Meta-Omic Platforms to Assist in the Understanding of NAFLD Gut Microbiota Alterations: Tools and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
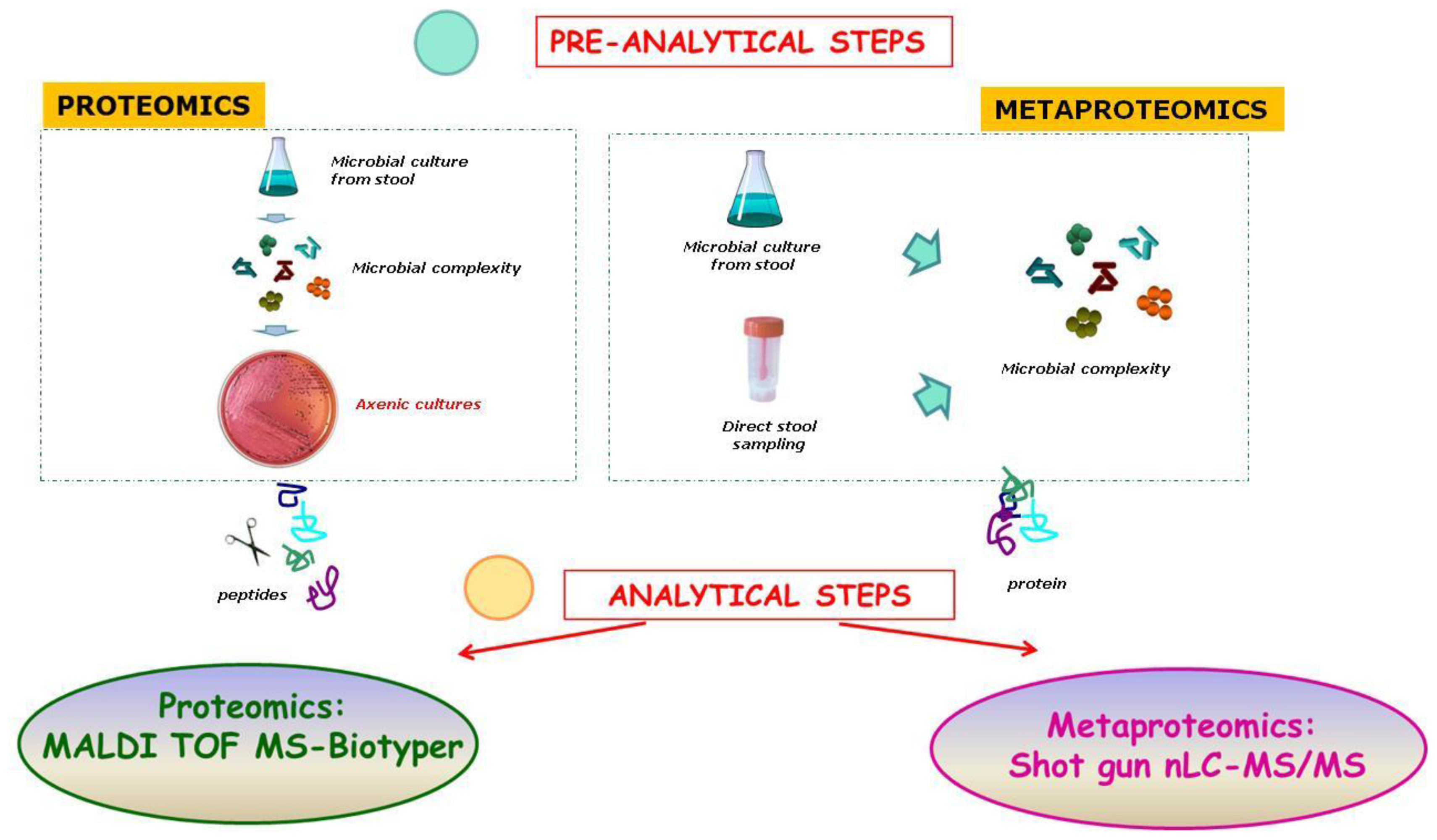
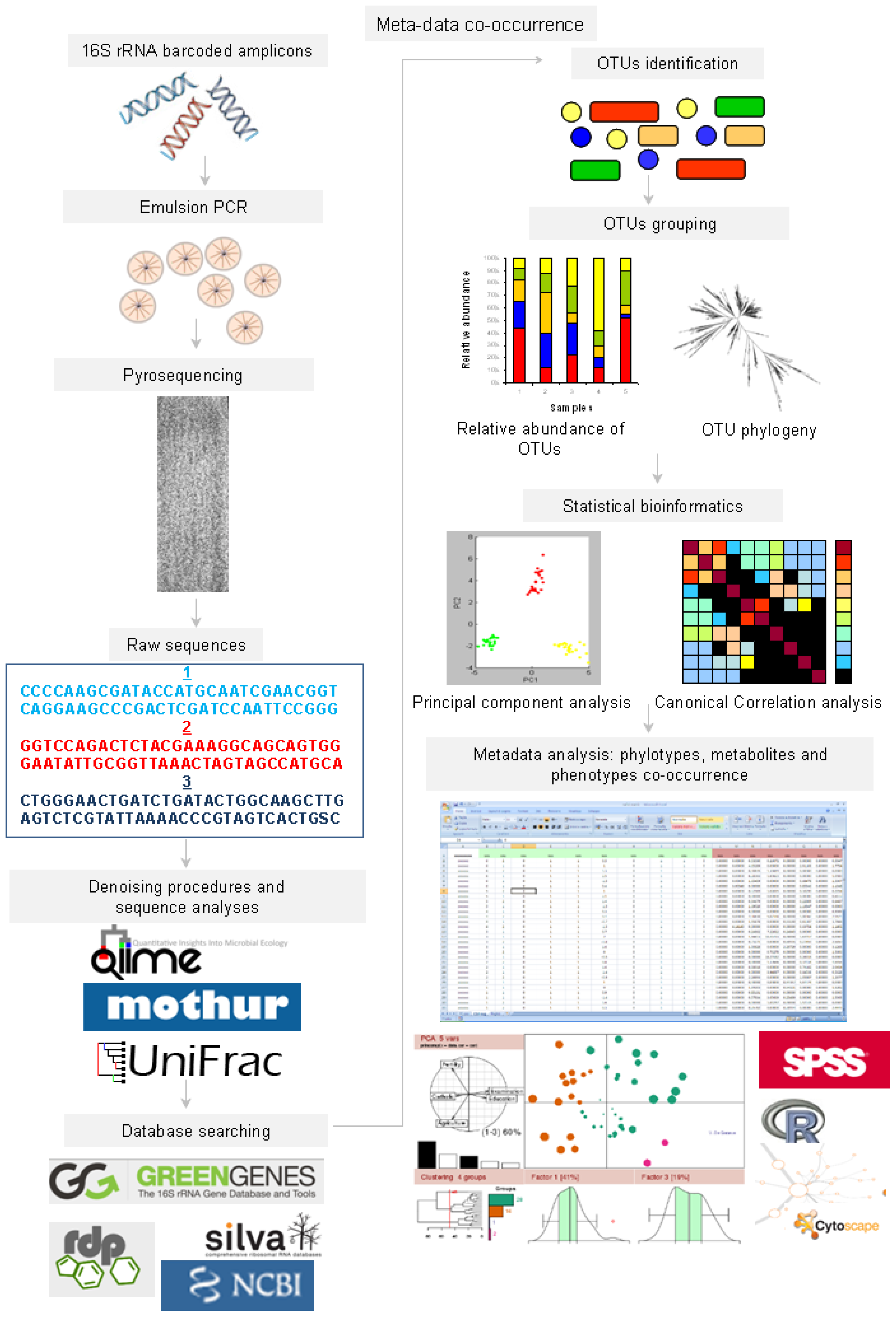
2. The New “Omics” Era and the Understanding of the Gut Microbiota in NAFLD: Descriptive and Functional Meta-Omics Approaches
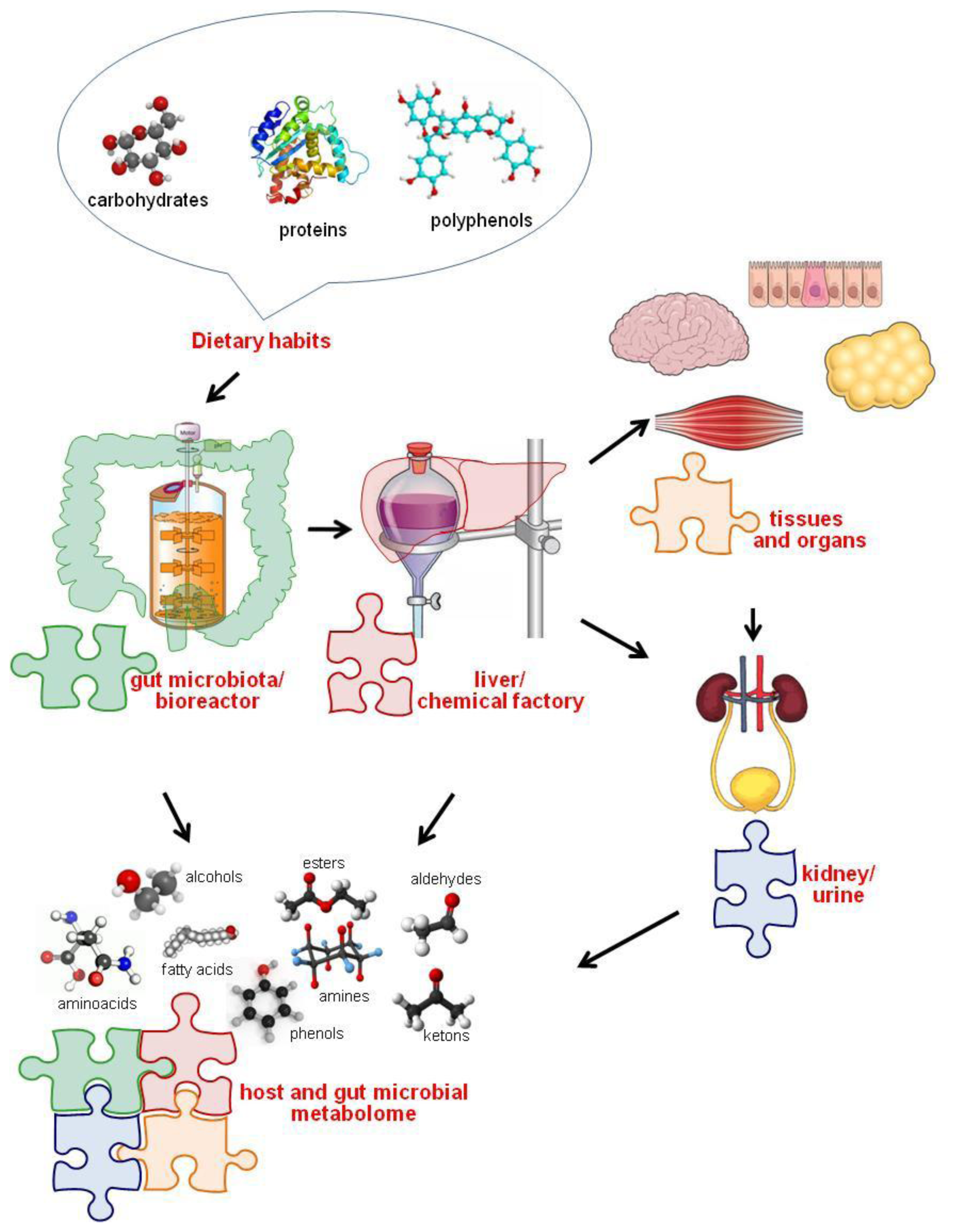
3. Diet-Gut Microbiota Interactions
The Role of Diet in Shaping and Modulating the Gut Microbiota
4. Gut Microbiota and Development of NAFLD
4.1. The Contribution of the Mouse Model
4.2. The Present Knowledge about NAFLD Patients
4.3. Gut-Induced Modulation: The Role of Prebiotics and Probiotics as External Xenobiotic Stimuli
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, J.; Guo, R.; Fung, M.L.; Liong, E.C.; Tipoe, G.L. Therapeutic approaches to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Past achievements and future challenges. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int 2013, 12, 125–135. [Google Scholar]
- Milić, S.; Stimac, D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/steatohepatitis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and treatment. Digest. Dis 2012, 30, 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Alisi, A.; Feldstein, A.E.; Villani, A.; Raponi, M.; Nobili, V. Pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A multidisciplinary approach. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 2012, 9, 152–161. [Google Scholar]
- Brunt, E.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: What the pathologist can tell the clinician. Digest. Dis 2012, 30, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Nobili, V.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Alisi, A.; Miele, L.; Valenti, L.; Vajro, P. A 360-degree overview of paediatric NAFLD: Recent insights. J. Hepatol 2013, 58, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.Y.; Qiao, L.; Fan, J.G. Clinical features of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int 2012, 11, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Day, C.P. Genetic and environmental susceptibility to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Digest. Dis 2010, 28, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- De Alwis, N.M.; Day, C.P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The mist gradually clears. J. Hepatol 2008, 48, 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- Tiniakos, D.G.; Vos, M.B.; Brunt, E.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathology and pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pathol 2010, 5, 145–171. [Google Scholar]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Insulin resistance, inflammation, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Trends Endocrin. Met 2008, 19, 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- Alisi, A.; Locatelli, M.; Nobili, V. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr 2010, 13, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Larrain, S.; Rinella, M.E. A myriad of pathways to NASH. Clin. Liver Dis 2012, 16, 525–548. [Google Scholar]
- Savary, S.; Trompier, D.; Andréoletti, P.; Le Borgne, F.; Demarquoy, J.; Lizard, G. Fatty acids—Induced lipotoxicity and inflammation. Curr. Drug Metab 2012, 13, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. DNA methylation and hepatic insulin resistance and steatosis. Curr. Drug Metab 2012, 15, 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Koek, G.H.; Liedorp, P.R.; Bast, A. The role of oxidative stress in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Cusi, K. Role of obesity and lipotoxicity in the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 711–725. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, H.; Kawada, N. Inflammation and fibrogenesis in steatohepatitis. J. Gastroenterol 2012, 47, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Kelishadi, R.; Mirghaffari, N.; Poursafa, P.; Gidding, S.S. Lifestyle and environmental factors associated with inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance in children. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein, A.E. Novel insights into the pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis 2010, 30, 391–401. [Google Scholar]
