Inhalation of Silver Nanomaterials—Seeing the Risks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
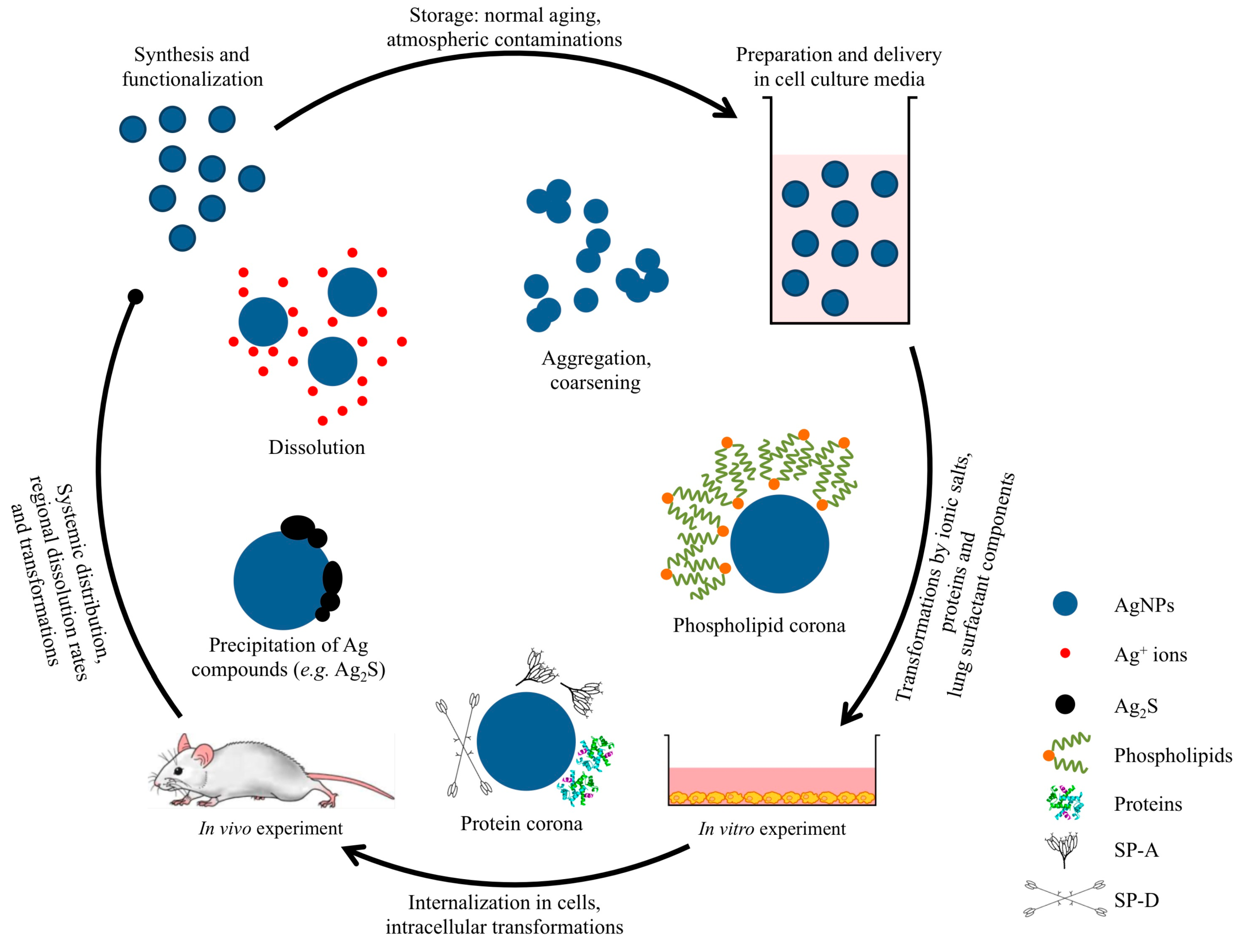
2. Pulmonary Exposure to Silver Nanoparticles
| Route of Exposure | Sources of Exposure |
|---|---|
| Respiratory System | Handling AgNPs in manufacturing or research facilities; |
| Aerosols directly applied in the nasal or oral cavities; | |
| Sprays (e.g., deodorants, shoe sprays, cleaning products); | |
| Air filters, breathing masks; | |
| Ambient airborne AgNPs | |
| Skin | Wound dressings; |
| Antibacterial textiles (e.g., sheet, towels, socks, underwear, fitness wear); | |
| Antibacterial surfaces, paints; | |
| Cosmetic products (e.g., lotions, roll-on deodorants, hair products); | |
| Computer hardware and mobile devices | |
| Gastrointestinal Tract | Food packaging, cooking utensils and coatings; |
| Water filters; | |
| Health supplements; | |
| Oral hygiene products (e.g., toothpastes, toothbrushes) | |
| Reproductive System | Contraceptive devices; |
| Feminine hygiene products | |
| Circulatory System | Intravenous injection of AgNP-enabled drugs or drug delivery/diagnostic systems; |
