Transplanted Neural Stem Cells Modulate Regulatory T, γδ T Cells and Corresponding Cytokines after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
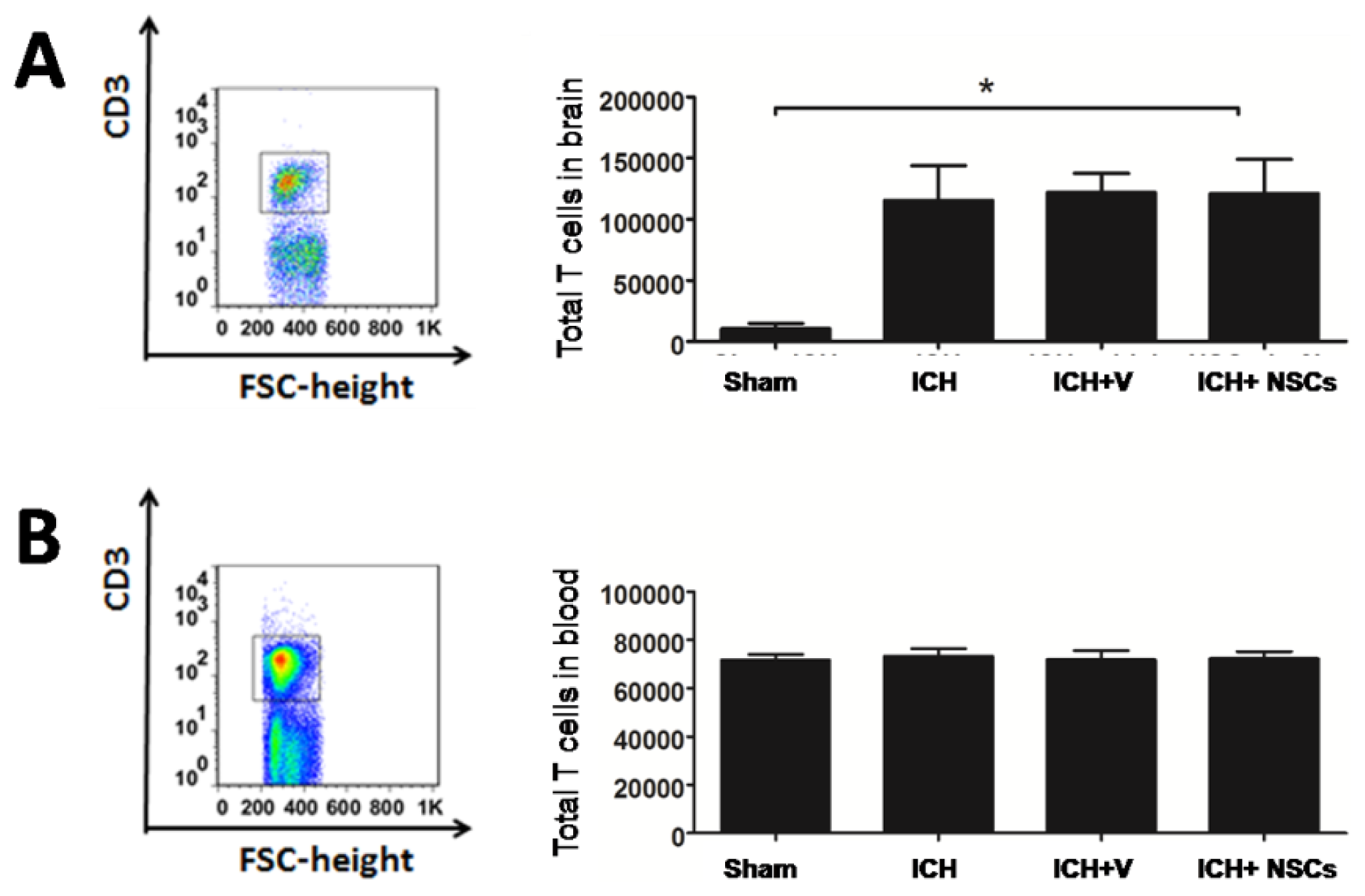
2.1. T Lymphocyte Profiles in the Brain and Peripheral Blood
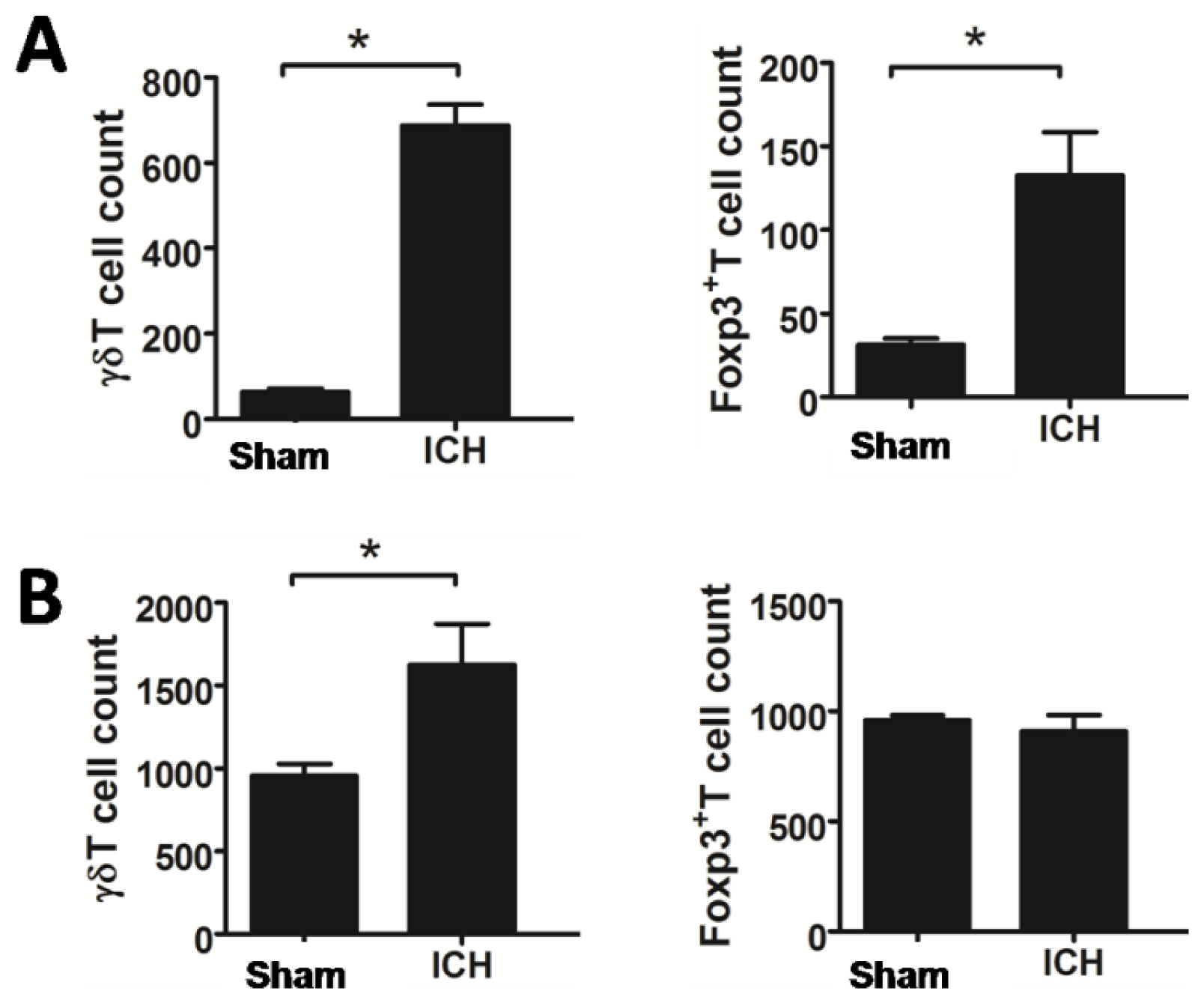
2.2. Increased T Lymphocyte Subpopulations after ICH
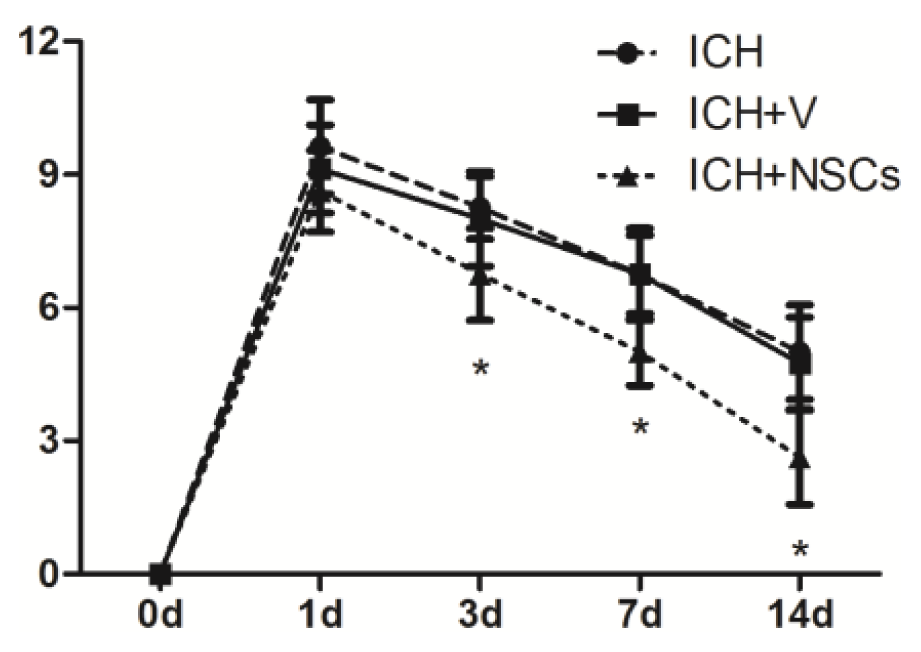
2.3. Transplanted NSCs Improve Neurological Function Recovery after ICH
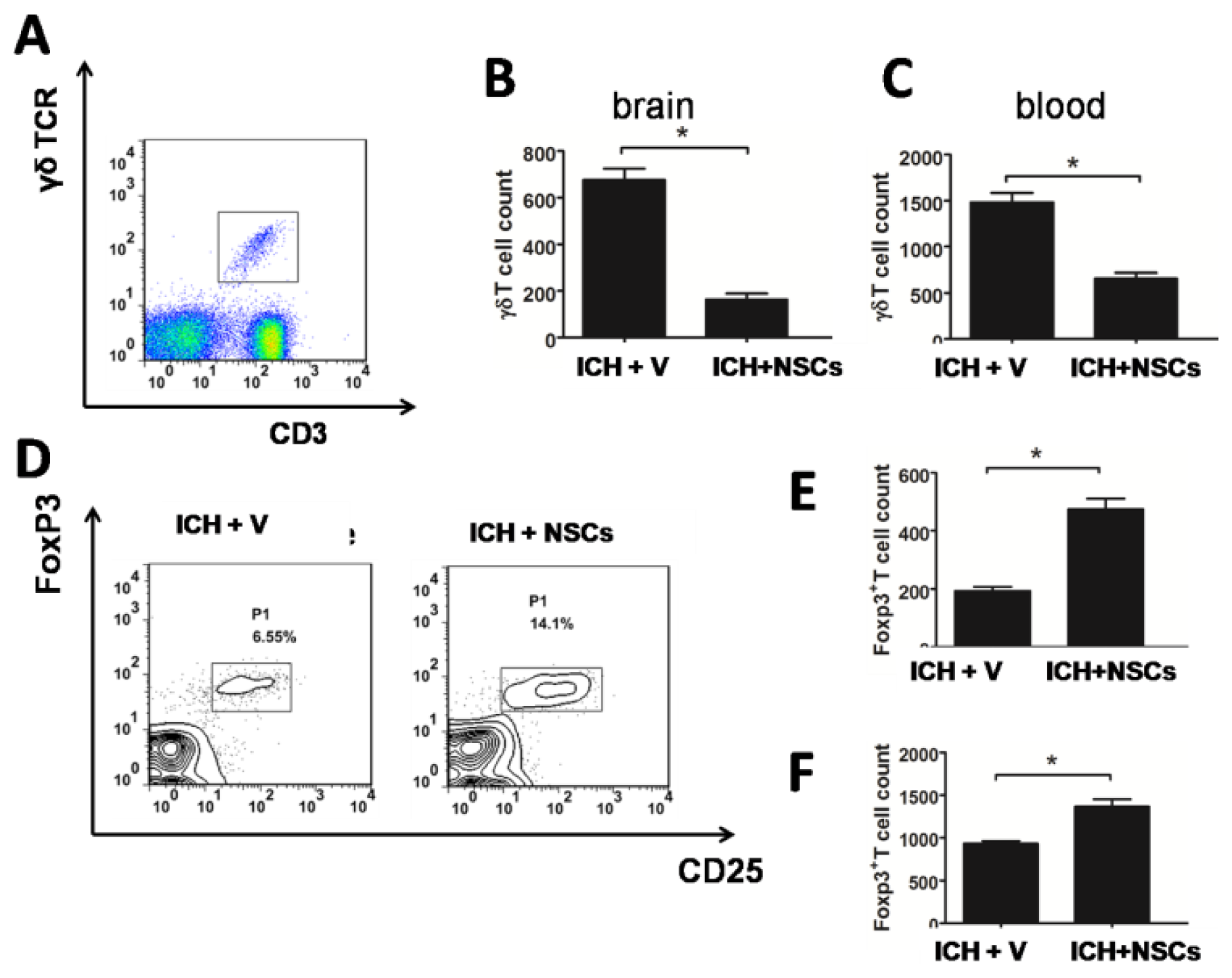
2.4. Transplanted NSCs Modulate γδT and Treg Cells after ICH
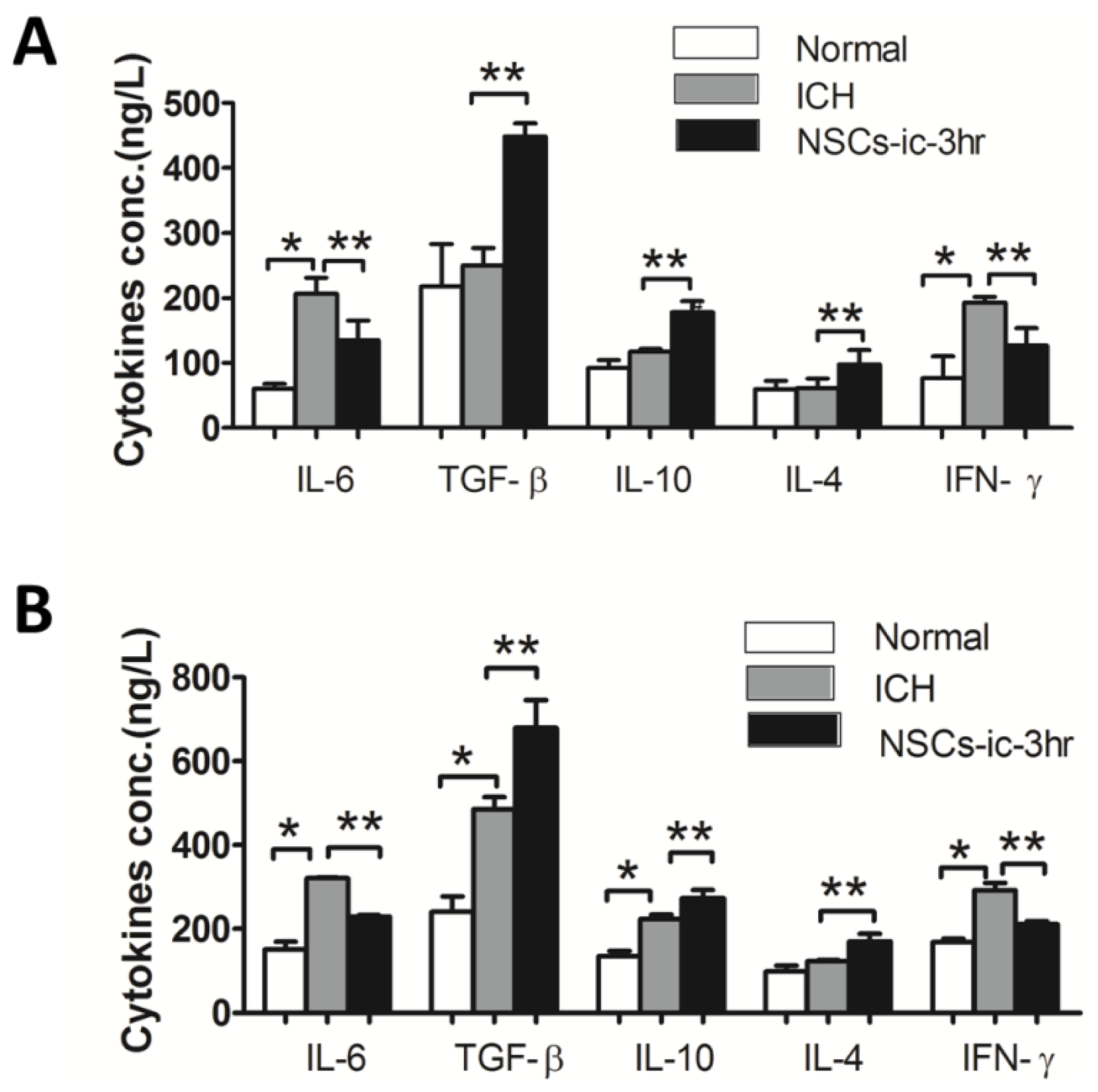
2.5. Transplanted NSCs Altered Cytokines in the Cerebral and Peripheral Blood
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Procedure
4.1. ICH Model
4.2. Cell Preparation and Transplantation Procedure
4.3. Behavioral Testing
4.4. Isolation of Brain and Blood Lymphocytes
4.5. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.6. Cytokine Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broderick, J.P.; Adams, H.P.; Barsan, W.; Feinberg, W.; Feldmann, E.; Grotta, J.; Kase, C.; Krieger, D.; Mayberg, M.; Tilley, B.; et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A statement for Healthcare Professionals From a Special Writing Group of the Stroke Council American Heart Association. Stroke 1999, 30, 905–915. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Mendelow, A.D.; Hanley, D.F. Intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet 2009, 373, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar]