- Nseir, W.; Shalata, A.; Marmor, A.; Assy, N. Mechanisms linking nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with coronary artery disease. Digest. Dis. Sci 2011, 56, 3439–3449. [Google Scholar]
- Wree, A.; Kahraman, A.; Gerken, G.; Canbay, A. Obesity affects the liver—The link between adipocytes and hepatocytes. Digestion 2011, 83, 124–133. [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg, A.M.; Afonso, Mda. S.; Lavrador, M.S.; Machado, R.M.; Nakandakare, E.R. The role of dietary fatty acids in the pathology of metabolic syndrome. J. Nutr. Biochem 2012, 23, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, C.A.; Adegboyega, P.; van Rooijen, N.; Tagalicud, A.; Allman, M.; Wallace, M. Toll-like receptor-4 signaling and Kupffer cells play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol 2007, 47, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, K.; Kodama, Y.; Inokuchi, S.; Schnabl, B.; Aoyama, T.; Ohnishi, H.; Olefsky, J.M.; Brenner, D.A.; Seki, E. Toll-like receptor 9 promotes steatohepatitis by induction of interleukin-1beta in mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 2012, 482, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Miele, L.; Marrone, G.; Lauritano, C.; Cefalo, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Day, C.; Grieco, A. Gut-liver axis and microbiota in NAFLD: Insight pathophysiology for novel therapeutic target. Curr. Pharm. Des 2013, 19, 5314–5324. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, N.N.; McGillicuddy, F.C.; Anderson, P.D.; Hinkle, C.C.; Shah, R.; Pruscino, L.; Tabita-Martinez, J.; Sellers, K.F.; Rickels, M.R.; Reilly, M.P. Experimental endotoxemia induces adipose inflammation and insulin resistance in humans. Diabetes 2010, 59, 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- Csak, T.; Ganz, M.; Pespisa, J.; Kodys, K.; Dolganiuc, A.; Szabo, G. Fatty acid and endotoxin activate inflammasomes in mouse hepatocytes that release danger signals to stimulate immune cells. Hepatology 2011, 54, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, A.G.; Casafont, F.; Crespo, J.; Cayón, A.; Mayorga, M.; Estebanez, A.; Fernadez-Escalante, J.C.; Pons-Romero, F. Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein plasma levels and liver TNF-alpha gene expression in obese patients: Evidence for the potential role of endotoxin in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Obes. Surg 2007, 17, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Ottman, N.; Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M.; Belzer, C. The function of our microbiota: Who is out there and what do they do? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol 2012, 2, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Visschers, R.G.; Luyer, M.D.; Schaap, F.G.; Olde Damink, S.W.; Soeters, P.B. The gut-liver axis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 576–581. [Google Scholar]
- Craciun, S.; Balskus, E.P. Microbial conversion of choline to trimethylamine requires a glycyl radical enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21307–21312. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, G.C.; van Rooyen, D.; Gan, L.; Chitturi, S. NASH is an inflammatory disorder: Pathogenic, prognostic and therapeutic implications. Gut Liver 2012, 6, 149–171. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, M.V.; Cortez-Pinto, H. Gut microbiota and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol 2012, 11, 440–449. [Google Scholar]