| Implants, medical catheters |
3. Bioreactivity of Silver in the Lung
3.1. The Bioreactivity of AgNPs in the Lung in Vivo
| Species | Size (nm) | Dose | Exposure Method | Exposure Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57BL/6 Mice, 8 weeks old | 20, 110 | 0.1, 0.5 and 1.0 mg/kg | Oropharyngeal aspiration | Single injection | [60] |
| Sprague-Dawley rats, 6 weeks old | 15 | 0.66 × 106 particles/cm3 (49 μg/m3) 1.41 × 106 particles/cm3 (117 μg/m3) 3.24 × 106 particles/cm3 (381 μg/m3) | Inhalation | 6 h/day, 5 days/week, for 12 weeks | [65] |
| Sprague-Dawley rats, 8 weeks old | 18 | 0.7 × 106, 1.4 × 106 and 2.9 × 106 particles/cm3 | Inhalation | 6 h/day, 90 days | [72] |
| Wistar rats, 8–10 weeks old | 15–40 | 4, 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg | Intravenous injection | 32 days (injected at 5 day intervals) | [73] |
| C57BL/6 mice | 20 | 1.91 × 107 particles/cm3 | Inhalation | 6 h/day, 5 days/week, for 2 weeks | [64] |
| Wistar rats, female | 50–100 | 62.8 mg/kg | Subcutaneous injection | Single injection | [59] |
| C57BL/6N mice, adult male | 30 | 100, 500 and 1000 mg/kg | Intraperitoneal injection | 24 h | [74] |
