MicroRNA-27a Is Induced by Leucine and Contributes to Leucine-Induced Proliferation Promotion in C2C12 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
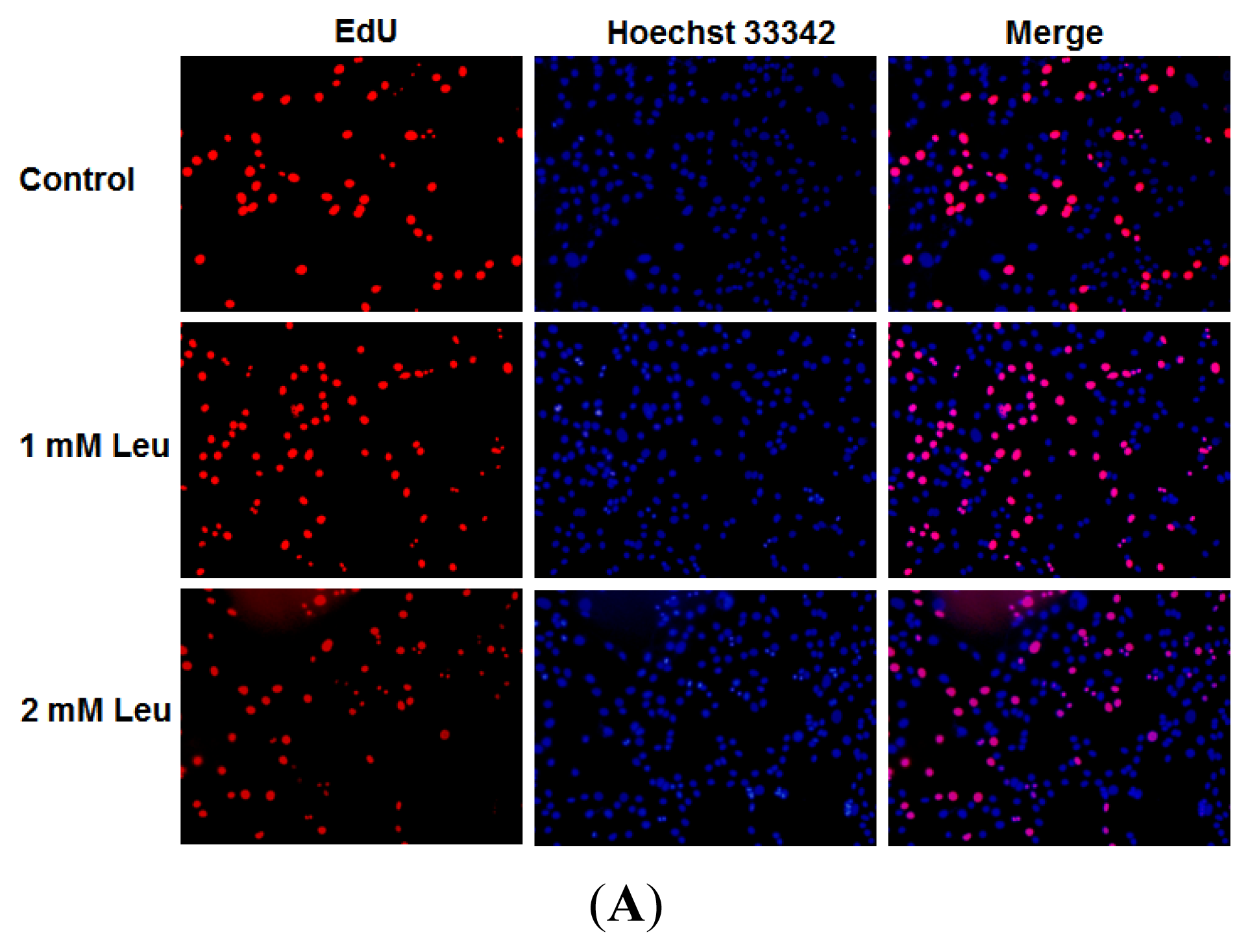
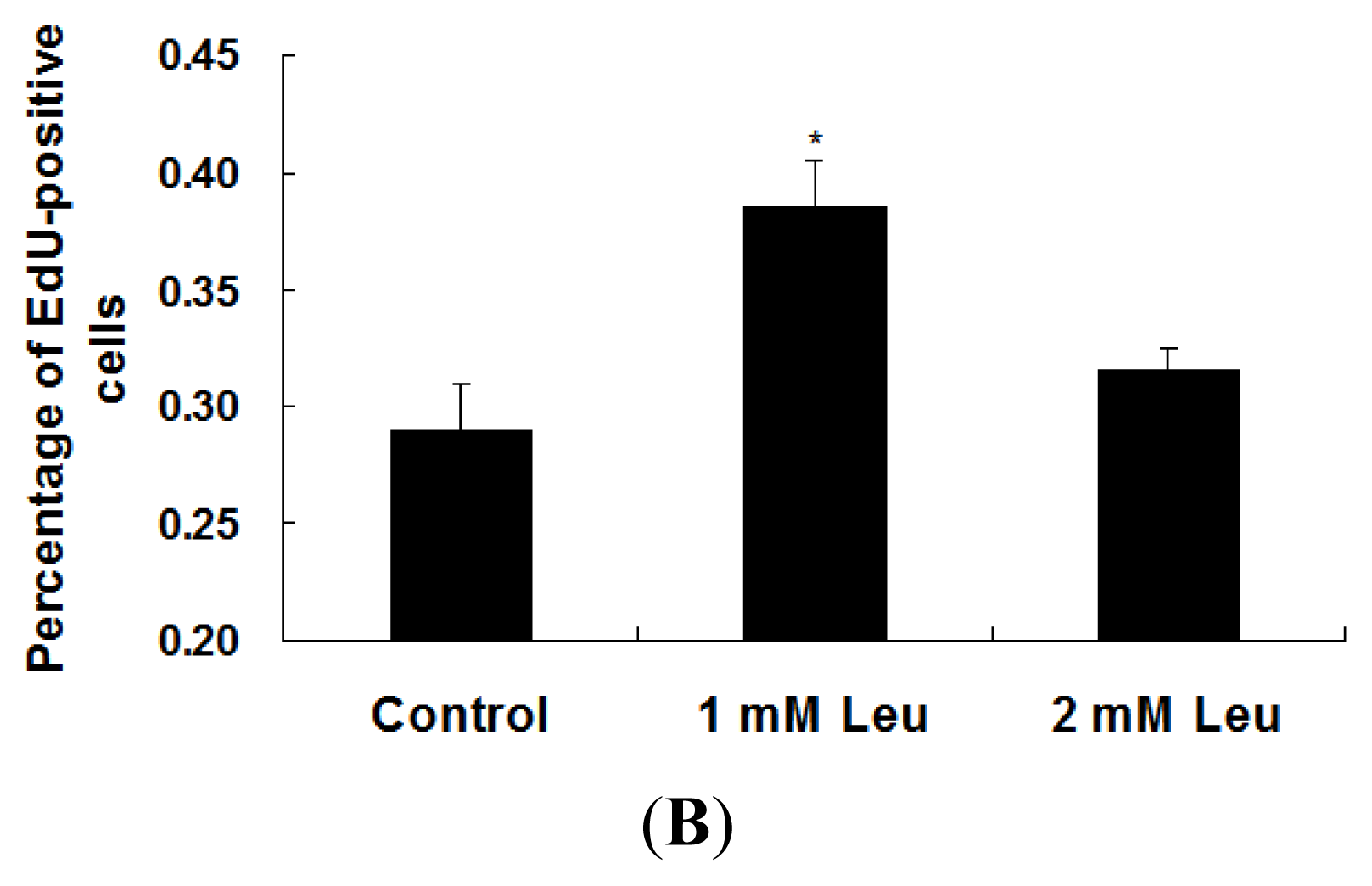
2.1. Effect of Leucine on Myoblast Proliferation
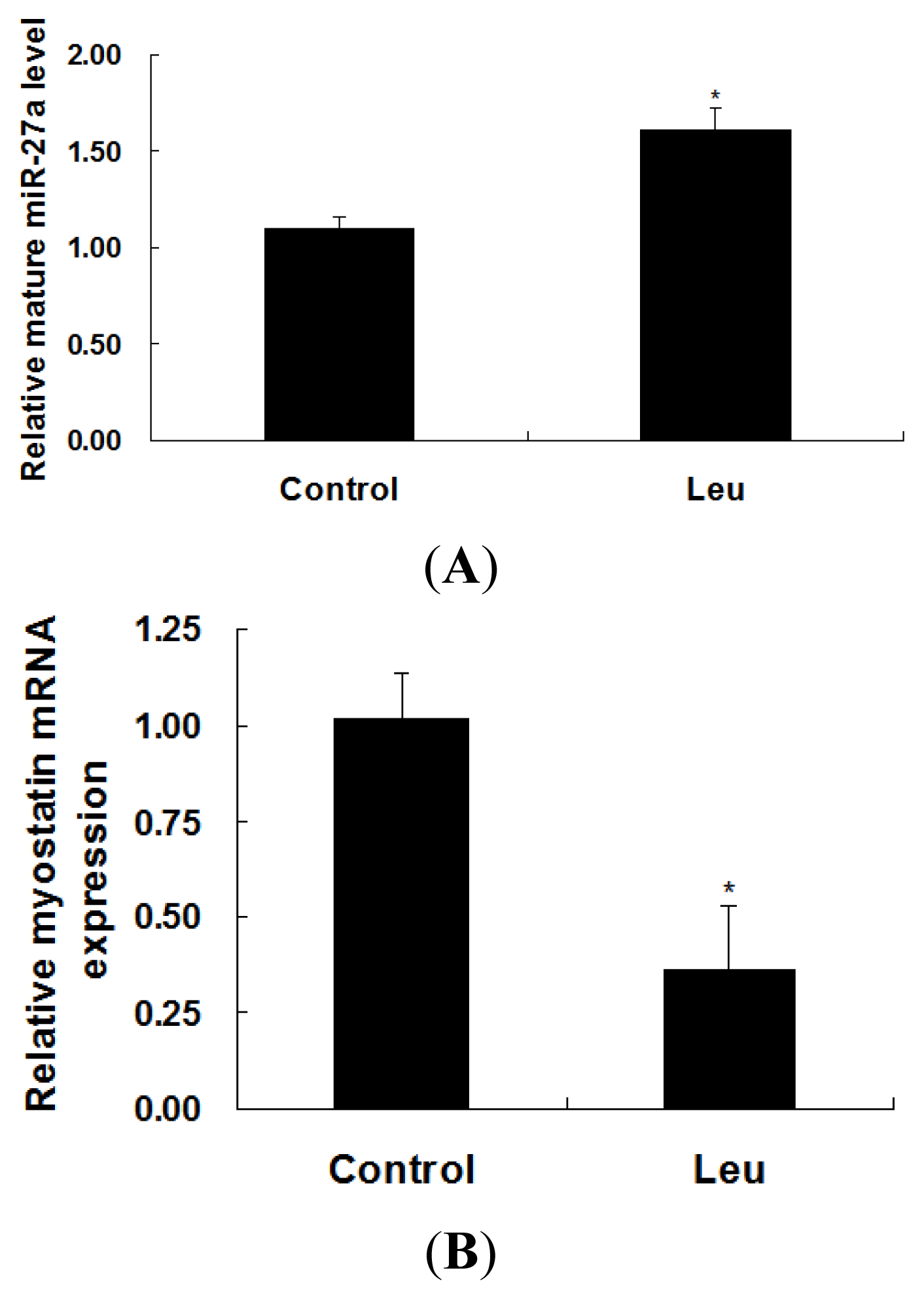
2.2. Effect of Leucine on Expressions of miR-27a and Myostatin
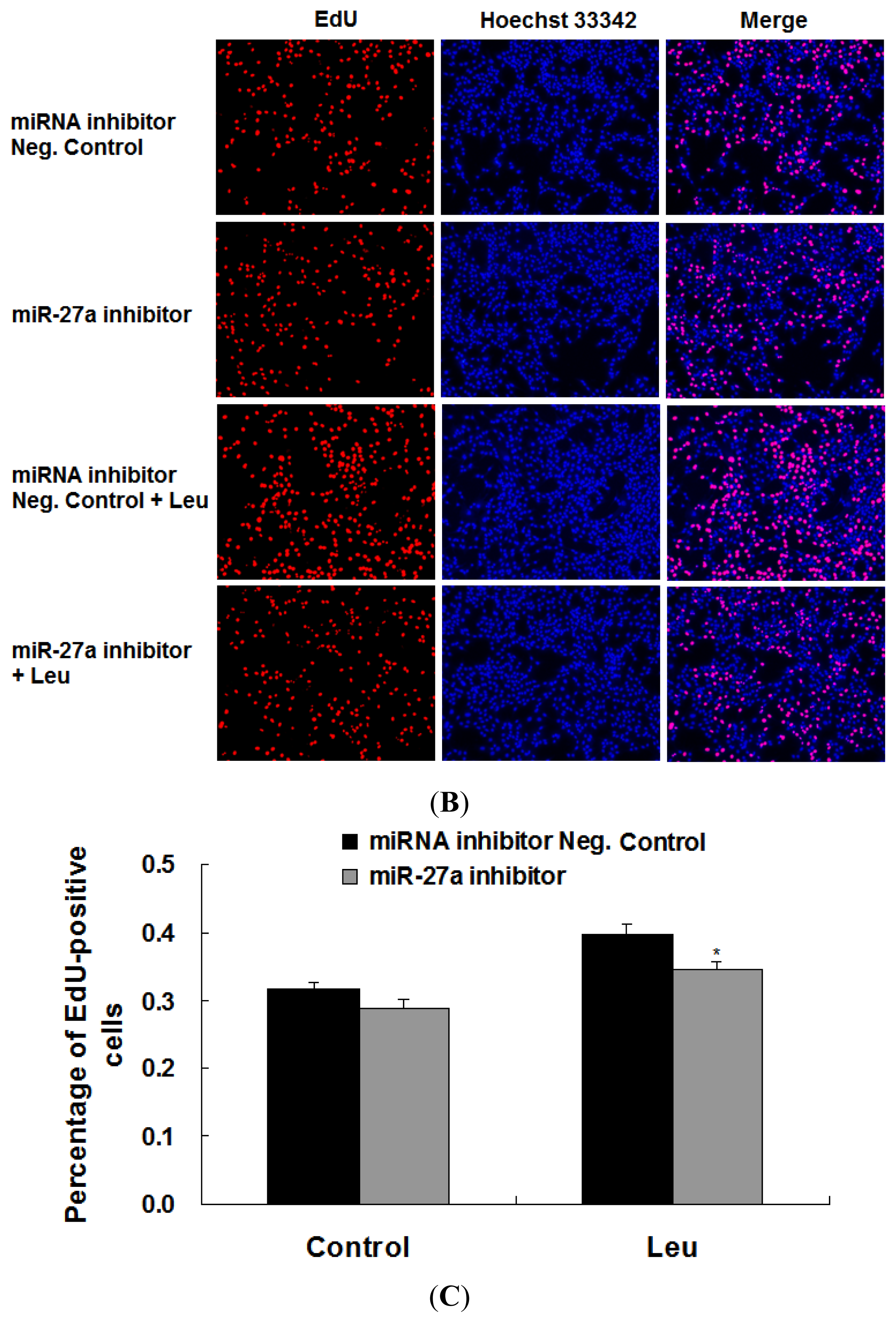
2.3. Promotion of Myoblast Proliferation by Leucine Is Reduced by miR-27a Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.3. Quantification of mRNA Expression
4.4. Detection of miRNA Expression
4.5. EdU Proliferation Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Buckingham, M. Skeletal muscle formation in vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev 2001, 11, 440–448. [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham, M. Myogenic progenitor cells and skeletal myogenesis in vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev 2006, 16, 525–532. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, J.C.; Anthony, T.G.; Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S. Signaling pathways involved in translational control of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle by leucine. J. Nutr 2001, 131, 856S–860S. [Google Scholar]