- Moschen, A.R.; Kaser, S.; Tilg, H. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A microbiota-driven disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab 2013, 24, 537–545. [Google Scholar]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Gaborit, B.; Dutour, A.; Clement, K. Gut microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: New insights. Clin. Microbiol. Infect 2013, 19, 338–348. [Google Scholar]
- Vajro, P.; Paolella, G.; Poeta, M.; Pizza, C.; Sangermano, M.; Massa, G. Pediatric non alcoholic fatty liver disease: More on novel treatment targets. BMC Pediatr 2013, 13, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Alisi, A.; Ceccarelli, S.; Panera, N.; Nobili, V. Causative role of gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol 2012, 2, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Y.; Yang, M.; Edwards, S.; Ye, S.Q. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: For better or worse, blame the gut microbiota? J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr 2013, 37, 787–793. [Google Scholar]
- Dubourg, G.; Lagier, J.C.; Armougom, F.; Robert, C.; Hamad, I.; Brouqui, P.; Raoult, D. The gut microbiota of a patient with resistant tuberculosis is more comprehensively studied by culturomics than by metagenomics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis 2013, 32, 637–645. [Google Scholar]
- Del Chierico, F.; Vernocchi, P.; Bonizzi, L.; Carsetti, R.; Castellazzi, A.M.; Dallapiccola, B.; de Vos, W.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Manco, M.; Marseglia, G.L.; et al. Early-life gut microbiota under physiological and pathological conditions: The central role of combined meta-omics-based approaches. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 4580–4587. [Google Scholar]
- Lagier, J.C.; Million, M.; Hugon, P.; Armougom, F.; Raoult, D. Human gut microbiota: Repertoire and variations. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2012, 2, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Lagier, J.C.; Armougom, F.; Million, M.; Hugon, P.; Pagnier, I.; Robert, C.; Bittar, F.; Fournous, G.; Gimenez, G.; Maraninchi, M.; et al. Microbial culturomics: Paradigm shift in the human gut microbiome study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect 2012, 18, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Satokari, R.M.; Vaughan, E.E.; Smidt, H.; Saarela, M.; Mättö, J.; de Vos, W.M. Molecular approaches for the detection and identification of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the human gastrointestinal tract. Syst. Appl. Microbiol 2003, 26, 572–584. [Google Scholar]
- Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Heilig, H.G.; Molenaar, D.; Kajander, K.; Surakka, A.; Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M. Development and application of the human intestinal tract chip, a phylogenetic microarray: Analysis of universally conserved phylotypes in the abundant microbiota of young and elderly adults. Environ. Microbiol 2009, 11, 1736–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Satokari, R.M.; Vaughan, E.E.; Akkermans, A.D.; Saarela, M.; de Vos, W.M. Polymerase chain reaction and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis monitoring of fecal bifidobacterium populations in a prebiotic and probiotic feeding trial. Syst. Appl. Microbiol 2001, 24, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Claesson, M.J.; Wang, Q.; O’Sullivan, O.; Greene-Diniz, R.; Cole, J.R.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W. Comparison of two next-generation sequencing technologies for resolving highly complex microbiota composition using tandem variable 16S rRNA gene regions. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, e200. [Google Scholar]