| Sprague-Dawley rats, 6 weeks old | 55 | 0.7 × 106, 1.4 × 106 and 2.9 × 106 particles/cm3 | Inhalation | 6 h/day for 90 days | [56] |
| Sprague-Dawley rats, 8 weeks old | 13–15 | 1.73 × 104 particles/cm3 (0.5 μg/m3) 1.27 × 105 particles/cm3 (3.5 μg/m3) 1.32 × 106 particles/cm3 (61 μg/m3) | Inhalation | 6 h/day, 5 days/week, for 4 weeks | [63] |
| Sprague-Dawley rats, 8 weeks old | 15 | 1.73 × 104,1.27 × 105 and 1.32 × 106 particles/cm3 | Inhalation | 6 h/day, 5 days/week, for 4 weeks | [62] |
| Fischer 344 rats, female | 15 | 3 × 106 particles/cm3 (133 μg/m3) | Inhalation | 6 h | [55] |
3.2. The Bioreactivity of AgNPs in Vitro
4. Evaluation of the in Vitro Testing of AgNPs
4.1. Preparation and Delivery to the Biological Media
4.2. Transformation in the Cell Culture Media

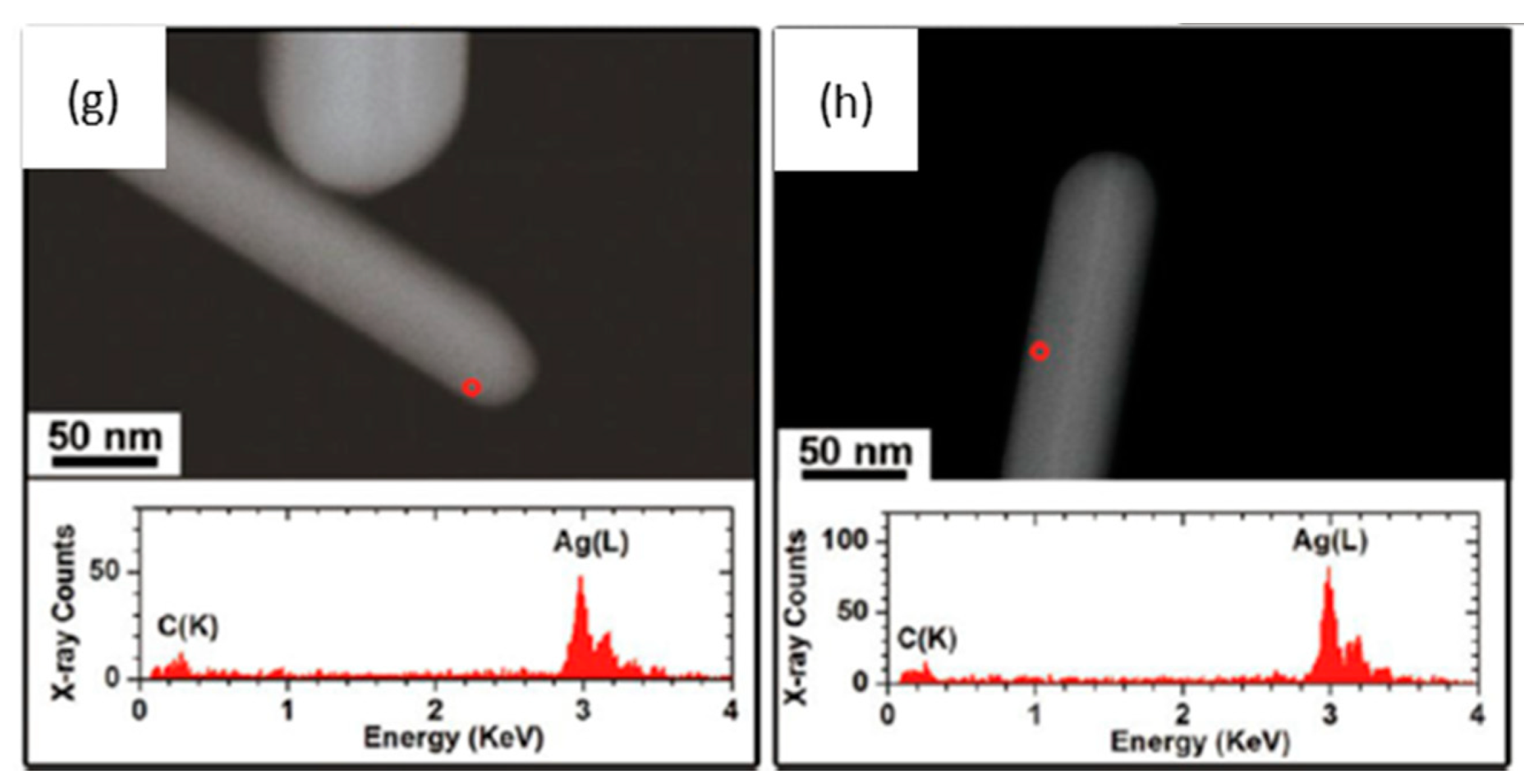
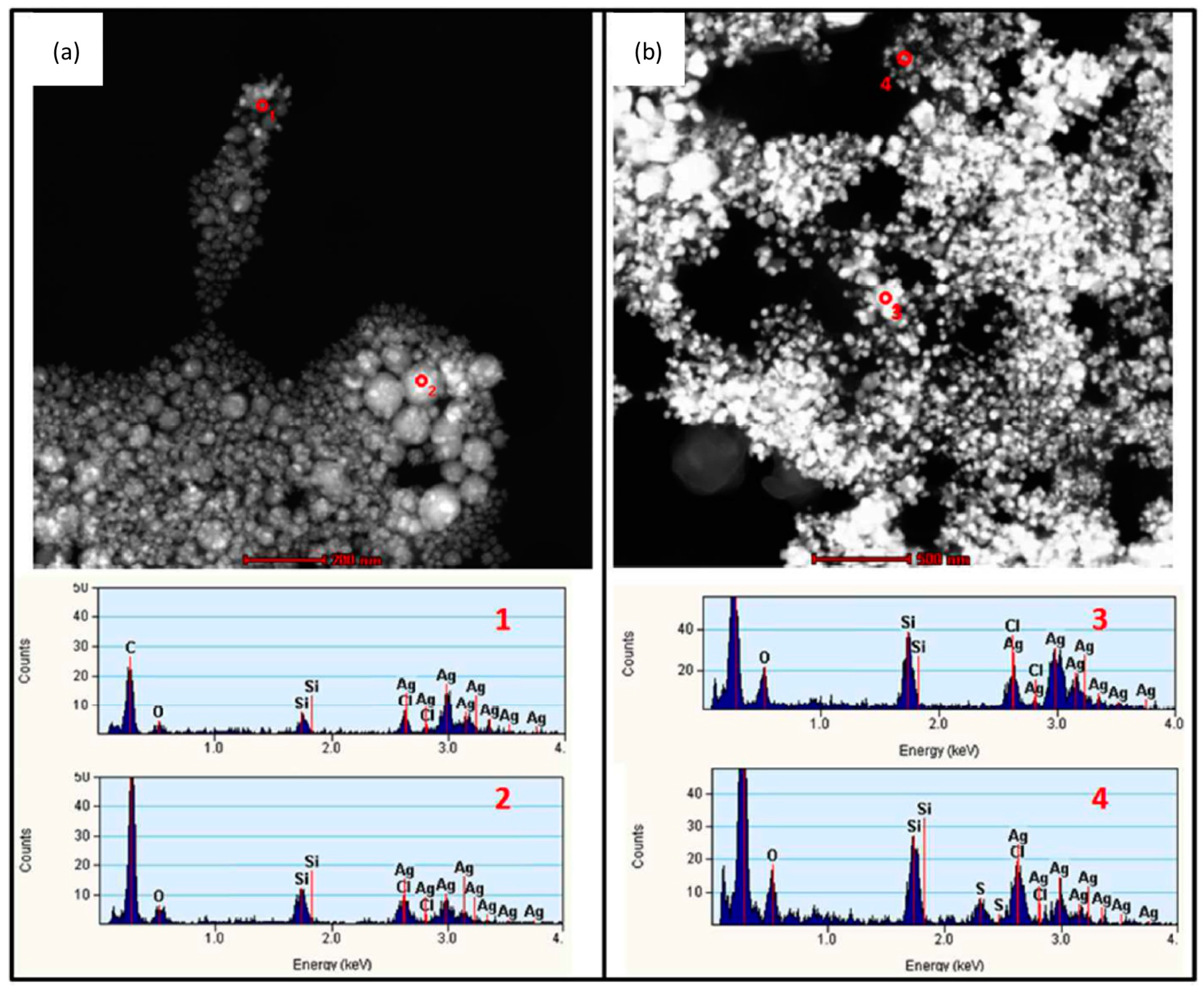
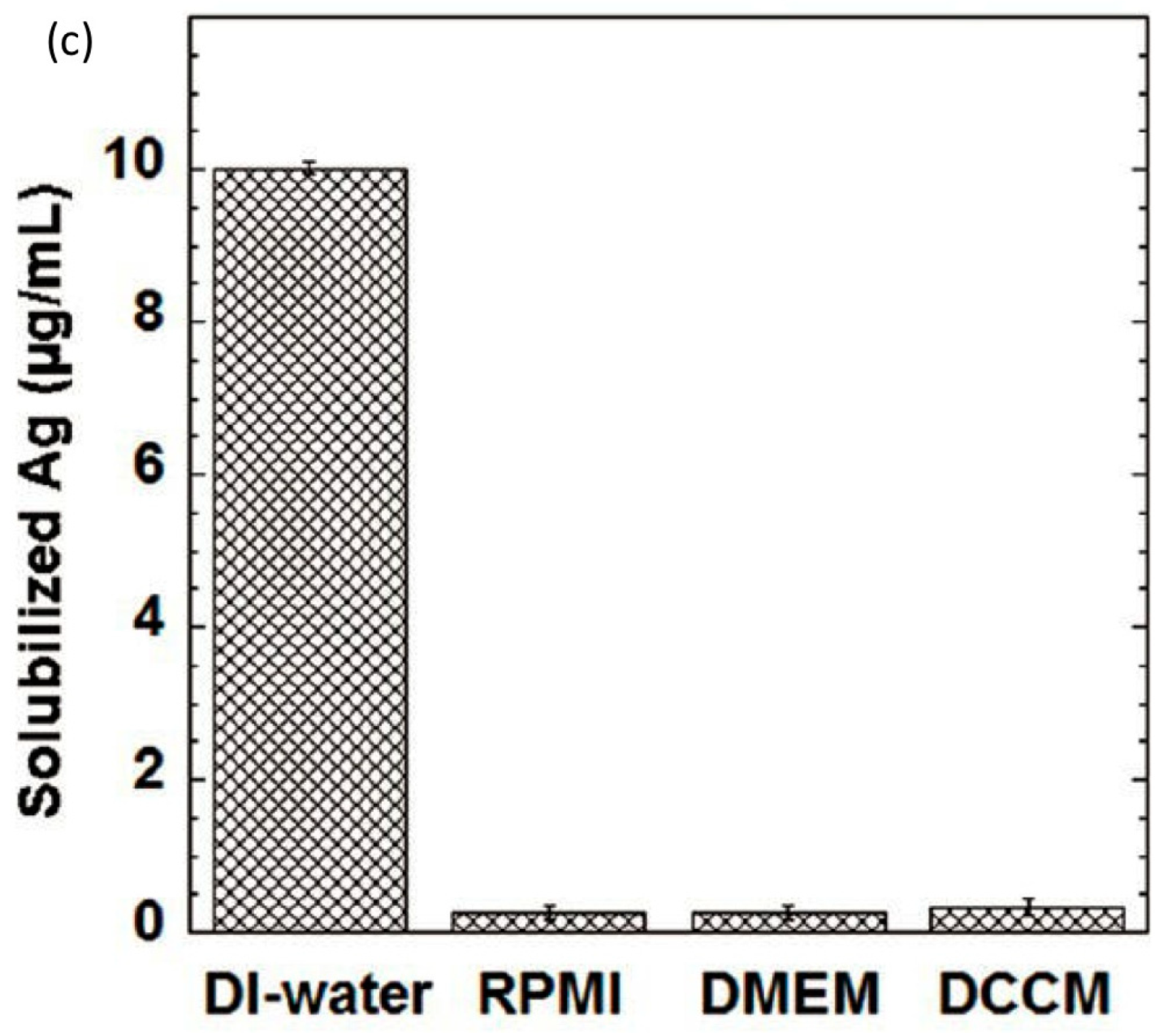
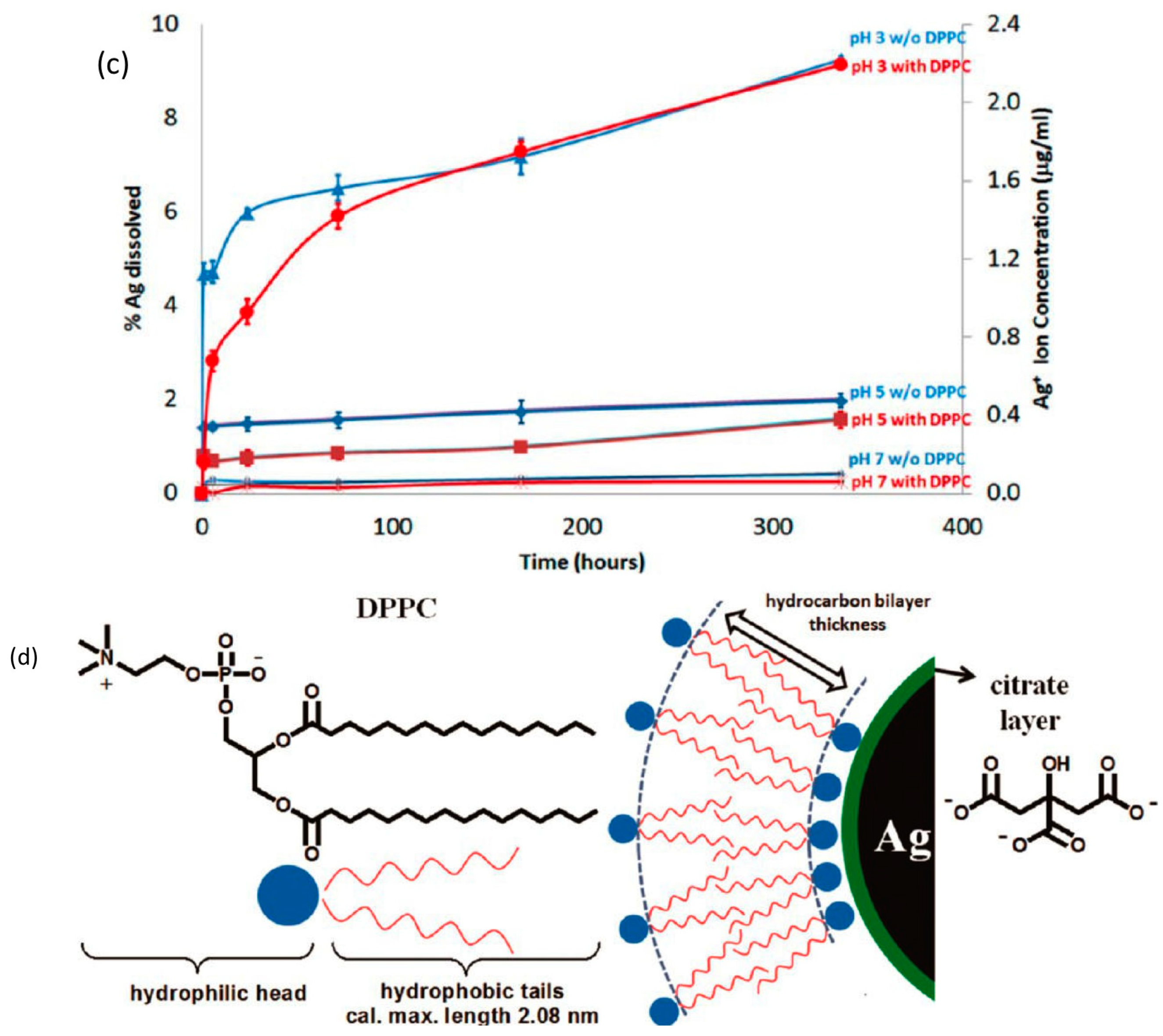
4.3. Transformation in Pulmonary Surfactant
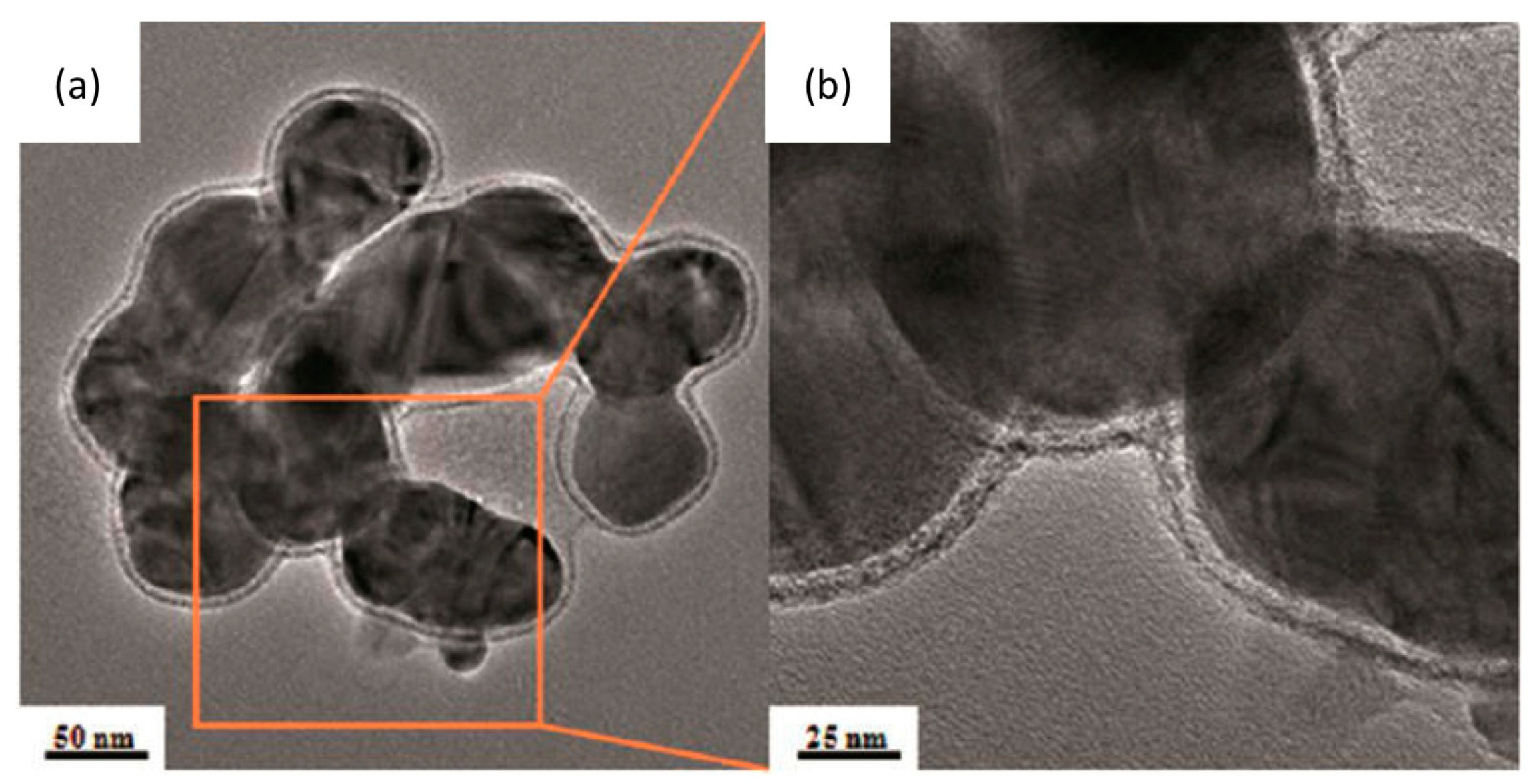
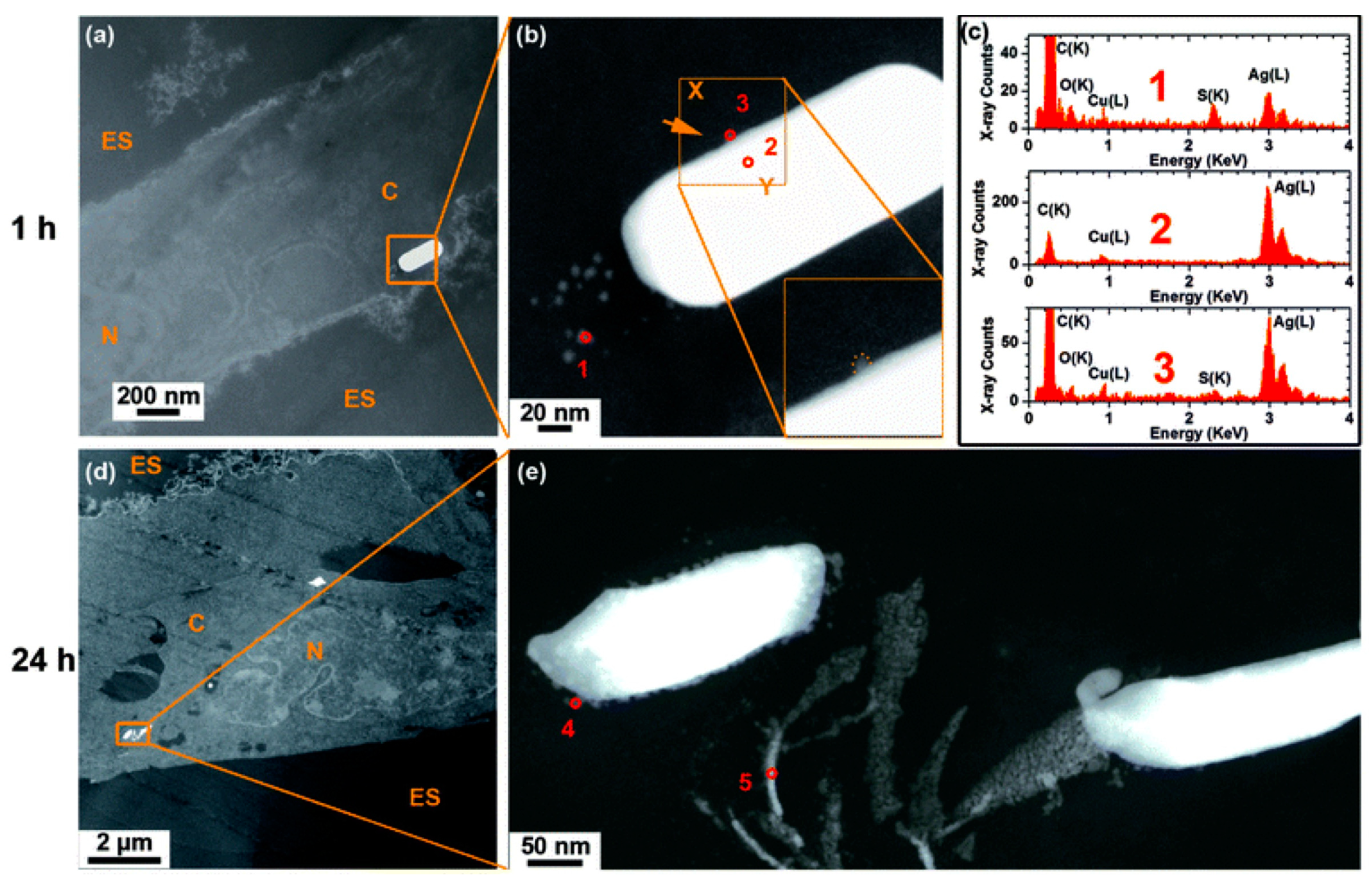
4.4. Internalization of AgNPs by Cells and Transformation Inside the Cell

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Schluesener, H.J. Nanosilver: A nanoproduct in medical application. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 176, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.F.; Baun, A. When enough is enough. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnhoven, S.; Peijnenburg, W.; Herberts, C.A.; Hagens, W.I.; Oomen, A.G.; Heugens, E.; Roszek, B.; Bisschops, J.; Gosens, I.; van de Meent, D.; et al. Nano-silver: A review of available data and knowledge gaps in human and environmental risk assessment. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, S.; el-Sayed, M.A. Spectral properties and relaxation dynamics of surface plasmon electronic oscillations in gold and silver nanodots and nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 8410–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.V. Photophysical, photochemical and photocatalytic aspects of metal nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7729–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies. http://www.nanotechproject.org/cpi/ (accessed on 14 October 2014).