- MacLellan, C.L.; Silasi, G.; Poon, C.C.; Edmundson, C.L.; Buist, R.; Peeling, J.; Colbourne, F. Intracerebral hemorrhage models in rat: Comparing collagenase to blood infusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 28, 516–525. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Doré, S. Inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 894–908. [Google Scholar]
- Aronowski, J.; Zhao, X. Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral hemorrhage: Secondary brain injury. Stroke 2011, 42, 1781–1786. [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck, J.; Hansson, G.; Becker, K. Immunology of ischemic vascular disease: Plaque to attack. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 550–556. [Google Scholar]
- Loftspring, M.C.; McDole, J.; Lu, A.; Clark, J.F.; Johnson, A.J. Intracerebral hemorrhage leads to infiltration of several leukocyte populations with concomitant pathophysiological changes. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2008, 29, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, G. Role of T lymphocytes and interferon-in ischemic stroke. Circulation 2006, 113, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Shichita, T.; Sugiyama, Y.; Ooboshi, H.; Sugimori, H.; Nakagawa, R.; Takada, I.; Iwaki, T.; Okada, Y.; Iida, M.; Cua, D.J.; et al. Pivotal role of cerebral interleukin-17—Producing γδT cells in the delayed phase of ischemic brain injury. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 946–950. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, A.E. The forgotten lymphocyte: Immunity and stroke. Circulation 2006, 113, 2035–2036. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Read, S.J.; Henderson, R.D.; Hull, R.; O’Sullivan, J.D.; McCombe, P.A.; Greer, J.M. Frequency and function of regulatory T cells after ischaemic stroke in humans. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 243, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Vignali, D.A.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.W.; Chu, K.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, M.; Roh, J.K. Human neural stem cell transplantation promotes functional recovery in rats with experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2003, 34, 2258–2263. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, S. Transplanted human fetal neural stem cells survive migrate and differentiate in ischemic rat cerebral cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11839–11844. [Google Scholar]
- Martino, G.; Pluchino, S. The therapeutic potential of neural stem cells. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 395–406. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, E.J.; Choi, H.B.; Lee, K.H.; Park, I.H.; Ko, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, S.U. Brain transplantation of immortalized human neural stem cells promotes functional recovery in mouse intracerebral hemorrhage stroke model. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Pluchino, S.; Zanotti, L.; Rossi, B.; Brambilla, E.; Ottoboni, L.; Salani, G.; Martinello, M.; Cattalini, A.; Bergami, A.; Furlan, R.; et al. Neurosphere-derived multipotent precursors promote neuroprotection by an immunomodulatory mechanism. Nature 2005, 436, 266–271. [Google Scholar]
- Pluchino, S.; Quattrini, A.; Brambilla, E.; Gritti, A.; Salani, G.; Dina, G.; Galli, R.; del Carro, U.; Amadio, S.; Bergami, A.; et al. Injection of adult neurospheres induces recovery in a chronic model of multiple sclerosis. Nature 2003, 422, 688–694. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-P.; Jeyakumar, M.; Gonzalez, R.; Takahashi, H.; Lee, P.-J.; Baek, R.C.; Clark, D.; Rose, H.; Fu, G.; Clarke, J.; et al. Stem cells act through multiple mechanisms to benefit mice with neurodegenerative metabolic disease. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 439–447. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Shi, J.; van Ginkel, F.W.; Lan, L.; Niemeyer, G.; Martin, D.R.; Snyder, E.Y.; Cox, N.R. Neural stem/progenitor cells modulate immune responses by suppressing T lymphocytes with nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 216, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Cho, H.-S.; Yang, S.-H.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, S.-T.; Chu, K.; Roh, J.-K.; Kim, S.U.; Park, C.-G. Soluble mediators from human neural stem cells play a critical role in suppression of T-cell activation and proliferation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2264–2272. [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom, M.; Leypoldt, F.; Steinbach, K.; Behrens, D.; Choe, C.U.; Siler, D.A.; Arumugam, T.V.; Orthey, E.; Gerloff, C.; Tolosa, E.; et al. Temporal and spatial dynamics of cerebral immune cell accumulation in stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Dirnagl, U.; Iadecola, C.; Moskowitz, M.A. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: An integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Wennersten, A.; Meier, X.; Holmin, S.; Wahlberg, L.; Mathiesen, T. Proliferation migration and differentiation of human neural stem progenitor cells after transplantation into a rat model of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, J.; Hackett, C.; Breton, J.; Mao-Draayer, Y. Cross-talk between CD4+ T-cells and neural stem/progenitor cells. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 306, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, G.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T. Mechanisms of brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, M.A.; Dohi, K.; Banks, W.A. Neuroinflammation: A common pathway in CNS diseases as mediated at the blood-brain barrier. Neuroimmunomodulation 2012, 19, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Elenkov, I.J.; Wilder, R.L.; Chrousos, G.P.; Vizi, E.S. The sympathetic nerve—An integrative interface between two supersystems: The brain and the immune syste. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 595–638. [Google Scholar]
- Woiciechowsky, C.; Asadullah, K.; Nestler, D.; Eberhardt, B.; Platzer, C.; Schöning, B.; Glöckner, F.; Lanksch, W.R.; Volk, H.D.; Döcke, W.D. Sympathetic activation triggers systemic interleukin-10 release in immunodepression induced by brain injury. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 808–813. [Google Scholar]
- Liesz, A.; Suri-Payer, E.; Veltkamp, C.; Doerr, H.; Sommer, C.; Rivest, S.; Giese, T.; Veltkamp, R. Regulatory T cells are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental stroke. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Liesz, A.; Zhou, W.; Mracsko, E.; Karcher, S.; Bauer, H.; Schwarting, S.; Sun, L.; Bruder, D.; Stegemann, S.; Cerwenka, A.; et al. Inhibition of lymphocyte trafficking shields the brain against deleterious neuroinflammation after stroke. Brain 2011, 134, 704–720. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, A.; Verhagen, J.; Blaser, K.; Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A. Mechanisms of immune suppression by interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-beta: The role of T regulatory cells. Immunology 2006, 117, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- O’Garra, A.; Vieira, P.L.; Vieira, P.; Goldfeld, A.E. IL-10-producing and naturally occurring CD4+ Tregs: Limiting collateral damage. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Prass, K.; Meisel, C.; Hoflich, C.; Braun, J.; Halle, E.; Wolf, T.; Ruscher, K.; Victorov, I.V.; Priller, J.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. Stroke-induced immunodeficiency promotes spontaneous bacterial infections and is mediated by sympathetic activation reversal by poststroke t helper cell type 1-like immunostimulation. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 725–736. [Google Scholar]
- Chesney, J.A.; Kondoh, T.; Conrad, J.A.; Low, W.C. Collagenase-induced intrastriatal hemorrhage in rats results in long-term locomotor deficits. Stroke 1995, 26, 312–316. [Google Scholar]
- Del Bigio, M.R.; Yan, H.J.; Buist, R.; Peeling, J. Experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in rats: Magnetic resonance imaging and histopathological correlates. Stroke 1996, 27, 2312–2319. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, D.; Lu, M.; Chopp, M. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 2001, 32, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, L.; Lu, Q.; Huang, L.-J.; Ruan, L.-H.; Yang, J.-J.; Huang, W.-L.; ZhuGe, W.-S.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Fu, B.; Jin, K.-L.; et al. Transplanted Neural Stem Cells Modulate Regulatory T, γδ T Cells and Corresponding Cytokines after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 4431-4441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034431
Gao L, Lu Q, Huang L-J, Ruan L-H, Yang J-J, Huang W-L, ZhuGe W-S, Zhang Y-L, Fu B, Jin K-L, et al. Transplanted Neural Stem Cells Modulate Regulatory T, γδ T Cells and Corresponding Cytokines after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(3):4431-4441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034431
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Lu, Qin Lu, Li-Jie Huang, Lin-Hui Ruan, Jian-Jing Yang, Wei-Long Huang, Wei-Shan ZhuGe, Yong-Liang Zhang, Biao Fu, Kun-Lin Jin, and et al. 2014. "Transplanted Neural Stem Cells Modulate Regulatory T, γδ T Cells and Corresponding Cytokines after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 3: 4431-4441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034431
APA StyleGao, L., Lu, Q., Huang, L.-J., Ruan, L.-H., Yang, J.-J., Huang, W.-L., ZhuGe, W.-S., Zhang, Y.-L., Fu, B., Jin, K.-L., & ZhuGe, Q.-C. (2014). Transplanted Neural Stem Cells Modulate Regulatory T, γδ T Cells and Corresponding Cytokines after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(3), 4431-4441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034431