- Salonen, A.; Nikkilä, J.; Jalanka-Tuovinen, J.; Immonen, O.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Kekkonen, R.A.; Palva, A.; de Vos, W.M. Comparative analysis of fecal DNA extraction methods with phylogenetic microarray: Effective recovery of bacterial and archaeal DNA using mechanical cell lysis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 81, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Petrucca, A.; del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L. Just keep going on description or interpret “life” of gut microbial ecosystems? Available online: http://www.cell.com/abstract/S0092-8674(12)00629-0# (accessed on 23 October 2012). Comments.
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Martins dos Santos, V.; Müller, M.; de Vos, W.M. Systems biology of the gut: The interplay of food, microbiota and host at the mucosal interface. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2010, 21, 539–550. [Google Scholar]
- Salonen, A.; de Vos, W.M.; Palva, A. Gastrointestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome: Present state and perspectives. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3205–3215. [Google Scholar]
- Zoetendal, E.G.; Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; de Vos, W.M. High-throughput diversity and functionality analysis of the gastrointestinal tract microbiota. Gut 2008, 57, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Booijink, C.C.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Kleerebezem, M.; de Vos, W.M. Microbial communities in the human small intestine: Coupling diversity to metagenomics. Future Microbiol 2007, 2, 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, C.; Bik, E.M.; DiGiulio, D.B.; Relman, D.A.; Brown, P.O. Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol 2007, 5, e177. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.X.; Geng, Z.L.; Zeng, Y.; Shen, Y.M. Enriching plant microbiota for a metagenomic library construction. Environ. Microbiol 2008, 10, 2684–2691. [Google Scholar]
- Chadeau-Hyam, M.; Ebbels, T.M.; Brown, I.J.; Chan, Q.; Stamler, J.; Huang, C.C.; Daviglus, M.L.; Ueshima, H.; Zhao, L.; Holmes, E.; et al. Metabolic profiling and the metabolome-wide association study: Significance level for biomarker identification. J. Proteome Res 2010, 9, 4620–4627. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, F.P.; Sprenger, N.; Montoliu, I.; Rezzi, S.; Kochhar, S.; Nicholson, J.K. Dietary modulation of gut functional ecology studied by fecal metabonomics. J. Proteome Res 2010, 9, 5284–5295. [Google Scholar]
- Vitali, B.; Ndagijimana, M.; Cruciani, F.; Carnevali, P.; Candela, M.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Brigidi, P. Impact of a synbiotic food on the gut microbial ecology and metabolic profiles. BMC Microbiol 2010, 10, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Saric, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Coen, M.; Utzinger, J.; Marchesi, J.R.; Keiser, J.; Veselkov, K.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; et al. Species variation in the fecal metabolome gives insight into differential gastrointestinal function. J. Proteome Res 2008, 7, 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. “Metabonomics”: Understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xie, Z.; Lin, J.; Song, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Su, M.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Song, K.; et al. Transcriptomic and metabonomic profiling of obesity-prone and obesity-resistant rats under high fat diet. J. Proteome Res 2008, 7, 4775–4783. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Wilson, I.D. Gut microorganisms, mammalian metabolism and personalized health care. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2005, 3, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.P.; Wallace, G.R. Metabolomic analysis of human disease and its application to the eye. J. Ocul. Biol. Dis. Infor 2009, 2, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Del Chierico, F.; Petrucca, A.; Mortera, S.L.; Vernocchi, P.; Rosado, M.M.; Pieroni, L.; Carsetti, R.; Urbani, A.; Putignani, L. A metaproteomic pipeline to identify newborn mouse gut phylotypes. J. Proteomics 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar]