- Eturska, M.; Obreshkova, E. Argyria in the prolonged use of adsorgan. Vutreshni Boles. 1979, 18, 121–123. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, W.H.; Garron, L.K.; Contreras, F.; Hayes, T.L.; Lai, C. Endogenous and exogenous ocular and systemic silver deposition. Trans. Ophthalmol. Soc. U. K. 1980, 100, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fabrega, J.; Luoma, S.N.; Tyler, C.R.; Galloway, T.S.; Lead, J.R. Silver nanoparticles: Behaviour and effects in the aquatic environment. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foldbjerg, R.; Dang, D.A.; Autrup, H. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in the human lung cancer cell line, A549. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.V.; Neigh, A.M.; Vermeulen, J.P.; de la Fonteyne, L.J.; Verharen, H.W.; Briede, J.J.; van Loveren, H.; de Jong, W.H. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9810–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.S.; Ronconi, J.V.; Daufenbach, J.F.; Goncalves, C.L.; Rezin, G.T.; Streck, E.L.; Paula, M.M. In vitro effects of silver nanoparticles on the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 342, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, A.K.; Pelletier, D.A.; Wang, W.; Morrell-Falvey, J.L.; Gu, B.; Doktycz, M.J. Cytotoxicity induced by engineered silver nanocrystallites is dependent on surface coatings and cell types. Langmuir 2012, 28, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Oh, S.M.; Chung, K.H. Genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles stimulated by oxidative stress in human normal bronchial epithelial (BEAS-2B) cells. Mutat. Res. 2011, 726, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoehr, L.C.; Gonzalez, E.; Stampfl, A.; Casals, E.; Duschl, A.; Puntes, V.; Oostingh, G.J. Shape matters: Effects of silver nanospheres and wires on human alveolar epithelial cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Jain, J.; Rajwade, J.M.; Paknikar, K.M. Cellular responses induced by silver nanoparticles: In vitro studies. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 179, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.; Jung, H.; Lim, J.S. Cell death by polyvinylpyrrolidine-coated silver nanoparticles is mediated by ROS-dependent signaling. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Lee, I.K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Hyun, J.W. Silver nanoparticles induce oxidative cell damage in human liver cells through inhibition of reduced glutathione and induction of mitochondria-involved apoptosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 201, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Mun, G.L.K.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinwald, A.; Donaldson, K. Use of back-scatter electron signals to visualise cell/nanowires interactions in vitro and in vivo; Frustrated phagocytosis of long fibres in macrophages and compartmentalisation in mesothelial cells in vivo. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Y.; Hurt, R.H. Ion release kinetics and particle persistence in aqueous nano-silver colloids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, B.F.; Chen, S.; Kyo, Y.; Herpoldt, K.L.; Terrill, N.J.; Dunlop, I.E.; McPhail, D.S.; Shaffer, M.S.; Schwander, S.; Gow, A.; et al. The stability of silver nanoparticles in a model of pulmonary surfactant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11232–11240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yao, Y.; Sullivan, N.; Chen, Y. Modeling the primary size effects of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles on their ion release kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4422–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejamaya, M.; Romer, I.; Merrifield, R.C.; Lead, J.R. Stability of citrate, PVP, and PEG coated silver nanoparticles in ecotoxicology media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7011–7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittler, S.; Greulich, C.; Diendorf, J.; Köller, M.; Epple, M. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles increases during storage because of slow dissolution under release of silver ions. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4548–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gondikas, A.P.; Marinakos, S.M.; Auffan, M.; Liu, J.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Meyer, J.N. Mechanism of silver nanoparticle toxicity is dependent on dissolved silver and surface coating in caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebounova, L.; Guio, E.; Grassian, V. Silver nanoparticles in simulated biological media: A study of aggregation, sedimentation, and dissolution. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sonshine, D.A.; Shervani, S.; Hurt, R.H. Controlled release of biologically active silver from nanosilver surfaces. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6903–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Z.M.; Zhang, Q.B.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, E.; Piccapietra, F.; Wagner, B.; Marconi, F.; Kaegi, R.; Odzak, N.; Sigg, L.; Behra, R. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8959–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, O.; Hu, Z. Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrega, J.; Fawcett, S.R.; Renshaw, J.C.; Lead, J.R. Silver nanoparticle impact on bacterial growth: Effect of pH, concentration, and organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7285–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Cheng, Y.; Espinasse, B.; Colman, B.P.; Auffan, M.; Wiesner, M.; Rose, J.; Liu, J.; Bernhardt, E.S. More than the ions: The effects of silver nanoparticles on lolium multiflorum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2360–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhardt, S.; Brunetto, P.S.; Gagnon, J.; Priebe, M.; Giese, B.; Fromm, K.M. Nanobio silver: Its interactions with peptides and bacteria, and its uses in medicine. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4708–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlbusch, T.A.; Asbach, C.; Fissan, H.; Gohler, D.; Stintz, M. Nanoparticle exposure at nanotechnology workplaces: A review. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.Y.; Gottschalk, F.; Hungerbuhler, K.; Nowack, B. Comprehensive probabilistic modelling of environmental emissions of engineered nanomaterials. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostraat, M.L.; Thornburg, J.W.; Malloy, Q.G.J. Measurement strategies of airborne nanomaterials. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 30, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kwak, B.K.; Bae, E.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Yi, J. Characterization of exposure to silver nanoparticles in a manufacturing facility. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-J.; Wu, C.-H.; Leu, M.-L.; Chen, S.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Tsai, P.-J.; Ko, F.-H. Dustiness test of nanopowders using a standard rotating drum with a modified sampling train. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko, Y.; Han, T.W.; Lioy, P.J.; Mainelis, G. Potential for exposure to engineered nanoparticles from nanotechnology-based consumer spray products. J. Expos. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, C.; Hagendorfer, H.; Goetz, N.; Kaegi, R.; Gehrig, R.; Ulrich, A.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Nanosized aerosols from consumer sprays: Experimental analysis and exposure modeling for four commercial products. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 3377–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Rimmele, E.; Wichser, A.; Erni, R.; Height, M.; Nowack, B. Presence of nanoparticles in wash water from conventional silver and nano-silver textiles. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7208–7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakand, S.; Hayes, A.; Dechsakulthorn, F. Nanoparticles: A review of particle toxicology following inhalation exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2012, 24, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Moreno, E.; Nawrot, T.S.; Nemmar, A.; Nemery, B. Particulate matter in the environment: Pulmonary and cardiovascular effects. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2007, 13, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Muralikrishnan, S.; Ng, C.T.; Yung, L.Y.; Bay, B.H. Nanoparticle-induced pulmonary toxicity. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 235, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetley, T.D. Health effects of nanomaterials. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, F.; Gehr, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. In vitro human lung cell culture models to study the toxic potential of nanoparticles. In Nanotoxicity; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009; pp. 379–395. [Google Scholar]
- Lundborg, M.; Johard, U.; Lastbom, L.; Gerde, P.; Camner, P. Human alveolar macrophage phagocytic function is impaired by aggregates of ultrafine carbon particles. Environ. Res. 2001, 86, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhlfeld, C.; Gehr, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Translocation and cellular entering mechanisms of nanoparticles in the respiratory tract. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2008, 138, 387–391. [Google Scholar]
- Hillery, A.M.; Lloyd, A.W.; Swarbrick, J. Drug Delivery and Targeting for Pharmacists and Pharmaceutical Scientist; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.M.; Schlager, J.J. Safety evaluation of silver nanoparticles: Inhalation model for chronic exposure. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, S.; Karg, E.; Roth, C.; Schulz, H.; Ziesenis, A.; Heinzmann, U.; Schramel, P.; Heyder, J. Pulmonary and systemic distribution of inhaled ultrafine silver particles in rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.H.; Ji, J.H.; Yoon, J.U.; Kim, D.S.; Song, M.Y.; Jeong, J.; Han, B.S.; Han, J.H.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, J.; et al. Lung function changes in sprague-dawley rats after prolonged inhalation exposure to silver nanoparticles. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, H.S.; Rha, D.S.; Kim, J.M.; Park, J.D.; Choi, B.S.; Lim, R.; Chang, H.K.; Chung, Y.H.; et al. Twenty-eight-day oral toxicity, genotoxicity, and gender-related tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles in sprague-dawley rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Kim, J.; Park, J.D.; Ryu, H.Y.; Yu, I.J. Histological study of gender differences in accumulation of silver nanoparticles in kidneys of fischer 344 rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2009, 72, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Xiong, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Yuan, F.; Xi, T. Distribution, translocation and accumulation of silver nanoparticles in rats. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 4924–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.-P.