- Stipanuk, M.H. Leucine and protein synthesis: mTOR and beyond. Nutr. Rev 2007, 65, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Casperson, S.L.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Hewlings, S.J.; Paddon-Jones, D. Leucine supplementation chronically improves muscle protein synthesis in older adults consuming the RDA for protein. Clin. Nutr 2012, 31, 512–519. [Google Scholar]
- Haegens, A.; Schols, A.M.; van Essen, A.L.; van Loon, L.J.; Langen, R.C. Leucine induces myofibrillar protein accretion in cultured skeletal muscle through mTOR dependent and -independent control of myosin heavy chain mRNA levels. Mol. Nutr. Food Res 2012, 56, 741–752. [Google Scholar]
- Hobert, O. miRNAs play a tune. Cell 2007, 131, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Djuranovic, S.; Nahvi, A.; Green, R. A parsimonious model for gene regulation by miRNAs. Science 2011, 331, 550–553. [Google Scholar]
- Mendell, J.T.; Olson, E.N. MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease. Cell 2012, 148, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.J.; Chen, J. MicroRNAs in skeletal myogenesis. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Q.; Chen, X.L.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Chen, D.W. MicroRNA-27a promotes myoblast proliferation by targeting myostatin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2012, 423, 265–269. [Google Scholar]