- Reeder, J.; Knight, R. Rapidly denoising pyrosequencing amplicon reads by exploiting rank-abundance distributions. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 668–669. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, A.; Bunge, J. Estimating the number of species in a stochastic abundance model. Biometrics 2002, 58, 531–539. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The mathematical theory of information. AT&T Tech. J 1949, 27, 359–423. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kohl, M.; Wiese, S.; Warscheid, B. Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. Methods Mol. Biol 2011, 696, 291–303. [Google Scholar]
- Penders, J.; Thijs, C.; Vink, C.; Stelma, F.F.; Snijders, B.; Kummeling, I.; van den Brandt, P.A.; Stobberingh, E.E. Factors influencing the composition of the intestinal microbiota in early infancy. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 511–521. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, J.E.; Spor, A.; Scalfone, N.; Fricker, A.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Angenent, L.T.; Ley, R.E. Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 15, 4578–4585. [Google Scholar]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.P.; Chassard, C. New insights in gut microbiota establishment in healthy breast fed neonates. PLoS One 2012, 7, e44595. [Google Scholar]
- Coppa, G.V.; Zampini, L.; Galeazzi, T.; Gabrielli, O. Prebiotics in human milk: A review. Dig. Liver Dis 2006, 38, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zivkovic, A.M.; Barile, D. Bovine milk as a source of functional oligosaccharides for improving human health. Adv. Nutr 2011, 2, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- White, R.A.; Bjørnholt, J.V.; Baird, D.D.; Midtvedt, T.; Harris, J.R.; Pagano, M.; Hide, W.; Rudi, K.; Moen, B.; Iszatt, N.; et al. Novel developmental analyses identify longitudinal patterns of early gut microbiota that affect infant growth. PLoS Comput. Biol 2013, 9, e1003042. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Han, R.; Cao, Y.; Hua, W.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, X.; Wie, C.; et al. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J 2010, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.; Caetano, L.; Antunes, M.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Am. Physiol. Soc 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome: A metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci. Transl. Med 2009, 1, 6ra14. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, A.W.; Ince, J.; Duncan, S.H.; Webster, L.M.; Holtrop, G.; Ze, X.; Brown, D.; Stares, M.D.; Scott, P.; Bergerat, A.; et al. Dominant and diet-responsive groups of bacteria within the human colonic microbiota. ISME J 2011, 5, 220–230. [Google Scholar]
- Santacruz, A.; Marcos, A.; Warnberg, J.; Marti, A.; Martin-Matillas, M.; Campoy, C.; Moreno, L.A.; Veiga, O.; Redondo-Figuero, C.; Garagorri, J.M.; et al. Interplay between weight loss and gut microbiota composition in overweight adolescents. Obesity 2009, 17, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar]
- Pokusaeva, K.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; van Sinderen, D. Carbohydrate metabolism in bifidobacteria. Genes Nutr 2011, 6, 285–306. [Google Scholar]