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Li, R.; Sun, B.; et al. Use of coated silver nanoparticles to understand the relationship of particle dissolution and bioavailability to cell and lung toxicological potential. Small 2014, 10, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danscher, G.; Norgaard, J.O.; Baatrup, E. Autometallography: Tissue metals demonstrated by a silver enhancement kit. Histochemistry 1987, 86, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.H.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, S.S.; Yoon, J.U.; Park, J.D.; Choi, B.S.; Chung, Y.H.; Kwon, I.H.; Jeong, J.; Han, B.S.; et al. Twenty-eight-day inhalation toxicity study of silver nanoparticles in sprague-dawley rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, J.-S.; Lee, B.S.; Ryu, H.Y.; Sung, J.H.; Chung, K.H.; Yu, I.J. Effects of repeated silver nanoparticles exposure on the histological structure and mucins of nasal respiratory mucosa in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 182, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Choi, Y.-J.; Jung, E.-J.; Yin, H.-Q.; Kwon, J.-T.; Kim, J.-E.; Im, H.-T.; Cho, M.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.-Y.; et al. Genomics-based screening of differentially expressed genes in the brains of mice exposed to silver nanoparticles via inhalation. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.S.; Sung, J.H.; Ji, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Ryu, H.R.; Lee, J.K.; Chung, Y.H.; Park, H.M.; Shin, B.S.; et al. Recovery from silver-nanoparticle-exposure-induced lung inflammation and lung function changes in sprague dawley rats. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACGIH. Silver and compounds. In Documentation of the Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances, 7th ed.; American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, J.H.; Ji, J.H.; Park, J.D.; Yoon, J.U.; Kim, D.S.; Jeon, K.S.; Song, M.Y.; Jeong, J.; Han, B.S.; Han, J.H.; et al. Subchronic inhalation toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackison, F.W.; Partridge, L.J.; Stricoff, R.S. NIOSH: Occupational Health Guidelines for Chemical Hazards: Silver Metal and Soluble Silver Compounds, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH); Department of Health and Human Services: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, S.-J.; Ada, E.; Isaacs, J.; Ellenbecker, M. Airborne nanoparticle exposures associated with the manual handling of nanoalumina and nanosilver in fume hoods. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwon, M.; Ji, J.H.; Kang, C.S.; Ahn, K.H.; Han, J.H.; Yu, I.J. Exposure assessment of workplaces manufacturing nanosized tio2 and silver. Inhal. Toxicol. 2011, 23, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Ahn, K.; Kim, S.; Jeon, K.; Lee, J.; Yu, I. Continuous 3-day exposure assessment of workplace manufacturing silver nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Sung, J.H.; Ji, J.H.; Song, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, C.S.; Yu, I.J. In vivo genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles after 90-day silver nanoparticle inhalation exposure. Saf. Health Work 2011, 2, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, D.K.; Jin, T.; Behari, J. Dose-dependent in vivo toxicity assessment of silver nanoparticle in wistar rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.F.; Wang, J.; Patterson, T.A.; Saini, U.T.; Robinson, B.L.; Newport, G.D.; Murdock, R.C.; Schlager, J.J.; Hussain, S.M.; Ali, S.F. Expression of genes related to oxidative stress in the mouse brain after exposure to silver-25 nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 187, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, B.; Seog, J.H.; Graham, L.M.; Lee, S.B. Experimental considerations on the cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, B.; Sanchez-Espinel, C.; Arruebo, M.; Faro, J.; de Miguel, E.; Magadan, S.; Yague, C.; Fernandez-Pacheco, R.; Ibarra, M.R.; Santamaria, J.; et al. Assessing methods for blood cell cytotoxic responses to inorganic nanoparticles and nanoparticle aggregates. Small 2008, 4, 2025–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, A.; Bai, X.; Son, S.J.; Lee, S.B.; Ghandehari, H. Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of silica nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2150–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.S.; Chang, K.L.; Hwang, D.F.; Kong, Z.L. In vitro cytotoxicitiy of silica nanoparticles at high concentrations strongly depends on the metabolic activity type of the cell line. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2064–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Ryu, D.Y. Silver nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress, genotoxicity and apoptosis in cultured cells and animal tissues. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima, R.; Seabra, A.B.; Duran, N. Silver nanoparticles: A brief review of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of chemically and biogenically synthesized nanoparticles. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, H.-J.; Choi, J. P38 MAPK activation, DNA damage, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis as mechanisms of toxicity of silver nanoparticles in jurkat T cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8337–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsin, Y.H.; Chen, C.F.; Huang, S.; Shih, T.S.; Lai, P.S.; Chueh, P.J. The apoptotic effect of nanosilver is mediated by a ROS- and JNK-dependent mechanism involving the mitochondrial pathway in NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 179, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanpui, P.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Induction of apoptosis in cancer cells at low silver nanoparticle concentrations using chitosan nanocarrier. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Choi, J.E.; Choi, J.; Chung, K.-H.; Park, K.; Yi, J.; Ryu, D.-Y. Oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles in human hepatoma cells. Toxicol. in Vitro 2009, 23, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, H.C.; Wang, T.; Liao, C.Y.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Q.F.; Yan, B.; Jiang, G.B. Impact of silver nanoparticles on human cells: Effect of particle size. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Lucas, B.; Schrand, A.; Murdock, R.C.; Lee, T.; Schlager, J.J.; Hussain, S.M.; Hofmann, M.-C. Silver nanoparticles disrupt GDNF/Fyn kinase signaling in spermatogonial stem cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 116, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braydich-Stolle, L.; Hussain, S.; Schlager, J.J.; Hofmann, M.C. In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 88, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrand, A.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Schlager, J.J.; Dai, L.; Hussain, S.M. Can silver nanoparticles be useful as potential biological labels? Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 235104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.M.; Hess, K.L.; Gearhart, J.M.; Geiss, K.T.; Schlager, J.J. In vitro toxicity of nanoparticles in BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicol. in Vitro 2005, 19, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.M.; Javorina, A.K.; Schrand, A.M.; Duhart, H.M.; Ali, S.F.; Schlager, J.J. The interaction of manganese nanoparticles with pc-12 cells induces dopamine depletion. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenberg, S.; Scherzed, A.; Kessler, M.; Hummel, S.; Technau, A.; Froelich, K.; Ginzkey, C.; Koehler, C.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Silver nanoparticles: Evaluation of DNA damage, toxicity and functional impairment in human mesenchymal stem cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 201, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Guan, R.; Ye, X.; Jiang, J.; Liu, M.; Huang, G.; Chen, X. Toxicity of nano- and micro-sized silver particles in human hepatocyte cell line L02. J. Phys. 2011, 304, 012036. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, M.; Karns, M.; Goodson, M.; Rowe, J.; Hussain, S.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Hong, Y. DNA damage response to different surface chemistry of silver nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 233, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, P.; Gogoi, S.K.; Sanpui, P.; Paul, A.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Signaling gene cascade in silver nanoparticle induced apoptosis. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 77, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Shinohara, Y. Cytotoxic effect and apoptosis induction by silver nanoparticles in HeLa cells. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-W.; Kuo, T.-H.; Chang, J.-H.; Yeh, J.-M.; Chan, W.-H. Induction of cytotoxicity and apoptosis in mouse blastocysts by silver nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 197, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; Xi, T. Investigation of the cytotoxicity mechanism of silver nanoparticles in vitro. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 5, 044103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, E.; Salar-Behzadi, S. Toxicological assessment of inhaled nanoparticles: Role of in vivo, ex vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 4795–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabner, J.; Karp, P.; Seiler, M.; Phillips, S.L.; Mitchell, C.J.; Saavedra, M.; Welsh, M.; Klingelhutz, A.J. Development of cystic fibrosis and noncystic fibrosis airway cell lines. Am. J. Physiol. 2003, 284, L844–L854. [Google Scholar]
- Worle-Knirsch, J.M.; Pulskamp, K.; Krug, H.F. Oops they did it again! Carbon nanotubes hoax scientists in viability assays. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, A.; Herzog, E.; Davoren, M.; Lyng, F.M.; Byrne, H.J.; Chambers, G. Spectroscopic analysis confirms the interactions between single walled carbon nanotubes and various dyes commonly used to assess cytotoxicity. Carbon 2007, 45, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofani, G.; Danti, S.; D’Alessandro, D.; Moscato, S.; Menciassi, A. Assessing cytotoxicity of boron nitride nanotubes: Interference with the mtt assay. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.V.; Annema, W.; Salvati, A.; Lesniak, A.; Elsaesser, A.; Barnes, C.; McKerr, G.; Howard, C.V.; Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A.; et al. In vitro developmental toxicity test detects inhibition of stem cell differentiation by silica nanoparticles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 240, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, C.; Schaefer, U.F.; Ruge, C.A.; Wohlleben, W.; Lehr, C.M. Interaction of metal oxide nanoparticles with lung surfactant protein A. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Oh, J.H.; Yoon, S.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, K.; Song, C.W. Silver nanoparticles induce apoptosis and G2/M arrest via PKCζ-dependent signaling in A549 lung cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, C.; Hussain, S.M.; Schrand, A.M.; K. Braydich-Stolle, L.; Hess, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Schlager, J.J. Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: Size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 13608–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.C.; Seligy, V.L.; Massarsky, A.; Moon, T.W.; Rippstein, P.; Tan, J.; Tayabali, A.F. Comparison of toxicity of uncoated and coated silver nanoparticles. J. Phys. 2013, 429, 012025. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, W.-K.; Kim, S.; Choi, M.; Kim, C.; Jeong, Y.S.; Cho, B.-R.; Hahn, J.-S.; Jang, J. Cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, and innate immune response of silica-titania hollow nanoparticles based on size and surface functionality. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5301–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawata, K.; Osawa, M.; Okabe, S. In vitro toxicity of silver nanoparticles at noncytotoxic doses to HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6046–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.H.; Jang, J.; Kim, S.; Kang, T.; Lee, K.; Choi, I.H. The effects of sub-lethal concentrations of silver nanoparticles on inflammatory and stress genes in human macrophages using cDNA microarray analysis. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4690–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, L.N. Chemical catalysis by colloids and clusters. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 2693–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, A.R.; Skoglund, S.; Wallinder, I.O.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H.L. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: The role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Hande, M.; Valiyaveettil, S. Anti-proliferative activity of silver nanoparticles. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.K.; Conroy, J.; Lyons, P.E.; Coleman, J.; O’Sullivan, M.P.; Kornfeld, H.; Kelleher, D.; Volkov, Y. Autophagy induction by silver nanowires: A new aspect in the biocompatibility assessment of nanocomposite thin films. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 264, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.J.; Cheng, J.; Lin, C.C.; Lam, Y.W.; Cheng, S.H.; Wong, W.T. Nuclear penetration of surface functionalized gold nanoparticles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 237, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Xing, G.; He, R.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Guo, H. Variation in the internalization of differently sized nanoparticles induces different DNA-damaging effects on a macrophage cell line. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, A.; Tentschert, J.; Jungnickel, H.; Graf, P.; Mantion, A.; Draude, F.; Plendl, J.; Goetz, M.E.; Galla, S.; Mašić, A.; et al. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in human macrophages: Uptake, intracellular distribution and cellular responses. J. Phys. 2011, 304, 012030. [Google Scholar]
- Cronholm, P.; Karlsson, H.L.; Hedberg, J.; Lowe, T.A.; Winnberg, L.; Elihn, K.; Wallinder, I.O.; Moller, L. Intracellular uptake and toxicity of Ag and CuO nanoparticles: A comparison between nanoparticles and their corresponding metal ions. Small 2013, 9, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panté, N.; Kann, M. Nuclear pore complex is able to transport macromolecules with diameters of ~39 nm. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Qian, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Size-mediated cytotoxicity and apoptosis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, P.; Mohanty, S.; Mallick, R.; Jacob, B.; Sonawane, A. Toxicity and antibacterial assessment of chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles on human pathogens and macrophage cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, F.; Clift, M.J.D.; Piccapietra, F.; Behra, R.; Schmid, O.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Exposure of silver-nanoparticles and silver-ions to lung cells in vitro at the air-liquid interface. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Goode, A.E.; Sweeney, S.; Theodorou, I.G.; Thorley, A.J.; Ruenraroengsak, P.; Chang, Y.; Gow, A.; Schwander, S.; Skepper, J.; et al. Sulfidation of silver nanowires inside human alveolar epithelial cells: A potential detoxification mechanism. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9839–9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleh, C.; Kreyling, W.G.; Lehr, C.M. Pulmonary surfactant is indispensable in order to simulate the in vivo situation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera Gil, P.; Oberdörster, G.; Elder, A.; Puntes, V.; Parak, W.J. Correlating physico-chemical with toxicological properties of nanoparticles: The present and the future. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5527–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Mueller, L.; Blank, F.; Brandenberger, C.; Muehlfeld, C.; Gehr, P. A newly developed in vitro model of the human epithelial airway barrier to study the toxic potential of nanoparticles. Altex 2008, 25, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blank, F.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Gehr, P. Dendritic cells and macrophages form a transepithelial network against foreign particulate antigens. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Muhlfeld, C.; Blank, F.; Musso, C.; Gehr, P. Translocation of particles and inflammatory responses after exposure to fine particles and nanoparticles in an epithelial airway model. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2007, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, F.; Wehrli, M.; Lehmann, A.; Baum, O.; Gehr, P.; von Garnier, C.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.M. Macrophages and dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and exchange particles in an in vitro model of the human airway wall. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Lim, B.; Skrabalak, S.E. Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanocrystals: Simple chemistry meets complex physics? Angew. Chem. 2009, 48, 60–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warheit, D.B. How meaningful are the results of nanotoxicity studies in the absence of adequate material characterization? Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, S.K.; Verma, M. Measurement of nanoparticles by light-scattering techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, E.; Soliwoda, K.; Kadziola, K.; Tkacz-Szczesna, B.; Celichowski, G.; Cichomski, M.; Szmaja, W.; Grobelny, J. Detection limits of dls and UV-Vis spectroscopy in characterization of polydisperse nanoparticles colloids. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, B.N.; Khlebtsov, N.G. On the measurement of gold nanoparticle sizes by the dynamic light scattering method. Colloid J. 2011, 73, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, J.L.S.; Borgnia, M.J.; Bartesaghi, A.; Tran, E.E.H.; Earl, L.A.; Schauder, D.M.; Lengyel, J.; Pierson, J.; Patwardhan, A.; Subramaniam, S. Cryo-electron microscopy—A primer for the non-microscopist. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elechiguerra, J.L.; Larios-Lopez, L.; Liu, C.; Garcia-Gutierrez, D.; Camacho-Bragado, A.; Yacaman, M.J. Corrosion at the nanoscale: The case of silver nanowires and nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 6042–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laban, G.; Nies, L.F.; Turco, R.F.; Bickham, J.W.; Sepulveda, M.S. The effects of silver nanoparticles on fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) embryos. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, C.; Foldbjerg, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Sutherland, D.S.; Autrup, H. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles—Nanoparticle or silver ion? Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 208, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Bae, S.; Lee, S.; Hong, I.S.; Kim, S.H. Ion-release kinetics and ecotoxicity effects of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, M.A.; Miller, L.F.; George, A.J.; Pettway, B.A.; Price, C.L.; Porter, B.E.; Bednar, A.J.; Seiter, J.M.; Kennedy, A.J.; Steevens, J.A. Simultaneous dispersion-dissolution behavior of concentrated silver nanoparticle suspensions in the presence of model organic solutes. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, F.D.; Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R.H. Chemical transformations of nanosilver in biological environments. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9887–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, R.D.; Miller, J.M.; Hutchison, J.E. Generation of metal nanoparticles from silver and copper objects: Nanoparticle dynamics on surfaces and potential sources of nanoparticles in the environment. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8950–8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Theodorou, I.G.; Goode, A.E.; Gow, A.; Schwander, S.; Zhang, J.; Chung, K.F.; Tetley, T.D.; Shaffer, M.S.; Ryan, M.P.; et al. High-resolution analytical electron microscopy reveals cell culture media-induced changes to the chemistry of silver nanowires. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13813–13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levard, C.; Hotze, E.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Brown, G.E., Jr. Environmental transformations of silver nanoparticles: Impact on stability and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6900–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levard, C.; Reinsch, B.C.; Michel, F.M.; Oumahi, C.; Lowry, G.V.; Brown, G.E. Sulfidation processes of PVP-coated silver nanoparticles in aqueous solution: Impact on dissolution rate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5260–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinsch, B.C.; Levard, C.; Li, Z.; Ma, R.; Wise, A.; Gregory, K.B.; Brown, G.E., Jr.; Lowry, G.V. Sulfidation of silver nanoparticles decreases escherichia coli growth inhibition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6992–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, O.; Ivask, A.; Kakinen, A.; Kurvet, I.; Kahru, A. Particle-cell contact enhances antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. PLoS One 2013, 8, e64060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Aberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Biomolecular coronas provide the biological identity of nanosized materials. Nat. Nano 2012, 7, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Protein-nanoparticle interactions. Nano Today 2008, 3, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggård, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Understanding the nanoparticle–protein corona using methods to quantify exchange rates and affinities of proteins for nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, C.M.; Badireddy, A.R.; Ryde, I.T.; Seidler, F.J.; Slotkin, T.A. Silver nanoparticles compromise neurodevelopment in PC12 cells: Critical contributions of silver ion, particle size, coating, and composition. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittler, S.; Greulich, C.; Gebauer, J.S.; Diendorf, J.; Treuel, L.; Ruiz, L.; Gonzalez-Calbet, J.M.; Vallet-Regi, M.; Zellner, R.; Koller, M.; et al. The influence of proteins on the dispersability and cell-biological activity of silver nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.J.; Hsu, S.H.; Tsai, C.L. Cytotoxicity and immunological response of gold and silver nanoparticles of different sizes. Small 2009, 5, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanadhas, D.P.; Ben Thomas, M.; Thomas, R.; Raichur, A.M.; Chakravortty, D. