) Aug. DC., a Malian medicinal plant, isolation and partial characterization. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 101, 204–214. [Google Scholar]
- Grønhaug, T.E.; Kiyohara, H.; Sveaass, A.; Diallo, D.; Yamada, H.; Paulsen, B.S. β-d-(1→4)-galactan-containing side chains in RG-I regions of pectic polysaccharides from Biophytum petersianum Klotzsch contribute to expression of immunomodulating activity against intestinal Peyer’s patch cells and macrophages. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar]
- Inngjerdingen, K.T.; Coulibaly, A.; Diallo, D.; Michaelsen, T.E.; Paulsen, B.S. A complement fixing polysaccharide from Biophytum petersianum Klotzsch, a medicinal plant from Mali, West Africa. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahat, A.A.; Hammouda, F.; Ismail, S.I.; Azzam, S.A.; de Bruyne, T.; Lasure, A.; van Poel, B.; Pieters, L.; Vlietinck, A.J. Anti-complementary activity of Crataegus sinaica. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallarès, V.; Calay, D.; Cedó, L.; Castell-Auví, A.; Raes, M.; Pinent, M.; Ardévol, A.; Arola, L.; Blay, M. Additive, antagonistic, and synergistic effects of procyanidins and polyunsaturated fatty acids over inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages activated by lipopolysaccharide. Nutrition 2012, 28, 447–457. [Google Scholar]
- Austarheim, I.; Christensen, B.E.; Hegna, I.K.; Petersen, B.O.; Duus, J.O.; Bye, R.; Michaelsen, T.E.; Diallo, D.; Inngjerdingen, M.; Paulsen, B.S. Chemical and biological characterization of pectin-like polysaccharides from the bark of the Malian medicinal tree Cola cordifolia. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Batbayar, S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.W. Immunomodulation of fungal β-glucan in host defense signaling by dectin-1. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, G.T.T.; Bräunlich, M.; Austarheim, I.; Wangensteen, H.; Malterud, K.E.; Slimestad, R.; Barsett, H. Immunomodulating Activity of Aronia melanocarpa Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11626-11636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150711626
Ho GTT, Bräunlich M, Austarheim I, Wangensteen H, Malterud KE, Slimestad R, Barsett H. Immunomodulating Activity of Aronia melanocarpa Polyphenols. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(7):11626-11636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150711626
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Giang T. T., Marie Bräunlich, Ingvild Austarheim, Helle Wangensteen, Karl E. Malterud, Rune Slimestad, and Hilde Barsett. 2014. "Immunomodulating Activity of Aronia melanocarpa Polyphenols" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 7: 11626-11636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150711626
APA StyleHo, G. T. T., Bräunlich, M., Austarheim, I., Wangensteen, H., Malterud, K. E., Slimestad, R., & Barsett, H. (2014). Immunomodulating Activity of Aronia melanocarpa Polyphenols. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(7), 11626-11636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150711626