- Averous, J.; Gabillard, J.C.; Seiliez, I.; Dardevet, D. Leucine limitation regulates myf5 and myoD expression and inhibits myoblast differentiation. Exp. Cell Res 2012, 318, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, S.D.; Abraham, S. Gene expression: nutrient control of pre- and posttranscriptional events. FASEB J 1992, 6, 3146–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, M.J.; Glynn, E.L.; Fry, C.S.; Dhanani, S.; Volpi, E.; Rasmussen, B.B. Essential amino acids increase microrna-499, -208b, and -23a and downregulate myostatin and myocyte enhancer factor 2c mrna expression in human skeletal muscle. J. Nutr 2009, 139, 2279–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, L.A.; Wang, N.; Shah, M.S.; Lupton, J.R.; Ivanov, I.; Chapkin, R.S. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids modulate carcinogen-directed non-coding microRNA signatures in rat colon. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Díaz, S.; Valle, N.; Ferrer-Mayorga, G.; Lombardía, L.; Herrera, M.; Domínguez, O.; Segura, M.F.; Bonilla, F.; Hernando, E.; Muñoz, A. MicroRNA-22 is induced by vitamin D and contributes to its antiproliferative, antimigratory and gene regulatory effects in colon cancer cells. Hum. Mol. Genet 2012, 21, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar]