- Begley, M.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Bile salt hydrolase activity in probiotics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2006, 72, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer, J.; Lange, B.; Frick, J.S.; Sauer, H.; Zimmermann, K.; Schwiertz, A.; Rusch, K.; Klosterhalfen, S.; Enck, P. A vegan or vegetarian diet substantially alters the human colonic faecal microbiota. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr 2012, 66, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from europe and rural africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar]
- Hehemann, J.H.; Correc, G.; Barbeyron, T.; Helbert, W.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Transfer of carbohydrate-active enzymes from marine bacteria to Japanese gut microbiota. Nature 2010, 8, 908–912. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Shanab, A.; Quigley, E.M. The role of the gut microbiota in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 2010, 7, 691–701. [Google Scholar]
- Frasinariu, O.E.; Ceccarelli, S.; Alisi, A.; Moraru, E.; Nobili, V. Gut-liver axis and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An input for novel therapies. Digest. Liver Dis 2013, 45, 543–551. [Google Scholar]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Gordon, J.I. The core gut microbiome, energy balance and obesity. J. Physiol 2009, 587, 4153–4158. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, M.D.; Hamp, T.J.; Reid, R.W.; Fischer, L.M.; Zeisel, S.H.; Fodor, A.A. Association between composition of the human gastrointestinal microbiome and development of fatty liver with choline deficiency. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 976–986. [Google Scholar]
- Le Roy, T.; Llopis, M.; Lepage, P.; Bruneau, A.; Rabot, S.; Bevilacqua, C.; Martin, P.; Philippe, C.; Walker, F.; Bado, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota determines development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut 2013, 62, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar]
- Mouzaki, M.; Comelli, E.M.; Arendt, B.M.; Bonengel, J.; Fung, S.K.; Fischer, S.E.; McGilvray, I.D.; Allard, J.P. Intestinal microbiota in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Bull-Otterson, L.; Feng, W.; Kirpich, I.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Gobejishvili, L.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Ayvaz, T.; Petrosino, J.; et al. Metagenomic analyses of alcohol induced pathogenic alterations in the intestinal microbiome and the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment. PLoS One 2013, 8, e53028. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Peng, J.; Zhao, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Feng, Q.; Hu, Y.; Pang, X. Structural changes of gut microbiota in a rat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease model treated with a Chinese herbal formula. Syst. Appl. Microbiol 2013, 36, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- De Minicis, S.; Rychlicki, C.; Agostinelli, L.; Saccomanno, S.; Candelaresi, C.; Trozzi, L.; Mingarelli, E.; Facinelli, B.; Magi, G.; Palmieri, C.; et al. Dysbiosis contributes to fibrogenesis in the course of chronic liver injury. Hepatology 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachikian, B.D.; Essaghir, A.; Demoulin, J.B.; Catry, E.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Dewulf, E.M.; Sohet, F.M.; Portois, L.; Clerbaux, L.A.; Carpentier, Y.A.; et al. Prebiotic approach alleviates hepatic steatosis: Implication of fatty acid oxidative and cholesterol synthesis pathways. Mol. Nutr. Food Res 2013, 57, 347–359. [Google Scholar]