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with serum proteins affects their antimicrobial activity in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4945–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.A.; Kramer, J.R. Structural chemistry and geochemistry of silver-sulfur compounds: Critical review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Creuwels, L.A.; van Golde, L.M.; Haagsman, H.P. The pulmonary surfactant system: Biochemical and clinical aspects. Lung 1997, 175, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, J.; Curstedt, T.; Robertson, B. The proteins of the surfactant system. Eur. Respir. J. 1994, 7, 372–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goerke, J. Pulmonary surfactant: Functions and molecular composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1408, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, D.; Sriram, K.; Wolfarth, M.; Jefferson, A.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Andrew, M.E.; Castranova, V. A biocompatible medium for nanoparticle dispersion. Nanotoxicology 2008, 2, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, T.M.; Porter, D.W.; Robinson, V.A.; Lindsley, W.G.; Schwegler-Berry, D.E.; Castranova, V. Improved method to disperse nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo investigation of toxicity. Nanotoxicology 2007, 1, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCuspie, R.I.; Allen, A.J.; Hackley, V.A. Dispersion stabilization of silver nanoparticles in synthetic lung fluid studied under in situ conditions. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, M.S.; Zhao, L.; Smith, R.; Possmayer, F.; Petersen, N.O. Metal nanoparticle pollutants interfere with pulmonary surfactant function in vitro. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, B.; Kobzik, L. Alveolar macrophage uptake of the environmental particulate titanium dioxide: Role of surfactant components. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1996, 14, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konduru, N.V.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Feng, W.; Basova, L.V.; Belikova, N.A.; Bayir, H.; Clark, K.; Rubin, M.; Stolz, D.; Vallhov, H.; et al. Phosphatidylserine targets single-walled carbon nanotubes to professional phagocytes in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One 2009, 4, e4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, M.; Wick, P.; Clift, M.J.; Blank, F.; Diener, L.; Yan, B.; Gehr, P.; Krug, H.F.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Pulmonary surfactant coating of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) influences their oxidative and pro-inflammatory potential in vitro. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, E.; Byrne, H.J.; Davoren, M.; Casey, A.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J. Dispersion medium modulates oxidative stress response of human lung epithelial cells upon exposure to carbon nanomaterial samples. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 236, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y. Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and cytotoxicity of nanomaterials. Small 2011, 7, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.E.; Madler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Stellacci, F. Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle–cell interactions. Small 2010, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailander, V.; Landfester, K. Interaction of nanoparticles with cells. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2379–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, S.D.; Schmid, S.L. Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature 2003, 422, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldati, T.; Schliwa, M. Powering membrane traffic in endocytosis and recycling. Nat. Rev. 2006, 7, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harush-Frenkel, O.; Debotton, N.; Benita, S.; Altschuler, Y. Targeting of nanoparticles to the clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 353, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greulich, C.; Diendorf, J.; Simon, T.; Eggeler, G.; Epple, M.; Köller, M. Uptake and intracellular distribution of silver nanoparticles in human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiser, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Kapp, N.; Schurch, S.; Kreyling, W.; Schulz, H.; Semmler, M.; Im Hof, V.; Heyder, J.; Gehr, P. Ultrafine particles cross cellular membranes by nonphagocytic mechanisms in lungs and in cultured cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimai, D.S.; Quesnel, D.J.; Busnaina, A.A. The adhesion of dry particles in the nanometer to micrometer-size range. Colloids Surf. A 2000, 165, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, A.D.; Parak, W.J.; Zhang, F.; Ali, Z.; Röcker, C.; Nienhaus, G.U.; Gehr, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Fluorescent–magnetic hybrid nanoparticles induce a dose-dependent increase in proinflammatory response in lung cells in vitro correlated with intracellular localization. Small 2010, 6, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiser, M.; Casaulta, M.; Kupferschmid, B.; Schulz, H.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Kreyling, W. The role of macrophages in the clearance of inhaled ultrafine titanium dioxide particles. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, H.J.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Brown, D.M.; Kreyling, W.; Tran, L.; Stone, V. Evaluating the uptake and intracellular fate of polystyrene nanoparticles by primary and hepatocyte cell lines in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 242, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motskin, M.; Wright, D.M.; Muller, K.; Kyle, N.; Gard, T.G.; Porter, A.E.; Skepper, J.N. Hydroxyapatite nano and microparticles: Correlation of particle properties with cytotoxicity and biostability. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3307–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Ji, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wei, T.; et al. Selective targeting of gold nanorods at the mitochondria of cancer cells: Implications for cancer therapy. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panyam, J.; Zhou, W.Z.; Prabha, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Labhasetwar, V. Rapid endo-lysosomal escape of poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles: Implications for drug and gene delivery. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Sun, B.; George, S.; Xia, T.; Nel, A.E.; Zink, J.I. Designed synthesis of CeO2 nanorods and nanowires for studying toxicological effects of high aspect ratio nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5366–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C.; Fang, C.-Y.; Rehor, I.; Cigler, P.; Chang, H.-C.; Lin, G.; Liu, R.; et al. Unambiguous observation of shape effects on cellular fate of nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Panariti, A.; Miserocchi, G.; Rivolta, I. The effect of nanoparticle uptake on cellular behavior: Disrupting or enabling functions? Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dausend, J.; Musyanovych, A.; Dass, M.; Walther, P.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V. Uptake mechanism of oppositely charged fluorescent nanoparticles in HeLa cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandenberger, C.; Mühlfeld, C.; Ali, Z.; Lenz, A.-G.; Schmid, O.; Parak, W.J.; Gehr, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Quantitative evaluation of cellular uptake and trafficking of plain and polyethylene glycol-coated gold nanoparticles. Small 2010, 6, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.; Murphy, F.; Schinwald, A.; Duffin, R.; Poland, C.A. Identifying the pulmonary hazard of high aspect ratio nanoparticles to enable their safety-by-design. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinwald, A.; Murphy, F.A.; Prina-Mello, A.; Poland, C.A.; Byrne, F.; Movia, D.; Glass, J.R.; Dickerson, J.C.; Schultz, D.A.; Jeffree, C.E.; et al. The threshold length for fiber-induced acute pleural inflammation: Shedding light on the early events in asbestos-induced mesothelioma. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 128, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teeguarden, J.G.; Hinderliter, P.M.; Orr, G.; Thrall, B.D.; Pounds, J.G. Particokinetics in vitro: Dosimetry considerations for in vitro nanoparticle toxicity assessments. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 95, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskalakis, K.D.; O’Connor, T.P.; Crecelius, E.A. Evaluation of digestion procedures for determining silver in mussels and oysters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2303–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Ramarao, P. Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 213, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratsinis, A.; Hervella, P.; Leroux, J.-C.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Sotiriou, G.A. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in macrophages. Small 2013, 9, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Yi, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Park, K. Silver nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity by a trojan-horse type mechanism. Toxicol. in Vitro 2010, 24, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanwinkle, B.A.; de Mesy Bentley, K.L.; Malecki, J.M.; Gunter, K.K.; Evans, I.M.; Elder, A.; Finkelstein, J.N.; Oberdorster, G.; Gunter, T.E. Nanoparticle (NP) uptake by type I alveolar epithelial cells and their oxidant stress response. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, K.H.; Kulkarni, J.; Motskin, M.; Goode, A.; Winship, P.; Skepper, J.N.; Ryan, M.P.; Porter, A.E. pH-Dependent toxicity of high aspect ratio ZnO nanowires in macrophages due to intracellular dissolution. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6767–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Theodorou, I.G.; Ryan, M.P.; Tetley, T.D.; Porter, A.E. Inhalation of Silver Nanomaterials—Seeing the Risks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23936-23974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151223936
Theodorou IG, Ryan MP, Tetley TD, Porter AE. Inhalation of Silver Nanomaterials—Seeing the Risks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(12):23936-23974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151223936
Chicago/Turabian StyleTheodorou, Ioannis G., Mary P. Ryan, Teresa D. Tetley, and Alexandra E. Porter. 2014. "Inhalation of Silver Nanomaterials—Seeing the Risks" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 12: 23936-23974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151223936
APA StyleTheodorou, I. G., Ryan, M. P., Tetley, T. D., & Porter, A. E. (2014). Inhalation of Silver Nanomaterials—Seeing the Risks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(12), 23936-23974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151223936