- Lovis, P.; Roggli, E.; Laybutt, D.R.; Gattesco, S.; Yang, J.Y.; Widmann, C.; Abderrahmani, A.; Regazzi, R. Alterations in microRNA expression contribute to fatty acid-induced pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2728–2736. [Google Scholar]
- McPherron, A.C.; Lawler, A.M.; Lee, S.J. Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-β superfamily member. Nature 1997, 387, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J. Regulation of muscle mass by myostatin. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol 2004, 20, 61–86. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Q.; Chen, D.W.; Zhang, K.Y.; Yu, B.; Chen, X.L.; Meng, J. Regulation of myostatin signaling by c-Jun N-terminal kinase in C2C12 cells. Cell Signal 2007, 19, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Q.; Chen, X.L.; Chen, D.W. Myostatin: A novel insight into its role in metabolism, signal pathways, and expression regulation. Cell Signal 2011, 23, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]

| Gene name | Primer | Sequence | GenBank ID | Product size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myostatin | Forward | 5′-GATGGGACTGGATTATCGC-3′ | NM_010834 | 102 bp |
| Reverse | 5′-GCACAAGATGAGTATGCGG-3′ | |||
| GAPDH | Forward | 5′-AGGGCATCTTGGGCTACAC-3′ | NM_008084 | 211 bp |
| Reverse | 5′-TGGTCCAGGGTTTCTTACTCC-3′ | |||
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, D.; Yang, T.; Liu, G. MicroRNA-27a Is Induced by Leucine and Contributes to Leucine-Induced Proliferation Promotion in C2C12 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14076-14084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140714076
Chen X, Huang Z, Chen D, Yang T, Liu G. MicroRNA-27a Is Induced by Leucine and Contributes to Leucine-Induced Proliferation Promotion in C2C12 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(7):14076-14084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140714076
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaoling, Zhiqing Huang, Daiwen Chen, Ting Yang, and Guangmang Liu. 2013. "MicroRNA-27a Is Induced by Leucine and Contributes to Leucine-Induced Proliferation Promotion in C2C12 Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 7: 14076-14084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140714076
APA StyleChen, X., Huang, Z., Chen, D., Yang, T., & Liu, G. (2013). MicroRNA-27a Is Induced by Leucine and Contributes to Leucine-Induced Proliferation Promotion in C2C12 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(7), 14076-14084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140714076