- Raman, M.; Ahmed, I.; Gillevet, P.M.; Probert, C.S.; Ratcliffe, N.M.; Smith, S.; Greenwood, R.; Sikaroodi, M.; Lam, V.; Crotty, P.; et al. Fecal microbiome and volatile organic compound metabolome in obese humans with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 2013, 11, 868–875. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Tse, C.H.; Lam, T.T.; Wong, G.L.; Chim, A.M.; Chu, W.C.; Yeung, D.K.; Law, P.T.; Kwan, H.S.; Yu, J.; et al. Molecular characterization of the fecal microbiota in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis—A longitudinal study. PLoS One 2013, 8, e62885. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: A connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, K.; Ohtake, T.; Hasebe, T.; Abe, M.; Tanaka, H.; Ikuta, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Fujiya, M.; Hasebe, C.; Kohgo, Y. Augmented hepatic Toll-like receptors by fatty acids trigger the pro-inflammatory state of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatol. Res 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M. Pathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol 2010, 7, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Jumpertz, R.; Le, D.S.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Trinidad, C.; Bogardus, C.; Gordon, J.I.; Krakoff, J. Energy-balance studies reveal associations between gut microbes, caloric load, and nutrient absorption in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr 2011, 94, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Compare, D.; Coccoli, P.; Rocco, A.; Tardone, O.M.; de Maria, S.; Cartenì, M.; Tardone, G. Gut-liver axis: The impact of gut microbiota on non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovas 2012, 22, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.M.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar]
- Blomstrand, R. Observations of the formation of ethanol in the intestinal tract in man. Life Sci. II 1971, 10, 575–582. [Google Scholar]
- Engeland, K.; Maret, W. Extrahepatic, differential expression of four classes of human alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1993, 193, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, D.M.; Gaudier, E.; van Duynhoven, J.; Vaughan, E.E. Non-digestible food ingredients, colonic microbiota and the impact on gut health and immunity: A role for metabolomics. Curr. Drug Metab 2009, 10, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiota and metabolic disorders: How prebiotic can work? Br. J. Nutr 2013, 109, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Won, G.L.; Chim, A.M.; Chu, W.C.; Yeung, D.K.; Li, K.C.; Chan, H.L. Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with probiotics. A proof-of-concept study. Ann. Hepatol 2013, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Abenavoli, L.; Scarpellini, E.; Rouabhia, S.; Balsano, C.; Luzza, F. Probiotics in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Which and when. Ann. Hepatol 2013, 12, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Vajro, P.; Mandato, C.; Veropalumbo, C.; de Micco, I. Probiotics: A possible role in treatment of adult and pediatric non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol 2013, 12, 161–163. [Google Scholar]
- Kelishadi, R.; Farajian, S.; Mirlohi, M. Probiotics as a novel treatment for non-alcoholic Fatty liver disease; a systematic review on the current evidences. Hepat. Mon 2013, 13, e7233. [Google Scholar]
- De Filippo, C.; Ramazzotti, M.; Fontana, P.; Cavalieri, D. Bioinformatic approaches for functional annotation and pathway inference in metagenomics data. Brief Bioinform 2012, 13, 696–710. [Google Scholar]
- Shoaie, S.; Karlsson, F.; Mardinoglu, A.; Nookaew, I.; Bordel, S.; Nielsen, J. Understanding the interactions between bacteria in the human gut through metabolic modeling. Sci. Rep 2013, 3, 2532. [Google Scholar]



| Animal models: induced disease and ameliorating factors | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | Model | Induced | Controls | Age range | Technology and experimental pipeline | Main bacterial phyla tendency | References | |||
| Firmicutes | Proteobacteria | Bacteroidetes | Actinobacteria | |||||||
| FL | Mouse | AF + HFD fed | isocaloric maltose dextrin HFD fed | 8–10 week old | V3–V5 16S rRNA pyrosequencing | ↓ Lachnospiraceae, Ruminococcaceae; ↑ Aerococcus spp., Listeria spp., Clostridiales spp., Allobaculum spp., Lactobacillus spp. | ↑ (particularly Alcaligenes spp.) | ↓ Bacteroides spp., Parabacteroides spp., Tannerella spp., Halella spp. | ↑ (particularly Corynebacterium spp.) | [102] |
| AF + LGG | AF | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | |||||
| NAFLD | Mouse | RR 3 weeks HFD fed | NRR 3 weeks HFD fed | 8 week old | V3–V4 16S rRNA pyrosequencing | ↑ | Stable | ↓ | ↓ | [99] |
| NAFLD | Rat | HFD fed for 6 weeks | normal chow fed for 6 weeks | Not reported | PCR-DGGE and V3 16S rRNA pyrosequencing | ↓ Allobaculum spp.;↑ Coprococcus spp., Blautia spp., Roseburia spp. | ↑ Escherichia/Shigella | ↓ Prevotella spp., Bacteroides spp. | ↑ | [103] |
| HFD + QHF | control-HFD | Stable | Stable | Stable | ↑ | |||||
| NAFLD | Mouse | HFD fed | control chow fed | 8–12 weeks | qRT-PCR and pyrosequencing | ↑ | Stable | ↓ | slight ↑ | [104] |
| HFD + BDL | Control + BDL | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | |||||
| NAFLD | Mouse | DEF fed | HFD fed | 9 weeks | PCR-DGGE | ↑ Roseburia spp. | Not reported | Stable | slight ↓ | [105] |
| DEF + FOS | DEF fed | ↓ Roseburia spp. | Not reported | Stable | ↑ Bifidobacterium spp. | |||||
| Human studies: disease-related factors | ||||||||||
| Disease | Model | N. enrolled patients | N. healthy controls | Age range | Technology and experimental pipeline | Main bacterial phyla tendency | References | |||
| Firmicutes | Proteobacteria | Bacteroidetes | Actinobacteria | |||||||
| NAFLD | Humans | 30 | 30 | Adults | 16S rRNA pyrosequencing | ↑ Lactobacillaceae, Veillonellaceae and Lachnospiraceae; ↓ Ruminococcaceae | ↑ Kiloniellaceae and Pasteurellaceae | ↓ Porphyromonadaceae | Not reported | [106] |
| NASH | Humans | 16 | 22 | 18–70 years | 16S rRNA pyrosequencing | ↓ Clostridia and unclassified Firmicutes | ↑ Succinivibrionaceae | ↑ Porphyromonadaceae | ↓ | [107] |
| NASH | Humans | 22 | 16 | Children and adolescents | 16S rRNA pyrosequencing | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | [108] |
| NASH | Humans | 22 NASH + 11 SS | 17 | Adults | qPCR | ↑ Clostridium coccoides | Equivalent presence of Escherichia coli | ↓ | Stable | [100] |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Chierico, F.; Gnani, D.; Vernocchi, P.; Petrucca, A.; Alisi, A.; Dallapiccola, B.; Nobili, V.; Lorenza, P. Meta-Omic Platforms to Assist in the Understanding of NAFLD Gut Microbiota Alterations: Tools and Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 684-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010684
Del Chierico F, Gnani D, Vernocchi P, Petrucca A, Alisi A, Dallapiccola B, Nobili V, Lorenza P. Meta-Omic Platforms to Assist in the Understanding of NAFLD Gut Microbiota Alterations: Tools and Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(1):684-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010684
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Chierico, Federica, Daniela Gnani, Pamela Vernocchi, Andrea Petrucca, Anna Alisi, Bruno Dallapiccola, Valerio Nobili, and Putignani Lorenza. 2014. "Meta-Omic Platforms to Assist in the Understanding of NAFLD Gut Microbiota Alterations: Tools and Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 1: 684-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010684
APA StyleDel Chierico, F., Gnani, D., Vernocchi, P., Petrucca, A., Alisi, A., Dallapiccola, B., Nobili, V., & Lorenza, P. (2014). Meta-Omic Platforms to Assist in the Understanding of NAFLD Gut Microbiota Alterations: Tools and Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(1), 684-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010684







